Pertinence of Salt-Related Knowledge and Reported Behaviour on Salt Intake in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
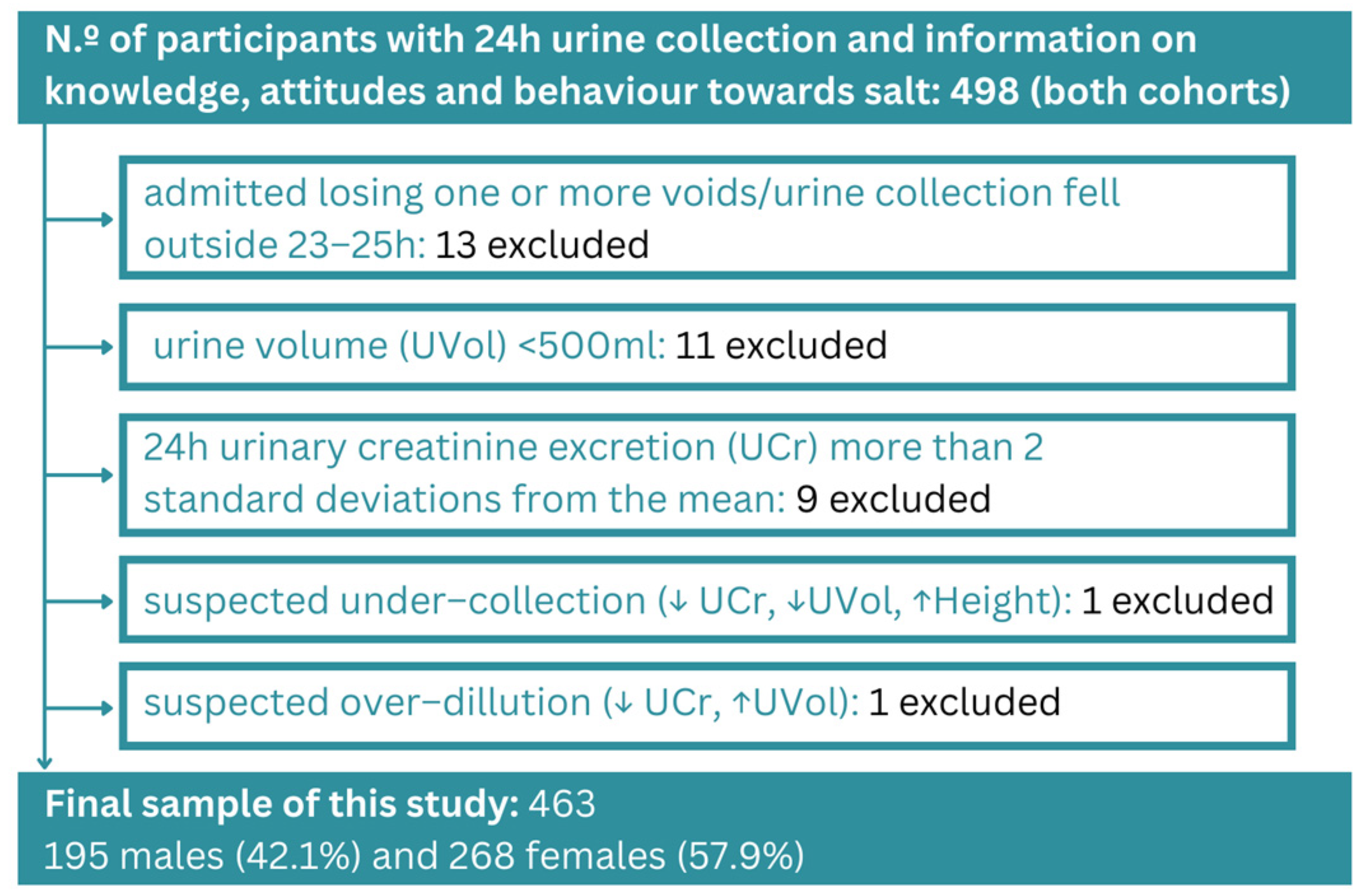
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study—Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Data and Salt Intake Estimation
2.3. Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude, and Behaviour Related to Salt
2.4. Score Calculations
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Salt Intake Consumption
3.3. Sociodemographic Characteristics and Knowledge and Attitudes Scores
3.4. Attitude and Perception Regarding the Salt Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, S.M.; Sheaff, R.; Sibbald, B.; Marshall, M.N.; Pickard, S.; Gask, L.; Halliwell, S.; Rogers, A.; Roland, M.O. Implementing Clinical Governance in English Primary Care Groups/Trusts: Reconciling Quality Improvement and Quality Assurance. Qual. Saf. Health Care 2002, 11, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, T.; Malavolti, M.; Whelton, P.K.; Naska, A.; Orsini, N.; Vinceti, M. Blood Pressure Effects of Sodium Reduction: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Experimental Studies. Circulation 2021, 143, 1542–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases: 2013–2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN 978-92-4-150623-6.
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of Modest Salt Reduction on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Implications for Public Health. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.L.; Li, N.; Dunford, E.K.; Nowson, C.A.; Neal, B.C. Consumer Awareness and Self-Reported Behaviours Related to Salt Consumption in Australia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 19, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority (ELSTAT). Causes of Death: Year 2020. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/documents/20181/7362cdf6-c0d0-ffd3-d27d-c042ddc4cd71 (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Magriplis, E.; Farajian, P.; Pounis, G.D.; Risvas, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Zampelas, A. High Sodium Intake of Children through “hidden” Food Sources and Its Association with the Mediterranean Diet: The GRECO Study. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Menti, A.; Kalpourtzi, N.; Gavana, M.; Vantarakis, A.; Chlouverakis, G.; Hajichristodoulou, C.; Trypsianis, G.; Voulgari, P.V.; Alamanos, Y.; et al. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control of Hypertension in Greece: EMENO National Epidemiological Study. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzi, K.; Protogerou, A.D.; Moschonis, G.; Tsirimiagou, C.; Androutsos, O.; Chrousos, G.P.; Lionis, C.; Manios, Y. Prevalence of Hypertension and Hypertension Phenotypes by Age and Gender among Schoolchildren in Greece: The Healthy Growth Study. Atherosclerosis 2017, 259, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasara, E.; Marakis, G.; Breda, J.; Skepastianos, P.; Hassapidou, M.; Kafatos, A.; Rodopaios, N.; Koulouri, A.A.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sodium and Potassium Intake in Healthy Adults in Thessaloniki Greater Metropolitan Area-The Salt Intake in Northern Greece (SING) Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsopoulou, A.V.; Magriplis, E.; Michas, G.; Micha, R.; Chourdakis, M.; Chrousos, G.P.; Roma, E.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Zampelas, A.; Karageorgou, D.; et al. Micronutrient Dietary Intakes and Their Food Sources in Adults: The Hellenic National Nutrition and Health Survey (HNNHS). J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 978-92-4-150483-6.
- European Commission. Implementation of the EU Salt Reduction Framework–Results of Member States Survey; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2012.
- WHO. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014: Attaining the Nine Global Noncommunicable Diseases Targets; a Shared Responsibility; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-92-4-156485-4. [Google Scholar]
- Spronk, I.; Kullen, C.; Burdon, C.; O’Connor, H. Relationship between Nutrition Knowledge and Dietary Intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Mohan, S.; Rogers, K.; Shivashankar, R.; Thout, S.R.; Gupta, P.; He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A.; Webster, J.; Krishnan, A.; et al. The Association of Knowledge and Behaviours Related to Salt with 24-h Urinary Salt Excretion in a Population from North and South India. Nutrients 2017, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Nie, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Luo, R.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; He, F.J. Salt-Related Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors and Their Relationship with 24-Hour Urinary Sodium Excretion in Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mawali, A.; D’Elia, L.; Jayapal, S.K.; Morsi, M.; Al-Shekaili, W.N.; Pinto, A.D.; Al-Kharusi, H.; Al-Balushi, Z.; Idikula, J.; Al-Harrasi, A.; et al. National Survey to Estimate Sodium and Potassium Intake and Knowledge Attitudes and Behaviours towards Salt Consumption of Adults in the Sultanate of Oman. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marakis, G.; Tsigarida, E.; Mila, S.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviour of Greek Adults towards Salt Consumption: A Hellenic Food Authority Project. Public. Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1877–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.; Marklund, M.; Henry, M.E.; Appel, L.J.; Croft, K.D.; Neal, B.; Wu, J.H.Y. A Systematic Review of the Sources of Dietary Salt Around the World. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Conclusions on Food Product Improvement (OJ C, C/269, 23.07.2016, p. 21, CELEX). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52016XG0723(01) (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Onyeaka, H.; Nwaiwu, O.; Obileke, K.; Miri, T.; Al-Sharify, Z.T. Global Nutritional Challenges of Reformulated Food: A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2483–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenke, R.; Barzi, F.; McMahon, E.; Webster, J.; Brimblecombe, J. Consumer Acceptance of Reformulated Food Products: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Salt-Reduced Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3357–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, D.; Strazzullo, P.; Serafini, M.; Porrini, M.; Pellegrini, N.; Angelino, D. SINU Young Working Sodium Content in Cereal-Based Products Sold in Italy: How Far Are We from the Global Benchmarks? Nutrients 2022, 14, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riis, N.L.; Lassen, A.D.; Bjoernsbo, K.; Toft, U.; Trolle, E. Dietary Effects of Introducing Salt-Reduced Bread with and without Dietary Counselling-A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marakis, G.; Katsioulis, A.; Kontopoulou, L.; Ehlers, A.; Heimberg, K.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Langerholc, T.; Adamska, H.; Matyjaszczyk, E.; Silva, K.D.R.; et al. Knowledge, Attitude and Behaviour of University Students Regarding Salt and Iodine: A Multicentre Cross-Sectional Study in Six Countries in Europe and Asia. Arch. Public. Health 2021, 79, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Lara, R.B.; Franks, A.T.; Agarwal, K.; Nawal, N.; Courville, A.B.; Guo, J.; Yang, S.; Brooks, B.E.; Roy, A.; Taylor, K.; et al. No Significant Salt or Sweet Taste Preference or Sensitivity Differences Following Ad Libitum Consumption of Ultra-Processed and Unprocessed Diets: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Chem. Senses 2023, 48, bjad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, M.; Pradhan, S.; Pradhan, S.R. Risk Factors Associated with Hypertension in Young Adults: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmilah, S.; Cahyana, Y.; Utama, G.L.; Aït-Kaddour, A. Strategies to Reduce Salt Content and Its Effect on Food Characteristics and Acceptance: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeble, M.; Adams, J.; Burgoine, T. Changes in Online Food Access during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Associations with Deprivation: Longitudinal Analysis. JMIR Public. Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e41822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Dyer, A.R.; Cooper, R.S.; Stamler, R.; Stamler, J. Can Overnight Urine Replace 24-Hour Urine Collection to Asses Salt Intake? Hypertension 1979, 1, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 463) | Cohort I Adults (Excl. Students) (n = 200) | Students (Both Cohorts) (n = 263) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Age (years) | 36.4 ± 17.7 | 34.2 ± 17.4 | 35.1 ± 17.6 | 52.3 ± 12.6 | 53.9 ± 11.1 | 21.7 ± 2.9 | 21.4 ± 1.8 |
| Height (cm) | 178.1 ± 7.2 | 164.2 ± 6.2 | 170.1 ± 9.6 | 176.9 ± 6.7 | 162.2 ± 6.5 | 179.3 ± 7.4 | 165.5 ± 5.7 |
| Weight (kg) | 82.1 ± 14.5 | 65.9 ± 12.7 | 72.8 ± 15.7 | 87.2 ± 13.3 | 73.4 ± 12.6 | 77.4 ± 13.9 | 62.1 ± 10.4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.8 ± 4.1 | 24.5 ± 4.9 | 25.1 ± 4.6 | 27.8 ± 3.7 | 27.9 ± 4.8 | 24.0 ± 3.6 | 22.3 ± 3.5 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 89.5 ± 13.4 | 76.9 ± 11.6 | 82.2 ± 13.9 | 97.4 ± 11.6 | 85.1 ± 12.4 | 82.5 ± 10.8 | 71.8 ± 7.3 |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| Daily Salt Intake (Tertiles) | |||||||
| I (≤7.54) | 6.01 (2.0–7.5) | 5.3 (1.2–7.5) | 5.5 (1.2–7.5) | 6.0 (2.0–7.4) | 5.8 (2.1–7.4) | 5.8 (2.8–7.5) | 4.9 (1.2–7.5) |
| II (7.57–10.63) | 9.3 (7.6–10.6) | 8.9 (7.6–10.6) | 9.1 (7.6–10.6) | 9.4 (7.7–10.6) | 9.05 (7.6–10.6) | 9.1 (7.6–10.4) | 8.9 (7.7–10.6) |
| III (≥10.64) | 13.5 (10.6–28.5) | 12.8 (10.6–21.6) | 13.3 (10.6–28.5) | 13.6 (10.6–28.5) | 13.4 (10.6–21.6) | 12.8 (10.8–27.3) | 12.3 (10.7–19.6) |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | N (%) | |
| Level of education (%) | |||||||
| Secondary (non-students) | 44 (23%) | 65 (24%) | 109 (23%) | 44 (47%) | 65 (61%) | ||
| Students | 101 (52%) | 162 (61%) | 263 (57%) | 101 (100%) | 162 (100%) | ||
| Tertiary (graduates) | 50 (25%) | 41 (15%) | 91 (20%) | 50 (53%) | 41 (39%) | ||
| Knowledge Score | Behavior Score (Discretionary Salt Use) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SD | p-Value ** | n | Mean ± SD | p-Value ** | |
| Sex | 0.009 | 0.07 | ||||
| Male | 190 | 31.57 ± 10.15 | 195 | 4.12 ± 2.31 | ||
| Female | 262 | 34.17 ± 10.47 | 266 | 4.48 ± 2.37 | ||
| Age (tertiles) | <0.001 | 0.01 | ||||
| ≤21 years | 137 | 33.37 ± 9.16 | 138 | 3.94 ± 2.29 | ||
| 22–44 years | 162 | 36.88 ± 9.89 | 163 | 4.68 ± 2.53 | ||
| ≥45 years | 151 | 28.91 ± 10.45 | 158 | 4.31 ± 1.42 | ||
| Cohorts | <0.001 | 0.28 | ||||
| Adults (excl. students) | 191 | 29.73 ± 10.91 | 199 | 4.20 ± 1.59 | ||
| All students | 261 | 35.53 ± 9.31 | 262 | 4.42 ± 2.50 | ||
| Education | <0.001 | 0.46 | ||||
| Secondary | 103 | 27.95 ± 11.25 | 108 | 4.12 ± 1.67 | ||
| Students | 261 | 35.53 ± 9.31 | 262 | 4.42 ± 2.50 | ||
| Tertiary | 88 | 31.81 ± 10.16 | 91 | 4.30 ± 1.50 | ||
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | 0.002 | 0.1 | ||||
| <25 | 260 | 34.57 ± 10.01 | 262 | 4.51 ± 2.29 | ||
| 25.0–29.9 | 128 | 31.0 ± 10.88 | 131 | 4.07 ± 2.06 | ||
| ≥30.0 | 60 | 31.43 ± 10.05 | 64 | 4.10 ± 2.16 | ||
| Daily Salt Intake (Tertiles) | 0.3 | 0.06 | ||||
| I (≤7.54) | 153 | 34.07 ± 10.73 | 154 | 4.27 ± 2.18 | ||
| II (7.57–10.63) | 149 | 32.66 ± 10.76 | 153 | 4.64 ± 2.23 | ||
| III (≥10.64) | 150 | 32.48 ± 9.68 | 154 | 4.07 ± 2.02 | ||
| Overall Cohort (463 Participants) | Cohort I Adults Excl. Students (191 Participants) | Students (Both Cohorts) (261 Participants) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic | β | 95% CI 1 | p-Value 2 | β | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | β | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | 0.26 | 0.17, 0.35 | <0.001 | 0.19 | 0.05, 0.32 | 0.006 | 0.27 | 0.14, 0.40 | <0.001 |
| Sex | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Male | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| Female | −2.1 | −2.9, −1.4 | −1.8 | −3.0, −0.70 | −2.2 | −3.1, −1.2 | |||
| Age (tertiles) | 0.307 | 0.060 | 0.016 | ||||||
| ≤21 years | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| 22–44 years | −0.59 | −1.5, 0.33 | 2.0 | −3.9, 7.8 | −1.2 | −2.1, −0.22 | |||
| ≥45 years | −0.74 | −1.8, 0.31 | 0.16 | −5.6, 6.0 | |||||
| Knowledge score | 0.01 | −0.03, 0.05 | 0.562 | 0.05 | −0.01, 0.10 | 0.098 | −0.01 | −0.06, 0.04 | 0.714 |
| Behavior score (discretionary salt use) | −0.11 | −0.28, 0.06 | 0.210 | −0.31 | −0.69, 0.07 | 0.105 | −0.01 | −0.20, 0.18 | 0.922 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marakis, G.; Marques Domingues, A.; Crispo, A.; Magriplis, E.; Vasara, E.; Kontopoulou, L.; Triantafyllou, C.; Skepastianos, P.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Rodopaios, N.E.; et al. Pertinence of Salt-Related Knowledge and Reported Behaviour on Salt Intake in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194114
Marakis G, Marques Domingues A, Crispo A, Magriplis E, Vasara E, Kontopoulou L, Triantafyllou C, Skepastianos P, Papadopoulou SK, Rodopaios NE, et al. Pertinence of Salt-Related Knowledge and Reported Behaviour on Salt Intake in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194114
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarakis, Georgios, Ana Marques Domingues, Anna Crispo, Emmanuella Magriplis, Eleni Vasara, Lamprini Kontopoulou, Christos Triantafyllou, Petros Skepastianos, Sousana K. Papadopoulou, Nikolaos E. Rodopaios, and et al. 2023. "Pertinence of Salt-Related Knowledge and Reported Behaviour on Salt Intake in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194114
APA StyleMarakis, G., Marques Domingues, A., Crispo, A., Magriplis, E., Vasara, E., Kontopoulou, L., Triantafyllou, C., Skepastianos, P., Papadopoulou, S. K., Rodopaios, N. E., Hassapidou, M., Zampelas, A., Cappuccio, F. P., & Breda, J. (2023). Pertinence of Salt-Related Knowledge and Reported Behaviour on Salt Intake in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 15(19), 4114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194114








