Validation of a Turkish Version of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire
Abstract
:1. Introduction
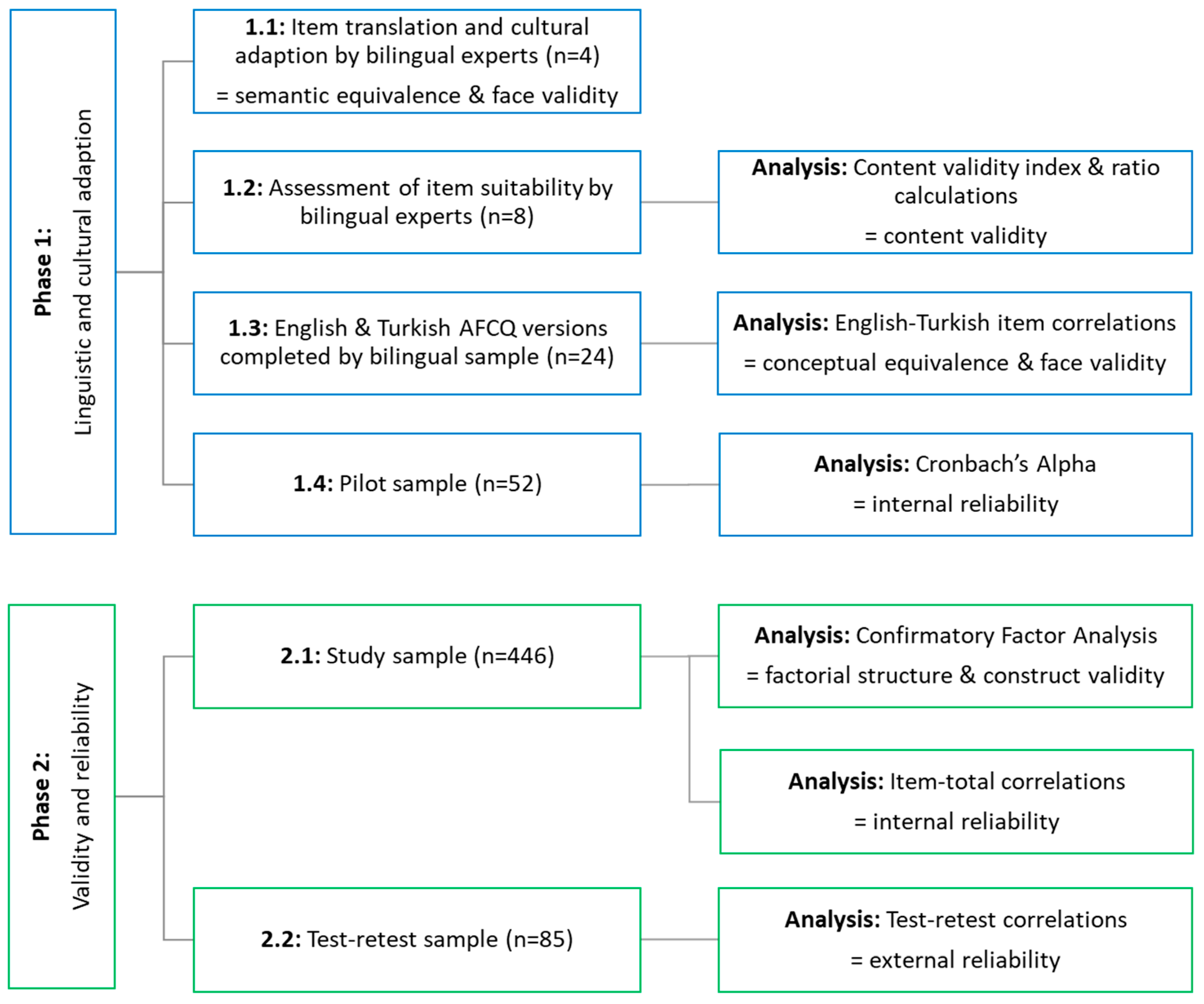
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phase 1: Language Validity
2.2. Phase 2: Validity and Reliability
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phase 1: Language Validity
3.2. Phase 2: Validity and Reliability
3.2.1. Explanatory Factor Analysis
3.2.2. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
3.2.3. Reliability
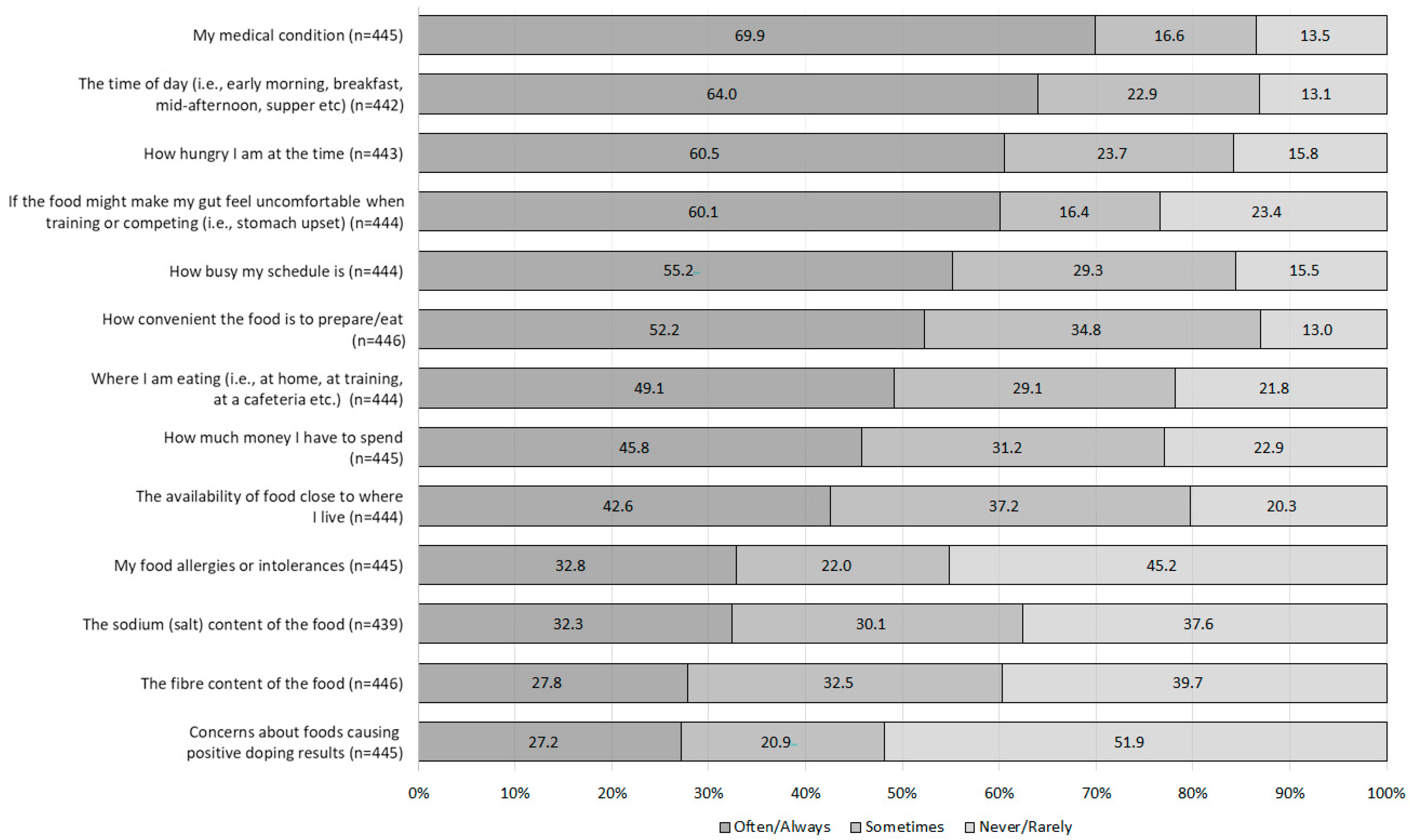
3.2.4. Descriptive Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jenner, S.L.; Buckley, G.L.; Belski, R.; Devlin, B.L.; Forsyth, A.K. Dietary Intakes of Professional and Semi-Professional Team Sport Athletes Do Not Meet Sport Nutrition Recommendations—A Systematic Literature Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, M.R.; Mitchell, N.; Sutton, L.; Backhouse, S.H. Sports nutritionists’ perspectives on enablers and barriers to nutritional adherence in high performance sport: A qualitative analysis informed by the COM-B model and theoretical domains framework. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, M.R.; Patterson, L.B.; Mitchell, N.; Backhouse, S.H. Athlete perspectives on the enablers and barriers to nutritional adherence in high-performance sport. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2021, 52, 101831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelly, F.E.; Thurecht, R. Evaluation of athletes’ food choices during competition with use of digital images. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelly, F.E.; Burkhart, S.J.; Dunn, P. Factors influencing food choice of athletes at international competition events. Appetite 2018, 121, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenhead, K.L.; Slater, G. A Review of Factors Influencing Athletes’ Food Choices. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelly, F.; Thurecht, R.; Slater, G. Determinants of food choice in athletes: A systematic scoping review. Sports Med. 2022, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarar, H.; Gökdemir, K.; Eroğlu, H.; Özdemir, G. Evaluation of knowledge for diet and dietary habits of elite athletes. Selçuk Üniversitesi Beden Eğitimi Ve Spor Bilim Derg. 2011, 13, 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Dikmen, D.; İnan-Eroğlu, E.; Göktaş, Z.; Barut-Uyar, B.; Karabulut, E. Validation of a Turkish version of the Food Choice Questionnaire. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 52, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, Y. Recreational Athletes’ Food Choices. In Scientific Researches in Health Sciences II; Aslan, F.E., Kurtulan, G., Yalin, H., Eds.; Peter Lang: Bern, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurecht, R.L.; Pelly, F.E. Development of a New Tool for Managing Performance Nutrition: The Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurecht, R.L.; Pelly, F.E. The Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire (AFCQ): Validity and Reliability in a Sample of International High-Performance Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurecht, R.L.; Pelly, F.E.; Burkhart, S. Reliability of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire in Diverse Settings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steptoe, A.; Pollard, T.M.; Wardle, J. Development of a measure of the motives underlying the selection of food: The Food Choice Questionnaire. Appetite 1995, 25, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.M.; Cabral, D.; Moura, A.P.; de Almeida, M.D.V. Application of the Food Choice Questionnaire across cultures: Systematic review of cross-cultural and single country studies. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 64, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M.; Fox-Rushby, J.; Badia, X. A Model of Equivalence in the Cultural Adaptation of HRQoL Instruments: The Universalist Approach. Qual. Life Res. 1998, 7, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambleton, R. Guidelines for Adapting Educational and Psychological Tests; The Annual Meeting of the National Council on Measurement in Education; National Center for Education Statistics (ED): New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lawshe, C.H. A quantitative approach to content validity. Pers. Psychol. 1975, 28, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, M.; Dennick, R. Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2011, 2, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, G.O.; Neilands, T.B.; Frongillo, E.A.; Melgar-Quiñonez, H.R.; Young, S.L. Best Practices for Developing and Validating Scales for Health, Social, and Behavioral Research: A Primer. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Exploratory Factor Analysis. In Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2014; pp. 89–151. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T. Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, T.A.; Chung, H. Confidence limits for intraclass reliability coefficients. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 5, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurecht, R.; Pelly, F. Key factors influencing the food choices of athletes at two distinct major international competitions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raykov, T. Scale reliability, Cronbach’s coefficient alpha, and violations of essential tau-equivalence with fixed congeneric components. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1997, 32, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.M. Congeneric and (essentially) tau-equivalent estimates of score reliability: What they are and how to use them. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2006, 66, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trizano-Hermosilla, I.; Alvarado, J.M. Best Alternatives to Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability in Realistic Conditions: Congeneric and Asymmetrical Measurements. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidgen, H.A.; Gallegos, D. Defining food literacy and its components. Appetite 2014, 76, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, R.; Beck, K.L.; Manore, M.M.; Gifford, J.; Flood, V.M.; O’Connor, H. Effectiveness of Education Interventions Designed to Improve Nutrition Knowledge in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, M.R.N.; Mitchell, N.; Backhouse, S.H. Sports nutrition interventions: A systematic review of behavioural strategies used to promote dietary behaviour change in athletes. Appetite 2020, 150, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Type of Athlete | Nutrition Education | ||||||
| Female | 178 | 41 | Recreational | 95 | 21 | Yes—nutritionist or dietitian | 70 | 15.7 |
| Male | 268 | 59 | Amateur | 215 | 48 | Yes (trainer) | 79 | 17.7 |
| Income | Professional/Elite | 136 | 31 | Yes (other) | 20 | 4.5 | ||
| Income < Expenses | 52 | 12 | Sport and Exercise Categories * | Yes (studied nutrition) | 12 | 2.7 | ||
| Income = Expenses | 232 | 52 | Aesthetic | 11 | 2.5 | Yes (doctor) | 6 | 1.3 |
| Income > Expenses | 162 | 36 | Weight category | 64 | 14.3 | No | 259 | 58.1 |
| Living Situation | Team | 213 | 47.8 | Religious Category | ||||
| Alone | 56 | 13 | Racket | 18 | 4.0 | Muslim | 364 | 82.4 |
| Roommate/friend | 32 | 7 | Outdoor sports | 7 | 1.6 | Christian | 2 | 0.5 |
| Partner | 10 | 2 | Skill-based | 2 | 0.4 | Prefer not to say | 14 | 3.2 |
| Family (married +/− children) | 32 | 7 | Swimming and athletics | 48 | 10.8 | Not religious | 62 | 14.0 |
| Parent/s | 316 | 71 | Gym | 83 | 18.6 | Strength of Religious Belief | ||
| Medical/Food Related Conditions | Education | Not religious | 139 | 31.2 | ||||
| Diagnosed chronic disease | 32 | 7.2 | High school-Secondary | 179 | 40 | A little religious | 60 | 13.5 |
| Eating behaviour disorder | 15 | 3.4 | University-Bachelor | 229 | 51 | Moderately religious | 151 | 33.9 |
| Food allergy | 20 | 4.5 | Postgraduate | 38 | 9 | Very religious | 53 | 11.9 |
| Food intolerance | 61 | 13.7 | Prefer not to say | 43 | 9.6 |
| EFA Variance Explained | CFA Factor Loadings | Composite Relibaility | Cronbach’s Alpha (95%CI) | CA, If Item Deleted | Item–Total Correlations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1: Nutritional attributes of the food | 19.24 | 0.928 | 0.751 (0.712–0.785) | |||
| The presence of vitamins and minerals in the food | 0.88 | 0.680 | 0.585 | |||
| The natural content of the food | 0.91 | 0.672 | 0.618 | |||
| The health or nutrition claims about the food | 0.74 | 0.718 | 0.482 | |||
| The nutritional content of the food (protein, fat carbohydrate) | 0.99 | 0.708 | 0.514 | |||
| Whether the food is a wholefood | 0.70 | 0.753 | 0.411 | |||
| Factor 2: Emotional influences | 15.99 | 0.850 | 0.878 (0.859–0.896) | |||
| How sad I feel | 0.67 | 0.818 | 0.802 | |||
| How stressed I feel | 0.82 | 0.802 | 0.840 | |||
| How angry I feel | 0.55 | 0.814 | 0.812 | |||
| Eating to comfort my emotions | 0.71 | 0.926 | 0.519 | |||
| Factor 3: Food and health awareness | 8.892 | 0.710 | 0.665 (0.611–0.713) | |||
| My ability to plan my foods ahead | 0.32 | 0.587 | 0.460 | |||
| My ability to cook for myself | 0.53 | 0.683 | 0.345 | |||
| My knowledge of nutritious foods | 0.90 | 0.565 | 0.508 | |||
| My awareness of the foods I already consumed today | 0.66 | 0.560 | 0.51 | |||
| Factor 4: Influence of others | 6.034 | 0.299 | 0.595 (0.525–0.656) | |||
| What other athletes in my sport are eating | 0.25 | 0.626 | 0.314 | |||
| What my friends are eating | 0.18 | 0.295 | 0.548 | |||
| What my family is eating | 0.61 | 0.547 | 0.372 | |||
| Factor 5: Usual eating practices | 5.478 | 0.813 | 0.519 (0.436–0.592) | |||
| How familiar the food is to me | 0.96 | 0.422 | 0.334 | |||
| The foods that I’ve grown up eating | 0.73 | 0.305 | 0.402 | |||
| My cultural style of eating (e.g., Aegean, Black Sea, Southeast Anatolia) | 0.59 | 0.528 | 0.276 | |||
| Factor 6: Weight control | 4.102 | 0.852 | 0.662 (0.607–0.710) | |||
| If I am trying to lose or gain weight | 0.78 | 0.608 | 0.423 | |||
| If the food is beneficial for my weight goal | 0.65 | 0.522 | 0.555 | |||
| How happy I am with my current weight/body image | 0.74 | 0.580 | 0.463 | |||
| Whether I am in the off season (no competitions or intense training for a period of time) | 0.89 | 0.662 | 0.344 | |||
| Factor 7: Food values and beliefs | 3.998 | 0.775 | 0.545 (0.466–0.613) | |||
| If the food aligns with my values for animal welfare (i.e., no animal products/vegan, cruelty-free raised animals) | 0.81 | 0.486 | 0.329 | |||
| My religious food beliefs | 0.84 | 0.509 | 0.337 | |||
| If the food is sustainably produced | 0.52 | 0.350 | 0.433 | |||
| Factor 8: Sensory appeal | 3.103 | 0.767 | 0.713 (0.663–0.756) | |||
| The flavour of the food | 0.80 | 0.498 | 0.656 | |||
| The taste of the food | 0.99 | 0.482 | 0.672 | |||
| The sensory appeal of available foods | 0.28 | 0.912 | 0.359 | |||
| Factor 9: Performance | 2.998 | 0.744 | 0.891 (0.873–0.908) | |||
| My need to fuel my body for competition | 0.81 | 0.869 | 0.773 | |||
| My need to feel energetic for training & competing | 0.74 | 0.810 | 0.834 | |||
| My need to fuel my body for recovery | 0.54 | 0.860 | 0.771 |
| Fit Indices | Good | Acceptable | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Model Fit | ||||
| Χ2/df | ≤3 | ≤4–5 | 2.12 | Good fit |
| Comparative Fit Indices | ||||
| NFI | ≥0.95 | 0.94–0.90 | 0.927 | Acceptable fit |
| NNFI | ≥0.95 | 0.94–0.90 | 0.938 | Acceptable fit |
| IFI | ≥0.95 | 0.94–0.90 | 0.972 | Good fit |
| CFI | ≥0.97 | ≥0.95 | 0.980 | Good fit |
| RMSEA | ≤0.05 | 0.06–0.08 | 0.017 | Good fit |
| Absolute Fit Indices | ||||
| GFI | ≥0.90 | 0.89–0.85 | 0.945 | Good fit |
| AGFI | ≥0.90 | 0.89–0.85 | 0.967 | Good fit |
| Residual-Based Fit Indices | ||||
| RMR | ≤0.05 | 0.06–0.08 | 0.023 | Good fit |
| Nutritional Attributes of the Food | Emotional Influences | Food and Health Awareness | Influence of Others | Usual Eating Practices | Weight Control | Food Values and Beliefs | Sensory Appeal | Perfor-Mance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional attributes of the food | 0.851 | ||||||||
| Emotional influences | 0.048 | 0.694 | |||||||
| Food and health awareness | 0.426 | −0.066 | 0.638 | ||||||
| Influence of others | 0.137 | 0.188 | 0.195 | 0.395 | |||||
| Usual eating practices | 0.319 | 0.105 | 0.300 | 0.345 | 0.775 | ||||
| Weight control | 0.402 | 0.063 | 0.321 | 0.179 | 0.199 | 0.770 | |||
| Food values and beliefs | 0.131 | 0.169 | 0.112 | 0.219 | 0.186 | 0.075 | 0.738 | ||
| Sensory appeal | −0.023 | 0.353 | −0.051 | 0.120 | 0.242 | 0.058 | 0.110 | 0.752 | |
| Performance | 0.352 | −0.046 | 0.312 | 0.186 | 0.177 | 0.435 | 0.089 | 0.062 | 0.706 |
| AVE | 0.724 | 0.482 | 0.407 | 0.156 | 0.601 | 0.593 | 0.544 | 0.566 | 0.498 |
| Discriminant Validity | Convergent Validity | Reliability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | √ AVE > Inter- Factor Correlation | AVE | Item Factor Loadings (# Items) | Composite Reliability | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Nutritional attributes of the food | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (5/5) | Good | Acceptable |
| Performance | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (2/3), acceptable (1/3) | Acceptable | Good |
| Weight control | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (3/4), acceptable (1/4) | Good | Tolerable |
| Usual eating practices | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (2/3), acceptable (1/3) | Good | Unacceptable |
| Food values and beliefs | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (2/3), acceptable (1/3) | Acceptable | Unacceptable |
| Sensory appeal | Acceptable | Acceptable | Ideal (2/3), unacceptable (1/3) | Acceptable | Acceptable |
| Emotional influences | Acceptable | Tolerable | Ideal (2/4), acceptable (2/4) | Good | Good |
| Food and health awareness | Acceptable | Tolerable | Ideal (1/4), acceptable (2/4), unacceptable (1/4) | Acceptable | Tolerable |
| Influence of others | Acceptable | Unacceptable | Acceptable (1/3), unacceptable (2/3) | Unacceptable | Tolerable |
| Factor | Sex | p | Nutrition Education | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Female | Male | Value | Yes | No | Value | |
| Performance | 4.33 | 4.00 | 4.67 | 0.005 | 4.33 | 4.33 | NS |
| Food and health awareness | 3.75 | 3.75 | 3.50 | NS | 4.00 | 3.50 | <0.001 |
| Sensory appeal | 3.67 | 4.00 | 3.67 | <0.001 | 4.00 | 3.67 | NS |
| Nutritional attributes of the food | 3.60 | 3.60 | 3.60 | NS | 3.80 | 3.40 | 0.011 |
| Weight control | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.75 | <0.001 | 3.75 | 3.50 | <0.001 |
| Usual eating practices | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | NS | 3.33 | 3.00 | 0.033 |
| Emotional influence | 2.75 | 3.00 | 2.25 | <0.001 | 2.50 | 2.75 | NS |
| Influence of others | 2.67 | 3.00 | 2.67 | NS | 3.00 | 2.67 | NS |
| Food values and beliefs | 2.67 | 2.67 | 2.67 | NS | 2.67 | 2.67 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sevim, Y.; Thurecht, R.L.; Pelly, F.E. Validation of a Turkish Version of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163612
Sevim Y, Thurecht RL, Pelly FE. Validation of a Turkish Version of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163612
Chicago/Turabian StyleSevim, Yonca, Rachael L. Thurecht, and Fiona E. Pelly. 2023. "Validation of a Turkish Version of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163612
APA StyleSevim, Y., Thurecht, R. L., & Pelly, F. E. (2023). Validation of a Turkish Version of the Athlete Food Choice Questionnaire. Nutrients, 15(16), 3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163612







