Phase Angle and Postoperative Complications in a Model of Immunonutrition in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Immunonutrition
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition Analysis
2.4. Inflammation
2.5. Assessment of Postoperative Complications
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Inflammation
3.3. Phase Angle
3.4. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tokajuk, A.; Car, H.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z. Problem niedożywienia u chorych na nowotwory. Med. Paliatywna Prakt. 2015, 9, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.; et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, M.D.; Carrott, P.W.; Patel, J.; Kiraly, L.; Martindale, R.G. Parenteral or Enteral Arginine Supplementation Safety and Efficacy. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2594S–2600S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evoy, D.; Lieberman, M.D.; Fahey, T.J.; Daly, J.M. Immunonutrition: The role of arginine. Nutrition 1998, 14, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drover, J.W.; Dhaliwal, R.; Weitzel, L.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Ochoa, J.B.; Heyland, D.K. Perioperative use of arginine-supplemented diets: A systematic review of the evidence. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2011, 212, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Tiong, C. Immunonutrition in patients with pancreatic cancer undergoing surgical intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.G.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4745–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical Nutrition in cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha, L.B. Physiology of exercise and phase angle: Another look at BIA. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Kusakabe, T.; Arai, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakao, K.; Ikeue, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Tagami, T.; Yasoda, A.; Ishii, K.; et al. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis is a useful indicator of muscle quality. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.C. Electrical bioimpedance: From the past to the future. J. Electr. Bioimpedance 2021, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Bansal, S.; Morgado, M.; Dev, R.; Chisholm, G.; Bruera, E. Phase angle for prognostication of survival in patients with advanced cancer: Preliminary findings. Cancer 2014, 120, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerty, C.C.; Mabvuure, N.T.; Kozar, R.A.; Herndon, D.N. The Surgically Induced Stress Response. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37 (Suppl. 5), 21S–29S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klek, S.; Szybinski, P.; Szczepanek, K. Perioperative immunonutrition in surgical cancer patients: A summary of a decade of research. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendifar, A.E.; Chang, J.I.; Huang, B.Z.; Tuli, R.; Wu, B.U. Cachexia, and not obesity, prior to pancreatic cancer diagnosis worsens survival and is negated by chemotherapy. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumas, J.; Tumiene, B.; Jurkeviciene, J.; Jasiunas, E.; Sileikis, A. Nutritional and immune impairments and their effects on outcomes in early pancreatic cancer patients undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżek, P.; Kurnol, K.; Hap, W.; Frejlich, E.; Diakun, A.; Karwowski, A.; Kotulski, K.; Rudno-Rudzińska, J. Assessment of body composition measure of bioelectrical impedance in patients operated for pancreatic, gastric and colorectal cancer. Pol. J. Surg. 2020, 92, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, S.; Santos, M.P.C.; Cunha, C.; Agostinho, L.; Cruz, R.; Costa, F.; Garcia, M.; Oliveira, P.; Maio, R.; Baracos, V.E.; et al. Body Composition Influences Post-Operative Complications and 90-Day and Overall Survival in Pancreatic Surgery Patients. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 28, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, J.; Heiligensetzer, M.; Krakowski-Roosen, H.; Büchler, M.W.; Friess, H.; Martignoni, M.E. Cachexia worsens prognosis in patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendifar, A.E.; Petzel, M.Q.; Zimmers, T.A.; Denlinger, C.S.; Matrisian, L.M.; Picozzi, V.J.; Rahib, L. Pancreas Cancer-Associated Weight Loss. Oncologist 2019, 24, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, K.; Coolsen, M.M.; Slim, K.; Carli, F.; de Aguilar-Nascimento, J.E.; Schäfer, M.; Parks, R.W.; Fearon, K.C.; Lobo, D.N.; Demartines, N.; et al. Guidelines for perioperative care for pancreaticoduodenectomy: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society recommendations. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka-Massalska, T.; Popiołek, J.; Teter, M.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Dec, M.; Makarewicz, A.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H. Wykorzystanie kąta fazowego do oceny stanu odżywienia pacjentów z jadłowstrętem psychicznym. Psychiatr. Pol. 2017, 51, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui-Yamada, S.; Oiwa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Aotani, N.; Matsubara, A.; Matsuura, S.; Tanimura, M.; Tani-Suzuki, Y.; Kashihara, H.; Nishi, M.; et al. Impact of phase angle on postoperative prognosis in patients with gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary–pancreatic cancer. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anja, B.W.; Danielzik, S.; Dörhöfer, R.P.; Later, W.; Wiese, S.; Müller, M.J. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis: Population reference values by age, sex, and body mass index. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2006, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.R.; Orsso, C.E.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Sicchieri, J.M.F.; Mialich, M.S.; Jordao, A.A.; Prado, C.M. Phase angle and cellular health: Inflammation and oxidative damage. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhao, H.; Dai, M.; Chen, W. The Relationship between Phase Angle, Nutrition Status, and Complications in Patients with Pancreatic Head Cancer. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjomsland, V.; Spångeus, A.; Välilä, J.; Sandström, P.; Borch, K.; Druid, H.; Falkmer, S.; Falkmer, U.; Messmer, D.; Larsson, M. Interleukin 1α sustains the expression of inflammatory factors in human pancreatic cancer microenvironment by targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadhu, K.; Xi, C. Inflammation and pancreatic cancer: An updated review. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; Basso, D. Inflammation and Pancreatic Cancer: Focus on Metabolism, Cytokines, and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 20, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, J.; Levring, T.; Hillingsø, J.; Hansen, C.P.; Andersen, J.R. The effect of preoperative oral immunonutrition on complications and length of hospital stay after elective surgery for pancreatic cancer-A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, T.; Furukawa, K.; Suzuki, D.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshidome, H.; Ohtsuka, M.; Kato, A.; Yoshitomi, H.; Miyazaki, M. Preoperative immunonutrition decreases postoperative complications by modulating prostaglandin E2 production and T-cell differentiation in patients undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy. Surgery 2014, 155, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, S.; Franchello, A.; Deiro, G.; Galletti, R.; Cassine, D.; Campra, D.; Bonfanti, D.; De Carli, L.; Fop, F.; Fronda, G. Preoperative oral immunonutrition versus standard preoperative oral diet in well nourished patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 31, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Suzuki, D.; Yoshitomi, H.; Takayashiki, T.; Kuboki, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Ohtsuka, M. Additional effect of perioperative, compared with preoperative, immunonutrition after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A randomized, controlled trial. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, D.; Furukawa, K.; Kimura, F.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshidome, H.; Ohtsuka, M.; Kato, A.; Yoshitomi, H.; Miyazaki, M. Effects of perioperative immunonutrition on cell-mediated immunity, T helper type 1 (Th1)/Th2 differentiation, and Th17 response after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surgery 2010, 148, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianotti, L.; Braga, M.; Gentilini, O.; Balzano, G.; Zerbi, A.; Di Carlo, V. Artificial nutrition after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Pancreas 2000, 21, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y. The Effect of immunonutrition in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, D.; Durlik, M. Jakość życia pacjentów leczonych chirurgicznie z powodu chorób trzustki—Praca pogladowa. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2010, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Hubner, R.A.; Siveke, J.T.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Belanger, B.; de Jong, F.A.; Mirakhur, B.; Chen, L.-T. NAPOLI-1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long-term survivors. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 108, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonini, V.; Zanni, M. Pancreatic cancer in 2021: What you need to know to win. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5851–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckett, Y.; Garfield, K. Cancer, Pancreas; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
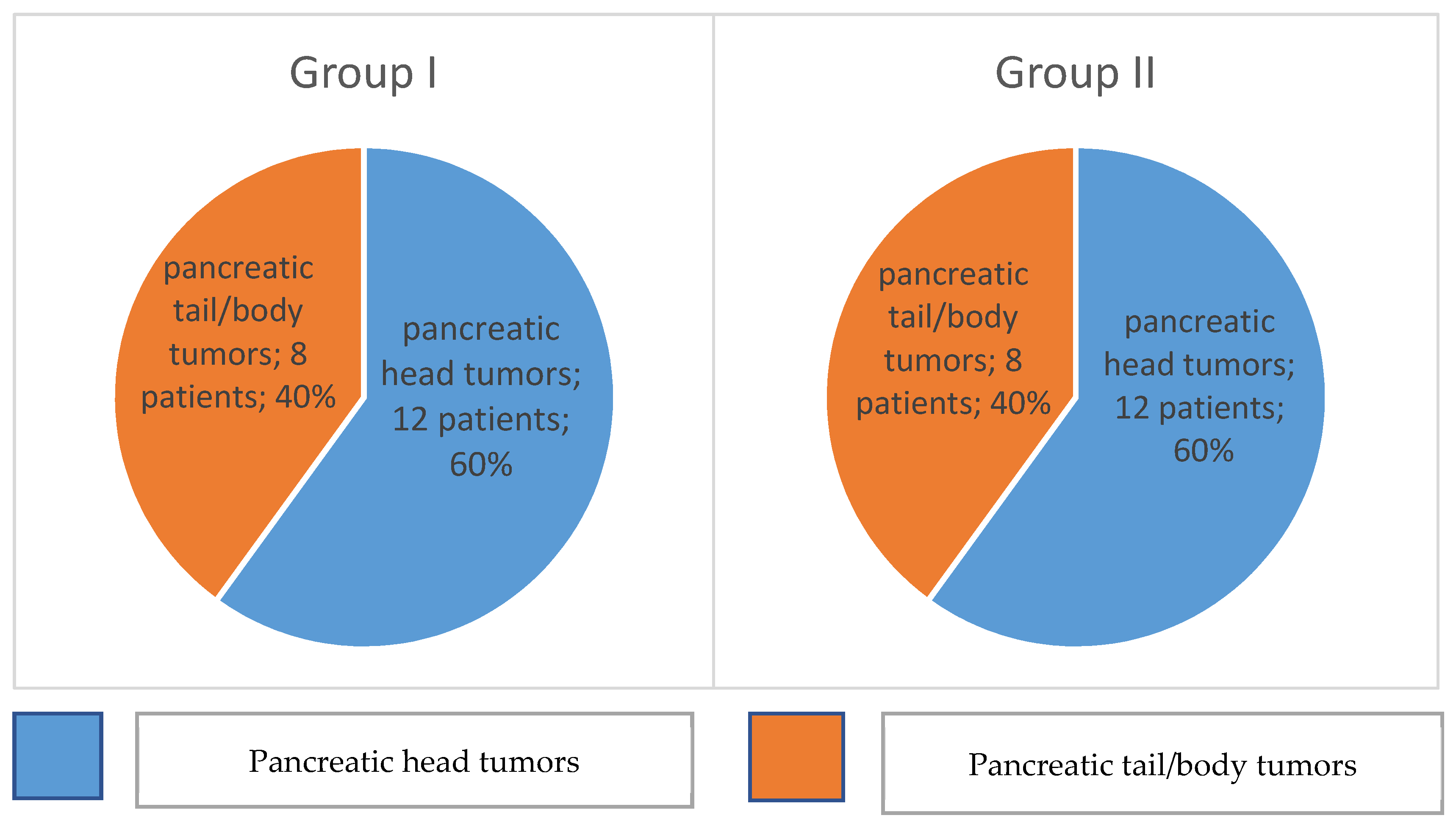

| Group I | Group II | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Q1–Q3 | Median | Q1–Q3 | |||||
| Sex | women 8; men 12 | women 11; men 9 | ||||||
| Age (years) | 68.0 | 63.5–71.5 | 64.5 | 61.0–66.5 | ||||
| Body weight (cm) | 78.2 | 61.1–87.7 | 69.8 | 59.0–73.9 | ||||
| Height (cm) | 171.5 | 164.5–177.0 | 169.0 | 161.5–175.0 | ||||
| Unintentional weight loss | kg | % | kg | % | kg | % | kg | % |
| 10.0 | 12.6 | 5.5–13.0 | 7.9–17 | 5.0 | 7.8 | 0.0–8.5 | 0.0–13.1 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 | 23.0–27.9 | 23.1 | 21.9–28.1 | ||||
| PA on admission to the hospital (°) | 5.0 | 4.70–5.85 | 5.1 | 5.00–6.25 | ||||
| On Admission to the Hospital | After 5 Days of Preoperative IN | Eighth Day | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | IL-1α (pg/mL) | CRP (mg/L) | IL-1α (pg/mL) | CRP (mg/L) | IL-1α (pg/mL) | ||
| Group I | Median | 5.4 | 11.1 | 8.3 p = 0.432 | 11.1 p = 0.600 | 68.4 p = 0.123 | 14.8 p = 0.179 |
| Q1–Q3 | 2.1–11.5 | 7.37–18.5 | 3.85–51.1 | 6.44–18.5 | 38.5–174.8 | 7.37–14.8 | |
| Group II | Median | 5.0 | 14.8 | - | - | 86.6 p < 0.02 | 18.5 p < 0.03 |
| Q1–Q3 | 3.2–11.2 | 11.1–18.5 | - | - | 37.75–142.9 | 11.1–25.8 | |
| On Admission to the Hospital | After 5 Days of Preoperative IN | Third Day | Eighth Day | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | 5.0° (4.70–5.85) | 5.35° (4.65–5.58) p < 0.02 | 4.65° (4.10–5.25) p < 0.001 | 4.85° (4.30–5.45) p = 0.16 |
| Group II | 5.1° (5.00–6.25) | - | 4.5° (3.75–5.36) p < 0.002 | 4.55° (4.0–5.1) p < 0.008 |
| No Complications | I | II | IIIa | IIIb | IVa | IVb | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | 9 | - | 7 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Group II | 7 | - | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| After 5 Days of Preoperative IN p-Value Spearman Correlations | Third Day p-Value Spearman Correlations | Eighth Day p-Value Spearman Correlations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | 5.35 (4.65–5.58) p < 0.02 −0.501106 | 4.65 (4.10–5.25) p < 0.02 −0.506894 | 4.85 (4.30–5.45) p = 0.364590 −0.214157 |
| Group II | 5.1 (5.00–6.25) p = 0.917630 −0.104881 | 4.5 (3.75–5.36) p = 0.687878 −0.095792 | 4.55 (4.0–5.1) p = 0.644497 −0.109942 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boćkowska, M.; Kostro, P.; Kamocki, Z.K. Phase Angle and Postoperative Complications in a Model of Immunonutrition in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204328
Boćkowska M, Kostro P, Kamocki ZK. Phase Angle and Postoperative Complications in a Model of Immunonutrition in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204328
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoćkowska, Magdalena, Przemysław Kostro, and Zbigniew Krzysztof Kamocki. 2023. "Phase Angle and Postoperative Complications in a Model of Immunonutrition in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204328
APA StyleBoćkowska, M., Kostro, P., & Kamocki, Z. K. (2023). Phase Angle and Postoperative Complications in a Model of Immunonutrition in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Nutrients, 15(20), 4328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204328






