Diet and Other Modifiable Factors in Long-Term Decline of Kidney Function: Observational and Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Assessment of the Five Modifiable Factors
2.2. Cumulative Score
2.3. Dependent Variables
2.4. Other Variables
2.5. Calculations and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Tertiles of the Modifiable Factors and Factor-Specific Scores
3.3. Cumulative Score
3.4. Cumulative Score and Mortality Rate
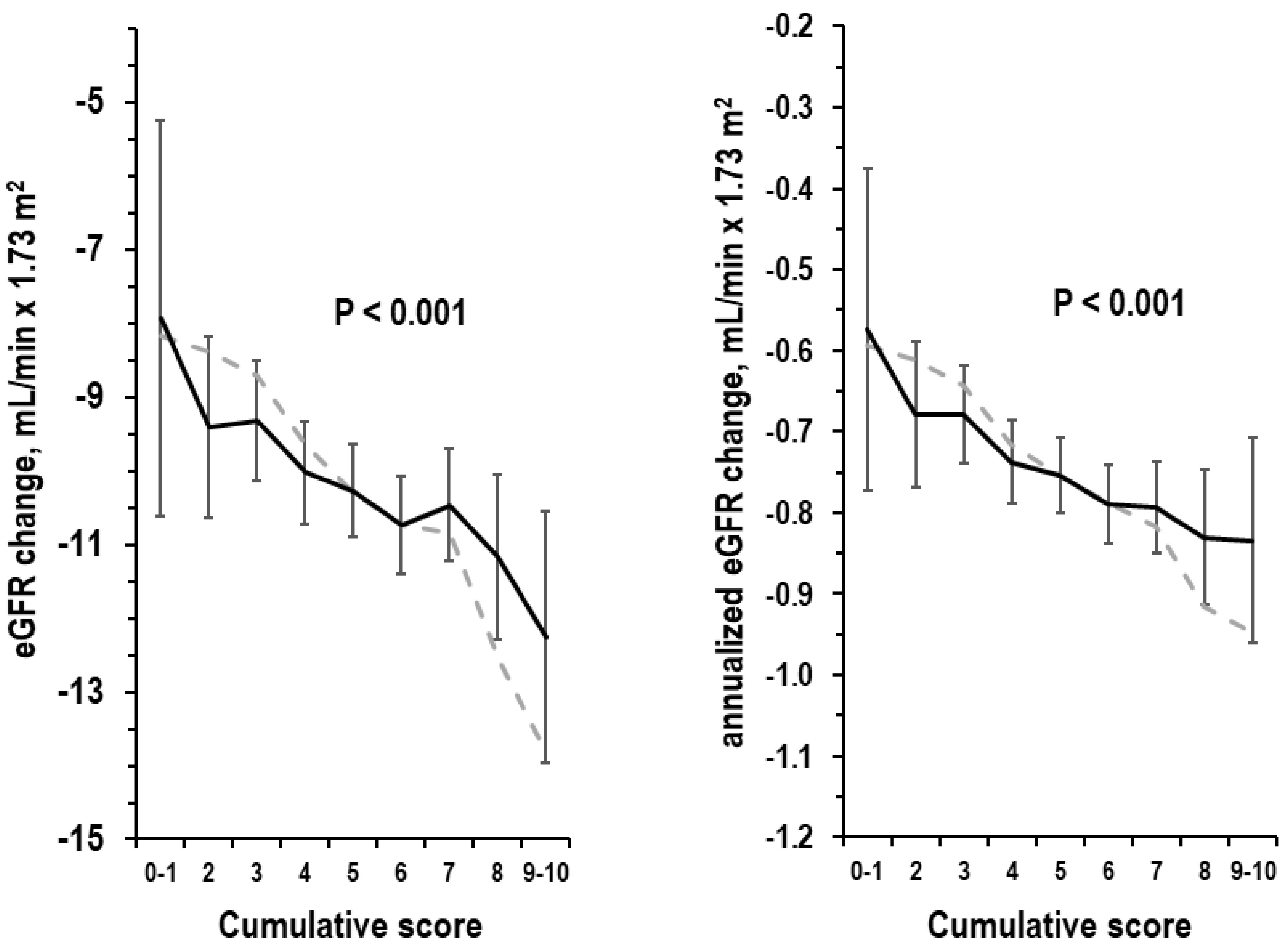
3.5. Cumulative Score and eGFR Change over Time
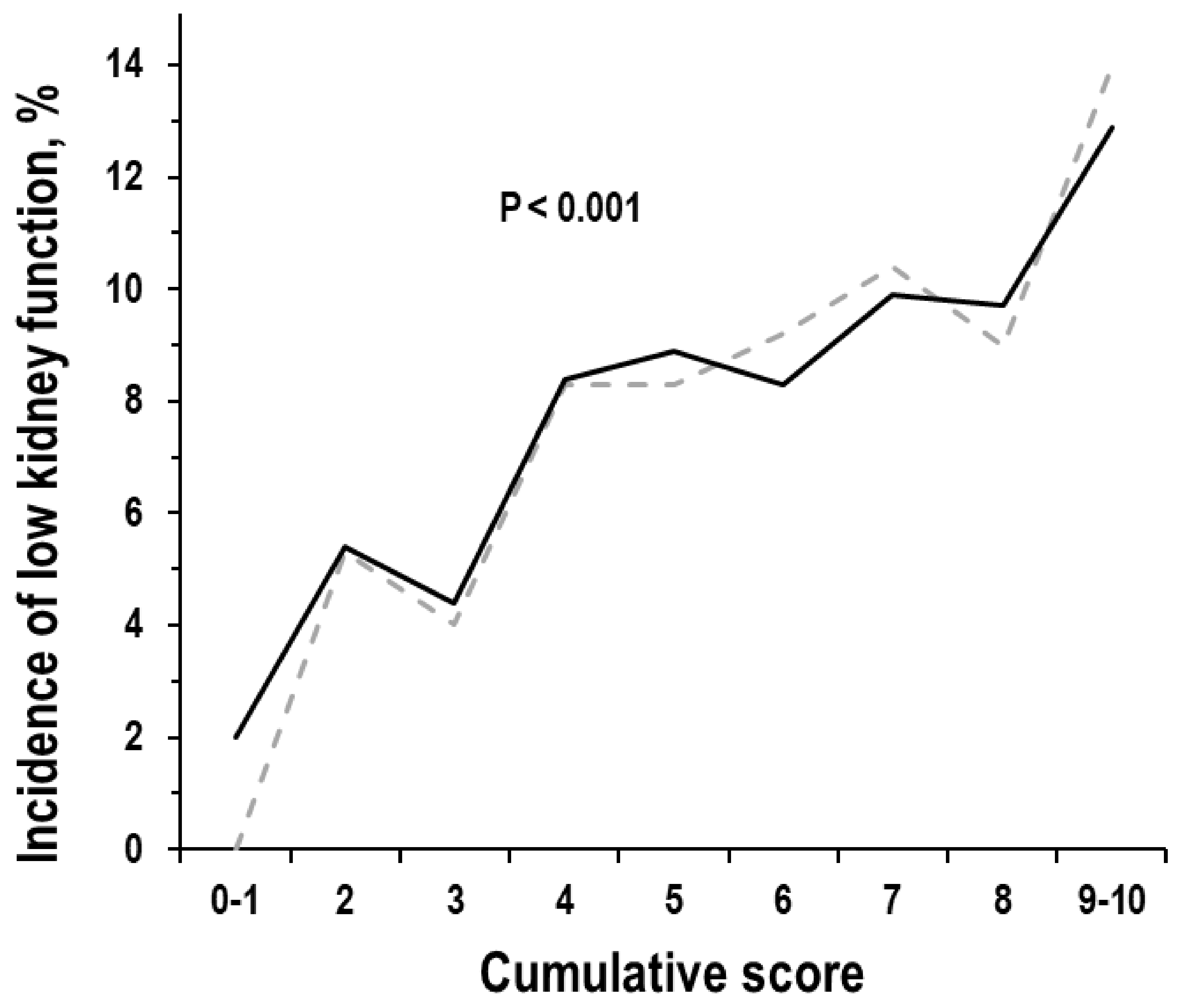
3.6. Cumulative Score and Incidence of Low Kidney Function
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UK Renal Registry (2022) UK Renal Registry 24th Annual Report—Data to 31/12/2020, Bristol, UK. Available online: https://ukkidney.org/audit-research/annual-report) (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Chen, X.; Gipson, D.; Gu, H.; Hirth, R.A.; Hutton, D.; Jin, Y.; et al. US Renal Data System 2019 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, A6–A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA-EDTA Registry: ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2019; Amsterdam UMC, Location AMC, Department of Medical Informatics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Weinstein, J.R.; Anderson, S. The Aging Kidney: Physiological Changes. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010, 17, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76 (Suppl. S1), S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.T.; Su, G.; Zhang, L.; Qin, X.; Marshall, S.; González-Ortiz, A.; Clase, C.M.; Campbell, K.L.; Xu, H.; Carrero, J.-J. Modifiable Lifestyle Factors for Primary Prevention of CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 32, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, M.; Bilancio, G.; Cavallo, P.; Palladino, R.; Terradura-Vagnarelli, O.; Laurenzi, M. Sodium intake and kidney function in the general population: An observational, population-based study. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 14, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, M.; Bilancio, G.; Secondulfo, C.; Iesce, G.; Ferrara, C.; Terradura-Vagnarelli, O.; Laurenzi, M. Relation of Alcohol Intake to Kidney Function and Mortality Observational, Population-Based, Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Lombardi, C.; Chiricone, D.; De Santo, N.G.; Zanchetti, A.; Bilancio, G. Protein intake and kidney function in the middle-age population: Contrast between cross-sectional and longitudinal data. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Bilancio, G.; Cavallo, P.; Palladino, R.; Zulli, E.; Villa, R.; Veneziano, R.; Laurenzi, M. Urinary Potassium and Kidney Function Decline in the Population—Observational Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenzi, M.; Cirillo, M.; Angeletti, M.; Buongiorno, A.; Morisi, G.; Panarelli, W.; Panfili, M.; Stamler, J.; Terradura, O.; Trevisan, M. Gubbio Population Study: Baseline findings. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1991, 1, S1–S18. [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo, M.; Terradura-Vagnarelli, O.; Mancini, M.; Menotti, A.; Zanchetti, A.; Laurenzi, M. Cohort profile: The Gubbio Population Study. Leuk. Res. 2013, 43, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, G.L.; Miller, W.G.; Coresh, J.; Fleming, J.; Greenberg, N.; Greene, T.; Hostetter, T.; Levey, A.S.; Panteghini, M.; Welch, M.; et al. Recommendations for Improving Serum Creatinine Measurement: A Report from the Laboratory Working Group of the National Kidney Disease Education Program. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.; Elliott, P.; Chee, D.; Stamler, J. Urinary biochemical markers of dietary intake in the INTERSALT study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1246S–1253S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, S.A. Urine Nitrogen as a Biomarker for the Validation of Dietary Protein Intake. J. Nutr. 2003, 133 (Suppl. S3), 921S–924S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogswell, M.E.; Maalouf, J.; Elliott, P.; Loria, C.M.; Patel, S.; Bowman, B.A. Use of Urine Biomarkers to Assess Sodium Intake: Challenges and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 349–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, C.I.; Cogswell, M.E.; Loria, C.M.; Liu, K.; Allen, N.; Gillespie, C.; Wang, C.-Y.; de Boer, I.H.; Wright, J. Validity of predictive equations for 24-h urinary potassium excretion based on timing of spot urine collection among adults: The MESA and CARDIA Urinary Sodium Study and NHANES Urinary Sodium Calibration Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ix, J.H.; Wassel, C.L.; Stevens, L.A.; Beck, G.J.; Froissart, M.; Navis, G.; Rodby, R.; Torres, V.E.; Zhang, Y.; Greene, T.; et al. Equations to Estimate Creatinine Excretion Rate. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology of the North American Society of Pacing Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chick, J.; Kreitman, N.; Plant, M. Mean cell volume and gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase as markers of drinking in working men. Lancet 1981, 317, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesteloot, H.E.; Joossens, J.V. Relationship between dietary protein intake and serum urea, uric acid and creatinine, and 24-hour urinary creatinine excretion: The BIRNH Study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1993, 12, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, M.; Baisch, F.; Kropp, J.; Gerzer, R.; Drummer, C.; Goswami, N.; Blaber, A.P.; Hinghofer-Szalkay, H.; Convertino, V.A.; Bie, P.; et al. High dietary sodium chloride consumption may not induce body fluid retention in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2000, 278, F585–F595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.B.; Lin, H.; McCabe, R.D.; Sorensen, C.M.; Braunstein, T.H.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.-H.; Salomonsson, M.; Yang, B.C.; Li, D.Y.; Weng, Y.F.; et al. Potassium’s cardiovascular protective mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1995, 268 Pt 2, R825–R837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Lombardi, C.; Luciano, M.G.; Bilancio, G.; Anastasio, P.; De Santo, N.G. Estimation of GFR: A Comparison of New and Established Equations. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Laurenzi, M.; Mancini, M.; Zanchetti, A.; De Santo, N.G. Low Muscular Mass and Overestimation of Microalbuminuria by Urinary Albumin/Creatinine Ratio. Hypertension 2006, 47, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Arteaga, C.; McManus, C.; Smith, J.; Moffitt, S. Measurement of muscle mass in humans: Validity of the 24-hour urinary creatinine method. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Levey, A.S. Dietary protein and renal function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1993, 3, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; Pelletier, S.; Mafra, D.; Chauveau, P. Nutrition and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.-Y.; Gritter, M.; Vogt, L.; de Borst, M.H.; Rotmans, J.I.; Hoorn, E.J. Dietary potassium and the kidney: Lifesaving physiology. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 952–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, R.L.; Carollo, C.; Caimi, G. Wine consumption and renal diseases: New perspectives. Nutrition 2007, 23, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M. Alcohol’s impact on kidney function. Alcohol. Health Res. World 1997, 21, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Choleva, M.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Wine and its metabolic effects. A comprehensive review of clinical trials. Metabolism 2018, 83, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, S.; Alexander, B.; Baranchuk, A. Wine and Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review. Circulation 2017, 136, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelle, D.M.; Klaassen, G.; van Adrichem, E.; Bakker, S.J.; Corpeleijn, E.; Navis, G. Physical inactivity: A risk factor and target for intervention in renal care. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2020 Alcohol Collaborators. Population-level risks of alcohol consumption by amount, geography, age, sex, and year: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2020. Lancet 2022, 400, 185–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| With Baseline Data | With Baseline Data and Follow-Up Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Examinees, n Men, %, n Age, years age 18–44 age 45–64 * age ≥ 65 | 4669 45.1% (2108) 50.0 ± 17.9 38.7% (1805) 36.7% (1714) 24.6% (1150) | 3039 43.9% (1334) 45.4 ± 14.7 45.8% (1391) 43.7% (1327) 10.6% (321) |
| Modifiable factors | ||
| Habitual physical activity in leisure time, min/d Habitual alcohol intake, g/d Urea to creatinine ratio in overnight urine, g/g estimated protein intake, g/d Sodium to creatinine ratio in overnight urine, mmol/g estimated sodium intake, mmol/d Potassium to creatinine ratio in overnight urine, mmol/g estimated potassium intake, mmol/d | 6 (0/15) 12 (0/24) 16 (12/20) 57 (44/72) 106 (69/153) 127 (84/184) 26 (19/35) 31 (23/42) | 6 (0/17) 12 (0/24) 16 (12/20) 57 (45/72) 101 (66/143) 124 (83/174) 24 (18/33) 30 (22/40) |
| Kidney function | ||
| Serum creatinine, µmol/L eGFR, mL/min × 1.73 m2 eGFR < 60 mL/min × 1.73 m2, % (n) | 79 (72/87) 87 ± 17 5.7% (267) | 78 (71/86) 90 ± 15 1.3% (39) |
| Covariates | ||
| Estimated 24-h urinary creatinine, g/d Obesity, % (n) Smoking, % (n) Hypertension, % (n) Diabetes, % (n) Hyperuricemia, % (n) Cardiovascular disease, % (n) | 1.24 ± 0.32 20.2% (942) 29.4% (1373) 34.3% (1601) 5.3% (248) 7.0% (329) 5.1% (240) | 1.27 ± 0.32 17.8% (541) 31.2% (948) 25.6% (779) 2.7% (82) 5.2% (157) 2.2% (66) |
| Score | N Examinees | Physical Activity, min/d | Alcohol Intake, g/d | Urinary Urea/ Creatinine, g/g | Urinary Sodium/ Creatinine, mmol/g | Urinary Potassium/ Creatinine, mmol/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 | 58 | 50.9 | 47.8 | 10.7 | 62 | 31 |
| 2 | 240 | 35.3 | 44.9 | 11.6 | 73 | 31 |
| 3 | 564 | 29.8 | 37.0 | 13.2 | 86 | 29 |
| 4 | 834 | 21.7 | 29.6 | 14.7 | 101 | 29 |
| 5 | 999 | 16.9 | 23.5 | 17.1 | 113 | 29 |
| 6 | 903 | 10.8 | 15.1 | 19.2 | 139 | 30 |
| 7 | 641 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 21.1 | 152 | 29 |
| 8 | 306 | 5.1 | 2.5 | 22.8 | 173 | 29 |
| 9–10 | 124 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 24.2 | 177 | 22 |
| p-Value for trend along cumulative score * | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.019 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cirillo, M.; Bilancio, G.; Secondulfo, C.; Terradura-Vagnarelli, O.; Pisani, A.; Riccio, E.; Laurenzi, M. Diet and Other Modifiable Factors in Long-Term Decline of Kidney Function: Observational and Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204337
Cirillo M, Bilancio G, Secondulfo C, Terradura-Vagnarelli O, Pisani A, Riccio E, Laurenzi M. Diet and Other Modifiable Factors in Long-Term Decline of Kidney Function: Observational and Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204337
Chicago/Turabian StyleCirillo, Massimo, Giancarlo Bilancio, Carmine Secondulfo, Oscar Terradura-Vagnarelli, Antonio Pisani, Eleonora Riccio, and Martino Laurenzi. 2023. "Diet and Other Modifiable Factors in Long-Term Decline of Kidney Function: Observational and Population-Based Cohort Study" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204337
APA StyleCirillo, M., Bilancio, G., Secondulfo, C., Terradura-Vagnarelli, O., Pisani, A., Riccio, E., & Laurenzi, M. (2023). Diet and Other Modifiable Factors in Long-Term Decline of Kidney Function: Observational and Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients, 15(20), 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204337







