Antidepressant-like Effect of Oroxylum indicum Seed Extract in Mice Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the OIS Extract
2.2. Inhibitory Effect on Monoamine Oxidase-A (MAO-A) Enzyme
2.3. Animals
2.4. Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress (UCMS) Paradigm
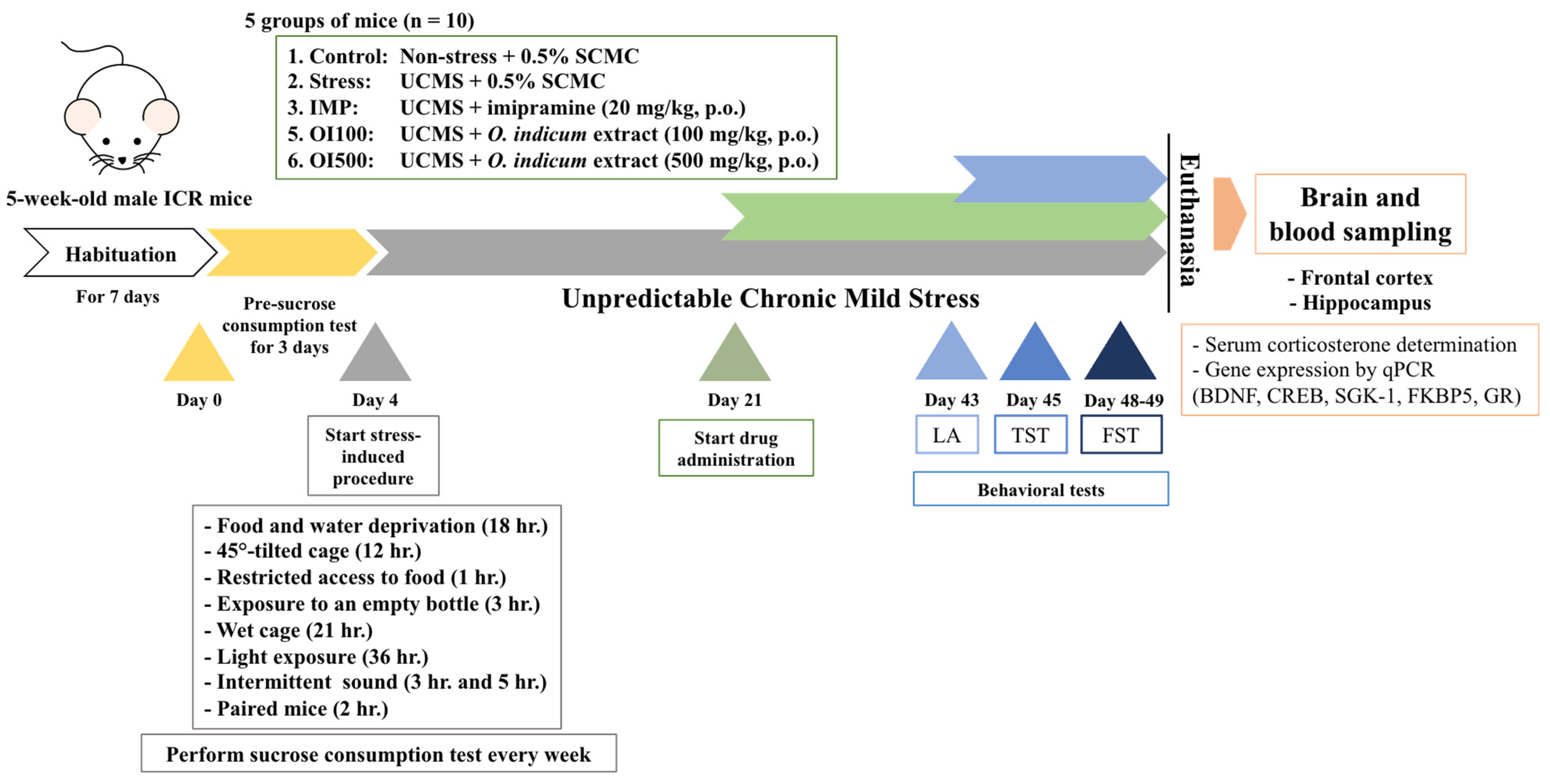
2.5. Experimental Design and Drug Administration
2.6. Behavioral Studies
2.6.1. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
2.6.2. Locomotor Activity (LA)
2.6.3. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
2.6.4. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
2.7. Determination of Serum Corticosterone Level
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.9. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis and Method Validation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibitory Activity of the OIS Extract on MAO-A and MAO-B Enzymes
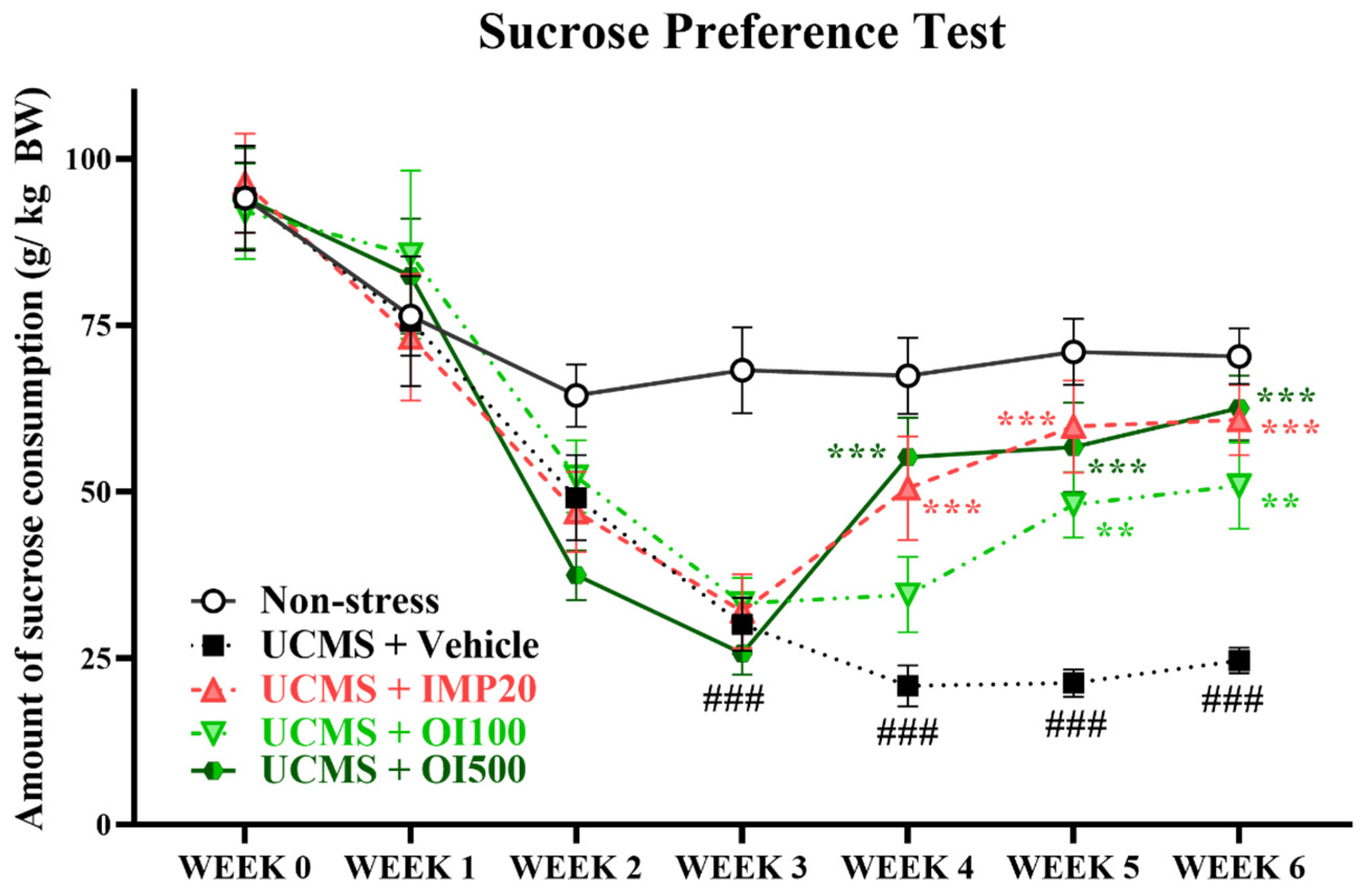
3.2. Effect of the OIS Extract on Anhedonia in Mice Subjected to UCMS
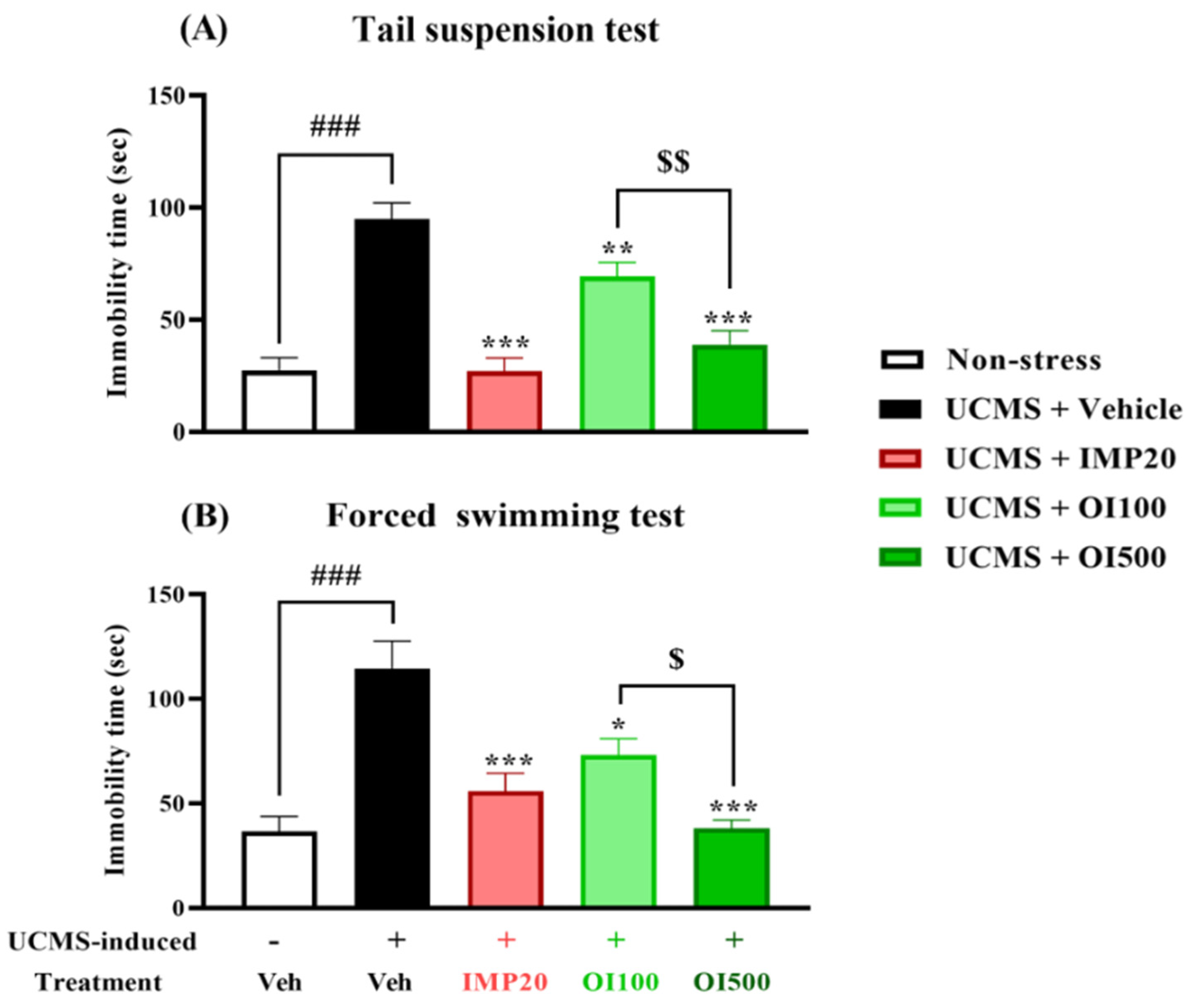
3.3. Effect of the OIS Extract on Despair Behavior Induced by UCMS and Locomotor Activity
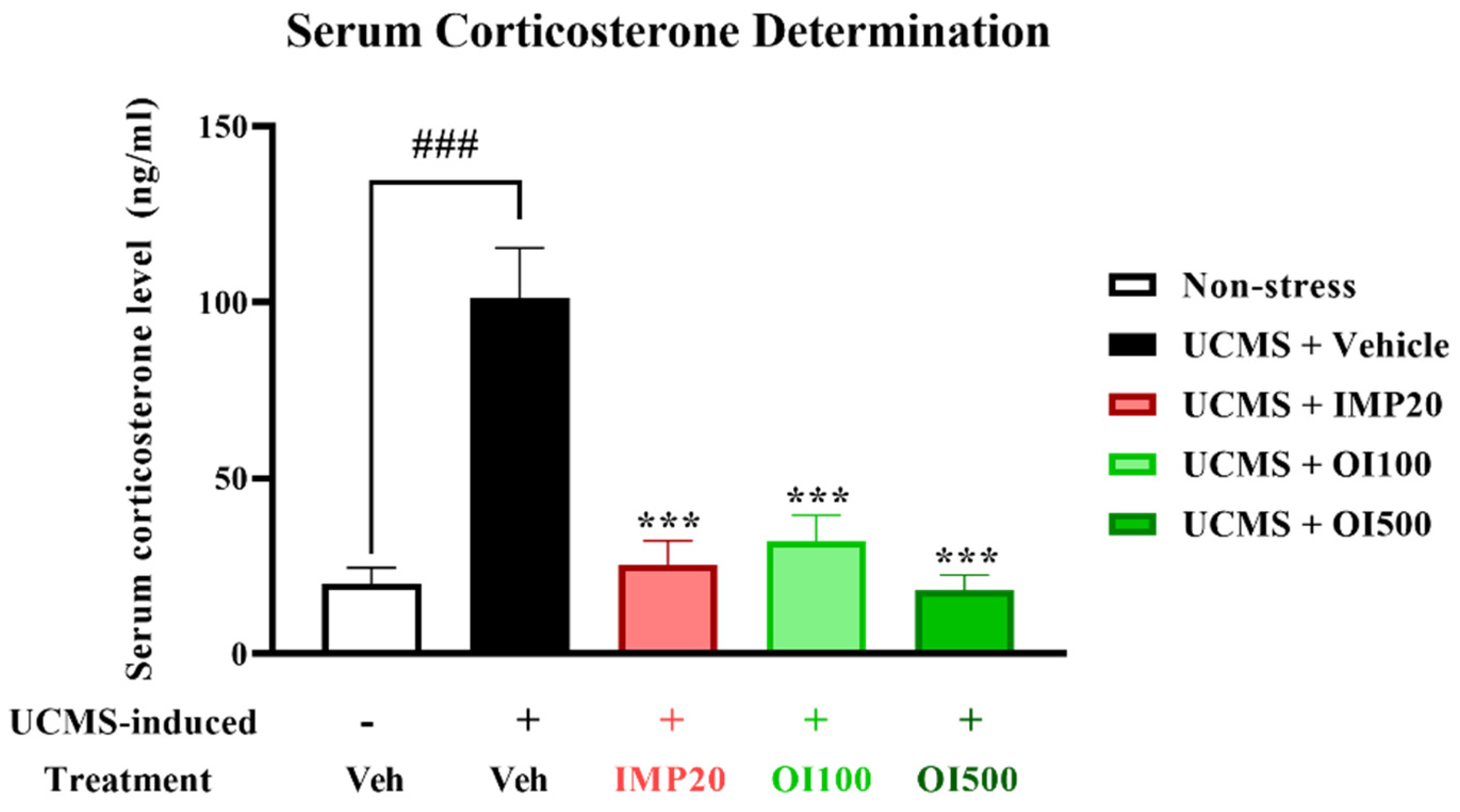
3.4. Effect of the OIS Extract on Serum Corticosterone (CORT) Level in UCMS-Induced Mice
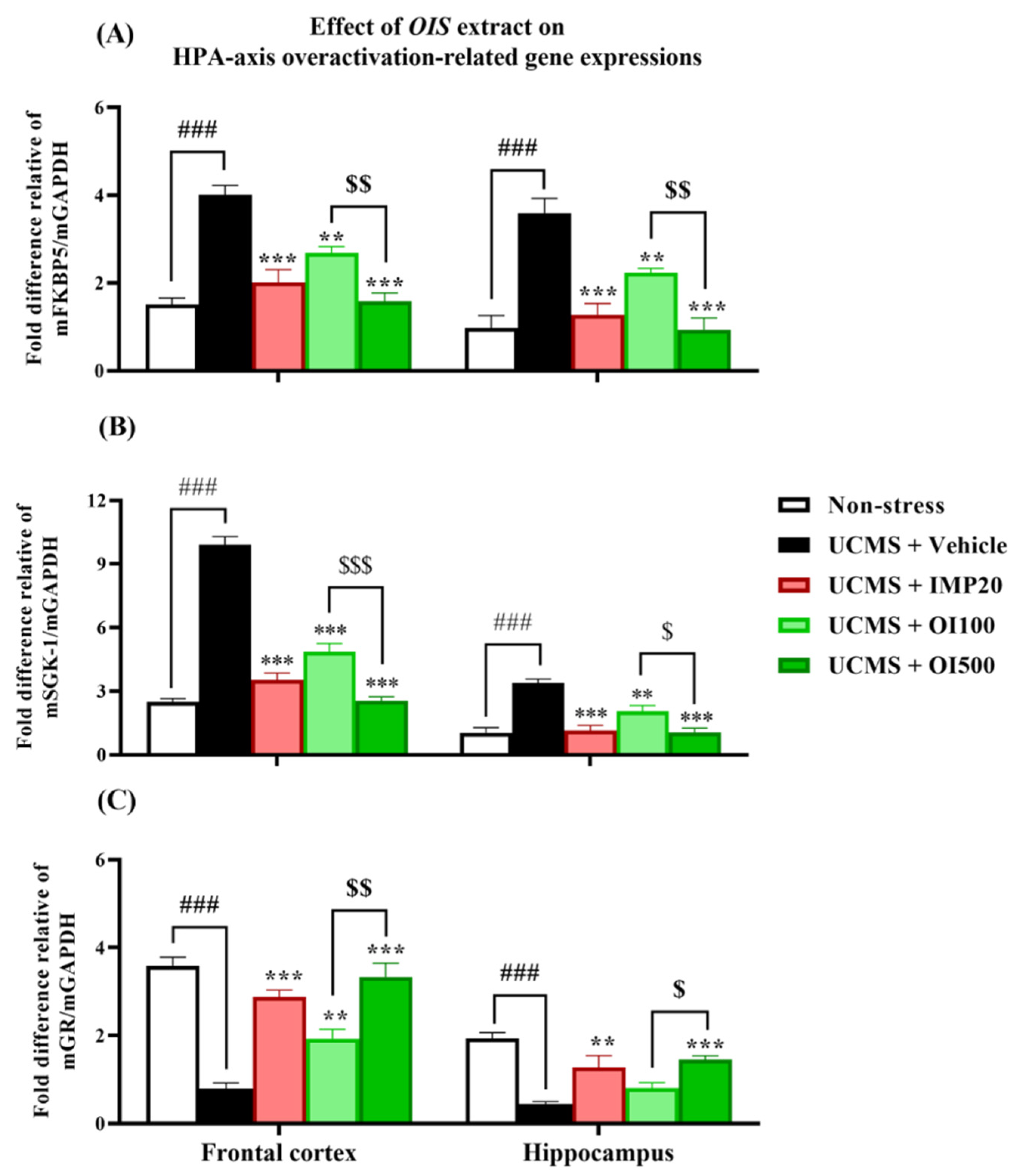
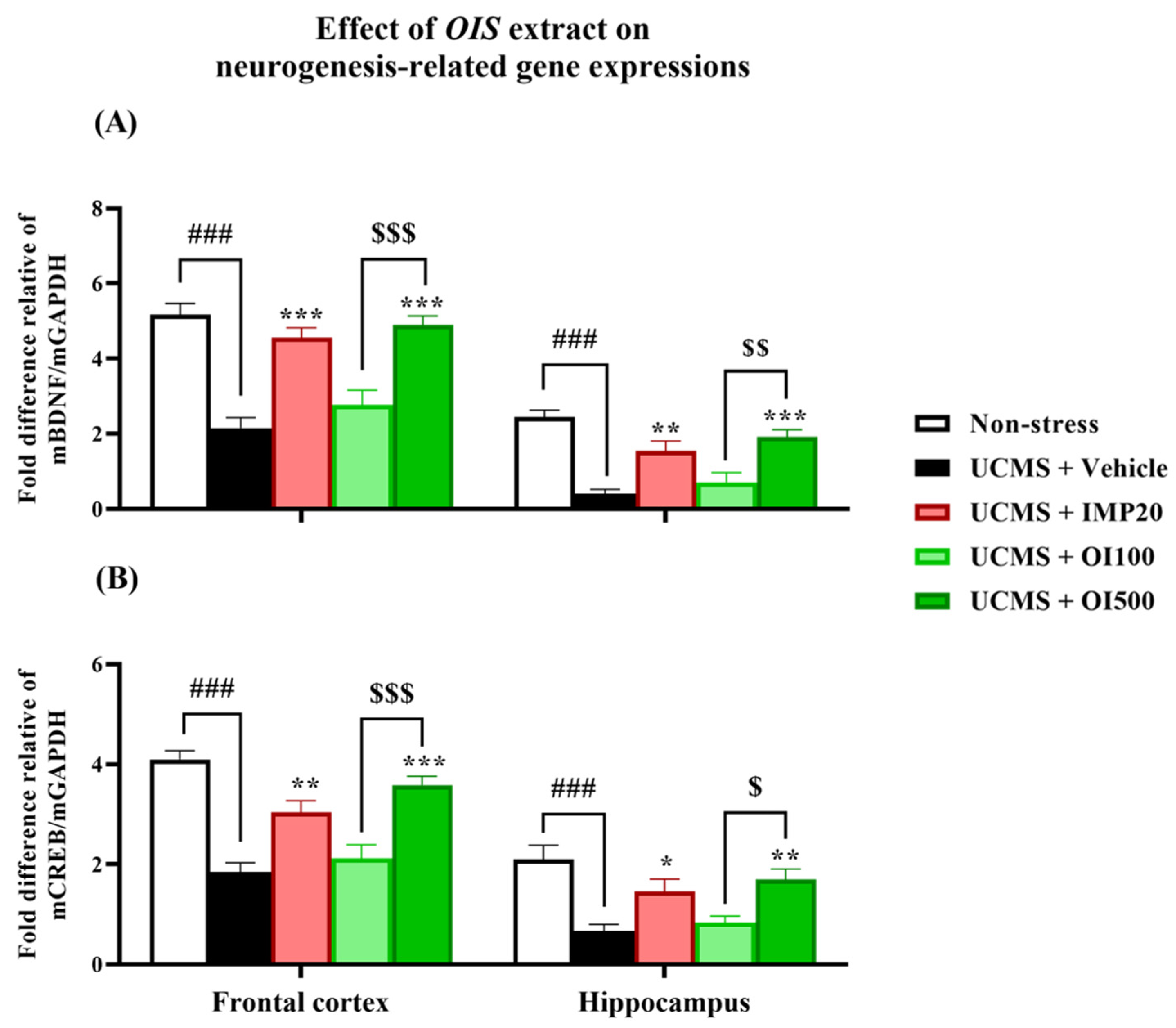
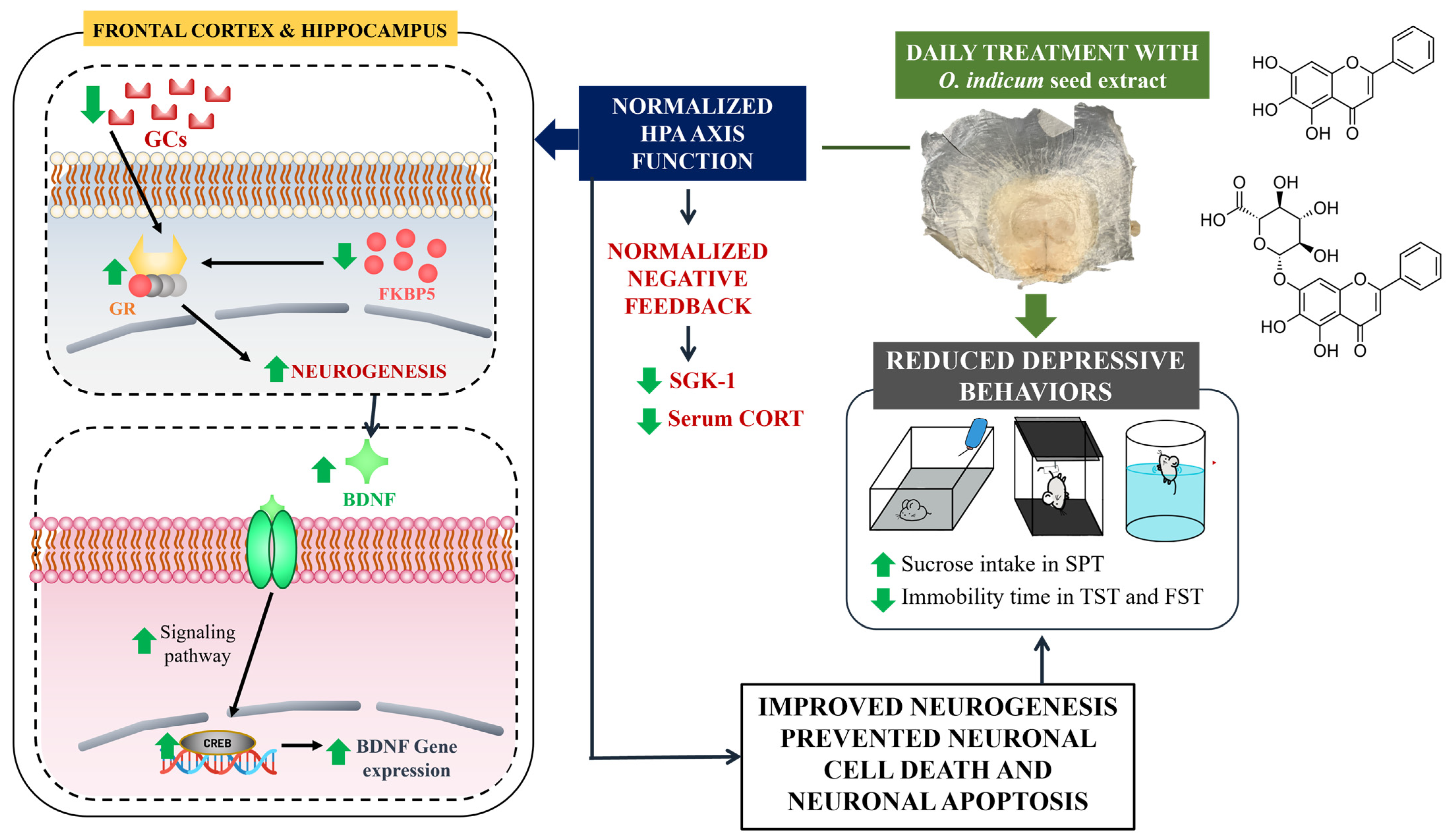
3.5. The OIS Extract Normalized HPA Axis Overactivation and Neurogenesis via Changes in FKBP5, GR, SGK-1, BDNF, and CREB mRNA Expressions in Affected Brains
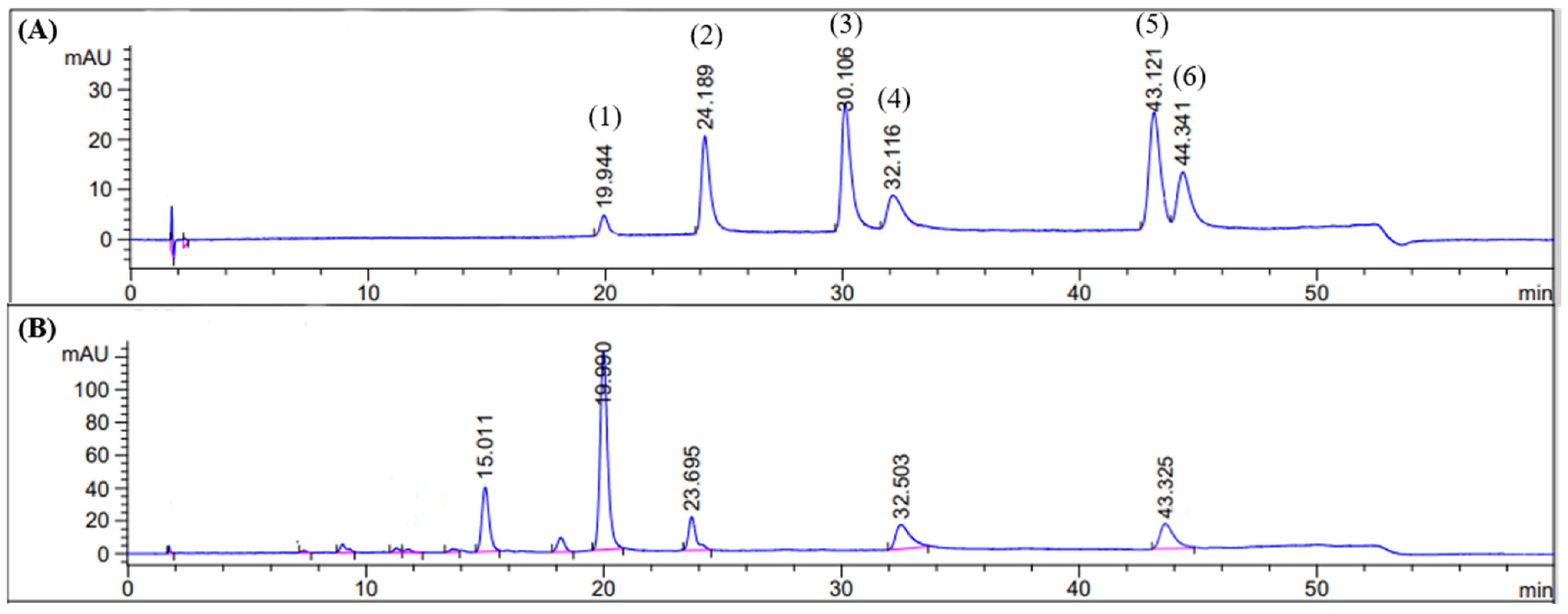
3.6. HPLC Analysis of the OIS Extract and Method Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilchrist, E.E.A.; Sadler, D.W. The Role of Depression in Unnatural Death: A Case-Based Retrospective Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 259, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Cui, R. The Effects of Psychological Stress on Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juruena, M.F.; Cleare, A.J.; Pariante, C.M. The Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis, Glucocorticoid Receptor Function and Relevance to Depression. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2004, 26, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricia Gaete, H. Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis, Chronic Stress, Hair Cortisol, Metabolic Syndrome and Mindfulness. Integr. Mol. Med. 2016, 3, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, G.; Calabrese, F.; Anacker, C.; Racagni, G.; Pariante, C.M.; Riva, M.A. Glucocorticoid Receptor and FKBP5 Expression Is Altered Following Exposure to Chronic Stress: Modulation by Antidepressant Treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, C.; Hanson, H.E.; Martin, L.B. FKBP5 Expression Is Related to HPA Flexibility and the Capacity to Cope with Stressors in the House Sparrow. Horm. Behav. 2021, 135, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, C.M.; Miller, A.H. Glucocorticoid Receptors in Major Depression: Relevance to Pathophysiology and Treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacker, C.; Zunszain, P.A.; Carvalho, L.A.; Pariante, C.M. The Glucocorticoid Receptor: Pivot of Depression and of Antidepressant Treatment? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattilo, V.; Amato, R.; Perrotti, N.; Gennarelli, M. The Emerging Role of SGK1 (Serum- and Glucocorticoid-Regulated Kinase 1) in Major Depressive Disorder: Hypothesis and Mechanisms. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik Salleh, N.N.H.; Othman, F.A.; Kamarudin, N.A.; Tan, S.C. The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum Indicum: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kong, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, G.; Song, J.; Liang, Y.; Du, G. Baicalein Alleviates Depression-like Behavior in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Model in Mice through Activating the BDNF/TrkB/CREB Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, M.Q. Research Progress on the Antidepressant Effects of Baicalin and Its Aglycone Baicalein: A Systematic Review of the Biological Mechanisms. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Zhang, K.; Dong, Y.X.; Song, S.J.; Lu, X.M.; Wu, C.F. Antidepressant-like effects of Xiaochaihutang in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. J. Ethnopharmaco. 2014, 152, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinda, B.; SilSarma, I.; Dinda, M.; Rudrapaul, P. Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz, an Important Asian Traditional Medicine: From Traditional Uses to Scientific Data for Its Commercial Exploitation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.L.; Sinhamahapatra, P.K.; Nayak, A.; Das, R.; Sannigrahi, S. In Vitro Antioxidant Potential of Different Parts of Oroxylum Indicum: A Comparative Study. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalrinzuali, K.; Vabeiryureilai, M.; Jagetia, G.C. Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of Ethanol Extract of Stem Bark of Sonapatha Oroxylum indicum In Vivo. Int. J. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8247014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Cheepsunthorn, P.; Buranrat, B. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Oroxylum indicum Kurz (L.) Fruit Extract in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondugula, S.R.; Majrashi, M.; Almaghrabi, M.; Ramesh, S.; Abbott, K.L.; Govindarajulu, M.; Gill, K.; Fahoury, E.; Narayanan, N.; Desai, D.; et al. Oroxylum indicum Ameliorates Chemotherapy Induced Cognitive Impairment. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-N.; Lin, B.-B.; Xie, G.-Y.; Li, J.-W.; Qin, M.-J. Chemical constitunents of seeds of Oroxylum indicum. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S.; Albaqami, J.J.; Hamdi, H.; Lawrence, L.; Padikkala, J.; Mathew, S.E.; Narayanankutty, A. Oroxylum indicum Vent Root Bark Extract Inhibits the Proliferation of Cancer Cells and Induce Apoptotic Cell Death. Processes 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Rahman, M.O.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Sultana, N.; Almarfadi, O.M.; Ali, M.A.; Lee, J. Anticancer Potential of Phytochemicals from Oroxylum indicum Targeting Lactate Dehydrogenase A through Bioinformatic Approach. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.-L.; Wu, Z.-W.; Yang, F.; Shen, X.-F.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Li, F.; Wang, M.-K. Flavonoids from the Seeds of Oroxylum indicum and Their Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxic Activities. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 32, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolato, M.; Chen, K.; Shih, J.C. Monoamine Oxidase Inactivation: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Ruengwinitwong, K.; Gatenakorn, K.; Maneenet, J.; Khamphukdee, C.; Sekeroglu, N.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Effects of the Ethanol Extract of Dipterocarpus Alatus Leaf on the Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression in ICR Mice and Its Possible Mechanism of Action. Molecules 2019, 24, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Wang, L.-L.; Pei, Y.-Y.; Shen, J.-D.; Li, H.-B.; Wang, B.-Y.; Bai, M. Baicalin Decreases SGK1 Expression in the Hippocampus and Reverses Depressive-like Behaviors Induced by Corticosterone. Neuroscience 2015, 311, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Pei, L. Baicalin ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression through the BDNF/ERK/CREB signaling pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 414, 113463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Shan, X.; Li, L.; Xia, B.; Wang, H. Anti-Depressive Effectiveness of Baicalin In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2019, 24, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Yin, C.-Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Zhu, X.-H.; Xu, C.; Luo, C.-X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-G. Sucrose Preference Test for Measurement of Stress-Induced Anhedonia in Mice. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Jaiswal, M.; Palit, G. Comparative Evaluation of Forced Swim Test and Tail Suspension Test as Models of Negative Symptom of Schizophrenia in Rodents. ISRN Psychiatry 2012, 2012, 595141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneenet, J.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Boonyarat, C.; Khamphukdee, C.; Kwankhao, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Awale, S.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Markou, A.; Lucki, I. Assessing Antidepressant Activity in Rodents: Recent Developments and Future Needs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, J.; Juszczyk, G.; Gawrońska-Grzywacz, M.; Herbet, M. HPA Axis in the Pathomechanism of Depression and Schizophrenia: New Therapeutic Strategies Based on Its Participation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, K.S. Treatment-Resistant Depression: Therapeutic Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2012, 6, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuijpers, P.; Smit, F. Subthreshold Depression as a Risk Indicator for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review of Prospective Studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2004, 109, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naber, D.; Bullinger, M. Should Antidepressants Be Used in Minor Depression? Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, K.; Colle, R.; Bouligand, J.; Trabado, S.; Fève, B.; Becquemont, L.; Corruble, E.; Verstuyft, C. The MAOA rs979605 Genetic Polymorphism Is Differentially Associated with Clinical Improvement Following Antidepressant Treatment between Male and Female Depressed Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Ma, S.; Qu, R.; Kang, D.; Liu, Y. Antidepressant Effect of Baicalin Extracted from the Root of Scutellaria baicalensis. in Mice and Rats. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbee, J.C.; Brooks, S.D.; Stanley, S.C.; d’Audiffret, A.C. An Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress Protocol for Instigating Depressive Symptoms, Behavioral Changes and Negative Health Outcomes in Rodents. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2015, 106, e53109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, M.; Maccarrone, G.; Brückl, T.; Scheuer, S.; Hennings, J.; Holsboer, F.; Turck, C.W.; Uhr, M.; Lucae, S. FKBP5 Gene Expression Predicts Antidepressant Treatment Outcome in Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacker, C.; Cattaneo, A.; Musaelyan, K.; Zunszain, P.A.; Horowitz, M.; Molteni, R.; Luoni, A.; Calabrese, F.; Tansey, K.; Gennarelli, M.; et al. Role for the Kinase SGK1 in Stress, Depression, and Glucocorticoid Effects on Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8708–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Richards, M.; Nakajima, S.; Adachi, N.; Furuta, M.; Odaka, H.; Kunugi, H. The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Comorbid Depression: Possible Linkage with Steroid Hormones, Cytokines, and Nutrition. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.-K. The Role of CREB and BDNF in Neurobiology and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; He, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, C. Revealing Antidepressant Mechanisms of Baicalin in Hypothalamus Through Systems Approaches in Corticosterone-Induced Depressed Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Jiang, B.; Wu, P.-F.; Tian, J.; Shi, L.-L.; Gu, J.; Hu, Z.-L.; Fu, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.-G. Antidepressant Effects of a Plant-Derived Flavonoid Baicalein Involving Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases Cascade. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.B.; Jesse, C.R.; Donato, F.; Del Fabbro, L.; Gomes de Gomes, M.; Rossito Goes, A.T.; Souza, L.C.; Boeira, S.P. Chrysin Promotes Attenuation of Depressive-like Behavior and Hippocampal Dysfunction Resulting from Olfactory Bulbectomy in Mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 260, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Landa, J.F.; German-Ponciano, L.J.; Puga-Olguín, A.; Olmos-Vázquez, O.J. Pharmacological, Neurochemical, and Behavioral Mechanisms Underlying the Anxiolytic- and Antidepressant-like Effects of Flavonoid Chrysin. Molecules 2022, 27, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | Genes | Primer Sequences | Product Length | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| House-keeping gene | GAPDH | Forward: 5′-ACC ACA GTC CAT GCC ATC AC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCC ACC ACC CTG TTG CTG TA-3′ | 452 bp | [30] |
| Neurogenesis | BDNF | Forward: 5′-GAC AAG GCA ACT TGG CCT AC-3′ Reverse: 5′-CCT GTC ACA CAC GCT CAG CTC-3′ | 334 bp | [30] |
| CREB | Forward: 5′-TAC CCA GGG AGG AGG AAT AC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GAG GCT GCT TGA ACA ACA AC-3′ | 183 bp | [30] | |
| HPA axis | SGK-1 | Forward: 5′-GGG TGC CAA GGA TGA CTT TA-3′ Reverse: 5′-CTC GGT AAA CTC GGG ATA GA-3′ | 154 bp | [30] |
| GR | Forward: 5′- CAC TAA TCC TCT CCA TCC TAC-3′ Reverse: 5′- AAT GTC TGC TGC CTT CTG-3′ | 479 bp | [25] | |
| FKBP5 | Forward: 5′- GAA CCC AAT GCT GAG CTT ATG-3′ Reverse: 5′- ATG TAC TTG CCT CCC TTG AAG-3′ | 149 bp | [5] |
| Extract/Substance | Inhibition of MAO-A Enzyme | Inhibition of MAO-B Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL for Extract and µM for Compound) | IC50 (µg/mL for Extract and µM for Compound) | |
| OIS extract | 36.07 ± 0.47 | 146.80 ± 4.94 |
| Clorgyline | 0.001201 ± 0.000014 | 20.38 ± 0.33 |
| Deprenyl | 10.49 ± 0.11 | 0.052 ± 0.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chalermwongkul, C.; Khamphukdee, C.; Maneenet, J.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Boonyarat, C.; Chotritthirong, Y.; Awale, S.; Kijjoa, A.; Chulikhit, Y. Antidepressant-like Effect of Oroxylum indicum Seed Extract in Mice Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224742
Chalermwongkul C, Khamphukdee C, Maneenet J, Daodee S, Monthakantirat O, Boonyarat C, Chotritthirong Y, Awale S, Kijjoa A, Chulikhit Y. Antidepressant-like Effect of Oroxylum indicum Seed Extract in Mice Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224742
Chicago/Turabian StyleChalermwongkul, Chorpeth, Charinya Khamphukdee, Juthamart Maneenet, Supawadee Daodee, Orawan Monthakantirat, Chantana Boonyarat, Yutthana Chotritthirong, Suresh Awale, Anake Kijjoa, and Yaowared Chulikhit. 2023. "Antidepressant-like Effect of Oroxylum indicum Seed Extract in Mice Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224742
APA StyleChalermwongkul, C., Khamphukdee, C., Maneenet, J., Daodee, S., Monthakantirat, O., Boonyarat, C., Chotritthirong, Y., Awale, S., Kijjoa, A., & Chulikhit, Y. (2023). Antidepressant-like Effect of Oroxylum indicum Seed Extract in Mice Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Nutrients, 15(22), 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224742










