No Associations between Dairy Intake and Markers of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy Adult Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Dietary Intake Assessment
2.3. Stool Collection
2.4. Plasma Collection
2.5. Quantification of Gut Inflammation Markers
2.6. Fecal Calprotectin and MPO
2.7. Fecal Neopterin
2.8. Plasma Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein (LBP)
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
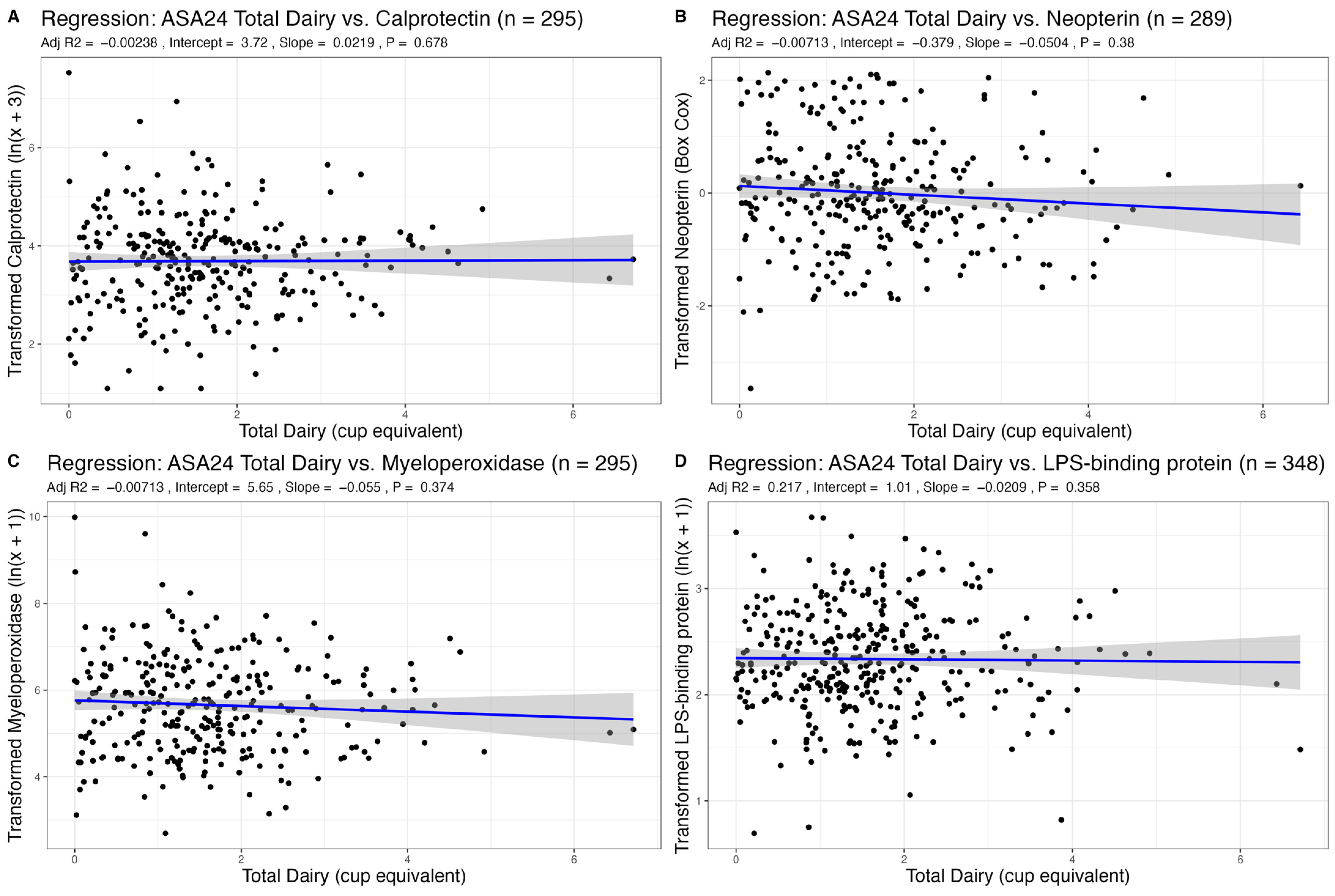
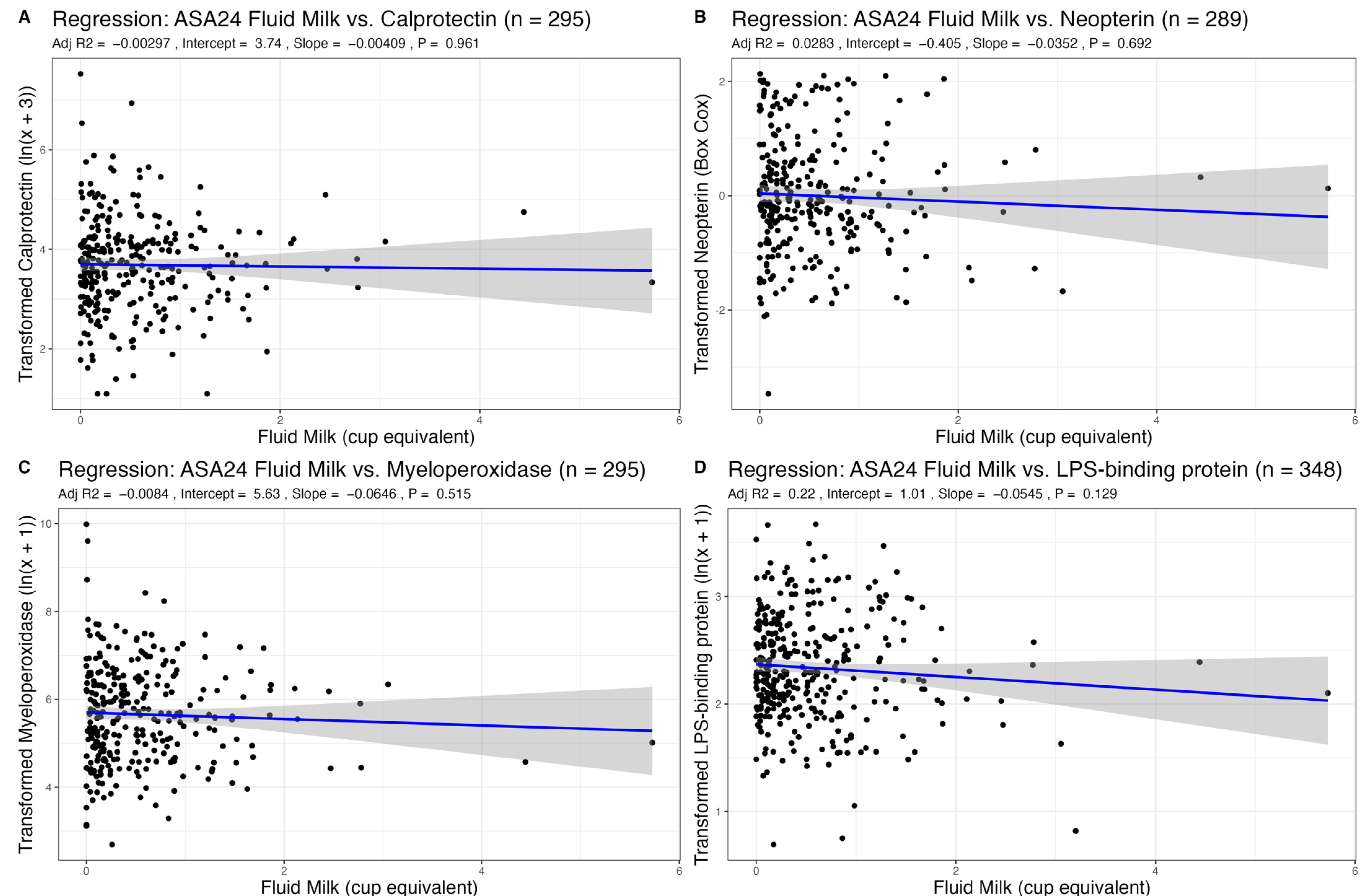
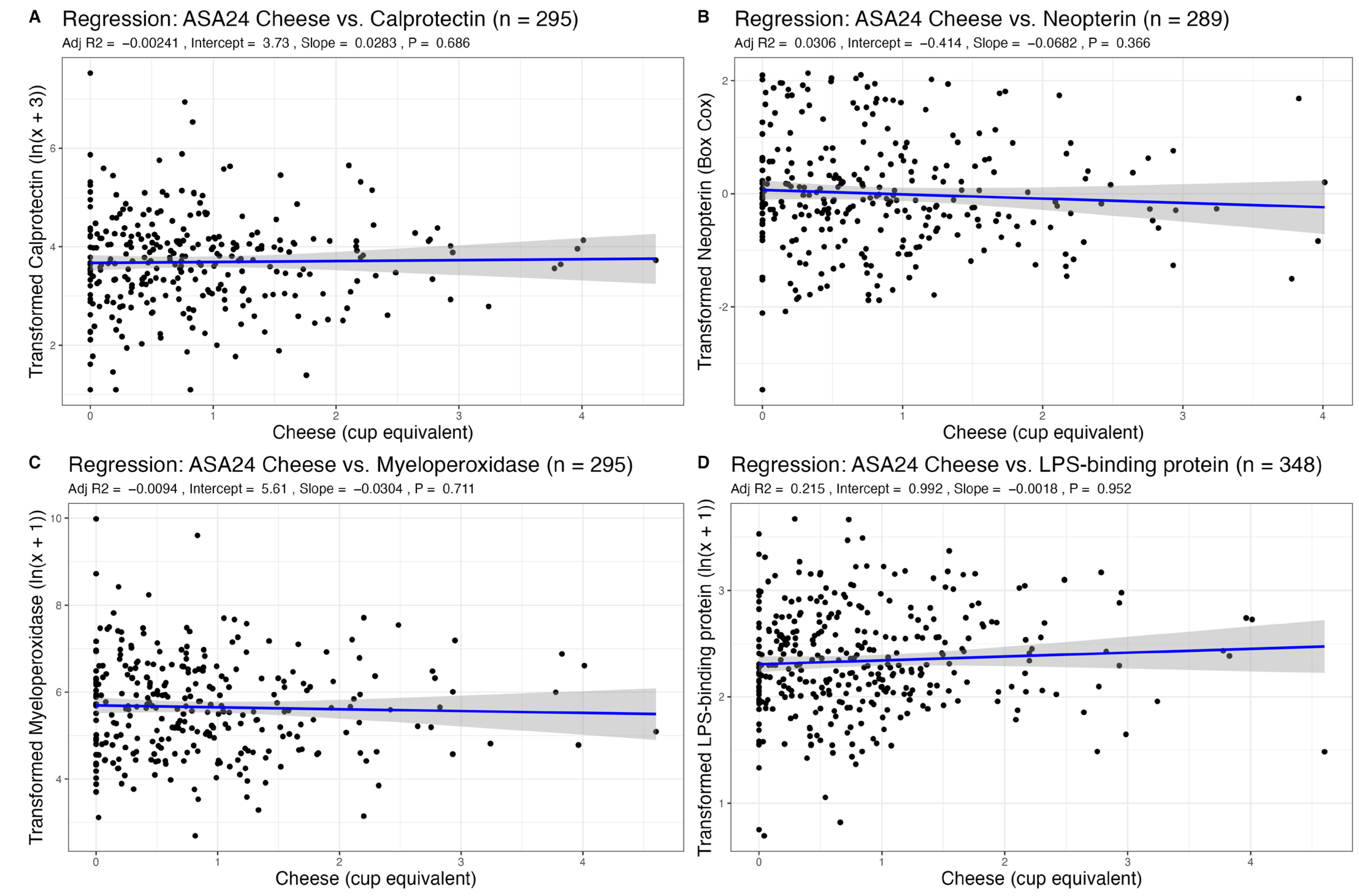
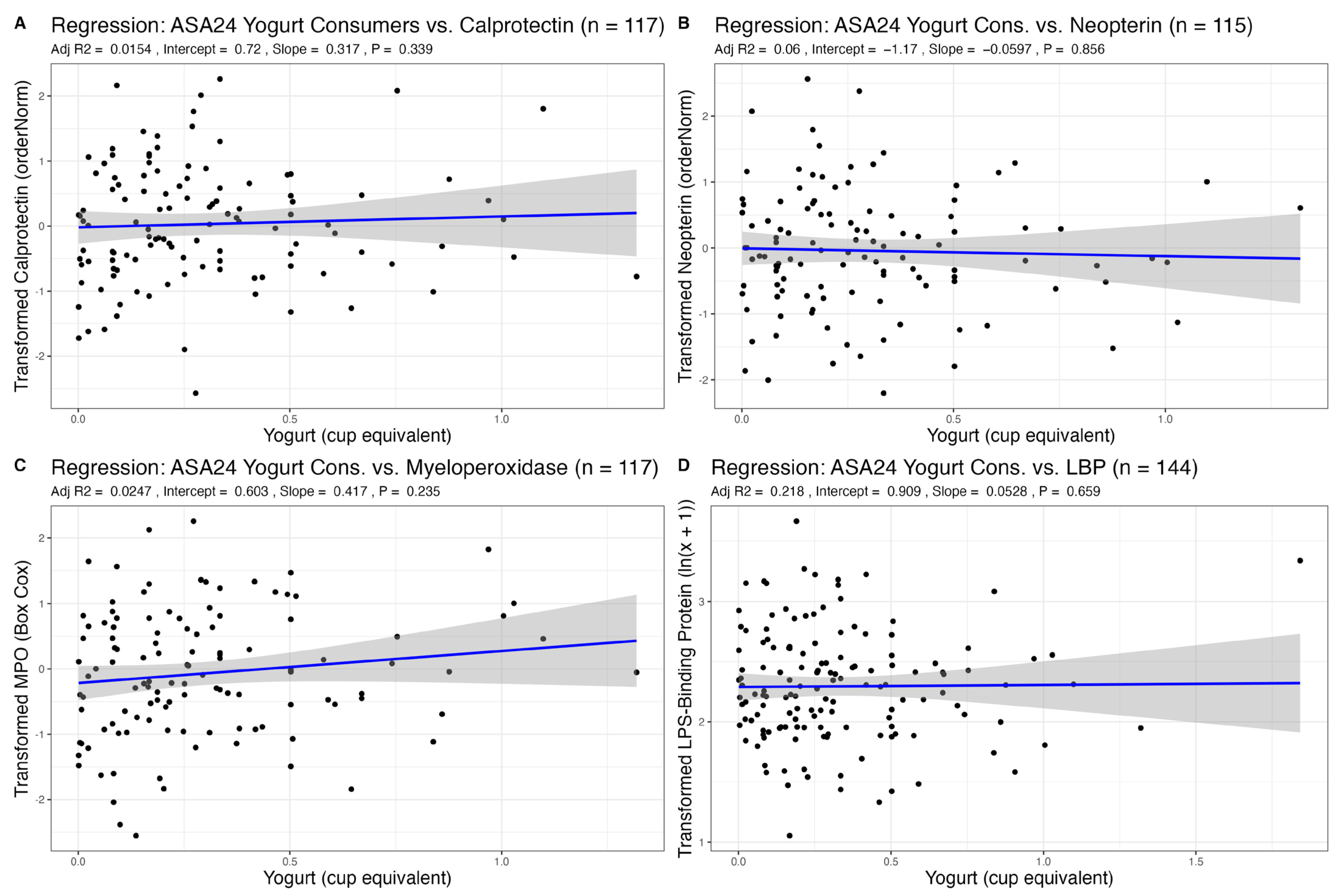
3.2. Association of Dairy Intake with Fecal Markers of GI Inflammation
3.3. Association of Dairy Intake with Plasma LBP, a Marker of Endotoxin Exposure
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of Agriculture; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025; 9th ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Mazidi, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Sattar, N.; Howard, G.; Graham, I.; Banach, M. Consumption of Dairy Product and Its Association with Total and Cause Specific Mortality—A Population-Based Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 38, 2833–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; Sheridan, P.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Gupta, R.; Lear, S.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Avezum, A.; et al. Association of Dairy Intake with Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in 21 Countries from Five Continents (PURE): A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, S.; Tucker, K.L.; Kiel, D.P.; Quach, L.; Casey, V.A.; Hannan, M.T. Milk and Yogurt Consumption Are Linked with Higher Bone Mineral Density but Not with Hip Fracture: The Framingham Offspring Study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2013, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gijsbers, L.; Ding, E.L.; Malik, V.S.; de Goede, J.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.S. Consumption of Dairy Foods and Diabetes Incidence: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulven, S.M.; Holven, K.B.; Gil, A.; Rangel-Huerta, O.D. Milk and Dairy Product Consumption and Inflammatory Biomarkers: An Updated Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S239–S250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavian, S.P.; Rahimlou, M.; Saneei, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of Dairy Products Consumption on Inflammatory Biomarkers among Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonté, M.-È.; Couture, P.; Richard, C.; Desroches, S.; Lamarche, B. Impact of Dairy Products on Biomarkers of Inflammation: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Nutritional Intervention Studies in Overweight and Obese Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.M.; Stephensen, C.B.; Kratz, M.; Bolling, B.W. Exploring the Links between Diet and Inflammation: Dairy Foods as Case Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, K.M.; Anderson, B.D.; Cifelli, C.J. The Effects of Dairy Product and Dairy Protein Intake on Inflammation: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, A.; Danesi, F.; Dardevet, D.; Dupont, D.; Fernandez, A.S.; Gille, D.; Nunes dos Santos, C.; Pinto, P.; Re, R.; Rémond, D.; et al. Dairy Products and Inflammation: A Review of the Clinical Evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2497–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, M.; Akpotaire, O. Diet and the Role of Food in Common Gastrointestinal Diseases. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, B.; Skurk, T.; Lagkouvardos, L.; Fischer, S.; Büttner, J.; Lichtenegger, M.; Clavel, T.; Lechner,, A.; Rychlik, M.; Haller, D.; et al. Short-Term Overfeeding with Dairy Cream Does Not Modify Gut Permeability, the Fecal Microbiota, or Glucose Metabolism in Young Healthy Men. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Woodford, K.; Kukuljan, S.; Pal, S. Comparative Effects of A1 versus A2 Beta-Casein on Gastrointestinal Measures: A Blinded Randomised Cross-over Pilot Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernlund, P.G.; Hvas, C.L.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Bahl, M.I.; Licht, T.R.; Knudsen, K.E.B.; Agnholt, J.S. Casein Glycomacropeptide Is Well Tolerated in Healthy Adults and Changes Neither High-Sensitive C-Reactive Protein, Gut Microbiota nor Faecal Butyrate: A Restricted Randomised Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.; DiMarco, D.M.; Putt, K.K.; Martin, D.A.; Gu, Q.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; White, H.M.; Scarlett, C.O.; Bruno, R.S.; Bolling, B.W. Low-Fat Yogurt Consumption Reduces Biomarkers of Chronic Inflammation and Inhibits Markers of Endotoxin Exposure in Healthy Premenopausal Women: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatayud, M.; Börner, R.A.; Ghyselinck, J.; Verstrepen, L.; Medts, J.D.; Abbeele, P.V.; Boulangé, C.L.; Priour, S.; Marzorati, M.; Damak, S. Water Kefir and Derived Pasteurized Beverages Modulate Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability and Cytokine Production In Vitro. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, X.-X.; Liu, Y.; Xi, E.-Z.; An, J.; Tabys, D.; Liu, N. The In Vitro Protective Role of Bovine Lactoferrin on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Molecules 2019, 24, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaiano, D.A.; Hutkins, R.W. Yogurt, Cultured Fermented Milk, and Health: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zuo, X.-L.; Zhen, Y.-B.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.-H. Clinical Trial: Effect of Active Lactic Acid Bacteria on Mucosal Barrier Function in Patients with Diarrhoea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Aliment. Pharm.. Ther. 2008, 28, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Houghton, L.A.; Morris, J.; Reilly, B.; Guyonnet, D.; Goupil Feuillerat, N.; Schlumberger, A.; Jakob, S.; Whorwell, P.J. Clinical Trial: The Effects of a Fermented Milk Product Containing Bifidobacterium lactis DN-173 010 on Abdominal Distension and Gastrointestinal Transit in Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2009, 29, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, M.; Öhman, L.; Olsson, J.; Svensson, U.; Ohlson, K.; Posserud, I.; Strid, H. Clinical Trial: The Effects of a Fermented Milk Containing Three Probiotic Bacteria in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 31, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, B.; Olsson, J.; Ohlson, K.; Svensson, U.; Bytzer, P.; Ekesbo, R. Effects of Probiotic Fermented Milk on Symptoms and Intestinal Flora in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.M.; McCahon, D.; Holder, R.; Wilson, S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. A Randomised Controlled Trial of a Probiotic ‘Functional Food’ in the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldiviez, L.M.; Keim, N.L.; Laugero, K.D.; Hwang, D.H.; Huang, L.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Burnett, D.J.; Zerofsky, M.S.; Bonnel, E.L.; Allen, L.H.; et al. Design and Implementation of a Cross-Sectional Nutritional Phenotyping Study in Healthy US Adults. BMC Nutr. 2017, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, Y.Y.; Arsenault, J.E.; Bonnel, E.L.; Cervantes, E.; Kan, A.; Keim, N.L.; Lemay, D.G.; Stephensen, C.B. Effect of Manual Data Cleaning on Nutrient Intakes Using the Automated Self-Administered 24-Hour Dietary Assessment Tool (ASA24). Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2021, 5, nzab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, D.G.; Baldiviez, L.M.; Chin, E.L.; Spearman, S.S.; Cervantes, E.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Keim, N.L.; Stephensen, C.B.; Laugero, K.D. Technician-Scored Stool Consistency Spans the Full Range of the Bristol Scale in a Healthy US Population and Differs by Diet and Chronic Stress Load. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Xue, Z.; Villanueva, Y.T.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Alkan, Z.; Taft, D.H.; Liu, J.; Korf, I.; Laugero, K.D.; Stephensen, C.B.; et al. Association of Diet and Antimicrobial Resistance in Healthy U.S. Adults. mBio 2022, 13, e00101-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larke, J.A.; Bacalzo, N.; Castillo, J.J.; Couture, G.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Alkan, Z.; Kable, M.E.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Stephensen, C.B.; et al. Dietary Intake of Monosaccharides from Foods Is Associated with Characteristics of the Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy US Adults. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Olivo-Marston, S.; Jin, Q.; Aroke, D.; Joseph, J.J.; Clinton, S.K.; Manson, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Fels Tinker, L.; et al. Associations of Dairy Intake with Circulating Biomarkers of Inflammation, Insulin Response, and Dyslipidemia among Postmenopausal Women. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 1984–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, E.L.; Huang, L.; Bouzid, Y.Y.; Kirschke, C.P.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Baldiviez, L.M.; Bonnel, E.L.; Keim, N.L.; Korf, I.; Stephensen, C.B.; et al. Association of Lactase Persistence Genotypes (Rs4988235) and Ethnicity with Dairy Intake in a Healthy U.S. Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.M., Jr.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Bleck, G.T.; Brown, E.M.; Butler, J.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Hicks, C.L.; Hollar, C.M.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F.; Swaisgood, H.E. Nomenclature of the Proteins of Cows & Milk; Sixth Revision. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.X. Effects of Cow’s Milk Beta-Casein Variants on Symptoms of Milk Intolerance in Chinese Adults: A Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Study. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, A.M.; Shrestha, A.; Karlström, H.J.; Martinsson, J.A.; Nilsson, N.J.; Perry, J.K.; Day, L.; Barnett, M.P.G.; Cameron-Smith, D. Comparison of the Impact of Bovine Milk β-Casein Variants on Digestive Comfort in Females Self-Reporting Dairy Intolerance: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirghafourvand, M.; Homayouni Rad, A.; Mohammad Alizadeh Charandabi, S.; Fardiazar, Z.; Shokri, K. The Effect of Probiotic Yogurt on Constipation in Pregnant Women: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2016, 18, e39870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, İ.; Dedeli, Ö.; Bor, S.; İlter, T. Effects of a Kefir Supplement on Symptoms, Colonic Transit, and Bowel Satisfaction Score in Patients with Chronic Constipation: A Pilot Study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieri, S.; Agnoli, C.; Pala, V.; Mattiello, A.; Panico, S.; Masala, G.; Assedi, M.; Tumino, R.; Frasca, G.; Sacerdote, C.; et al. Dietary Habits and Cancer: The Experience of EPIC-Italy. Epidemiol. Prev. 2015, 39, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Li, F.L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Cho, H.C. Chronic Inflammation and Colorectal Cancer: The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, P.; Gallini, C.A.; Beal, C.; Michaud, M.; Delaney, M.L.; DuBois, A.; Khlebnikov, A.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; Punit, S.; Glickman, J.N.; et al. Bifidobacterium Animalis Subsp. Lactis Fermented Milk Product Reduces Inflammation by Altering a Niche for Colitogenic Microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18132–18137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.R.; Rubinson, D.A.; Nowak, J.A.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Dunne, R.F.; Kozak, M.M.; Welch, M.W.; Brais, L.K.; Da Silva, A.; Li, T.; et al. Association of Alterations in Main Driver Genes With Outcomes of Patients With Resected Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Hara, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Mike, A.; Mitsuyama, K.; Sako, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kado, S.; Takada, T. A Component of Polysaccharide Peptidoglycan Complex on Lactobacillus Induced an Improvement of Murine Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colitis-Associated Cancer. Immunology 2009, 128, e170–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, A.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Lian, L.; Pan, D.; Wu, Z. Anti-Inflammation and Gut Microbiota Regulation Properties of Fatty Acids Derived from Fermented Milk in Mice with Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7865–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, K.; Miyazawa, K.; Hosoda, M.; Hiramatsu, M.; Yan, F.; He, F. Lactobacillus GG-Fermented Milk Prevents DSS-Induced Colitis and Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis through Activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Masui, A.; Nakamura, J.; Shiozawa, H.; Aoki, J.; Nakae, H.; Tsuda, S.; Imai, J.; Hideki, O.; Matsushima, M.; et al. Yogurt Containing Lactobacillus Gasseri Mitigates Aspirin-Induced Small Bowel Injuries: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastroenterologia 2017, 95, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comerford, K.B.; Miller, G.D.; Boileau, A.C.; Masiello Schuette, S.N.; Giddens, J.C.; Brown, K.A. Global Review of Dairy Recommendations in Food-Based Dietary Guidelines. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 671999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
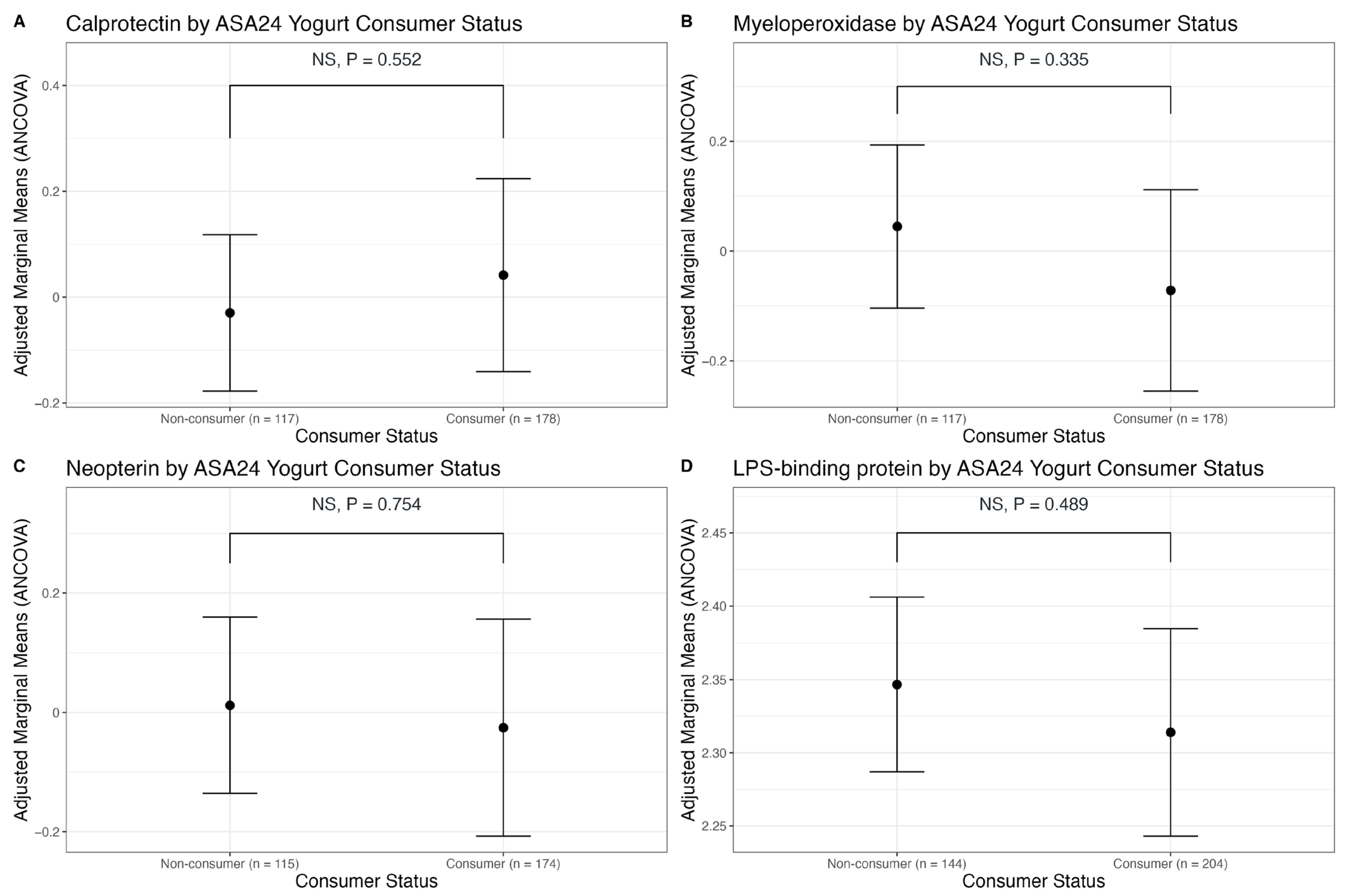
| Transformed Calprotectin | Transformed Myeloperoxidase | Transformed Neopterin | Transformed LPS-Binding Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Total Dairy | 0.02 (−0.08–0.13) | 0.678 | −0.06 (−0.18–0.07) | 0.374 | −0.05 (−0.16–0.06) | 0.380 | −0.02 (−0.07–0.02) | 0.358 |
| Age | −0.01 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.215 | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | 0.860 | −0.00 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.353 | 0.00 (−0.00–0.01) | 0.195 |
| Sex | 0.15 (−0.07–0.38) | 0.175 | 0.11 (−0.15–0.37) | 0.414 | 0.34 (0.10–0.57) | 0.005 | 0.13 (0.04–0.23) | 0.005 |
| BMI | 0.00 (−0.02–0.02) | 0.846 | 0.00 (−0.03–0.03) | 0.993 | 0.02 (−0.01–0.04) | 0.166 | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | <0.001 |
| R2/R2 adjusted | 0.011/−0.002 | 0.007/−0.007 | 0.044/0.030 | 0.226/0.217 | ||||
| Transformed Calprotectin | Transformed Myeloperoxidase | Transformed Neopterin | Transformed LPS-Binding Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Fluid Milk | −0.00 (−0.17–0.16) | 0.961 | −0.06 (−0.26–0.13) | 0.515 | −0.04 (−0.21–0.14) | 0.692 | −0.05 (−0.12–0.02) | 0.129 |
| Age | −0.00 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.226 | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | 0.860 | −0.00 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.338 | 0.00 (−0.00–0.01) | 0.169 |
| Sex | 0.14 (−0.08–0.36) | 0.199 | 0.13 (−0.13–0.38) | 0.332 | 0.35 (0.12–0.58) | 0.003 | 0.13 (0.04–0.23) | 0.004 |
| BMI | 0.00 (−0.02–0.02) | 0.799 | −0.00 (−0.03–0.02) | 0.914 | 0.02 (−0.01–0.04) | 0.202 | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | <0.001 |
| R2/R2 adjusted | 0.011/−0.003 | 0.005/−0.008 | 0.042/0.028 | 0.229/0.220 | ||||
| Transformed Calprotectin | Transformed Myeloperoxidase | Transformed Neopterin | Transformed LPS-Binding Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Cheese | 0.03 (−0.11–0.17) | 0.686 | −0.03 (−0.19–0.13) | 0.711 | −0.07 (−0.22–0.08) | 0.366 | −0.00 (−0.06–0.06) | 0.952 |
| Age | −0.00 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.227 | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | 0.908 | −0.00 (−0.01–0.00) | 0.312 | 0.00 (−0.00–0.01) | 0.216 |
| Sex | 0.15 (−0.07–0.37) | 0.178 | 0.13 (−0.13–0.39) | 0.333 | 0.34 (0.11–0.57) | 0.004 | 0.14 (0.05–0.23) | 0.003 |
| BMI | 0.00 (−0.02–0.02) | 0.869 | −0.00 (−0.03–0.03) | 0.972 | 0.02 (−0.01–0.04) | 0.151 | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | <0.001 |
| R2/R2 adjusted | 0.011/−0.002 | 0.004/−0.009 | 0.044/0.031 | 0.224/0.215 | ||||
| Transformed Calprotectin | Transformed Myeloperoxidase | Transformed Neopterin | Transformed LPS-Binding Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimates (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Yogurt | 0.32 (−0.34–0.97) | 0.339 | 0.42 (−0.27–1.11) | 0.235 | −0.06 (−0.71–0.59) | 0.856 | 0.05 (−0.18–0.29) | 0.659 |
| Age | −0.01 (−0.03–−0.00) | 0.026 | 0.00 (−0.01–0.02) | 0.711 | 0.01 (−0.00–0.02) | 0.155 | 0.00 (−0.00–0.01) | 0.120 |
| Sex | 0.10 (−0.24–0.43) | 0.570 | 0.19 (−0.16–0.55) | 0.283 | 0.46 (0.12–0.79) | 0.008 | 0.18 (0.04–0.31) | 0.011 |
| BMI | −0.01 (−0.05–0.03) | 0.622 | −0.04 (−0.08–0.00) | 0.061 | 0.02 −0.02–0.06) | 0.278 | 0.04 (0.03–0.06) | <0.001 |
| R2/R2 adjusted | 0.049/0.015 | 0.058/0.025 | 0.093/0.060 | 0.240/0.218 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouzid, Y.Y.; Chin, E.L.; Spearman, S.S.; Alkan, Z.; Stephensen, C.B.; Lemay, D.G. No Associations between Dairy Intake and Markers of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy Adult Cohort. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163504
Bouzid YY, Chin EL, Spearman SS, Alkan Z, Stephensen CB, Lemay DG. No Associations between Dairy Intake and Markers of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy Adult Cohort. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163504
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouzid, Yasmine Y., Elizabeth L. Chin, Sarah S. Spearman, Zeynep Alkan, Charles B. Stephensen, and Danielle G. Lemay. 2023. "No Associations between Dairy Intake and Markers of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy Adult Cohort" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163504
APA StyleBouzid, Y. Y., Chin, E. L., Spearman, S. S., Alkan, Z., Stephensen, C. B., & Lemay, D. G. (2023). No Associations between Dairy Intake and Markers of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Healthy Adult Cohort. Nutrients, 15(16), 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163504





