Circadian Variation in Human Milk Hormones and Macronutrients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Study Design
2.2. Measurement of 24 h Milk Intake and Sample Collection
2.3. Biochemical Analysis of Human Milk
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Within-Feed Variation
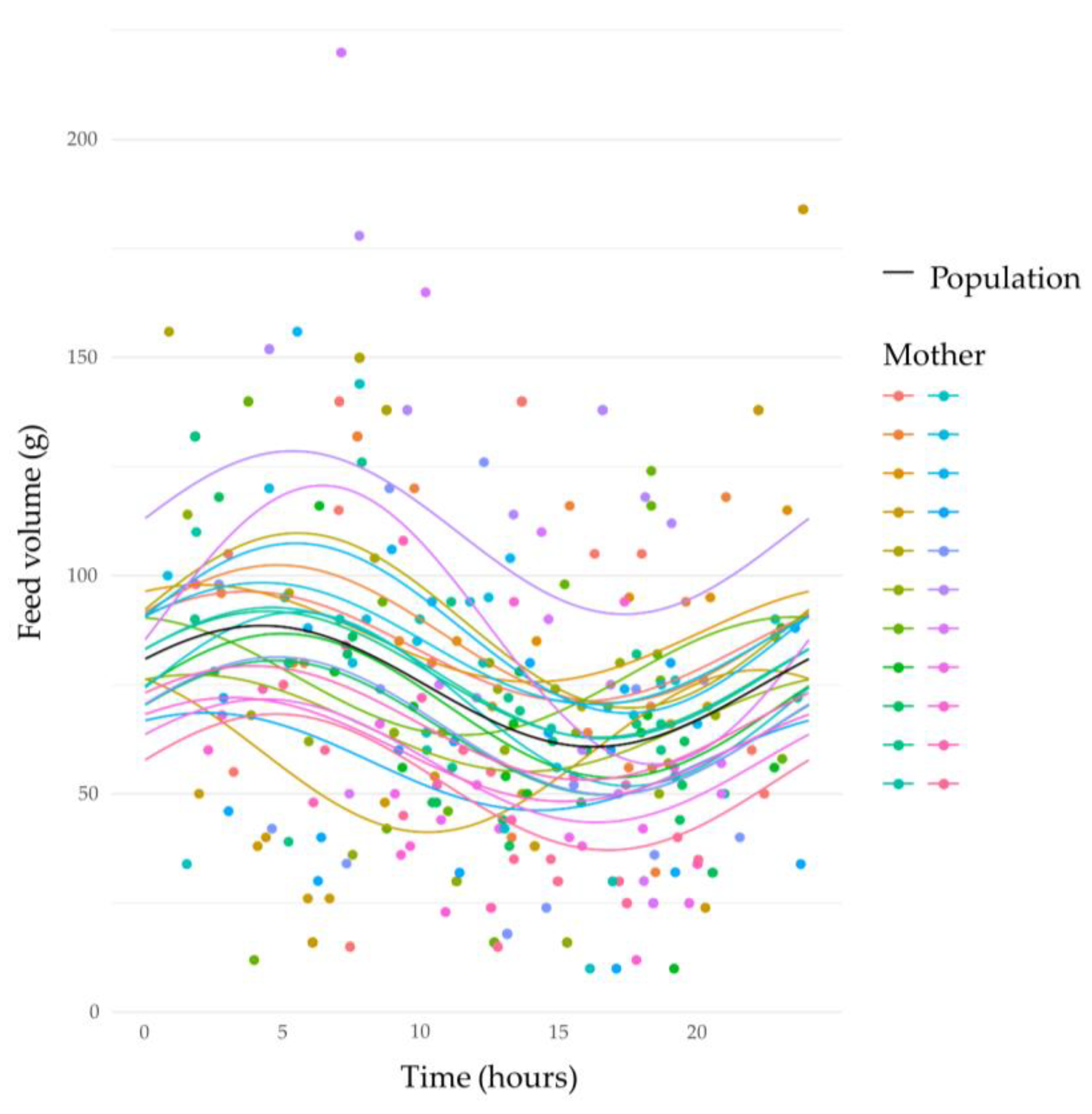
3.3. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Feed Volumes
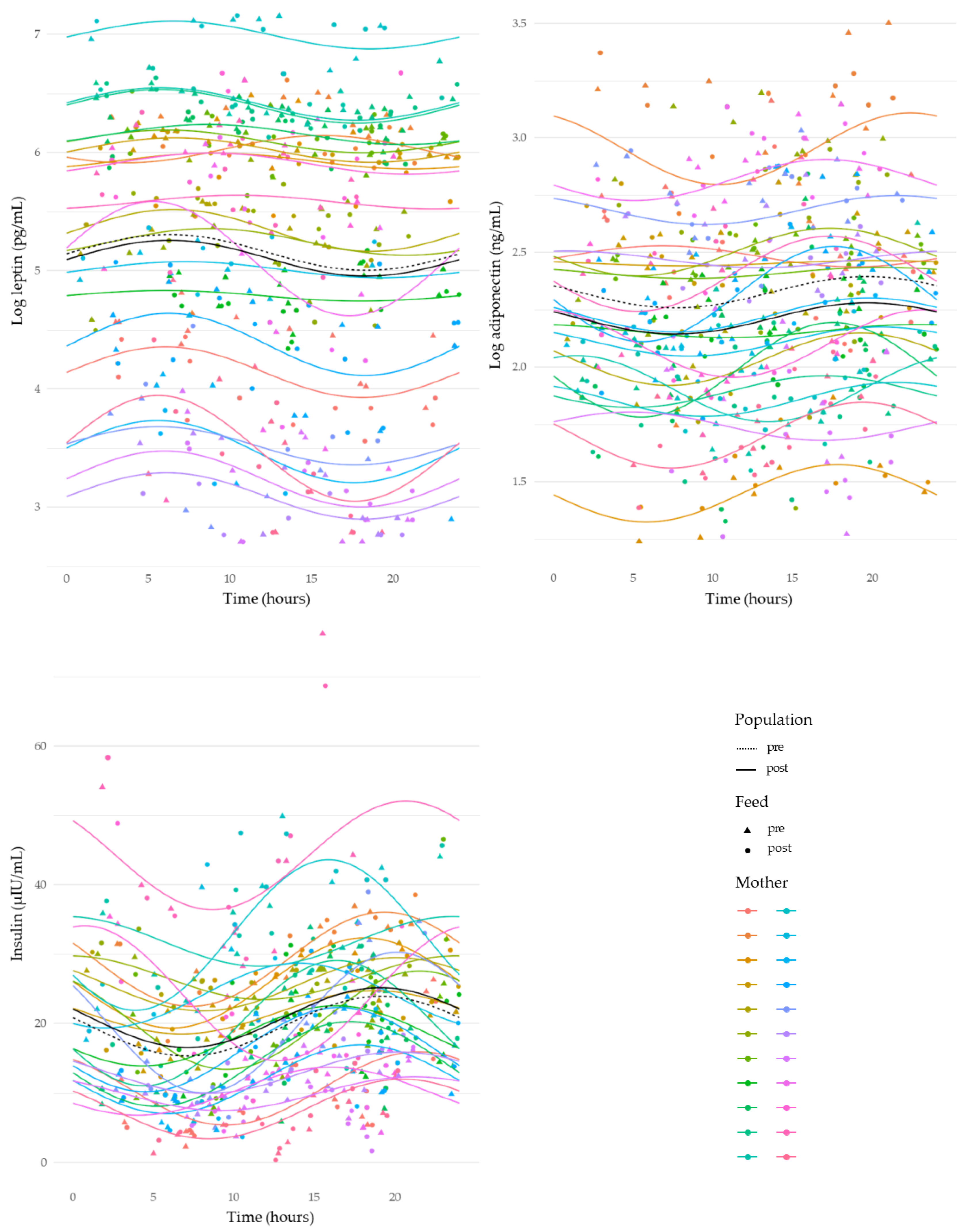
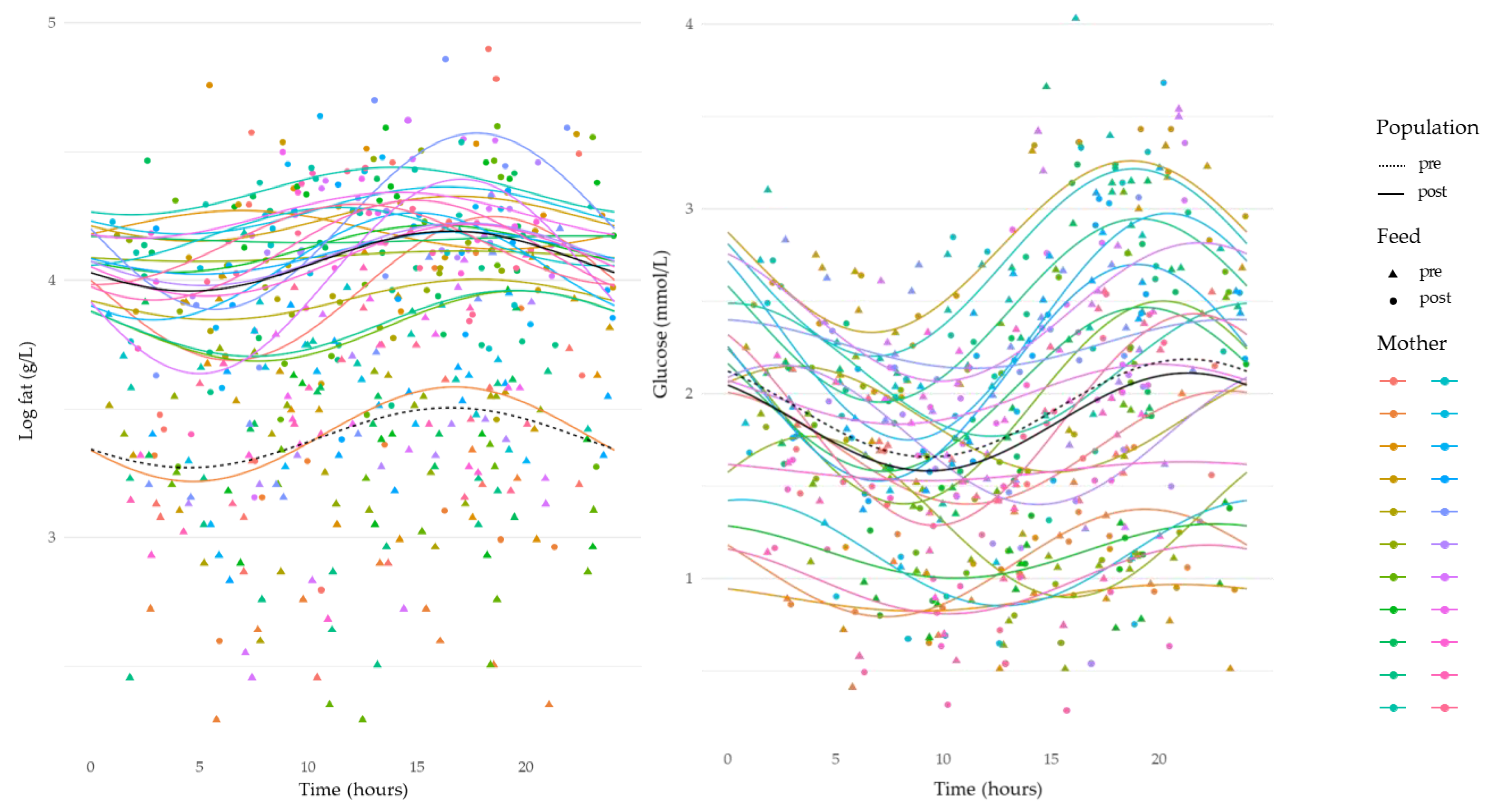
3.4. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Component Concentrations
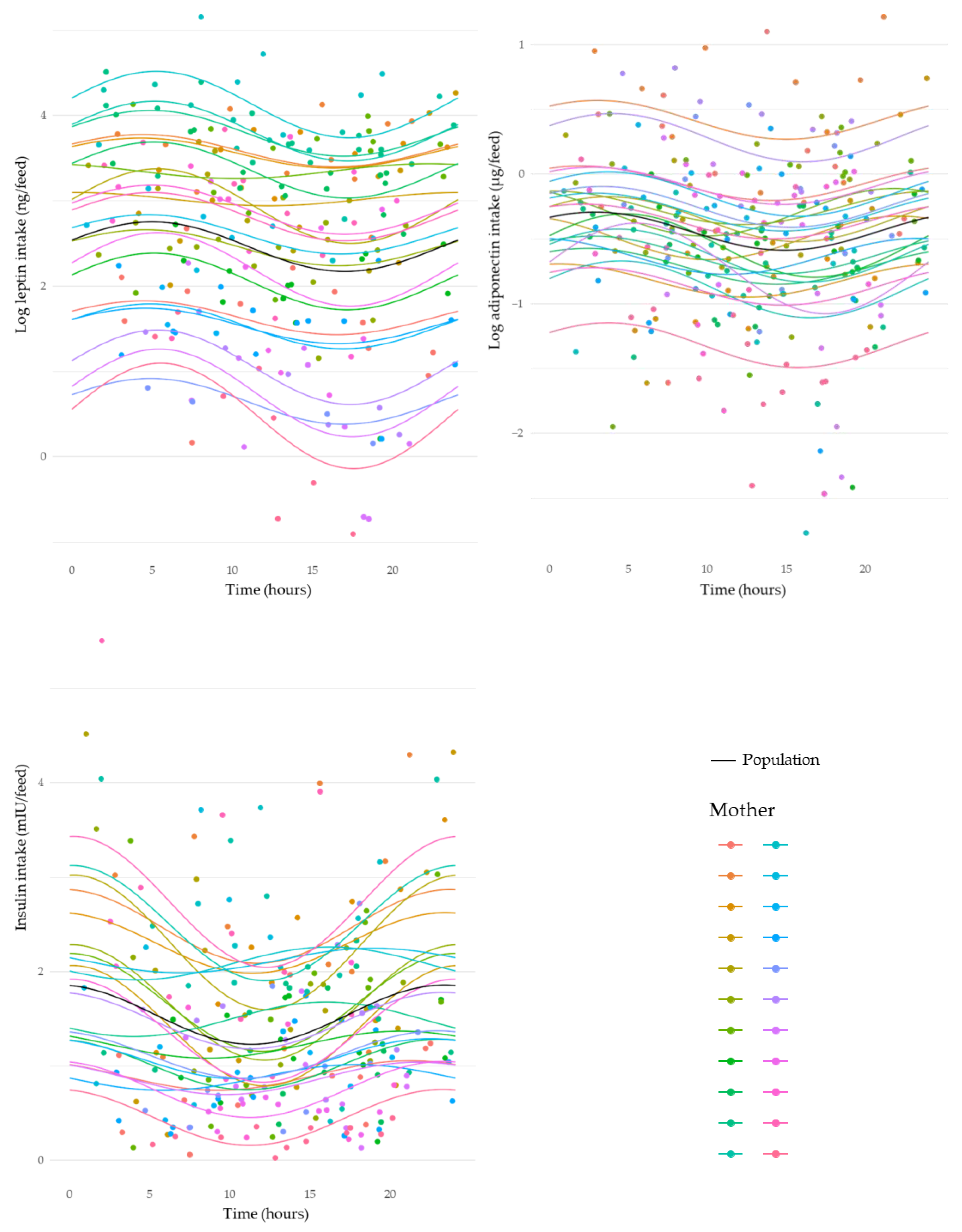
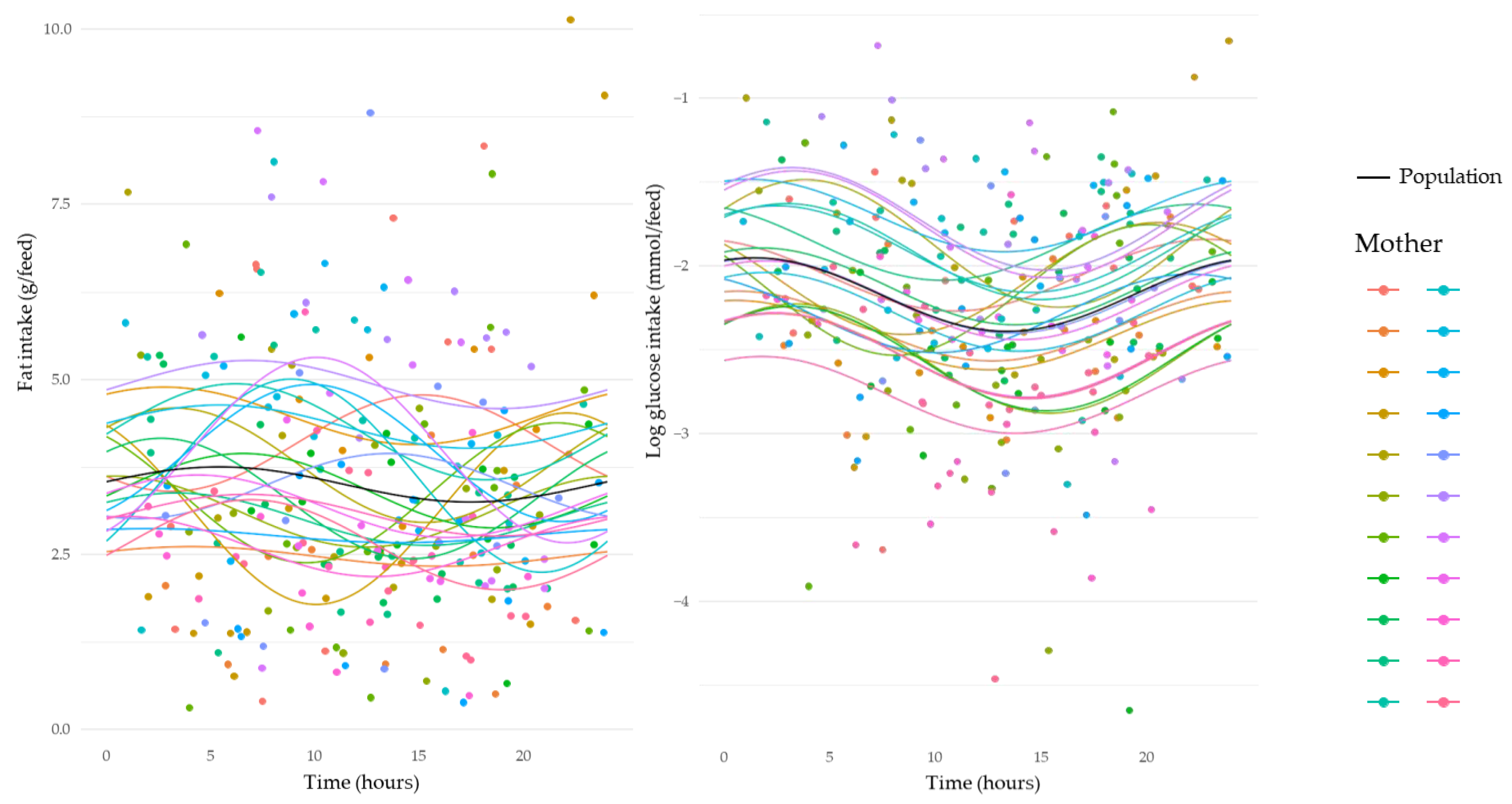
3.5. Circadian Variation in Intakes of Human Milk Components
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christian, P.; Smith, E.R.; Lee, S.E.; Vargas, A.J.; Bremer, A.A.; Raiten, D.J. The need to study human milk as a biological system. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, S.; Gridneva, Z.; Lai, C.T.; Stinson, L.; George, A.; Bilston-John, S.; Geddes, D. Human milk composition promotes optimal infant growth, development and health. Semin. Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, E.A. Centering human milk composition as normal human biological variation. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2021, 33, e23564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C.; Demerath, E.W.; Hahn-Holbrook, J.; Hovey, R.C.; Martin-Carli, J.; McGuire, M.A.; Newton, E.R.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Rudolph, M.C.; Raiten, D.J. Parental factors that impact the ecology of human mammary development, milk secretion, and milk composition-a report from “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Working Group 1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S11–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowitz, J.T.; Allen, L.H.; Dallas, D.C.; McManaman, J.; Raiten, D.J.; Rozga, M.; Sela, D.A.; Seppo, A.; Williams, J.E.; Young, B.E.; et al. Ecologies, synergies, and biological systems shaping human milk composition-a report from “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Working Group 2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S28–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, N.F.; Belfort, M.B.; Meier, P.P.; Mennella, J.A.; O’Connor, D.L.; Taylor, S.N.; Raiten, D.J. Infant factors that impact the ecology of human milk secretion and composition-a report from “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Working Group 3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S43–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiten, D.J.; Steiber, A.L.; Papoutsakis, C.; Rozga, M.; Handu, D.; Proano, G.V.; Moloney, L.; Bremer, A.A. The “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Project—Executive summary. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S.M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Andres, A.; Azad, M.B.; Becker, M.; Carlson, S.E.; Jarvinen, K.M.; Lin, W.; Lonnerdal, B.; Slupsky, C.M.; et al. Evidence for human milk as a biological system and recommendations for study design-a report from “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Working Group 4. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S61–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L.; Section on, B. Policy statement: Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Italianer, M.F.; Naninck, E.F.G.; Roelants, J.A.; van der Horst, G.T.J.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Goudoever, J.B.V.; Joosten, K.F.M.; Chaves, I.; Vermeulen, M.J. Circadian variation in human milk composition, a systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoulas, L.R.; Kent, J.C.; Cox, D.B.; Owens, R.A.; Sherriff, J.L.; Hartmann, P.E. Variation in fat, lactose and protein in human milk over 24 h and throughout the first year of lactation. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, T.M.; Zhou, Q.; Giuffrida, F.; Munblit, D.; Verhasselt, V.; Thakkar, S.K. Nutritional and Non-nutritional Composition of Human Milk Is Modulated by Maternal, Infant, and Methodological Factors. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 576133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn-Holbrook, J.; Saxbe, D.; Bixby, C.; Steele, C.; Glynn, L. Human milk as “chrononutrition”: Implications for child health and development. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, G.D.; Cade, J.E.; Grant, P.J.; Hardie, L.J. Nutrition and the circadian system. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Merrow, M. The circadian clock and human health. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R432–R443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.C.; Honorio-França, A.C.; Silva, R.R.; Fujimori, M.; Fagundes, D.L.G.; França, E.L. Temporal fluctuations of cytokine concentrations in human milk. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2015, 46, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.C.; Cubero, J.; Sanchez, J.; Franco, L.; Rodriguez, B.A.; Rivero, M.; Barriga, C. Evolution of the circadian profile of human milk amino acids during breastfeeding. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013, 11, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaydi, M.A.; Gridneva, Z.; Perrella, S.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Lai, C.T.; Geddes, D.T. Human milk metabolic hormones: Analytical methods and current understanding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghi, G.E.; Middleton, P.F.; Netting, M.J.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Muhlhausler, B.S. A Systematic review of collection and analysis of human milk for macronutrient composition. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1652–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.C.; Mitoulas, L.R.; Cregan, M.D.; Ramsay, D.T.; Doherty, D.A.; Hartmann, P.E. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e387–e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridneva, Z.; Kugananthan, S.; Hepworth, A.R.; Tie, W.J.; Lai, C.T.; Ward, L.C.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T. Effect of human milk appetite hormones, macronutrients, and infant characteristics on gastric emptying and breastfeeding patterns of term fully breastfed infants. Nutrients 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, P.P.; Engstrom, J.L.; Zuleger, J.L.; Motykowski, J.E.; Vasan, U.; Meier, W.A.; Hartmann, P.E.; Williams, T.M. Accuracy of a user-friendly centrifuge for measuring creamatocrits on mothers’ milk in the clinical setting. Breastfeed. Med. 2006, 1, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.D.; Gay, M.C.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Trengove, R.D.; Murray, K.; Geddes, D.T. Untargeted lipidomics using liquid chromatography-ion mobility-mass spectrometry reveals novel triacylglycerides in human milk. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolridge, M.W.; Ingram, J.C.; Baum, J.D. Do changes in pattern of breast usage alter the baby’s nutrient intake? Lancet 1990, 336, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassiotou, F.; Geddes, D.T. Programming of appetite control during breastfeeding as a preventative strategy against the obesity epidemic. J. Hum. Lact. 2014, 30, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, S.E.; Di Rosso, A.; Owens, R.A.; Hartmann, P.E. Degree of breast emptying explains changes in the fat content, but not fatty acid composition, of human milk. Exp. Physiol. 1993, 78, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, T.J.; Trengove, N.J.; Graham, D.F.; Hartmann, P.E. Analysis of insulin in human breast milk in mothers with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 296368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, P.G.; Kent, J.C.; Hartmann, P.E. Metabolites of lactose synthesis in milk from women during established lactation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1991, 13, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi-Keefe, C.J.; Ferris, A.M.; Jensen, R.G. Changes in human milk at 0600, 1000, 1400, 1800, and 2200 h. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1990, 11, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic-Peterson, L.; Fuhrmann, K.; Hedden, K.; Walker, L.; Peterson, C.M. Maternal milk and plasma glucose and insulin levels: Studies in normal and diabetic subjects. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1989, 8, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, G.B.; De Feo, P.; De Cosmo, S.; Perriello, G.; Ventura, M.M.; Calcinaro, F.; Lolli, C.; Campbell, P.; Brunetti, P.; Gerich, J.E. Demonstration of a dawn phenomenon in normal human volunteers. Diabetes 1984, 33, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggiogalle, E.; Jamshed, H.; Peterson, C.M. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism 2018, 84, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.M.; Kakulas, F.; Hepworth, A.R.; Lai, C.T.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T. The effects of leptin on breastfeeding behaviour. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12340–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.F.; Riad-Gabriel, M.G.; Khan, A.; Sharma, A.; Michael, R.; Jinagouda, S.D.; Boyadjian, R.; Steil, G.M. Diurnal and ultradian rhythmicity of plasma leptin: Effects of gender and adiposity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.K.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Magosin, S.; Marco, C.; Caro, J.F. Nocturnal rise of leptin in lean, obese, and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendonk, J.G.; Pijl, H.; Toornvliet, A.C.; Burggraaf, J.; Frolich, M.; Schoemaker, R.C.; Doornbos, J.; Cohen, A.F.; Meinders, A.E. Circadian rhythm of plasma leptin levels in upper and lower body obese women: Influence of body fat distribution and weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkovic, V.; Ilich, J.Z.; Badenhop, N.E.; Skugor, M.; Clairmont, A.; Klisovic, D.; Landoll, J.D. Gain in body fat is inversely related to the nocturnal rise in serum leptin level in young females. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Yen, S.S. Hypoleptinemia in women athletes: Absence of a diurnal rhythm with amenorrhea. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, M.; Beermann, C.; Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D. Adiponectin and leptin in maternal serum, cord blood, and breast milk. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabiell, X.; Pineiro, V.; Tome, M.A.; Peino, R.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Presence of leptin in colostrum and/or breast milk from lactating mothers: A potential role in the regulation of neonatal food intake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrila, A.; Peng, C.K.; Chan, J.L.; Mietus, J.E.; Goldberger, A.L.; Mantzoros, C.S. Diurnal and ultradian dynamics of serum adiponectin in healthy men: Comparison with leptin, circulating soluble leptin receptor, and cortisol patterns. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Abellan, P.; Gomez-Santos, C.; Madrid, J.A.; Milagro, F.I.; Campion, J.; Martinez, J.A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Garaulet, M. Circadian expression of adiponectin and its receptors in human adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.H.; Hanley, A.J.; Stone, D.; O’Connor, D.L. Effects of pasteurization on adiponectin and insulin concentrations in donor human milk. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, R.A.; Bell, E.F.; Roghair, R.D.; Kiss, G.; Funke, S.; Bokor, S.; Molnar, D.; Miseta, A.; Bodis, J.; Kovacs, K.; et al. Insulin, testosterone, and albumin in term and preterm breast milk, donor milk, and infant formula. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, R.A.; Kiss, G.; Bell, E.F.; Miseta, A.; Bodis, J.; Funke, S.; Bokor, S.; Molnar, D.; Kosa, B.; Kiss, A.A.; et al. Thyroxine thyroid-stimulating hormone in own mother’s milk, donor milk, and infant formula. Life 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resto, M.; O’Connor, D.; Leef, K.; Funanage, V.; Spear, M.; Locke, R. Leptin levels in preterm human breast milk and infant formula. Pediatrics 2001, 108, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Nishihara, K.; Horiuchi, S.; Eto, H. The influence of feeding method on a mother’s circadian rhythm and on the development of her infant’s circadian rest-activity rhythm. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 145, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | n = 22 |
|---|---|
| Maternal | |
| Age (years) | 32.7 ± 5.5 a (25.0–46.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.1 ± 6.0 (19.2–38.8) |
| Infant | |
| Sex (male, female) | 12, 10 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 38.9 ± 1.4 (36.0–41.0) |
| Birth weight (g) | 3453 ± 398 (4455–2940) |
| Breastfeeding characteristics | |
| Time postpartum (months) | 3.8 ± 1.0 (3.0–6.0) |
| 24 h milk intake (g) | 879 ± 309 (455–1850) |
| Number of breastfeeds per 24 h | 12.1 ± 3.5 (7.0–16.0) |
| Components | Pre-Feed, (n) | Post-Feed, (n) | Estimate ± SE | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log leptin, pg/mL | 2.28 ± 0.52 a, (234) | 2.27 ± 0.50, (232) | 0.05 ± 0.03 b | 0.16 |
| Log adiponectin, ng/mL | 1.01 ± 0.19, (251) | 0.96 ± 0.20, (248) | 0.11 ± 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Insulin, µIU/mL | 19.45 ± 11.00, (236) | 20.83 ± 11.30, (234) | −1.24 ± 0.54 | 0.02 |
| Log fat, g/L | 1.47 ± 0.18, (241) | 1.77 ± 0.16, (240) | −0.69 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Glucose mmol/L | 1.91 ± 0.73, (247) | 1.84 ± 0.72, (243) | 0.07± 0.03 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suwaydi, M.A.; Lai, C.T.; Rea, A.; Gridneva, Z.; Perrella, S.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Hormones and Macronutrients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173729
Suwaydi MA, Lai CT, Rea A, Gridneva Z, Perrella SL, Wlodek ME, Geddes DT. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Hormones and Macronutrients. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173729
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuwaydi, Majed A., Ching Tat Lai, Alethea Rea, Zoya Gridneva, Sharon L. Perrella, Mary E. Wlodek, and Donna T. Geddes. 2023. "Circadian Variation in Human Milk Hormones and Macronutrients" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173729
APA StyleSuwaydi, M. A., Lai, C. T., Rea, A., Gridneva, Z., Perrella, S. L., Wlodek, M. E., & Geddes, D. T. (2023). Circadian Variation in Human Milk Hormones and Macronutrients. Nutrients, 15(17), 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173729






