New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Gut–Liver–Heart Crosstalk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
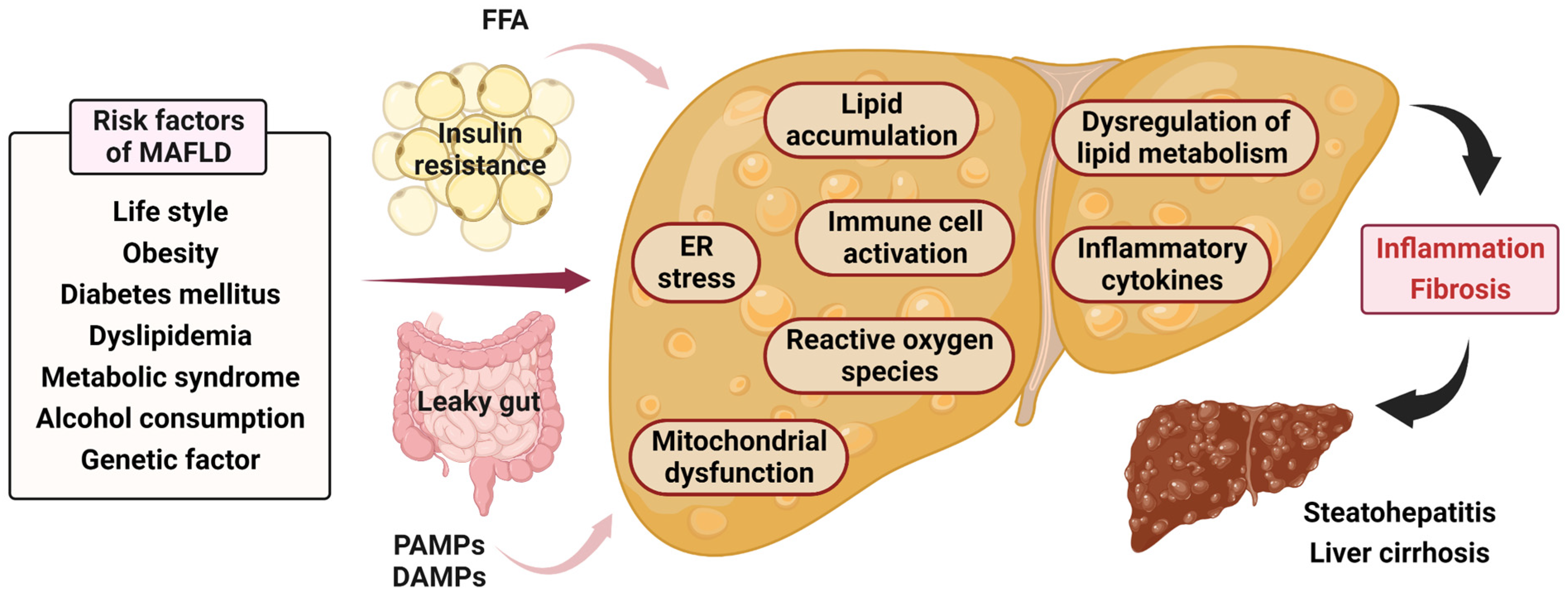
2. Pathophysiology and Molecular Mechanism of MAFLD
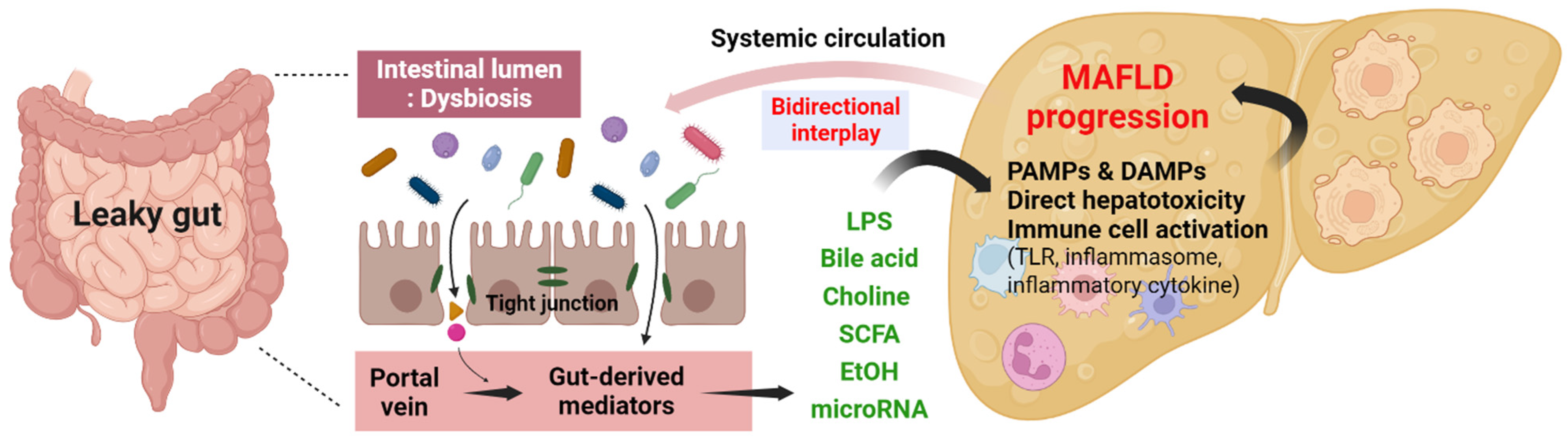
3. Gut–Liver Axis in MAFLD
3.1. Gut Dysbiosis in MAFLD
3.2. Mechanism of Gut–Liver Axis in MAFLD
3.2.1. Intestinal Permeability
3.2.2. Metabolites Produced by the Gut Microbiome
3.3. Gut-Derived Signaling Pathway in MAFLD
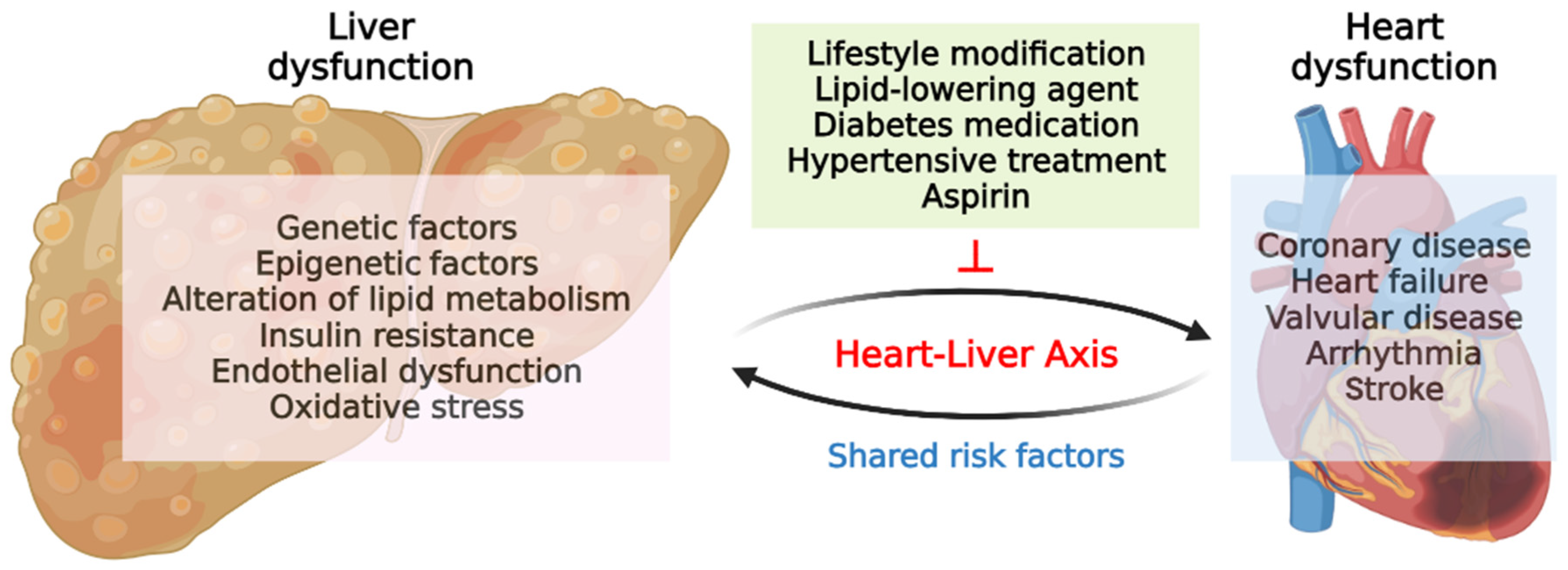
4. Liver–Heart Axis in MAFLD
4.1. Relationship between MAFLD and Heart Diseases
4.2. Gut Microbiota and Liver–Heart Axis in MAFLD
4.3. Possible Mechanisms in Liver–Heart Axis
4.3.1. Genetic and Epigenetic Manifestations
4.3.2. Inflammation and Cytokines
4.3.3. Endothelial Dysfunction
4.3.4. Lipid Metabolism
4.3.5. Insulin Resistance
4.3.6. Clonal Hematopoiesis in CVD and MAFLD
5. Therapeutic Approaches in MAFLD
5.1. Therapeutic Approaches for Targeting Gut–Liver Axis
5.2. Therapeutic Approaches for Targeting Liver–Heart Axis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gofton, C.; Upendran, Y.; Zheng, M.-H.; George, J. MAFLD: How is it different from NAFLD? Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S17–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, M.; An, Z.; Meng, J.; Jiang, J.; Song, J.; Wu, W. Prevalence and risk factors of metabolic associated fatty liver disease in Xinxiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ayada, I.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Ma, Z.; Bruno, M.J.; de Knegt, R.J.; Cao, W. Estimating global prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in overweight or obese adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e573–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Nguyen, M.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease versus metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: Prevalence, outcomes and implications of a change in name. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Weickert, M.O. Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: A Review of Complex Interlinks. Metabolites 2023, 13, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.Z. New insight into inter-organ crosstalk contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Protein Cell 2018, 9, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.-R.; Jeong, W.-I. Recent advances of sterile inflammation and inter-organ cross-talk in alcoholic liver disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Hashida, R.; Sano, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Amano, K.; Kawaguchi, T. The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tian, H.; Lam, K.S.; Lin, S.; Hoo, R.C.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N.; Wang, Y.; Bornstein, S.R.; Xu, A. Adiponectin mediates the metabolic effects of FGF21 on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pan, X.; Wu, F.; Ye, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lian, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ding, H. Fibroblast growth factor 21 prevents atherosclerosis by suppression of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 and induction of adiponectin in mice. Circulation 2015, 131, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Mateos, R.; Albillos, A. The role of the gut-liver axis in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Muynck, K.; Vanderborght, B.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Devisscher, L. The Gut–Liver Axis in Chronic Liver Disease: A Macrophage Perspective. Cells 2021, 10, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J. Gut–liver axis and sterile signals in the development of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2017, 52, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, L.; Eiseler, S.; Apfel, T.; Pyrsopoulos, N. Fatty liver disease and gut microbiota: A comprehensive update. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzino, S.; Sofia, M.; Faletra, G.; Mazzone, C.; Litrico, G.; La Greca, G.; Latteri, S. Gut–Liver Axis and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Vicious Circle of Dysfunctions Orchestrated by the Gut Microbiome. Biology 2022, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Gut–liver axis, nutrition, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Ni, L.; Zhuge, F.; Fu, Z. The gut microbiota and its metabolites, novel targets for treating and preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.M.; Galsgaard, K.D.; Elmelund, E.; Knop, F.K.; Suppli, M.P.; Holst, J.J.; Winther-Sørensen, M.; Kjeldsen, S.A.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J. The liver–α-cell axis in health and in disease. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gómez, A.; Brescia, P.; Rescigno, M.; Romero-Gómez, M. Gut–liver axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The impact of the metagenome, end products, and the epithelial and vascular barriers. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.N.; Liu, J.Y.; Shi, T.T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xin, Z.; Cao, X.; Yang, J.K. Angiotensin-(1-7), the product of ACE2 ameliorates NAFLD by acting through its receptor Mas to regulate hepatic mitochondrial function and glycolipid metabolism. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 16291–16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Nakajima, A.; Nogami, A.; Yoneda, M. Current Research on the Pathogenesis of NAFLD/NASH and the Gut–Liver Axis: Gut Microbiota, Dysbiosis, and Leaky-Gut Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, J.H.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.C.; Cho, S.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, M. Proton pump inhibitors use and the risk of fatty liver disease: A nationwide cohort study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Day, C.P.; Bonora, E. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, M.; Nakamura, K.; Nishihara, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Nakayama, R.; Takaya, Y.; Toh, N.; Akagi, S.; Miyoshi, T.; Akagi, T. Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Liver Disease, from a Clinically Pragmatic Perspective as a Cardiologist. Nutrients 2023, 15, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A. Association of Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Metabolic Syndrome with non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease: A retrospective analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebi, M.; Seyedian, S.S.; Hashemi, S.J.; Parsi, A.; Hajiani, E. Association between high-sensitivity-CRP and liver elastography and cardiac ischemic diseases in patients with fatty liver. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 5495. [Google Scholar]
- Bisaccia, G.; Ricci, F.; Mantini, C.; Tana, C.; Romani, G.L.; Schiavone, C.; Gallina, S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease phenotypes. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120933804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Genetics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of risk alleles through the lens of immune response. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, M.; Szabo, G. Immune and inflammatory pathways in NASH. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, B. The metabolic triad of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, visceral adiposity and type 2 diabetes: Implications for treatment. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, D.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M. New insights into the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and oxidative stress. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flessa, C.M.; Kyrou, I.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Kaltsas, G.; Kassi, E.; Randeva, H.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in nonalcoholic (metabolic associated) fatty liver disease (NAFLD/MAFLD). J. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 123, 1585–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Du, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Hu, N.; Ma, S.; Wang, W.; Ren, J. Effects of melatonin on fatty liver disease: The role of NR 4A1/DNA-PK cs/p53 pathway, mitochondrial fission, and mitophagy. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.J.; Malhi, H. The unfolded protein response and hepatic lipid metabolism in non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 203, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, A.; Hundertmark, J.; Guillot, A.; Tacke, F. Molecular and cellular mediators of the gut-liver axis in the progression of liver diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 725390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perla, F.M.; Prelati, M.; Lavorato, M.; Visicchio, D.; Anania, C. The role of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Children 2017, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Radovanovic Spurnic, A.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N. Gut-liver axis, gut microbiota, and its modulation in the management of liver diseases: A review of the literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.-t.; Xu, M.-Z. Characterization of gut dominant microbiota in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, Y. Sea buckthorn pulp and seed oils ameliorate lipid metabolism disorders and modulate gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice on high-fat diet. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1067813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Shibolet, O.; Elinav, E. The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, F.M.; Disciglio, V.; Franco, I.; Sorino, P.; Bonfiglio, C.; Bianco, A.; Campanella, A.; Lippolis, T.; Pesole, P.L.; Polignano, M. A low glycemic index Mediterranean diet combined with aerobic physical activity rearranges the gut microbiota signature in NAFLD patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Hsu, C.; Lo, M.T.; Liu, A.; Bettencourt, R.; Ajmera, V.H.; Bassirian, S.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Richards, L. Link between gut-microbiome derived metabolite and shared gene-effects with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in NAFLD. Hepatology 2018, 68, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonder, M.J.; Kurilshikov, A.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Mujagic, Z.; Imhann, F.; Vila, A.V.; Deelen, P.; Vatanen, T.; Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P. The effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhong, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Jia, W. Chronic ethanol consumption alters mammalian gastrointestinal content metabolites. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Torralba, M.; Tan, J.; Embree, M.; Zengler, K.; Stärkel, P.; Van Pijkeren, J.-P.; DePew, J.; Loomba, R.; Ho, S.B. Supplementation of saturated long-chain fatty acids maintains intestinal eubiosis and reduces ethanol-induced liver injury in mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 203–214.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P.; Seebauer, C.T.; Schnabl, B. Alcoholic liver disease: The gut microbiome and liver cross talk. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Masciana, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.-W.; Tang, H.-Y.; Zhao, T.; Tan, X.-Y.; Bi, J.; Wang, B.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D. Intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction participates in the progress of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3648. [Google Scholar]
- Gudan, A.; Kozłowska-Petriczko, K.; Wunsch, E.; Bodnarczuk, T.; Stachowska, E. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: What do We Know in 2023? Nutrients 2023, 15, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippai, D.; Bala, S.; Catalano, D.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Micro-RNA-155 deficiency prevents alcohol-induced serum endotoxin increase and small bowel inflammation in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunagan, M.; Chaudhry, K.; Samak, G.; Rao, R.K. Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions in Caco-2 cell monolayers by a protein phosphatase 2A-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1356–G1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Chang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B. Effects of alcohol on intestinal epithelial barrier permeability and expression of tight junction-associated proteins. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Schnabl, B. Host-microbiome interactions in alcoholic liver disease. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Arrese, M.; Shah, V.H. Gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcohol-related liver disease: Current concepts and perspectives. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, S.I.; Wahlström, A.; Felin, J.; Jäntti, S.; Marschall, H.-U.; Bamberg, K.; Angelin, B.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Orešič, M.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Bile acid–microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Tarling, E.J.; Edwards, P.A. Pleiotropic roles of bile acids in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Krausz, K.W.; Shi, J.; Brocker, C.N.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.G.; Bisson, W.H. Intestine-selective farnesoid X receptor inhibition improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhardt, J.; Haider, R.S.; Sponholz, C.; Leonhardt, S.; Drube, J.; Spengler, K.; Mihaylov, D.; Neugebauer, S.; Kiehntopf, M.; Lambert, N.A. Circulating bile acids in liver failure activate TGR5 and induce monocyte dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatz, M.; Ciocan, D.; Merlen, G.; Rainteau, D.; Humbert, L.; Gomes-Rochette, N.; Hugot, C.; Trainel, N.; Mercier-Nomé, F.; Domenichini, S. Bile acid-receptor TGR5 deficiency worsens liver injury in alcohol-fed mice by inducing intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, Z.; Freedman, N.D.; Sampson, J.N.; Falk, R.T.; Koshiol, J.; Weinstein, S.J.; Albanes, D.; Sinha, R.; Loftfield, E. A prospective investigation of serum bile acids with risk of liver cancer, fatal liver disease, and biliary tract cancer. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, L.; Mei, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, P.; Liu, J.; Meng, C.; Li, R.; Zhong, R.; Wang, K. Vitamin C and vitamin D3 alleviate metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by regulating the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism via the gut-liver axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Baj, J.; Garruti, G.; Celano, G.; De Angelis, M.; Wang, H.H.; Di Palo, D.M.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P. Liver steatosis, gut-liver axis, microbiome and environmental factors. A never-ending bidirectional cross-talk. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumy, A.B.; Mulder, C.J.; Mol, J.J.; Tushuizen, M.E. Gut fermentation syndrome: A systematic review of case reports. UEG J. 2021, 9, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Lu, J.; Yan, C.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Xue, G. Fatty liver disease caused by high-alcohol-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 675–688.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, K.A.; Vivas, E.I.; Amador-Noguez, D.; Rey, F.E. Intestinal microbiota composition modulates choline bioavailability from diet and accumulation of the proatherogenic metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide. MBio 2015, 6, e02481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.W.; Wang, Z.; Kennedy, D.J.; Wu, Y.; Buffa, J.A.; Agatisa-Boyle, B.; Li, X.S.; Levison, B.S.; Hazen, S.L. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A.; Frank, D.; Harnke, B.; Bambha, K. Systematic review: Microbial dysbiosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Fan, J.-G. Microbial metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Rehman, A.; Dittrich, M.; Groen, A.K.; Hermanns, H.M.; Seyfried, F.; Beyersdorf, N.; Dandekar, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Geier, A. Fecal SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria in gut microbiome of human NAFLD as a putative link to systemic T-cell activation and advanced disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-Q.; An, Y.-X.; Yu, C.-G.; Ke, J.; Zhao, D.; Yu, K. The association between fecal short-chain fatty acids, gut microbiota, and visceral fat in monozygotic twin pairs. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2022, 15, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tripathi, M.; Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Gut microbiota and their metabolites in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatoma Res. 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, M.; Cabrera, D.; Kalergis, A.M.; Feldstein, A.E. Innate immunity and inflammation in NAFLD/NASH. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, X.; Hu, G.; He, F.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Fu, S. Phytic acid improves hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice by modulating the gut–liver axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11401–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Xu, C.; Yu, C.; Li, Y. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Progression of NAFLD to NASH. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2016, 6489012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G. Gut–liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Kuchay, M.S. Toll-like receptors and metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 185, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Tang, J.; Hou, Y.J.; Chang, Y.X.; Tu, Q.Q.; Feng, G.S. Nuclear factor high-mobility group box1 mediating the activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in hepatocytes in the early stage of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheril, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 signaling in obese NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Brinkmann, M.M.; Spooner, E.; Lee, C.C.; Kim, Y.-M.; Ploegh, H.L. Proteolytic cleavage in an endolysosomal compartment is required for activation of Toll-like receptor 9. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Inokuchi, S.; Schnabl, B.; Aoyama, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Olefsky, J.M.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of interleukin-1β in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 323–334.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; De Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebru, Y.A.; Gupta, H.; Kim, H.S.; Eom, J.A.; Kwon, G.H.; Park, E.; Jeong, J.-J.; Won, S.-M.; Sharma, S.P.; Ganesan, R. T Cell subsets and natural killer cells in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M. Targeting T Cell Subtypes for NAFLD and NAFLD-Related HCC Treatment: An Opinion. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 789859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Xue, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, K. Gut microbiome contributes to liver fibrosis impact on T cell receptor immune repertoire. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 571847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Dirchwolf, M.; Alvares-da-Silva, M.R.; Barrera, F.; Benítez, C.; Castellanos-Fernandez, M.; Castro-Narro, G.; Chavez-Tapia, N.; Chiodi, D.; Cotrim, H. Latin American Association for the study of the liver (ALEH) practice guidance for the diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Padovani, R.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Zenari, L.; Cigolini, M.; Falezza, G.; Arcaro, G. Relations between carotid artery wall thickness and liver histology in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracanzani, A.L.; Burdick, L.; Raselli, S.; Pedotti, P.; Grigore, L.; Santorelli, G.; Valenti, L.; Maraschi, A.; Catapano, A.; Fargion, S. Carotid artery intima-media thickness in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, P.; Ruffini, R.; Agnoletti, D.; Magnani, E.; Pagliarani, G.; Comandini, G.; Pratico, A.; Borghi, C.; Benetos, A.; Pazzi, P. Increased arterial stiffness in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Cardio-GOOSE study. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Shim, J.-Y.; Moon, B.-S.; Shin, Y.-H.; Jung, D.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, H.-R. The relationship between arterial stiffness and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanova, N.; Moscatiello, S.; Ramilli, S.; Bugianesi, E.; Magalotti, D.; Vanni, E.; Zoli, M.; Marchesini, G. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk profile in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 42, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assy, N.; Djibre, A.; Farah, R.; Grosovski, M.; Marmor, A. Presence of coronary plaques in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Radiology 2010, 254, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.S.; Wong, G.L.H.; Yeung, J.C.L.; Fung, C.Y.K.; Chan, J.K.L.; Chang, Z.H.Y.; Kwan, C.T.Y.; Lam, H.W.; Limquiaco, J.; Chim, A.M.L. Long-term clinical outcomes after fatty liver screening in patients undergoing coronary angiogram: A prospective cohort study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, Z. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.F.; Wang, Y.W.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Ding, Y.Z.; Liou, T.L.; Huang, S.S.; Lu, T.M.; Chan, W.L.; Lin, S.J. The association of the steatosis severity in fatty liver disease with coronary plaque pattern in general population. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchner, S.B.; Lu, M.T.; Mayrhofer, T.; Liu, T.; Pursnani, A.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Truong, Q.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Fleg, J.L.; Hoffmann, U. High-risk coronary plaque at coronary CT angiography is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, independent of coronary plaque and stenosis burden: Results from the ROMICAT II trial. Radiology 2015, 274, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Park, G.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, B.U.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Jung, S.W.; Du Jeong, I.; Bang, S.-J.; Shin, J.W. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis: An observational cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikat, R.; Nguyen, M.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and non-liver comorbidities. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, s86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perseghin, G.; Lattuada, G.; De Cobelli, F.; Esposito, A.; Belloni, E.; Ntali, G.; Ragogna, F.; Canu, T.; Scifo, P.; Del Maschio, A. Increased mediastinal fat and impaired left ventricular energy metabolism in young men with newly found fatty liver. Hepatology 2008, 47, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, F.M.; Martines, G.F.; Catalano, D.; Musumeci, G.; Pirri, C.; Trovato, G.M. Echocardiography and NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbusa, F.; Agnoletti, D.; Scala, L.; Grillo, C.; Arduini, P.; Bonapace, S.; Calabria, S.; Scaturro, G.; Mantovani, A.; Zoppini, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of all-cause mortality in elderly patients admitted for acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 265, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. NAFLD and increased risk of cardiovascular disease: Clinical associations, pathophysiological mechanisms and pharmacological implications. Gut 2020, 69, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Targher, G.; Bernardi, M.; Bonino, F.; Bugianesi, E.; Casini, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Marchesini, G.; Marra, F. AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Updates and future directions. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Mantovani, A.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Risk of cardiomyopathy and cardiac arrhythmias in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Pernigo, M.; Bergamini, C.; Bonapace, S.; Lipari, P.; Valbusa, F.; Bertolini, L.; Zenari, L.; Pichiri, I.; Dauriz, M. Heart valve calcification in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2015, 64, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Paolini, E.; Corsini, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Ruscica, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease diagnoses and cardiovascular diseases: From epidemiology to drug approaches. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Lonardo, A.; Bonapace, S.; Byrne, C.D.; Loria, P.; Targher, G. Risk of cardiovascular, cardiac and arrhythmic complications in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Valbusa, F.; Bonapace, S.; Bertolini, L.; Zenari, L.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Mantovani, W.; Barbieri, E.; Byrne, C.D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Rigolon, R.; Pichiri, I.; Bonapace, S.; Morani, G.; Zoppini, G.; Bonora, E.; Targher, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of heart block in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Dauriz, M.; Sandri, D.; Bonapace, S.; Zoppini, G.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of atrial fibrillation in adult individuals: An updated meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariou, B.; Byrne, C.D.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a metabolic disease in humans: A literature review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.S.; Tseng, P.H.; Tu, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Liao, W.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Chiu, H.M.; Lin, H.J.; Ho, Y.L.; Yang, W.S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with QT prolongation in the general population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Changes of intestinal bacterial microbiota in coronary heart disease complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadieienko, G.; Gridnyev, O.; Kurinna, O.; Chereliuk, N. Gut microbiota changes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and concomitant coronary artery disease. Vasa 2023, 65, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, R.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S. Alterations of gut microbiome and serum metabolome in coronary artery disease patients complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 805812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Changes and roles of intestinal fungal microbiota in coronary heart disease complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-C.; Zhao, G.-J.; Chen, Z.; She, Z.-G.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging driver of hypertension. Hypertension 2020, 75, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, W. Associations between polymorphisms of the ADIPOQ gene and hypertension risk: A systematic and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Saba, F.; Cassader, M.; Paschetta, E.; De Michieli, F.; Pinach, S.; Framarin, L.; Berrutti, M.; Leone, N.; Parente, R. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor rs5186 gene variant predicts incident NAFLD and associated hypertension: Role of dietary fat-induced pro-inflammatory cell activation. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2019, 114, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-O.; Li, H.-L.; Tsoi, M.-F.; Cheung, C.-L.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Association between the liver fat score (LFS) and cardiovascular diseases in the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999–2016. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazac, G.-D.; Lăcătușu, C.-M.; Mihai, C.; Grigorescu, E.-D.; Onofriescu, A.; Mihai, B.-M. New insights into non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease: The liver-heart axis. Life 2022, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.M.; Van Der Graaff, D.; Kwanten, W.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiological mechanisms and implications. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.S.; Zhang, H.; Cheung, C.Y.; Xu, M.; Ho, J.C.; Zhou, W.; Cherny, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Holmen, O.; Au, K.-W. Exome-wide association analysis reveals novel coding sequence variants associated with lipid traits in Chinese. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-L.; Sui, J.-Q.; Lu, L.-L.; Zhang, N.-N.; Xu, X.; Dong, Q.-Y.; Xin, Y.-N.; Xuan, S.-Y. Gene polymorphisms associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease: A concise review. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Otgonsuren, M.; Younoszai, Z.; Allawi, H.; Raybuck, B.; Younossi, Z. Circulating miRNA in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2016, 3, e000096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jichitu, A.; Bungau, S.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Vesa, C.M.; Toma, M.M.; Bustea, C.; Iurciuc, S.; Rus, M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Diaconu, C.C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular comorbidities: Pathophysiological links, diagnosis, and therapeutic management. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kuetting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.-M. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: A clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Meschiari, E.; Baldelli, E.; Musumeci, F.E.; Romagnoli, D.; Trenti, T.; Zennaro, R.G.; Lonardo, A.; Loria, P. Relationship of serum fetuin-A levels with coronary atherosclerotic burden and NAFLD in patients undergoing elective coronary angiography. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2013, 11, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; An, B.; Jiang, M.; Xin, Y.; Xuan, S. Association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e26818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Trejo, M.E.P.; McClelland, R.; Bradley, R.; Blaha, M.J.; Zeb, I.; Corey, K.E.; Budoff, M.J.; Chung, R.T. Circulating Interleukin-6 is a biomarker for coronary atherosclerosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 259, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, E.H.; Lee, W.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, D.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with coronary artery calcification. Hepatology 2012, 56, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meex, R.C.; Watt, M.J. Hepatokines: Linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, K.P.; de Oliveira, A.A.; Mowry, F.E.; Biancardi, V.C. Targeting toll-like receptor 4 signalling pathways: Can therapeutics pay the toll for hypertension? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1864–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Vordoni, A.; Nakas, N.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Endothelial dysfunction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Life 2022, 12, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Androutsakos, T.; Flessa, C.-M.; Kyrou, I.; Siasos, G.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A concise review. Cells 2022, 11, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hadi, H.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Relationship between heart disease and liver disease: A two-way street. Cells 2020, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magtanong, L.; Ko, P.; Dixon, S. Emerging roles for lipids in non-apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikura, T.; Imajo, K.; Ozaki, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Honda, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Kirikoshi, H. Coronary artery disease is more severe in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis than fatty liver. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.-X.; Zhang, H.-W.; Jin, J.-L.; Liu, H.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.-X.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.-L.; Zhu, C.-G.; Hua, Q. Prognostic utility of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein-related markers in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Caputi, A. JNKs, insulin resistance and inflammation: A possible link between NAFLD and coronary artery disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2011, 17, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebato, C.; Uchida, T.; Arakawa, M.; Komatsu, M.; Ueno, T.; Komiya, K.; Azuma, K.; Hirose, T.; Tanaka, K.; Kominami, E. Autophagy is important in islet homeostasis and compensatory increase of beta cell mass in response to high-fat diet. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, S.; Kitamura, T. Clonal hematopoiesis and associated diseases: A review of recent findings. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busque, L.; Patel, J.P.; Figueroa, M.E.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Provost, S.; Hamilou, Z.; Mollica, L.; Li, J.; Viale, A.; Heguy, A. Recurrent somatic TET2 mutations in normal elderly individuals with clonal hematopoiesis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Natarajan, P.; Silver, A.J.; Gibson, C.J.; Bick, A.G.; Shvartz, E.; McConkey, M.; Gupta, N.; Gabriel, S.; Ardissino, D. Clonal hematopoiesis and risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.J.; Emdin, C.; Bick, A.G.; Zekavat, S.M.; Niroula, A.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Dichtel, L.; Griffin, G.; Uddin, M.M.; Gibson, C.J. Clonal haematopoiesis and risk of chronic liver disease. Nature 2023, 616, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; He, J.; Gao, N.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, J. Probiotics may delay the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by restoring the gut microbiota structure and improving intestinal endotoxemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in non-alcoholic fat liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Duan, K.; Wang, C.; McClain, C.; Feng, W. Probiotics and alcoholic liver disease: Treatment and potential mechanisms. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 5491465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Harsch, I.A.; Konturek, K.; Schink, M.; Konturek, T.; Neurath, M.F.; Zopf, Y. Gut–liver axis: How do gut bacteria influence the liver? Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Gao, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, Z.; Mao, G.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z. The effects of supplementation of probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1024678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashimada, M.; Honda, M. Effect of microbiome on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the role of probiotics, prebiotics, and biogenics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrello, C.; Garavaglia, F.; Cribiù, F.M.; Ercoli, G.; Lopez, G.; Troisi, J.; Colucci, A.; Guglietta, S.; Carloni, S.; Guglielmetti, S. Therapeutic faecal microbiota transplantation controls intestinal inflammation through IL10 secretion by immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, L.; Rahman, A.; Parvathy, S.N.; Beaton, M.; Silverman, J.; Qumosani, K.; Hramiak, I.; Hegele, R.; Joy, T.; Meddings, J. Allogenic fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease improves abnormal small intestinal permeability: A randomized control trial. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2020, 115, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, A.; Paik, J.M.; Austin, P.; Eberly, K.E.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, I.; Henry, L.; Gerber, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Vigorous physical activity provides protection against all-cause deaths among adults patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 57, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging driving force in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Gossios, T.D.; Griva, T.; Anagnostis, P.; Kargiotis, K.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Theocharidou, E.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Safety and efficacy of long-term statin treatment for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease and abnormal liver tests in the Greek Atorvastatin and Coronary Heart Disease Evaluation (GREACE) Study: A post-hoc analysis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Wong, R.J.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease review: Diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, E.; Charbonnel, B.; Wilcox, R.G.; Skene, A.M.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Yates, J.; Tan, M.; Spanheimer, R.; Standl, E.; Dormandy, J.A. Pioglitazone use and heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes and preexisting cardiovascular disease: Data from the PROactive study (PROactive 08). Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Meer, R.W.; Rijzewijk, L.J.; de Jong, H.W.; Lamb, H.J.; Lubberink, M.; Romijn, J.A.; Bax, J.J.; de Roos, A.; Kamp, O.; Paulus, W.J. Pioglitazone improves cardiac function and alters myocardial substrate metabolism without affecting cardiac triglyceride accumulation and high-energy phosphate metabolism in patients with well-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2009, 119, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Desai, A.P.; Gawrieh, S.; Ghabril, M.; Saxena, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Chalasani, N. Long-term metformin use may improve clinical outcomes in diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederseer, D.; Wernly, B.; Aigner, E.; Stickel, F.; Datz, C. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: Epidemiological, mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprince, A.; Haas, J.T.; Staels, B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A. Beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on fatty liver in type 2 diabetes: A common comorbidity associated with severe complications. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maejima, Y. SGLT2 inhibitors play a salutary role in heart failure via modulation of the mitochondrial function. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, N.; Husain, M.; Lehrke, M.; Verma, S.; Sattar, N. GLP-1 receptor agonists for the reduction of atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Circulation 2022, 146, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.; Pratley, R.E. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, P.B.; Welty, F.K.; Miller, M.; Chait, A.; Hammond, G.; Ahmad, Z.; Cohen, D.E.; Horton, J.D.; Pressman, G.S.; Toth, P.P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, e168–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Li, L. Clinical application of angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Henson, J.; Osganian, S.; Masia, R.; Chan, A.T.; Chung, R.T.; Corey, K.E. Daily aspirin use associated with reduced risk for fibrosis progression in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2776–2784.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Jeon, M.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.-H.; Kim, S.U. Influence of hepatic steatosis on the outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir and tenofovir. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, P.R.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, B.-Y.; Do Mun, K.; Park, J.G.; Kang, M.W.; Hur, W.; Han, J.W.; Nam, H.; Yoon, S.K. Tenofovir alafenamide alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice by blocking the phosphorylation of AKT in intrahepatic mononuclear phagocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Song, M. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Gut–Liver–Heart Crosstalk. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183970
Yang K, Song M. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Gut–Liver–Heart Crosstalk. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183970
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Keungmo, and Myeongjun Song. 2023. "New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Gut–Liver–Heart Crosstalk" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183970
APA StyleYang, K., & Song, M. (2023). New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Gut–Liver–Heart Crosstalk. Nutrients, 15(18), 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183970





