Vitamins and Minerals for Blood Pressure Reduction in the General, Normotensive Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Six Supplements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Collection Process and Data Items
2.5. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Effect Measures and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Syntheses/Statistical Analyses
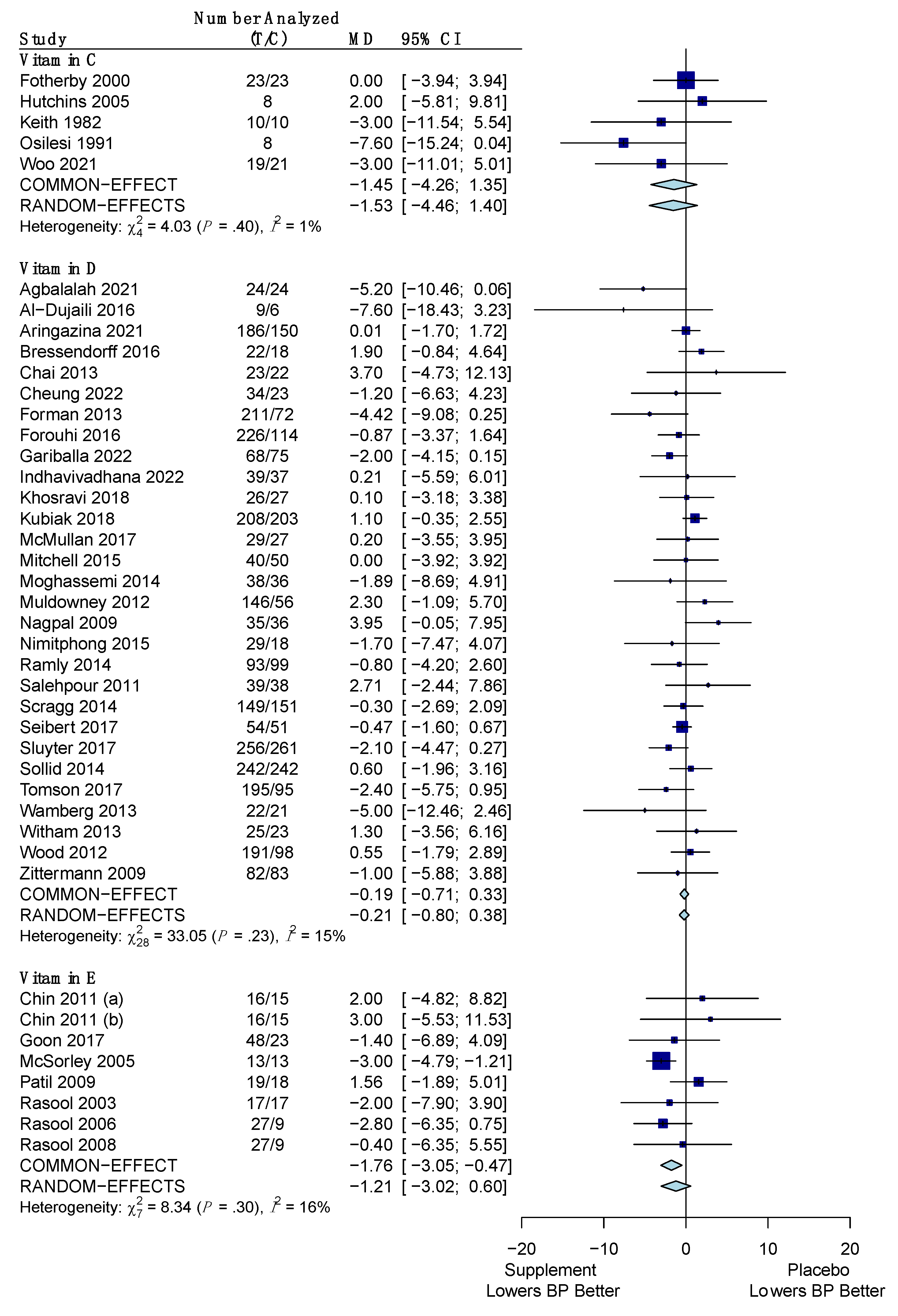
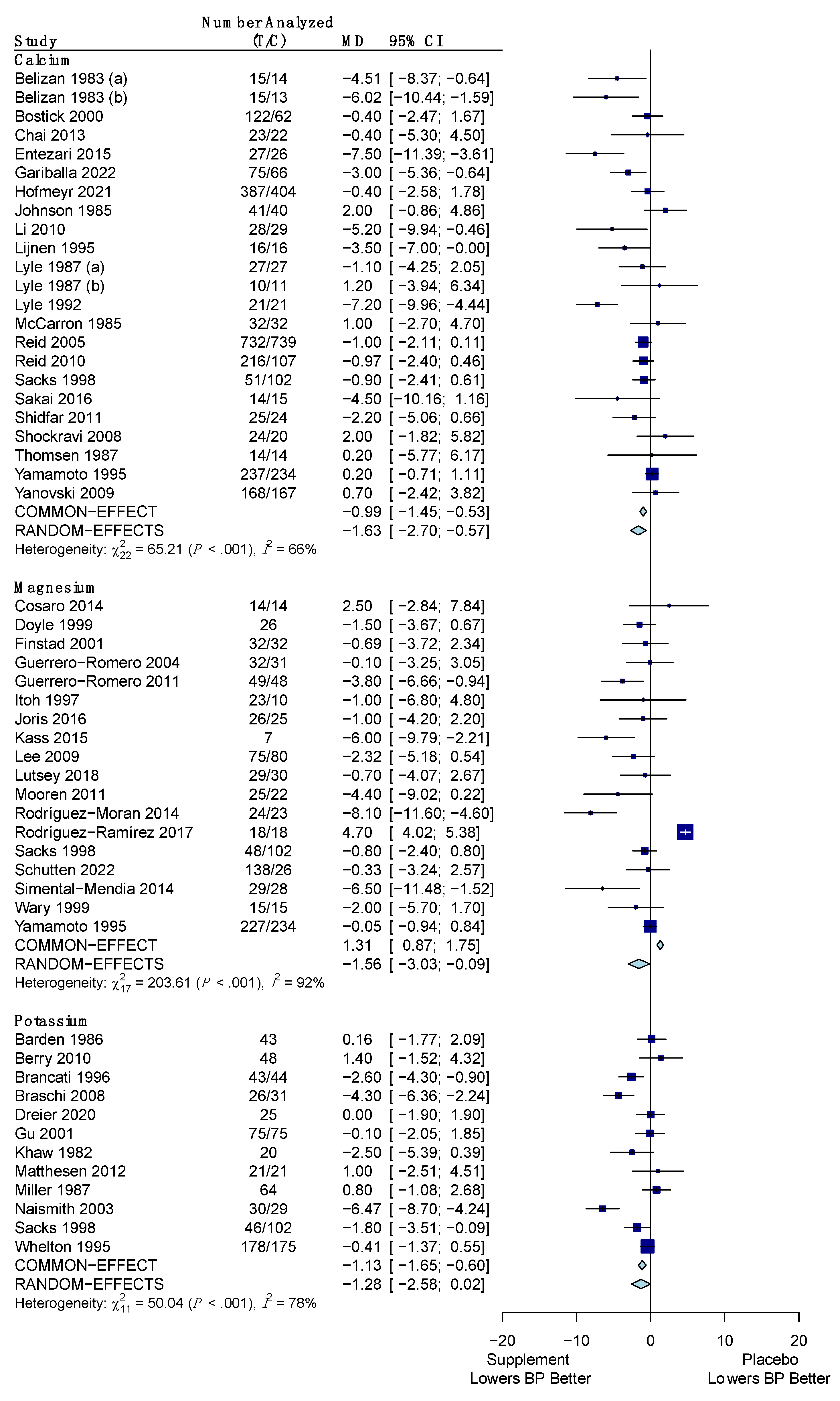
3.4.1. Systolic Blood Pressure
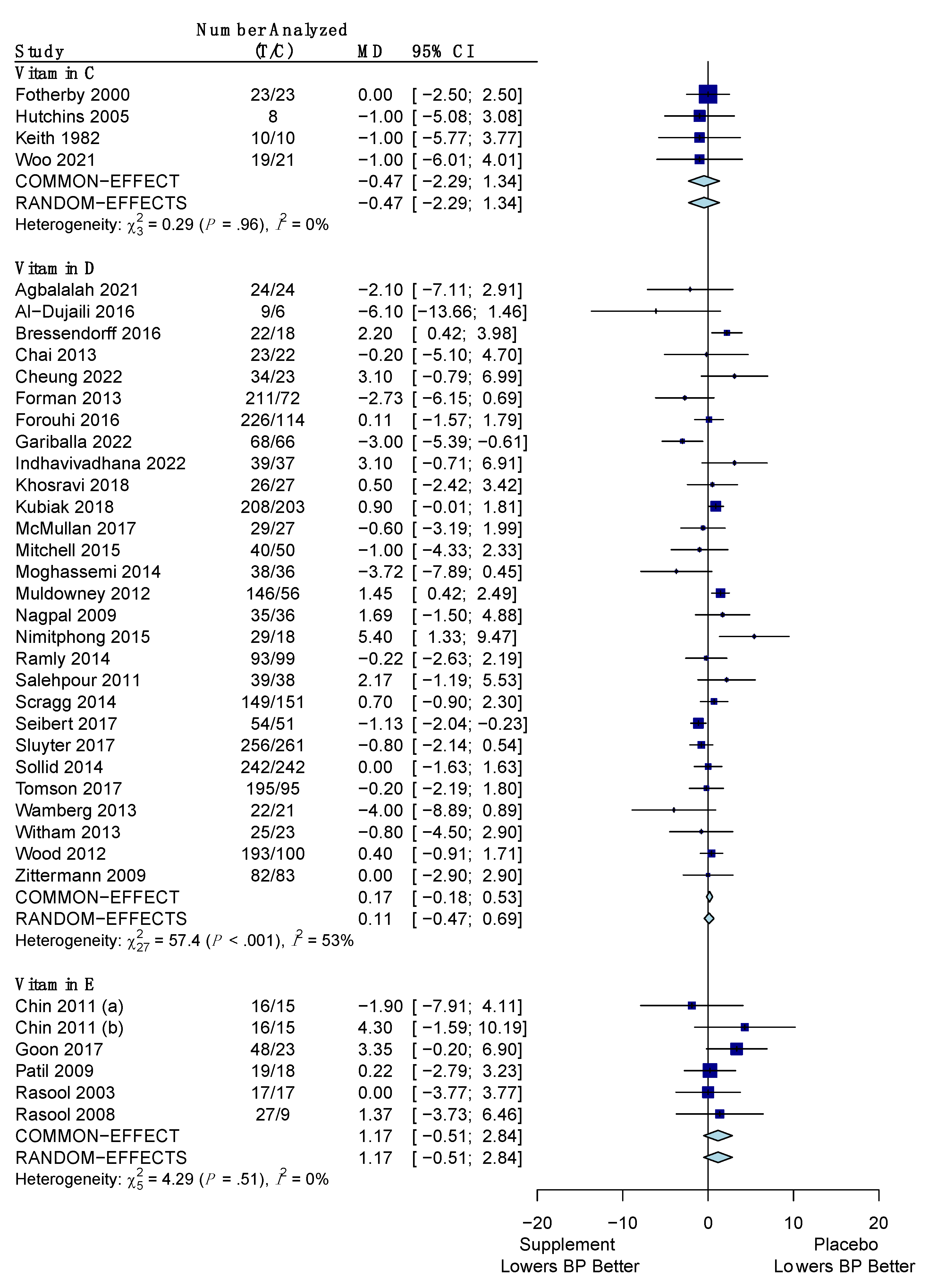
3.4.2. Diastolic Blood Pressure
3.4.3. Summary
3.4.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.4.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanek, K.D.; Murphy, S.L.; Xu, J.; Arias, E. Deaths: Final Data for 2017 pdf Icon [PDF—1.76 MB]. In National Vital Statistics Reports; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2019; Volume 68. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr68/nvsr68_09-508.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J., Jr.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline For The Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, And Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2199–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissner, L. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-Specific Relevance of Usual Blood Pressure to Vascular Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Individual Data For One Million Adults in 61 Prospective Studies. Lancet (Br. Ed.) 2002, 360, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.R.; Morris, J.K.; Wald, N.J. Use of Blood Pressure Lowering Drugs in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Meta-Analysis of 147 Randomised Trials in the Context of Expectations From Prospective Epidemiological Studies. BMJ 2009, 338, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.G. Nutraceuticals with A Clinically Detectable Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect: A Review of Available Randomized Clinical Trials and Their Meta-Analyses. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Golovinskaia, O.; Wang, C.K. Impact of Micronutrients on Hypertension: Evidence from Clinical Trials with A Special Focus on Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Vita, J.A.; Venema, R.C.; Keaney, J.F. Ascorbic Acid Enhances Endothelial Nitric-Oxide Synthase Activity By Increasing Intracellular Tetrahydrobiopterin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17399–17406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K.; Rink, C.; Khanna, S. Palm Oil-Derived Natural Vitamin E A-Tocotrienol In Brain Health And Disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 314S–323S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvanshi, R.; Chandra, M.; Mishra, A.; Misra, M.K. Effect of Vitamin E Administration on Blood Pressure Following Reperfusion of Patients With Myocardial Infarction. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2007, 12, 87–90. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2359599/ (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Forman, J.P.; Williams, J.S.; Fisher, N.D.L. Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Regulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Humans. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Etchegoyen, C.; Lombarte, M.; Matamoros, N.; Belizán, J.M.; Cormick, G. Mechanisms Involved in the Relationship Between Low Calcium Intake and High Blood Pressure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, A.R.; Umbelino, B.; Correia, M.L.; Neves, M.F. Magnesium and Vascular Changes in Hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 754250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, S.B.; Fenton, R.A. K+ and the Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone System: New Insights into Their Role in Blood Pressure Control and Hypertension Treatment. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4451–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Dai, P.; Wang, H. Effects of Vitamin C Supplementation on Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, S.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X. Effect of Vitamin D on Blood Pressure And Hypertension In The General Population: An Update Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies And Randomized Controlled Trials. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2020, 17, E03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, M.R.; Safabakhsh, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Asbaghi, O.; Khosroshahi, M.Z. Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormick, G.; Ciapponi, A.; Cafferata, M.L.; Cormick, M.S.; Belizán, J.M. Calcium Supplementation for Prevention of Primary Hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD010037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Rosanoff, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials. Hypertension 2016, 68, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Naska, A.; Kasdagli, M.I.; Torres, D.; Lopes, C.; Carvalho, C.; Moreira, P.; Malavolti, M.; Orsini, N.; Whelton, P.K.; et al. Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, E015719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, N71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covidence Systematic Review Software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia [Internet]. 2022. Available online: www.covidence.org (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Sterne, J.A.C. Assessing Risk of Bias in a Randomized Trial. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Li, T.; Deeks, J.J. Choosing Effect Measures and Computing Estimates of Effect. In Cochrane Handbook For Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Eldridge, S.; Li, T. Including Variants on Randomized Trials. In Cochrane Handbook For Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 569–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. The Combination of Estimates From Different Experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, D.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Jackson, D.; Bowden, J.; Veroniki, A.A.; Kontopantelis, E.; Viechtbauer, W.; Simmonds, M. A Comparison of Heterogeneity Variance Estimators in Simulated Random-Effects Meta-Analyses. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Gilbody, S. Bias In Meta-Analysis Detected By A Simple, Graphical Test. Increase in Studies of Publication Bias Coincided with Increasing Use of Meta-Analysis. BMJ 1998, 316, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Light, R.J.; Pillemer, D.B. Summing Up: The Science of Reviewing Research; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Wu, C.; Lin, L. The Effect Direction Should Be Taken into Account When Assessing Small-Study Effects. J. Evid. -Based Dent. Pract. 2023, 23, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, G.; Carpenter, J.R.; Rücker, G. Meta-Analysis With R, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbalalah, T.; Mushtaq, S. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on cardiometabolic disease risk among overweight/obese adult males in United Kingdom-A pilot randomised controlled trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 36, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dujaili, E.A.S.; Munir, N.; Iniesta, R.R. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular disease risk factors and exercise performance in healthy participants: A randomized placebo-controlled preliminary study. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 7, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringazina, R.; Kurmanalina, G.; Kurmanalin, B.; Degtyarevskaya, T. Role of vitamin d in prevention of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2021, 20, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, A.E.; Vandongen, R.; Beilin, L.J.; Margetts, B.; Rogers, P. Potassium supplementation does not lower blood pressure in normotensive women. J. Hypertens. 1986, 4, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizan, J.M.; Villar, J.; Pineda, O.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Sainz, E.; Garrera, G.; Sibrian, R. Reduction of blood pressure with calcium supplementation in young adults. JAMA 1983, 249, 1161–1165. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-00030027/full (accessed on 9 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.E.; Mulla, U.Z.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Sanders, T.A. Increased potassium intake from fruit and vegetables or supplements does not lower blood pressure or improve vascular function in UK men and women with early hypertension: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostick, R.M. Effect of calcium supplementation on serum cholesterol and blood pressure: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Arch. Fam. Med. 2000, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancati, F.L.; Appel, L.J.; Seidler, A.J.; Whelton, P.K. Effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in African Americans on a low-potassium diet. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996, 156, 61–67. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-00121900/full (accessed on 9 September 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braschi, A.; Naismith, D.J. The effect of a dietary supplement of potassium chloride or potassium citrate on blood pressure in predominantly normotensive volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressendorff, I.; Brandi, L.; Schou, M.; Nygaard, B.; Frandsen, N.E.; Rasmussen, K.; Ødum, L.; Østergaard, O.V.; Hansen, D. The Effect of High Dose Cholecalciferol on Arterial Stiffness and Peripheral and Central Blood Pressure in Healthy Humans: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Cooney, R.V.; Franke, A.A.; Bostick, R.M. Effects of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure and serum lipids and carotenoids: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Ann. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.M.; Dall, R.D.; Shewokis, P.A.; Altasan, A.; Volpe, S.L.; Amori, R.; Singh, H.; Sukumar, D. The effect of combined magnesium and vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D status, systemic inflammation, and blood pressure: A randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Nutrition 2022, 99–100, 111674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosaro, E.; Bonafini, S.; Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Trettene, M.S.; Minuz, P.; Delva, P.; Fava, C. Effects of magnesium supplements on blood pressure, endothelial function and metabolic parameters in healthy young men with a family history of metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.; Flynn, A.; Cashman, K. The effect of magnesium supplementation on biochemical markers of bone metabolism or blood pressure in healthy young adult females. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, R.; Abdolalizadeh, B.; Asferg, C.L.; Hölmich, L.R.; Buus, N.H.; Forman, J.L.; Andersen, U.B.; Egfjord, M.; Sheykhzade, M.; Jeppesen, J.L. Effect of increased potassium intake on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and subcutaneous resistance arteries: A randomized crossover study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 36, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstad, E.W.; Newhouse, I.J.; Lukaski, H.C.; McAuliffe, J.E.; Stewart, C.R. The effects of magnesium supplementation on exercise performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, J.P.; Scott, J.B.; Ng, K.; Drake, B.F.; Suarez, E.G.; Hayden, D.L.; Bennett, G.G.; Chandler, P.D.; Hollis, B.W.; Emmons, K.M.; et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure in blacks. Hypertension 2013, 61, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Menon, R.K.; Sharp, S.J.; Mannan, N.; Timms, P.M.; Martineau, A.R.; Rickard, A.P.; Boucher, B.J.; Chowdhury, T.A.; Griffiths, C.J.; et al. Effects of vitamin D2 or D3 supplementation on glycaemic control and cardiometabolic risk among people at risk of type 2 diabetes: Results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotherby, M.D.; Williams, J.C.; Forster, L.A.; Craner, P.; Ferns, G.A. Effect of vitamin C on ambulatory blood pressure and plasma lipids in older persons. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariballa, S.; Yasin, J.; Alessa, A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation with or without calcium in community-dwelling vitamin D deficient subjects. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; He, J.; Wu, X.; Duan, X.; Whelton, P.K. Effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in Chinese: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Tamez-Perez, H.E.; González-González, G.; Salinas-Martínez, A.M.; Montes-Villarreal, J.; Treviño-Ortiz, J.H.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic subjects with insulin resistance. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeyr, G.J.; Seuc, A.; Betrán, A.P.; Cormick, G.; Singata, M.; Fawcus, S.; Mose, S.; Frank, K.; Hall, D.; Belizán, J.; et al. The effect of calcium supplementation on blood pressure in non-pregnant women with previous pre-eclampsia: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Pregnancy Hypertens. Int. J. Women’s Cardiovasc. Health 2021, 23, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, A.M.; McIver, I.E.; Johnston, C.S. Soy isoflavone and ascorbic acid supplementation alone or in combination minimally affect plasma lipid peroxides in healthy postmenopausal women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhavivadhana, S.; Boonyachan, W.; Rattanachaiyanont, M.; Wongwananuruk, T.; Techatraisak, K.; Sa-nga-areekul, N. Effectiveness of vitamin D2 supplementation on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and other metabolic indices in menopausal Thai women: A randomized-controlled trial. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2022, 38, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Kawasaka, T.; Nakamura, M. The effects of high oral magnesium supplementation on blood pressure, serum lipids and related variables in apparently healthy Japanese subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 78, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; Bakker, S.J.; Mensink, R.P. Long-term magnesium supplementation improves arterial stiffness in overweight and obese adults: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, L.S.; Poeira, F. The effect of acute vs chronic magnesium supplementation on exercise and recovery on resistance exercise, blood pressure and total peripheral resistance on normotensive adults. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, R.E.; Driskell, J.A. Lung function and treadmill performance of smoking and nonsmoking males receiving ascorbic acid supplements. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, K.T.; Thom, S. Randomised double-blind cross-over trial of potassium on blood-pressure in normal subjects. Lancet 1982, 2, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, Z.S.; Kafeshani, M.; Tavasoli, P.; Zadeh, A.H.; Entezari, M.H. Effect of Vitamin D supplementation on weight loss, glycemic indices, and lipid profile in obese and overweight women: A clinical trial study. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, J.; Thorsby, P.M.; Kamycheva, E.; Jorde, R. Vitamin D supplementation does not improve CVD risk factors in vitamin D-insufficient subjects. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.K.; Son, S.P.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, H.J. Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on insulin sensitivity and blood pressure in normo-magnesemic nondiabetic overweight Korean adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, K.; Feng, R.N.; Sun, C.H. Effects of multivitamin and mineral supplementation on adiposity, energy expenditure and lipid profiles in obese Chinese women. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijnen, P.; Petrov, V. Dietary calcium, blood pressure and cell membrane cation transport systems in males. J. Hypertens. 1995, 13, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, F.C.; Aronoff, G.R.; Fineberg, N.S.; Weinberger, M.H. Effects of oral calcium, potassium, digoxin, and nifedipine on natriuresis in normal humans. Am. J. Hypertens. 1989, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Eaton, A.; Jaeb, M.; Rudser, K.D.; Neaton, J.D.; Alonso, A. A Pilot Randomized Trial of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Nutrients 2018, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyle, R.M.; Melby, C.L.; Hyner, G.C.; Edmondson, J.W.; Miller, J.Z.; Weinberger, M.H. Blood pressure and metabolic effects of calcium supplementation in normotensive white and black men. JAMA 1987, 257, 1772–1776. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-00046796/full (accessed on 9 September 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyle, R.M. Does baseline serum total calcium level influence the blood pressure response to calcium supplementation? A double-blind study. Neth. J. Med. 1992, 41, 48–55. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-00087707/full (accessed on 9 September 2023). [PubMed]
- Matthesen, S.K.; Larsen, T.; Vase, H.; Lauridsen, T.G.; Pedersen, E.B. Effect of potassium supplementation on renal tubular function, ambulatory blood pressure and pulse wave velocity in healthy humans. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, D.A.; Morris, C.D. Blood pressure response to oral calcium in persons with mild to moderate hypertension. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Annu. Intern. Med. 1985, 103, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, C.J.; Borgi, L.; Curhan, G.C.; Fisher, N.; Forman, J.P. The effect of vitamin D on renin-angiotensin system activation and blood pressure: A randomized control trial. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.M.; Leder, B.Z.; Cagliero, E.; Mendoza, N.; Henao, M.P.; Hayden, D.L.; Finkelstein, J.S.; Burnett-Bowie, S.A. Insulin secretion and sensitivity in healthy adults with low vitamin D are not affected by high-dose ergocalciferol administration: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Völker, K.; Golf, S.W.; Wadepuhl, M.; Kraus, A. Oral magnesium supplementation reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects—A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-D Mostafa, S.; Garner, D.D.; Garrett, L.; Whaley, R.F.; el-Sekate, M.; Kiker, M. Beneficial effects of vitamin C on risk factors of cardiovascular diseases. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 1989, 64, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mottram, P.; Shige, H.; Nestel, P. Vitamin E improves arterial compliance in middle-aged men and women. Atherosclerosis 1999, 145, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldowney, S.; Lucey, A.J.; Hill, T.R.; Seamans, K.M.; Taylor, N.; Wallace, J.M.; Horigan, G.; Barnes, M.S.; Bonham, M.P.; Duffy, E.M.; et al. Incremental cholecalciferol supplementation up to 15 μg/d throughout winter at 51-55° N has no effect on biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in healthy young and older adults. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, J.T.; O’Connor, D.T. Potassium effects on blood pressure: Is the conjugate anion important? J. Hum. Hypertens. 1990, 4, 589–596. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-00075895/full (accessed on 9 September 2023). [PubMed]
- Nagpal, J.; Pande, J.N.; Bhartia, A. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the short-term effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy, middle-aged, centrally obese men. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naismith, D.J.; Braschi, A. The effect of low-dose potassium supplementation on blood pressure in apparently healthy volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimitphong, H.; Samittarucksa, R.; Saetung, S.; Bhirommuang, N.; Chailurkit, L.O.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Metabolic Phenotypes in Thais with Prediabetes. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2015, 98, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Nowson, C.; Morgan, T. Effect of calcium carbonate on blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive people. Hypertension 1989, 13, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osilesi, O.; Trout, D.L.; Ogunwole, J.O.; Glover, E.E. Blood pressure and plasma lipids during ascorbic acid supplementation in borderline hypertensive and normotensive adults. Nutr. Res. 1991, 11, 405–412. Available online: https://www.embase.com/search/results?subaction=viewrecord&id=L21185540&from=export (accessed on 9 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Chaudhuri, D.; Dhanakshirur, G.B. Role of alpha-tocopherol in cardiopulmonary fitness in endurance athletes, cyclists. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Ramly, M.; Ming, M.F.; Chinna, K.; Suboh, S.; Pendek, R. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on cardiometabolic risks and health-related quality of life among urban premenopausal women in a tropical country--a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, A.H.; Rehman, A.; Wan Yusuf, W.N.; Rahman, A.R. Vitamin E and its effect on arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women--a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 41, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.H.; Yuen, K.H.; Yusoff, K.; Wong, A.R.; Rahman, A.R. Dose dependent elevation of plasma tocotrienol levels and its effect on arterial compliance, plasma total antioxidant status, and lipid profile in healthy humans supplemented with tocotrienol rich vitamin E. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2006, 52, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.H.; Rahman, A.R.; Yuen, K.H.; Wong, A.R. Arterial compliance and vitamin E blood levels with a self emulsifying preparation of tocotrienol rich vitamin E. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, I.R.; Horne, A.; Mason, B.; Ames, R.; Bava, U.; Gamble, G.D. Effects of calcium supplementation on body weight and blood pressure in normal older women: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3824–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, I.R.; Ames, R.; Mason, B.; Bolland, M.J.; Bacon, C.J.; Reid, H.E.; Kyle, C.; Gamble, G.D.; Grey, A.; Horne, A. Effects of calcium supplementation on lipids, blood pressure, and body composition in healthy older men: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Moran, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves the metabolic profile of metabolically obese, normal-weight individuals: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ramírez, M.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Reyes-Romero, M.A.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on the transcription of TRPM6, TRPM7, and SLC41A1 in individuals newly diagnosed of pre-hypertension. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Magnes. Res. 2017, 30, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Willett, W.C.; Smith, A.; Brown, L.E.; Rosner, B.; Moore, T.J. Effect on blood pressure of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in women with low habitual intake. Hypertension 1998, 31, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Hien, V.T.T.; Tuyen, L.D.; Duc, H.A.; Masuda, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Effects of Eggshell Calcium Supplementation on Bone Mass in Postmenopausal Vietnamese Women. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2017, 63, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehpour, A.; Shidfar, F.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Vafa, M.; Razaghi, M.; Hoshiarrad, A.; Gohari, M. Vitamin D3 and the risk of CVD in overweight and obese women: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutten, J.C.; Joris, P.J.; Groendijk, I.; Eelderink, C.; Groothof, D.; van der Veen, Y.; Westerhuis, R.; Goorman, F.; Danel, R.M.; de Borst, M.H.; et al. Effects of Magnesium Citrate, Magnesium Oxide, and Magnesium Sulfate Supplementation on Arterial Stiffness: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Intervention Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e021783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scragg, R.; Slow, S.; Stewart, A.W.; Jennings, L.C.; Chambers, S.T.; Priest, P.C.; Florkowski, C.M.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Murdoch, D.R. Long-term high-dose vitamin D3 supplementation and blood pressure in healthy adults: A randomized controlled trial. Hypertension 2014, 64, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, E.; Lehmann, U.; Riedel, A.; Ulrich, C.; Hirche, F.; Brandsch, C.; Dierkes, J.; Girndt, M.; Stangl, G.I. Vitamin D3 supplementation does not modify cardiovascular risk profile of adults with inadequate vitamin D status. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shidfar, F.; Moghayedi, M.; Kerman, S.R.J.; Hosseini, S.; Shidfar, S. Effects of a calcium supplement on serum lipoproteins, apolipoprotein B, and blood pressure in overweight men. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 8, 194–200. Available online: https://www.embase.com/search/results?subaction=viewrecord&id=L362482536&from=export (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Shockravi, S.; Jalali, M.T.; Rokn, M.; Karandish, M. Effect of calcium supplementation on blood pressure in overweight or obese women. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 8, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation decreases C-reactive protein levels in subjects with prediabetes and hypomagnesemia: A clinical randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, J.D.; Camargo, C.A.; Stewart, A.W.; Waayer, D.; Lawes, C.M.M.; Toop, L.; Khaw, K.T.; Thom, S.A.M.; Hametner, B.; Wassertheurer, S.; et al. Effect of Monthly, High-Dose, Long-Term Vitamin D Supplementation on Central Blood Pressure Parameters: A Randomized Controlled Trial Substudy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, S.T.; Hutchinson, M.Y.; Fuskevåg, O.M.; Figenschau, Y.; Joakimsen, R.M.; Schirmer, H.; Njølstad, I.; Svartberg, J.; Kamycheva, E.; Jorde, R. No effect of high-dose vitamin D supplementation on glycemic status or cardiovascular risk factors in subjects with prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.; Nilas, L.; Christiansen, C. Dietary calcium intake and blood pressure in normotensive subjects. Acta Medica Scand. 1987, 222, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomson, J.; Hin, H.; Emberson, J.; Kurien, R.; Lay, M.; Cox, J.; Hill, M.; Arnold, L.; Leeson, P.; Armitage, L.; et al. Effects of Vitamin D on Blood Pressure, Arterial Stiffness, and Cardiac Function in Older People After 1 Year: BEST-D (Biochemical Efficacy and Safety Trial of Vitamin D). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamberg, L.; Kampmann, U.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Rejnmark, L.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on body fat accumulation, inflammation, and metabolic risk factors in obese adults with low vitamin D levels—Results from a randomized trial. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wary, C.; Brillault-Salvat, C.; Bloch, G.; Leroy-Willig, A.; Roumenov, D.; Grognet, J.M.; Leclerc, J.H.; Carlier, P.G. Effect of chronic magnesium supplementation on magnesium distribution in healthy volunteers evaluated by 31P-NMRS and ion selective electrodes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Buring, J.; Borhani, N.O.; Cohen, J.D.; Cook, N.; Cutler, J.A.; Kiley, J.E.; Kuller, L.H.; Satterfield, S.; Sacks, F.M.; et al. The effect of potassium supplementation in persons with a high-normal blood pressure: Results from phase I of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP). Ann. Epidemiol. 1995, 5, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witham, M.D.; Adams, F.; Kabir, G.; Kennedy, G.; Belch, J.J.; Khan, F. Effect of short-term vitamin D supplementation on markers of vascular health in South Asian women living in the UK--a randomised controlled trial. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, K.S.; Yip, T.W.C.; Chook, P.; Koon, K.V.; Leong, H.C.; Feng, X.H.; Lee, A.P.W.; Kwok, T.C.Y. Vitamins B-12 and C Supplementation Improves Arterial Reactivity and Structure in Passive Smokers: Implication in Prevention of Smoking-Related Atherosclerosis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.D.; Secombes, K.R.; Thies, F.; Aucott, L.; Black, A.J.; Mavroeidi, A.; Simpson, W.G.; Fraser, W.D.; Reid, D.M.; Macdonald, H.M. Vitamin D3 supplementation has no effect on conventional cardiovascular risk factors: A parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled RCT. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3557–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.E.; Applegate, W.B.; Klag, M.J.; Borhani, N.O.; Cohen, J.D.; Kirchner, K.A.; Lakatos, E.; Sacks, F.M.; Taylor, J.O.; Hennekens, C.H. Lack of blood pressure effect with calcium and magnesium supplementation in adults with high-normal blood pressure: Results from phase I of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP). Ann. Epidemiol. 1995, 5, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.F.; Ibahim, J.; Makpol, S.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.; Abdul Latiff, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, M.; Mohd Yusof, Y.A.; Abdul Karim, A.; Wan Ngah, W.Z. Tocotrienol Rich Fraction Supplementation Improved Lipid Profile And Oxidative Status in Healthy Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari, M.H. The Effect of Supplementary Calcium on Blood Pressure in Healthy Adult Women Aged 18-30 Years in Tehran, Iran. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2015, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goon, J.A.; Nor Azman, N.H.E.; Abdul Ghani, S.M.; Hamid, Z.; Wan Ngah, W.Z. Comparing Palm Oil Tocotrienol Rich Fraction With A-Tocopherol Supplementation on Oxidative Stress in Healthy Older Adults. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Magnesium Improves The Beta-Cell Function To Compensate Variation of Insulin Sensitivity: Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.E.; Smith, E.L.; Freudenheim, J.L. Effects on blood pressure of calcium supplementation of women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 42, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSorley, P.T.; Bell, P.M.; Young, I.S.; Atkinson, A.B.; Sheridan, B.; Fee, J.P.H.; McCance, D.R. Endothelial Function, Insulin Action And Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Young Healthy Adult Offspring of Parents With Type 2 Diabetes: Effect of Vitamin E in A Randomized Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.Z.; Weinberger, M.H.; Christian, J.C. Blood Pressure Response to Potassium Supplementation in Normotensive Adults And Children. Hypertension 1987, 10, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghassemi, S.; Marjani, A. The Effect of Short-Term Vitamin D Supplementation on Lipid Profile and Blood Pressure In Post-Menopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery Res. 2014, 19, 517–521. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4223970/ (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Yanovski, J.A.; Parikh, S.J.; Yanoff, L.B.; Denkinger, B.I.; Calis, K.A.; Reynolds, J.C.; Sebring, N.G.; McHugh, T. Effects of calcium supplementation on body weight and adiposity in overweight and obese adults: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Frisch, S.; Berthold, H.K.; Götting, C.; Kuhn, J.; Kleesiek, K.; Stehle, P.; Koertke, H.; Koerfer, R. Vitamin D Supplementation Enhances The Beneficial Effects of Weight Loss on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; He, J.; Appel, L.J.; Cutler, J.A.; Havas, S.; Kotchen, T.A.; Roccella, E.J.; Stout, R.; Vallbona, C.; Winston, M.C.; et al. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. Primary prevention of hypertension: Clinical and public health advisory from The National High Blood Pressure Education Program. JAMA 2002, 288, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golzarand, M.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Koochakpoor, G.; Speakman, J.R.; Djafarian, K. Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Blood Pressure In Adults: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, L.A.; Struthers, A.D.; Khan, F.; Jorde, R.; Scragg, R.; Macdonald, H.M.; Alvarez, J.A.; Boxer, R.S.; Dalbeni, A.; Gepner, A.D.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Incorporating Individual Patient Data. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hao, X. The effect of vitamin D3 on blood pressure in people with vitamin D deficiency: A system review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mierlo, L.A.J.; Arends, L.R.; Streppel, M.T.; Zeegers, M.P.A.; Kok, F.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Geleijnse, J.M. Blood pressure response to calcium supplementation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2006, 20, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvaridzadeh, M.; Sepidarkish, M.; Fazelian, S.; Rahimlou, M.; Omidi, A.; Ardehali, S.H.; Sanoobar, M.; Heshmati, J. Effect of Calcium and Vitamin D Co-supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, e45–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanoff, A.; Costello, R.B.; Johnson, G.H. Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorolajal, J.; Zeraati, F.; Soltanian, A.R.; Sheikh, V.; Hooshmand, E.; Maleki, A. Oral potassium supplementation for management of essential hypertension: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godswill, A.G.; Somtochukwu, I.V.; Ikechukwu, A.O.; Kate, E.C. Health benefits of micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and their Associated Deficiency Diseases: A systematic review. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R.; Bundy, J.D.; Williams, B. Harmonization of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension Blood Pressure/Hypertension Guidelines: Comparisons, Reflections, and Recommendations. Circulation 2022, 146, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
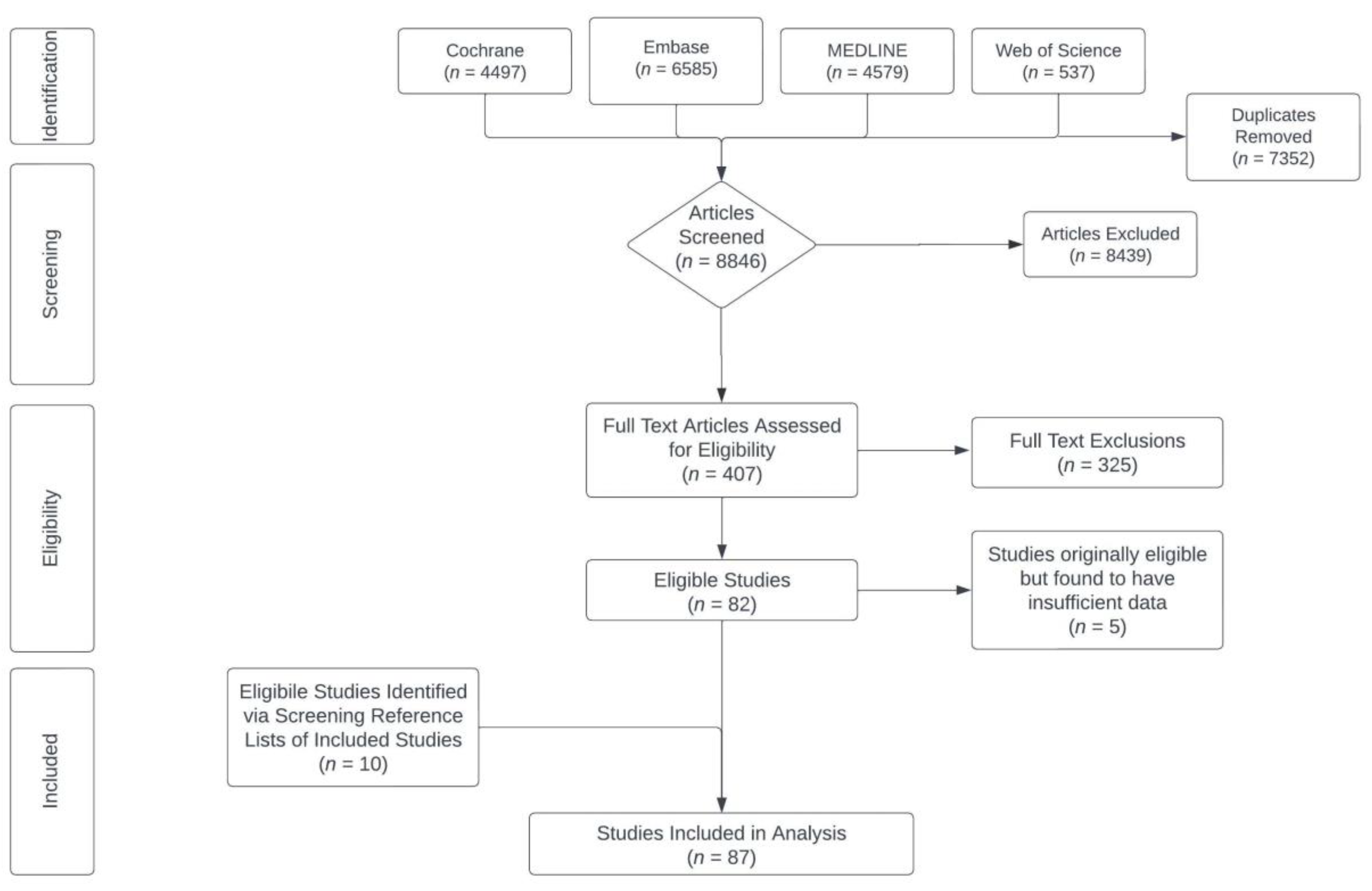


| Supplement (Total Number of Studies) | Type of Studies | Data | Sample Size | Population | Dose Range | Treatment Length Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (n = 5) | P: 1 (20%) CO: 4 (80%) | Sys: 5 (100%) Dia: 4 (80%) | Sys: 122 Dia: 114 | Healthy: 4 (80%) General: 1 (20%) | 200–1000 mg/day | 2–52 weeks |
| Vitamin D (n = 29) | P: 29 (100%) CO: 0 (0%) | Sys: 29 (100%) Dia: 28 (96.6%) | Sys: 4897 Dia: 4578 | Healthy: 9 (31.0%) General: 8 (27.6%) Obese: 8 (27.6%) Postmenopausal: 4 (13.8%) | 200–8000 IU/day | 2–208 weeks |
| Vitamin E (n = 7) | P: 5 (71.4%) CO: 2 (28.6%) | Sys: 7 (100%) Dia: 5 (71.4%) | Sys: 302 Dia: 240 | Healthy: 6 (85.7%) Postmenopausal: 1 (14.3%) | 50–320 mg/day | 3–26 weeks |
| Calcium (n = 21) | P: 20 (95.2%) CO: 1 (4.8%) | Sys: 21 (100%) Dia: 21 (100%) | Sys: 4534 Dia: 4525 | Healthy: 12 (57.1%) General: 3 (14.3%) Obese: 3 (14.3%) Postmenopausal: 3 (14.3%) | 162–2000 mg/day | 4–208 weeks |
| Magnesium (n = 18) | P: 14 (77.8%) CO: 4 (22.2%) | Sys: 18 (100%) Dia: 18 (100%) | Sys: 1575 Dia: 1575 | Healthy: 11 (61.1%) Obese: 4 (22.2%) General: 3 (16.7%) | 212–636 mg/day | 4–26 weeks |
| Potassium (n = 12) | P: 7 (58.3%) CO: 5 (41.7%) | Sys: 12 (100%) Dia: 12 (100%) | Sys: 1096 Dia: 1096 | Healthy: 7 (58.3%) General: 5 (41.7%) | 24–100 mmol/day (938.4–3910 mg/day) | 3–26 weeks |
| Total (n = 87) | P: 71 (81.6%) CO: 16 (18.4%) | Sys: 87 (100%) Dia: 83 (95.4%) | Sys: 12,526 Dia: 12,128 | Healthy: 44 (50.6%) General: 20 (23.0%) Obese: 15 (17.2%) Postmenopausal: 8 (9.2%) |
| Supplement | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C (n = 5) | Low: 4 (80%) Some concerns: 1 (20%) High: 0 (0%) |
| Vitamin D (n = 29) | Low: 25 (86.2%) Some concerns: 3 (10.3%) High: 1 (3.4%) |
| Vitamin E (n = 7) | Low: 6 (85.7%) Some concerns: 0 (0%) High: 1 (14.3%) |
| Calcium (n = 21) | Low: 17 (81.0%) Some concerns: 2 (9.5%) High: 2 (9.5%) |
| Magnesium (n = 18) | Low: 17 (94.4%) Some concerns: 1 (5.6%) High: 0 (0%) |
| Potassium (n = 12) | Low: 9 (75%) Some concerns: 2 (16.7%) High: 1 (8.3%) |
| Supplement | Systolic | Diastolic |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | −1.45 mm Hg (−4.26, 1.35) | −0.47 mm Hg (−2.29, 1.34) |
| Vitamin D | −0.19 mm Hg (−0.71, 0.33) | +0.11 mm Hg (−0.47, 0.69) |
| Vitamin E | −1.76 mm Hg (−3.05, −0.47) * | +1.17 mm Hg (−0.51, 2.84) |
| Calcium | −1.37 mm Hg (−2.03, −0.71) * | −1.63 mm Hg (−2.70, −0.57) * |
| Magnesium | −2.79 mm Hg (−5.25, −0.34) * | −1.56 mm Hg (−3.03, −0.09) * |
| Potassium | −2.10 mm Hg (−3.81, −0.38) * | −1.28 mm Hg (−2.58, 0.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behers, B.J.; Melchor, J.; Behers, B.M.; Meng, Z.; Swanson, P.J.; Paterson, H.I.; Mendez Araque, S.J.; Davis, J.L.; Gerhold, C.J.; Shah, R.S.; et al. Vitamins and Minerals for Blood Pressure Reduction in the General, Normotensive Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Six Supplements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194223
Behers BJ, Melchor J, Behers BM, Meng Z, Swanson PJ, Paterson HI, Mendez Araque SJ, Davis JL, Gerhold CJ, Shah RS, et al. Vitamins and Minerals for Blood Pressure Reduction in the General, Normotensive Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Six Supplements. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194223
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehers, Benjamin J., Julian Melchor, Brett M. Behers, Zhuo Meng, Palmer J. Swanson, Hunter I. Paterson, Samuel J. Mendez Araque, Joshua L. Davis, Cameron J. Gerhold, Rushabh S. Shah, and et al. 2023. "Vitamins and Minerals for Blood Pressure Reduction in the General, Normotensive Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Six Supplements" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194223
APA StyleBehers, B. J., Melchor, J., Behers, B. M., Meng, Z., Swanson, P. J., Paterson, H. I., Mendez Araque, S. J., Davis, J. L., Gerhold, C. J., Shah, R. S., Thompson, A. J., Patel, B. S., Mouratidis, R. W., & Sweeney, M. J. (2023). Vitamins and Minerals for Blood Pressure Reduction in the General, Normotensive Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Six Supplements. Nutrients, 15(19), 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194223






