Effect of 8-Week Consumption of a Dietary Pattern Based on Fruit, Avocado, Whole Grains, and Trout on Postprandial Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in Obese People
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
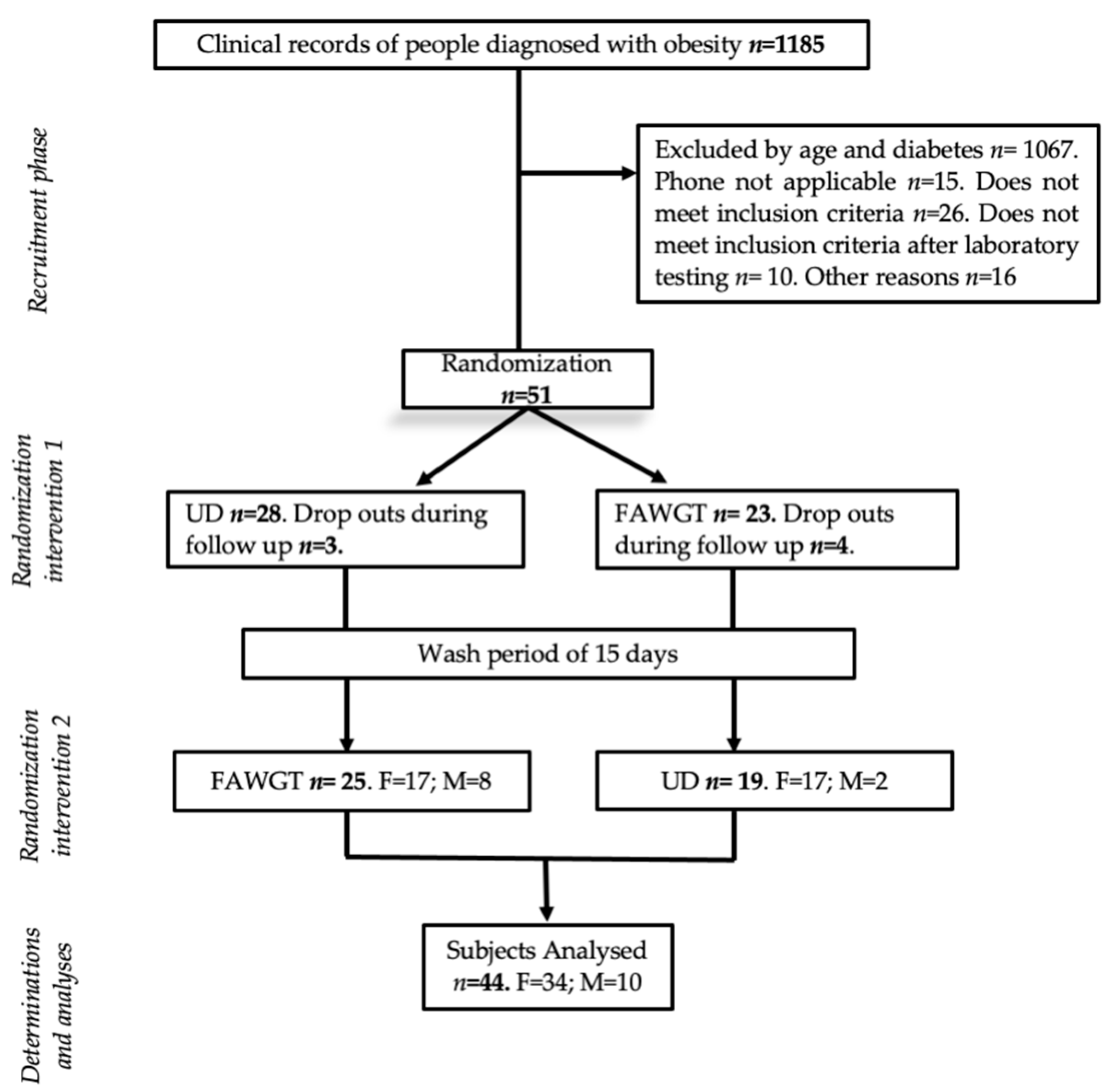
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Diet, Dietary Assessment, and Follow-Up Visits
2.3. Postprandial Study
2.4. Biochemical Measurements of Metabolic Parameters
2.5. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) Isolation
2.6. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Generation
2.7. qRT-PCR Analysis of Gene Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Dietary Intervention on Clinical Variables of the Subjects Included in The Study
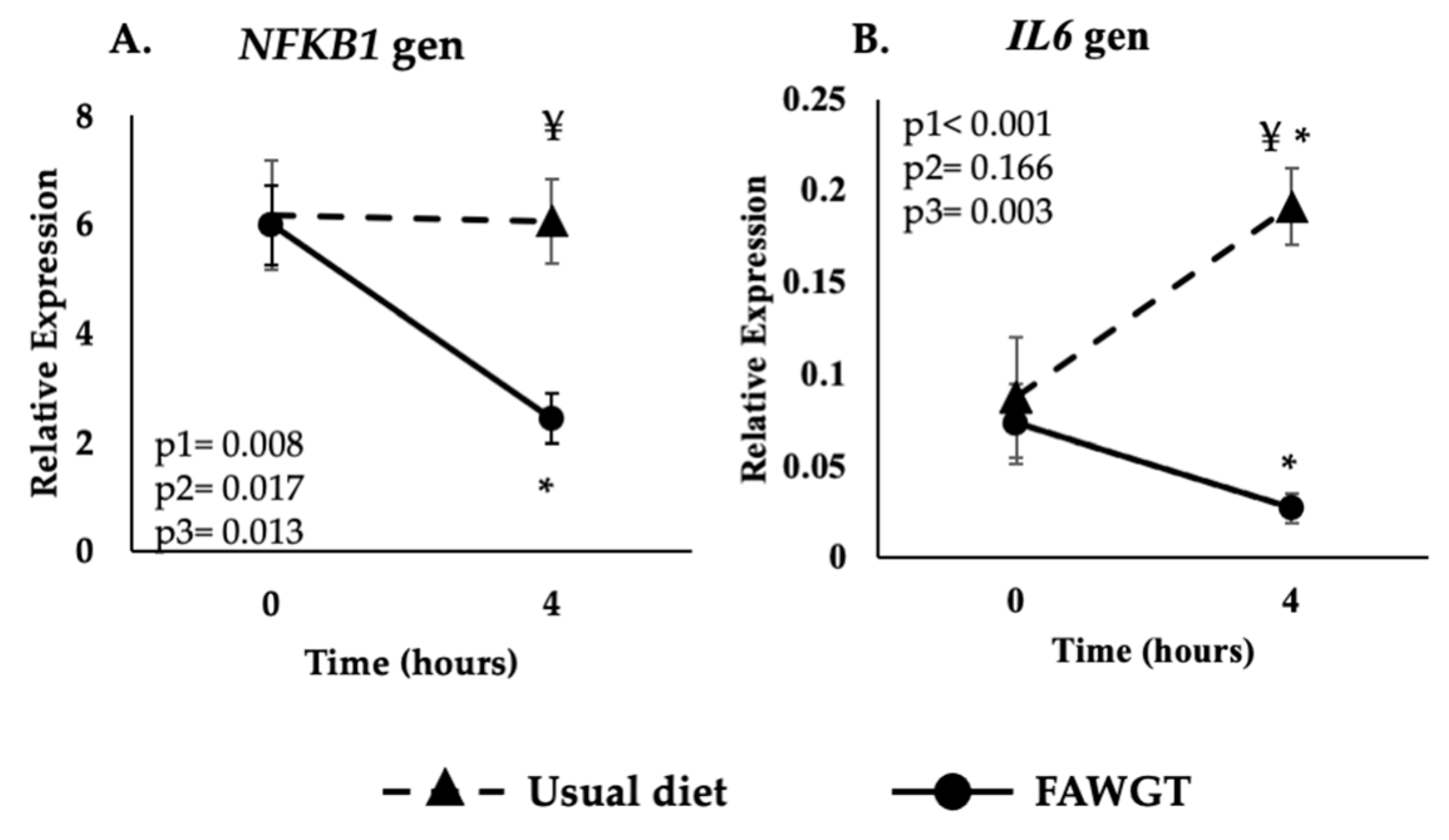
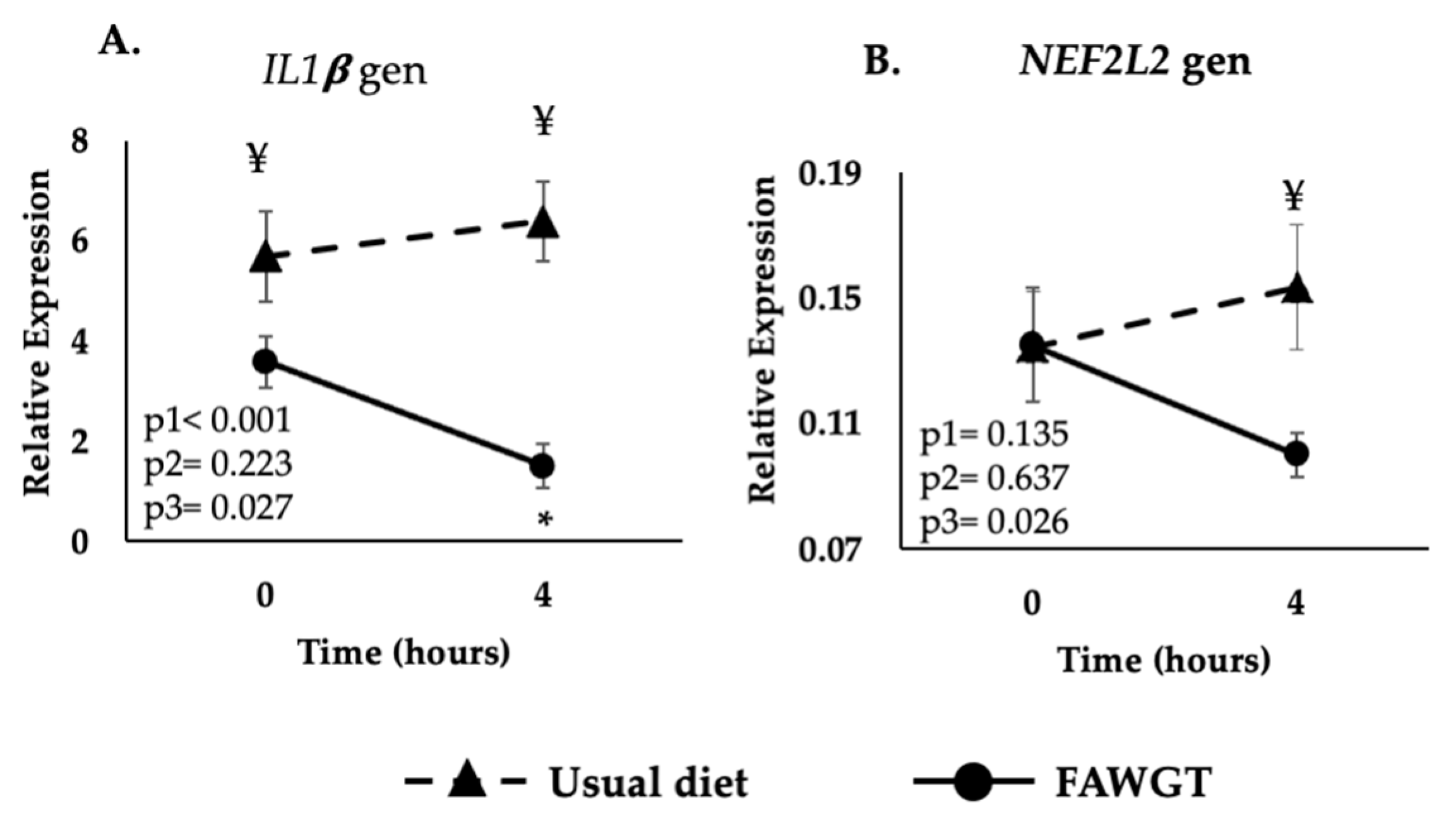
3.2. Effect of the Dietary Intervention on the Postprandial Expression of the Inflammatory-Related Genes
3.3. Effect of the Dietary Intervention on the Postprandial Expression of the Oxidative Stress Gen
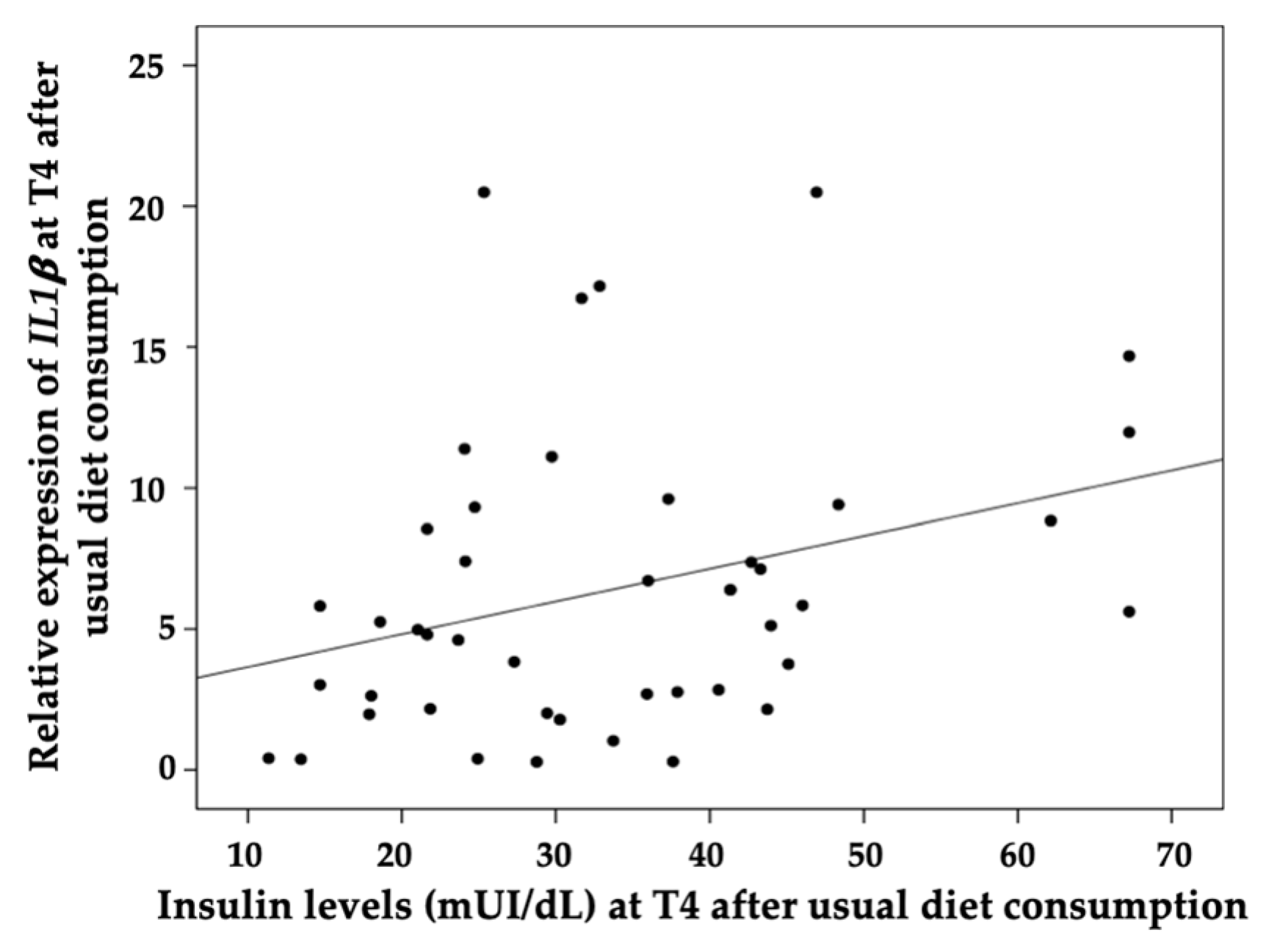
3.4. Correlation Analysis between the Gene Expression of the Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress-Related Genes and Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2021: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Lecube, A.; Lopez-Cano, C. Obesity, a Diet-Induced Inflammatory Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros Perez, M.; Medina-Gomez, G. [Obesity, adipogenesis and insulin resistance]. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2011, 58, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, T.A.F.; Quintanilha, B.J.; Norde, M.M.; Pinhel, M.A.S.; Nonino, C.B.; Rogero, M.M. Nutritional genomics, inflammation and obesity. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 64, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Cruz-Teno, C.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Lora-Aguilar, P.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Fuentes-Jimenez, F.; et al. Expression of proinflammatory, proatherogenic genes is reduced by the Mediterranean diet in elderly people. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfort-Pires, M.; Crisma, A.R.; Bordin, S.; Ferreira, S.R.G. Greater expression of postprandial inflammatory genes in humans after intervention with saturated when compared to unsaturated fatty acids. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, H.; Calder, P.C. Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for The Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastorini, C.M.; Milionis, H.J.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Panagiotakos, D.B. The effect of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome and its components: A meta-analysis of 50 studies and 534,906 individuals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leder, L.; Kolehmainen, M.; Narverud, I.; Dahlman, I.; Myhrstad, M.C.; de Mello, V.D.; Paananen, J.; Carlberg, C.; Schwab, U.; Herzig, K.H.; et al. Effects of a healthy Nordic diet on gene expression changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to an oral glucose tolerance test in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A SYSDIET sub-study. Genes Nutr. 2016, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Mediterranean dietary pattern, inflammation and endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, B.; Proctor, S.D.; Mamo, J.C.; Botham, K.M.; Castro Cabezas, M. Understanding postprandial inflammation and its relationship to lifestyle behaviour and metabolic diseases. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 947417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Miranda, J.; Williams, C.; Lairon, D. Dietary, physiological, genetic and pathological influences on postprandial lipid metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Perez, D.M.; Gonzalez-Correa, C.H.; Astudillo-Munoz, E.Y.; Porras-Hurtado, G.L.; Sanchez-Giraldo, M.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Camargo, A.; Rangel-Zuniga, O.A. Alternative Foods in Cardio-Healthy Dietary Models That Improve Postprandial Lipemia and Insulinemia in Obese People. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Marin, C.; Peerez-Martinez, P.; Hartwich, J.; Malczewska-Malec, M.; Golabek, I.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Cruz-Teno, C.; Rodriguez, F.; Gomez, P.; et al. A low-fat, high-complex carbohydrate diet supplemented with long-chain (n-3) fatty acids alters the postprandial lipoprotein profile in patients with metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astudillo-Muñoz, E.Y.; González-Correa, C.H.; Muñoz-Perez, D.M.; Martinez-Lopez, E.; Aguirre-Acevedo, D.C.; Lopez-Alvarez, M.E. Diet Based on Food from the Colombian Andean Region Decreases C-reactive Protein, IL6, and Leptin in Women with Obesity. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 7, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social. República de Colombia. Resolución Número 3803 de 2016—Recomendaciones de Ingesta de Energia y Nutrientes (RIEN) para la Población Colombiana; Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Colombiano de Bienestar Familiar. Guías Alimentarias Basadas en Alimentos para la población Colombiana, Primera Edición ed; Instituto Colombiano de Bienestar Familiar: Bogotá, Colombia, 2018; pp. 24–301. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Teno, C.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Marin, C.; Gomez, P.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Camargo, A.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; et al. Dietary fat modifies the postprandial inflammatory state in subjects with metabolic syndrome: The LIPGENE study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper--Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.B.; Nasrullah, A.; Haq, S.; Akhtar, A.; Ghazanfar, H.; Nasir, A.; Afzal, R.M.; Bukhari, M.M.; Chaudhary, A.Y.; Naqvi, S.W. The Interplay of Genetics and Environmental Factors in the Development of Obesity. Cureus 2017, 9, e1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampofo, A.G.; Boateng, E.B. Beyond 2020: Modelling obesity and diabetes prevalence. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 167, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumatey, A.P.; Lashley, K.S.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, G.; Amoah, A.; Agyenim-Boateng, K.; Oli, J.; Fasanmade, O.; Adebamowo, C.A.; et al. Relationships among obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance in African Americans and West Africans. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010, 18, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, K.G.; Poppitt, S.D.; Minihane, A.M. Postprandial lipemia and cardiovascular disease risk: Interrelationships between dietary, physiological and genetic determinants. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Milagro, F.I.; Allayee, H.; Chmurzynska, A.; Sook Choi, M.; Curi, R.; De Caterina, R.; Ferguson, L.R.; Goni, L.; Kang, J.X.; et al. Guide for Current Nutrigenetic, Nutrigenomic, and Nutriepigenetic Approaches for Precision Nutrition Involving the Prevention and Management of Chronic Diseases Associated with Obesity. J. Nutr. Nutr. 2017, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Coltell, O.; Macian, F.; Ordovas, J.M. Advances in Understanding the Molecular Basis of the Mediterranean Diet Effect. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Gonzalez-Guardia, L.; Rangel-Zuniga, O.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Delgado-Casado, N.; Cruz-Teno, C.; Tinahones, F.J.; Villalba, J.M.; et al. Mediterranean diet supplemented with coenzyme Q10 modifies the expression of proinflammatory and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in elderly men and women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolehmainen, M.; Ulven, S.M.; Paananen, J.; de Mello, V.; Schwab, U.; Carlberg, C.; Myhrstad, M.; Pihlajamaki, J.; Dungner, E.; Sjolin, E.; et al. Healthy Nordic diet downregulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation in subcutaneous adipose tissue in individuals with features of the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Yang, L.; Shu, G.; Lu, H.; Sun, G. Effects of the n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratio on postprandial metabolism in hypertriacylglycerolemia patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, D.; Simao, A.N.; Urbano, M.R.; Dichi, I. Effects of extra virgin olive oil and fish oil on lipid profile and oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome. Nutrition 2015, 31, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibaeenezhad, M.J.; Ghavipisheh, M.; Attar, A.; Aslani, A. Comparison of the effect of omega-3 supplements and fresh fish on lipid profile: A randomized, open-labeled trial. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson-Vazquez, H.; Cabrera, S.; Lozano, R.; Gonzalez-Inciarte, L. Effect of avocado (Persea Americana Mill) consumption on lipid profile in adults with dyslipidemia. An. Venez. Nutr. 2009, 22, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoori, A.; Sotoudeh, G.; Djalali, M.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Keramatipour, M.; Nasli-Esfahani, E.; Shidfar, F.; Alvandi, E.; Toupchian, O.; Koohdani, F. Effect of DHA-rich fish oil on PPARgamma target genes related to lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, S.; Alivand, M.; KhajeBishak, Y.; AsghariJafarabadi, M.; Alipour, M.; Faghfouri, A.; Alipour, B. The Effect of omega3 Fatty Acids Supplementation on Levels of PPARgamma and UCP2 Genes Expression, Serum Level of UCP2 Protein, Metabolic Status, and Appetite in Elite male Athletes: Protocol for a Randomized Control Trial. Int. J. Surg. Protoc. 2021, 25, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Cowart, L.A.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Huang, Y. Docosahexaenoic acid antagonizes the boosting effect of palmitic acid on LPS inflammatory signaling by inhibiting gene transcription and ceramide synthesis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ownby, S.L.; Fortuno, L.V.; Au, A.Y.; Grzanna, M.W.; Rashmir-Raven, A.M.; Frondoza, C.G. Expression of pro-inflammatory mediators is inhibited by an avocado/soybean unsaponifiables and epigallocatechin gallate combination. J. Inflamm. (Lond) 2014, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Hernandez, J.C.; Taborda-Ocampo, G.; Valdez, J.C.; Bolling, B.W.; Gonzalez-Correa, C.H. Polyphenol Extracts from Three Colombian Passifloras (Passion Fruits) Prevent Inflammation-Induced Barrier Dysfunction of Caco-2 Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, B.F.; Costa, D.C.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A.; Chaves, M.M. beta-Carotene, alpha-tocopherol and ascorbic acid: Differential profile of antioxidant, inflammatory status and regulation of gene expression in human mononuclear cells of diabetic donors. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2013, 29, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Hernández, J.E.; Rey-Buitrago, M. Whole fruits and inflammatory gene expression: In vivo pilot study in humans. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Diet. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, N.M.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Moreira, M.E.C.; Martino, H.S.D.; Benjamin, L.D.A.; de Queiroz, J.H.; Ribeiro, A.Q.; Ribeiro, S.M.R. Anti-obesity effects of tea from Mangifera indica L. leaves of the Uba variety in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Biomed Pharm. 2017, 91, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| FAWGT | UD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Baseline | 8 weeks | Baseline | 8 weeks | p time | p diet | p Diet vs. Time |
| Weight (kg) | 88.5 ± 2.0 | 87.0 ± 2.0 (a) | 88.3 ± 2.1 | 88.4 ± 2.1 (b) | <0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 35.7 ± 0.6 | 35.1 ± 0.7 (a) | 35.5 ± 0.6 | 35.6 ± 0.7 (b) | 0.001 | 0.015 | <0.001 |
| Fat (%) | 42.7 ± 0.5 | 41.9 ± 0.6 | 42.4 ± 0.7 | 42.1 ± 0.6 | 0.006 | 0.748 | 0.285 |
| Waist–hip ratio | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 0.488 | 0.017 | 0.764 |
| Systolic blood (mmHg) | 122.1 ± 1.8 | 119.8 ± 1.6 | 120.15 ± 1.9 | 120.0 ± 1.9 | 0.267 | 0.539 | 0.364 |
| Diastolic blood (mmHg) | 78.6 ± 1.4 | 77.6 ± 1.2 | 80.1 ± 1.2 | 77.6 ± 1.3 | 0.850 | 0.450 | 0.313 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 94.3 ± 1.6 | 94.4 ± 2.0 | 95.9 ± 1.7 | 96.0 ± 2.0 | 0.923 | 0.079 | 0.935 |
| Insulin (mUI/mL) | 22.5 ± 1.9 | 21.6 ± 1.4 | 20.16 ± 1.2 | 24.3 ± 1.8 (a,b) | 0.870 | 0.399 | 0.016 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 201.3 ± 5.5 | 201.3 ± 5.6 | 202.0 ± 5.3 | 200.4 ± 5.4 | 0.764 | 0.962 | 0.765 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 40.1 ± 1.5 | 41.0 ± 1.4 | 43.4 ± 1.6 (b) | 41.6 ± 1.6 (a) | 0.494 | 0.005 | 0.039 |
| Non-c HDL-c (mg/dL) | 161.1 ± 5.8 | 160.3 ± 5.5 | 159.3 ± 5.5 | 159.0 ± 5.6 | 0.840 | 0.525 | 0.936 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 118.4 ± 5.4 | 124.3 ± 5.3 | 118.0 ± 5.3 | 118.8 ± 4.8 | 0.212 | 0.303 | 0.439 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 198.2 ± 13.4 | 182.7 ± 10.1 | 191.2 ± 13 | 200.9 ± 14.3 | 0.726 | 0.444 | 0.100 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.35 ± 0.4 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 0.002 | 0.326 | 0.898 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Pérez, D.M.; González-Correa, C.H.; Astudillo Muñoz, E.Y.; Sánchez-Giraldo, M.; Carmona-Hernández, J.C.; López-Miranda, J.; Camargo, A.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A. Effect of 8-Week Consumption of a Dietary Pattern Based on Fruit, Avocado, Whole Grains, and Trout on Postprandial Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in Obese People. Nutrients 2023, 15, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020306
Muñoz-Pérez DM, González-Correa CH, Astudillo Muñoz EY, Sánchez-Giraldo M, Carmona-Hernández JC, López-Miranda J, Camargo A, Rangel-Zúñiga OA. Effect of 8-Week Consumption of a Dietary Pattern Based on Fruit, Avocado, Whole Grains, and Trout on Postprandial Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in Obese People. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Pérez, Diana María, Clara Helena González-Correa, Elcy Yaned Astudillo Muñoz, Maite Sánchez-Giraldo, Juan Carlos Carmona-Hernández, José López-Miranda, Antonio Camargo, and Oriol Alberto Rangel-Zúñiga. 2023. "Effect of 8-Week Consumption of a Dietary Pattern Based on Fruit, Avocado, Whole Grains, and Trout on Postprandial Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in Obese People" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020306
APA StyleMuñoz-Pérez, D. M., González-Correa, C. H., Astudillo Muñoz, E. Y., Sánchez-Giraldo, M., Carmona-Hernández, J. C., López-Miranda, J., Camargo, A., & Rangel-Zúñiga, O. A. (2023). Effect of 8-Week Consumption of a Dietary Pattern Based on Fruit, Avocado, Whole Grains, and Trout on Postprandial Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in Obese People. Nutrients, 15(2), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020306







