The Effects of Agave Fructans in a Functional Food Consumed by Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Subjects
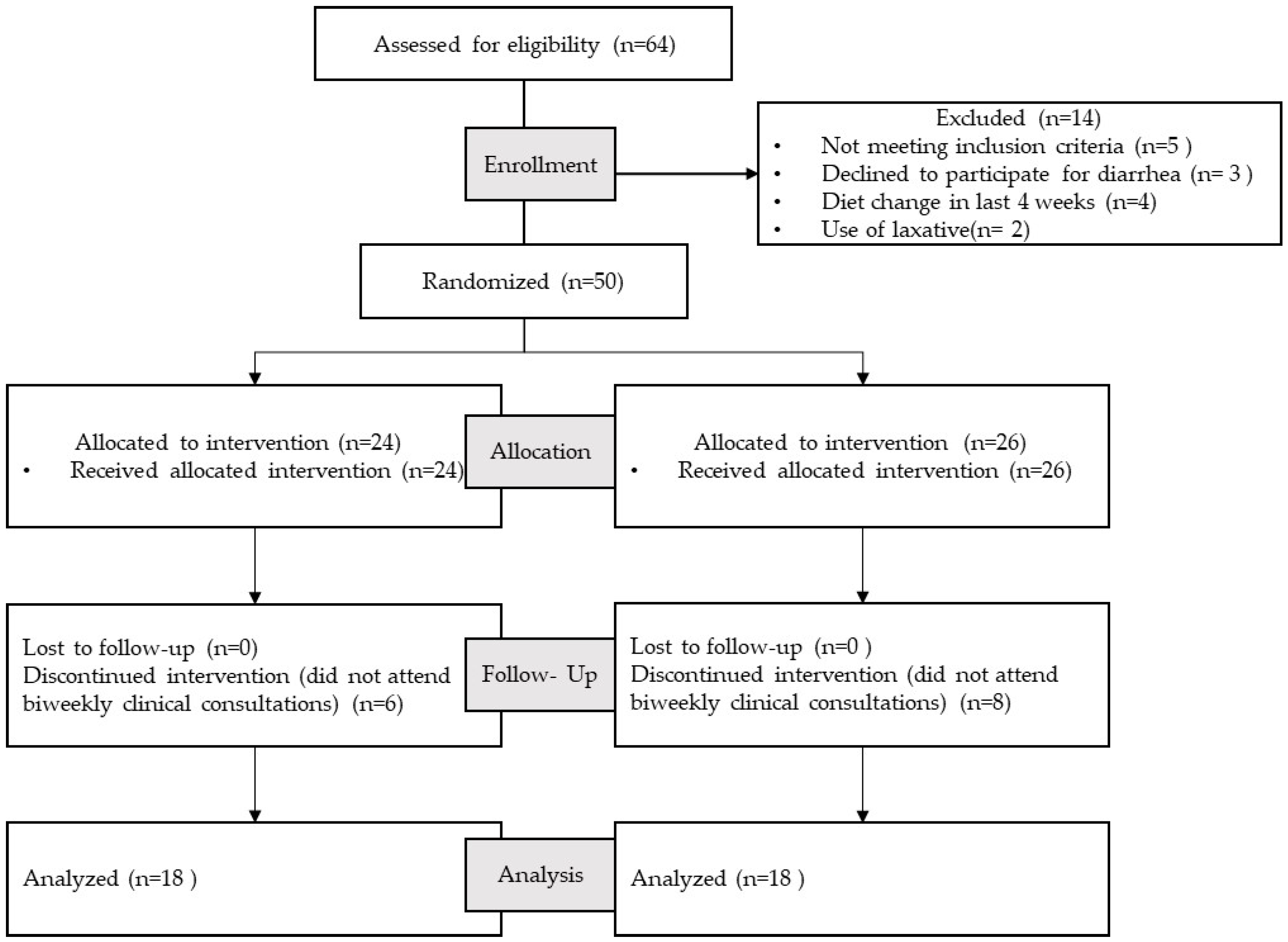
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Quality of Life (IBS-QOL)
2.5. Anxiety and Depression (HADS)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics and Anthropometric Measures
3.2. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
3.3. Stool Characteristics and Bowel Movements
3.4. Quality of Life (IBS-QOL) and Subscales
3.5. Anxiety and Depression (HADS) Score
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmona-Sánchez, R.; Icaza-Chávez, M.E.; Bielsa-Fernández, M.V.; Gómez-Escudero, O.; Bosques-Padilla, F.; Coss-Adame, E.; Esquivel-Ayanegui, F.; Flores-Rendón, R.; González-Martínez, M.A.; Huerta-Iga, F.; et al. Consenso Mexicano Sobre El Síndrome de Intestino Irritable. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2016, 81, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sebastián Domingo, J.J. The New Rome Criteria (IV) of Functional Digestive Disorders in Clinical Practice. Med. Clínica 2017, 148, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-López, M.C.; Coss-Adame, E. Quality of Life in Patients with Different Constipation Subtypes Based on the Rome III Criteria. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2015, 80, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niv, E.; Naftali, T.; Hallak, R.; Vaisman, N. The Efficacy of Lactobacillus Reuteri ATCC 55730 in the Treatment of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Study. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainsbury, A.; Ford, A.C. Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Beyond Fiber and Antispasmodic Agents. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.; Lea, R.; Agrawal, A.; Whorwell, P.J. Bran and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Primary-Care Perspective. Dig. Liver Dis. 2006, 38, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmulson, M. Does a Low FODMAP Diet Improve Symptoms in Mexican Patients with IBS? Una Dieta Baja En FODMAP Mejora Los Síntomas En Pacientes Mexicanos. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2015, 80, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaman, J.; Mego, M.; Manichanh, C.; Cañellas, N.; Cañueto, D.; Segurola, H.; Jansana, M.; Malagelada, C.; Accarino, A.; Vulevic, J.; et al. Effects of Prebiotics Vs a Diet Low in Fodmaps in Patients With Functional Gut Disorder. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Clinical Review. JAMA 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, D.K.; Mitchell, S.B.; Barrett, J.S.; Shepherd, S.J.; Irving, P.M.; Biesiekierski, J.R.; Smith, S.; Gibson, P.R.; Muir, J.G. Manipulation of Dietary Short Chain Carbohydrates Alters the Pattern of Gas Production and Genesis of Symptoms in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Rossi, M.; Dimidi, E.; Whelan, K. Prebiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional Bowel Disorders in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Serra, J.; Fernandez-Bañares, F.; Mearin, F. The Low-FODMAP Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Lights and Shadows. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 39, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnani, P.; Costabile, A.; Bustillo, A.G.R.; Gibson, G.R. A Randomised, Double- Blind, Cross-over Study Investigating the Prebiotic Effect of Agave Fructans in Healthy Human Subjects. J. Nutr. Sci. 2015, 4, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Martínez, J.R.; González-Cervantes, R.M.; Hernández-Gallegos, M.A.; Campos Mendiola, R.; Jiménez Aparicio, A.; Arenas Ocampo, M.L. Prebiotic Potential of Agave Angustifolia Haw Fructans with Different Degrees of Polymerization. Molecules 2014, 19, 12660–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Jasso, G.M.; Camacho-Díaz, B.H.; Lucía, M.; Ocampo, A.; Jiménez-Ferrer, J.E.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Osorio-Díaz, P.; De Desarrollo, C.; Bióticos, D.P.; Nacional, I.P.; et al. Prebiotic Effects of a Mixture of Agavins and Green Banana Flour in a Mouse Model of Obesity. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: The Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, D.L.; Drossman, D.A.; Frederick, I.; Glogau, C.L.; Puder, K. Quality of Life with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-QOL): Development and Validation of a New Measure. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A.; Patrick, D.L.; Whitehead, W.E.; Toner, B.B.; Diamant, N.E.; Hu, Y.; Jia, H.; Bangdiwala, S.I. Further Validation of the IBS-QOL: A Disease-Specific Quality-of-Life Questionnaire. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Park, J.M.; Lim, C.H.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, M.G.; Chung, I.S.; Chung, Y.K. Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gut Liver 2011, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, C.; Algera, J.; Colomier, E.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M. Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Food-Related Symptoms: Future Directions in the Clinical Management. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, D.; Murphy, E.F.; Tan, H.T.T.; Larsen, I.S.; O’Neill, I.; Quigley, E.M.M. Interactions between Symptoms and Psychological Status in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Exploratory Study of the Impact of a Probiotic Combination. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, T.J.; Martinez, C.; Niesler, B.; Van Der Voort, I.; Monnikes, H.; Stengel, A.; Goebel-Stengel, M. The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 531385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.L.S. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Clinical Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12144–12160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersryd, A.; Posserud, I.; Abrahamsson, H.; Simrén, M. Subtyping the Irritable Bowel Syndrome by Predominant Bowel Habit: Rome II versus Rome III. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, M.R.; Raker, J.M.; Whelan, K. Validity and Reliability of the Bristol Stool Form Scale in Healthy Adults and Patients with Diarrhoea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Sarkhel, S.; Sarkar, R.; Dhali, G. Anxiety and Depression in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2017, 39, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Hall, G.B.; Ghajar, K.; Nardelli, A.; Bolino, C.; Lau, J.T.; Martin, F.P.; Cominetti, O.; Welsh, C.; Rieder, A.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium Longum NCC3001 Reduces Depression Scores and Alters Brain Activity: A Pilot Study in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 448–459.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Moayyedi, P. Meta-Analysis: Factors Affecting Placebo Response Rate in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Targeting Gut Microbiota with a Complex Mix of Dietary Fibers Improves Metabolic Diseases. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Adame, M.B.; Martínez-Alvarado, A.; Martínez-Silva, A.V.; Samaniego-Méndez, V.; López, M.G. Agavins Impact on Gastrointestinal Tolerability-Related Symptoms during a Five-Week Dose-Escalation Intervention in Lean and Obese Mexican Adults: Exploratory Randomized Clinical Trial. Foods 2022, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdovinos, M.A.; Coss-Adame, E.; Martínez-Vázquez, S.E.; Remes-Troche, J.M. Estreñimiento Crónico, Síndrome de Intestino Irritable y Enfermedad Inflamatoria Intestinal; Permanyer: Cataluña, Spain, 2020; ISBN 9788418150302. [Google Scholar]
- Altobelli, E.; Del Negro, V.; Angeletti, P.M.; Latella, G. Low-FODMAP Diet Improves Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjú, P.; Farkas, N.; Hegyi, P.; Garami, A.; Szabo, I.; Illes, A.; Solymár, M.; Vincze, A.; Balaskó, M.; Pár, G.; et al. Low Fermentable Oligosaccharies, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides and Polyols (FODMAP) Diet Improves Symptoms in Adults Suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Compared to Standard IBS Diet: A Meta- Analysis of Clinical Studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, D.; Klose, P.; Lauche, R.; Dobos, G.; Langhorst, J.; Cramer, H. Low Fermentable, Oligo-, Di-, Mono-Saccharides and Polyol Diet in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrition 2018, 45, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M. A Role for the Gut Microbiota in IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. 2014, 11, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, H.M.; Whelan, K. Altered Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Modification by Diet: Probiotics, Prebiotics and the Low FODMAP Diet. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, C.; Altomare, A.; Terrigno, V.; Carbone, F.; Tack, J.; Cicala, M.; Pier Luca Guarino, M. Constipation-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-C): Effects of Different Nutritional Patterns on Intestinal Dysbiosis and Symptoms. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrae, D.A.; Patrick, D.L.; Drossman, D.A.; Covington, P.S. Evaluation of the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Quality of Life (IBS-QOL) Questionnaire in Diarrheal-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2013, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudacher, H.M.; Whelan, K.; Irving, P.M.; Lomer, M.C.E. Comparison of Symptom Response Following Advice for a Diet Low in Fermentable Carbohydrates (FODMAPs) versus Standard Dietary Advice in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 24, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRorie, J.W.; McKeown, N.M. Understanding the Physics of Functional Fibers in the Gastrointestinal Tract: An Evidence-Based Approach to Resolving Enduring Misconceptions about Insoluble and Soluble Fiber. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; Coss-Adame, E.; Lopéz-Colombo, A.; Amieva-Balmori, M.; Carmona Sánchez, R.; Charúa Guindic, L.; Flores Rendón, R.; Gómez Escudero, O.; González Martínez, M.; Icaza Chávez, M.E.; et al. The Mexican Consensus on Chronic Constipation. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2018, 83, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.M.; Botelho, P.B. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Chronic Constipation: Outstanding Aspects to Be Considered for the Current Evidence. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 935830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibowski, P.; Skrzypek, M.; Ćwiklińska, M.; Drozd, M.; Kowalska, A. Chemical Stability of Fructans in Apple Beverages and Their Influence on Chronic Constipation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3860–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micka, A.; Siepelmeyer, A.; Holz, A.; Theis, S.; Schön, C. Effect of Consumption of Chicory Inulin on Bowel Function in Healthy Subjects with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 68, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilipenko, V.I.; Teplyuk, D.A.; Shakhovskaya, A.K.; Isakov, V.A.; Vorobyova, V.M.; Vorobyova, I.S.; Glazkova, I.V.; Kochetkova, A.A.; Mikheeva, G.A.; Yudina, A.V. Dry jelly concentrate with vitamins and dietary fiber in patients with IBS with constipation: A comparative controlled study. Vopr. Pitan. 2015, 84, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko, V.I.; Teplyuk, D.A.; Shakhovskaya, A.K.; Isakov, V.A.; Vorobyova, V.M.; Vorobyova, I.S.; Sarkisyan, V.A.; Kochetkova, A.A.; Mikheeva, G.A.; Yudina, A.V. Using a multicomponent functional food in IBS patients with constipation a comparative controlled study. Vopr. Pitan. 2016, 85, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-González, F.; Parra-Montes de Oca, M.A.; Ávila-Reyes, S.V.; Camacho-Díaz, B.H.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Arenas-Ocampo, M.L. A Rheological Study of Chicory and Agave Tequilana Fructans for Use in Foods. LWT 2019, 115, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J. Impact of the proposed definition of dietary fiber on nutrient databases. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; McCahon, D.; Holder, R.; Wilson, S.; Hobbs, R. A Randomised Controlled Trial of a Probiotic “Functional Food” in the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freijy, T.M.; Cribb, L.; Oliver, G.; Metri, N.J.; Opie, R.S.; Jacka, F.N.; Hawrelak, J.A.; Rucklidge, J.J.; Ng, C.H.; Sarris, J. Effects of a High-Prebiotic Diet versus Probiotic Supplements versus Synbiotics on Adult Mental Health: The “Gut Feelings” Randomised Controlled Trial. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1097278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gelyfun®gastro | Test Jelly | Placebo Jelly | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrition Facts | g/Serving | kcal/Serving | g/Serving | kcal/Serving |
| Carbohydrates | 13.2 | 52.8 | 13.2 | 52.8 |
| Proteins | 2.9 | 11.6 | 2.9 | 11.6 |
| Lipids | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Fiber (as powder with 95% agave fructans) | 7.8 | 11.7 | ___ | ___ |
| Total | 76.1 | Total | 64.4 | |
| Study Parameter | Baseline Study Group (n = 24) | 30 Days Baseline Study Group (n = 18) | p Value * (Change from Baseline) | Baseline Placebo Group (n = 26) | 30 Days Placebo Group (n = 18) | p Value * (Change from Baseline) | p Value ** (Study vs. Placebo Group 30 Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 70.98 | 71.38 | 0.846 | 67.99 | 58.87 | 0.951 | 0.373 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.34 | 28.11 | 0.765 | 27.65 | 24.15 | 0.839 | 0.494 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 90.13 | 91.03 | 0.607 | 89.43 | 77.75 | 0.607 | 0.710 |
| MUAC(cm) | 31.16 | 31.18 | 0.684 | 31.44 | 27.43 | 0.072 | 0.039 ** |
| Body fat (%) | 38.47 | 38.42 | 0.181 | 37.47 | 32.80 | 0.090 | 0.571 |
| Fat-free mass (%) | 60.99 | 62.04 | 0.370 | 62.52 | 53.78 | 0.102 | 0.585 |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 53,78 | 53.70 | 0.957 | 55,45 | 51.71 | 0.344 | 0.319 |
| Proteins (%) | 16.74 | 18.55 | 0.145 | 16.77 | 17.50 | 0.314 | 0.594 |
| Lipids (%) | 31.0 | 29.65 | 0.812 | 29.62 | 31.97 | 0.693 | 0.207 |
| Fiber (g) | 16.09 | 23.48 | 0.021 * | 13.98 | 10.66 | 0.171 | 0.388 |
| Energy (kcal) | 1771.2 | 1841 | 0.625 | 1614 | 1580.86 | 0.850 | 0.218 |
| MET (kcal/kg/h) | 1687 | 1315 | 0.189 | 941.9 | 568 | 0.310 | 0.005 ** |
| Study Parameter | Baseline Study Group n = 24 (n, %) | Day 15 Study Group n = 18 (n, %) | Day 30 Study Group n = 18 (n, %) | p Value * (Change from Baseline) | Baseline Placebo Group n = 26 (n, %) | Day 15 Placebo Group n = 18 (n, %) | Day 30 Placebo Group n = 18 (n, %) | p Value * (Change from Baseline) | p Value ** (Study Group/ Placebo Group 30 Day) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 1 | 4.2% | 3 | 16.7% | 2 | 11.1% | 0.549 | 2 | 7.7% | 3 | 16.7% | 2 | 11.1% | 0.174 | 0.694 |
| Constipation | 24 | 100% | 3 | 16.7% | 6 | 33.3% | 0.000 * | 26 | 100% | 10 | 55.6% | 8 | 44.4% | 0.000 * | 0.014 ** |
| Gastritis | 11 | 45.8% | 2 | 11.1% | 5 | 27.8% | 0.016 * | 18 | 69.2% | 8 | 44.4% | 9 | 50.0% | 0.018 * | 0.217 |
| Reflux | 14 | 58.3% | 4 | 22.2% | 4 | 22.2% | 0.125 | 15 | 57.7% | 8 | 44.4% | 8 | 44.4% | 0.368 | 0.570 |
| Vomiting | 2 | 8.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.135 | 3 | 11.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.135 | 0.817 |
| Bloating | 11 | 45.8% | 14 | 77.8% | 11 | 61.1% | 0.368 | 23 | 88.5% | 15 | 83.3% | 13 | 72.2% | 0.016 * | 0.161 |
| Flatulence | 8 | 33.3% | 15 | 83.3% | 13 | 72.2% | 0.368 | 19 | 73.1% | 16 | 88.9% | 11 | 61.1% | 0.074 | 0.000 ** |
| Abdominal pain | 7 | 29.2% | 6 | 33.3% | 3 | 16.7% | 0.097 | 19 | 73.1% | 13 | 72.2% | 9 | 50.0% | 0.093 | 0.702 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorder Bristol Subscale | Bowel Movements per Week | % Study Group | Bowel Movements per Week | % Placebo Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal | Constipation | 2 | 69.6% a | 4 | 76.9% a |
| Normal | 3 | 30.4% a | 3 | 23.1% a | |
| Diarrhea | 0 | 0.0% a | 0 | 0.0% a | |
| Day 15 | Constipation | 7 | 10.5% b | 8 | 41.7% a |
| Normal | 12 | 73.7% b | 9 | 54.2% a | |
| Diarrhea | 14 | 15.8% a | 14 | 4.2% a | |
| Day 30 | Constipation | 4 | 25.0% a | 4 | 25.0% a |
| Normal | 12 | 70.0% b | 10 | 55.0% a | |
| Diarrhea | 7 | 5.0% a | 18 | 20.0% a |
| Study Parameter | Baseline Study Group (n = 24) ±(SD) | 30 Days Study Group (n = 18) ±(SD) | Mean Change from Baseline | p Value * | Baseline Placebo Group (n = 26) ±(SD) | 30 Days Placebo Group (n = 18) ±(SD) | Mean Change from Baseline | p Value * | p Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall IBS-QOL (%) | 61.47 ±5.84 | 76.06 ±4.24 | 14.59 | 0.001 * | 70.76 ±4.52 | 79.94 ±3.45 | 9.18 | 0.003 * | 0.456 |
| Dysphoria | 65.13 ±9.19 | 79.13 ±8.04 | 14.00 | 0.001 * | 75.00 ±9.35 | 84.25 ±7.69 | 9.25 | 0.005 * | 0.810 |
| Interference with activity | 64.00 ±6.58 | 77.86 ±4.67 | 13.86 | 0.004 * | 70.57 ±7.56 | 81.57 ±6.11 | 11.00 | 0.002 * | 0.723 |
| Body image | 55.75 ±5.01 | 71.75 ±4.15 | 16.00 | 0.002 * | 64.75 ±5.09 | 74.50 ±4.81 | 9.75 | 0.001 * | 0.666 |
| Health worry | 46.00 ±2.79 | 61.33 ±3.23 | 15.33 | 0.005 * | 57.33 ±2.35 | 69.33 ±2.90 | 12.00 | 0.003 * | 0.504 |
| Food avoidance | 56.00 ±3.28 | 71.33 ±2.95 | 15.33 | 0.006 * | 62.67 ±3.27 | 69.33 ±2.53 | 6.67 | 0.188 | 0.203 |
| Social reaction | 63.50 ±4.15 | 78.50 ±3.38 | 15.00 | 0.001 * | 78.67 ±2.76 | 84.00 ±3.24 | 5.33 | 0.368 | 0.958 |
| Sexual | 64.50 ±2.81 | 79.50 ±2.62 | 15.00 | 0.017 * | 79.00 ±3.15 | 86.00 ±2.12 | 7.00 | 0.096 | 0.222 |
| Relationship | 69.33 ±3.36 | 83.33 ±2.56 | 14.00 | 0.006 * | 74.00 ±1.91 | 84.00 ±1.64 | 10.00 | 0.003 * | 0.719 |
| Overall HADS | 29.04 ±4.60 | 21.58 ±2.84 | 7.46 | 0.003 * | 27.35 ±5.47 | 20.54 ±3.11 | 6.81 | 0.015 * | 0.333 |
| Anxiety | 13.92 ±1.00 | 10.00 ±0.75 | 3.92 | 0.003 * | 12.77 ±3.89 | 10.08 ±1.92 | 2.69 | 0.051 | 0.215 |
| Depression | 15.13 ±0.75 | 11.58 ±0.16 | 3.55 | 0.006 * | 14.58 ±0.51 | 10.46 ±0.87 | 4.12 | 0.007 * | 0.609 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camacho-Díaz, B.H.; Arenas-Ocampo, M.L.; Osorio-Díaz, P.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Alvarado-Jasso, G.M.; Saavedra-Briones, E.V.; Valdovinos-Díaz, M.Á.; Gómez-Reyes, E. The Effects of Agave Fructans in a Functional Food Consumed by Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163526
Camacho-Díaz BH, Arenas-Ocampo ML, Osorio-Díaz P, Jiménez-Aparicio AR, Alvarado-Jasso GM, Saavedra-Briones EV, Valdovinos-Díaz MÁ, Gómez-Reyes E. The Effects of Agave Fructans in a Functional Food Consumed by Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163526
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamacho-Díaz, Brenda Hildeliza, Martha Lucía Arenas-Ocampo, Perla Osorio-Díaz, Antonio Ruperto Jiménez-Aparicio, Guadalupe Monserrat Alvarado-Jasso, Edén Valfré Saavedra-Briones, Miguel Ángel Valdovinos-Díaz, and Elisa Gómez-Reyes. 2023. "The Effects of Agave Fructans in a Functional Food Consumed by Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163526
APA StyleCamacho-Díaz, B. H., Arenas-Ocampo, M. L., Osorio-Díaz, P., Jiménez-Aparicio, A. R., Alvarado-Jasso, G. M., Saavedra-Briones, E. V., Valdovinos-Díaz, M. Á., & Gómez-Reyes, E. (2023). The Effects of Agave Fructans in a Functional Food Consumed by Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 15(16), 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163526







