The Association of Human Milk Proportion with the Clinical Outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
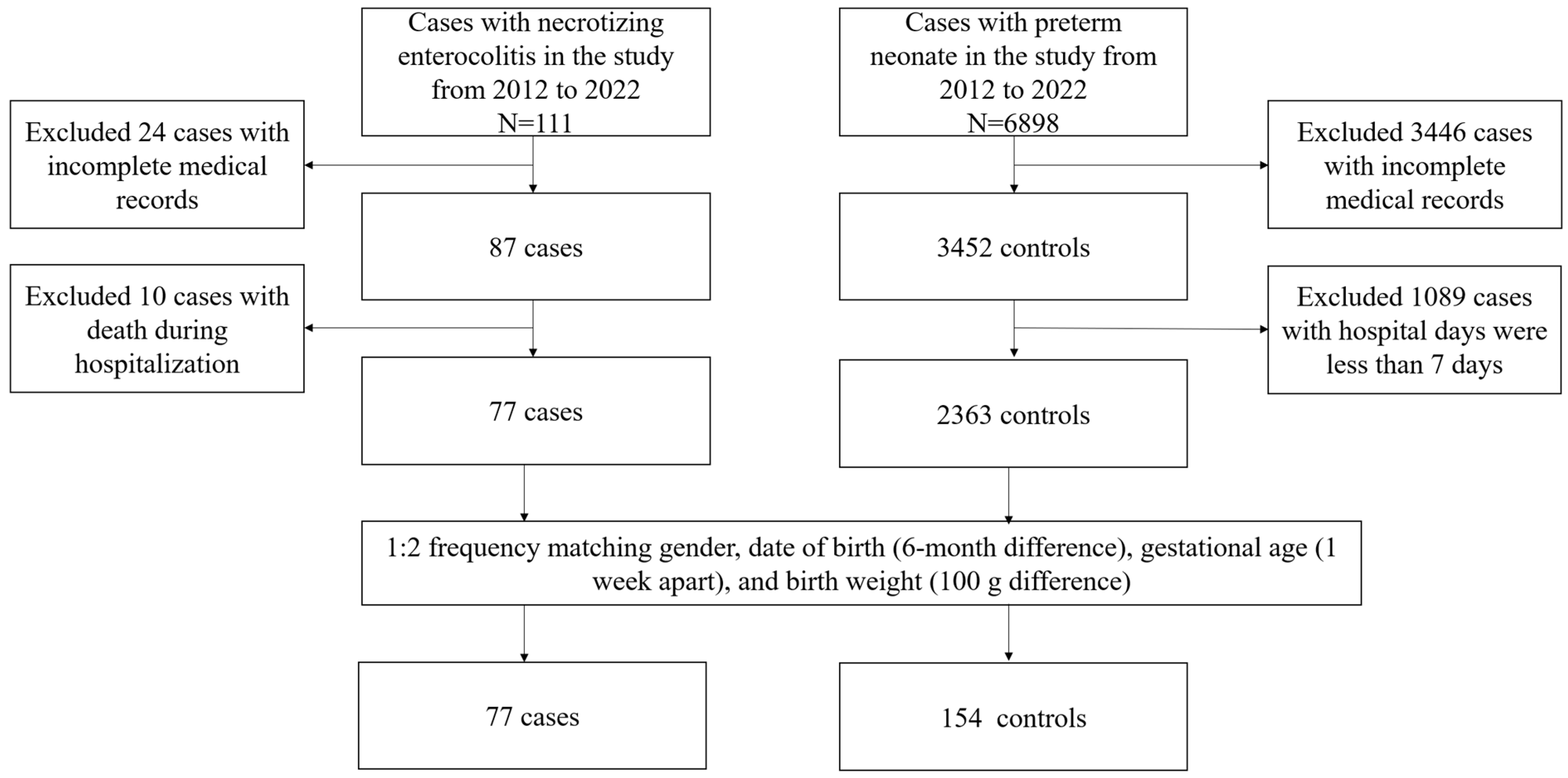
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Association between HM Proportion and NEC
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
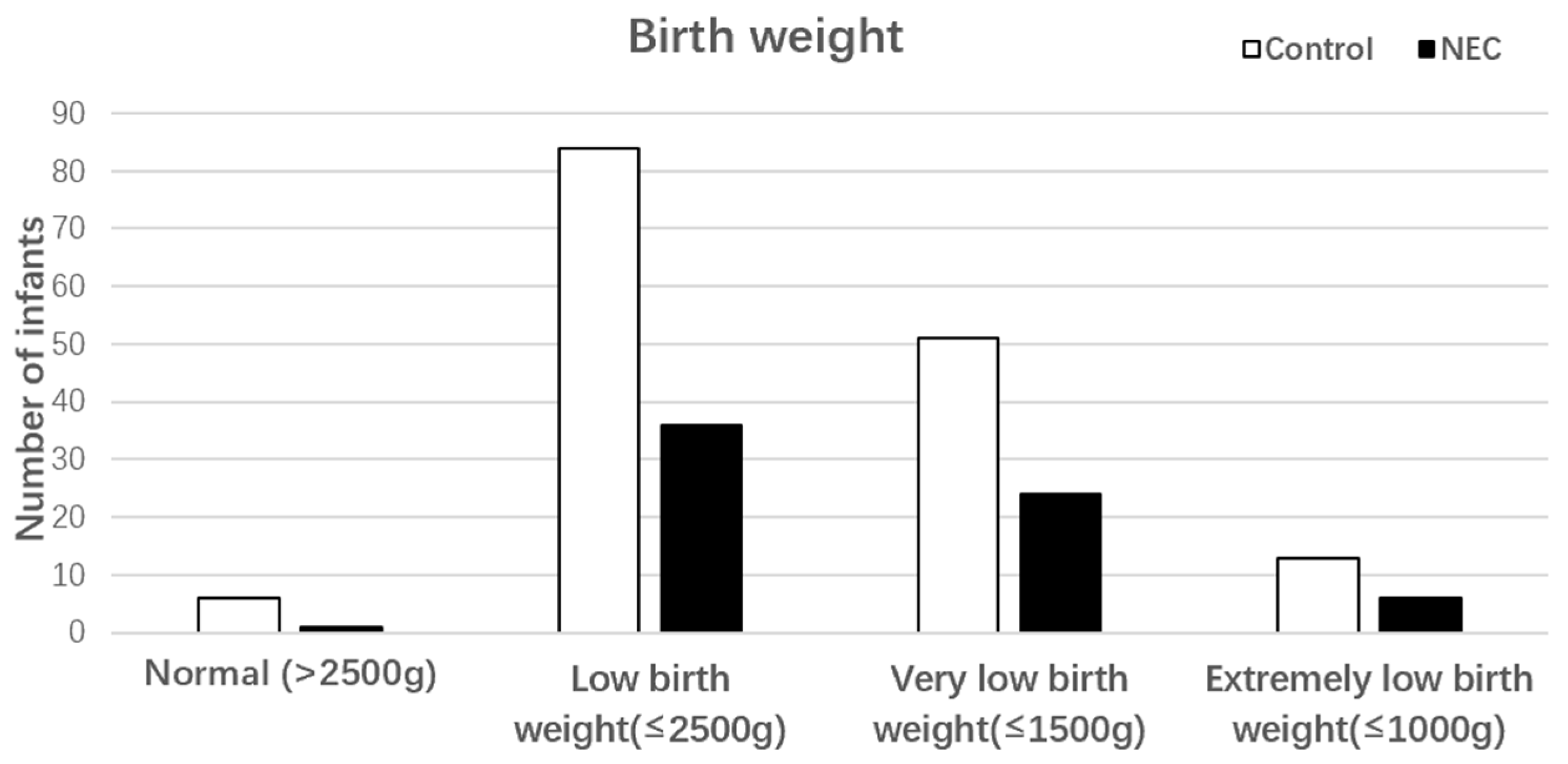
3.1. General Characteristic
3.2. The Associations of Different HM Proportions and the Occurrence of NEC in Preterm Infants
3.3. The Associations of Different HM Proportions with the Outcomes of NEC in Preterm Infants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Walsh, M.C.; Hale, E.C.; Newman, N.S.; Schibler, K.; Carlo, W.A.; et al. Neonatal Outcomes of Extremely Preterm Infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 443–456. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.M.; Kandefer, S.; Walsh, M.C.; Bell, E.F.; Carlo, W.A.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Shankaran, S.; Van Meurs, K.P.; Ball, M.B.; et al. Causes and timing of death in extremely premature infants from 2000 through 2011. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shulhan, J.; Dicken, B.; Hartling, L.; Larsen, B.M. Current Knowledge of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants and the Impact of Different Types of Enteral Nutrition Products. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, P.M.; Britt, A.B.; Ansari, M.A.Y.; Sobisek, S.; Block, D.K.; Paschal, J.L.; Ojeda, N.B.; Askenazi, D.; Sanderson, K.R. Severe acute kidney injury in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis: Risk factors and outcomes. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 642–649. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, K.D.; Lake, D.E.; Kattwinkel, J.; Moorman, J.R.; Bateman, D.A.; Grieve, P.G.; Isler, J.R.; Sahni, R. Vital signs and their cross-correlation in sepsis and NEC: A study of 1,065 very-low-birth-weight infants in two NICUs. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Mao, J.; Yang, J.; Su, Y. Effects of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum on the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, late-onset sepsis, and death in preterm infants: A meta-analysis of RCTs. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.L.; Johnson, T.J.; Engstrom, J.L.; Fogg, L.F.; Jegier, B.J.; Bigger, H.R.; Meier, P.P. Impact of early human milk on sepsis and health-care costs in very low birth weight infants. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 514–519. [Google Scholar]
- Cortez, J.; Makker, K.; Kraemer, D.F.; Neu, J.; Sharma, R.; Hudak, M.L. Maternal milk feedings reduce sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis and improve outcomes of premature infants. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xiu, W.; Dai, Y.; Yang, C. Protective effects of different doses of human milk on neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Medicine 2020, 99, e22166. [Google Scholar]
- York, D.J.; Smazal, A.L.; Robinson, D.T.; De Plaen, I.G. Human Milk Growth Factors and Their Role in NEC Prevention: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bering, S.B. Human Milk Oligosaccharides to Prevent Gut Dysfunction and Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Neonates. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgin, T.G.; Kern, S.L.; McElroy, S.J. Development of the Neonatal Intestinal Microbiome and Its Association with Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Tonkin, E.; Damarell, R.A.; McPhee, A.J.; Suganuma, M.; Suganuma, H.; Middleton, P.F.; Makrides, M.; Collins, C.T. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Milk Feeding and Morbidity in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Nutrients 2018, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 70, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, T.L.; Bhatia, A.M.; Kane, A.F.; Patel, R.M.; Denning, P.W. Pathogenesis of NEC: Role of the innate and adaptive immune response. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.K.; He, B.; Wang, T.; Tran, D.Q.; Rhoads, J.M.; Liu, Y. Protective effect of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 against experimental necrotizing enterocolitis is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G231–G240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Mukherjee, S.; DesMarais, V.; Albanese, J.M.; Rafti, E.; Draghi Ii, A.; Maher, L.A.; Khanna, K.M.; Mani, S.; Matson, A.P. Targeting the PXR-TLR4 signaling pathway to reduce intestinal inflammation in an experimental model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoo, T.B.; Popoola, T.; Lucas, R. Promoting the practice of exclusive breastfeeding: A philosophic scoping review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisk, P.M.; Lovelady, C.A.; Dillard, R.G.; Gruber, K.J.; O’Shea, T.M. Early human milk feeding is associated with a lower risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. J. Perinatol. 2007, 27, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, M.L.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. Human milk protein vs. formula protein and their use in preterm infants. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasani, J.; Ceroni, F.; De Cosmi, V.; Mazzocchi, A.; Morniroli, D.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F.; Agostoni, C.; Gianni, M.L. Human Milk Feeding and Preterm Infants’ Growth and Body Composition: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.V.E.; Walsh, V.; McGuire, W. Formula versus maternal breast milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, CD002972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lapidaire, W.; Lucas, A.; Clayden, J.D.; Clark, C.; Fewtrell, M.S. Human milk feeding and cognitive outcome in preterm infants: The role of infection and NEC reduction. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 91, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Ternberg, J.L.; Feigin, R.D.; Keating, J.P.; Marshall, R.; Barton, L.; Brotherton, T. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann. Surg. 1978, 187, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.L.; Engstrom, J.L.; Meier, P.P.; Kimura, R.E. Accuracy of methods for calculating postnatal growth velocity for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altobelli, E.; Angeletti, P.M.; Verrotti, A.; Petrocelli, R. The Impact of Human Milk on Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho, N.T.; Parker, L.A.; Neu, J. Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Human Milk Feeding: A Systematic Review. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowning, R.; Radmacher, P.; Lewis, S.; Serke, L.; Pettit, N.; Adamkin, D.H. A retrospective analysis of the effect of human milk on prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis and postnatal growth. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrington, J.E.; Embleton, N.D. Time of Onset of Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Focal Perforation in Preterm Infants: Impact on Clinical, Surgical, and Histological Features. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 724280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemizadeh, R.; Mandal, S.; Gollins, L.; Shah, S.; Premkumar, M.; Hair, A. Incidence of spontaneous intestinal perforations exceeds necrotizing enterocolitis in extremely low birth weight infants fed an exclusive human milk-based diet: A single center experience. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofalo, E.A.; Schanler, R.J.; Blanco, C.L.; Sullivan, S.; Trawoeger, R.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Dudell, G.; Rechtman, D.J.; Lee, M.L.; Lucas, A.; et al. Randomized trial of exclusive human milk versus preterm formula diets in extremely premature infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1592–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.D.; Richard, C.; Larsen, B.M.; Field, C.J. The Importance of Human Milk for Immunity in Preterm Infants. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | NEC (n = 77) | Control (n = 154) | Test | p Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or Mean (SD) | n (%) or Mean (SD) | |||
| Matched parameters | ||||
| Male, sex | 47(61.04%) | 94(61.04%) | χ2 = 0.036 | 0.849 |
| GA, weeks | 31.68 ± 2.60 | 31.77 ± 2.55 | t = −0.256 | 0.798 |
| BW, grams | 1660.65 ± 481.36 | 1654.74 ± 483.02 | t = 0.088 | 0.930 |
| Maternal factors | ||||
| Natural birth delivery | 16(20.78%) | 40(25.97%) | χ2 = 0.754 | 0.385 |
| Prenatal GC therapy | 54(70.13%) | 98(63.64%) | χ2 = 0.962 | 0.327 |
| GDM | 15(19.48%) | 25(16.23%) | χ2 = 0.378 | 0.539 |
| PHI | 18(23.38%) | 33(21.43%) | χ2 = 0.113 | 0.736 |
| Neonatal factors | ||||
| Exclusive breastfeeding | 24(31.17%) | 62(40.26%) | χ2 = 1.005 | 0.316 |
| First feeding a, days | 2.38 ± 1.79 | 2.69 ± 1.45 | t = −1.419 | 0.157 |
| ARDS | 28(36.35%) | 56(36.36%) | χ2 = 0.000 | 1.000 |
| PDA | 23(29.87%) | 63(40.91%) | χ2 = 2.677 | 0.102 |
| Neonatal asphyxia | 18(23.38%) | 58(37.66%) | χ2 = 4.746 | 0.029 * |
| Human Milk Intake | NEC (n = 77) | Control (n = 154) | OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NHM (0%), n (%) | 53(68.83%) | 102(66.23%) | 1.00 | |
| LHM (<70%), n (%) | 13(16.88%) a | 19(12.34%) | 1.257(0.565–2.799) | 1.045(0.452–2.417) |
| HHM (≥70%), n (%) | 11(14.29%) a | 33(21.43%) | 0.599(0.261–1.377) | 0.573(0.246–1.336) |
| p value # | 0.317 | 0.386 |
| Parameter | Grouped by Proportion of Human Milk to Total Enteral Feeding | p Value # | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All subjects | ≥70% | <70% | 0% | ||
| n = 77 | n = 11 | n = 13 | n = 53 | ||
| CRP (mg/mL) | 9.10 ± 12.58 | 16.09 ± 26.47 | 28.99 ± 53.37 | 0.312 | |
| WBCs (×109/L) | 12.76 ± 6.28 | 16.24 ± 10.67 | 14.44 ± 9.56 | 0.634 | |
| N (%) | 41.25 ± 19.58 | 50.27 ± 19.22 | 48.31 ± 21.43 | 0.545 | |
| PLTs (×109/L) | 281.60 ± 139.37 | 270.38 ± 145.31 | 263.78 ± 164.68 | 0.960 | |
| Weight gain (g/kg−1/day−1) a | 14.99 ± 9.41 | 9.35 ± 4.14 | 8.99 ± 6.88 | 0.035 * | |
| Onset day (d) | 21.9 ± 12.9 | 17.9 ± 11.2 | 11.7 ± 7.3 | 0.024 * | |
| Diagnosis day (d) | 25.9 ± 11.7 | 19.8 ± 11.3 | 13.9 ± 7.9 | 0.003 * | |
| Hospital day (d) | 31.1 ± 12.5 | 36.3 ± 16.5 | 29.2 ± 19.8 | 0.275 | |
| Hospitalization cost (CNY) | 77,802.46 ± 29,454.21 | 95,554.65 ± 47,002.48 | 64,773.89 ± 49,409.47 | 0.030 * | |
| Surgical treatment, n (%) | 3(27.27%) | 6(46.15%) | 17(32.08%) | 0.620 | |
| Duration of antibiotic use (d) | 10.5 ± 4.8 | 10.5 ± 7.5 | 9.8 ± 6.8 | 0.902 | |
| Severity of NEC, n (%) b | |||||
| Mild c | 9(81.82%) | 9 (69.23%) | 21(39.62%) | 0.013 * | |
| Severe d | 2(18.18%) | 4 (30.77%) | 32(60.38%) | ||
| Prognosis of NEC, n (%) | |||||
| Improvement e | 9(81.82%) | 10 (76.92%) | 39(73.58%) | 0.922 | |
| Not healed f | 2(18.18%) | 3 (23.08%) | 14(26.42%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Su, Y. The Association of Human Milk Proportion with the Clinical Outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173796
Liu K, Guo J, Yang J, Su Y. The Association of Human Milk Proportion with the Clinical Outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Keqin, Jinjin Guo, Jixin Yang, and Yanwei Su. 2023. "The Association of Human Milk Proportion with the Clinical Outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Study" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173796
APA StyleLiu, K., Guo, J., Yang, J., & Su, Y. (2023). The Association of Human Milk Proportion with the Clinical Outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Study. Nutrients, 15(17), 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173796






