Gastrointestinal Tolerance of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Study Product
2.3. Safety Evaluation
2.4. Parameters of Gastrointestinal Tolerance
2.4.1. Stool Characteristics
2.4.2. Infant Gastrointestinal Symptom Questionnaire (IGSQ)
2.4.3. Sleeping Behaviour
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Stool Characteristics
2.5.2. IGSQ
2.5.3. Sleeping Behaviour
2.5.4. Study Population
3. Results
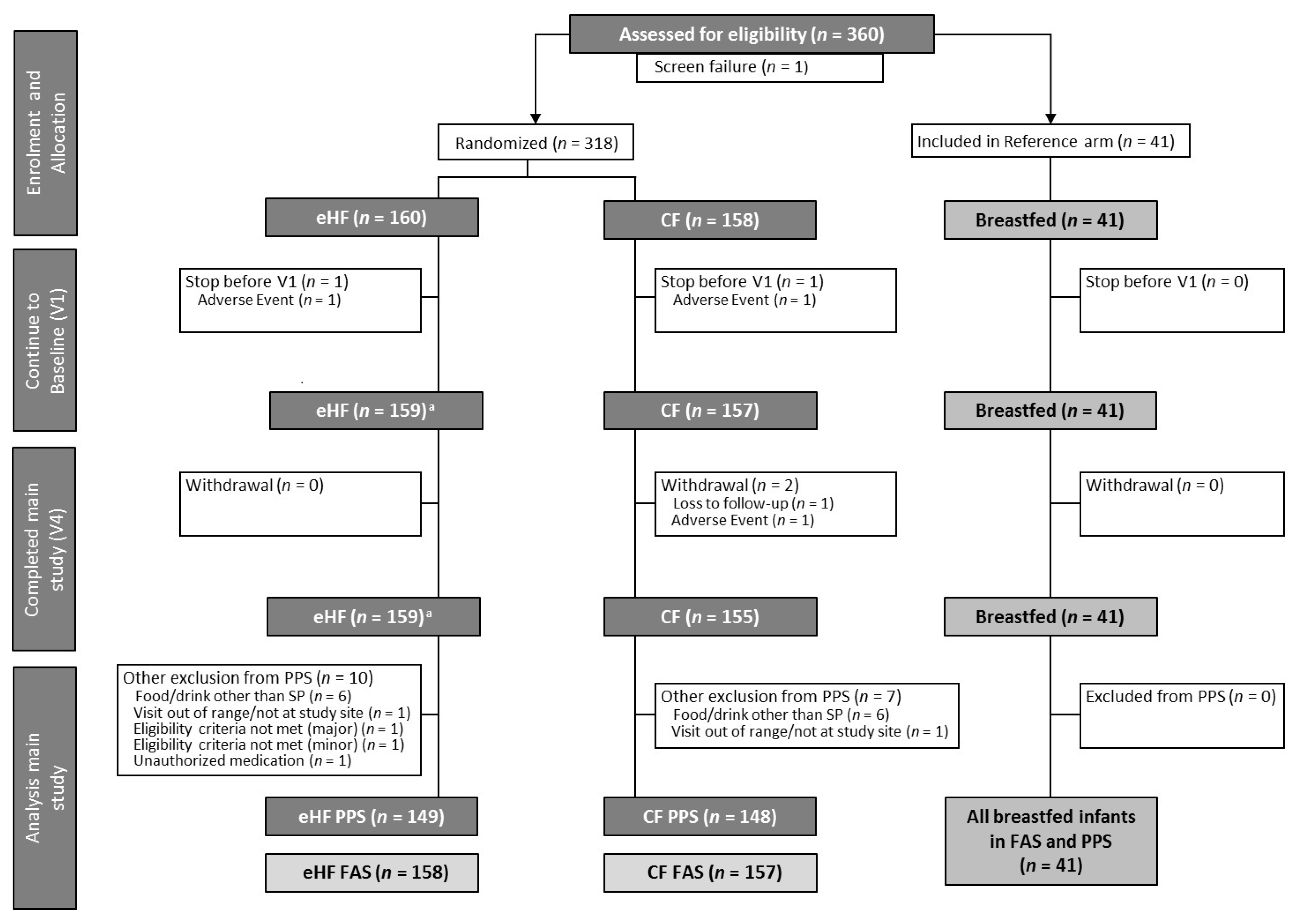
3.1. Study Participants and Population Characteristics
3.2. Compliance
3.3. Safety Evaluation
3.4. Gastrointestinal Tolerance
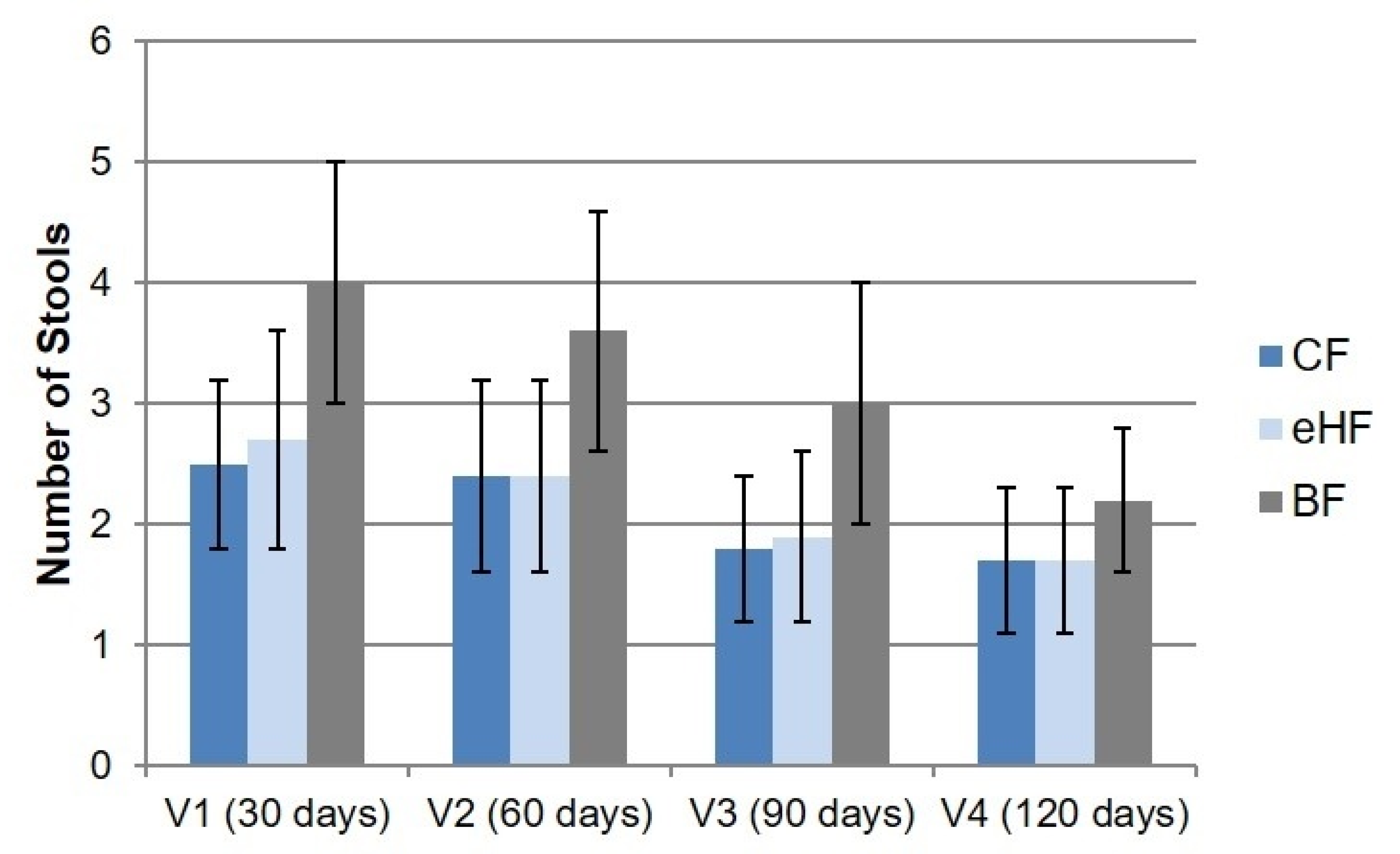
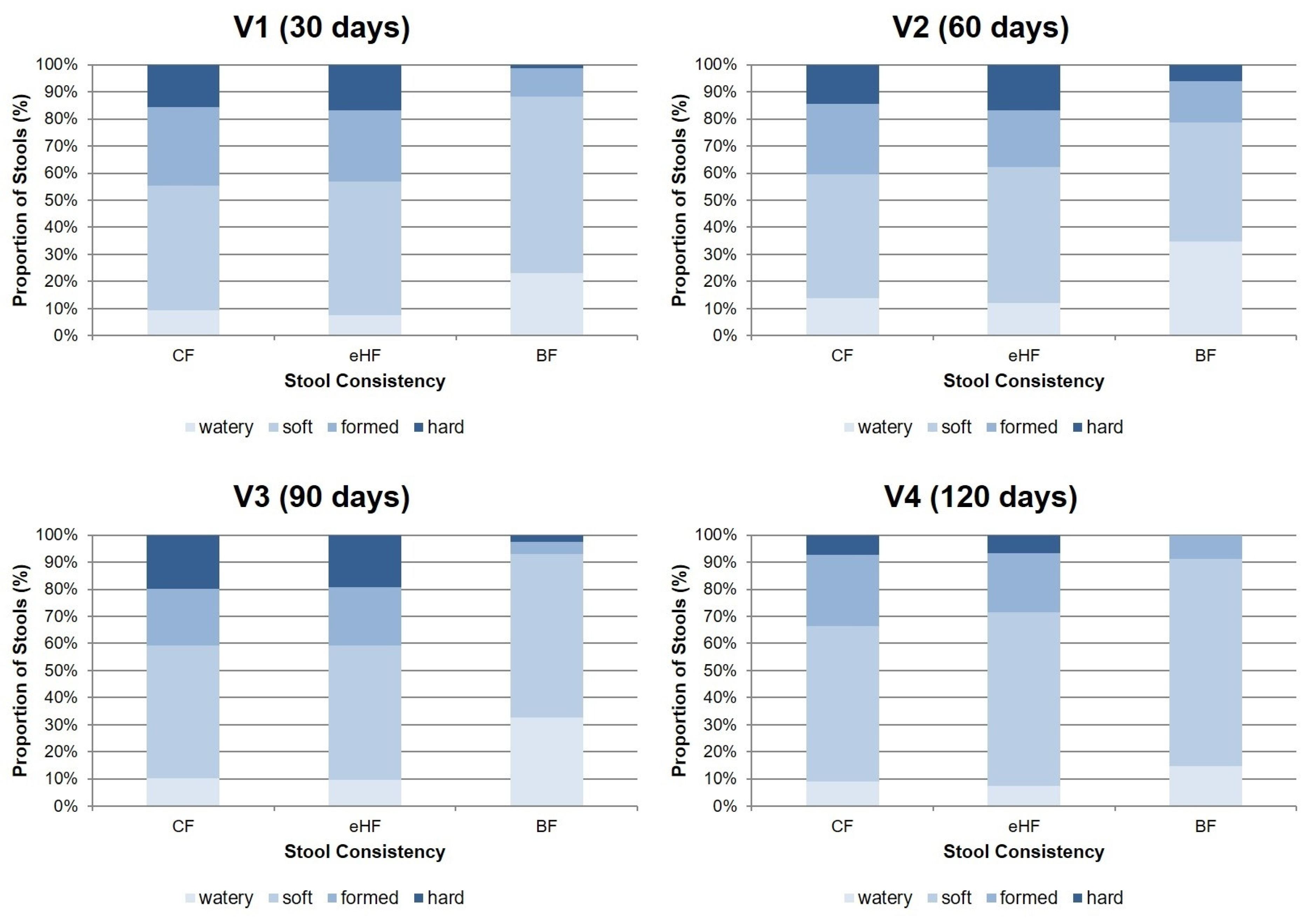
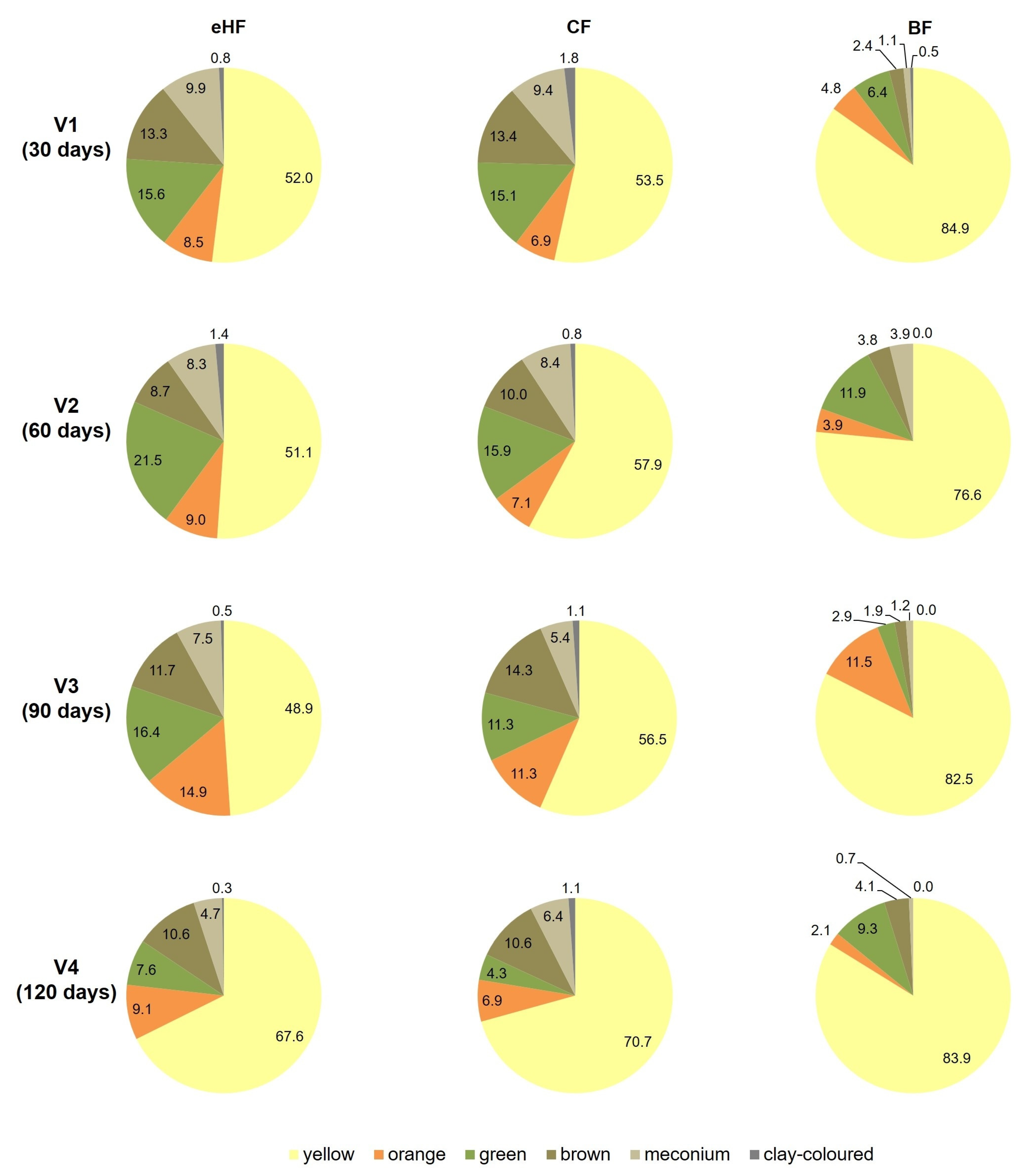
3.4.1. Stool Characteristics
3.4.2. IGSQ
3.4.3. Sleeping Behaviour
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koletzko, B.; Godfrey, K.M.; Poston, L.; Szajewska, H.; van Goudoever, J.B.; de Waard, M.; Brands, B.; Grivell, R.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Dodd, J.M.; et al. Nutrition During Pregnancy, Lactation and Early Childhood and Its Implications for Maternal and Long-Term Child Health: The Early Nutrition Project Recommendations. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaiche, M.; Oozeer, R.; Gerardi-Temporel, G.; Faure, C.; Vandenplas, Y. Multiple Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Are Frequent in Formula-fed Infants and Decrease Their Quality of Life. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, G.; Merolla, R.; D’Amico, D.; Bonci, E.; Cavataio, F.; Di Prima, L.; Scalici, C.; Indinnimeo, L.; Averna, M.R.; Carroccio, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Infancy: A Population-Based Prospective Study. Dig. Liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2005, 37, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tilburg, M.A.L.; Hyman, P.E.; Walker, L.; Rouster, A.; Palsson, O.S.; Kim, S.M.; Whitehead, W.E. Prevalence of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevenhooven, J.; Koppen, I.J.N.; Benninga, M.A. The New Rome IV Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2017, 20, 1080924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chogle, A.; Velasco-Benitez, C.A.; Koppen, I.J.; Moreno, J.E.; Ramírez Hernández, C.R.; Saps, M. A Population-Based Study on the Epidemiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Young Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 139–143.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Abkari, A.; Bellaiche, M.; Benninga, M.; Chouraqui, J.P.; Çokura, F.; Harb, T.; Hegar, B.; Lifschitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; et al. Prevalence and Health Outcomes of Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Infants From Birth to 12 Months of Age. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Hauser, B.; Salvatore, S. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infancy: Impact on the Health of the Infant and Family. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steutel, N.F.; Zeevenhooven, J.; Scarpato, E.; Vandenplas, Y.; Tabbers, M.M.; Staiano, A.; Benninga, M.A. Prevalence of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in European Infants and Toddlers. J. Pediatr. 2020, 221, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, B.; Hellmuth, C.; Haiden, N.; Olbertz, D.; Hamelmann, E.; Vusurovic, M.; Fleddermann, M.; Roehle, R.; Knoll, A.; Koletzko, B.; et al. Hydrolyzed Formula With Reduced Protein Content Supports Adequate Growth: A Randomized Controlled Noninferiority Trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çamurdan, A.; Beyazova, U.; Özkan, S.; Tunç, V. Defecation Patterns of the Infants Mainly Breastfed from Birth till the 12th Month: Prospective Cohort Study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Turk. Soc. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, E.; Rakza, T.; Mestdagh, B.; Labreuche, J.; Turck, D. The Bowel Movement Characteristics of Exclusively Breastfed and Exclusively Formula Fed Infants Differ during the First Three Months of Life. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picaud, J.-C.; Pajek, B.; Arciszewska, M.; Tarczón, I.; Escribano, J.; Porcel, R.; Adelt, T.; Hassink, E.; Rijnierse, A.; Abrahamse-Berkeveld, M.; et al. An Infant Formula with Partially Hydrolyzed Whey Protein Supports Adequate Growth and Is Safe and Well-Tolerated in Healthy, Term Infants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Equivalence Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Palumeri, E.; Castagno, E.; Cresi, F.; Dalmasso, P.; Cavallo, F.; Oggero, R. Reduction of Crying Episodes Owing to Infantile Colic: A Randomized Controlled Study on the Efficacy of a New Infant Formula. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovou, M.; Ralston, R.A.; Muir, J.; Walker, K.Z.; Truby, H. Dietary Management of Infantile Colic: A Systematic Review. Matern. Child Health J. 2012, 16, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Salvatore, S. Infant Formula with Partially Hydrolyzed Proteins in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Protein Neonatal Infant Nutr. Recent Updat. 2016, 86, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Nutritional Safety and Suitability of a Specific Protein Hydrolysate Derived from Whey Protein Concentrate and Used in an Infant and Follow-on Formula Manufactured from Hydrolysed Protein by Danone Trading ELN B.V. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, L.; Schelker, E.; Petersen, H.; Nomayo, A.; Fleddermann, M.; Arendt, B.M.; Britzl, T.; Haberl, E.M.; Jochum, F. Safety and Suitability of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/127 as Regards the Specific Compositional and Information Requirements for Infant Formula and Follow-on Formula. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2016/127/oj (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- EU Commission Directive 2006/141/EC on Infant Formulae and Follow-on Formulae. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2006/141/oj (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Bekkali, N.; Hamers, S.L.; Reitsma, J.B.; Van Toledo, L.; Benninga, M.A. Infant Stool Form Scale: Development and Results. J. Pediatr. 2009, 154, 521–526.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.W.; Trabulsi, J.; Yao, M.; Bevans, K.B.; DeRusso, P.A. Validation of a Parent Report Questionnaire: The Infant Gastrointestinal Symptom Questionnaire. Clin. Pediatr. 2015, 54, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, F.; Giannotti, F.; Ottaviano, S. Sleep Problems and Daytime Behavior in Childhood Idiopathic Epilepsy. Epilepsia 1999, 40, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandoná, B.; Matos, S.; Bernardi, J.R.; Goldani, M.Z.; Kieling, R.R.; Silva, C.H. da Influence of Intra- and Extrauterine Factors on Infant Sleep in the First 6 Months of Life. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunc, V.T.; Camurdan, A.D.; Ilhan, M.N.; Sahin, F.; Beyazova, U. Factors Associated with Defecation Patterns in 0-24-Month-Old Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, X.-M.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.-T.; Shi, S.-Y.; Lu, Y.-D.; Chen, R.; Zhou, X.-Y. Low Level of Galacto-Oligosaccharide in Infant Formula Stimulates Growth of Intestinal Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6564–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, M.; Verduci, E.; Gregori, D.; Ballali, S.; Soldi, S.; Ghisleni, D.; Riva, E.; PLAGOS Trial Study Group. Prebiotic Effect of an Infant Formula Supplemented with Galacto-Oligosaccharides: Randomized Multicenter Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, C.; Bernal, M.-J.; Blasco, J.; Martínez, R.; Dalmau, J.; Ortuño, I.; Espín, B.; Vasallo, M.-I.; Gil, D.; Vidal, M.-L.; et al. Prebiotic Effect during the First Year of Life in Healthy Infants Fed Formula Containing GOS as the Only Prebiotic: A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind and Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troesch, B.; Demmelmair, J.; Gimpfl, M.; Hecht, C.; Lakovic, G.; Roehle, R.; Sipka, L.; Trisic, B.; Vusurovic, M.; Schoop, R.; et al. Suitability and Safety of L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate as a Folate Source in Infant Formula: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, J.; Gibb, R.; Kenneally, D.; Kutay, B.; Siu, S.W.; Roe, D. Characterizing Exclusively Breastfed Infant Stool via a Novel Infant Stool Scale. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, S5–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borschel, M.W.; Baggs, G.E. A New Hydrolyzed Formula Is Well Tolerated in Infants with Suspected Food Protein Allergy or Intolerance. Open Nutr. J. 2015, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjad-Guillou, N.; Henocq, A.; Arnaud-Battandier, F. Does the hydrolysis of proteins change the acceptability and the digestive tolerance of milk for infants? The results of a comparative and randomized prospective study. Ann. Pediatr. 1992, 39, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog, J.; van Leengoed, E.; Kolk, F.; van den Broek, L.; Kramer, E.; Bakker, E.-J.; Gijssel, E.B.; Bulk, A.; Kneepkens, F.; Benninga, M.A. The Defecation Pattern of Healthy Term Infants up to the Age of 3 Months. Arch. Dis. Child.–Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012, 97, F465–F470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pados, B.F.; Basler, A. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Healthy, Full-Term Infants Under 7 Months of Age. J. Pediatr. Nurs. Nurs. Care Child. Fam. 2020, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkees, S.A. Developing Circadian Rhythmicity in Infants. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Every Baby Needs a Sugar Mama. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtens, P.A.; Goossens, D.A.; Staiano, A. Stool Characteristics of Infants Receiving Short-Chain Galacto-Oligosaccharides and Long-Chain Fructo-Oligosaccharides: A Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 13446–13452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Jafar, N.K.; Tham, E.K.H.; Pang, W.W.; Fok, D.; Chua, M.C.; Teoh, O.-H.; Goh, D.Y.T.; Shek, L.P.-C.; Yap, F.; Tan, K.H.; et al. Association between Breastfeeding and Sleep Patterns in Infants and Preschool Children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.; Gardiner, A.; Gay, C.L.; Lee, K.A. Breast-Feeding Increases Sleep Duration of New Parents. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 2007, 21, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, B.; Dias, C.C.; Pinto, T.M.; Field, T. Exclusive Breastfeeding at Three Months and Infant Sleep-Wake Behaviors at Two Weeks, Three and Six Months. Infant Behav. Dev. 2017, 49, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Products Intended to Positively Influence GI Tolerance | All Infants (n = 338) | eHF (n = 149) | CF (n = 148) | BF (n = 41) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 92 (27.2) | 40 (26.8) | 43 (29.1) | 9 (22.0) |
| No | 246 (72.8) | 109 (73.2) | 105 (70.9) | 32 (78.0) |
| Visit | Age at Visit (Days) | eHF (n = 149) | CF (n = 148) | BF (n = 41) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | Mean (SD) | 26.5 (7.2) | 26.5 (6.8) | 24.8 (6.5) |
| Median (Q1; Q3) | 26.0 (20.2; 31.4) | 27.1 (20.2; 31.2) | 24.6 (18.9; 27.4) | ||
| 2 | 60 | Mean (SD) | 24.0 (6.3) | 23.3 (6.7) | 22.4 (6.1) |
| Median (Q1; Q3) | 23.0 (19.5; 28.9) | 22.8 (18.0; 27.3) | 21.7 (17.9; 25.0) | ||
| 3 | 90 | Mean (SD) | 22.1 (4.9) | 21.8 (4.8) | 21.1 (4.5) |
| Median (Q1; Q3) | 21.7 (18.2; 24.8) | 21.3 (18.8; 24.9) | 21.7 (18.9; 23.8) | ||
| 4 | 120 | Mean (SD) | 18.5 (4.2) | 18.4 (4.4) | 19.1 (4.6) |
| Median (Q1; Q3) | 17.3 (15.9; 22.1) | 17.3 (14.6; 21.9) | 20.1 (14.6; 22.1) |
| Visit | Age at Visit (Days) | 24 h Sleep | Nocturnal Sleep | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eHF (n = 149) | CF (n = 148) | BF (n = 41) | eHF (n = 149) | CF (n = 148) | BF (n = 41) | ||
| 1 | 30 | 16.3 (1.9) | 16.3 (1.8) | 16.0 (2.0) | 7.6 (1.7) | 7.7 (1.9) | 7.7 (2.3) |
| (11.3; 22.3) | (11.0; 23.0) | (12.9; 19.7) | (4.7; 11.7) | (2.3; 12.0) | (4.8; 12.0) | ||
| 2 | 60 | 15.1 (2.3) | 15.0 (2.2) | 14.9 (2.1) | 7.6 (1.5) | 7.7 (1.6) | 7.6 (1.6) |
| (9.3; 22.0) | (10.6; 22.7) | (12.1; 21.7) | (5.0; 12.0) | (4.3; 11.7) | (5.1; 10.5) | ||
| 3 | 90 | 13.8 (2.8) | 13.8 (2.5) | 13.1 (2.4) | 7.7 (1.5) | 7.8 (1.6) | 7.7 (1.5) |
| (9.8; 22.2) | (9.9; 22.5) | (10.6; 21.3) | (4.7; 12.3) | (5.1; 12.0) | (5.7; 11.2) | ||
| 4 | 120 | 13.3 (2.7) | 13.3 (2.5) | 13.2 (2.8) | 8.3 (1.0) | 8.5 (1.2) | 8.6 (1.0) |
| (8.0; 21.2) | (8.9; 22.3) | (9.7; 20.0) | (4.7; 11.1) | (6.0; 11.7) | (7.0; 10.8) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otten, L.; Schelker, E.; Petersen, H.; Nomayo, A.; Conzade, R.; Günther, J.; Grieger, A.; Jochum, F.; on behalf of the HASI Study Group. Gastrointestinal Tolerance of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214674
Otten L, Schelker E, Petersen H, Nomayo A, Conzade R, Günther J, Grieger A, Jochum F, on behalf of the HASI Study Group. Gastrointestinal Tolerance of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214674
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtten, Lindsey, Elisabeth Schelker, Hanna Petersen, Antonia Nomayo, Romy Conzade, Julia Günther, Andrea Grieger, Frank Jochum, and on behalf of the HASI Study Group. 2023. "Gastrointestinal Tolerance of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214674
APA StyleOtten, L., Schelker, E., Petersen, H., Nomayo, A., Conzade, R., Günther, J., Grieger, A., Jochum, F., & on behalf of the HASI Study Group. (2023). Gastrointestinal Tolerance of an Infant Formula Manufactured from Extensively Hydrolysed Protein in Healthy Term Infants. Nutrients, 15(21), 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214674





