Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Starch Removal of CGM
2.3. Preparation of Corn Protein Hydrolysates
2.4. H. pylori and GES-1 Cell Line Culture Conditions
2.5. Labeling of H. pylori with FITC
2.6. Anti-Adhesion Assay
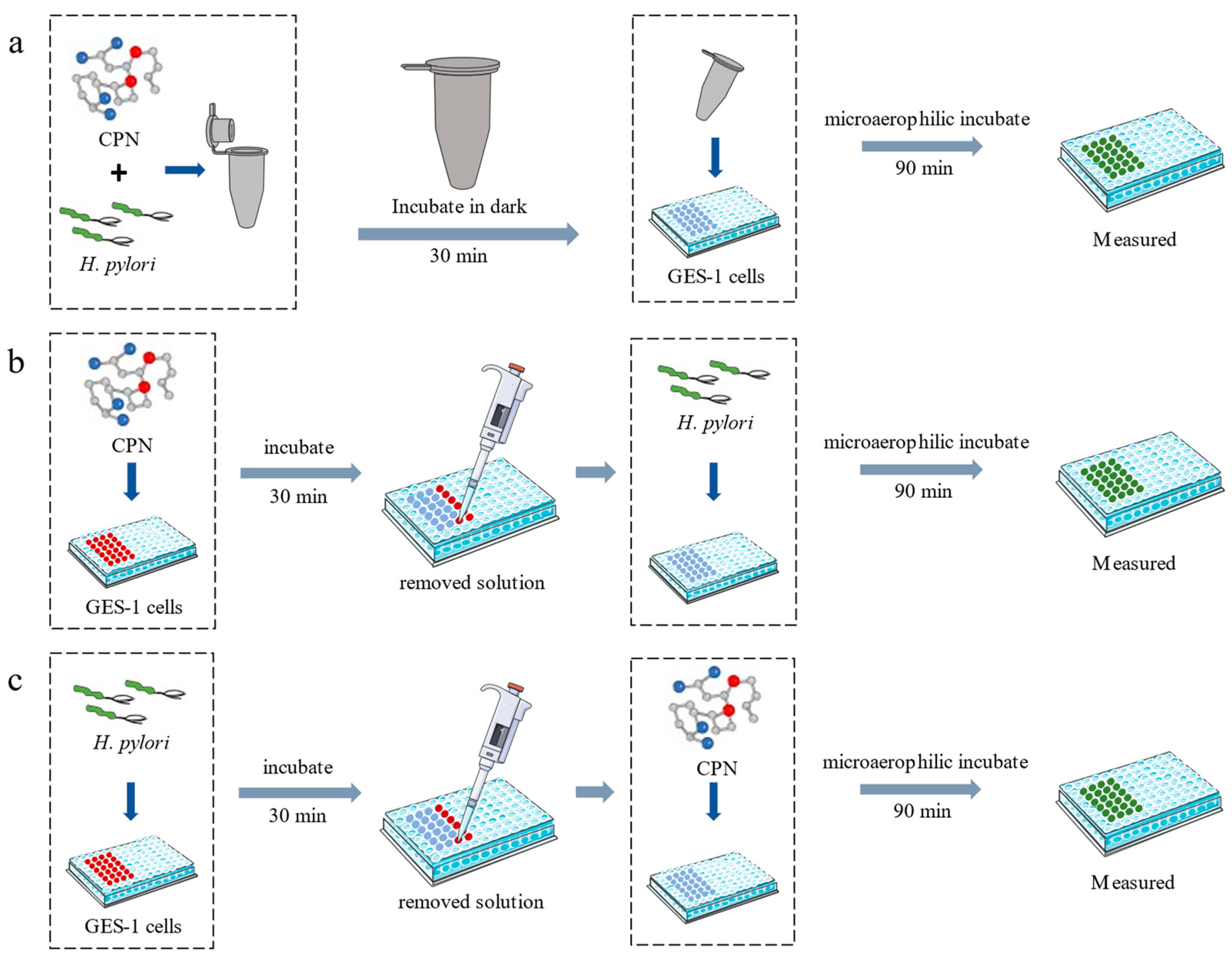
2.7. Animals and Experimental Design
2.8. Analysis of H. pylori Enumeration of Gastric Tissue
2.9. Measurement of Biochemical Parameters by ELISA
2.10. Histopathologic Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Corn Protein-Derived Peptides Preparation
3.2. Assay of Anti-Adhesive Activity of CPN
3.3. Effect of CPN on the Colonization of H. pylori in the Mice Gastric Mucosa
3.4. CPN Alleviates Oxidative Stress with H. pylori Infection-Induced Gastric Injury in Mice
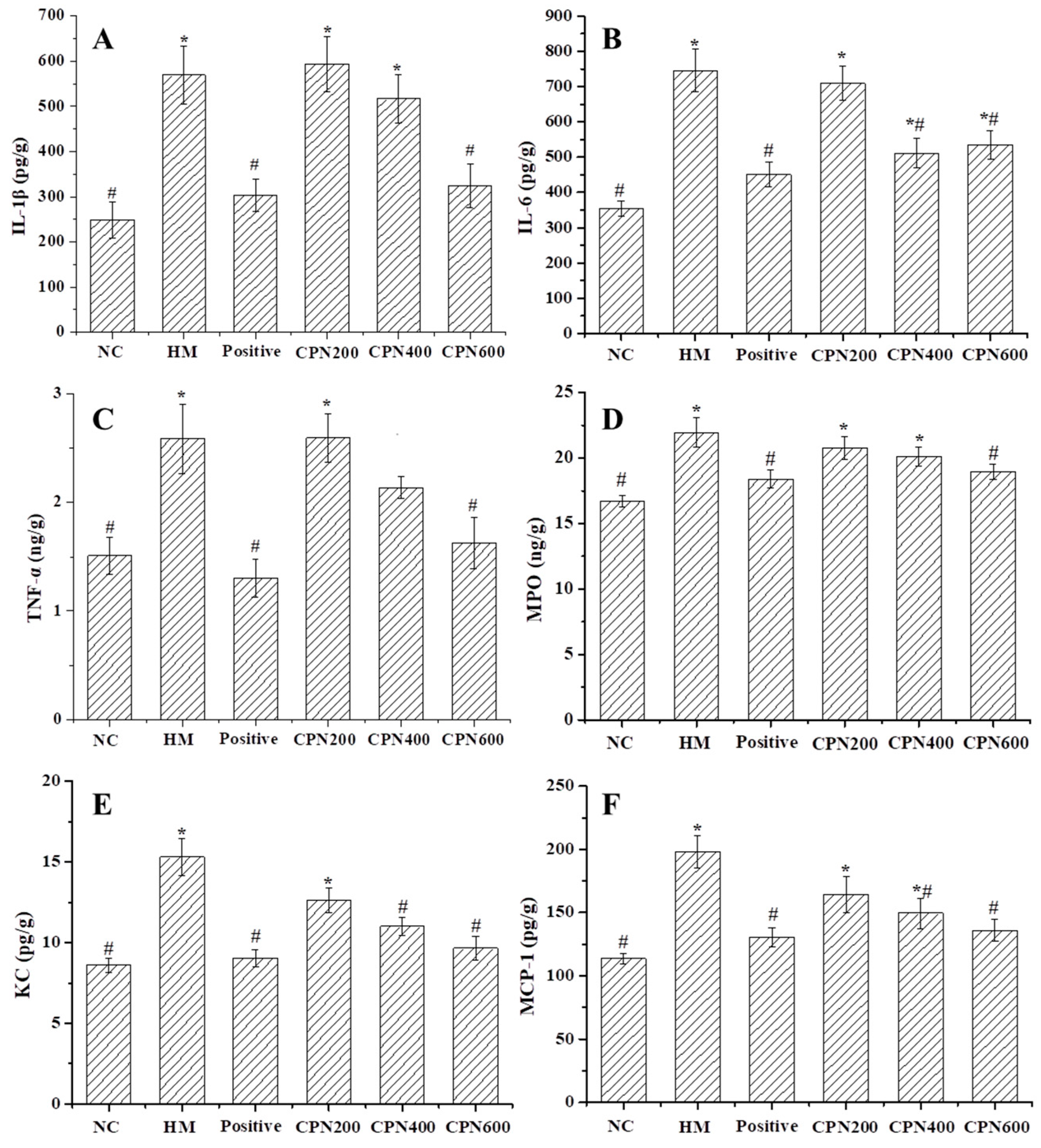
3.5. Effects of CPN on the Expression of Gastric Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines
3.6. Effects of CPN on Key Metabolites in NF-κB Signaling Pathway
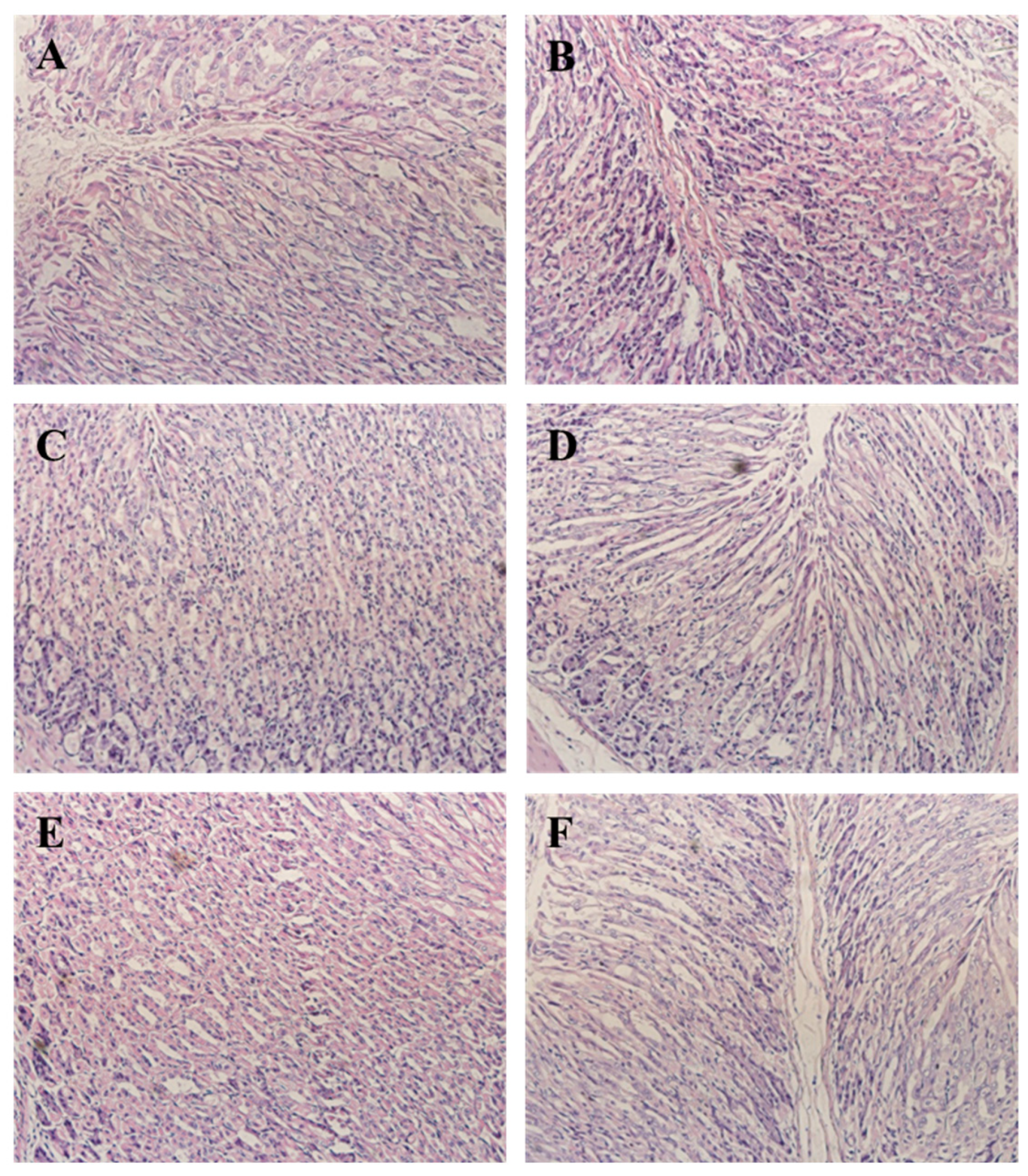
3.7. CPN Antagonism H. pylori-Induced Histological Changes in Gastric Tissue
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neshani, A.; Zare, H.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; Hooshyar Chichaklu, A.; Movaqar, A.; Ghazvini, K. Review of antimicrobial peptides with anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, W.; Hirata, Y.; Maeda, S.; Ogura, K.; Ohmae, T.; Yanai, A. CagA protein secreted by the intact type IV secretion system leads to gastric epithelial inflammation in the Mongolian gerbil model. J. Pathol. 2006, 210, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.H. Novel and effective therapeutic regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Arif, M.; Dong, Q.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Ureido-modified carboxymethyl chitosan-graft-stearic acid polymeric nano-micelles as a targeted delivering carrier of clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori: Preparation and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Tang, G.Y.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Natural products for the prevention and management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersson, C.; Forsberg, M.; Aspholm, M.; Olfat, F.O.; Forslund, T.; Boren, T.; Magnusson, K.E. Helicobacter pylori SabA adhesin evokes a strong inflammatory response in human neutrophils which is down-regulated by the neutrophil-activating protein. Med. Microbiol. Immun. 2006, 195, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Wu, J. Food derived anti-adhesive components against bacterial adhesion: Current progresses and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Udenigwe, C.C. Wheat germ-derived peptides exert antiadhesive activity against Helicobacter pylori: Insights into structural characteristics of identified peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11954–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehues, M.; Euler, M.; Georgi, G.; Mank, M.; Stahl, B.; Hensel, A. Peptides from Pisum sativum L. enzymatic protein digest with anti-adhesive activity against Helicobacter pylori: Structure activity and inhibitory activity against BabA, SabA, HpaA and a fibronectin-binding adhesin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesmann, M.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Mohammed, A.; Falcone, F.H.; Hensel, A. BabA and LPS inhibitors against Helicobacter pylori: Pectins and pectin-like rhamnogalacturonans as adhesion blockers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, O.; Ofek, I.; Tabak, M.; Weiss, E.I.; Sharon, N.; Neeman, I. A high molecular mass constituent of cranberry juice inhibits Helicobacter pylori adhesion to human gastric mucus. Fems Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 29, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, P.; Goode, P.; Mobasseri, A.; Zopf, D. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori binding to gastrointestinal epithelial cells by sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, Y.; Cui, N.; Wang, D.Y.; Zheng, X.Q. Conjugation of the glutelin hydrolysates-glucosamine by transglutaminase and functional properties and antioxidant activity of the products. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Song, C.L.; Chen, J.P.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Zheng, X.Q. Preparation and evaluation of new glycopeptides obtained by proteolysis from corn gluten meal followed by transglutaminase-induced glycosylation with glucosamine. Foods 2020, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.D.; Lin, S.Y.; Cheng, S. Contribution of specific amino acid and secondary structure to the antioxidant property of corn gluten proteins. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qu, Y. Preparation of corn glycopeptides and evaluation of their antagonistic effects on alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.S.; Ma, H.L.; Ding, Q.Z.; Lin, L.; Yu, X.J.; Luo, L.; Yagoub, A.E.G.A. Ultrasonic pretreatment of corn gluten meal proteins and neutrase: Effect on protein conformation and preparation of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory peptides. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, E.K.; Uhm, C.S.; Chung, M.S.; Kim, K.H. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori adhesion to human gastric adenocarcinoma epithelial cells by acidic polysaccharides from artemisia capillaris and panax ginseng. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilberg, D.; Ottemann, K.M. How Helicobacter pylori senses, targets and interacts with the gastric epithelium. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Wang, J.; Kasman, L.; Jiang, X.; Haley-Zitlin, V. Activities of muscadine grape skin and quercetin against Helicobacter pylori infection in mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Park, M.H.; Kim, C.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Keum, C.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Yun, C.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, Y.C. Effect of beta-caryophyllene from cloves extract on Helicobacter pylori eradication in mouse model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Protective effect of kinsenoside on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.H.; Wang, H.H.; Hu, F.L. Efficacy of sucralfate-combined quadruple therapy on gastric mucosal injury induced by Helicobacter pylori and its effect on gastrointestinal flora. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4936318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.T.; Hood, M.; Burns, C.; Scholten, J.; Chuang, J.; Tian, F.; Pan, X.C.; Du, J.; Gui, M. A novel combination of wheat peptides and fucoidan attenuates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage through anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and pro-survival mechanisms. Nutrients 2017, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, H.N.; Wang, Z.C.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, B.F. Protective effect of cod (Gadus macrocephalus) skin collagen peptides on acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.F.; Liang, Q.F.; Zhang, X.; Hou, T.; Li, S.Y.; Ma, H.L. Stability and antioxidant activities of corn protein hydrolysates under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Cereal Chem. 2018, 95, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, L.; Xue, C.; Ma, S.; Du, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Corn gluten hydrolysate regulates the expressions of antioxidant defense and ROS metabolism relevant genes in H2O2-induced HepG2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.L.; Li, R.J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, Y.J. Protective effects of wheat peptides against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesions in rats: Vasodilation and anti-inflammation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.N.; Wen, B.; Zhu, J.G.; Zhang, Y.S.; Gao, J.Z.; Chen, Z.Z. Exposure to microplastics impairs digestive performance, stimulates immune response and induces microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of juvenile guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.Q.; He, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Shu, H.; Ngwa, A.N.; Chen, Y.T.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, M.H. Protective effect of total triterpenoids from Chaenomeles speciosa against Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis in mice. J. Chin. Mat. Med. 2021, 46, 4782–4792. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, D.T.; Rodrigues, R.F.; Machado, N.M.; Maurer, L.H.; Ferreira, L.F.; Somacal, S.; Veiga, M.L.; Da Rocha, M.I.D.M.; Vizzotto, M.; Rodrigues, E.; et al. Natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES)-based blueberry extracts protect against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory and oncogenic responses in gastric mucosal tissues of mice. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 25, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Q.; Lv, R.Z.; Xu, X.M.; Ge, Q.; Lin, S.Y. Tricholoma matsutake-Derived Peptides Show Gastroprotective Effects against Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastric Injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14985–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Li, F.Y.; Guan, J.J.; Liu, L.X.; Huang, P.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.X.; Liu, Z.Q.; Lu, L.L.; Wang, D.W. Artemisinin and its derivatives prevent Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis via inhibition of NF-κB signaling. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 152968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.; Lopes, T.; Oleastro, M.; Gato, I.V.; Floch, P.; Benejat, L.; Chaves, P.; Pereira, T.; Seixas, E.; Machado, J.; et al. Curcumin inhibits gastric inflammation induced by Helicobacter pylori infection in a mouse model. Nutrients 2015, 7, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, L.G.; Pan, D.; Liu, H.C.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.K.; Sun, G.J. Wheat peptide protects against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.H.; Li, B.Q.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.Q.; Du, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics cooperate with Helicobacter pylori to promote gastric injury and inflammation in mice. Chemosphere 2021, 288, 132579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction and interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori infected gastric epithelial cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, H. Supplementation with angelica keiskei inhibits expression of inflammatory mediators in the gastric mucosa of Helicobacter pylori–infected mice. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Enzyme | pH | Temperature (°C) | Anti-Adhesive Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trypsin | 8.0 | 37 | 12.37 ± 0.61 f |
| Alcalase | 8.5 | 60 | 40.72 ± 2.61 c |
| Protamex | 7.0 | 55 | 39.79 ± 4.71 c |
| Neutral | 7.0 | 45 | 50.44 ± 0.27 a |
| Protease N | 7.0 | 50 | 44.16 ± 1.99 b |
| Protease P | 7.0 | 45 | 47.44 ± 4.50 b |
| Protease M | 6.0 | 50 | 39.93 ± 3.76 c |
| Papain | 8.0 | 50 | 0 |
| Rebamipide | 22.30 ± 0.62 e |
| No. | Sequence | Position in Protein | Protein Name | Accession No. on Uniprot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LL | 8–9, 11–12, 35–36, 155–156 | Zein | P04703 |
| 2 | LLAL | 11–14 | Zein | P04703 |
| 3 | APIA | 30–33 | Zein | P04703 |
| 4 | LLPP | 35–38 | Zein | P04703 |
| 5 | AIAA | 61–64 | Zein | P04703 |
| 6 | VALA | 106–109 | Zein | P04703 |
| 7 | LAAL | 161–164 | Zein | P04703 |
| 8 | LAAA | 181–184 | Zein | P04703 |
| 9 | 104–105, 153–154, 157–158, 199–200, 208–209 | Glutelin | P04706 | |
| 10 | QQQ | 181–183 | Glutelin | P04706 |
| Group | 1–2 Weeks | 3–4 Weeks | 5 Weeks | cfu/g Gastric Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 0.3 mL saline | 0.3 mL saline | 0.3 mL saline | 0 |
| HM | 0.3 mL saline | 0.3 mL saline + 0.4 mL H. pylori | 0.3 mL saline | (1.44 ± 0.42) × 107 c |
| CPN-200 | 200 mg/kg·bw | 200 mg/kg·bw + 0.4 mL H. pylori | 200 mg/kg·bw | (2.08 ± 0.93) × 105 a |
| CPN-400 | 400 mg/kg·bw | 400 mg/kg·bw + 0.4 mL H. pylori | 400 mg/kg·bw | (1.63 ± 0.75) × 105 b |
| CPN-600 | 600 mg/kg·bw | 600 mg/kg·bw + 0.4 mL H. pylori | 600 mg/kg·bw | (1.79 ± 0.77) × 105 b |
| Positive control 1 | 0.3 mL antibiotic | 0.3 mL antibiotic + 0.4 mL H. pylori | 0.3 mL antibiotic | (0.70 ± 0.31) × 104 d |
| Groups 1 | SOD (U/g) | GSH-Px (U/g) | MDA (nmol/g) | LDH (ng/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 2124.35 ± 102.76 # | 3257.91 ± 133.91 # | 199.49 ± 7.62 # | 111.28 ± 4.83 # |
| HM | 1264.23 ± 89.33 * | 2097.31 ± 150.49 * | 289.03 ± 10.70 * | 157.96 ± 6.59 * |
| CPN-200 | 1436.88 ± 107.18 * | 2599.14 ± 128.78 * | 293.98 ± 9.26 * | 137.14 ± 7.65 * |
| CPN-400 | 1758.01 ± 107.93 # | 2879.65 ± 125.19 # | 255.13 ± 11.69 * | 133.48 ± 7.47 |
| CPN-600 | 1934.29 ± 110.75 # | 2933.47 ± 179.52 # | 223.34 ± 10.84 # | 118.16 ± 6.96 # |
| Positive control | 1909.61 ± 66.88 # | 3079.95 ± 139.21 # | 223.46 ± 8.62 # | 102.35 ± 3.14 # |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Liu, X.; Miao, Z.; Hu, N.; Zheng, X. Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153467
Li G, Liu X, Miao Z, Hu N, Zheng X. Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153467
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanlong, Xiaolan Liu, Zhengfei Miao, Nan Hu, and Xiqun Zheng. 2023. "Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153467
APA StyleLi, G., Liu, X., Miao, Z., Hu, N., & Zheng, X. (2023). Preparation of Corn Peptides with Anti-Adhesive Activity and Its Functionality to Alleviate Gastric Injury Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection In Vivo. Nutrients, 15(15), 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153467





