Ketogenic Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
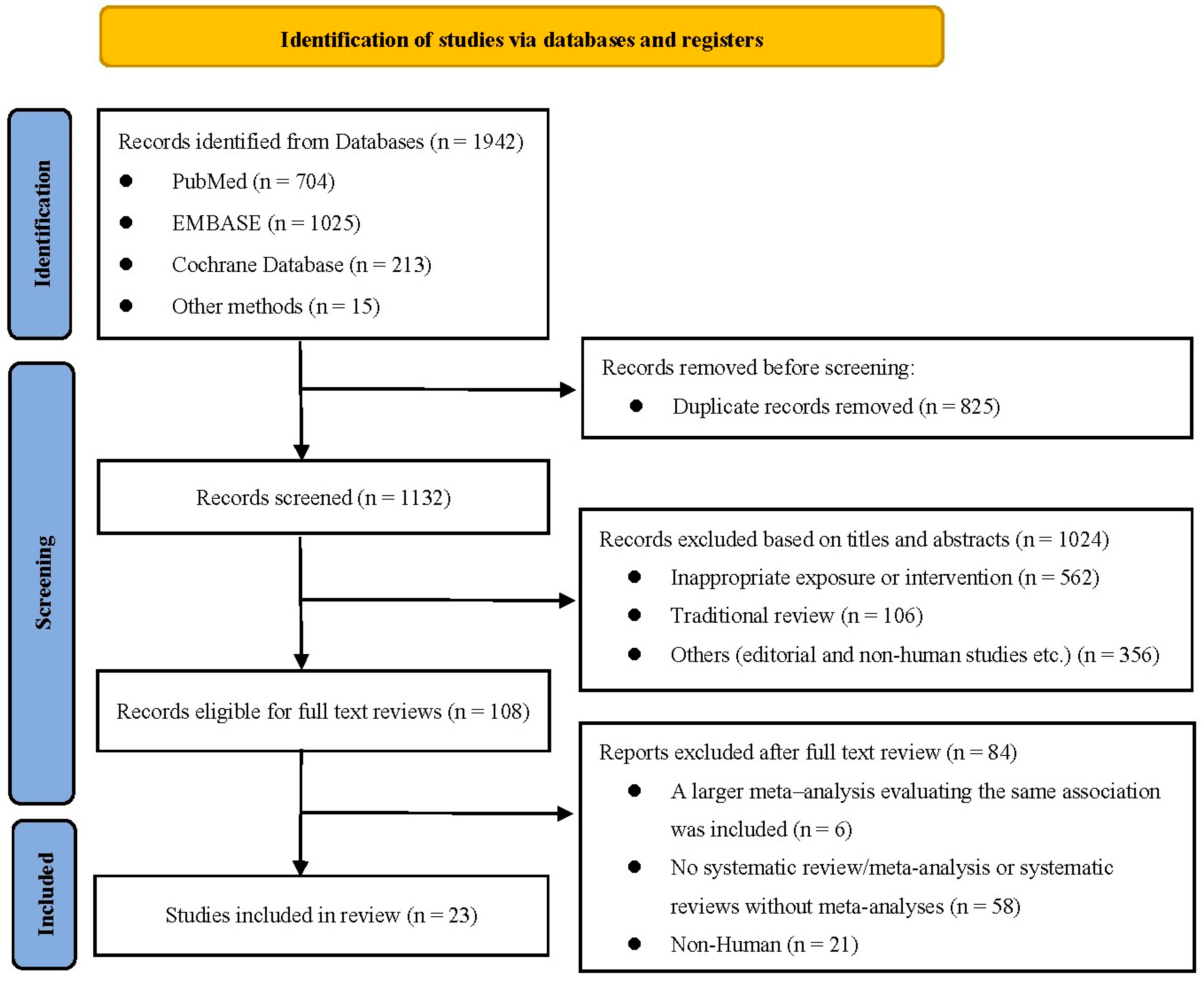
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Estimate of Methodological Quality
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Assessment of Evidence Credibility
3. Results
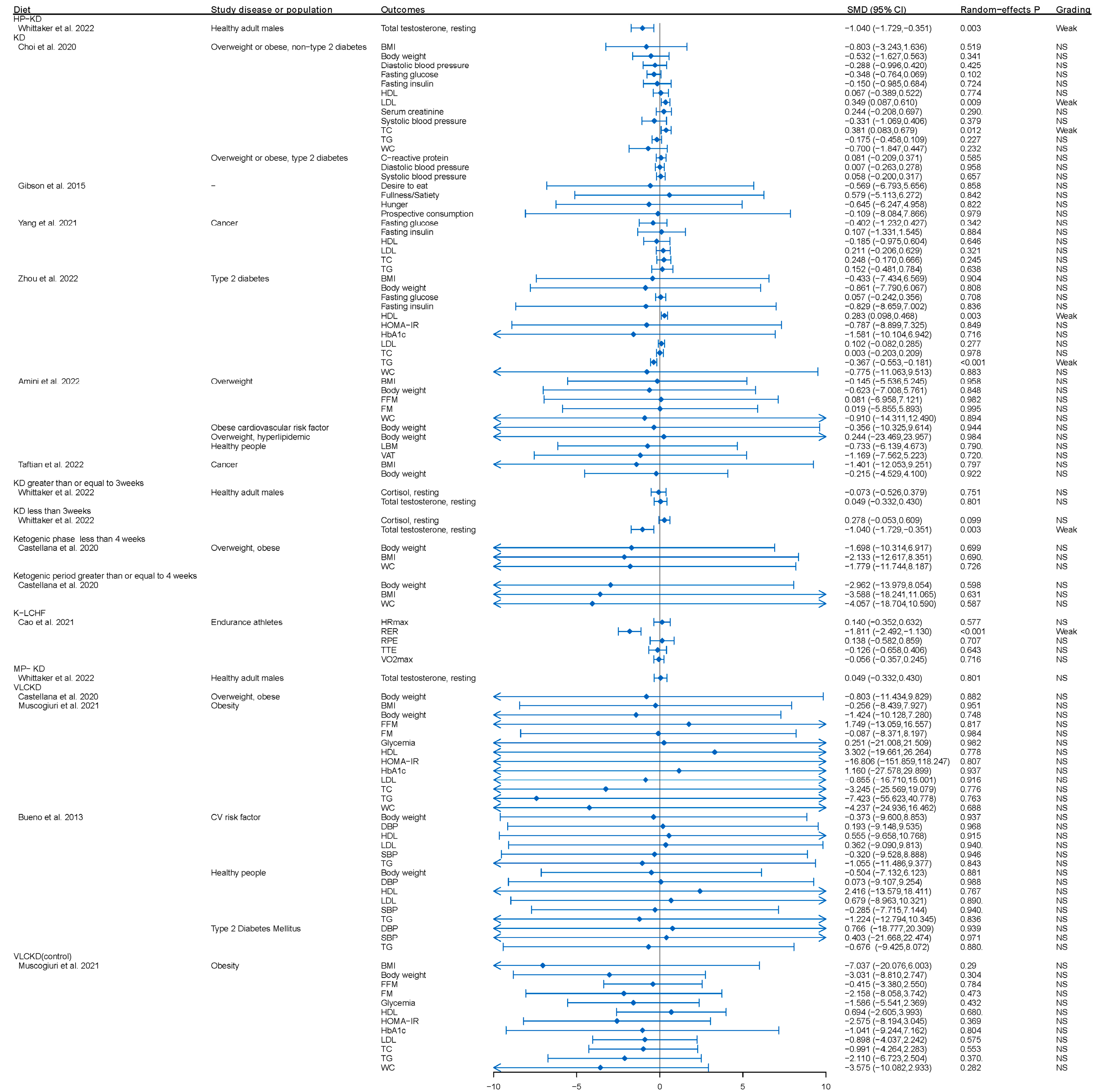
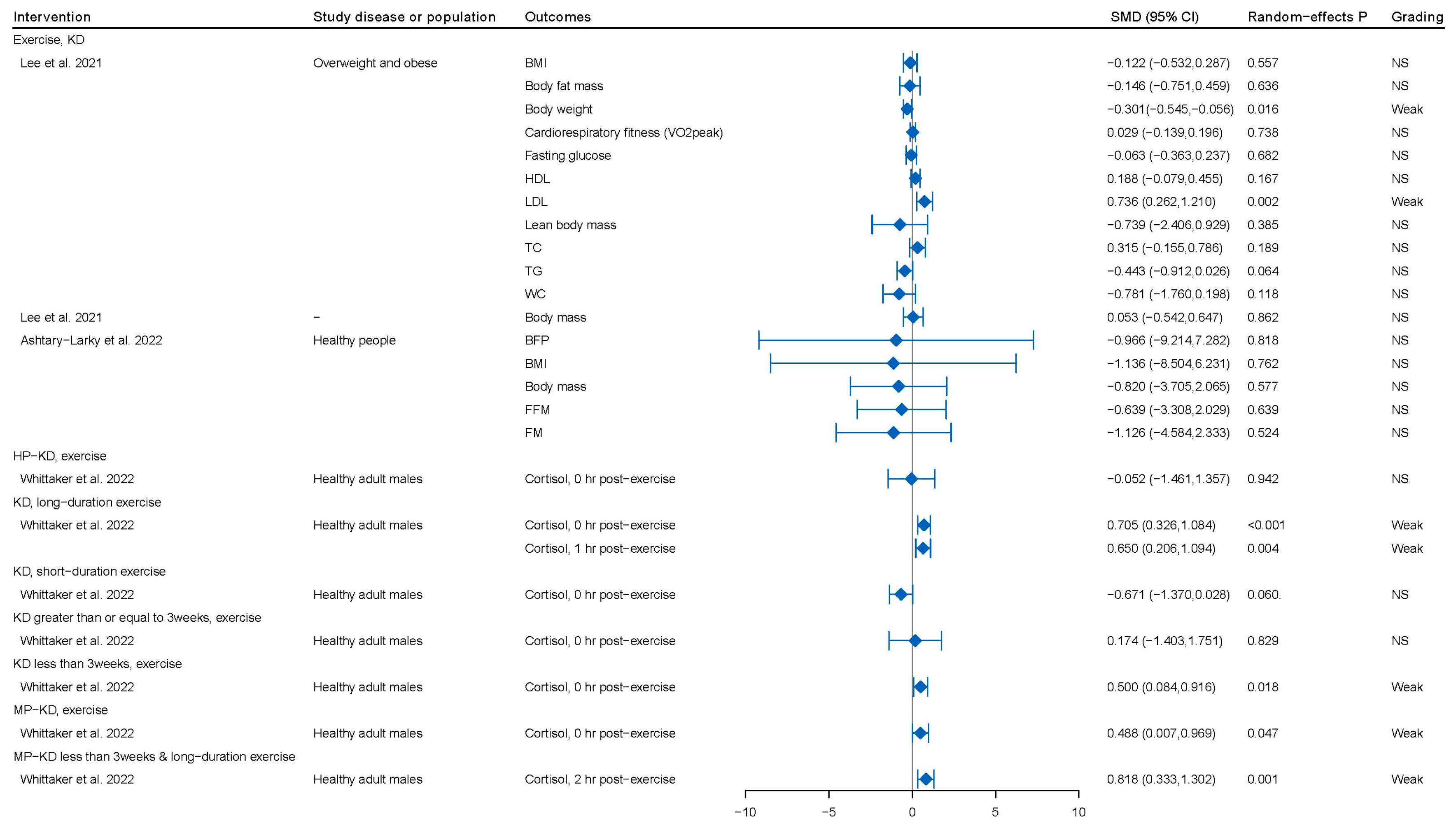
3.1. KD or KD Combined with Physical Activity among Healthy Individuals
3.2. KD or KD Combined with Physical Activity and Obesity or Overweight Individuals with or without Diabetes
3.3. KD and Seizures or Epilepsy Reduction
3.4. KD and Cancer
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of KD or KD Combined with Physical Activity among the General Population
4.2. The Effect of KD or KD Combined with Physical Activity among the Population with Metabolic Risk Factors
4.3. KD and Seizures or Epilepsy Reduction
4.4. KD and Cancer
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilder, R.J.M.C.B. High fat diets in epilepsy. Mayo Clin. Bull. 1921, 2, 308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Heber, D. Ketogenic Diets. Jama 2020, 323, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, C.; Du, J.; Wu, X.; Wei, Q.; Qin, H. Ketogenic diet for human diseases: The underlying mechanisms and potential for clinical implementations. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Alalwan, T.A.; Mahdi, A.M.; Guido, D.; Tagliabue, A. Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, S.; Abdurahman, A.A.; Saghazadeh, A.; Badv, R.S.; Mahmoudi, M. Short-term and long-term efficacy of classical ketogenic diet and modified Atkins diet in children and adolescents with epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, G.A. Brain Glucose Metabolism: Integration of Energetics with Function. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 949–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, J.; Gao, R.; Kalady, M.F.; Goel, A.; Qin, H.; et al. Ketogenic diet alleviates colitis by reduction of colonic group 3 innate lymphoid cells through altering gut microbiome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusek, M.; Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J. Ketogenic Diet in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.A.; Seimon, R.V.; Lee, C.M.; Ayre, J.; Franklin, J.; Markovic, T.P.; Caterson, I.D.; Sainsbury, A. Do ketogenic diets really suppress appetite? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients With Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Prevedello, L.; Markovich, M.; Busetto, L.; Vettor, R.; Foletto, M. Pre-operative Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) vs. Very Low Calorie Diet (VLCD): Surgical Impact. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D.; Phinney, S.D. Dietary carbohydrate restriction induces a unique metabolic state positively affecting atherogenic dyslipidemia, fatty acid partitioning, and metabolic syndrome. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; Forsythe, C.E.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Puglisi, M.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet. Lipids 2009, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Gaballa, D.; Roslin, M.; Gianos, E.; Kane, J. Novel Nutritional and Dietary Approaches to Weight Loss for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Ketogenic Diet, Intermittent Fasting, and Bariatric Surgery. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundi, M.S.; Mohamed Elfadil, O.; Patel, I.; Patel, J.; Hurt, R.T. Ketogenic diet and cancer: Fad or fabulous? JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45 (Suppl. S2), 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.W.; Fontaine, K.R.; Arend, R.C.; Alvarez, R.D.; Leath, C.A., III; Huh, W.K.; Bevis, K.S.; Kim, K.H.; Straughn, J.M., Jr.; Gower, B.A. A Ketogenic Diet Reduces Central Obesity and Serum Insulin in Women with Ovarian or Endometrial Cancer. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Pierro, R.; Asteria, C.; Calabrese, P.; Di Biasio, A.; Coluzzi, I.; Severino, L.; Giovanelli, A.; Pilone, V.; Silecchia, G. Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure to Alleviate Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Patients with Obesity Scheduled for Bariatric/Metabolic Surgery: A Pilot, Prospective, Randomized Multicenter Comparative Study. Obes. Surg. 2022, 32, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtary-Larky, D.; Bagheri, R.; Asbaghi, O.; Tinsley, G.M.; Kooti, W.; Abbasnezhad, A.; Afrisham, R.; Wong, A. Effects of resistance training combined with a ketogenic diet on body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5717–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Kong, Z.; Shi, Q.; Hu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Nie, J. Non-Energy-Restricted Low-Carbohydrate Diet Combined with Exercise Intervention Improved Cardiometabolic Health in Overweight Chinese Females. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, J.; Lan, R.; Gan, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, B.; Qian, M.; Du, B. Long-term ketogenic diet contributes to glycemic control but promotes lipid accumulation and hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetic mice. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Liu, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, Y. Effects of low-carbohydrate diet and ketogenic diet on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedland, S.J.; Howard, L.; Allen, J.; Smith, J.; Stout, J.; Aronson, W.; Inman, B.A.; Armstrong, A.J.; George, D.; Westman, E.; et al. A lifestyle intervention of weight loss via a low-carbohydrate diet plus walking to reduce metabolic disturbances caused by androgen deprivation therapy among prostate cancer patients: Carbohydrate and prostate study 1 (CAPS1) randomized controlled trial. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, J.H.; Lee, H.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, E.J.; Kang, C.M.; Lee, S.M. The Potential Use of a Ketogenic Diet in Pancreatobiliary Cancer Patients After Pancreatectomy. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6519–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Jeon, S.M.; Shin, S. Impact of a Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Obesity or Overweight and with or without Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batch, J.T.; Lamsal, S.P.; Adkins, M.; Sultan, S.; Ramirez, M.N. Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review Article. Cureus 2020, 12, e9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Lentz, S.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: Etiologies, evaluation, and management. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 44, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.W.; Fontaine, K.R.; Arend, R.C.; Gower, B.A. A Ketogenic Diet Is Acceptable in Women with Ovarian and Endometrial Cancer and Has No Adverse Effects on Blood Lipids: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Isley, W.L. Ketoacidosis during a Low-Carbohydrate Diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.S.; Turos, E. The Chemistry of the Ketogenic Diet: Updates and Opportunities in Organic Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, N.; Fritsch, M.; Priyambada, L.; Rewers, A.; Cherubini, V.; Estrada, S.; Wolfsdorf, J.I.; Codner, E. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2022: Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, B.; Fahmy, A.A.; Raza, F.; Banerjee, M. Non-diabetic ketoacidosis: A case series and literature review. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, B.M.; Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. Euglycemic Ketoacidosis. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukkar, S.G.; Muscaritoli, M. A Clinical Perspective of Low Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diets: A Narrative Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 642628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P. Integration of evidence from multiple meta-analyses: A primer on umbrella reviews, treatment networks and multiple treatments meta-analyses. CMAJ 2009, 181, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbasis, L.; Bellou, V.; Evangelou, E.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Tzoulaki, I. Environmental risk factors and multiple sclerosis: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet. Neurol. 2015, 14, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churuangsuk, C.; Hall, J.; Reynolds, A.; Griffin, S.J.; Combet, E.; Lean, M.E.J. Diets for weight management in adults with type 2 diabetes: An umbrella review of published meta-analyses and systematic review of trials of diets for diabetes remission. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Köhler, C.A.; Stubbs, B.; Koyanagi, A.; Bortolato, B.; Monaco, F.; Vancampfort, D.; Machado, M.O.; Maes, M.; Tzoulaki, I.; et al. Environmental risk factors and nonpharmacological and nonsurgical interventions for obesity: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of cohort studies and randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Son, M.J.; Son, C.Y.; Radua, J.; Eisenhut, M.; Gressier, F.; Koyanagi, A.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; et al. Environmental risk factors and biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder: An umbrella review of the evidence. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, C.; Purgato, M.; Abdulmalik, J.; Acarturk, C.; Eaton, J.; Gastaldon, C.; Gureje, O.; Hanlon, C.; Jordans, M.; Lund, C.; et al. Efficacy of psychosocial interventions for mental health outcomes in low-income and middle-income countries: An umbrella review. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.P.; Gillett, R. How to do a meta-analysis. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2010, 63, 665–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Cox, D.R.; Smith, G.D. Sifting the evidence—What’s wrong with significance tests? Another comment on the role of statistical methods. BMJ 2001, 322, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Tarone, R.; McLaughlin, J.K. The False-positive to False-negative Ratio in Epidemiologic Studies. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Evangelou, E. Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses. BMJ 2007, 335, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Spiegelhalter, D.J. A Re-Evaluation of Random-Effects Meta-Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2008, 172, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Deeks, J.J. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ 2011, 342, d549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Trikalinos, T.A. An exploratory test for an excess of significant findings. Clin. Trials 2007, 4, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, J.H.; Gail, M.H. On power and sample size for studying features of the relative odds of disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 131, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veettil, S.K.; Wong, T.Y.; Loo, Y.S.; Playdon, M.C.; Lai, N.M.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Role of Diet in Colorectal Cancer Incidence: Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Prospective Observational Studies. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragioti, E.; Solmi, M.; Favaro, A.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Dazzan, P.; Thompson, T.; Stubbs, B.; Firth, J.; Fornaro, M.; Tsartsalis, D.; et al. Association of Antidepressant Use With Adverse Health Outcomes: A Systematic Umbrella Review. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Gasevic, D.; Brunt, E.; McLachlan, F.; Millenson, M.; Timofeeva, M.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Campbell, H.; Theodoratou, E. Statins and Multiple Noncardiovascular Outcomes: Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Observational Studies and Randomized Controlled Trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, M.; Conte, E.; Cignarelli, A.; Perrini, S.; Giustina, A.; Giovanella, L.; Giorgino, F.; Trimboli, P. Efficacy and safety of very low calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; El Ghoch, M.; Colao, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Yumuk, V.; Busetto, L. European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Facts 2021, 14, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lei, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S. The Effect of a Ketogenic Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet on Aerobic Capacity and Exercise Performance in Endurance Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, N.B.; de Melo, I.S.; de Oliveira, S.L.; da Rocha Ataide, T. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Mattamel, P.B.; Joseph, T.; Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Akinwunmi, B.O.; Zhang, C.J.P.; Ming, W.K. Efficacy of Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet as an Adjuvant Cancer Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, J. Effects of Combined Exercise and Low Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet Interventions on Waist Circumference and Triglycerides in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, J. Influences of Ketogenic Diet on Body Fat Percentage, Respiratory Exchange Rate, and Total Cholesterol in Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, J.; Harris, M. Low-carbohydrate diets and men’s cortisol and testosterone: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Health 2022, 28, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, M.; Liang, J.; He, G.; Chen, N. Ketogenic Diet Benefits to Weight Loss, Glycemic Control, and Lipid Profiles in Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R.; Aminianfar, A.; Naghshi, S.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. The effect of ketogenic diet on body composition and anthropometric measures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taftian, M.; Beigrezaei, S.; Arabi, V.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. The Effect of Ketogenic Diet on Weight Loss in Adult Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbron, J.; Klinkenberg, S.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Lagae, L.; Lambrechts, D.; Braakman, H.M.H.; Majoie, M. Ketogenic diet for the treatment of pediatric epilepsy: Review and meta-analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-McGill, K.J.; Bresnahan, R.; Levy, R.G.; Cooper, P.N. Ketogenic diets for drug-resistant epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, Cd001903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Fang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, L.L.; Jiang, L. Efficacy of the ketogenic diet in patients with Dravet syndrome: A meta-analysis. Seizure 2020, 81, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawat, I.K.; Panda, P.K.; Sihag, R.K.; Panda, P.; Dawman, L. Efficacy and safety of corpus callosotomy and ketogenic diet in children with Lennox Gastaut syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.; Schoeler, N.E.; Langan, D.; Cross, J.H. Use of ketogenic diet therapy in infants with epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 1261–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Ketogenic diet for treatment of intractable epilepsy in adults: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Epilepsia Open 2018, 3, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzo, F.; Collotta, A.D.; Di Nora, A.; Costanza, G.; Ruggieri, M.; Falsaperla, R. Ketogenic diet in pediatric seizures: A randomized controlled trial review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2022, 22, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Chang, X.; Wu, P.; Li, S.; Wu, Y. Efficacy of ketogenic diet in CDKL5-related epilepsy: A single arm meta-analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinguely, D.; Gross, J.; Kosinski, C. Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets on Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Curr. Diabates Rep. 2021, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravata, D.M.; Sanders, L.; Huang, J.; Krumholz, H.M.; Olkin, I.; Gardner, C.D.; Bravata, D.M. Efficacy and safety of low-carbohydrate diets: A systematic review. JAMA 2003, 289, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Jiménez, A.; Hernández-Torres, R.P.; Torres-Durán, P.V.; Romero-Gonzalez, J.; Mascher, D.; Posadas-Romero, C.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A. The Respiratory Exchange Ratio is Associated with Fitness Indicators Both in Trained and Untrained Men: A Possible Application for People with Reduced Exercise Tolerance. Clin. Med. Circ. Respirat. Pulm. Med. 2008, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.E.; Zack, E.; Battaglini, C.; Viru, M.; Viru, A.; Hackney, A.C. Exercise and circulating cortisol levels: The intensity threshold effect. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2008, 31, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Bergstrom, J. Low serum testosterone and mortality in older men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Barrett, T.J.; Fisher, E.A. HDL and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppert, J.; Lehrke, M.; Marx, N.; Jankowski, J.; Noels, H. Lipoproteins and lipids in cardiovascular disease: From mechanistic insights to therapeutic targeting. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michas, G.; Micha, R.; Zampelas, A. Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease: Putting together the pieces of a complicated puzzle. Atherosclerosis 2014, 234, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Thompson, C.H.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Wittert, G.A.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Brinkworth, G.D. A very low-carbohydrate, low-saturated fat diet for type 2 diabetes management: A randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achten, J.; Jeukendrup, A.E. Optimizing fat oxidation through exercise and diet. Nutrition 2004, 20, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Januszewski, S.; Pluta, R. Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.E.; Todorova, M.T.; Seyfried, T.N. Perspectives on the metabolic management of epilepsy through dietary reduction of glucose and elevation of ketone bodies. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasior, M.; Hartman, A.L.; Rogawski, M.A. The anticonvulsant activity of acetone does not depend upon its metabolites. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, N.; Gray, J.A.; Omote, H.; Miyaji, T.; Inoue, T.; Hara, C.; Uneyama, H.; Edwards, R.H.; Nicoll, R.A.; Moriyama, Y. Metabolic control of vesicular glutamate transport and release. Neuron 2010, 68, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Bergqvist, C.; Hunter, J.V.; Jin, D.; Wang, D.J.; Wehrli, S.; Zimmerman, R.A. In vivo measurement of brain metabolites using two-dimensional double-quantum MR spectroscopy--exploration of GABA levels in a ketogenic diet. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 49, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melø, T.M.; Nehlig, A.; Sonnewald, U. Neuronal-glial interactions in rats fed a ketogenic diet. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngson, N.A.; Morris, M.J.; Ballard, J.W.O. The mechanisms mediating the antiepileptic effects of the ketogenic diet, and potential opportunities for improvement with metabolism-altering drugs. Seizure 2017, 52, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutas, A.; Yellen, G. The ketogenic diet: Metabolic influences on brain excitability and epilepsy. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbek, A.; Wojtala, M.; Pirola, L.; Balcerczyk, A. Modulation of Cellular Biochemistry, Epigenetics and Metabolomics by Ketone Bodies. Implications of the Ketogenic Diet in the Physiology of the Organism and Pathological States. Nutrients 2020, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.D.; Aminazdeh-Gohari, S.; Kofler, B. Ketogenic diet in cancer therapy. Aging 2018, 10, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiterovich, P.O., Jr.; Vining, E.P.; Pyzik, P.; Skolasky, R., Jr.; Freeman, J.M. Effect of a high-fat ketogenic diet on plasma levels of lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins in children. JAMA 2003, 290, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergati, M.; Krasniqi, E.; Monte, G.D.; Riondino, S.; Vallone, D.; Guadagni, F.; Ferroni, P.; Roselli, M. Ketogenic Diet and Other Dietary Intervention Strategies in the Treatment of Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1170–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.G.; Bhatia, S.K.; Anderson, C.M.; Eichenberger-Gilmore, J.M.; Sibenaller, Z.A.; Mapuskar, K.A.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Buatti, J.M.; Spitz, D.R.; Fath, M.A. Ketogenic diets as an adjuvant cancer therapy: History and potential mechanism. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Dang, B.N.; Moore, T.B.; Clemens, R.; Pressman, P. A review of nutrition and dietary interventions in oncology. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120926877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Tuccinardi, D.; Moriconi, E.; Di Renzo, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could ketogenic diet “starve” cancer? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study, Year (Ref) | Study Disease or Population | Outcome Assessments | No. of Studies (Participants, n) | Study Design | Intervention/Comparison | Effect Metrics | AMSTAR 2 Rating2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castellana et al. 2020 [56] | Overweight, obese | Body weight, BMI, WC, RR for discontinuation | 12 (695) | RCT, cohort | VLCKD vs. control | MD, RR | Low |
| Choi et al. 2020 [24] | Overweight or obese, non-type 2 diabetes; overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes | BMI, Body weight, C-reactive protein, Diastolic blood pressure, Fasting glucose, Fasting insulin, HDL, LDL, Serum creatinine, TC, TG, WC | 6 (290) | RCT | LCKD/LCD/KD vs. MCCRD/HCD/regular diet/hypocaloric diet/normal diet/LFD/orlistat therapy plus low-fat diet/ | SMD | Low |
| Muscogiuri et al. 2021 [57] | Obesity | BMI, Body weight, FFM FM, Glycemia, HDL, HOMA-IR, HbA1c, LDL TC, TG, WC | 13 (674) | RCT, cohort | VLCKD vs. control/LCD/MD/VLCD | MD | Critically low |
| Cao et al. 2021 [58] | Endurance athletes | Hrmax, RER, RPE, TTE, VO2max | 10 (171) | RCT, cohort | K-LCHF vs. HCD/HD | SMD | Low |
| Bueno et al. 2013 [59] | CV risk factor, healthy, type 2 diabetes | Body weight, DBP, HDL, LDL, SBP, TAG | 12 (1470) | RCT | VLCKD vs. LFD | MD | Low |
| Gibson et al. 2015 [9] | - | Desire to eat, fullness/satiety, hunger, prospective consumption | 5 (246) | RCT | KVLED/KLCD vs. control/non-KD | WMD | Critically low |
| Yang et al. 2021 [60] | Cancer | Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HDL, LDL, TC, TG, RR for ketosis, RR for adverse events | 5 (406) | RCT | LCKD vs. ACS/GD | SMD, RR | Critically low |
| Lee et al. 2021 [61] | Overweight and obese | BMI, body fat mass, body weight, cardiorespiratory fitness (VO2peak), fasting glucose, HDL, LDL, lean body mass, TC, TG, WC | 4 (121) | RCT | Combined exercise, LCKD vs. control/exercise, regular diet/exercise, standard diet | SMD | Critically low |
| Lee et al. 2021 [62] | Athletes | Body mass | 2 (39) | RCT | Exercise, KD vs. control/exercise, regular diet/habitual diet/ | SMD | Critically low |
| Whittaker et al. 2022 [63] | Men’s cortisol and testosterone | Cortisol, total testosterone | 16 (168) | RCT | KD/MP-KD HP-KD/KD, long-duration exercise/Short-term, MP-KD, long-duration exercise vs. HCD | SMD | High |
| Zhou et al. 2022 [64] | Type 2 diabetes | BMI, body weight, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HDL, HOMA-IR, HbA1c, LDL, TC, TG, WC | 7 (526) | RCT | LCKD/LCD/KD vs. LCD/MCCRD/Low glycemic index, reduced-calorie diet/American Diabetes Associations’ “Create Your Plate” diet/HCD | MD | Low |
| Amini et al. 2022 [65] | Overweight; obese cardiovascular risk factor; overweight, hyperlipidemic; healthy people | BMI, body weight, FFM, FM, LBM, PBF | 17 (1550) | RCT | LCD/LCKD/High-fat Atkins Diet/KD/VLCD vs. Low-calorie, high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet/low-fat diet/high-carbohydrate, high-fiber diet/high-protein, Zone Diet/low-fat, nonketogenic, low-carbohydrate diet/non-KD/low-fat, reduced-calorie diet/regular diet, exercise/regular diet/very low fat diet/high unsaturated fat diet/control group/low-calorie diet/moderate carbohydrate, calorie-restricted diet/American cancer society diet | WMD | High |
| Taftian et al. 2022 [66] | Cancer | BMI, body weight | 8 (246) | RCT, NRCT | KD vs. control | WMD | Low |
| Ashtary-Larky et al. 2022 [18] | Healthy people | BFP, BMI, body mass, FFM, FM | 11 (212) | RCT | Exercise, KD vs. exercise, regular diet/Western diet/carbohydrate-restricted diet/non-KD group/control/usual diet/mixed diet | WMD | Low |
| Study, Year (Ref) | Study Disease or Population | Outcome Assessments | No. of Studies (Participants, n) | Study Design | Intervention/Comparison | Effect Metrics | AMSTAR 2 Rating2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sourbron et al. 2020 [67] | Pediatric seizures | RR of SFR, ≥50% | 5 (374) | RCT | KD/MAD vs. standard therapy/control group | Proportion, RR | Critically low |
| Rezaei et al. 2019 [5] | Epilepsy | ≥50%, ≥90%, SF | 75 (3799) | RCT, cohort | KD/MAD vs. control | Proportion | Low |
| Martin-McGill et al. 2020 [68] | Drug-resistant epilepsy | RR of ≥50%, SF, treatment withdrawal | 7 (566) | RCT | KD vs. usual care | RR | High |
| Wang et al. 2020 [69] | Dravet syndrome | ≥50% | 6 (157) | Cohort | KD vs. control | Proportion | Critically low |
| Sharawat et al. 2021 [70] | Lennox Gastaut syndrome | ≥50%, SF | 3 (55) | Cohort | KD vs. control | Proportion | Critically low |
| Lyons et al. 2020 [71] | Epilepsy | ≥50%, SF | 32 (430) | Cohort | KD vs. control | Proportion | Critically low |
| Liu et al. 2018 [72] | Intractable epilepsy | ≥50%, ≥90%, SF | 9 (223) | Cohort | KD/MAD/KD, MAD vs. control | Proportion | Critically low |
| Pizzo et al. 2022 [73] | Pediatric seizure | OR of ≥50% | 7 (413) | RCT | KD/MAD vs. standard therapy | OR | Low |
| Zhang et al. 2022 [74] | CDKL5-related epilepsy | OR of clinical responder rate, OR of definite responder rate | 11 (183) | Cohort | KD vs. control | OR | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Su, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, R.; Liao, M.; Fan, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Cai, J.; et al. Ketogenic Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194161
Chen S, Su X, Feng Y, Li R, Liao M, Fan L, Liu J, Chen S, Zhang S, Cai J, et al. Ketogenic Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194161
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shiyun, Xin Su, Yonghui Feng, Ruojie Li, Minqi Liao, Laina Fan, Jiazi Liu, Shasha Chen, Shiwen Zhang, Jun Cai, and et al. 2023. "Ketogenic Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194161
APA StyleChen, S., Su, X., Feng, Y., Li, R., Liao, M., Fan, L., Liu, J., Chen, S., Zhang, S., Cai, J., Zhu, S., Niu, J., Ye, Y., Lo, K., & Zeng, F. (2023). Ketogenic Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 15(19), 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194161






