Maternal Prenatal Factors and Child Adiposity in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Chinese Children at the Age of 2 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements in Children at the Age of 2 Years
2.4. Blood Pressures at the Age of 2 Years
2.5. Assessment of Blood Glucose, Insulin and Lipids at the Age of 2 Years
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Anthropometric Measures and Metabolic Risk Factors in Boys and Girls at the Age of 2 Years
3.2. Child Adiposity Measures and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors at the Age of 2 Years
3.3. Child OWO and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors at the Age of 2 Years
3.4. Maternal Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy and GDM in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Children at the Age of 2 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, B.; Perel, P.; Mensah, G.A.; Ezzati, M. Global epidemiology, health burden and effective interventions for elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2023: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Bennett, J.E.; Stevens, G.A.; Mathers, C.D.; Bonita, R.; Rehm, J.; Kruk, M.E.; Riley, L.M.; Dain, K.; Kengne, A.P.; Chalkidou, K.; et al. NCD Countdown 2030: Worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4. Lancet 2018, 392, 1072–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, A.E.; Srinivasapura Venkateshmurthy, N.; Mohan, S.; Prabhakaran, D. Hypertension in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Gluckman, P.D.; Godfrey, K.M.; Harding, J.E.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S. Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet 1993, 341, 938–941. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, J.C.K. The capacity-load model of non-communicable disease risk: Understanding the effects of child malnutrition, ethnicity and the social determinants of health. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Marc, I.; Bouchard, L.; Ouyang, F.; Luo, Z.C.; Fan, J.; Dubois, L.; Mâsse, B.; Zhang, J.; Leung, P.C.K.; et al. Study protocol for the Sino-Canadian Healthy Life Trajectories Initiative (SCHeLTI): A multicentre, cluster-randomised, parallel-group, superiority trial of a multifaceted community-family-mother-child intervention to prevent childhood overweight and obesity. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obita, G.; Alkhatib, A. Disparities in the Prevalence of Childhood Obesity-Related Comorbidities: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 923744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parcha, V.; Heindl, B.; Kalra, R.; Li, P.; Gower, B.; Arora, G.; Arora, P. Insulin Resistance and Cardiometabolic Risk Profile Among Nondiabetic American Young Adults: Insights From NHANES. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e25–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Li, W.R.; Lyu, Y.B.; Astell-Burt, T.; Zhao, P.Y.; Shi, X.M. Gender Differences in the Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity, Associated Behaviors, and Weight-related Perceptions in a National Survey of Primary School Children in China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredella, M.A. Sex Differences in Body Composition. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1043, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermín-Martínez, C.A.; Márquez-Salinas, A.; Guerra, E.C.; Zavala-Romero, L.; Antonio-Villa, N.E.; Fernández-Chirino, L.; Sandoval-Colin, E.; Barquera-Guevara, D.A.; Campos Muñoz, A.; Vargas-Vázquez, A.; et al. AnthropoAge, a novel approach to integrate body composition into the estimation of biological age. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zegher, F.; Devlieger, H.; Eeckels, R. Fetal growth: Boys before girls. Horm. Res. 1999, 51, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Wang, X.; Wells, J.C.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J. The Associations of Birthweight for Gestational Age Status with Its Differential 0-2 Year Growth Trajectory and Blood Pressure at Two Years of Age in Chinese Boys and Girls. Nutrients 2023, 15, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADA. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S67–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Tang, N.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, W. Maternal urinary triclosan level, gestational diabetes mellitus and birth weight in Chinese women. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Onis, M.; MartÍnez-Costa, C.; NÚnez, F.; Nguefack-Tsague, G.; Montal, A.; Brines, J. Association between WHO cut-offs for childhood overweight and obesity and cardiometabolic risk. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima Borges, L.; Rodrigues de Lima, T.; Augusto Santos Silva, D. Accuracy of anthropometric indicators of obesity to identify high blood pressure in adolescents-systematic review. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.; Ramos, E.; Barros, H. Decreases in adiposity reduce the risk of hypertension: Results from a prospective cohort of adolescents. Prev. Med. 2019, 120, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, M.J.; Severo, M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Barros, H.; Santos, A.C. Direct and BMI-mediated effect of birthweight on childhood cardio-metabolic health-a birth cohort study. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, L.S.; Martorell, R.; Stein, A.D.; Hallal, P.C.; Sachdev, H.S.; Prabhakaran, D.; Wills, A.K.; Norris, S.A.; Dahly, D.L.; Lee, N.R.; et al. Size at birth, weight gain in infancy and childhood, and adult blood pressure in 5 low- and middle-income-country cohorts: When does weight gain matter? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, N.; Putri, R.R.; Reinehr, T.; Danielsson, P.; Weghuber, D.; Norman, M.; Rochow, N.; Marcus, C.; Holl, R.W.; Hagman, E. The association between perinatal factors and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity: A retrospective two-cohort study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Bacha, F.; Tfayli, H.; Michaliszyn, S.F.; Yousuf, S.; Arslanian, S. Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance in Youth on the Spectrum From Normal Weight to Obese and From Normal Glucose Tolerance to Impaired Glucose Tolerance to Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, J.; Sharma, S.; Jasik, C.B.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Tinajero-Deck, L. Gender differences in prediabetes and insulin resistance among 1356 obese children in Northern California. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2013, 7, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, E.A.; Singh, G.R.; Sayers, S.M. Large waist but low body mass index: The metabolic syndrome in Australian Aboriginal children. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Auinger, P.; Huang, T.T. Growth curves for cardio-metabolic risk factors in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, S6.E15–S6.E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azita, F.; Asghar, Z.; Gholam-Reza, S. Relationship of body mass index with serum lipids in elementary school students. Indian J. Pediatr. 2009, 76, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Tse, L.A.; Deng, X.Q.; Jiang, Z.Q. Cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese Chinese children: A comparison of weight-for-height index and BMI as the screening criterion. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, J.R.; Bradley, J.; Silverwood, R.J.; Howe, L.D.; Tilling, K.; Lawlor, D.A.; Macdonald-Wallis, C. Associations of blood pressure in pregnancy with offspring blood pressure trajectories during childhood and adolescence: Findings from a prospective study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, M.A.; Pluymen, L.P.; Dalmeijer, G.W.; Groenhof, T.K.J.; Uiterwaal, C.S.; Smit, H.A.; van Rossem, L. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and cardiometabolic outcomes in childhood: A systematic review. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1718–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Bhatta, L.; Moen, G.H.; Hwang, L.D.; Kemp, J.P.; Bond, T.A.; Åsvold, B.O.; Brumpton, B.; Evans, D.M.; Warrington, N.M. Investigating a Potential Causal Relationship Between Maternal Blood Pressure During Pregnancy and Future Offspring Cardiometabolic Health. Hypertension 2022, 79, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adua, E. Decoding the mechanism of hypertension through multiomics profiling. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2023, 37, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedagi, A.M.; Bello, N.A. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, F.A.; Gholizadeh, L.; Heydari, M. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Risk of Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women. Nurs. Women’s Health 2020, 24, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Ramos, T.; Paley, C.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Gallagher, D. Body composition during fetal development and infancy through the age of 5 years. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Andres, A.; Fields, D.A.; Evans, W.J.; Kuczmarski, R.; Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Lumeng, J.C.; Oken, E.; Shepherd, J.A.; Sun, S.; et al. Body Composition Measurements from Birth through 5 Years: Challenges, Gaps, and Existing & Emerging Technologies-A National Institutes of Health workshop. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2020, 21, e13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, D.A.; Krishnan, S.; Wisniewski, A.B. Sex differences in body composition early in life. Gend. Med. 2009, 6, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnamoorthy, M.; Whyte, K.; Horowitz, M.; Widen, E.; Toro-Ramos, T.; Johnson, J.; Gidwani, S.; Paley, C.; Rosenn, B.; Lin, S.; et al. Anthropometric models to estimate fat mass at 3 days, 15 weeks and 54 weeks. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.M.; Kaar, J.L.; Ringham, B.M.; Hockett, C.W.; Glueck, D.H.; Dabelea, D. Sex differences in infant body composition emerge in the first 5 months of life. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2019, 32, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, L.; Cofini, M.; Leonardi, A.; Penta, L.; Esposito, S. Up-To-Date Review About Minipuberty and Overview on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis Activation in Fetal and Neonatal Life. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidlingmaier, F.; Strom, T.M.; Dorr, H.G.; Eisenmenger, W.; Knorr, D. Estrone and estradiol concentrations in human ovaries, testes, and adrenals during the first two years of life. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 65, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomon, S.J.; Nelson, S.E. Body composition of the male and female reference infants. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 1–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Boys (n = 285) | Girls (n = 264) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mothers | |||
| Maternal prepregnancy BMI (kg/m2) categories | |||
| <18.5 | 47 (16.5) | 41 (15.5) | 0.73 |
| 18.5–23.9 | 185 (65.1) | 180 (68.2) | |
| 24–27.9 | 42 (14.8) | 29 (11.0) | |
| >28 | 10 (3.5) | 14 (5.3) | |
| Gestational Weight Gain | |||
| Adequate | 108 (38.3) | 83 (31.6) | 0.48 |
| Excessive | 124 (44.0) | 140 (53.2) | |
| Inadequate | 50 (17.7) | 40 (15.2) | |
| GDM, yes | 36 (12.6) | 33 (12.5) | 0.96 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | |||
| none | 258 (90.5) | 252 (95.5) | 0.01 |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 19 (6.7) | 11 (4.2) | |
| Preeclampsia | 8 (2.8) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Children | |||
| Age, months | 23.8 ± 0.6 | 23.8 ± 0.5 | 0.92 |
| Birth weight (gram) | 3504.8 ± 403.1 | 3369.6 ± 425.9 | <0.001 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 39.0 ± 1.0 | 39.0 ± 1.0 | 0.55 |
| Anthropometric measures | |||
| Weight, kg | 13.1 ± 1.4 | 12.5 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Length, cm | 89.5 ± 3.1 | 88.1 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Head circumference, cm | 49.0 ± 1.3 | 47.9 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 16.4 ± 1.4 | 16.2 ± 1.4 | 0.02 |
| MUAC, cm | 16.0 ± 1.2 | 15.8 ± 1.2 | 0.14 |
| Skinfold thickness, mm | |||
| Triceps | 9.1 ± 1.8 | 9.4 ± 2.1 | 0.03 |
| Subscapular | 6.6 ± 1.7 | 6.9 ± 1.8 | 0.04 |
| Abdominal | 6.7 ± 1.9 | 7.2 ± 2.0 | 0.007 |
| Sum of three sites | 22.3 ± 4.8 | 23.5 ± 5.3 | 0.009 |
| Weight-for-length z-score | 0.44 ± 0.99 | 0.40 ± 0.92 | 0.65 |
| Weight-for-age z-score | 0.65 ± 0.92 | 0.65 ± 0.93 | 0.98 |
| Length-for-age z-score | 0.61 ± 1.01 | 0.59 ± 0.95 | 0.74 |
| BMI-for-age z-score | 0.41 ± 1.01 | 0.43 ± 0.93 | 0.82 |
| Head circumference-for-age z-score | 0.57 ± 0.93 | 0.56 ± 0.91 | 0.94 |
| Arm circumference-for-age z-score | 0.64 ± 0.98 | 0.72 ± 0.91 | 0.38 |
| Subscapular skinfold-for-age z-score | 0.29 ± 1.30 | 0.34 ± 1.20 | 0.59 |
| Triceps skinfold-for-age z-score | 0.70 ± 0.94 | 0.76 ± 1.04 | 0.48 |
| Weight-for-length z-score | n (%) | ||
| <−2 (wasting) | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.4) | 0.91 |
| −2 to 2 (normal) | 271 (95.1) | 253 (96.2) | |
| >2 to 3 (overweight) | 10 (3.5) | 7 (2.7) | |
| >3 (obesity) | 3 (1.1) | 2 (0.8) | |
| Length-for-age z-score < −2 (stunting) | 5 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0.06 |
| Cardiometabolic risk factors | |||
| Glucose, mmol/L | 5.02 ± 0.56 | 4.87 ± 0.61 | 0.01 |
| Insulin, pmol/L | 37.80 ± 33.91 | 38.90 ± 32.01 | 0.73 |
| log(insulin), pmol/L | 3.26 ± 0.92 | 3.35 ± 0.84 | 0.28 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.12 ± 0.69 | 4.22 ± 0.74 | 0.16 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.11 ± 0.68 | 1.06 ± 0.55 | 0.40 |
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.41 ± 0.35 | 1.37 ± 0.29 | 0.18 |
| LDL, mmol/L | 2.31 ± 0.49 | 2.41 ± 0.56 | 0.04 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 93.12 ± 8.17 | 91.88 ± 7.60 | 0.10 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 61.35 ± 6.24 | 61.29 ± 5.72 | 0.92 |
| Child Anthropometric Measures | Child Cardiometabolic Risk Factors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | Glucose | log(insulin) | TC | TG | HDL | LDL | |
| Boys | ||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 0.49 *** | 0.29 *** | −0.08 | 0.16 * | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.11 | −0.03 |
| Length (cm) | 0.23 ** | 0.08 | −0.15 | 0.07 | −0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 | −0.08 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.43 *** | 0.30 *** | 0.02 | 0.15 * | 0.08 | −0.02 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| Length-for-age z-score | 0.24 ** | 0.08 | −0.15 | 0.07 | −0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 | −0.08 |
| Weight-for-age z-score | 0.47 *** | 0.27 *** | −0.08 | 0.17 * | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.10 | −0.02 |
| Weight-for-length z-score | 0.43 *** | 0.28 *** | −0.0004 | 0.17 * | 0.09 | −0.004 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| BMI-for-age z-score | 0.40 *** | 0.27 *** | 0.02 | 0.16 * | 0.11 | −0.01 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| MUAC (cm) | 0.55 *** | 0.39 *** | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | −0.004 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Sum of skinfold thickness at three sites (mm) | 0.46 *** | 0.31 *** | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.05 | −0.03 | 0.08 |
| Girls | ||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 0.44 *** | 0.32 *** | 0.04 | 0.15 | −0.01 | −0.02 | 0.14 | −0.02 |
| Length (cm) | 0.26 *** | 0.21 ** | 0.09 | 0.13 | −0.09 | −0.04 | 0.10 | −0.07 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.40 *** | 0.28 *** | −0.03 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.003 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| Length-for-age z-score | 0.26 ** | 0.21 ** | 0.09 | 0.13 | −0.09 | −0.04 | 0.10 | −0.07 |
| Weight-for-age z-score | 0.43 *** | 0.30 *** | 0.04 | 0.14 | −0.003 | −0.03 | 0.13 | −0.005 |
| Weight-for-length z-score | 0.41 *** | 0.28 *** | −0.03 | 0.10 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| BMI-for-age z-score | 0.39 *** | 0.26 *** | −0.04 | 0.09 | 0.07 | −0.002 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| MUAC (cm) | 0.46 *** | 0.39 *** | 0.01 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.01 | 0.05 | −0.02 |
| Sum of skinfold thickness at three sites (mm) | 0.53 *** | 0.44 *** | 0.02 | −0.04 | 0.10 | −0.05 | 0.13 | 0.06 |
| Child Adiposity Measures | Boys | Girls | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SD | β (95% CI) | p Value | Mean ± SD | β (95% CI) | p Value | ||
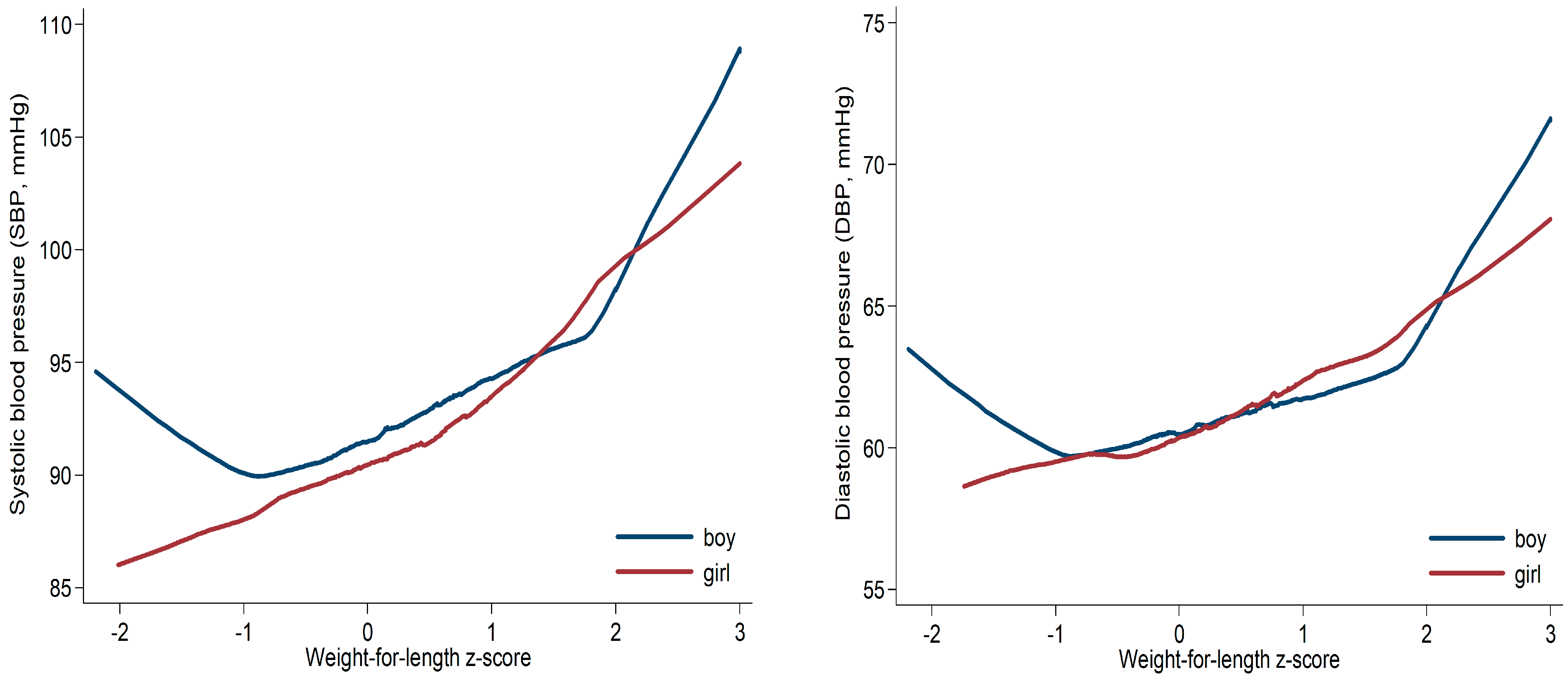
| ZWFL | SBP (mmHg) | |||||||
| −1 to 1 | 153 | 91.6 ± 6.6 | Ref. | 137 | 90.9 ± 6.5 | Ref. | ||
| >1 to 2 | 47 | 96.1 ± 8.4 | 4.3 (1.8, 6.8) | 0.0008 | 47 | 95.0 ± 8.1 | 4.0 (1.7, 6.3) | 0.0005 |
| >2 (OWO) | 10 | 104.4 ± 15.7 | 12.6 (7.7, 17.4) | <0.0001 | 6 | 103.3 ± 9.8 | 12.5 (6.9, 18.2) | <0.0001 |
| <−1 | 17 | 91.6 ± 7.4 | 0.07 (−3.7, 3.8) | 0.97 | 16 | 86.4 ± 7.5 | −4.2 (−7.8, −0.7) | 0.02 |
| ZWFL continuous | 3.2 (2.2, 4.2) | <0.0001 | 3.0 (2.0, 4.1) | <0.0001 | ||||
| DBP (mmHg) | ||||||||
| −1 to 1 | 153 | 60.5 ± 5.9 | Ref. | 137 | 60.6 ± 5.7 | Ref. | ||
| >1 to 2 | 47 | 62.7 ± 5.6 | 2.1 (0.1, 4.1) | 0.04 | 47 | 63.1 ± 5.0 | 2.4 (0.6, 4.2) | 0.009 |
| >2 (OWO) | 10 | 68.5 ± 10.3 | 7.9 (4.1, 11.8) | <0.0001 | 6 | 67.5 ± 8.2 | 7.0 (2.5, 11.4) | 0.002 |
| <−1 | 17 | 61.2 ± 5.5 | 0.7 (−2.3, 3.7) | 0.65 | 16 | 59.3 ± 4.6 | −1.1 (−4.0, 1.8) | 0.46 |
| ZWFL continuous | 1.7 (0.9, 2.5) | <0.0001 | 1.8 (1.0, 2.6) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Child Cardiometabolic Risk Factors at Age 2 Years | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal Prenatal Factors | n | Mean ± SD | β (95% CI) | p Value |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | SBP, mm Hg | |||
| none | 402 | 92.3 ± 7.75 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 96.69 ± 9.61 | 2.95 (0.08, 5.82) | 0.04 |
| Preeclampsia | 5 | 90 ± 7.07 | −3.63 (−9.99, 2.74) | 0.26 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | DBP, mm Hg | |||
| none | 400 | 61.1 ± 5.7 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 65 ± 8.83 | 3.17 (0.90, 5.44) | 0.006 |
| Preeclampsia | 5 | 60 ± 6.12 | −1.46 (−6.50, 3.57) | 0.57 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | Glucose, mmol/L | |||
| none | 384 | 4.93 ± 0.59 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 5.18 ± 0.43 | 0.24 (0.01, 0.47) | 0.04 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 5.23 ± 0.82 | 0.25 (−0.18, 0.69) | 0.26 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | log (insulin), pmol/L | |||
| none | 383 | 3.29 ± 0.88 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 3.62 ± 0.97 | 0.31 (−0.04, 0.65) | 0.08 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 3.16 ± 0.8 | −0.16 (−0.81, 0.49) | 0.63 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | TC, mmol/L | |||
| none | 384 | 4.17 ± 0.73 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 4.09 ± 0.64 | −0.08 (−0.37, 0.20) | 0.56 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 4.26 ± 0.33 | 0.09 (−0.44, 0.63) | 0.74 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | Triglycerides, mmol/L | |||
| none | 384 | 1.07 ± 0.59 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 1.34 ± 0.95 | 0.26 (0.01, 0.51) | 0.04 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 0.81 ± 0.45 | −0.3 (−0.76, 0.17) | 0.21 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | HDL, mmol/L | |||
| none | 384 | 1.39 ± 0.32 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 1.34 ± 0.38 | −0.06 (−0.19, 0.07) | 0.38 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 1.74 ± 0.29 | 0.33 (0.09, 0.57) | 0.007 |
| Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy | LDL, mmol/L | |||
| none | 384 | 2.37 ± 0.54 | Ref. | |
| Chronic hypertension/gestational hypertention | 26 | 2.26 ± 0.43 | −0.1 (−0.31, 0.11) | 0.35 |
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 2.34 ± 0.22 | 0.02 (−0.38, 0.41) | 0.93 |
| Maternal Prenatal Factors | Child Cardiometabolic Risk Factors at Age 2 Years | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean ± SD | β (95% CI) | p Value | |
| GDM | SBP, mm Hg | |||
| no | 382 | 92.34 ± 7.7 | Ref. | |
| yes | 51 | 93.96 ± 9.37 | 2.2 (0.10, 4.30) | 0.04 |
| DBP, mm Hg | ||||
| no | 380 | 61.18 ± 5.72 | Ref. | |
| yes | 51 | 62.41 ± 7.7 | 1.6 (−0.07, 3.28) | 0.06 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | ||||
| no | 364 | 4.92 ± 0.58 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 5.09 ± 0.61 | 0.16 (−0.01, 0.33) | 0.06 |
| log (insulin), pmol/L | ||||
| no | 363 | 3.29 ± 0.87 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 3.41 ± 0.93 | 0.13 (−0.12, 0.38) | 0.31 |
| TC, mmol/L | ||||
| no | 364 | 4.17 ± 0.71 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 4.13 ± 0.77 | −0.04 (−0.24, 0.17) | 0.73 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | ||||
| no | 364 | 1.10 ± 0.64 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 0.93 ± 0.45 | −0.17 (−0.35, 0.00) | 0.06 |
| HDL, mmol/L | ||||
| no | 364 | 1.4 ± 0.31 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 1.36 ± 0.39 | −0.04 (−0.13, 0.06) | 0.45 |
| LDL, mmol/L | ||||
| no | 364 | 2.36 ± 0.53 | Ref. | |
| yes | 53 | 2.33 ± 0.53 | −0.03 (−0.18, 0.13) | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, F.; Wells, J.C.; Zhang, G.-H.; Du, K.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Luo, Z.-C.; Zhang, J. Maternal Prenatal Factors and Child Adiposity in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Chinese Children at the Age of 2 Years. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153342
Ouyang F, Wells JC, Zhang G-H, Du K, Wang X, Shen L, Luo Z-C, Zhang J. Maternal Prenatal Factors and Child Adiposity in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Chinese Children at the Age of 2 Years. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153342
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Fengxiu, Jonathan C. Wells, Guang-Hui Zhang, Kun Du, Xia Wang, Lixiao Shen, Zhong-Cheng Luo, and Jun Zhang. 2023. "Maternal Prenatal Factors and Child Adiposity in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Chinese Children at the Age of 2 Years" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153342
APA StyleOuyang, F., Wells, J. C., Zhang, G.-H., Du, K., Wang, X., Shen, L., Luo, Z.-C., & Zhang, J. (2023). Maternal Prenatal Factors and Child Adiposity in Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Term-Born Chinese Children at the Age of 2 Years. Nutrients, 15(15), 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153342







