The Sterilization of Human Milk by Holder Pasteurization or by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Leads to Differential Intestinal Effects in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Collection and HoP and HHP Processing
2.2. Mice, Tissues Collections and Intestinal Permeability Assay
2.3. Gene Expression
2.4. Cecal SCFAs Quantification
2.5. Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
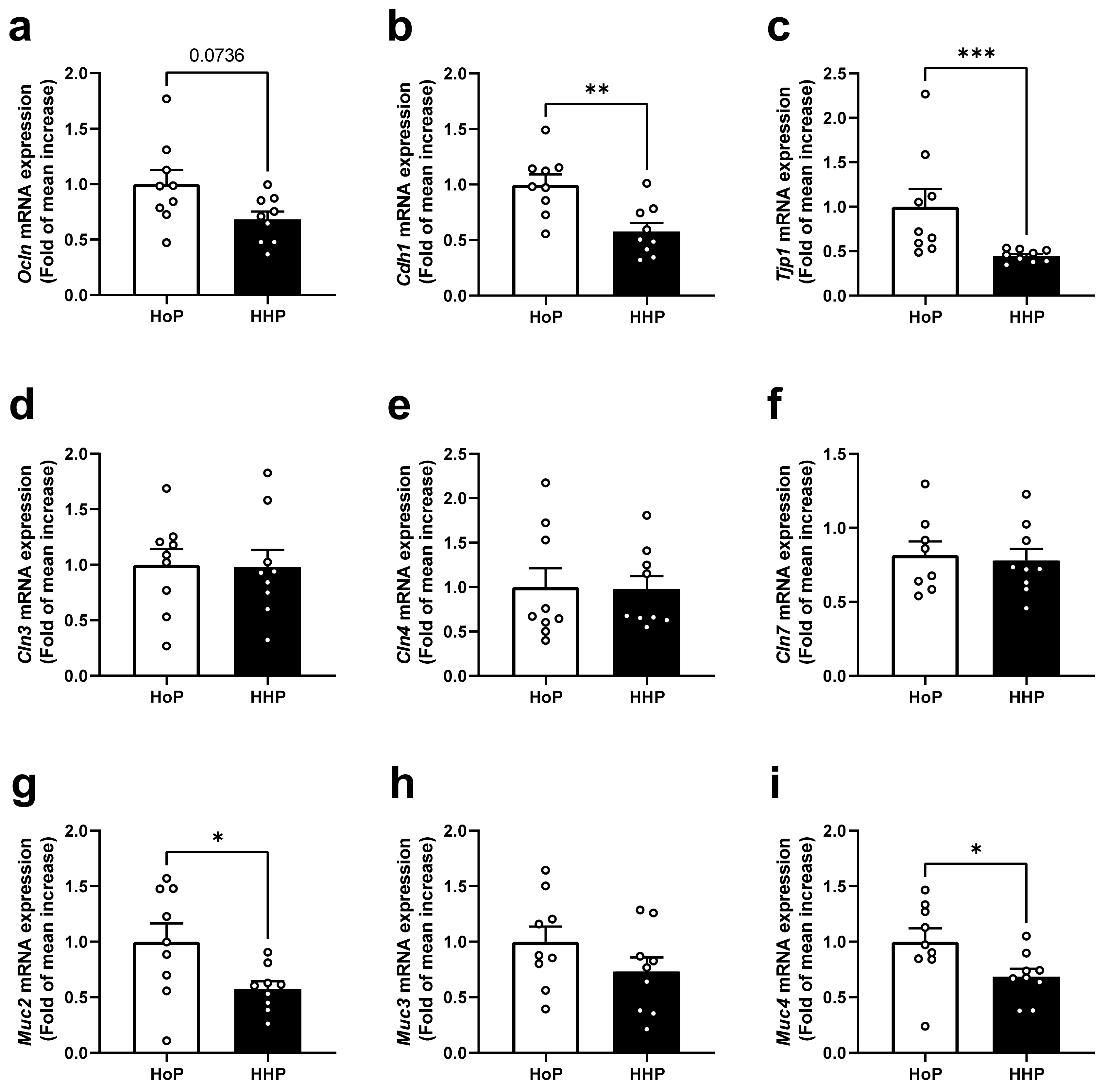
3.1. Effect of Treatment of Mice with HoP- and HHP-DM on Gene Expression Level of Selected Markers of the Intestinal Barrier in the Ileum
3.2. Effect of Treatment of Mice with HoP- and HHP-DM on Gene Expression Level of Selected Markers of the Intestinal Barrier in the Colon
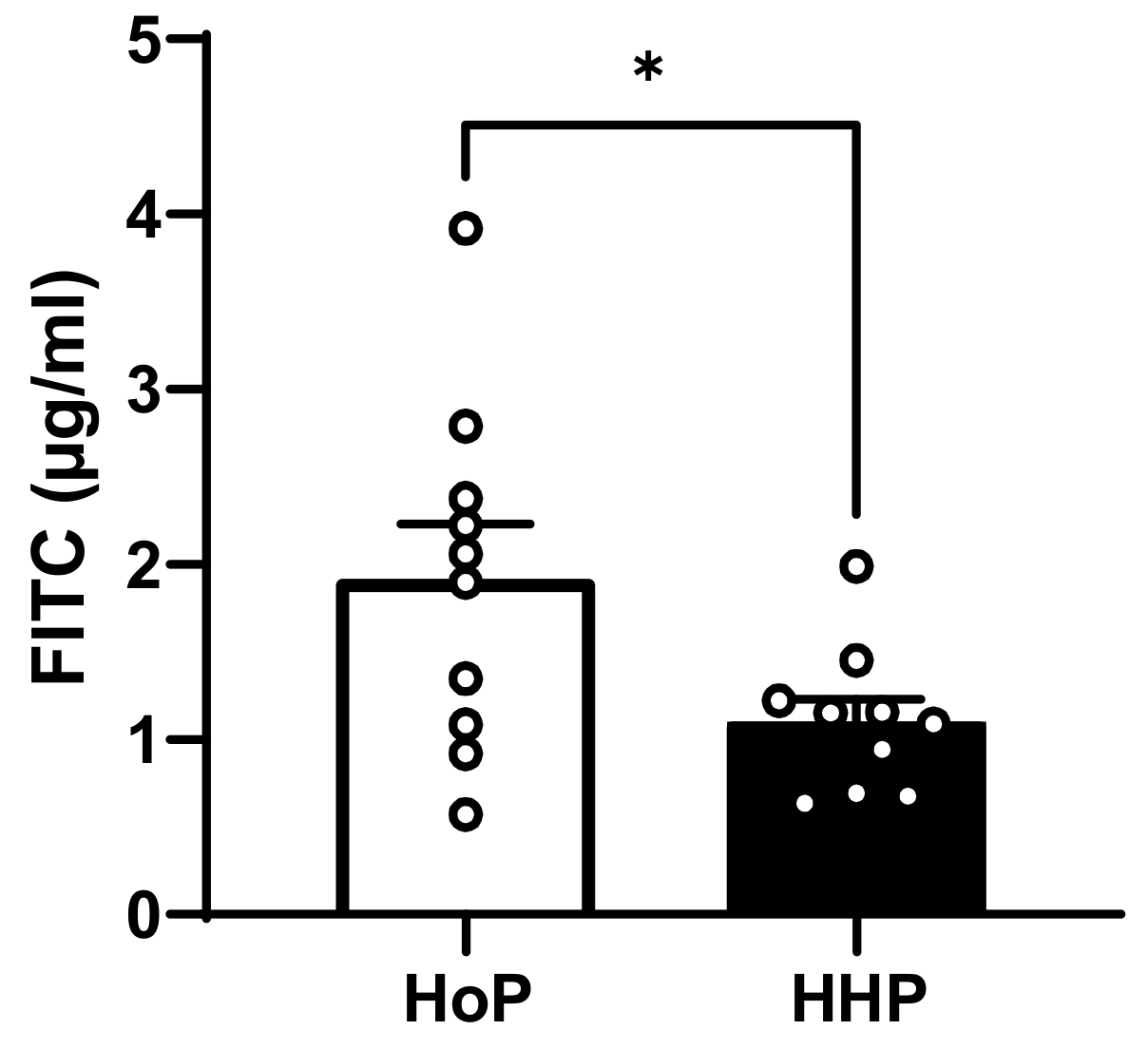
3.3. In Vivo Intestinal Paracellular Permeability in HoP- and HHP-DM Mice
3.4. Cecal SCFAs Levels in HoP- and HHP-DM Mice
3.5. Microbiota Analysis in the Cecum of HoP- and HHP-DM Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckle, A.; Taylor, C. Cost and Cost-Effectiveness of Donor Human Milk to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Systematic Review. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, G.; Bertino, E.; Gebauer, C.; Grovslien, A.; Mileusnic-Milenovic, R.; Arslanoglu, S.; Barnett, D.; Boquien, C.-Y.; Buffin, R.; Gaya, A.; et al. Recommendations for the Establishment and Operation of Human Milk Banks in Europe: A Consensus Statement From the European Milk Bank Association (EMBA). Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peila, C.; Moro, G.E.; Bertino, E.; Cavallarin, L.; Giribaldi, M.; Giuliani, F.; Cresi, F.; Coscia, A. The Effect of Holder Pasteurization on Nutrients and Biologically-Active Components in Donor Human Milk: A Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.C.; Marousez, L.; De Lamballerie, M.; McCulloch, S.; Hermann, E.; Gottrand, F.; Ley, D.; Lesage, J. The metabolome of human milk is altered differentially by Holder pasteurization and high hydrostatic pressure processing. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska, A.; Sinkiewicz-Darol, E.; Barbarska, O.; Bernatowicz-Lojko, U.; Borszewska-Kornacka, M.K.; van Goudoever, J.B. Innovative Techniques of Processing Human Milk to Preserve Key Components. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escuder-Vieco, D.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, L.; Pallás-Alonso, C.R. Effect of HTST and Holder Pasteurization on the Concentration of Immunoglobulins, Growth Factors, and Hormones in Donor Human Milk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 02222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marousez, L.; Tran, L.; Micours, E.; De Lamballerie, M.; Gottrand, F.; Pierrat, V.; Eberlé, D.; Ley, D.; Lesage, J. Metabolic hormones in human breast milk are preserved by high hydrostatic pressure processing but reduced by Holder pasteurization. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, G.E.; Billeaud, C.; Rachel, B.; Calvo, J.; Cavallarin, L.; Christen, L.; Escuder-Vieco, D.; Gaya, A.; Lembo, D.; Wesolowska, A.; et al. Processing of Donor Human Milk: Update and Recommendations From the European Milk Bank Association (EMBA). Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demazeau, G.; Rivalain, N. The development of high hydrostatic pressure processes as an alternative to other pathogen reduction methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demazeau, G.; Plumecocq, A.; Lehours, P.; Martin, P.; Couëdelo, L.; Billeaud, C. A New High Hydrostatic Pressure Process to Assure the Microbial Safety of Human Milk While Preserving the Biological Activity of Its Main Components. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marousez, L.; Sprenger, N.; De Lamballerie, M.; Jaramillo-Ortiz, S.; Tran, L.; Micours, E.; Gottrand, F.; Howsam, M.; Tessier, F.J.; Ley, D.; et al. High hydrostatic pressure processing of human milk preserves milk oligosaccharides and avoids formation of Maillard reaction products. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackam, D.J.; Sodhi, C.P. Bench to bedside-new insights into the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waard, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ayede, A.I.; Berrington, J.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Busari, O.O.; Cormack, B.E.; Embleton, N.D.; Goudoever, J.B.; et al. Time to Full Enteral Feeding for Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants Varies Markedly Among Hospitals Worldwide But May Not Be Associated With Incidence of Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The NEOMUNE-NeoNutriNet Cohort Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2019, 43, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.M.; Gao, Y.; de Groot, N.; Vonk, M.M.; Ulfman, L.; van Neerven, R.J.J. Babies, Bugs, and Barriers: Dietary Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Function in Early Life. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 165–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abot, A.; Wemelle, E.; Laurens, C.; Paquot, A.; Pomie, N.; Carper, D.; Bessac, A.; Orea, X.M.; Fremez, C.; Fontanie, M.; et al. Identification of new enterosynes using prebiotics: Roles of bioactive lipids and mu-opioid receptor signalling in humans and mice. Gut 2021, 70, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemelle, E.; Marousez, L.; Lesage, J.; De Lamballerie, M.; Knauf, C.; Carneiro, L. In Vivo Assessment of Antioxidant Potential of Human Milk Treated by Holder Pasteurization or High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing: A Preliminary Study on Intestinal and Hepatic Markers in Adult Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Stern, A.; Peng, H.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Yang, H.-C. Redox and Metabolic Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function and Associated Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woting, A.; Blaut, M. Small Intestinal Permeability and Gut-Transit Time Determined with Low and High Molecular Weight Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Dextrans in C3H Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Kotani, T.; Konno, T.; Setiawan, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Imada, S.; Usui, Y.; Hatano, N.; Shinohara, M.; Saito, Y.; et al. Promotion of Intestinal Epithelial Cell Turnover by Commensal Bacteria: Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, G.F.; Fouser, L.A.; Artis, D. Border patrol: Regulation of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis at barrier surfaces by IL-22. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockinger, B.; Di Meglio, P.; Gialitakis, M.; Duarte, J.H. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Multitasking in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghteling, P.D.; Walker, W.A. Why is initial bacterial colonization of the intestine important to infants’ and children’s health? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornef, M.W.; Torow, N. “Layered immunity” and the “neonatal window of opportunity”-timed succession of non-redundant phases to establish mucosal host-microbial homeostasis after birth. Immunology 2020, 159, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, F.; Zheng, C. The Role of Microbiota in Infant Health: From Early Life to Adulthood. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.J.; Ajami, N.J.; O’brien, J.L.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Smith, D.P.; Wong, M.C.; Ross, M.C.; Lloyd, R.E.; Doddapaneni, H.; Metcalf, G.A.; et al. Temporal development of the gut microbiome in early childhood from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Toh, H.; Hase, K.; Oshima, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tobe, T.; Clarke, J.M.; Topping, D.L.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2011, 469, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Z.-R.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Lin, J. Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Paul, S.; Kundu, P. NF-κB Regulation by Gut Microbiota Decides Homeostasis or Disease Outcome During Ageing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 874940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.-R.; Wu, J.; Li, H.-S.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Zhou, X.-M.; Xu, C.-H.; Ding, N.; Zha, J.-M.; He, W.-Q. In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches to Determine Intestinal Epithelial Cell Permeability. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 140, e57032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanca, A.; Manghina, V.; Fraumene, C.; Palomba, A.; Abbondio, M.; Deligios, M.; Silverman, M.; Uzzau, S. Metaproteogenomics Reveals Taxonomic and Functional Changes between Cecal and Fecal Microbiota in Mouse. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Targeted Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Ocln | atgtccggccgatgctctc | tttggctgctcttgggtctgtat |
| Cdh1 | ccaatcctgatgaaattggaaact | aacaccaacagagagtcgtaag |
| Cln3 | ccaggagaggagccgttaag | cccttcgaaaactgacggac |
| Cln4 | cgttactccagcgctactc | tcactcagcacaccatgact |
| Cln7 | tgatgagctgcaaaatgtacg | ccagggacaccaccattaag |
| Tjp1 | gttggtacggtgccctgaaaga | gctgacaggtaggacagacgat |
| Muc2 | cggaactccagaaagaagcca | ggcagtcagacgcaaagttgta |
| Muc3 | caccttccagccttccctaa | caacgatgtcatgactacctgg |
| Muc4 | agaggcagaagaggagtggaga | ggtggtagcctttgtagccatc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, L.; Marousez, L.; Van Hul, M.; Tran, L.C.; De Lamballerie, M.; Ley, D.; Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C.; Lesage, J. The Sterilization of Human Milk by Holder Pasteurization or by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Leads to Differential Intestinal Effects in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184043
Carneiro L, Marousez L, Van Hul M, Tran LC, De Lamballerie M, Ley D, Cani PD, Knauf C, Lesage J. The Sterilization of Human Milk by Holder Pasteurization or by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Leads to Differential Intestinal Effects in Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184043
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Lionel, Lucie Marousez, Matthias Van Hul, Léa Chantal Tran, Marie De Lamballerie, Delphine Ley, Patrice D. Cani, Claude Knauf, and Jean Lesage. 2023. "The Sterilization of Human Milk by Holder Pasteurization or by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Leads to Differential Intestinal Effects in Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184043
APA StyleCarneiro, L., Marousez, L., Van Hul, M., Tran, L. C., De Lamballerie, M., Ley, D., Cani, P. D., Knauf, C., & Lesage, J. (2023). The Sterilization of Human Milk by Holder Pasteurization or by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Leads to Differential Intestinal Effects in Mice. Nutrients, 15(18), 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184043









