Investigating Nutritional and Inflammatory Status as Predictive Biomarkers in Oligoreccurent Prostate Cancer—A RADIOSA Trial Preliminary Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
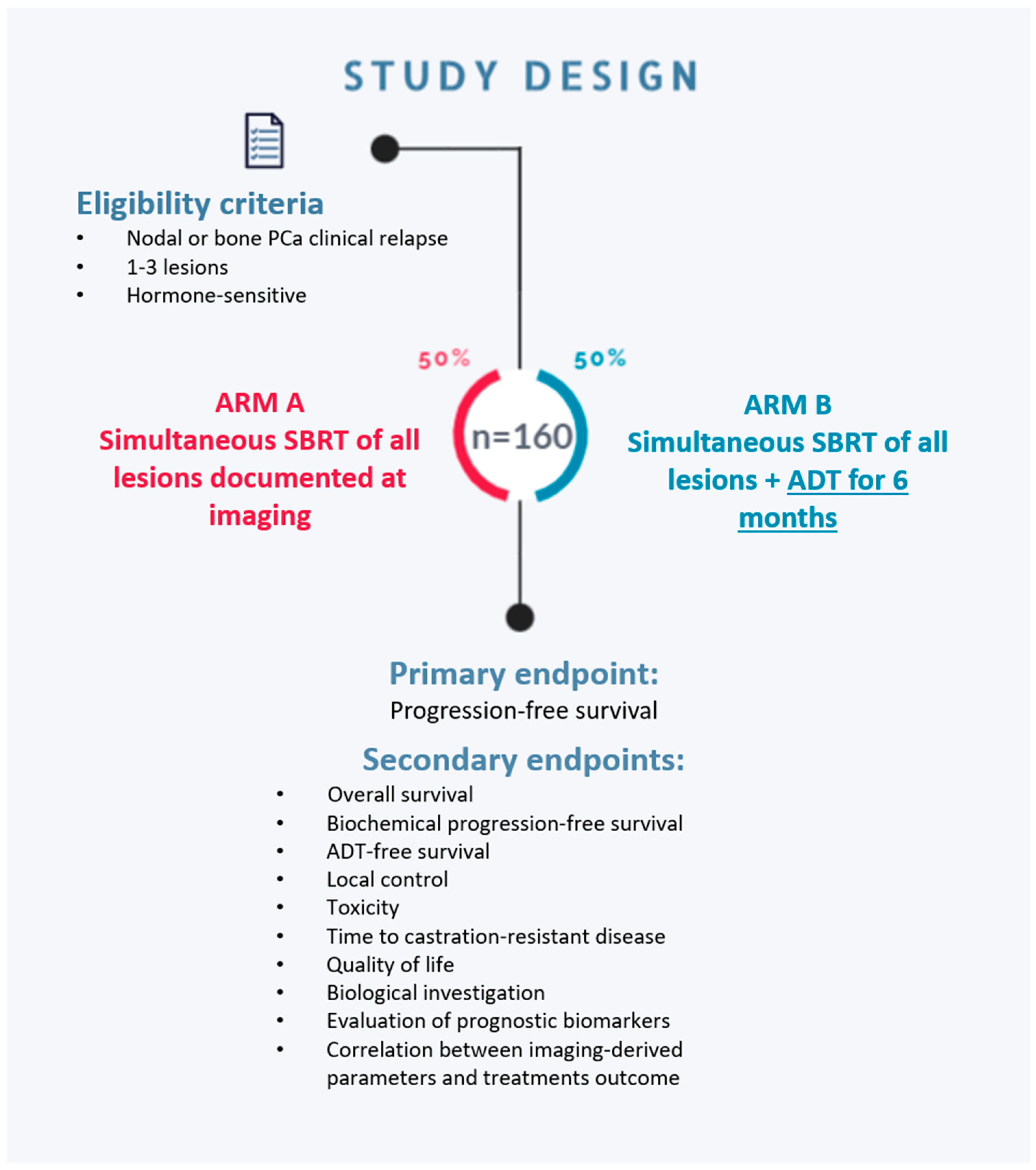
2.1. Study Design
- Arm A—MDT with stereotactic radiotherapy on all metastatic sites;
- Arm B—MDT with stereotactic radiotherapy on all metastatic sites + 6 months of ADT.
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Treatment Characteristics
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
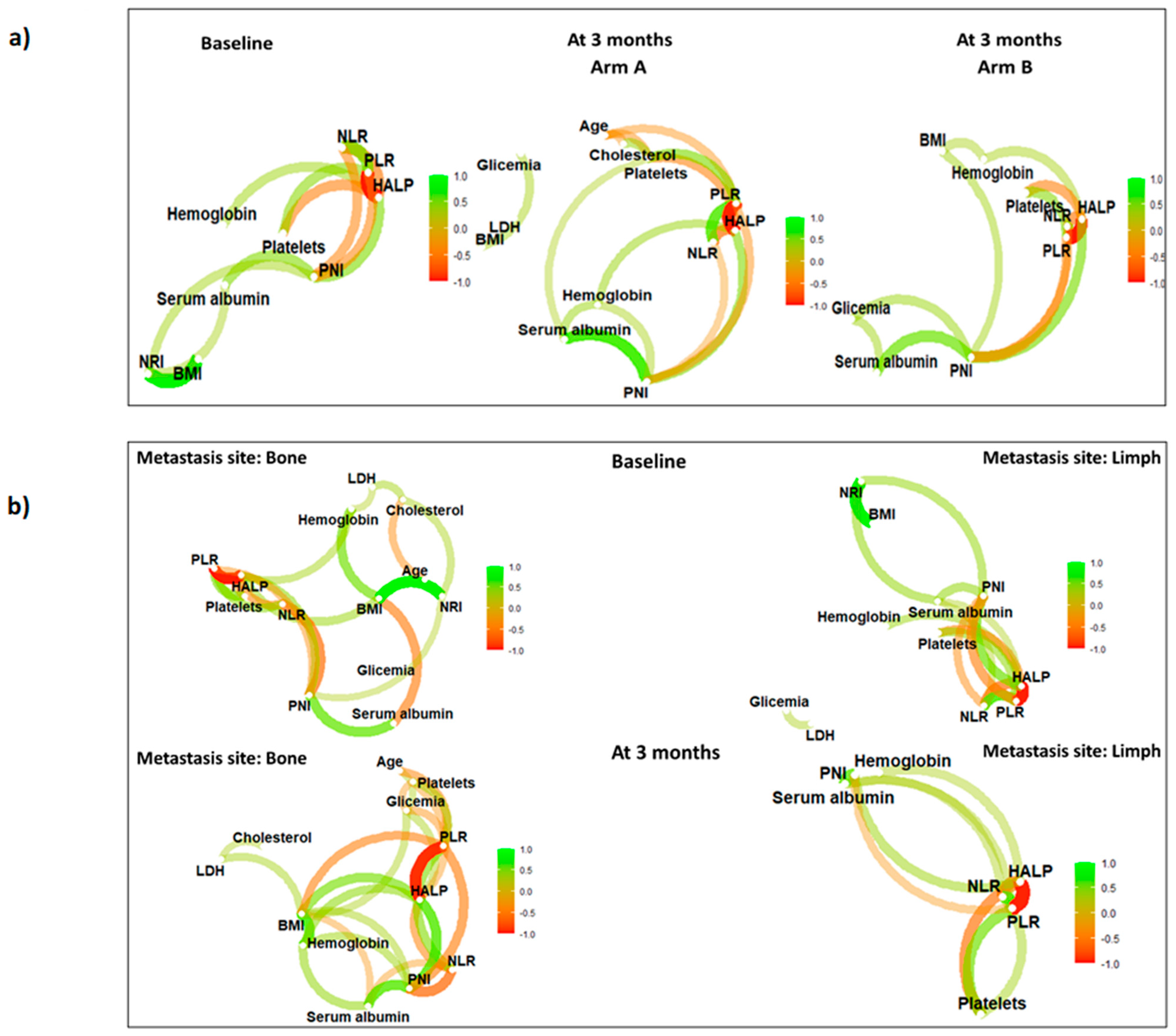
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADT | Androgen deprivation therapy |
| BCR | Biochemical recurrence |
| BED | Biologically Effective Dose |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CONUT | Controlling nutritional status |
| HALP | Hemoglobin-albumin-lymphocyte-platelet |
| IQR | Inter quartile range |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LHRH | Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone |
| MDT | Metastasis-directed therapy |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| NLRAR | NLR–albumin ratio |
| NRI | Nutrition Risk Index |
| PCa | Prostate cancer |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PSMA-PET | Prostate-specific membrane antigen—positron emission tomography |
| PNI | Prognostic Nutritional Index |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiation therapy |
References
- Phillips, R.; Shi, W.Y.; Deek, M.; Radwan, N.; Lim, S.J.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Ross, A.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Deville, C.; et al. Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ost, P.; Reynders, D.; Decaestecker, K.; Fonteyne, V.; Lumen, N.; De Bruycker, A.; Lambert, B.; Delrue, L.; Bultijnck, R.; Claeys, T.; et al. Surveillance or Metastasis-Directed Therapy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Recurrence: A Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Phase II Trial. JCO 2018, 36, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): A randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deek, M.P.; Taparra, K.; Phillips, R.; Velho, P.I.; Gao, R.W.; Deville, C.; Song, D.Y.; Greco, S.; Carducci, M.; Eisenberger, M.; et al. Metastasis-directed Therapy Prolongs Efficacy of Systemic Therapy and Improves Clinical Outcomes in Oligoprogressive Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deek, M.P.; Phillips, R.M.; Tran, P.T. Local Therapies in Oligometastatic and Oligoprogressive Prostate Cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 31, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Visschere, P.J.L.; Standaert, C.; Fütterer, J.J.; Villeirs, G.M.; Panebianco, V.; Walz, J.; Maurer, T.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Lecouvet, F.E.; Giannarini, G.; et al. A Systematic Review on the Role of Imaging in Early Recurrent Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubmüller, B.; Baltzer, P.; Hartenbach, S.; D’Andrea, D.; Helbich, T.H.; Haug, A.R.; Goldner, G.M.; Wadsak, W.; Pfaff, S.; Mitterhauser, M.; et al. PSMA Ligand PET/MRI for Primary Prostate Cancer: Staging Performance and Clinical Impact. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6300–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deek, M.P.; Van der Eecken, K.; Sutera, P.; Deek, R.A.; Fonteyne, V.; Mendes, A.A.; Decaestecker, K.; Kiess, A.P.; Lumen, N.; Phillips, R.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Genetic Predictors of Response to Metastasis-Directed Therapy Versus Observation in Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: Analysis of STOMP and ORIOLE Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3377–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Zaffaroni, M.; Bergamaschi, L.; Augugliaro, M.; Volpe, S.; Pepa, M.; Bonizzi, G.; Pece, S.; Amodio, N.; Mistretta, F.A.; et al. Exploring miRNA Signature and Other Potential Biomarkers for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Characterization: The Biological Challenge behind Clinical Practice. A Narrative Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Eecken, K.; Vanwelkenhuyzen, J.; Deek, M.P.; Tran, P.T.; Warner, E.; Wyatt, A.W.; Kwan, E.M.; Verbeke, S.; Van Dorpe, J.; Fonteyne, V.; et al. Tissue- and Blood-derived Genomic Biomarkers for Metastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deek, M.P.; Van der Eecken, K.; Phillips, R.; Parikh, N.R.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Lotan, T.L.; Kishan, A.U.; Maurer, T.; GAP6 Consortium; Boutros, P.C.; et al. The Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Castration-sensitive Prostate Cancer: The Spectrum Theory Revisited. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Galon, J. Natural immunity to cancer in humans. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; de Visser, K.E. Cancer: Inflammation lights the way to metastasis. Nature 2014, 507, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, R.; Chi, C.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, H.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Pan, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the combined clinical outcome after sequential therapy with abiraterone and docetaxel for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Prostate 2018, 78, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidaway, P. Prostate cancer: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts prostate cancer prognosis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, D.; Mateo, J.; Templeton, A.J.; Zafeiriou, Z.; Bianchini, D.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Bahl, A.; Shen, L.; Su, Z.; Sartor, O.; et al. Baseline neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with survival and response to treatment with second-line chemotherapy for advanced prostate cancer independent of baseline steroid use. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, D.; Zhang, J.; Mao, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; Yang, B.; Ye, L.; et al. The Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, and Platelet (HALP) Score is a Novel Significant Prognostic Factor for Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Undergoing Cytoreductive Radical Prostatectomy. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, C.-J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K.-W.; Yu, X.-T.; Gong, Y.; Li, X.-S.; He, Z.-S.; Zhou, L.-Q. Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin and albumin levels and lymphocyte and platelet counts (HALP) in patients with renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, C.-J.; Gong, Y.-Q.; Hao, H.; Guan, B.; Li, X.-S.; Zhou, L.-Q. Prognostic significance of HALP (hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet) in patients with bladder cancer after radical cystectomy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Xue, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.-N.; Zhang, W.-H.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.-Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.-X.; et al. Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet in patients with gastric carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41370–41382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Tang, E.; Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.; et al. Preoperative combined hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet levels predict survival in patients with locally advanced colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 72076–72083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, C.L.; Doyle, C.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Meyerhardt, J.; Courneya, K.S.; Schwartz, A.L.; Bandera, E.V.; Hamilton, K.K.; Grant, B.; McCullough, M.; et al. Nutrition and physical activity guidelines for cancer survivors. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 243–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Chi, C.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Shao, X.; Xu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shangguan, X.; et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts initial response to treatment and prognosis in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone. Prostate 2017, 77, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, Q.H.; Ye, Y.; Hildebrandt, M.A.T.; Gu, J.; Wu, X. Prognostic significance of pretreatment serum levels of albumin, LDH and total bilirubin in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, J.J.; Salas, M.; Ward, A.; Goss, G. Anemia as an independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with cancer: A systemic, quantitative review. Cancer 2001, 91, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzby, G.P.; Williford, W.O.; Peterson, O.L.; Crosby, L.O.; Page, C.P.; Reinhardt, G.F.; Mullen, J.L. A randomized clinical trial of total parenteral nutrition in malnourished surgical patients: The rationale and impact of previous clinical trials and pilot study on protocol design. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 47, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.; Nadal, E.; Peiró, I.; Masuet-Aumatell, C.; Macia, I.; Rivas, F.; Rosado, G.; Rodriguez, P.; Ureña, A.; Padrones, S.; et al. Preoperative nutritional status assessment predicts postoperative outcomes in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, J.G.; Paik, H.C.; Park, M.S. Usefulness of the preoperative prognostic nutritional index score as a predictor of the outcomes of lung transplantation: A single-institution experience. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasahara, M.; Kanda, M.; Ito, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Teramoto, H.; Ishigure, K.; Murai, T.; Asada, T.; Ishiyama, A.; Matsushita, H.; et al. The Preoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index Predicts Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes of Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: Analysis of a Multi-Institution Dataset. Dig. Surg. 2020, 37, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokorovic, A.; So, A.I.; Serag, H.; French, C.; Hamilton, R.J.; Izard, J.P.; Nayak, J.G.; Pouliot, F.; Saad, F.; Shayegan, B.; et al. Canadian Urological Association guideline on androgen deprivation therapy: Adverse events and management strategies—Executive summary. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2021, 15, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, C.; Crawley, D.; Adolfsson, J.; Rudman, S.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Quantifying the evidence for the risk of metabolic syndrome and its components following androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, M.; Leone, G.; Buttigliero, C.; Zichi, C.; DI Stefano, R.F.; Pignataro, D.; Vignani, F.; Scagliotti, G.V.; DI Maio, M. Hormonal treatment and quality of life of prostate cancer patients: New evidence. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2018, 70, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenfeld, J.; Samson, D.J.; Hasselblad, V.; Aronson, N.; Albertsen, P.C.; Bennett, C.L.; Wilt, T.J. Single-therapy androgen suppression in men with advanced prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, F.; Di Prima, L.; Pisano, C.; Poletto, S.; De Filippis, M.; Crespi, V.; Farinea, G.; Cani, M.; Calabrese, M.; Saporita, I.; et al. How to Improve the Quality of Life of Patients with Prostate Cancer Treated with Hormone Therapy? Res. Rep. Urol. 2023, 15, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvaso, G.; Ciardo, D.; Corrao, G.; Gandini, S.; Fodor, C.; Zerini, D.; Rojas, D.P.; Augugliaro, M.; Bonizzi, G.; Pece, S.; et al. Radioablation +/− hormonotherapy for prostate cancer oligorecurrences (Radiosa trial): Potential of imaging and biology (AIRC IG-22159). BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Institute of Oncology. Radioablation With or Without Androgen DeprIvation Therapy in Metachronous Prostate Cancer OligometaStAsis (RADIOSA). 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03940235 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Mao, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X. Controlling Nutritional Status score: A new prognostic indicator for patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszno, J.; Kołosza, Z.; Mrochem-Kwarciak, J.; Telka, E.; Jochymek, B.; Miszczyk, L. Role of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-monocyte ratio and platelets in prognosis of patients with prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, W.; Niu, X. Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio to Albumin Ratio and White Blood Cell to Hemoglobin Ratio as Prognostic Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Who Underwent Curative Hepatectomy. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.; Christidis, D.; Perera, M.; Hong, S.K.; Manning, T.; Vela, I.; Lawrentschuk, N. Prostate cancer biomarkers: Are we hitting the mark? Prostate Int. 2016, 4, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuzuka, K.; Arai, Y. Metabolic changes in patients with prostate cancer during androgen deprivation therapy. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 25, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, F.J.; McNaughton Collins, M.; Walker Corkery, E.; Elliott, D.B.; Barry, M.J. The impact of androgen deprivation on quality of life after radical prostatectomy for prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovic, P.; De Meerleer, G.; Delrue, L.; Lambert, B.; Fonteyne, V.; Lumen, N.; Decaestecker, K.; Villeirs, G.; Vuye, P.; Ost, P. Salvage stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with limited prostate cancer metastases: Deferring androgen deprivation therapy. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2013, 11, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Ge, P.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Zhao, M.; Ren, L. Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio or Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Prediction of Bone Metastasis of Prostate Cancer. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Qi, X.; Ma, M.; Qin, S.; Yu, H.; Sun, S.; Zhou, D.; Wang, W. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in prostate cancer: Evidence from 16,266 patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, F.; Qi, S.; Yin, Z.; Gao, J. Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Whole Cohort (n = 88) | ARM A (n = 45) | ARM B (n = 43) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Median (IQR) | ||
| Age (years) | 69 (64–75) | 68 (63–74) | 70 (66–76) |
| Height (cm) | 172 (170–178) | 173 (169–178) | 172 (170–178) |
| Weight (kg) | 81 (72–91) | 82 (70–91) | 81 (75–92) |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 26.9 (24.69–29.24) | 26.8 (24.2–29.5) | 27.4 (25.1–29.2) |
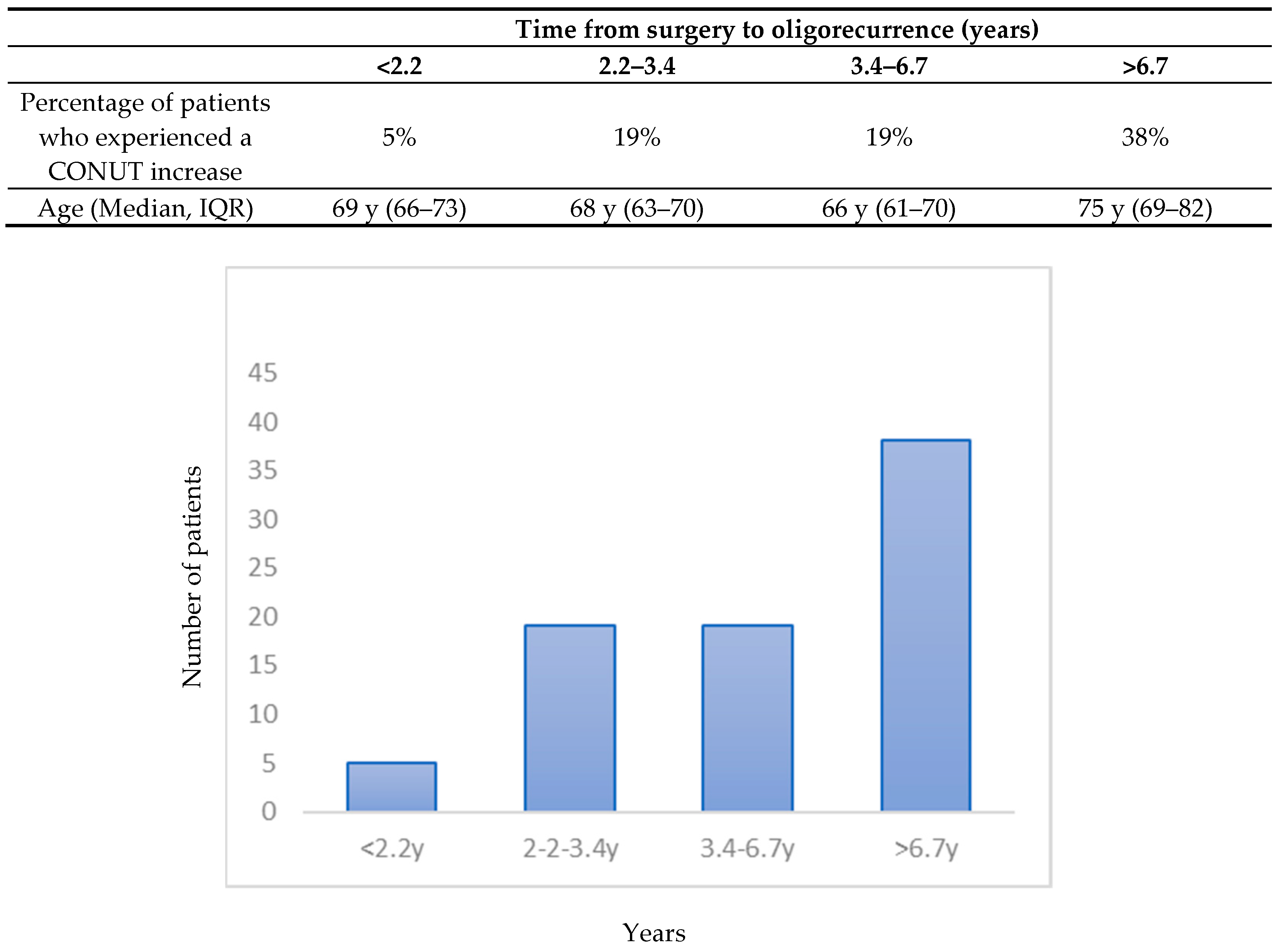
| Time from surgery to oligorecurrence (months) | 42 (28–81) | 40 (27–79) | 42 (32–88) |
| Time from last active treatment to oligorecurrence (months) | 36 (17–64) | 33 (17–58) | 38 (19–69) |
| Neutrophils (103/µlitro) | 3.9 (3.4–5.1) | 4.0 (3.4–5.0) | 3.9 (3.5–5.5) |
| Lymphocites (103/µlitro) | 1.5 (1.3–1.9) | 1.4 (1.3–1.8) | 1.5 (1.2–2.0) |
| Platelets (103/µlitro) | 214 (184–246) | 218 (189–244) | 214 (177–246) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.9 (14.3–15.7) | 14.9 (14.5–15.5) | 14.9 (14.2–15.8) |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 3.8 (3.2–4.9) | 3.6 (3.0–4.7) | 4.0 (3.4–5.6) |
| Cholesterol (ml/dL) | 193 (180–218) | 194 (186–219) | 193 (173–215) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 4.3 (4.2–4.4) |
| Glicemia (mg/dL) | 96 (89–106) | 98 (89–106) | 95 (89–106) |
| LDH (mU/mL) | 177 (157–201) | 177 (159–208) | 177 (156–194) |
| NLR | 2.6 (2.1–3.4) | 2.6 (2.2–3.5) | 2.7 (2.0–3.2) |
| NLRAR | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.06 (0.05–0.07) |
| HALP | 46 (34–67) | 44 (33–63) | 50 (36–70) |
| PLR | 144 (101–186) | 145 (106–194) | 134 (95–180) |
| PNI | 51 (49–53) | 51 (49–53) | 51 (49–54) |
| NRI | 115 (111–120) | 114 (110–121) | 117 (111–120) |
| Counts (%) | |||
| Lesion site | |||
| Lymphnode(s) | 56 | 27 | 29 |
| Bone | 32 | 18 | 14 |
| CONUT SCORE | |||
| 0 | 27 | 14 | 13 |
| 1 | 33 | 18 | 15 |
| 2 | 13 | 6 | 7 |
| 3 | 10 | 4 | 6 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Missing | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| ARM A Median (IQR) | ARM B Median (IQR) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3 Months FU | Change | Baseline | 3 Months FU | Change | p Value ARM A vs. ARM B | |
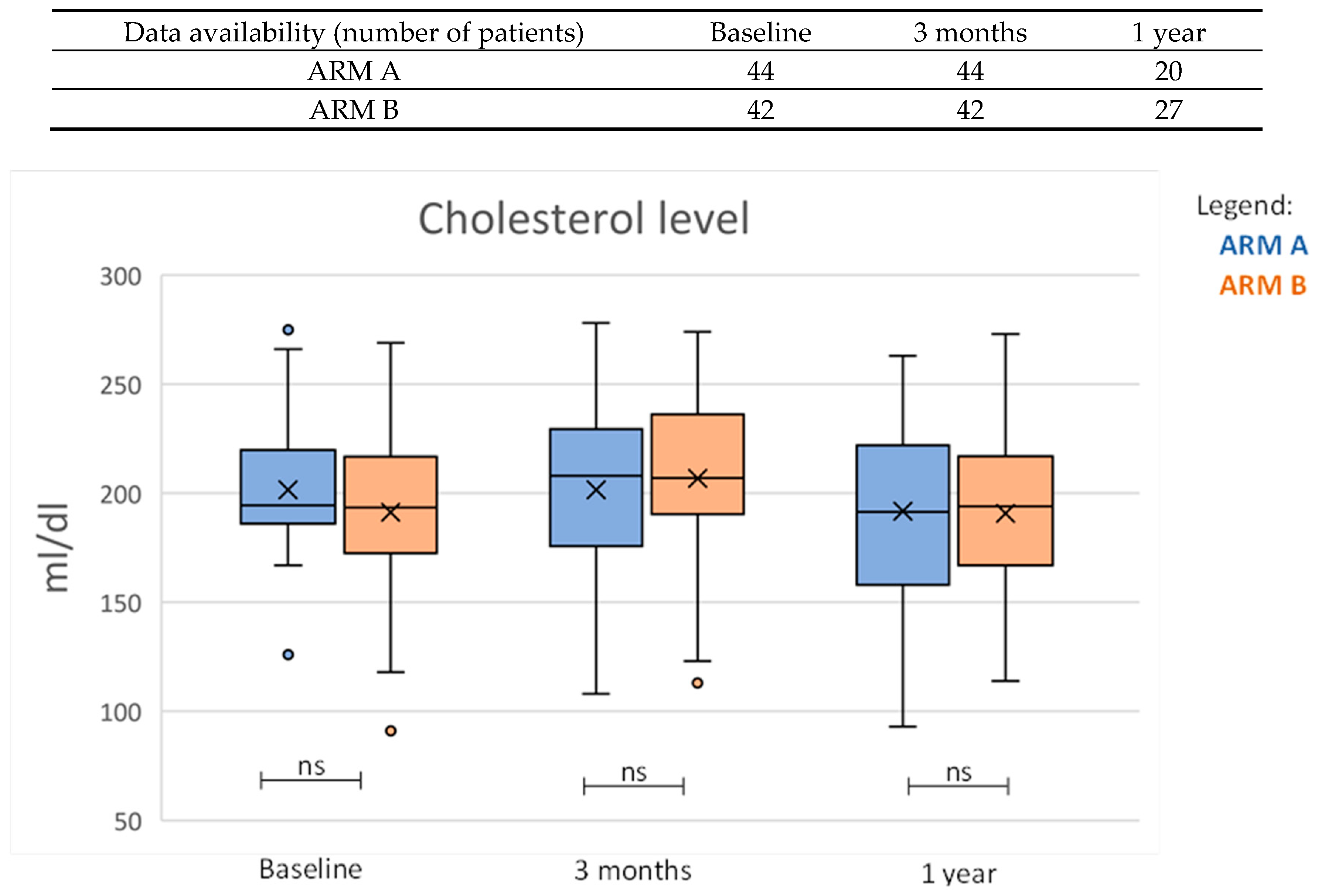
| Cholesterol (mL/dL) | 194 (186–219) | 208 (176–229) | −1 (−22–18) | 193 (173–215) | 207 (191–235) | 15 (1–29) | 0.005 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 4.4 (4.2–4.5) | 0.0 (−0.1–0.1) | 4.3 (4.2–4.4) | 4.2 (4.1–4.4) | −0.1 (−0.2–0) | 0.024 |
| Glicemia (mg/dL) | 98 (88–106) | 99 (86–107) | 0 (−4–5) | 95 (89–105) | 99 (89–106) | 1 (−5–9) | 0.542 |
| LDH (mU/mL) | 177 (159–208) | 181 (166–201) | 4 (−9–25) | 177 (156–193) | 188 (168–204) | 16 (4–27) | 0.174 |
| NLR | 2.6 (2.2–3.5) | 2.7 (2.06–3.7) | 0.1 (−0.5–0.4) | 2.7 (2.0–3.2) | 2.4 (1.9–3.1) | −0.2 (−0.7–0.1) | 0.141 |
| NLRAR | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | 0.06 (0.05–0.07) | 0.06 (0.05–0.07) | 0.00 (−0.02–0.01) | 0.369 |
| HALP | 43.9 (33.2–63.1) | 44.0 (30.3–60.1) | 0.2 (−7.9–7.4) | 49.6 (35.7–70.1) | 43.3 (29.3–57.5) | −4.1 (−11.2–−0.5) | 0.067 |
| PLR | 145.3 (106.4–194.9) | 145.4 (113.8–197.1) | −0.1 (−19.7–16.2) | 133.7 (94.8–179.8) | 140.4 (100.7–184.1) | 2.5 (−10.0–11.1) | 0.829 |
| PNI | 50.9 (48.7–53.3) | 51.0 (48.4–52.4) | 0.0 (−2.0–1.7) | 51.3 (49.4–53.7) | 49.9 (47.6–53.1) | −1.1 (−3.4–0.8) | 0.132 |
| ARM A Median (IQR) | ARM B Median (IQR) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1 Year FU | Change | Baseline | 1 Year FU | Change | p Value ARM A vs. ARM B | |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 3.6 (3.0–4.7) | 4.2 (3–4.9) | 0.4 (−0.3–0.9) | 4.0 (3.4–5.6) | 3.8 (2.1–5.5) | 0.0 (−2.3–0.8) | 0.204 |
| Cholesterol (mL/dL) | 194 (186–219) | 192 (158–222) | −1 (−15–14) | 193 (173–215) | 194 (170–216) | −2 (−20–5) | 0.945 |
| Glicemia (mg/dL) | 98 (88–106) | 95 (86–109) | −1 (−5–6) | 95 (89–105) | 96 (89–107) | −2 (−6–14) | 0.936 |
| LDH (mU/mL) | 177 (159–208) | 179 (168–200) | 1 (−13–13) | 177 (156–193) | 172 (149–193) | −3 (−11–8) | 0.683 |
| Site of Metastases = Lymphnodal | Site of Metastases = Bone | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3 Months FU | Change | Baseline | 3 Months FU | Change | p Value | |
| Cholesterol (mL/dL) | 191 (178–214) | 210 (179–230) | 13 (−7–26) | 203 (186–227) | 205 (190–233) | 1 (−14–18) | 0.174 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 4.3 (4.1–4.5) | −0.1 (−0.2–0.1) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 4.3 (4.2–4.5) | 0.0 (−0.1–0.1) | 0.889 |
| Glicemia (mg/dL) | 95 (88–106) | 97 (86–106) | 1 (−5–5) | 100 (91–105) | 100 (91–108) | 0 (−5–7) | 0.865 |
| LDH (mU/mL) | 178 (156–203) | 181 (168–201) | 12 (−7–26) | 169 (159–193) | 190 (168–206) | 8 (−6–27) | 0.936 |
| NLR | 2.7 (2.1–3.4) | 2.4 (1.9–3.4) | −0.2 (−0.7–0.2) | 2.6 (2.1–3.2) | 2.7 (2.1–3.8) | 0.1 (−0.3–0.6) | 0.020 |
| NLRAR | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.05 (0.05–0.08) | −0.01 (−0.02–0.01) | 0.06 (0.05–0.07) | 0.06 (0.05–0.09) | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | 0.049 |
| HALP | 47.5 (33.8–64.3) | 46.4 (31.0–63.0) | −2.1 (−8.4–4.4) | 44.3 (34.9–67.5) | 39.7 (28.9–52.9) | −4.5 (−10.7–1.1) | 0.226 |
| PLR | 137.6 (106.5–190.8) | 138.2 (101.0–184.1) | −1.6 (−14.7–9.1) | 148.0 (100.0–180.5) | 159.7 (128.9–192.9) | 5.9 (−2.8–27.7) | 0.061 |
| PNI | 51.7 (49.3–53.4) | 51.3 (48.4–52.6) | −0.8 (−2.8–1.3) | 50.6 (49.1–53.0) | 49.5 (47.6–51.9) | −0.7 (−2.2–0.6) | 0.912 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaffaroni, M.; Vincini, M.G.; Corrao, G.; Lorubbio, C.; Repetti, I.; Mastroleo, F.; Putzu, C.; Villa, R.; Netti, S.; D’Ecclesiis, O.; et al. Investigating Nutritional and Inflammatory Status as Predictive Biomarkers in Oligoreccurent Prostate Cancer—A RADIOSA Trial Preliminary Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214583
Zaffaroni M, Vincini MG, Corrao G, Lorubbio C, Repetti I, Mastroleo F, Putzu C, Villa R, Netti S, D’Ecclesiis O, et al. Investigating Nutritional and Inflammatory Status as Predictive Biomarkers in Oligoreccurent Prostate Cancer—A RADIOSA Trial Preliminary Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaffaroni, Mattia, Maria Giulia Vincini, Giulia Corrao, Chiara Lorubbio, Ilaria Repetti, Federico Mastroleo, Costantino Putzu, Riccardo Villa, Sofia Netti, Oriana D’Ecclesiis, and et al. 2023. "Investigating Nutritional and Inflammatory Status as Predictive Biomarkers in Oligoreccurent Prostate Cancer—A RADIOSA Trial Preliminary Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214583
APA StyleZaffaroni, M., Vincini, M. G., Corrao, G., Lorubbio, C., Repetti, I., Mastroleo, F., Putzu, C., Villa, R., Netti, S., D’Ecclesiis, O., Luzzago, S., Mistretta, F. A., Musi, G., Cattani, F., Gandini, S., Marvaso, G., & Jereczek-Fossa, B. A. (2023). Investigating Nutritional and Inflammatory Status as Predictive Biomarkers in Oligoreccurent Prostate Cancer—A RADIOSA Trial Preliminary Analysis. Nutrients, 15(21), 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214583








