Decoding the Influence of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Its Transgenerational Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
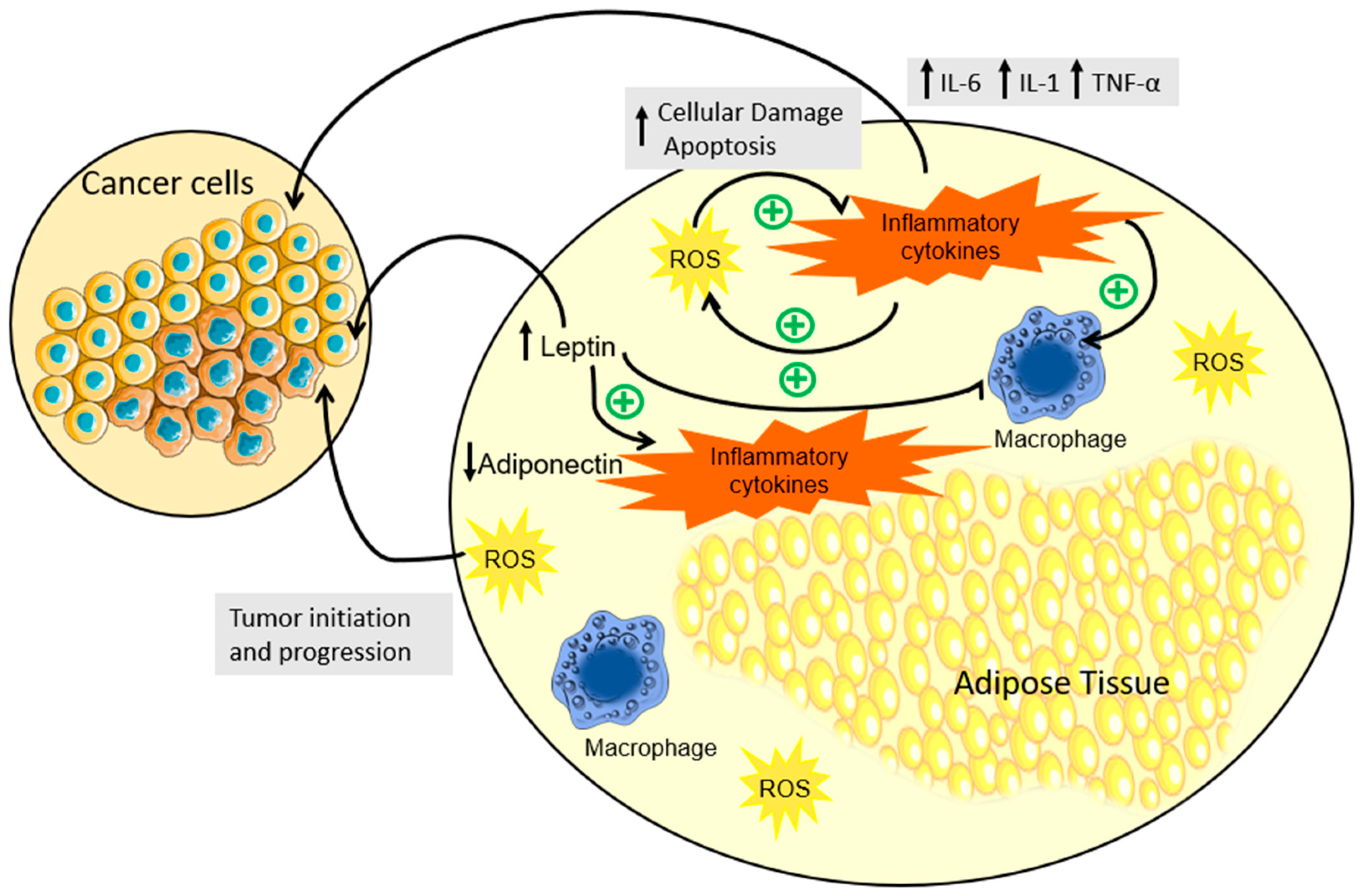
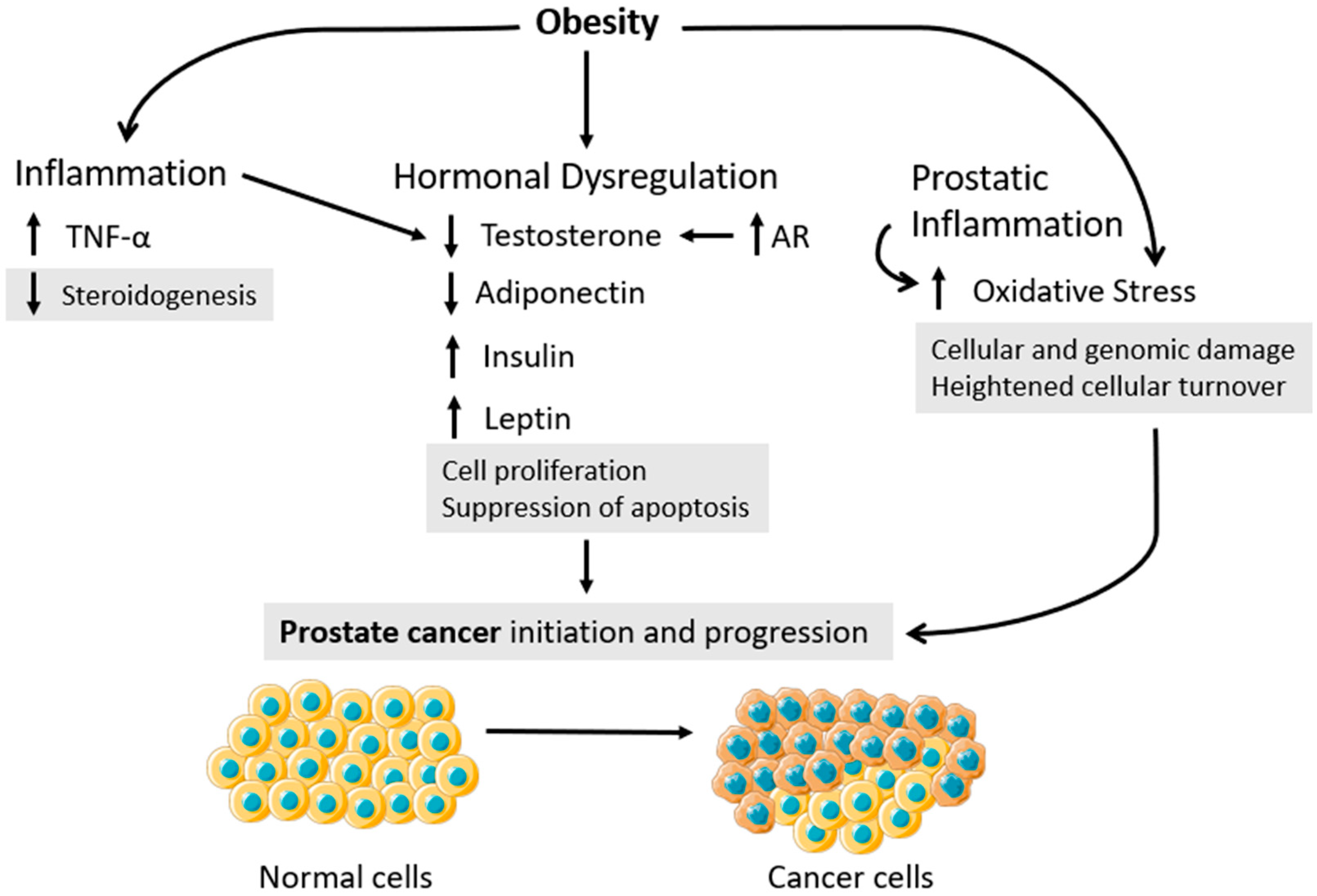
2. Deciphering How Obesity Fuels Carcinogenesis—A Role for Inflammation, Hormonal Dysregulation, and Oxidative Stress
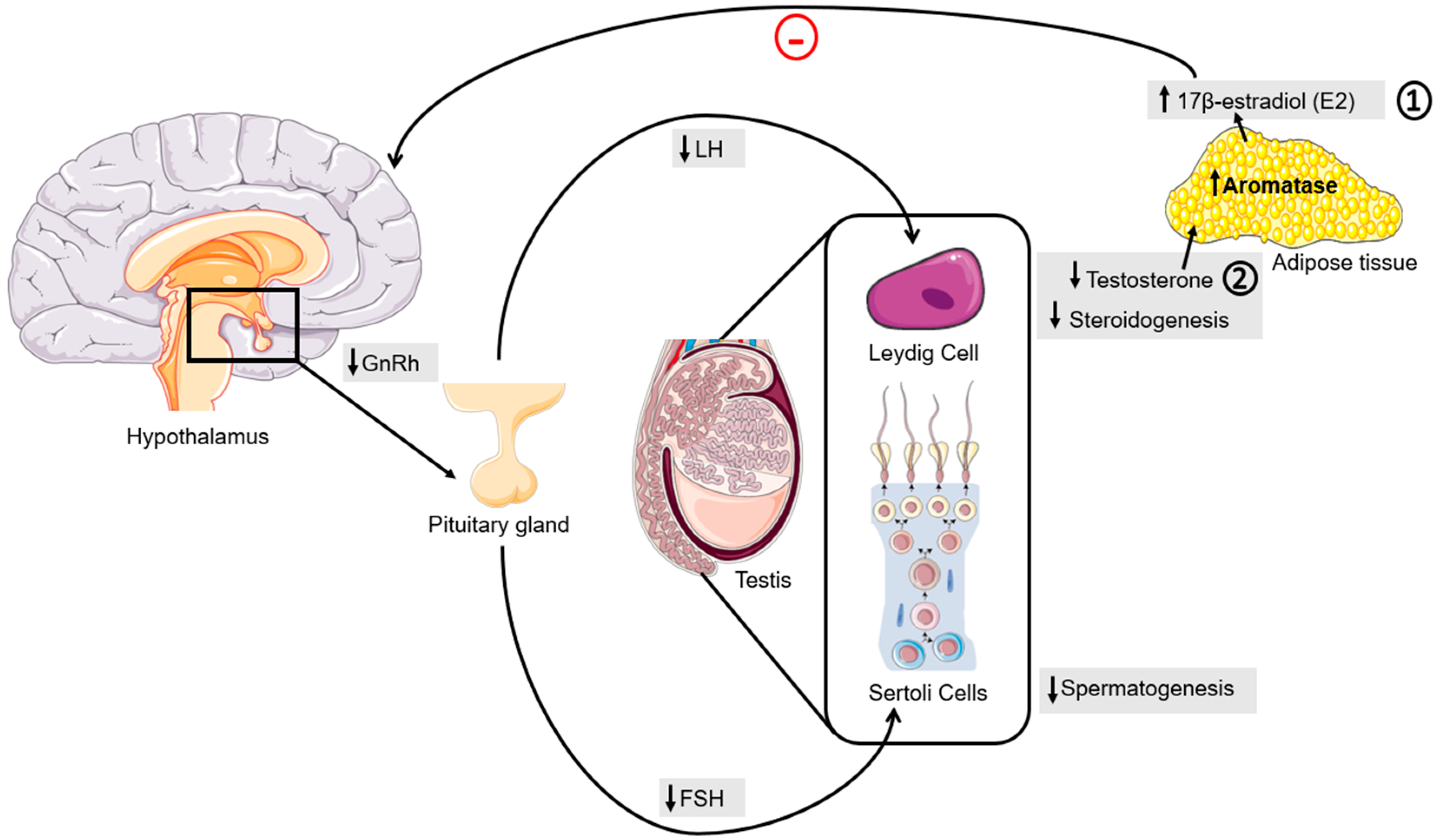
3. Obesity Is an Amplifier Factor for PCa Development
4. Can Paternal Obesity Be Promoting PCa Development in the Offspring?
4.1. Is It Possible to Determine a Biomarker for the Inheritance of PCa (And Obesity)?
4.1.1. Androgen Receptor
4.1.2. Homeobox B13
4.1.3. DNA Hypermethylation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fock, K.M.; Khoo, J. Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. S4), 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, K.; Keller, M.; la Cour Poulsen, L.; Blüher, M.; Kovacs, P.; Böttcher, Y. Genetics and epigenetics in obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haththotuwa, R.; Wijeyaratne, C.; Senarath, U. Obesity and Obstetrics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2023; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Spalding, K.L.; Britton, T.; Rydén, M.; Frisén, J.; Bernard, S.; Arner, P. Adipocyte turnover: Relevance to human adipose tissue morphology. Diabetes 2010, 59, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, F.; Blumberg, B. Minireview: The case for obesogens. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.; Rene, A. Obesity as a disease: No lightweight matter. Obes. Rev. 2004, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.M.; Aronne, L.J. Causes of obesity. Abdom. Imaging 2012, 37, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvenne, H.; Dubern, B. Monogenic forms of obesity. In Molecular Mechanisms Underpinning the Development of Obesity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, B.M.; Keildson, S.; Lindgren, C.M. Genetics and epigenetics of obesity. Maturitas 2011, 69, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, S.; Drong, A.; Lehne, B.; Loh, M.; Scott, W.R.; Kunze, S.; Tsai, P.-C.; Ried, J.S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Epigenome-wide association study of body mass index, and the adverse outcomes of adiposity. Nature 2017, 541, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, K.J.; Nelson, C.P.; Tsaprouni, L.; Sandling, J.K.; Aïssi, D.; Wahl, S.; Meduri, E.; Morange, P.-E.; Gagnon, F.; Grallert, H.; et al. DNA methylation and body-mass index: A genome-wide analysis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.; Abed, Y.; Rahmat, A.; Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F. Epidemiology of obesity in developing countries: Challenges and prevention. Glob. Epidemic Obes. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22 (Suppl. S7), s176–s185. [Google Scholar]
- De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 291546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.B.; Thomas, C.C.; Henley, S.J.; Massetti, G.M.; Galuska, D.A.; Agurs-Collins, T.; Puckett, M.; Richardson, L.C. Vital Signs: Trends in Incidence of Cancers Associated with Overweight and Obesity—United States, 2005–2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artac, M.; Altundag, K. Leptin and breast cancer: An overview. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Au, C.C.; Benito-Martin, A.; Ladumor, H.; Oshchepkova, S.; Moges, R.; Brown, K.A. Estrogens and breast cancer: Mechanisms involved in obesity-related development, growth and progression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 189, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, T.; Schwartz, B. Leptin promotes motility and invasiveness in human colon cancer cells by activating multiple signal-transduction pathways. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; Chalfant, M.C.; Gorden, L.D.; VanSaun, M.N. Modulation of the Leptin Receptor Mediates Tumor Growth and Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.-Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Österreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and Genetic Obesity Promote Liver Inflammation and Tumorigenesis by Enhancing IL-6 and TNF Expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Song, K.; Choi, D.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Park, P.H. Autophagy induction by leptin contributes to suppression of apoptosis in cancer cells and xenograft model: Involvement of p53/FoxO3A axis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7166–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.-H.; Kuo, M.-L.; Chen, C.-A.; Chou, C.-H.; Cheng, W.-F.; Chang, M.-C.; Su, J.-L.; Hsieh, C.-Y. The anti-apoptotic role of interleukin-6 in human cervical cancer is mediated by up-regulation of Mcl-1 through a PI 3-K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5799–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-T.; Juan, C.-Y.; Chang, K.-J.; Chen, W.-J.; Kuo, M.-L. IL-6 inhibits apoptosis and retains oxidative DNA lesions in human gastric cancer AGS cells through up-regulation of anti-apoptotic gene mcl-1. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Hao, J. Leptin upregulates telomerase activity and transcription of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernar, C.H.; Ebot, E.M.; Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A. The Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Gao, Y.-T.; Chua, S., Jr.; Deng, J.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Insulin Resistance and Prostate Cancer Risk. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.L.; Taaffe, D.R.; Newton, R.U.; Hart, N.H.; Lyons-Wall, P.; Galvão, D.A. Obesity and prostate cancer: A narrative review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 169, 103543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, M.; Bub, J.D.; Rummel, T.L.; Iwamoto, Y. Prostate cancer cell-adipocyte interaction: Leptin mediates androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42660–42667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Bub, J.D.; Iwamoto, Y. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mediates leptin-stimulated androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and Akt. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allott, E.H.; Masko, E.M.; Freedland, S.J. Obesity and Prostate Cancer: Weighing the Evidence. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, L.A.; Neeley, C.K.; Meyer, K.A.; Baker, N.A.; Brosius, A.M.; Washabaugh, A.R.; Varban, O.A.; Finks, J.F.; Zamarron, B.F.; Flesher, C.G.; et al. Adipose tissue fibrosis, hypertrophy, and hyperplasia: Correlations with diabetes in human obesity. Obesity 2016, 24, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, B.; Gogg, S.; Hedjazifar, S.; Jenndahl, L.; Hammarstedt, A.; Smith, U. Inflammation and impaired adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity in man. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E999–E1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, I.H.A.; Boushel, R.; Kalliokoski, K.K. The Circulatory and Metabolic Responses to Hypoxia in Humans—With Special Reference to Adipose Tissue Physiology and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuela, F.; Grazia, M.; Marco de, R.; Maria Paola, L.; Giorgio, F.; Marco, B. Inflammation as a Link between Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 476380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ashcraft, K. An IL-6 link between obesity and cancer. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2013, 5, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Krämer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin resistance associated to obesity: The link TNF-alpha. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; María Aguilera, C.; Gil-Campos, M.; Cañete, R. Altered signalling and gene expression associated with the immune system and the inflammatory response in obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98 (Suppl. S1), S121–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Berriguete, G.; Sánchez-Espiridión, B.; Cansino, J.R.; Olmedilla, G.; Martínez-Onsurbe, P.; Sánchez-Chapado, M.; Paniagua, R.; Fraile, B.; Royuela, M. Clinical significance of both tumor and stromal expression of components of the IL-1 and TNF-α signaling pathways in prostate cancer. Cytokine 2013, 64, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.; Charles, K.A.; Balkwill, F.R. Tumour necrosis factor-α as a tumour promoter. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. TNF-α in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.R.; Libutti, S.K. Targeting TNF-α for cancer therapy. J. Biol. 2009, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marseglia, L.; Manti, S.; D’Angelo, G.; Nicotera, A.; Parisi, E.; Di Rosa, G.; Gitto, E.; Arrigo, T. Oxidative stress in obesity: A critical component in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, Á.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epingeac, M.E.; Gaman, M.A.; Diaconu, C.C.; Gad, M.; Gaman, A.M. The evaluation of oxidative stress levels in obesity. Rev. Chim. (Buchar.) 2019, 70, 2241–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondia-Pons, I.; Ryan, L.; Martinez, J.A. Oxidative stress and inflammation interactions in human obesity. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 68, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Yokomizo, A.; Naito, S. Oxidative stress and androgen receptor signaling in the development and progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udensi, U.K.; Tchounwou, P.B. Oxidative stress in prostate hyperplasia and carcinogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Schoneveld, O.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Oxidative stress, DNA methylation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Kaaks, R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.L.; Vidal-Puig, A.J. Adipose Tissue Expandability in the Maintenance of Metabolic Homeostasis. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Sell, H. Adipokines: A treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, V.d.O.; Mafra, D. Adipokines in obesity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 419, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P. The role of adipokines in chronic inflammation. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2016, 5, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denver, R.J.; Bonett, R.M.; Boorse, G.C. Evolution of Leptin Structure and Function. Neuroendocrinology 2011, 94, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, M.L.; Hao, M.; Piston, D.W.; Hasty, A.H. Leptin requires canonical migratory signaling pathways for induction of monocyte and macrophage chemotaxis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C1481–C1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundar, P.; Yu, A.K.; Vona-Davis, L.; McFadden, D.W. Differential effects of leptin on cancer in vitro. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 113, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikuni, N.; Kwan Lam, Q.L.; Lu, L.; Matarese, G.; Cava, A.L. Leptin and inflammation. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 4, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisegang, K.; Sengupta, P.; Agarwal, A.; Henkel, R. Obesity and male infertility: Mechanisms and management. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Hontoria, P.L.; Pérez-Matute, P.; Fernández-Galilea, M.; Bustos, M.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Role of obesity-associated dysfunctional adipose tissue in cancer: A molecular nutrition approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1807, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsey, C.C.; Harbuzariu, A.; Daley-Brown, D.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role of leptin and Notch interleukin-1 leptin crosstalk outcome in cancer. World J. Methodol. 2016, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, S.; Gelsomino, L.; Panza, S.; Giordano, C.; Bonofiglio, D.; Barone, I.; Catalano, S. Obesity, Leptin and Breast Cancer: Epidemiological Evidence and Proposed Mechanisms. Cancers 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kitayama, J.; Nagawa, H. Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB-R) in human breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4325–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deng, L.-L.; Cui, J.-Q.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.-C.; Luo, J.-H.; Qin, D.; Wang, L. Association between serum leptin levels and breast cancer risk: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, L. The association between obesity related adipokines and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.-i.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical Decrease of an Adipose-Specific Protein, Adiponectin, in Obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihn, A.S.; Bruun, J.M.; He, G.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jensen, P.F.; Richelsen, B. Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 219, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, M.; Pendzialek, M.; Grybel, K.J.; Seeling, T.; Gürke, J.; Fischer, B.; Navarrete Santos, A. Adiponectin stimulates lipid metabolism via AMPK in rabbit blastocysts. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitfeld, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Kovacs, P. Genetics of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, K.; Ishihara, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Murono, K.; Yasuda, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kiyomatsu, T.; Hata, K.; Kawai, K.; et al. Adiponectin and colorectal cancer. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, L.; Wei, X.; Jin, D.; Qian, T.; Yu, A.; Sun, J.; Cui, J.; Yang, Z. The multimerization and secretion of adiponectin are regulated by TNF-alpha. Endocrine 2016, 51, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kitayama, J.; Kazama, S.; Hiramatsu, T.; Hatano, K.; Nagawa, H. Plasma Adiponectin and Gastric Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktas, S.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Caglar, K.; Sonmez, A.; Kilic, S.; Bedir, S. Prostate cancer and adiponectin. Urology 2005, 65, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, F.; Condorelli, R.A.; Mongioì, L.M.; Cannarella, R.; Cimino, L.; Magagnini, M.C.; Crafa, A.; La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Relationship between Obesity and Male Infertility. Metabolites 2021, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, S.S.; Cabler, S.; McAlister, D.A.; Sabanegh, E.; Agarwal, A. The effect of obesity on sperm disorders and male infertility. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna C, J.A.; Gómez-Pérez, R.; Arata-Bellabarba, G.; Villaroel, V. Relationship Between BMI, Total Testosterone, Sex Hormone-Binding-Globulin, Leptin, Insulin and Insulin Resistance in Obese Men. Arch. Androl. 2006, 52, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Luo, D.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Feng, L.; Gao, L.; Yu, C.; et al. Effect of Testosterone Synthesis and Conversion on Serum Testosterone Levels in Obese Men. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Arjonilla, M.; Schwarcz, M.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wang, C. Obesity, low testosterone levels and erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2009, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Wu, S.; Sharkey, C.; Tabatabaei, S.; Wu, C.-L.; Tao, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Strand, D.; Olumi, A.F.; Wang, Z. Obesity-associated inflammation induces androgenic to estrogenic switch in the prostate gland. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.W.; Cunha, G.R. The Prostate: Development and Physiology. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittmann, M. Anatomy and Histology of the Human and Murine Prostate. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, J.A.; Rider, J.R.; Carlsson, J.; Gerke, T.; Tyekucheva, S.; Penney, K.L.; Sesso, H.D.; Loda, M.; Fall, K.; Stampfer, M.J.; et al. Molecular differences in transition zone and peripheral zone prostate tumors. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.L.; Martin, F.L. The initiation of breast and prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, B.S.; Vasioukhin, V. Mechanisms of prostate cancer initiation and progression. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 109, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, D.A.; Zong, Y.; Memarzadeh, S.; Xin, L.; Huang, J.; Witte, O.N. Basal epithelial stem cells are efficient targets for prostate cancer initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, J.E.; Redwine, E.A.; Freiha, F.S.; Stamey, T.A. Zonal Distribution of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma: Correlation with Histologic Pattern and Direction of Spread. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1988, 12, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Marchi, V.L.; Epstein, J.I.; Nelson, W.G. Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate: Implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Mucci, N.R.; Amin, A.; Macoska, J.A.; Rubin, M.A. Postatrophic hyperplasia of the prostate gland: Neoplastic precursor or innocent bystander? Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsilieris, M.; Mitsiades, C.S. Molecular biology and cellular physiology of refractoriness to androgen ablation therapy in advanced prostate cancer. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2001, 10, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Khera, M. Physiological normal levels of androgen inhibit proliferation of prostate cancer cells in vitro. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.C.; Lu, J.J.; Xu, X.L.; Sun, J.M. MicroRNAs in androgen-dependent PCa. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2013, 18, 748–755. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mendonca, J.; Owoyemi, O.; Boyapati, K.; Thomas, N.; Kanacharoen, S.; Coffey, M.; Topiwala, D.; Gomes, C.; Ozbek, B.; et al. Supraphysiologic Testosterone Induces Ferroptosis and Activates Immune Pathways through Nucleophagy in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5948–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Wang, H.; Lim ScM, S.J.; Rifkind, I.; Ngomba, N.; Isaacs, J.T.; Luo, J.; Pratz, C.; Sinibaldi, V.; Carducci, M.A.; et al. Bipolar androgen therapy sensitizes castration-resistant prostate cancer to subsequent androgen receptor ablative therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 144, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.T.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Wang, H.; Spitz, A.N.; Cao, H.; Pacheco, A.; Eisenberger, M.A.; Carducci, M.A.; Denmeade, S.R. A pilot study of supraphysiologic testosterone (T) and oral etoposide (E) in men with castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltering, K.K.; Helenius, M.A.; Sahu, B.; Manni, V.; Linja, M.J.; Jänne, O.A.; Visakorpi, T. Increased Expression of Androgen Receptor Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Low Levels of Androgens. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8141–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulvat, M.C. Cancer Incidence and Trends. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 100, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelusi, C.; Pasquali, R. The Significance of Low Testosterone Levels in Obese Men. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mauduit, C.; Gasnier, F.o.; Rey, C.; Chauvin, M.-A.s.; Stocco, D.M.; Louisot, P.; Benahmed, M. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibits Leydig Cell Steroidogenesis through a Decrease in Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Expression. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2863–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivam, M.; Ramatchandirin, B.; Balakrishnan, S.; Prahalathan, C. TNF-α-mediated suppression of Leydig cell steroidogenesis involves DAX-1. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschemeyer, W.C., III; Freedland, S.J. Obesity and prostate cancer: Epidemiology and clinical implications. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, A.; Benoit, G. Percutaneous 17 β-estradiol in treatment of cancer of prostate. Urology 1979, 14, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, B.; Nelson, P.S.; Vessella, R.; Kalhorn, T.; Hess, D.; Corey, E. Estradiol suppresses tissue androgens and prostate cancer growth in castration resistant prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, A.M.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Pons, D.G.; Valle, A.; Roca, P.; Oliver, J. 17β-Estradiol regulates oxidative stress in prostate cancer cell lines according to ERalpha/ERbeta ratio. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 123, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnoeller, T.J.; Steinestel, J.; Zengerling, F.; Schrader, A.J.; Jentzmik, F. Serum 17β-estradiol fails as a marker in identification of aggressive tumour disease in patients with localized prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1979–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaker, H.; Sacco, K.; Alfraidi, A.; Muhammad, A.; Winkler, M.; Pchejetski, D. Leptin signalling, obesity and prostate cancer: Molecular and clinical perspective on the old dilemma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35556–35563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, T.; Digby, J.E.; Desai, K.M.; Randeva, H.S. Obesity and Prostate Cancer: A Role for Adipokines. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Magnuson, A.; Fouts, J.; Foster, M. Adipose tissue, obesity and adipokines: Role in cancer promotion. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 21, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, P.; Khanal, S. Leptin in Atherosclerosis: Focus on Macrophages, Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.P.; Oka, R.K. Does Leptin Cause Vascular Disease? Circulation 2002, 106, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffreda, S.; Yang, S.Q.; Lin, H.Z.; Karp, C.L.; Brengman, M.L.; Wang, D.J.; Klein, A.S.; Bulkley, G.B.; Bao, C.; Noble, P.W.; et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, L.; Ye, C.; Yang, Z.; Choi, B.; Chua, S.; Lowell, B.B. Leptin action on GABAergic neurons prevents obesity and reduces inhibitory tone to POMC neurons. Neuron 2011, 71, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Byun, S.-S.; Lee, S.E.; Hong, S.K. Clinical significance of serum adipokines according to body mass index in patients with clinically localized prostate cancer undergoing radical prostatectomy. World J. Mens. Health 2018, 36, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundar, P.; Frankenberry, K.A.; Skinner, H.; Vedula, G.; McFadden, D.W.; Riggs, D.; Jackson, B.; Vangilder, R.; Hileman, S.M.; Vona-Davis, L.C. Prostate cancer cell proliferation is influenced by leptin. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 118, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberry, K.A.; Somasundar, P.; McFadden, D.W.; Vona-Davis, L.C. Leptin induces cell migration and the expression of growth factors in human prostate cancer cells. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 188, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, C.N.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Tolba, M.F.; Khalifa, A.E.; Khedr, A.; Mosli, H.A.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Leptin influences estrogen metabolism and accelerates prostate cell proliferation. Life Sci. 2015, 121, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Tsiaousi, E. The role of adiponectin in the pathogenesis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, S.; Oakhill, J.S.; Steinberg, G.R. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, C.Z.; Iguacel, I.; Mullee, A.; Guha, N.; Wasson, R.; McKenna, D.J.; Gunter, M.J.; Smelov, V.; Huybrechts, I. Appetite-regulating hormones—Leptin, adiponectin and ghrelin—And the development of prostate cancer: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.M.; Schwartz, K.; Pollak, M.; Graubard, B.I.; Li, Z.; Ruterbusch, J.; Rothman, N.; Davis, F.; Wacholder, S.; Colt, J.; et al. Serum leptin and adiponectin levels and risk of renal cell carcinoma. Obesity 2013, 21, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.P.; Hou, Z.F.; Duivenvoorden, W.C.; Whelan, K.; Honig, A.; Pinthus, J.H. Adiponectin inhibits oxidative stress in human prostate carcinoma cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2012, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschos, S.J.; Mantzoros, C.S. The Role of the IGF System in Cancer: From Basic to Clinical Studies and Clinical Applications. Oncology 2002, 63, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Tzonou, A.; Signorello, L.B.; Stampfer, M.; Trichopoulos, D.; Adami, H.O. Insulin-like growth factor 1 in relation to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca, C.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmott, R.M.; Dennis, P.A. Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR regulation in cancer. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.H.; Su, Y.C.; Lai, P.L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhao, A.; Yao, G.Y.; Jia, C.H.; Lin, J.; Xu, S.; et al. Critical role of arachidonic acid-activated mTOR signaling in breast carcinogenesis and angiogenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Komninou, D.; Stephenson, G.D. Obesity, adipocytokines, and insulin resistance in breast cancer. Obes. Rev. 2004, 5, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloz, Y.; Stambolic, V. Obesity and cancer, a case for insulin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Krishnaswamy, G.; Karnad, A.; Peiris, A.N. Insulin: A Novel Factor in Carcinogenesis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 323, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronakos, C.; Janthly, U.; Lehoux, J.-G.; Koutsilieris, M. Mitogenic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factors on PA-III rat prostate adenocarcinoma cells: Characterization of the receptors involved. Prostate 1991, 19, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiovanni, J.; Kiguchi, K.; Frijhoff, A.; Wilker, E.; Bol, D.K.; Beltrán, L.; Moats, S.; Ramirez, A.; Jorcano, J.; Conti, C. Deregulated expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 in prostate epithelium leads to neoplasia in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3455–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Chua, S., Jr.; Gao, Y.T.; Gentzschein, E.; Chang, L.; Deng, J.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Prostate cancer risk and serum levels of insulin and leptin: A population-based study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lehrer, S.; Diamond, E.J.; Stagger, S.; Stone, N.N.; Stock, R.G. Increased serum insulin associated with increased risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate 2002, 50, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Deng, J.; Sesterhenn, I.A.; Mostofi, F.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Benichou, J.; Xie, T.; Gao, Y.-T. Body size and prostate cancer: A population-based case-control study in China. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Iiritano, S.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Nevolo, M.T.; Ventura, V.; Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, A. Insulin Resistance and Cancer Risk: An Overview of the Pathogenetic Mechanisms. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 789174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, R.J.; Aronson, W.J.; Tymchuk, C.N.; Ngo, T.H. Prostate cancer: Another aspect of the insulin-resistance syndrome? Obes. Rev. 2002, 3, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, A.; Pandya, R.; Duivenvoorden, W.C.M.; Pinthus, J.H. Oxidative stress in prostate cancer: Changing research concepts towards a novel paradigm for prevention and therapeutics. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.P.; Monardo, L.; Bryskin, I.; Hou, Z.F.; Trachtenberg, J.; Wilson, B.C.; Pinthus, J.H. Androgens induce oxidative stress and radiation resistance in prostate cancer cells though NADPH oxidase. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta-Elera, G.; Garrett, A.R.; Robison, R.A.; O’Neill, K.L. The role of oxidative stress in prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 21, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.D.; Pulford, D.J. The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: Regulation of GST and the contribution of the lsoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance part I. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 445–520. [Google Scholar]
- Arsova-Sarafinovska, Z.; Matevska, N.; Eken, A.; Petrovski, D.; Banev, S.; Dzikova, S.; Georgiev, V.; Sikole, A.; Erdem, O.; Sayal, A. Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) genetic polymorphism, erythrocyte GPX activity, and prostate cancer risk. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Lamark, T.; Sjøttem, E.; Larsen, K.B.; Awuh, J.A.; Øvervatn, A.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22576–22591. [Google Scholar]
- Sfanos, K.S.; De Marzo, A.M. Prostate cancer and inflammation: The evidence. Histopathology 2012, 60, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Bustos-Aibar, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Mendez-Gutierrez, A.; Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Aguilera, C.M.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J. Omics Approaches in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Addressing the Role of Extracellular Matrix in Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2756. [Google Scholar]
- Leisegang, K.; Henkel, R.; Agarwal, A. Obesity and metabolic syndrome associated with systemic inflammation and the impact on the male reproductive system. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 82, e13178. [Google Scholar]
- Samblas, M.; Milagro, F.I.; Martínez, A. DNA methylation markers in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and weight loss. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-García, R.; Blumberg, B. Transgenerational effects of obesogens and the obesity epidemic. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 19, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkies, P. Molecular mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance: Possible evolutionary implications. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 97, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann, R.; Buchner, D.A. Transgenerational inheritance of metabolic disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lecoutre, S.; Petrus, P.; Rydén, M.; Breton, C. Transgenerational Epigenetic Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue Development. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 675–685. [Google Scholar]
- King, S.E.; Skinner, M.K. Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Obesity Susceptibility. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 478–494. [Google Scholar]
- Lacal, I.; Ventura, R. Epigenetic Inheritance: Concepts, Mechanisms and Perspectives. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Barouki, R.; Melén, E.; Herceg, Z.; Beckers, J.; Chen, J.; Karagas, M.; Puga, A.; Xia, Y.; Chadwick, L.; Yan, W.; et al. Epigenetics as a mechanism linking developmental exposures to long-term toxicity. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cortessis, V.K.; Thomas, D.C.; Levine, A.J.; Breton, C.V.; Mack, T.M.; Siegmund, K.D.; Haile, R.W.; Laird, P.W. Environmental epigenetics: Prospects for studying epigenetic mediation of exposure–response relationships. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1565–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Suter, M.A.; Aagaard-Tillery, K.M. Environmental Influences on Epigenetic Profiles. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2009, 27, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.K. Endocrine disruptor induction of epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 398, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, B.; Barnes, S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Morrow, C.; Salvador, C.; Skibola, C.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Influences of diet and the gut microbiome on epigenetic modulation in cancer and other diseases. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul, Q.A.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Epigenetic modifications of gene expression by lifestyle and environment. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2017, 40, 1219–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Wykes, S.M.; Krawetz, S.A. The structural organization of sperm chromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29471–29477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, J.R.; Emery, B.R.; Jenkins, T.G.; Carrell, D.T. The Sperm Epigenome: Implications for the Embryo. In Genetic Damage in Human Spermatozoa; Baldi, E., Muratori, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Carrell, D.T. Epigenetics of the male gamete. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 97, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpanahi, A.; Brinkworth, M.; Iles, D.; Krawetz, S.A.; Paradowska, A.; Platts, A.E.; Saida, M.; Steger, K.; Tedder, P.; Miller, D. Endonuclease-sensitive regions of human spermatozoal chromatin are highly enriched in promoter and CTCF binding sequences. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, I.; Versteyhe, S.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Qian, K.; Mechta, M.; Nordkap, L.; Mortensen, B.; Appel, E.V.R.; Jørgensen, N.; Kristiansen, V.B. Obesity and bariatric surgery drive epigenetic variation of spermatozoa in humans. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.; Zander-Fox, D.L.; Robker, R.L.; McPherson, N.O. Peri-conception parental obesity, reproductive health, and transgenerational impacts. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullston, T.; Teague, E.M.C.O.; Palmer, N.O.; DeBlasio, M.J.; Mitchell, M.; Corbett, M.; Print, C.G.; Owens, J.A.; Lane, M. Paternal obesity initiates metabolic disturbances in two generations of mice with incomplete penetrance to the F2 generation and alters the transcriptional profile of testis and sperm microRNA content. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4226–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisóstomo, L.; Rato, L.; Jarak, I.; Silva, B.M.; Raposo, J.F.; Batterham, R.L.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. A switch from high-fat to normal diet does not restore sperm quality but prevents metabolic syndrome. Reproduction 2019, 158, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Feng, G.-h.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Sperm tsRNAs contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired metabolic disorder. Science 2016, 351, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andolfi, C.; Fisichella, P.M. Epidemiology of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2018, 28, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. Comorbidities of overweight and obesity: Current evidence and research issues. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, S602–S608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Morriseau, T.S.; Kereliuk, S.M.; Doucette, C.A.; Wicklow, B.A.; Dolinsky, V.W. Maternal obesity, diabetes during pregnancy and epigenetic mechanisms that influence the developmental origins of cardiometabolic disease in the offspring. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 71–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, E.; Priest, J.R. Maternal Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus as Risk Factors for Congenital Heart Disease in the Offspring. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e011541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.R.; Simon, M.; Wentling, C.; Spencer, D.M.; Parker, A.N.; Rogers, C.A. A review of inherited cancer susceptibility syndromes. Jaapa 2020, 33, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantus, R.J.; Helfand, B.T. Germline Genetics of Prostate Cancer: Time to Incorporate Genetics into Early Detection Tools. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.L.; Schumacher, F.R.; Easton, D.; Muir, K.; Henderson, B.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Eeles, R.A. Genetic variants associated with predisposition to prostate cancer and potential clinical implications. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 271, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhage, B.A.; Kiemeney, L.A. Inherited predisposition to prostate cancer. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri, M.T.; D’Elia, G.; Caliendo, G.; Resse, M.; Casamassimi, A.; Passariello, L.; Albanese, L.; Cioffi, M.; Molinari, A.M. Hereditary Prostate Cancer: Genes Related, Target Therapy and Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oto, J.; Fernández-Pardo, Á.; Royo, M.; Hervás, D.; Martos, L.; Vera-Donoso, C.D.; Martínez, M.; Heeb, M.J.; España, F.; Medina, P.; et al. A predictive model for prostate cancer incorporating PSA molecular forms and age. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.D.; Chang, B.L.; Rao, A.; Hawkins, G.A.; Zheng, S.L.; Wade, W.N.; Cooke, R.T.; Thomas, L.N.; Bleecker, E.R.; Catalona, W.J.; et al. Association between genetic polymorphisms in the prostate-specific antigen gene promoter and serum prostate-specific antigen levels. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baio, R.; Napodano, G.; Caruana, C.; Molisso, G.; Di Mauro, U.; Intilla, O.; Pane, U.; D’Angelo, C.; Francavilla, A.B.; Guarnaccia, C.; et al. Association between obesity and frequency of high-grade prostate cancer on biopsy in men: A single-center retrospective study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, M.E.; Neuzillet, Y.; Dreyfus, J.F.; Schneider, M.; Rouprêt, M.; Cathelineau, X.; Raynaud, J.P.; Lebret, T.; Botto, H. PSA and obesity among men with localized prostate cancer: Results of the ANDROCAN study. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 2945–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, A.T.; Vincent, A.D.; O’Callaghan, M.E.; Martin, S.A.; Sutherland, P.D.; Hoy, A.J.; Butler, L.M.; Wittert, G.A. The inverse relationship between prostate specific antigen (PSA) and obesity. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yin, X.; Li, D.; Yin, Z.; Qi, S.; Shi, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X. Association between obesity-related plasma hemodilution and the concentration of prostate specific antigen. J. South. Med. Univ. 2015, 35, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, M.A.; Mekary, R.A.; Chiu, G.R.; Ding, E.L.; Wittert, G.A.; Araujo, A.B. Sex steroid hormone levels and body composition in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowke, J.H.; Signorello, L.B.; Underwood, W., 3rd; Ukoli, F.A.; Blot, W.J. Obesity and prostate cancer screening among African-American and Caucasian men. Prostate 2006, 66, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, A.; Neugut, A.I. Obesity and screening PSA levels among men undergoing an annual physical exam. Prostate 2008, 68, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamroze, A.; Chatta, G.; Tang, D.G. Androgen receptor (AR) heterogeneity in prostate cancer and therapy resistance. Cancer Lett. 2021, 518, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.P.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Androgen deprivation therapy: Progress in understanding mechanisms of resistance and optimizing androgen depletion. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2009, 6, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Student, S.; Hejmo, T.; Poterała-Hejmo, A.; Leśniak, A.; Bułdak, R. Anti-androgen hormonal therapy for cancer and other diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 866, 172783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkinghorn, W.R.; Parker, J.S.; Lee, M.X.; Kass, E.M.; Spratt, D.E.; Iaquinta, P.J.; Arora, V.K.; Yen, W.-F.; Cai, L.; Zheng, D.; et al. Androgen Receptor Signaling Regulates DNA Repair in Prostate Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.M.; Centenera, M.M.; Swinnen, J.V. Androgen control of lipid metabolism in prostate cancer: Novel insights and future applications. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R219–R227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Gao, S.; Barrett, D.; Ahmed, M.; Han, D.; Macoska, J.A.; He, H.H.; Cai, C. Reactivation of androgen receptor-regulated lipid biosynthesis drives the progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uo, T.; Sprenger, C.C.; Plymate, S.R. Androgen Receptor Signaling and Metabolic and Cellular Plasticity During Progression to Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 580617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, J.V.; Ulrix, W.; Heyns, W.; Verhoeven, G. Coordinate regulation of lipogenic gene expression by androgens: Evidence for a cascade mechanism involving sterol regulatory element binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12975–12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate-Shen, C.; Nunes de Almeida, F. Establishment of the LNCaP Cell Line—The Dawn of an Era for Prostate Cancer Research. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, J.V.; Esquenet, M.; Goossens, K.; Heyns, W.; Verhoeven, G. Androgens Stimulate Fatty Acid Synthease in the Human Prostate Cancer Cell Line LNCaP1. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Zadra, G.; Ribeiro, C.F.; Chetta, P.; Ho, Y.; Cacciatore, S.; Gao, X.; Syamala, S.; Bango, C.; Photopoulos, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of de novo lipogenesis targets androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Chung, L.W.K. Activation of Androgen Receptor, Lipogenesis, and Oxidative Stress Converged by SREBP-1 Is Responsible for Regulating Growth and Progression of Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benafif, S.; Eeles, R. Genetic predisposition to prostate cancer. Br. Med. Bull. 2016, 120, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. WJMH 2018, 37, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisermann, K.; Wang, D.; Jing, Y.; Pascal, L.E.; Wang, Z. Androgen receptor gene mutation, rearrangement, polymorphism. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Corti, M.; Lorenzetti, S.; Ubaldi, A.; Zilli, R.; Marcoccia, D. Endocrine Disruptors and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ledet, E.; Velasco-Gonzalez, C.; Mandal, D.M.; Koochekpour, S. Identification of a novel germline missense mutation of the androgen receptor in African American men with familial prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2010, 12, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, P.A.; Hyytinen, E.-R.; Matikainen, M.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Ikonen, T.; Schleutker, J. Germline Mutation Analysis of the Androgen Receptor Gene in Finnish Patients With Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mononen, N.; Syrjäkoski, K.; Matikainen, M.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Schleutker, J.; Kallioniemi, O.-P.; Trapman, J.; Koivisto, P.A. Two Percent of Finnish Prostate Cancer Patients Have a Germ-line Mutation in the Hormone-binding Domain of the Androgen Receptor Gene1. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6479–6481. [Google Scholar]
- Gore, A.C. Developmental programming and endocrine disruptor effects on reproductive neuroendocrine systems. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salian, S.; Doshi, T.; Vanage, G. Perinatal exposure of rats to Bisphenol A affects the fertility of male offspring. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, A.S.; Ghoniem, K.; Ahmed, M.E.; Joshi, V.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Saeed, N.; Khater, N.; Elsharkawy, M.S.; Gamal, A.; Kwon, E.; et al. Prostate Cancer: Advances in Genetic Testing and Clinical Implications. Uro 2023, 3, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhtit, A.; Al-Kindi, M.N.; Kumar, P.R.; Gupta, I.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Tamimi, Y. Hoxb13, a potential prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2016, 8, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechka, H.; Bhanvadia, R.R.; VanOpstall, C.; Vander Griend, D.J. HOXB13 mutations and binding partners in prostate development and cancer: Function, clinical significance, and future directions. Genes. Dis. 2017, 4, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Park, R.-Y.; Kim, Y.-R.; Kim, I.-J.; Kang, T.W.; Nam, K.I.; Ahn, K.Y.; Bae, C.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, S.S.; et al. HOXB13 is co-localized with androgen receptor to suppress androgen-stimulated prostate-specific antigen expression. ACB 2010, 43, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Oh, K.-J.; Choi, C.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, T.W.; Jung, C. Abstract 1228: HOXB13 promotes androgen independent growth of prostate cancer cells by the activation of E2F signaling. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, K.A.; Beebe-Dimmer, J.L. HOXB13 mutations and prostate cancer risk. BJU Int. 2016, 118, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, W.D.; Breyer, J.P.; Johnson, S.H.; Plummer, W.D.; Smith, J.R. Prostate cancer risk variants of the HOXB genetic locus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalza, C.V.; Adam, M.; Burdelski, C.; Wilczak, W.; Wittmer, C.; Kraft, S.; Krech, T.; Steurer, S.; Koop, C.; Hube-Magg, C.; et al. HOXB13 overexpression is an independent predictor of early PSA recurrence in prostate cancer treated by radical prostatectomy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12822–12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.B.; Faisal, F.A.; Davicioni, E.; Karnes, R.J.; Griend, D.J.V.; Lotan, T.L.; Schaeffer, E.M. Somatic HOXB13 Expression Correlates with Metastatic Progression in Men with Localized Prostate Cancer Following Radical Prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Toom, E.E.; Axelrod, H.D.; de la Rosette, J.J.; de Reijke, T.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Valkenburg, K.C. Prostate-specific markers to identify rare prostate cancer cells in liquid biopsies. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.T.; Syed, J.; Nguyen, K.A.; Leapman, M.S.; Agarwal, N.; Brierley, K.; Llor, X.; Hofstatter, E.; Shuch, B. Genetic testing for hereditary prostate cancer: Current status and limitations. Cancer 2018, 124, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R.; Aly, M.; Clements, M.; Zheng, L.; Adolfsson, J.; Xu, J.; Grönberg, H.; Wiklund, F. A Population-based Assessment of Germline HOXB13 G84E Mutation and Prostate Cancer Risk. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Thompson, Z.J.; Eroshkin, A.M.; Nerlakanti, N.; Patel, A.K.; Agarwal, N.; Teer, J.K.; Dhillon, J.; et al. The Homeobox gene, HOXB13, Regulates a Mitotic Protein-Kinase Interaction Network in Metastatic Prostate Cancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.O.; Oh, K.J.; Xuan Nguyen, N.T.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.D.; Ryu, S.B.; Jung, C. Evaluation of HOXB13 as a molecular marker of recurrent prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Greenwood, C.; Isaacs, W.B.; Foulkes, W.D.; Sun, J.; Zheng, S.L.; Condreay, L.D.; Xu, J. The G84E mutation of HOXB13 is associated with increased risk for prostate cancer: Results from the Reduce trial. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, T.; Govindasami, K.; Leslie, G.; Dadaev, T.; Bancroft, E.; Ni Raghallaigh, H.; Brook, M.N.; Hussain, N.; Keating, D.; Lee, A.; et al. Homeobox B13 G84E Mutation and Prostate Cancer Risk. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, C.M.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Robbins, C.M.; Tembe, W.D.; Wiley, K.E.; Isaacs, S.D.; Johng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Germline Mutations in HOXB13 and Prostate-Cancer Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fong, K.W.; Gritsina, G.; Wang, F.; Baca, S.C.; Brea, L.T.; Berchuck, J.E.; Spisak, S.; Ross, J.; Morrissey, C.; et al. HOXB13 suppresses de novo lipogenesis through HDAC3-mediated epigenetic reprogramming in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.; Lupien, L.; Kuemmerle, N.B.; Kinlaw, W.B.; Swinnen, J.V.; Smans, K. Lipogenesis and lipolysis: The pathways exploited by the cancer cells to acquire fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Bouchard, C. FTO: The first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, K.A.; Barroso, I. The genetics of obesity: FTO leads the way. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.B.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A Common Variant in the FTO Gene Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Predisposes to Childhood and Adult Obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.K.; Resende, C.M.; Durso, D.F.; Rodrigues, L.A.; Silva, J.L.P.; Reis, R.C.; Pereira, S.S.; Ferreira, D.C.; Franco, G.R.; Alvarez-Leite, J. A single FTO gene variant rs9939609 is associated with body weight evolution in a multiethnic extremely obese population that underwent bariatric surgery. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.C.; Martins, A.C.; Moreira, B.P.; Bernardino, R.L.; Barros, A.; Monteiro, M.P.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Obesity-related genes are expressed in human Sertoli cells and modulated by energy homeostasis regulating hormones. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 5265–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosovic, M.; Molares, H.C.; Gregorova, P.; Hrossova, D.; Kudla, G.; Vanacova, S. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO targets pre-mRNAs and regulates alternative splicing and 3′-end processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11356–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Haim, M.S.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Rechavi, G. FTO: Linking m6A demethylation to adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.C.; He, C. m6A RNA methylation: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. m6A binding protein YTHDF2 in cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chu, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, L. HOXB13 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via IGF-1R upregulation and subsequent activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Lang, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, L. FTO demethylates m6A modifications in HOXB13 mRNA and promotes endometrial cancer metastasis by activating the WNT signalling pathway. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M. Epigenetic Inheritance and the Missing Heritability Problem. Genetics 2009, 182, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.K. Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoff, L.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Lebosq, M.; Gely-Pernot, A.; Bouchekhchoukha, K.; Monfort, C.; Kernanec, P.-Y.; Tevosian, S.; Multigner, L.; Smagulova, F. Developmental exposure to chlordecone induces transgenerational effects in somatic prostate tissue which are associated with epigenetic histone trimethylation changes. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Buonerba, C.; Terracciano, D.; Lucarelli, G.; Cosimato, V.; Bottero, D.; Deliu, V.M.; Ditonno, P.; Perdonà, S.; Autorino, R.; et al. Biomarkers in localized prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka-Zawisza, M.; Wiśnik, E. DNA methylation and histone modifications as epigenetic regulation in prostate cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Xavier, F.C.A.; Esteves, C.D.; Nascimento, R.B.; Nobile, J.S.; Severino, P.; de Cicco, R.; Toporcov, T.N.; Tajara, E.H.; Nunes, F.D. Homeobox gene amplification and methylation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 129, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, H.; Toyota, M.; Ishida, W.; Furihata, M.; Tsuchiya, M.; Kamada, M.; Tokino, T.; Shuin, T. Epigenetic inactivation of the candidate tumor suppressor gene HOXB13 in human renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, T.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Pfeifer, G.P. MIRA-assisted microarray analysis, a new technology for the determination of DNA methylation patterns, identifies frequent methylation of homeodomain-containing genes in lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7939–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, B.Q.; Zhang, C.D.; Liu, J.C.; Wang, L.; Dai, D.Q. HOXB13 expression and promoter methylation as a candidate biomarker in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8833–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albany, C.; Alva, A.S.; Aparicio, A.M.; Singal, R.; Yellapragada, S.; Sonpavde, G.; Hahn, N.M. Epigenetics in Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer 2011, 2011, 580318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Buckles, E.; Estrada, J.; Koochekpour, S. Aberrant DNA methylation and prostate cancer. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 486–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.G.; Chen, W.S.; Li, H.; Foye, A.; Zhang, M.; Sjöström, M.; Aggarwal, R.; Playdle, D.; Liao, A.; Alumkal, J.J.; et al. The DNA methylation landscape of advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.C.; Andrés, G.; Ashour, N.; Sánchez-Chapado, M.; López, J.I.; Ropero, S. Development of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer can be Predicted by a DNA Hypermethylation Profile. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, C.E.; Mills, I.G.; Lynch, A.G. The importance of DNA methylation in prostate cancer development. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 166, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.-M.; Ho, S.-M.; Chen, J.; Medvedovic, M.; Tam, N.N.C. Bisphenol A disrupts HNF4α-regulated gene networks linking to prostate preneoplasia and immune disruption in noble rats. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-M.; Tang, W.-Y.; Belmonte de Frausto, J.; Prins, G.S. Developmental exposure to estradiol and bisphenol A increases susceptibility to prostate carcinogenesis and epigenetically regulates phosphodiesterase type 4 variant 4. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5624–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Trevino, L.S.; Wong, R.L.Y.; Medvedovic, M.; Chen, J.; Ho, S.-m.; Shen, J.; Foulds, C.E.; Coarfa, C.; O’Malley, B.W.; et al. Reprogramming of the Epigenome by MLL1 Links Early-Life Environmental Exposures to Prostate Cancer Risk. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, A.; Zhang, X.; Cheung, Y.-Y.; Tang, W.-y.; Chen, J.; Ye, S.-H.; Medvedovic, M.; Leung, Y.-K.; Prins, G.S.; Ho, S.-M. DNA methylome changes by estradiol benzoate and bisphenol A links early-life environmental exposures to prostate cancer risk. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauluseviciute, I.; Drabløs, F.; Rye, M.B. DNA hypermethylation associated with upregulated gene expression in prostate cancer demonstrates the diversity of epigenetic regulation. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, F.; He, W.; Zong, H.; Fan, Q.; Wang, L. Correlation between the expression of DNMT1, and GSTP1 and APC, and the methylation status of GSTP1 and APC in association with their clinical significance in prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewska, A.; Dabrowska, M.; Goryca, K.; Antoniewicz, A.; Dobruch, J.; Mikula, M.; Jarosz, D.; Zapala, L.; Borowka, A.; Ostrowski, J. DNA methylation status is more reliable than gene expression at detecting cancer in prostate biopsy. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniunaite, K.; Jarmalaite, S.; Kalinauskaite, N.; Petroska, D.; Laurinavicius, A.; Lazutka, J.R.; Jankevicius, F. Prognostic value of RASSF1 promoter methylation in prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, K.; Pethe, V.; Briollais, L.; Sadikovic, B.; Ozcelik, H.; Sunderji, A.; Venkateswaran, V.; Pinthus, J.; Fleshner, N.; van der Kwast, T.; et al. Discovery of novel hypermethylated genes in prostate cancer using genomic CpG island microarrays. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M.; Sato, H.; Kanesaka, M.; Imamura, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Kaneda, A. Epigenetic modifications in prostate cancer. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.L.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. Epigenetic markers for molecular detection of prostate cancer. Dis. Markers 2007, 23, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carone, B.R.; Fauquier, L.; Habib, N.; Shea, J.M.; Hart, C.E.; Li, R.; Bock, C.; Li, C.; Gu, H.; Zamore, P.D.; et al. Paternally Induced Transgenerational Environmental Reprogramming of Metabolic Gene Expression in Mammals. Cell 2010, 143, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandovici, I.; Smith, N.H.; Nitert, M.D.; Ackers-Johnson, M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Ito, Y.; Jones, R.H.; Marquez, V.E.; Cairns, W.; Tadayyon, M.; et al. Maternal diet and aging alter the epigenetic control of a promoter–enhancer interaction at the Hnf4a gene in rat pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5449–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrès, R.; Osler, M.E.; Yan, J.; Rune, A.; Fritz, T.; Caidahl, K.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R. Non-CpG methylation of the PGC-1α promoter through DNMT3B controls mitochondrial density. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.-F.; Lin, R.C.Y.; Laybutt, D.R.; Barres, R.; Owens, J.A.; Morris, M.J. Chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs β-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring. Nature 2010, 467, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.A.; Bale, T.L. Maternal high-fat diet promotes body length increases and insulin insensitivity in second-generation mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4999–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Pan, X.; Shin, K.C.; Kwak, S.-H.; Bassas, A.F.; Sallam, R.M.; Park, K.S.; Alfadda, A.A.; Xu, A.; et al. Obesity-induced DNA hypermethylation of the adiponectin gene mediates insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.L.; de Angel, R.E.; Bowers, L.W.; Khatib, S.A.; Smith, L.A.; Van Buren, E.; Bhardwaj, P.; Giri, D.; Estecio, M.R.; Troester, M.A.; et al. Obesity-Associated Alterations in Inflammation, Epigenetics, and Mammary Tumor Growth Persist in Formerly Obese Mice. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila. Pa.) 2016, 9, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisóstomo, L.; Videira, R.A.; Jarak, I.; Starčević, K.; Mašek, T.; Rato, L.; Raposo, J.F.; Batterham, R.L.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Inherited Metabolic Memory of High-Fat Diet Impairs Testicular Fatty Acid Content and Sperm Parameters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisóstomo, L.; Jarak, I.; Rato, L.P.; Raposo, J.F.; Batterham, R.L.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Inheritable testicular metabolic memory of high-fat diet causes transgenerational sperm defects in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Long, S.; Cao, Z. Role of Adiponectin in prostate cancer. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2019, 45, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, Q.; Qi, M.; Lu, N.; Zhang, L.; Han, B. Adiponectin as a potential tumor suppressor inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition but frequently silenced in prostate cancer by promoter methylation. Prostate 2015, 75, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Monteiro, C.; Matos, A.; You, J.; Fraga, A.; Pereira, C.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. Epigenome-wide DNA methylation profiling of periprostatic adipose tissue in prostate cancer patients with excess adiposity—A pilot study. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sarkissyan, M.; Vadgama, J.V. Epigenetics in breast and prostate cancer. In Cancer Epigenetics: Risk Assessment, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 425–466. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Pereira, M.; Pereira, S.C.; Rebelo, I.; Spadella, M.A.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Decoding the Influence of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Its Transgenerational Impact. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234858
Santos-Pereira M, Pereira SC, Rebelo I, Spadella MA, Oliveira PF, Alves MG. Decoding the Influence of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Its Transgenerational Impact. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234858
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Pereira, Mariana, Sara C. Pereira, Irene Rebelo, Maria A. Spadella, Pedro F. Oliveira, and Marco G. Alves. 2023. "Decoding the Influence of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Its Transgenerational Impact" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234858
APA StyleSantos-Pereira, M., Pereira, S. C., Rebelo, I., Spadella, M. A., Oliveira, P. F., & Alves, M. G. (2023). Decoding the Influence of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Its Transgenerational Impact. Nutrients, 15(23), 4858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234858







