Tolerability and Acceptability of an Exogenous Ketone Monoester and Ketone Monoester/Salt Formulation in Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
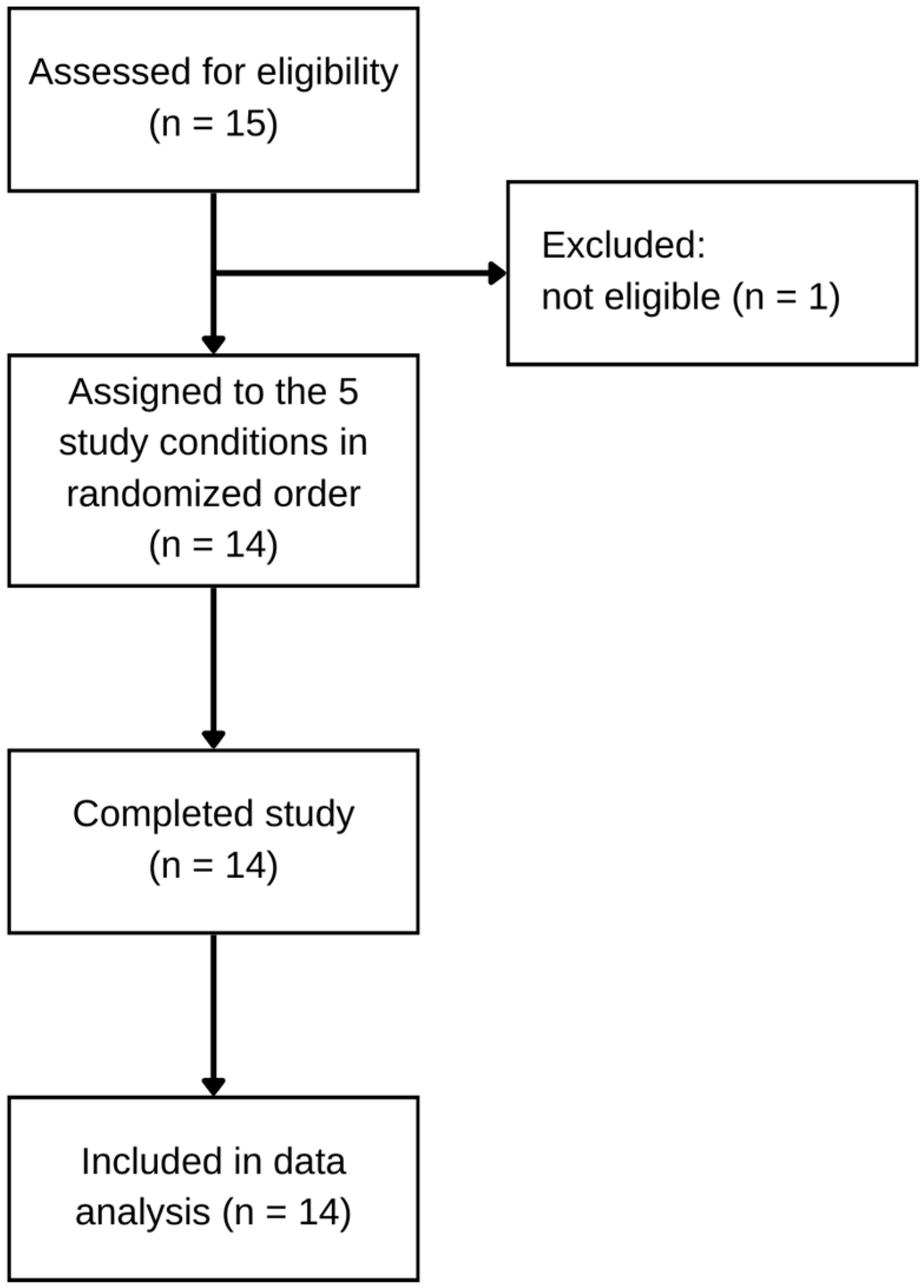
3.1. Participant Recruitment and Characteristics
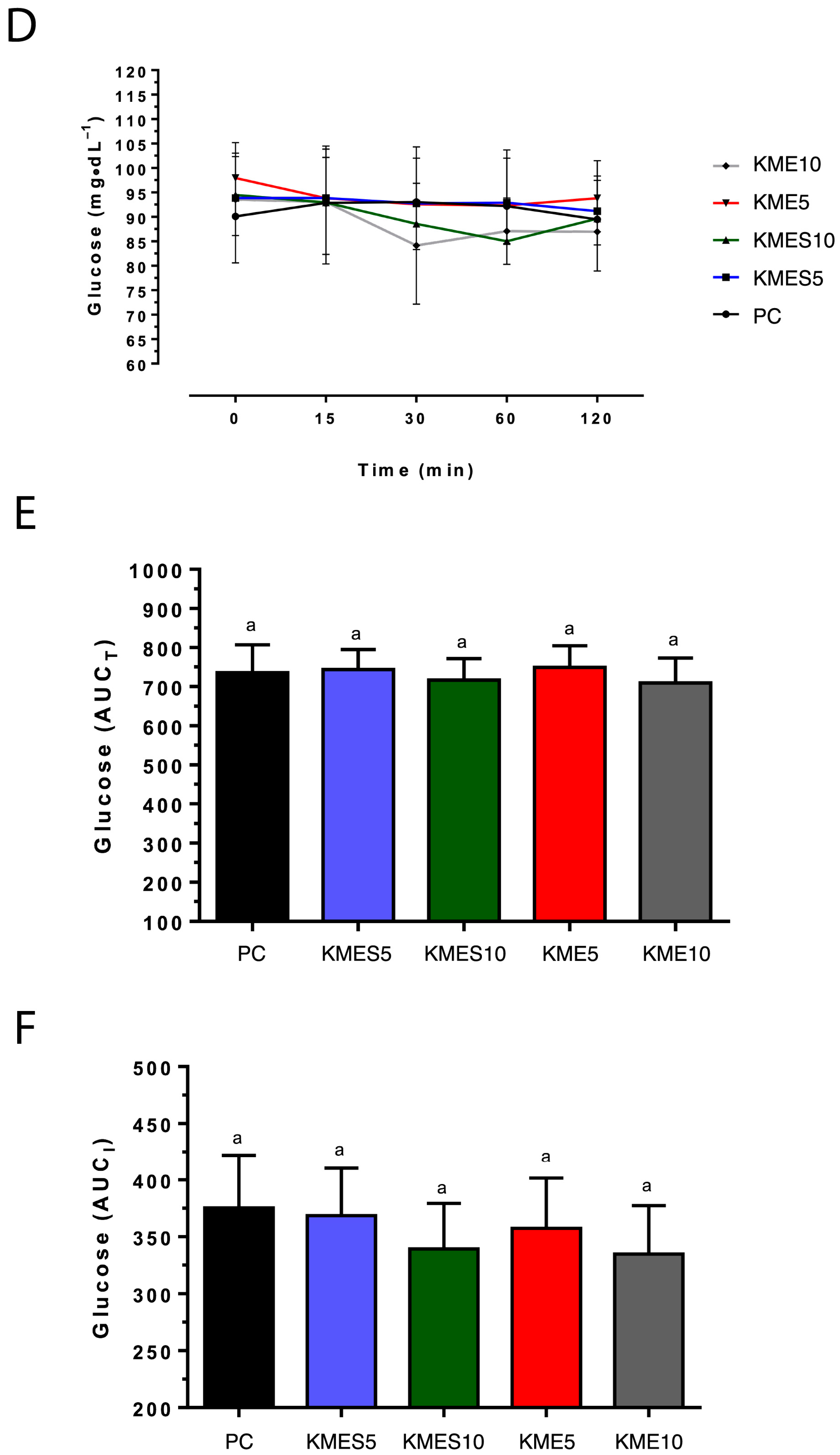
3.2. Effects of KME and KMES Drinks on Circulating R-βHB and Glucose Concentrations
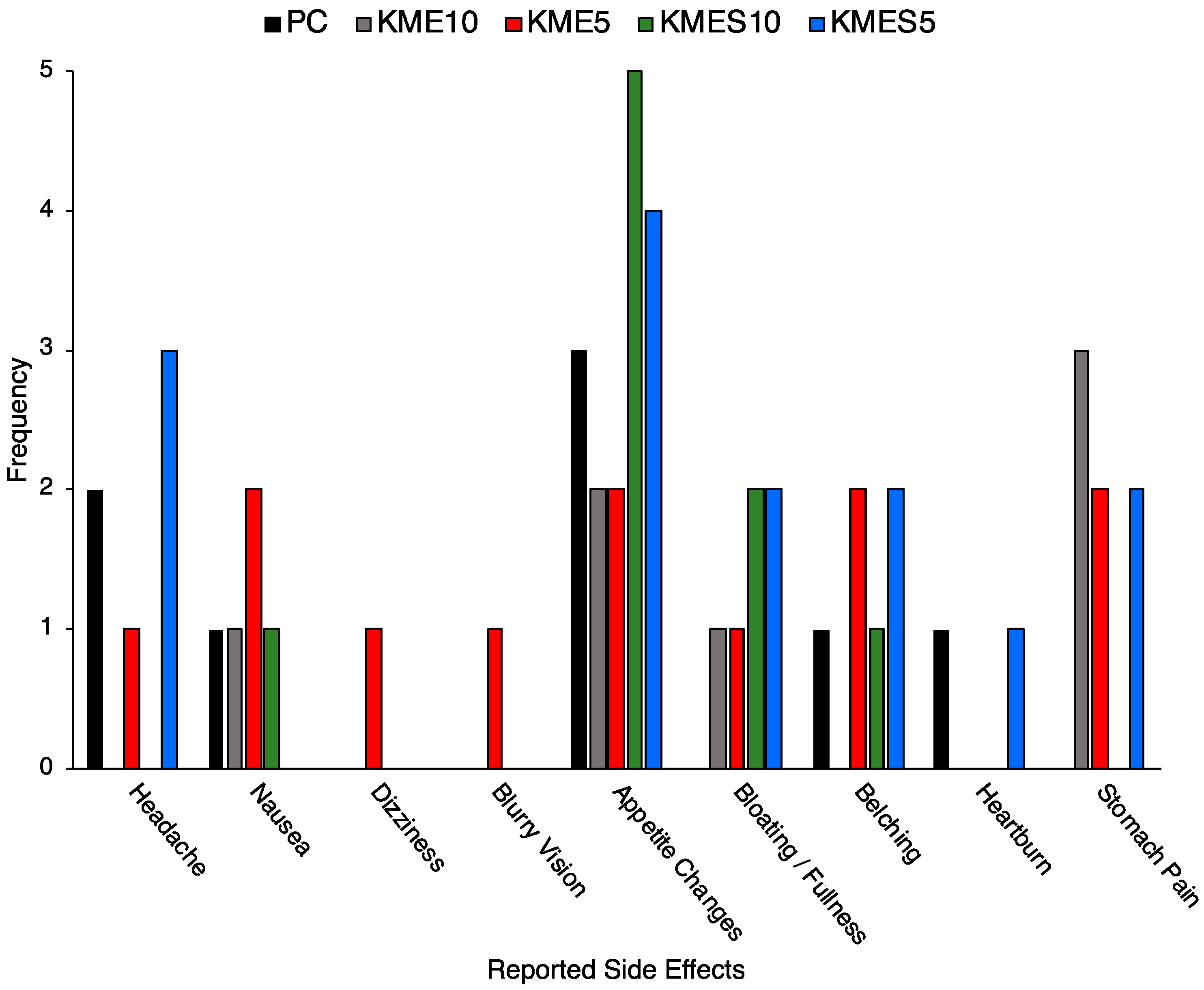
3.3. Acceptability and Tolerability of KME and KMES Drinks
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Metabolic and signaling roles of ketone bodies in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batch, J.T.; Lamsal, S.P.; Adkins, M.; Sultan, S.; Ramirez, M.N. Advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet: A review article. Cureus 2020, 12, e9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, N.B.; de Melo, I.S.V.; de Oliveira, S.L.; da Rocha Ataide, T. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabińska, N.; Wiczkowski, W.; Piskuła, M.K. Recent advances in the application of a ketogenic diet for obesity management. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, A.M.; Horgan, G.W.; Murison, S.D.; Bremner, D.M.; Lobley, G.E. Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Sun, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tong, T.K.; Nie, J. Short-term ketogenic diet improves abdominal obesity in overweight/obese Chinese young females. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S. The effect of periodic ketogenic diet on newly diagnosed overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Jenkins, T.J. A ketogenic diet for reducing obesity and maintaining capacity for physical activity: Hype or hope? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perticone, M.; Maio, R.; Sciacqua, A.; Suraci, E.; Pinto, A.; Pujia, R.; Zito, R.; Gigliotti, S.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Ketogenic diet-induced weight loss is associated with an increase in vitamin D levels in obese adults. Molecules 2019, 24, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saslow, L.R.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Moskowitz, J.T.; Kim, S.; Murphy, E.J.; Phinney, S.D.; Ploutz-Snyder, R.; Goldman, V.; Cox, R.M.; Mason, A.E.; et al. Twelve-month outcomes of a randomized trial of a moderate-carbohydrate versus very low-carbohydrate diet in overweight adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Ketosis and appetite-mediating nutrients and hormones after weight loss. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, W.S.; Olsen, M.K.; Guyton, J.R.; Bakst, R.P.; Westman, E.C. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Effect of the ketogenic diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism in patients with T2DM: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groleau, V.; Schall, J.I.; Stallings, V.A.; Bergqvist, C.A. Long-term impact of the ketogenic diet on growth and resting energy expenditure in children with intractable epilepsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bertoli, S.; Trentani, C.; Borrelli, P.; Veggiotti, P. Effects of the ketogenic diet on nutritional status, resting energy expenditure, and substrate oxidation in patients with medically refractory epilepsy: A 6-month prospective observational study. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 31, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, A.A.; Seimon, R.V.; Lee, C.M.Y.; Ayre, J.; Franklin, J.; Markovic, T.P.; Caterson, I.D.; Sainsbury, A. Do ketogenic diets really suppress appetite? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistrian, B.R. Some musings about differential energy metabolism with ketogenic diets. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Chen, K.Y.; Guo, J.; Lam, Y.Y.; Leibel, R.L.; Mayer, L.E.; Reitman, M.L.; Rosenbaum, M.; Smith, S.R.; Walsh, B.T.; et al. Energy expenditure and body composition changes after an isocaloric ketogenic diet in overweight and obese men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.; Raggi, P. The ketogenic diet: Pros and cons. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cenci, L.; Grimaldi, K.A. Effect of ketogenic Mediterranean diet with phytoextracts and low carbohydrates/high-protein meals on weight, cardiovascular risk factors, body composition and diet compliance in Italian council employees. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.H.; Deemer, S.E.; Bergeron, J.M.; Little, J.T.; Warren, J.L.; Fisher, G.; Smith, D.L.; Fontaine, K.R.; Dickinson, S.L.; Allison, D.B.; et al. Dietary R,S-1,3-butanediol diacetoacetate reduces body weight and adiposity in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deemer, S.E.; Davis, R.A.H.; Gower, B.A.; Koutnik, A.P.; Poff, A.M.; Dickinson, S.L.; Allison, D.B.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Plaisance, E.P. Concentration-dependent effects of a dietary ketone ester on components of energy balance in mice. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.P.; Cunningham, R.P.; Davis, R.A.H.; Deemer, S.E.; Roberts, B.M.; Plaisance, E.P.; Rector, R.S. A dietary ketone ester mitigates histological outcomes of NAFLD and markers of fibrosis in high-fat diet fed mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G564–G572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushing, K.A.; Bolyard, M.L.; Kelty, T.; Wieschhaus, N.; Pavela, G.; Rector, R.S.; Plaisance, E.P. Dietary ketone ester attenuates the accretion of adiposity and liver steatosis in mice fed a high-fat, high-sugar diet. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1165224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Kashiwaya, Y.; King, M.T.; Baxa, U.; Tam, J.; Niu, G.; Chen, X.; Clarke, K.; Veech, R.L. Mitochondrial biogenesis and increased uncoupling protein 1 in brown adipose tissue of mice fed a ketone ester diet. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cox, P.J.; Evans, R.D.; Cyranka, M.; Clarke, K.; de Wet, H. A ketone ester drink lowers human ghrelin and appetite. Obesity 2018, 26, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, K.H.; Seifert, T.; Secher, N.H.; Grøndal, T.; van Hall, G. Systemic, cerebral and skeletal muscle ketone body and energy metabolism during acute hyper-D-β-hydroxybutyratemia in post-absorptive healthy males. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myette-Côté, É.; Neudorf, H.; Rafiei, H.; Clarke, K.; Little, J.P. Prior ingestion of exogenous ketone monoester attenuates the glycaemic response to an oral glucose tolerance test in healthy young individuals. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagata, T.; Tamura, Y.; Kaga, H.; Sato, M.; Yamasaki, N.; Someya, Y.; Kadowaki, S.; Sugimoto, D.; Satoh, H.; Kawamori, R.; et al. Ingestion of an exogenous ketone monoester improves the glycemic response during oral glucose tolerance test in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance: A crossover randomized trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 12, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cook, C.; Blonquist, T.M.; Taggart, K.; Beckman, D.; Kruger, C.; Conze, D.; Boileau, A.C. A randomized, open-label, cross-over pilot study investigating metabolic product kinetics of the palatable novel ketone ester, bis-octanoyl (R)-1,3-butanediol, and bis-hexanoyl (R)-1,3-butanediol ingestion in healthy adults. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2023, 7, 23978473231197836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Tchabanenko, K.; Pawlosky, R.; Carter, E.; Todd King, M.; Musa-Veloso, K.; Ho, M.; Roberts, A.; Robertson, J.; Vanitallie, T.B.; et al. Kinetics, safety and tolerability of (R)-3-hydroxybutyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate in healthy adult subjects. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cox, P.J.; Evans, R.D.; Santer, P.; Miller, J.J.; Faull, O.K.; Magor-Elliott, S.; Hiyama, S.; Stirling, M.; Clarke, K. On the metabolism of exogenous ketones in humans. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleeker, J.C.; Visser, G.; Clarke, K.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Haan, F.H.; Houtkooper, R.H.; IJlst, L.; Kok, I.L.; Langeveld, M.; Pol, W.L.; et al. Nutritional ketosis improves exercise metabolism in patients with very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.; Munten, S.; Herzig, K.-H.; Gagnon, D.D. Exogenous ketone salt supplementation and whole-body cooling do not improve short-term physical performance. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 663206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Ashmore, T.; Willerton, K.; Evans, R.; Smith, A.; Murray, A.J.; Stubbs, B.; West, J.; McLure, S.W.; et al. Nutritional ketosis alters fuel preference and thereby endurance performance in athletes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenoud, B.; Hartweg, M.; Godin, J.-P.; Croteau, E.; Maltais, M.; Castellano, C.-A.; Carpentier, A.C.; Cunnane, S.C. Metabolism of exogenous D-beta-hydroxybutyrate, an energy substrate avidly consumed by the heart and kidney. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearlove, D.J.; Faull, O.K.; Rolls, E.; Clarke, K.; Cox, P.J. Nutritional ketoacidosis during incremental exercise in healthy athletes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Mcswiney, F.T.; Brady, A.J.; Egan, B. No benefit of ingestion of a ketone monoester supplement on 10-km running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdsworth, D.A.; Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Stradling, H.; Impey, S.G.; Clarke, K. A ketone ester drink increases postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis in humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Silva, M.S.C.; Auslander, P.A.T.; Arreglado, M.J.P.; Elam, P.M.L.; Osmond, M.A.D.; Steinberg, M.R.; Wong, M.M.W.H. The effects of 10-day exogenous ketone consumption on repeated time trial running performances: A randomized-control trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2020, 19, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Løkken, N.; Storgaard, J.H.; Revsbech, K.L.; Voermans, N.C.; van Hall, G.; Vissing, J.; Ørngreen, M.C. No effect of oral ketone ester supplementation on exercise capacity in patients with McArdle disease and healthy controls: A randomized placebo-controlled cross-over study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2022, 45, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myette-Côté, É.; Caldwell, H.G.; Ainslie, P.N.; Clarke, K.; Little, J.P. A ketone monoester drink reduces the glycemic response to an oral glucose challenge in individuals with obesity: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudorf, H.; Myette-Côté, É.; Little, P.J. The impact of acute ingestion of a ketone monoester drink on LPS-stimulated NLRP3 activation in humans with obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norwitz, N.G.; Dearlove, D.J.; Lu, M.; Clarke, K.; Dawes, H.; Hu, M.T. A ketone ester drink enhances endurance exercise performance in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 584130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poffé, C.; Ramaekers, M.; Bogaerts, S.; Hespel, P. Exogenous ketosis impacts neither performance nor muscle glycogen breakdown in prolonged endurance exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodger, S.; Plews, D.J.; Laursen, P.B.; Driller, M.W. Oral β-hydroxybutyrate salt fails to improve 4-minute cycling performance following submaximal exercise. J. Sci. Cycl. 2017, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Mota, A.; Vansant, H.; Evans, R.D.; Clarke, K. Safety and tolerability of sustained exogenous ketosis using ketone monoester drinks for 28 days in healthy adults. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 109, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Nepocatych, S. Beta-hydroxybutyrate (bhb) ketone salt supplement alters energy metabolism, blood glucose and ketone levels. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandoorne, T.; de Smet, S.; Ramaekers, M.; van Thienen, R.; de Bock, K.; Clarke, K.; Hespel, P. Intake of a ketone ester drink during recovery from exercise promotes mtorc1 signaling but not glycogen resynthesis in human muscle. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Egan, B. Intermittent running and cognitive performance after ketone ester ingestion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Evans, R.D.; Clarke, K. Gastrointestinal effects of exogenous ketone drinks are infrequent, mild, and vary according to ketone compound and dose. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.N.; Altman, D.G.; Campbell, M.J.; Royston, P. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ 1990, 300, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Mota, A.; Norwitz, N.G.; Evans, R.D.; Clarke, K. Exogenous d-β-hydroxybutyrate lowers blood glucose in part by decreasing the availability of L-alanine for gluconeogenesis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e00300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | Mean ± SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 21.0 ± 2.0 | 18.0 | 25.0 |
| Height (m) | 1.67 ± 0.09 | 1.55 | 1.84 |
| Weight (kg) | 69.7 ± 14.2 | 48.5 | 92.4 |
| Fat (%) | 28.1 ± 9.3 | 17.3 | 47.0 |
| Lean (%) | 33.1 ± 6.4 | 21.7 | 41.9 |
| Waist (cm) | 78.9 ± 10.5 | 67.0 | 94.0 |
| Hip (cm) | 99.7 ± 6.7 | 90.5 | 112.0 |
| WHR 1 | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolyard, M.L.; Graziano, C.M.; Fontaine, K.R.; Sayer, R.D.; Fisher, G.; Plaisance, E.P. Tolerability and Acceptability of an Exogenous Ketone Monoester and Ketone Monoester/Salt Formulation in Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234876
Bolyard ML, Graziano CM, Fontaine KR, Sayer RD, Fisher G, Plaisance EP. Tolerability and Acceptability of an Exogenous Ketone Monoester and Ketone Monoester/Salt Formulation in Humans. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234876
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolyard, Mickey L., Christina M. Graziano, Kevin R. Fontaine, R. Drew Sayer, Gordon Fisher, and Eric P. Plaisance. 2023. "Tolerability and Acceptability of an Exogenous Ketone Monoester and Ketone Monoester/Salt Formulation in Humans" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234876
APA StyleBolyard, M. L., Graziano, C. M., Fontaine, K. R., Sayer, R. D., Fisher, G., & Plaisance, E. P. (2023). Tolerability and Acceptability of an Exogenous Ketone Monoester and Ketone Monoester/Salt Formulation in Humans. Nutrients, 15(23), 4876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234876









