Ghrelin as a Biomarker of “Immunometabolic Depression” and Its Connection with Dysbiosis
Abstract
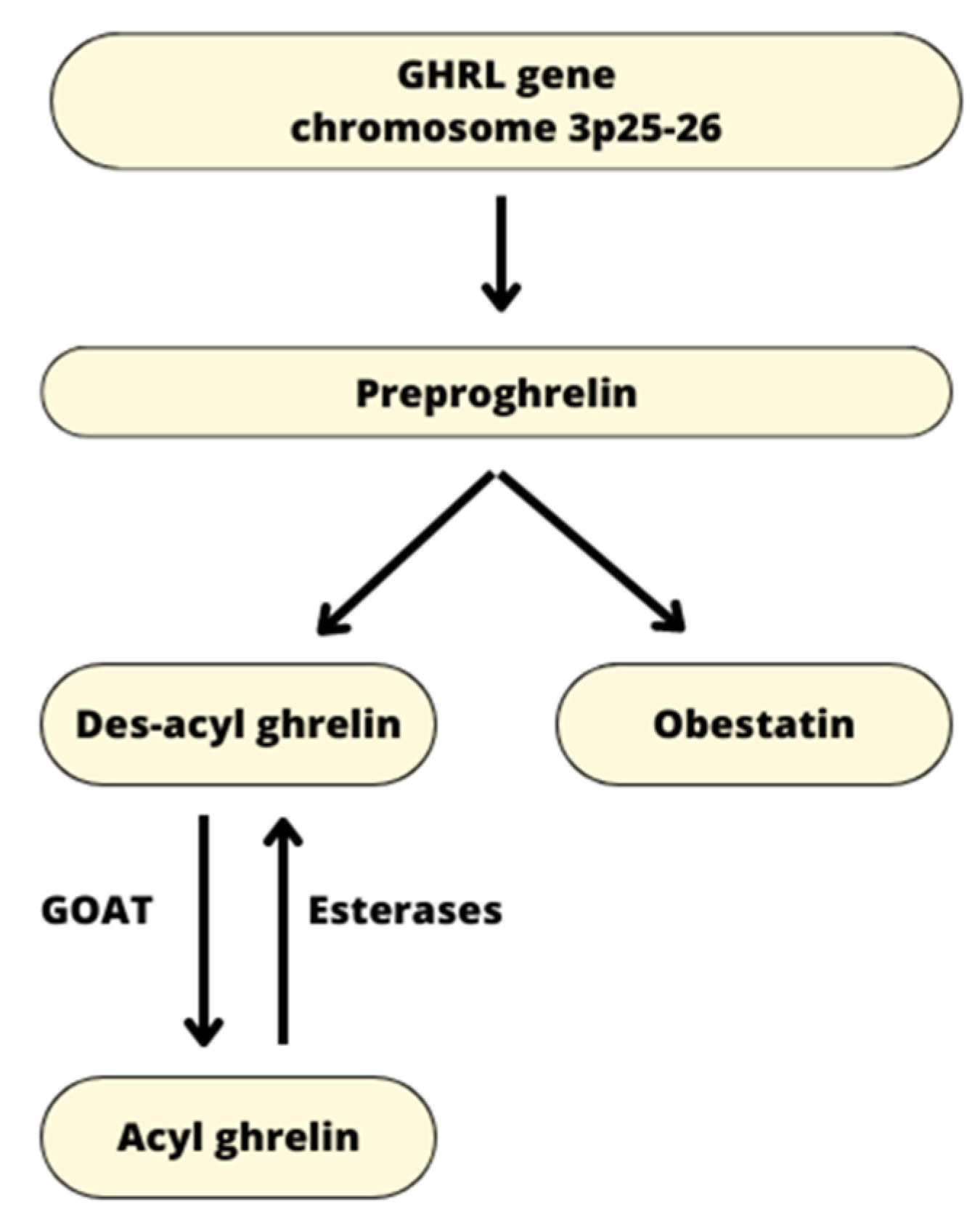
1. Ghrelin Characteristics
1.1. Origin of Ghrelin
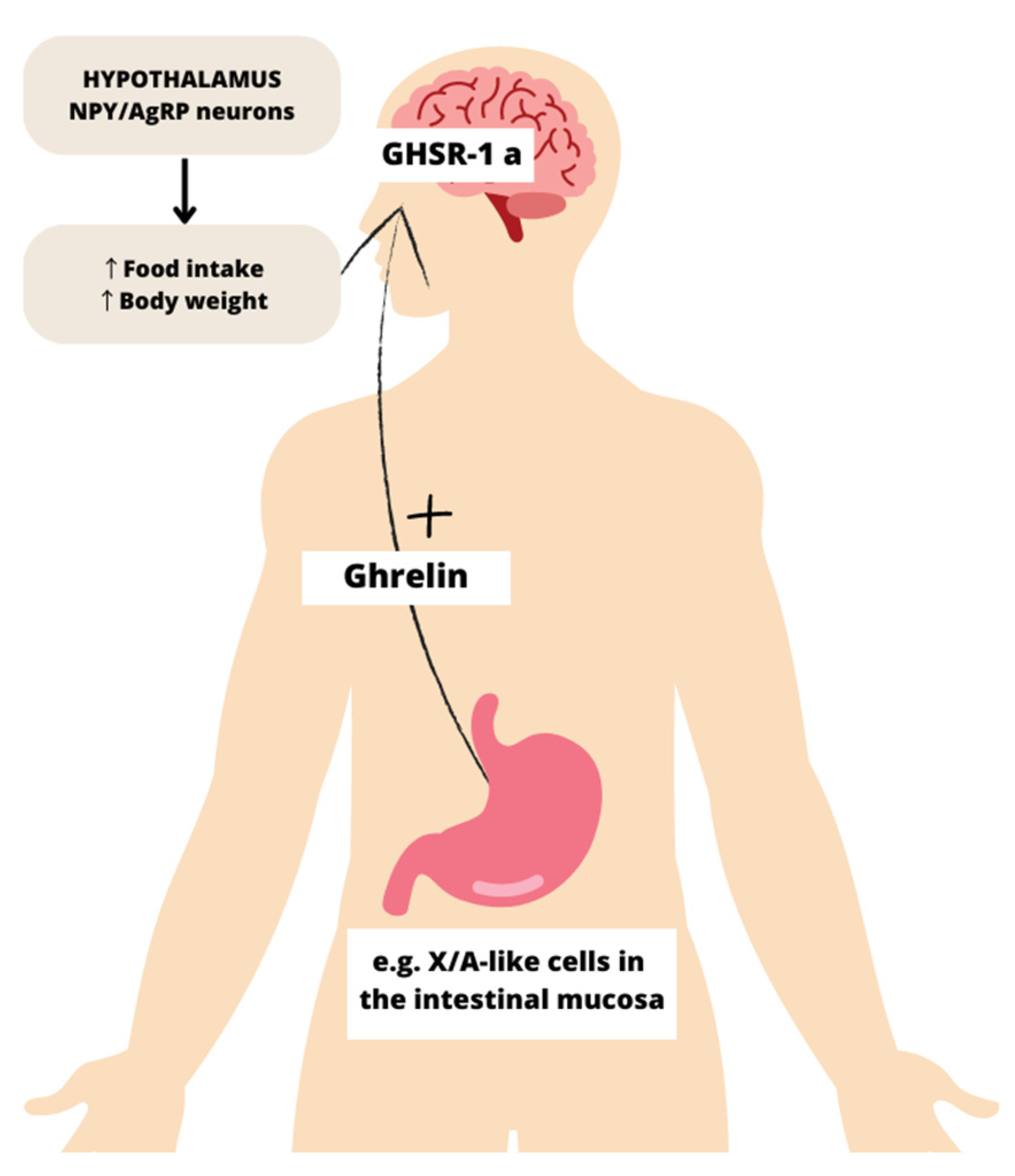
1.2. Functions of Ghrelin
1.3. Regulation of Circulating Ghrelin
2. Immunometabolic Depression
3. Ghrelin and Its Link to Immunometabolic Depression
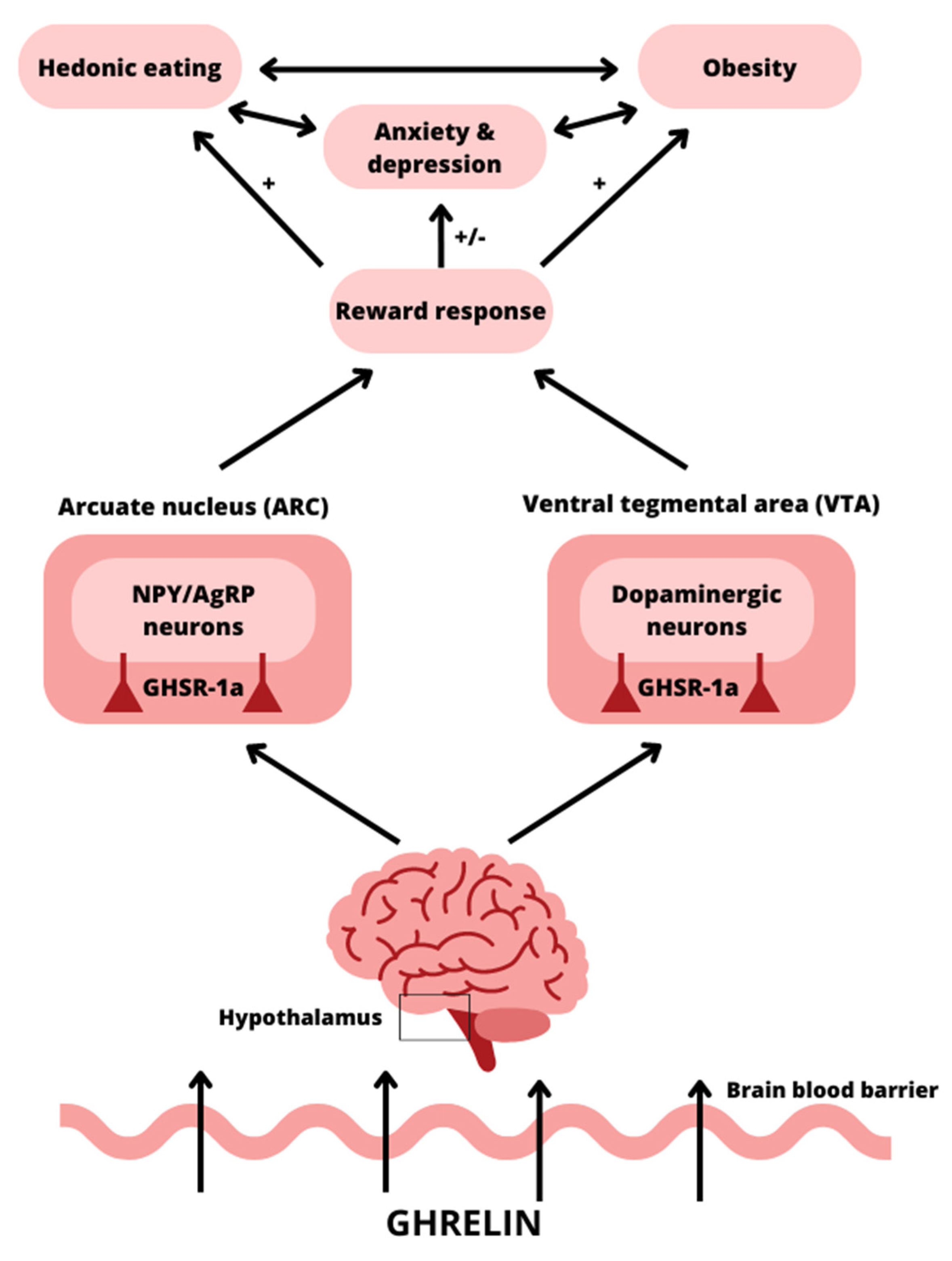
3.1. Ghrelin and Its Impact on the Brain
3.2. Ghrelin Gene Polymorphism in Psychiatric Disorders and Obesity
3.3. Ghrelin Levels in Psychiatric Diseases
3.4. Ghrelin Levels in Obesity
3.5. Possible Mechanisms Linking Ghrelin to Psychiatric Disorders
3.6. Possible Mechanisms Linking Ghrelin to Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
4. Ghrelin, and the Microbiota and Its Link to Immunometabolic Depression
4.1. Ghrelin Levels, and the Composition of Gut Microbiota and Its Link to “Metabolic Depression”
4.2. Microbiota Metabolites and Ghrelin Connection
5. Ghrelin-Related Factors in Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Immunometabolic Depression
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Is a Growth-Hormone-Releasing Acylated Peptide from Stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Nogueiras, R.; Andermann, M.L.; Andrews, Z.B.; Anker, S.D.; Argente, J.; Batterham, R.L.; Benoit, S.C.; Bowers, C.Y.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y.; Mifune, H.; Kojima, M. Ghrelin Acylation by Ingestion of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 514, pp. 303–315. [Google Scholar]
- Sassi, M.; Morgan, A.H.; Davies, J.S. Ghrelin Acylation—A Post-Translational Tuning Mechanism Regulating Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the Acyltransferase That Octanoylates Ghrelin, an Appetite-Stimulating Peptide Hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shiimura, Y.; Ohgusu, H.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M. Structure, Regulation and Function of Ghrelin. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, K.M.; Chaudhary, N.; Müller, T.D.; Kirchner, H.; Habegger, K.M.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; DiMarchi, R.; Hofmann, S.M.; Woods, S.C.; et al. Acylation Type Determines Ghrelin’s Effects on Energy Homeostasis in Rodents. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4687–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Effect of Ghrelin on Glucose-Insulin Homeostasis: Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Pept. 2010, 2010, 234709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, N.J.; Skinner, V.O.; Tan, T.M.M.; Ramesh, B.S.; Byrne, D.J.; MacColl, G.S.; Keen, J.N.; Bouloux, P.M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Bruckdorfer, K.R.; et al. Ghrelin Can Bind to a Species of High Density Lipoprotein Associated with Paraoxonase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8877–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhanty, P.J.D.; Neggers, S.J.; Van Der Lely, A.J. Ghrelin: The Differences between Acyl- and Des-Acyl Ghrelin. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Dave, N.; Mugundu, G.M.; Davis, H.W.; Gaylinn, B.D.; Thorner, M.O.; Tschöp, M.H.; D’Alessio, D.; Desai, P.B. The Pharmacokinetics of Acyl, Des-Acyl, and Total Ghrelin in Healthy Human Subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 168, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhanty, P.J.; Neggers, S.J.; Van Der Lely, A.J. Des-Acyl Ghrelin: A Metabolically Active Peptide. Endocr. Dev. 2013, 25, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filigheddu, N.; Gnocchi, V.F.; Coscia, M.; Cappelli, M.; Porporato, P.E.; Taulli, R.; Traini, S.; Baldanzi, G.; Chianale, F.; Cutrupi, S.; et al. Ghrelin and Des-Acyl Ghrelin Promote Differentiation and Fusion of C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Ke, Z. Acylated and Unacylated Ghrelin Inhibit Atrophy in Myotubes Co-Cultured with Colon Carcinoma Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72872–72885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, C.S.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Kim, D.M.; Balderas, M.; Wu, G.; Lawler, J.; Safe, S.; Guo, S.; Devaraj, S.; et al. Protective Effects of Ghrelin on Fasting-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Aging Mice. J. Gerontol.-Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, P.V.; Iglesias, M.J.; Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Rodríguez-Penas, D.; Mosquera-Leal, A.; García-Rúa, V.; Gualillo, O.; Ghè, C.; Arnoletti, E.; Muccioli, G.; et al. Des-Acyl Ghrelin Has Specific Binding Sites and Different Metabolic Effects from Ghrelin in Cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3286–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chai, B.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Mulholland, M.W. Effect of Des-Acyl Ghrelin on Adiposity and Glucose Metabolism. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 4710–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howick, K.; Griffin, B.T.; Cryan, J.F.; Schellekens, H. From Belly to Brain: Targeting the Ghrelin Receptor in Appetite and Food Intake Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Guia, R.M.; Hassing, A.S.; Skov, L.J.; Ratner, C.; Plucińska, K.; Madsen, S.; Diep, T.A.; Dela Cruz, G.V.; Trammell, S.A.J.; Sustarsic, E.G.; et al. Fasting- and Ghrelin-Induced Food Intake Is Regulated by NAMPT in the Hypothalamus. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, M.; Zigman, J.M. The Role of Ghrelin in Reward-Based Eating. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Mannea, E.; Aimé, P.; Pfluger, P.T.; Yi, C.X.; Castaneda, T.R.; Davis, H.W.; Ren, X.; Pixley, S.; Benoit, S.; et al. Ghrelin Enhances Olfactory Sensitivity and Exploratory Sniffing in Rodents and Humans. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5841–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, N.; Hölscher, C. Beyond Appetite: Acylated Ghrelin as a Learning, Memory and Fear Behavior-Modulating Hormone. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, V.; Hozer, F.; Costemale-Lacoste, J.F. The Effects of Ghrelin on Sleep, Appetite, and Memory, and Its Possible Role in Depression: A Review of the Literature. Encephale 2018, 44, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewiński, A.; Karbownik-Lewińska, M.; Wieczorek-Szukała, K.; Stasiak, M.; Stawerska, R. Contribution of Ghrelin to the Pathogenesis of Growth Hormone Deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecori Giraldi, F.; Bucciarelli, L.G.; Saccani, A.; Scacchi, M.; Pesce, S.; Losa, M.; Cavagnini, F. Ghrelin Stimulates Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH) Secretion by Human ACTH-Secreting Pituitary Adenomas in Vitro. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2007, 19, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, E.; Lambert, G.; Ika-Sari, C.; Dawood, T.; Lee, K.; Chopra, R.; Straznicky, N.; Eikelis, N.; Drew, S.; Tilbrook, A.; et al. Ghrelin Modulates Sympathetic Nervous System Activity and Stress Response in Lean and Overweight Men. Hypertension 2011, 58, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin: Much More than a Hunger Hormone. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, A.; Shcherbina, L.; Prasad, R.B.; Miskelly, M.G.; Abels, M.; Martínez-Lopéz, J.A.; Fred, R.G.; Nergård, B.J.; Hedenbro, J.; Groop, L.; et al. Ghrelin Suppresses Insulin Secretion in Human Islets and Type 2 Diabetes Patients Have Diminished Islet Ghrelin Cell Number and Lower Plasma Ghrelin Levels. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 511, 110835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauna, C.; Meyler, F.M.; Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Delhanty, P.J.D.; Abribat, T.; Van Koetsveld, P.; Hofland, L.J.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; Van Der Lely, A.J. Administration of Acylated Ghrelin Reduces Insulin Sensitivity, Whereas the Combination of Acylated plus Unacylated Ghrelin Strongly Improves Insulin Sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poher, A.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Müller, T.D. Ghrelin Regulation of Glucose Metabolism. Peptides 2018, 100, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlebowicz, J.; Lindstedt, S.; Björgell, O.; Dencker, M. The Effect of Endogenously Released Glucose, Insulin, Glucagon-like Peptide 1, Ghrelin on Cardiac Output, Heart Rate, Stroke Volume, and Blood Pressure. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2011, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.; van den Heuvel, R. Ghrelin Improves Cardiac Output in HFrEF. In Proceedings of the HFA 2022, Madrid, Spain, 21–24 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, M.; Rizvi, A.; Sudar, E.; Soskic, S.; Obradovic, M.; Montalto, G.; Boutjdir, M.; Mikhailidis, D.; Isenovic, E. A Review of the Cardiovascular and Anti-Atherogenic Effects of Ghrelin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 4953–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollstein, T.; Basolo, A.; Unlu, Y.; Ando, T.; Walter, M.; Krakoff, J.; Piaggi, P. Effects of Short-Term Fasting on Ghrelin/GH/IGF-1 Axis in Healthy Humans: The Role of Ghrelin in the Thrifty Phenotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3769–e3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, F.; Edholm, T.; Schmidt, P.T.; Grybäck, P.; Jacobsson, H.; Degerblad, M.; Höybye, C.; Holst, J.J.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Hellström, P.M.; et al. Ghrelin Stimulates Gastric Emptying and Hunger in Normal-Weight Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Inomata, N.; Ohnuma, N.; Tanaka, S.; Itoh, Z.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Stimulates Gastric Acid Secretion and Motility in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, T.; Kaiya, H. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Motility by Motilin and Ghrelin in Vertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, H.; Yin, Y.; Xiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Mulholland, M.; et al. Ghrelin Promotes Hepatic Lipogenesis by Activation of MTOR-PPARγ Signaling Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13163–13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Yu, L. Potential Role of Ghrelin in the Regulation of Inflammation. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiguchi, S.; Takata, A.; Murakami, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Yanagimoto, Y.; Kurokawa, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Clinical Application of Ghrelin Administration for Gastric Cancer Patients Undergoing Gastrectomy. Gastric Cancer 2014, 17, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, A.M.; Horgan, G.W.; Murison, S.D.; Bremner, D.M.; Lobley, G.E. Effects of a High-Protein Ketogenic Diet on Hunger, Appetite, and Weight Loss in Obese Men Feeding Ad Libitum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Jue, Y. Acute Effects of High-Protein versus Normal-Protein Isocaloric Meals on Satiety and Ghrelin. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, B.K.; Shankar, K.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin’s Relationship to Blood Glucose. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.S.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.M.; Yuan, J.H.; Wang, B.; Dong, J. The Correlation between Circulating Ghrelin and Insulin Resistance in Obesity: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, Y.; Toshinai, K.; Koda, S.; Miyazato, M.; Shimbara, T.; Tsuruta, T.; Niijima, A.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Peripheral Interaction of Ghrelin with Cholecystokinin on Feeding Regulation. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Waise, T.M.Z.; Toshinai, K.; Tsuchimochi, W.; Naznin, F.; Islam, M.N.; Tanida, R.; Sakoda, H.; Nakazato, M. Functional Interaction between Ghrelin and GLP-1 Regulates Feeding through the Vagal Afferent System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Singh, S. Role of Somatostatin in the Regulation of Central and Peripheral Factors of Satiety and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.L.; Cummings, D.E.; Grill, H.J.; Kaplan, J.M. Meal-Related Ghrelin Suppression Requires Postgastric Feedback. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2765–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancampfort, D.; Correll, C.U.; Wampers, M.; Sienaert, P.; Mitchell, A.J.; De Herdt, A.; Probst, M.; Scheewe, T.W.; De Hert, M. Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Abnormalities in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Prevalences and Moderating Variables. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, L.; Luppino, F.; van Straten, A.; Penninx, B.; Zitman, F.; Cuijpers, P. Depression and Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Community-Based Studies. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 178, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Simmons, W.K.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; Penninx, B.W. Depression and Obesity: Evidence of Shared Biological Mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.S.; Salagre, E.; Enduru, N.; Grande, I.; Vieta, E.; Zhao, Z. Insulin Resistance in Depression: A Large Meta-Analysis of Metabolic Parameters and Variation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.; Silva, N.; Golden, S.H.; Rajala, U.; Timonen, M.; Stahl, D.; Ismail, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Depression and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, F.; Milaneschi, Y.; De Jonge, P.; Giltay, E.J.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers: Associations with Individual Depressive Symptoms. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Guo, L. Swimming Intervention Alleviates Insulin Resistance and Chronic Inflammation in Metabolic Syndrome. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 17, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Gozashti, M.H.; Aghadavood, M.; Mehdizadeh, M.R.; Hayatbakhsh, M.M. Clinical Significance of Serum IL-6 and TNF-α Levels in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Reports Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 6, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, N.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Y.; He, H. Altered Serum Levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-18 in Depressive Disorder Patients. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 32, e2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Emon, M.P.Z.; Shahriar, M.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, S.N.; Islam, M.R. Higher Levels of Serum IL-1β and TNF-α Are Associated with an Increased Probability of Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 295, 113568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.A.; Mohammad, D.; Qureshi, M.F.H.; Abbas, M.Z.; Aleem, S. Prevalence, Psychological Responses and Associated Correlates of Depression, Anxiety and Stress in a Global Population, During the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Community Ment. Health J. 2021, 57, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, T.F.; Glaser, R.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Out of Balance: A New Look at Chronic Stress, Depression, and Immunity. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 14, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtyes, E.; Keaton, S.A.; Smart, L.A.; Burmeister, A.R.; Heilman, P.L.; Krzyzanowski, S.; Nagalla, M.; Guillemin, G.J.; Escobar Galvis, M.L.; Lim, C.K.; et al. Inflammation and Kynurenine Pathway Dysregulation in Post-Partum Women with Severe and Suicidal Depression. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 83, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Buttenschøn, H.N.; Tansey, K.E.; Maier, W.; Hauser, J.; Dernovsek, M.Z.; Henigsberg, N.; Souery, D.; Farmer, A.; Rietschel, M.; et al. Association between C-Reactive Protein (CRP) with Depression Symptom Severity and Specific Depressive Symptoms in Major Depression. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redwine, L.S.; Pung, M.A.; Wilson, K.; Bangen, K.J.; Delano-Wood, L.; Hurwitz, B. An Exploratory Randomized Sub-Study of Light-to-Moderate Intensity Exercise on Cognitive Function, Depression Symptoms and Inflammation in Older Adults with Heart Failure. J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 128, 109883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, A.A.; Deuster, P.A.; Francis, J.L.; Bonsall, R.W.; Tracy, R.P.; Kop, W.J. Neurohormonal and Inflammatory Hyper-Responsiveness to Acute Mental Stress in Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 84, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remla, N.; Hadjidj, Z.; Ghezzaz, K.; Moulessehoul, S.; Aribi, M. Increased Gustatory Response Score in Obesity and Association Levels with IL-6 and Leptin. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 2016, 7924052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alzamil, H. Elevated Serum TNF- α Is Related to Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Is Associated with Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance. J. Obes. 2020, 2020, 5076858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Yu, R. Relationship of Obesity and Visceral Adiposity with Serum Concentrations of CRP, TNF-α and IL-6. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 69, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandipati, K.C.; Subramanian, S.; Agrawal, D.K. Protein Kinases: Mechanisms and Downstream Targets in Inflammation-Mediated Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 426, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, V.; Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H. Inflammation, Cytokines and Insulin Resistance: A Clinical Perspective. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2013, 61, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.T.; Simard, J.F.; Henderson, V.W.; Nutkiewicz, L.; Lamers, F.; Nasca, C.; Rasgon, N.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Incident Major Depressive Disorder Predicted by Three Measures of Insulin Resistance: A Dutch Cohort Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2021, 178, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Kader, S.M.; Saiem Al-Dahr, M.H. Impact of Weight Loss on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Afr. Health Sci. 2016, 16, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Capuron, L.; Poitou, C.; MacHaux-Tholliez, D.; Frochot, V.; Bouillot, J.L.; Basdevant, A.; Layà, S.; Clément, K. Relationship between Adiposity, Emotional Status and Eating Behaviour in Obese Women: Role of Inflammation. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Tschöp, M.; Robinson, S.M.; Heiman, M.L. Extent and Direction of Ghrelin Transport across the Blood-Brain Barrier Is Determined by Its Unique Primary Structure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A Role for Ghrelin in the Central Regulation of Feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; McGlone, F.; Bedrossian, D.; Dagher, A. Ghrelin Modulates Brain Activity in Areas That Control Appetitive Behavior. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.P.; Ghersi, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; de Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin and Memory: Differential Effects on Acquisition and Retrieval. Peptides 2010, 31, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, J.R.W.; Skibicka, K.P.; Leng, G.; Dickson, S.L. Ghrelin, Reward and Motivation. Endocr. Dev. 2013, 25, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.C.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin’s Roles in Stress, Mood, and Anxiety Regulation. Int. J. Pept. 2010, 2010, 460549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.; Kim, H.G.; Hwang, L.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Chung, H.; Oh, M.S.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Ghrelin in the 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6- Tetrahydropyridine Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease by Blocking Microglial Activation. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, N.; Hölscher, C. Acylated Ghrelin as a Multi-Targeted Therapy for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 614828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.A.; Pijl, H.; Frölich, M.; Schröder-Van Der Elst, J.P.; Van Der Bent, C.; Roelfsema, F.; Roos, R.A.C. Growth Hormone and Ghrelin Secretion Are Associated with Clinical Severity in Huntington’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, G.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Anxiety, Depression, and the Microbiome: A Role for Gut Peptides. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, L.A.; Harmatz, E.S.; Goosens, K.A. Ghrelin as a Stress Hormone: Implications for Psychiatric Illness. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 88, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Akiyoshi, J.; Hatano, K.; Hanada, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsuru, J.; Matsushita, H.; Kodama, K.; Isogawa, K. Ghrelin Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with Depression, but Not Panic Disorder. Psychiatr. Genet. 2008, 18, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, C.; Annerbrink, K.; Nilsson, S.; Bah, J.; Olsson, M.; Allgulander, C.; Andersch, S.; Sjödin, I.; Eriksson, E.; Dickson, S.L. A Possible Association between Panic Disorder and a Polymorphism in the Preproghrelingene. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 206, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llamas-Covarrubias, I.M.; Llamas-Covarrubias, M.A.; Martinez-López, E.; Zepeda-Carrillo, E.A.; Rivera-León, E.A.; Palmeros-Sánchez, B.; Alcalá-Zermeño, J.L.; Sánchez-Enríquez, S. Association of A-604G Ghrelin Gene Polymorphism and Serum Ghrelin Levels with the Risk of Obesity in a Mexican Population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 44, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsoy, S.; Besirli, A.; Abdulrezzak, U.; Basturk, M. Serum Ghrelin and Leptin Levels in Patients with Depression and the Effects of Treatment. Psychiatry Investig. 2014, 11, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algul, S.; Ozcelik, O. Evaluating the Levels of Nesfatin-1 and Ghrelin Hormones in Patients with Moderate and Severe Major Depressive Disorders. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçel, Ö.K.; Akbaş, S.; Bilgici, B. Increased Ghrelin Levels and Unchanged Adipocytokine Levels in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atescelik, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Korkmaz, S.; Goktekin, M.C.; Gurger, M.; Ilhan, N. The Relationship between Ghrelin and Copeptin Levels, and Anxiety and Depression Levels in Suicide Attempts. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, M.; Schüssler, P.; Schmid, D.; Uhr, M.; Kleyer, S.; Yassouridis, A.; Steiger, A. Ghrelin Plasma Levels Are Not Altered in Major Depression. Neuropsychobiology 2009, 59, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barim, A.O.; Aydin, S.; Colak, R.; Dag, E.; Deniz, O.; Sahin, I. Ghrelin, Paraoxonase and Arylesterase Levels in Depressive Patients before and after Citalopram Treatment. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Kaga, T.; Yuzuriha, H.; Nagata, T.; Fujimiya, M.; Katsuura, G.; Makino, S.; Fujino, M.A.; Kasuga, M. A Role of Ghrelin in Neuroendocrine and Behavioral Responses to Stress in Mice. Neuroendocrinology 2001, 74, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristenssson, E.; Sundqvist, M.; Astin, M.; Kjerling, M.; Mattsson, H.; Dornonville de la Cour, C.; Håkanson, R.; Lindström, E. Acute Psychological Stress Raises Plasma Ghrelin in the Rat. Regul. Pept. 2006, 134, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutter, M.; Sakata, I.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Rovinsky, S.A.; Anderson, J.G.; Jung, S.; Birnbaum, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. The Orexigenic Hormone Ghrelin Defends against Depressive Symptoms of Chronic Stress. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousufzai, M.I.U.A.; Harmatz, E.S.; Shah, M.; Malik, M.O.; Goosens, K.A. Ghrelin Is a Persistent Biomarker for Chronic Stress Exposure in Adolescent Rats and Humans. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, V.P.; MacHado, D.G.; Buteler, F.; Ghersi, M.; Ponzio, M.F.; Martini, A.C.; Schiöth, H.B.; De Cuneo, M.F.; Rodrigues, A.L.S.; De Barioglio, S.R. Acute Ghrelin Administration Reverses Depressive-like Behavior Induced by Bilateral Olfactory Bulbectomy in Mice. Peptides 2012, 35, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, C.; Haage, D.; Taube, M.; Egecioglu, E.; Salomé, N.; Dickson, S.L. Central Administration of Ghrelin Alters Emotional Responses in Rats: Behavioural, Electrophysiological and Molecular Evidence. Neuroscience 2011, 180, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.P.; Monzón, M.E.; Varas, M.M.; Cragnolini, A.B.; Schiöth, H.B.; Scimonelli, T.N.; De Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Memory Retention in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.M.; Ostrowski, T.D.; Middlemas, D.S. Intra Cerebro Ventricular Ghrelin Administration Increases Depressive-like Behavior in Male Juvenile Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, M.A.; Holst, B. The Complex Signaling Pathways of the Ghrelin Receptor. Endocrinology 2021, 161, bqaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.; Abizaid, A. Driving the Need to Feed: Insight into the Collaborative Interaction between Ghrelin and Endocannabinoid Systems in Modulating Brain Reward Systems. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 66, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, L.; Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Michelotto, B.; Di Nisio, C.; Vacca, M. Effects of Ghrelin and Amylin on Dopamine, Norepinephrine and Serotonin Release in the Hypothalamus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 454, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, C.; Duman, R.S. Stress, Depression, and Neuroplasticity: A Convergence of Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Nie, Z.; Shu, H.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, H. The Role of BDNF on Neural Plasticity in Depression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Lopes, M.; Fregni, F. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies on Major Depression and BDNF Levels: Implications for the Role of Neuroplasticity in Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandolini, G.M.; Lazzaretti, M.; Delvecchio, G.; Bressi, C.; Soares, J.C.; Brambilla, P. Association between Serum BDNF Levels and Maternal Perinatal Depression: A Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 261, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Bagnardi, V.; Zanardini, R.; Molteni, R.; Gabriela Nielsen, M.; Placentino, A.; Giovannini, C.; Rillosi, L.; Ventriglia, M.; Riva, M.A.; et al. Serum and Plasma BDNF Levels in Major Depression: A Replication Study and Meta-Analyses. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 11, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea Vega, M.L.; Sanchez, M.S.; Fernández, G.; Paglini, M.G.; Martin, M.; de Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin Treatment Leads to Dendritic Spine Remodeling in Hippocampal Neurons and Increases the Expression of Specific BDNF-MRNA Species. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2021, 179, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haqq, A.M.; Sadaf Farooqi, I.; O’Rahilly, S.; Stadler, D.D.; Rosenfeld, R.G.; Pratt, K.L.; LaFranchi, S.H.; Purnell, J.Q. Serum Ghrelin Levels Are Inversely Correlated with Body Mass Index, Age, and Insulin Concentrations in Normal Children and Are Markedly Increased in Prader-Willi Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, V.; Carlson, J.J.; Hunt, S.C.; Adams, T.D. Relationship of Ghrelin and Leptin Hormones with Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in a Random Sample of Adults. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöp, M.; Weyer, C.; Tataranni, P.A.; Devanarayan, V.; Ravussin, E.; Heiman, M.L. Circulating Ghrelin Levels Are Decreased in Human Obesity. Diabetes 2001, 50, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalla, M.A.; Stengel, A. The Role of Ghrelin in Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, M.N.; Gaidhane, A.; Gaidhane, S.; Quazi, Z.S. Ghrelin as a Promising Therapeutic Option for Cancer Cachexia. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2172–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Weigle, D.S.; Frayo, R.S.; Breen, P.A.; Ma, M.K.; Dellinger, E.P.; Purnell, J.Q. Plasma Ghrelin Levels after Diet-Induced Weight Loss or Gastric Bypass Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Fissore, M.F.; Oggero, R.; Silvestro, L.; Miniero, R. Serum Ghrelin Concentration and Weight Gain in Healthy Term Infants in the First Year of Life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, B.; Cuntz, U.; Fruehauf, E.; Wawarta, R.; Folwaczny, C.; Riepl, R.L.; Heiman, M.L.; Lehnert, P.; Fichter, M.; Tschöp, M. Weight Gain Decreases Elevated Plasma Ghrelin Concentrations of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 145, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.C.H.; Wang, T.N.; Lu, M.L.; Chou, J.Y.; Ju, P.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Lin, Z.R.; Ji, T.T.; Chou, C.E.; Lee, C.T.; et al. Weight Gain and Ghrelin Level after Olanzapine Monotherapy. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, C.M.; Lightman, S.L. The HPA Axis in Major Depression: Classical Theories and New Developments. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Capuron, L.; Miller, A.H. Cytokines Sing the Blues: Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Depression. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, L.; Sheng, C.; Cheng, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, T.; Yau, T.O.; Li, F.; et al. Increased Serum Levels of Cortisol and Inflammatory Cytokines in People with Depression. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2019, 207, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haam, J.; Halmos, K.C.; Di, S.; Tasker, J.G. Nutritional State-Dependent Ghrelin Activation of Vasopressin Neurons via Retrograde Trans-Neuronal-Glial Stimulation of Excitatory GABA Circuits. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6201–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos-Santos, R.C.; Grover, H.M.; Reis, L.C.; Ferguson, A.V.; Mecawi, A.S. Electrophysiological Effects of Ghrelin in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozid, A.M.; Tringali, G.; Forsling, M.L.; Hendricks, M.S.; Ajodha, S.; Edwards, R.; Navarra, P.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. Ghrelin Is Released from Rat Hypothalamic Explants and Stimulates Corticotrophin-Releasing Hormone and Arginine-Vasopressin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2003, 35, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tassone, F.; Broglio, F.; Destefanis, S.; Rovere, S.; Benso, A.; Gottero, C.; Prodam, F.; Rossetto, R.; Gauna, C.; Van Der Lely, A.J.; et al. Neuroendocrine and Metabolic Effects of Acute Ghrelin Administration in Human Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5478–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouach, V.; Bloch, M.; Rosenberg, N.; Gilad, S.; Limor, R.; Stern, N.; Greenman, Y. The Acute Ghrelin Response to a Psychological Stress Challenge Does Not Predict the Post-Stress Urge to Eat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juruena, M.F.; Bocharova, M.; Agustini, B.; Young, A.H. Atypical depression and non-atypical depression: Is HPA axisb function a biomarker? A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 233, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.D.; Schaffer, E.M.; Pyle, R.S.; Collins, G.D.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Palaniappan, R.; Lillard, J.W.; Taub, D.D. Ghrelin Inhibits Leptin- and Activation-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression by Human Monocytes and T Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, T.; Duxbury, M.; Ito, H.; Ashley, S.W.; Robinson, M.K. Exogenous Ghrelin Modulates Release of Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages through Distinct Signaling Pathways. Surgery 2008, 143, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Cui, X.; Zhou, M.; Simms, H.H.; Ravikumar, T.S.; Wang, P. Ghrelin Down-Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokines in Sepsis through Activation of the Vagus Nerve. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Ryu, S.Y.; Blow, C.; Costantini, T.; Loomis, W.; Eliceiri, B.; Baird, A.; Wolf, P.; Coimbra, R. The Hormone Ghrelin Prevents Traumatic Brain Injury Induced Intestinal Dysfunction. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Davis, H.W.; Gastaldelli, A.; D’alessio, D. Ghrelin Impairs Prandial Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Secretion in Healthy Humans despite Increasing GLP-1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, B.K.; Puzziferri, N.; He, Z.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Metzger, N.P.; Chhina, N.; Gaylinn, B.; Thorner, M.O.; Louise Thomas, E.; et al. LEAP2 Changes with Body Mass and Food Intake in Humans and Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3909–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benso, A.; St-Pierre, D.H.; Prodam, F.; Gramaglia, E.; Granata, R.; Van Der Lely, A.J.; Ghigo, E.; Broglio, F. Metabolic Effects of Overnight Continuous Infusion of Unacylated Ghrelin in Humans. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kakei, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Endogenous Ghrelin in Pancreatic Islets Restricts Insulin Release by Attenuating Ca2+ Signaling in β-Cells. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, L.; Poggiogalle, E.; Costantino, F.; Anania, C.; Ferraro, F.; Chiarelli, F.; Chiesa, C. Acylated and Nonacylated Ghrelin Levels and Their Associations with Insulin Resistance in Obese and Normal Weight Children with Metabolic Syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalán, V.; Gil, M.J.; Becerril, S.; Sáinz, N.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Frühbeck, G. Acylated and Desacyl Ghrelin Stimulate Lipid Accumulation in Human Visceral Adipocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, B.; Neggers, S.J.C.M.M.; Miller, A.R.; Yang, H.C.; Lucaites, V.; Abribat, T.; Allas, S.; Huisman, M.; Visser, J.A.; Themmen, A.P.N.; et al. Does Des-Acyl Ghrelin Improve Glycemic Control in Obese Diabetic Subjects by Decreasing Acylated Ghrelin Levels? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.M.; Weschenfelder, J.; Sander, C.; Minkwitz, J.; Thormann, J.; Chittka, T.; Mergl, R.; Kirkby, K.C.; Faßhauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Inflammatory Cytokines in General and Central Obesity and Modulating Effects of Physical Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guria, S.; Hoory, A.; Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Mukherjee, S. Adipose Tissue Macrophages and Their Role in Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance: An Overview of the Complex Dynamics at Play. Biosci. Rep. 2023, 43, BSR20220200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The Semantics of Microglia Activation: Neuroinflammation, Homeostasis, and Stress. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders: The Roles of Microglia and Astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Jeon, S.W. Neuroinflammation and the Immune-Kynurenine Pathway in Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, G.A.; O’Connor, J.C. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Inflammation in Depression: Pathogenic Partners in Crime? World J. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buntwal, L.; Sassi, M.; Morgan, A.H.; Andrews, Z.B.; Davies, J.S. Ghrelin-Mediated Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Implications for Health and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Bouret, S.G.; Andrews, Z.B. Obesity Impairs the Action of the Neuroendocrine Ghrelin System. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.I.; Enriori, P.J.; Lemus, M.B.; Cowley, M.A.; Andrews, Z.B. Diet-Induced Obesity Causes Ghrelin Resistance in Arcuate NPY/AgRP Neurons. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naznin, F.; Toshinai, K.; Waise, T.M.Z.; NamKoong, C.; Md Moin, A.S.; Sakoda, H.; Nakazato, M. Diet-Induced Obesity Causes Peripheral and Central Ghrelin Resistance by Promoting Inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, S.; Kaliaperumal, C. Vagal Nerve Stimulator: Evolving Trends. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R. The Vagus Nerve, Food Intake and Obesity. Regul. Pept. 2008, 149, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A. The Evolving Obesity Challenge: Targeting the Vagus Nerve and the Inflammatory Reflex in the Response. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 222, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austelle, C.W.; O’Leary, G.H.; Thompson, S.; Gruber, E.; Kahn, A.; Manett, A.J.; Short, B.; Badran, B.W. A Comprehensive Review of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Depression. Neuromodulation 2022, 25, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutter, M.; Elmquist, J. Depression and Metabolism: Linking Changes in Leptin and Ghrelin to Mood. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2009, 1, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmatz, E.S.; Stone, L.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, G.; McGrath, A.; Gisabella, B.; Peng, X.; Kosoy, E.; Yao, J.; Liu, E.; et al. Central Ghrelin Resistance Permits the Overconsolidation of Fear Memory. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, A.; Clinger, E.; Hao, L. Effect of Diet and Dietary Components on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam-Ndoul, B.; Castonguay-Paradis, S.; Veilleux, A. Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Trans-Epithelial Permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.B.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.C. The Relationship between Stress, Inflammation, and Depression. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalla, M.A.; Stengel, A. Effects of Microbiome Changes on Endocrine Ghrelin Signaling—A Systematic Review. Peptides 2020, 133, 170388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered Fecal Microbiota Composition in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wen, J.; Deng, K.; Qin, X.W.; Wang, D.H. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Interaction in Regulating Host Metabolic Adaptation to Cold in Male Brandt’s Voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii). ISME J. 2019, 13, 3037–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Pang, G.; Ren, F.; Fang, B. Effects of Diethyl Phosphate, a Non-Specific Metabolite of Organophosphorus Pesticides, on Serum Lipid, Hormones, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2019, 24, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M. Effects of Heat Stress on Gut-Microbial Metabolites, Gastrointestinal Peptides, Glycolipid Metabolism, and Performance of Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Hui, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Healthy Subjects Differentially Respond to Dietary Capsaicin Correlating with Specific Gut Enterotypes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4681–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Arango, L.F.; Barrett, H.L.; McIntyre, H.D.; Callaway, L.K.; Morrison, M.; Nitert, M.D.; Tremellen, A.; Tobin, J.; Wilkinson, S.; McSweeney, C.; et al. Connections between the Gut Microbiome and Metabolic Hormones in Early Pregnancy in Overweight and Obese Women. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Ling, Y.; Fu, H.; Dong, W.; Shen, J.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota Associated with Clinical Parameters in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Seoane, L.M.; Murri, M.; Pardo, M.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Cardona, F.; Casanueva, F.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut Microbiota Composition in Male Rat Models under Different Nutritional Status and Physical Activity and Its Association with Serum Leptin and Ghrelin Levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, S.; Vester Boler, B.M.; Kerr, K.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Swanson, K.S. The Gut Microbiome of Kittens Is Affected by Dietary Protein:Carbohydrate Ratio and Associated with Blood Metabolite and Hormone Concentrations. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Indias, I. Helicobacter Pylori Eradication Therapy Affect the Gut Microbiota and Ghrelin Levels. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 712908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, J.S.; Ticer, T.D.; Engevik, M.A. Characterizing the Mucin-Degrading Capacity of the Human Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut Microbiota Functions: Metabolism of Nutrients and Other Food Components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Barry, N.A.; Cline, G.W.; Zhang, D.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G.; Goodman, A.L.; Shulman, G.I. Acetate Mediates a Microbiome-Brain-β-Cell Axis to Promote Metabolic Syndrome. Nature 2016, 534, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; Zhdanov, A.V.; Wallace, S.; Arboleya, S.; Papkovsky, D.B.; El Aidy, S.; Ross, P.; Roy, B.L.; Stanton, C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Microbiota Metabolites Attenuate Ghrelin Receptor Signaling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13546–13559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon-Minois, J.B.; Trousselard, M.; Thivel, D.; Gordon, B.A.; Schmidt, J.; Moustafa, F.; Oris, C.; Dutheil, F. Ghrelin as a Biomarker of Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Yin, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W. Ghrelin Based Therapy of Metabolic Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Kaga, T.; Katsuura, G.; Fujimiya, M.; Fujino, M.A.; Kasuga, M. Antagonism of Ghrelin Receptor Reduces Food Intake and Body Weight Gain in Mice. Gut 2003, 52, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegg, K.; Bernasconi, L.; Hutter, M.; Whiting, L.; Pietra, C.; Giuliano, C.; Lutz, T.A.; Riediger, T. Ghrelin Receptor Inverse Agonists as a Novel Therapeutic Approach against Obesity-Related Metabolic Disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalla, M.A.; Stengel, A. Pharmacological Modulation of Ghrelin to Induce Weight Loss: Successes and Challenges. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, L.P.; Wang, S.P.; Helmling, S.; Stribling, D.S.; Mazur, P.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Klussmann, S.; Macintyre, D.E.; Howard, A.D.; et al. Ghrelin Neutralization by a Ribonucleic Acid-SPM Ameliorates Obesity in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotkvic, V.; Altabas, V. Anti-Ghrelin Antibodies in Appetite Suppression: Recent Advances in Obesity Pharmacotherapy. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2015, 4, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pfluger, P.T.; Kirchner, H.; Günnel, S.; Schrott, B.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Fu, S.; Benoit, S.C.; Horvath, T.; Joost, H.G.; Wortley, K.E.; et al. Simultaneous Deletion of Ghrelin and Its Receptor Increases Motor Activity and Energy Expenditure. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G610–G618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, K.A.; Charoenthongtrakul, S.; Giuliana, D.J.; Govek, E.K.; McDonagh, T.; Qi, Y.; DiStefano, P.S.; Geddes, B.J. Improved Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Flexibility in Ghrelin Receptor Knockout Mice. Regul. Pept. 2008, 150, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Blockade of Pancreatic Islet-Derived Ghrelin Enhances Insulin Secretion to Prevent High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brial, F.; Lussier, C.R.; Belleville, K.; Sarret, P.; Boudreau, F. Ghrelin Inhibition Restores Glucose Homeostasis in Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-1a (MODY3)-Deficient Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeuwendaal, N.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Schellekens, H. Gut Peptides and the Microbiome: Focus on Ghrelin. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Organ | Ghrelin’s Physiological Effects | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Hypothalamus | ↑ Appetite | [18] |
| ↑ Food intake | [19] | |
| Reward behavior | [20] | |
| Olfaction and sniffing | [21] | |
| Learning and memory | [22] | |
| Depression | [23] | |
| Sleep/wake rhythm | [23] | |
| Pituitary | ↑ Growth hormone | [1,24] |
| ↑ ACTH | [25] | |
| Sympathetic nervous system | Modulation of the sympathetic nervous system | [26] |
| Brown adipose tissues | ↓ Thermogenesis | [27] |
| Pancreas | ↓ Insulin secretion | [28] |
| Modulation of insulin sensitivity | [29] | |
| Glucose metabolism | [30] | |
| Heart | ↑ Cardiac output | [31,32] |
| ↑ Vasodilatation | [33] | |
| Liver | ↑ IGF-1 | [34] |
| Stomach | ↑ Gastric emptying and ↑ acid secretion | [35,36] |
| Intestine | ↑ Intestinal motility | [37] |
| Adipose tissue | ↑ Lipogenesis | [38] |
| Regulation of inflammation | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gajewska, A.; Strzelecki, D.; Gawlik-Kotelnicka, O. Ghrelin as a Biomarker of “Immunometabolic Depression” and Its Connection with Dysbiosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183960
Gajewska A, Strzelecki D, Gawlik-Kotelnicka O. Ghrelin as a Biomarker of “Immunometabolic Depression” and Its Connection with Dysbiosis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183960
Chicago/Turabian StyleGajewska, Agata, Dominik Strzelecki, and Oliwia Gawlik-Kotelnicka. 2023. "Ghrelin as a Biomarker of “Immunometabolic Depression” and Its Connection with Dysbiosis" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183960
APA StyleGajewska, A., Strzelecki, D., & Gawlik-Kotelnicka, O. (2023). Ghrelin as a Biomarker of “Immunometabolic Depression” and Its Connection with Dysbiosis. Nutrients, 15(18), 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183960








