Detection of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
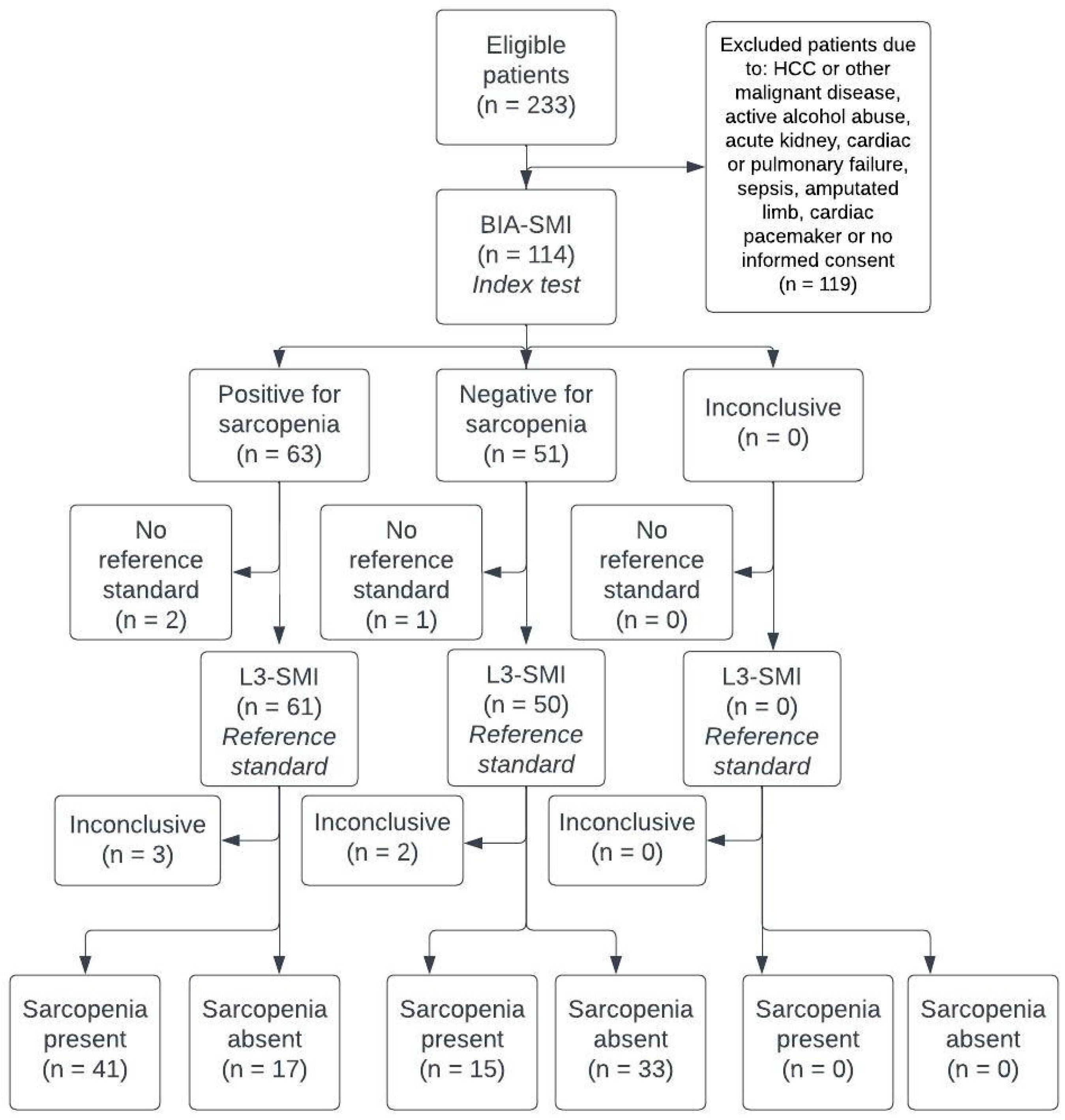
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
3.2. Correlation between BIA Parameters and the L3-SMI
3.3. Patient Characteristics Regarding the Presence of Sarcopenia
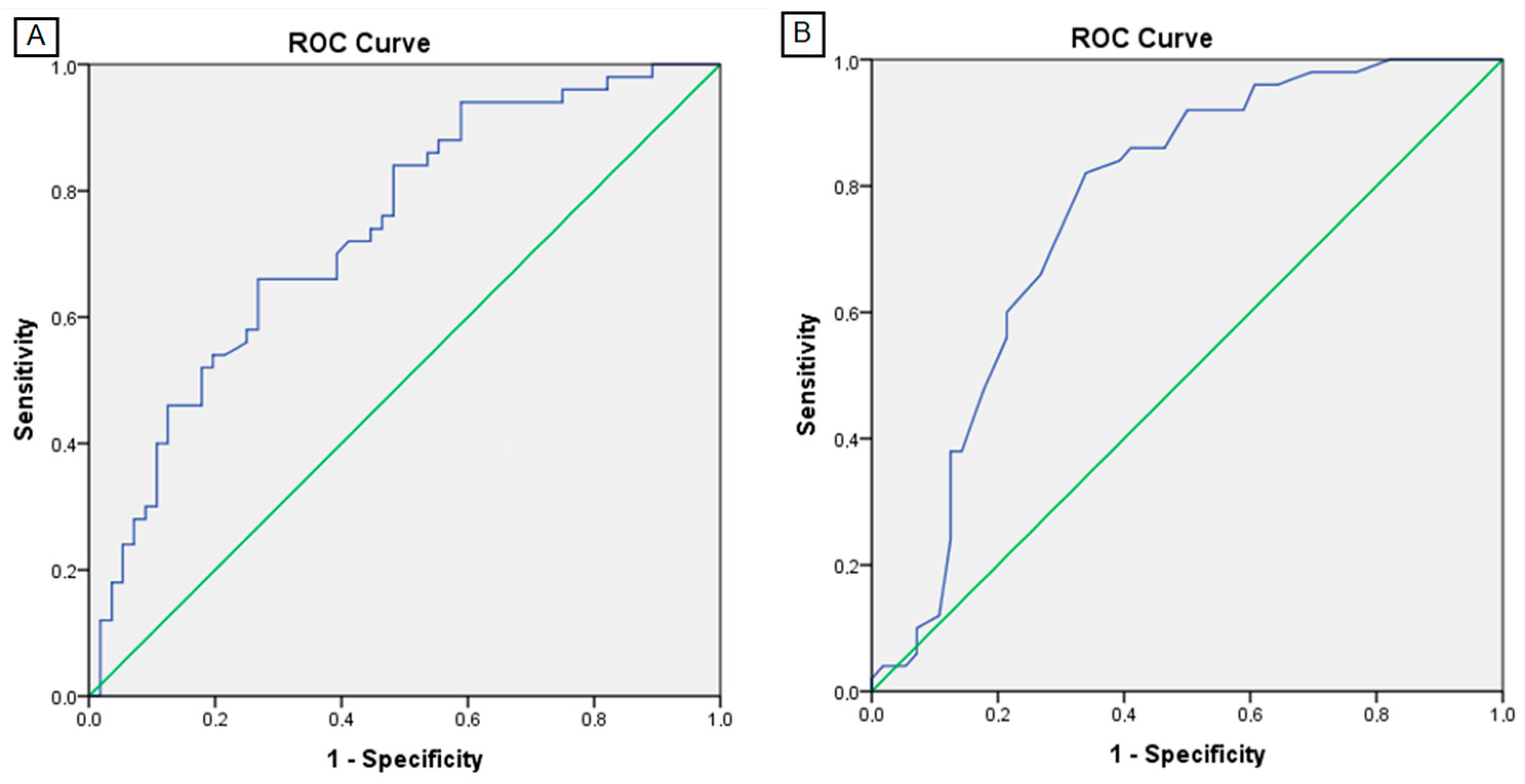
3.4. BIA Performance and Cut-Off Values in Detection of Sarcopenia
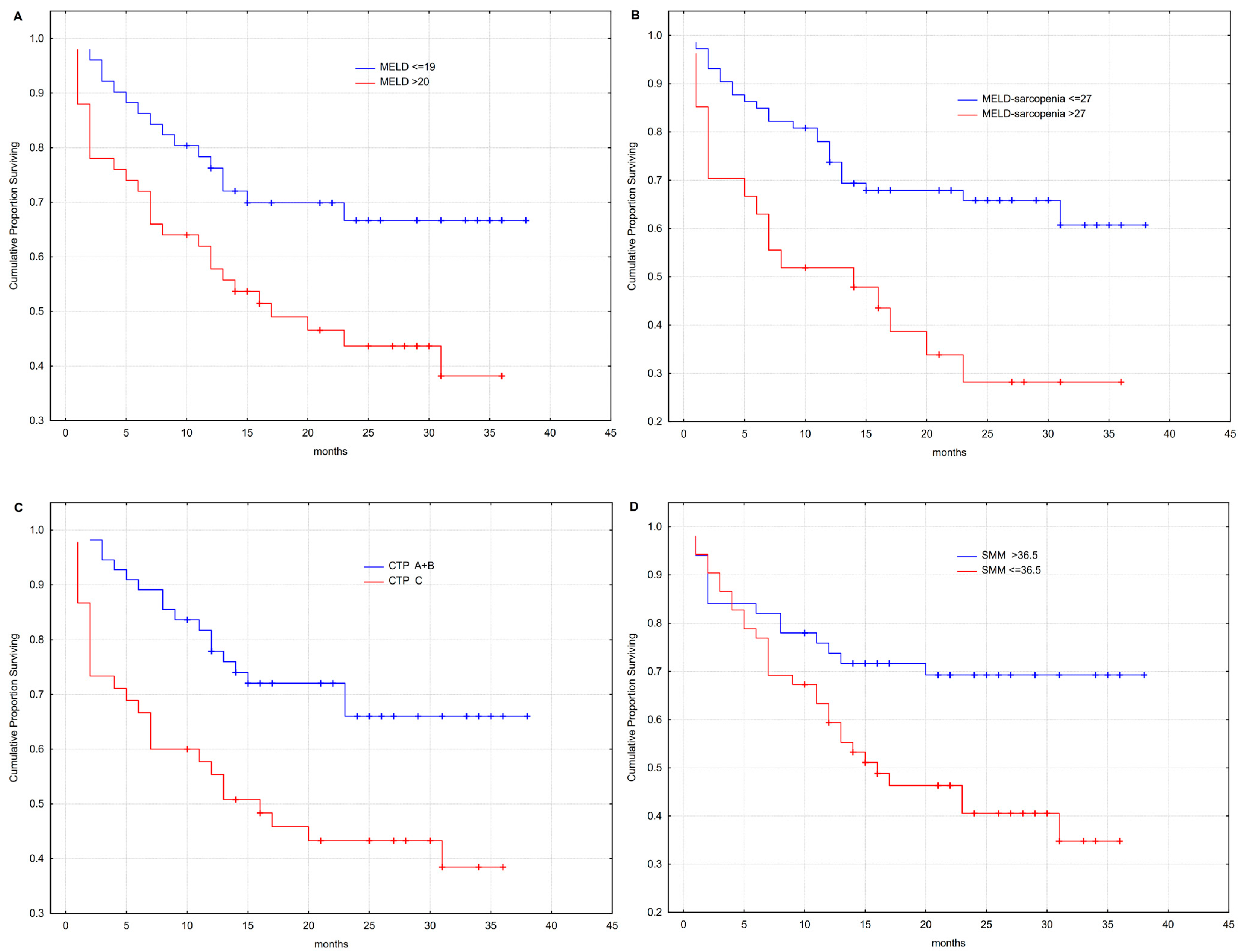
3.5. Outcome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Bosch, J.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Clària, J.; Szabo, G.; Bosch, J.; Bernardi, M. Pathophysiology of decompensated cirrhosis: Portal hypertension, circulatory dysfunction, inflammation, metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172193. [Google Scholar]
- Mazeaud, S.; Zupo, R.; Couret, A.; Panza, F.; Sardone, R.; Castellana, F. Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, M.; Gow, P.J.; Grossmann, M.; Angus, P.W. Review article: Sarcopenia in cirrhosis-aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Merli, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Muscle Alterations Are Associated With Minimal and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Ampuero, J.; Cubero, F.J.; Chi-Cervera, L.; Ríos-Torres, S.L.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Espinosa-Cuevas, Á.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Torre, A. Low phase angle is associated with the development of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10064–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafateli, M.; Mantzoukis, K.; Choi Yau, Y.; Mohammad, A.O.; Arora, S.; Rodrigues, S.; de Vos, M.; Papadimitriou, K.; Thorburn, D.; O'Beirne, J.; et al. Malnutrition and sarcopenia predict post-liver transplantation outcomes independently of the Model for End-stage Liver Disease score. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.; Armstrong, M.J. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: A practical overview. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Tandon, P.; Bernal, W.; Tapper, E.B.; Ekong, U.; Dasarathy, S.; Carey, E.J. Malnutrition, Frailty, and Sarcopenia in Patients With Cirrhosis: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1611–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Plauth, M. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3533–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Won, D.D.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, I.K. Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Compared with Computed Tomography for Assessment of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Primary Colorectal Malignancy: A Predictor of Short-Term Outcome After Surgery. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Baik, S.K. Prognostic value of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, E.J.; Lai, J.C.; Wang, C.W.; Dasarathy, S.; Lobach, I.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Dunn, M.A. Fitness, Life Enhancement, and Exercise in Liver Transplantation Consortium. A multicenter study to define sarcopenia in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, M.; Lattanzi, B.; Albanese, C.; Galtieri, A.; Farcomeni, A.; Giannelli, V.; Lucidi, C.; Di Martino, M.; Catalano, C.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis: The role of computed tomography scan for the assessment of muscle mass compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vugt, J.L.; Levolger, S.; de Bruin, R.W.; van Rosmalen, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; IJzermans, J.N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Computed Tomography-Assessed Skeletal Muscle Mass on Outcome in Patients Awaiting or Undergoing Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2277–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Buyse, S.; Francoz, C.; Laouénan, C.; Bruno, O.; Belghiti, J.; Moreau, R.; Vilgrain, V.; Valla, D. Prognostic value of muscle atrophy in cirrhosis using psoas muscle thickness on computed tomography. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Meza-Junco, J.; Baracos, V.E.; Sawyer, M.B.; Pang, J.X.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Myers, R.P. Inclusion of Sarcopenia Within MELD (MELD-Sarcopenia) and the Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Manuel Gómez, J.; Lilienthal Heitmann, B.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TANITA Corporation. Body Composition Analyzer MC-780 U Instruction Manual. Available online: https://www.tanita.com/data/Manuals/MC-780manual_R0.pdf?rev=C87A (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Addolorato, G.; Triarico, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Perna, A.; Silvestri, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Phase angle and impedance ratio: Two specular ways to analyze body composition. Ann. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M. Controversies in Diagnosing Sarcopenia in Cirrhosis-Moving from Research to Clinical Practice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.J.; Wallen, M.P.; Ryan, J.; Ward, L.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A. Evaluation of techniques used to assess skeletal muscle quantity in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 44, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, M.; Hara, N.; Terasaka, E.; Hattori, A.; Ishidome, M.; Mifuji-Moroka, R.; Miyachi, H.; Sugimoto, R.; Tanaka, H.; Fujita, N.; et al. Evaluation and prognosis of sarcopenia using impedance analysis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, E316–E317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Kishino, K.; Moriwaki, E.I.; Nishikawa, H.; Nishimura, T.; Iwata, Y.; Iijima, H.; Nishiguchi, S. Arm Skeletal Muscle Mass Is Associated with the Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengpradidgun, L.; Chamroonkul, N.; Sripongpun, P.; Kaewdech, A.; Tanutit, P.; Ina, N.; Piratvisuth, T. Utility of handgrip strength (HGS) and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) in the diagnosis of sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Xie, J.J.; Román-Calleja, B.M.; Pauly, M.; White, M.G.; Chapa-Ibargüengoitia, M.; Campos-Murguía, A.; González-Regueiro, J.A.; Macias-Rodríguez, R.U.; Duarte-Rojo, A. Phase Angle from Bioelectrical Impedance for the Assessment of Sarcopenia in Cirrhosis with or Without Ascites. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sun, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.M. Comparative assessment of skeletal muscle mass using computerized tomography and bioelectrical impedance analysis in critically ill patients. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.H.; Lim, T.S.; Jeon, M.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Kim, S.U. Predictors of Discordance in the Assessment of Skeletal Muscle Mass between Computed Tomography and Bioimpedance Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espirito Santo Silva, D.D.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Passos de Jesus, R.; Oliveira, L.P.M.; Torrinhas, R.S.; Belarmino, G. Phase angle as a marker for sarcopenia in cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Ríos-Torres, S.L.; Espinosa-Cuevas, Á.; Torre, A. Malnutrition assessed through phase angle and its relation to prognosis in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belarmino, G.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Torrinhas, R.S.; Sala, P.; Andraus, W.; D'Albuquerque, L.A.; Pereira, R.M.; Caparbo, V.F.; Ravacci, G.R.; Damiani, L.; et al. Phase angle obtained by bioelectrical impedance analysis independently predicts mortality in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, A.P.; Sicchieri, J.M.F.; Schiavoni, I.L.; Barbeiro, D.; Manca, C.S.; da Silva, B.R.; Bezerra, A.E.; Pinto, L.C.M.; Araújo, R.C.; Teixeira, A.C.; et al. Phase angle as a severity indicator for liver diseases. Nutrition 2020, 70, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saueressig, C.; Glasenapp, J.H.; Luft, V.C.; Alves, F.D.; Ferreira, P.K.; Hammes, T.O.; Dall'Alba, V. Phase Angle Is an Independent Predictor of 6-Month Mortality in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Conde, M.; Llop, E.; Gómez-Pimpollo, L.; Blanco, S.; Rodríguez, L.; Fernández Carrillo, C.; Perelló, C.; López-Gómez, M.; Martínez-Porras, J.L.; Fernández-Puga, N.; et al. A nomogram as an indirect method to identify sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantai, X.; Liu, Y.; Yeo, Y.H.; Praktiknjo, M.; Mauro, E.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Engelmann, C.; Zhang, P.; Jeong, J.Y.; van Vugt, J.L.A.; et al. Effect of sarcopenia on survival in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vugt, J.L.A.; Alferink, L.J.M.; Buettner, S.; Gaspersz, M.P.; Bot, D.; Darwish Murad, S.; Feshtali, S.; van Ooijen, P.M.A.; Polak, W.G.; Porte, R.J.; et al. A model including sarcopenia surpasses the MELD score in predicting waiting list mortality in cirrhotic liver transplant candidates: A competing risk analysis in a national cohort. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topan, M.M.; Sporea, I.; Dănilă, M.; Popescu, A.; Ghiuchici, A.M.; Lupuşoru, R.; Şirli, R. Impact of Sarcopenia on Survival and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 766451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, T.Y.; Nam, S.W.; Sohn, J.H. Computed Tomography-Determined Body Composition Abnormalities Usefully Predict Long-term Mortality in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2021, 45, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
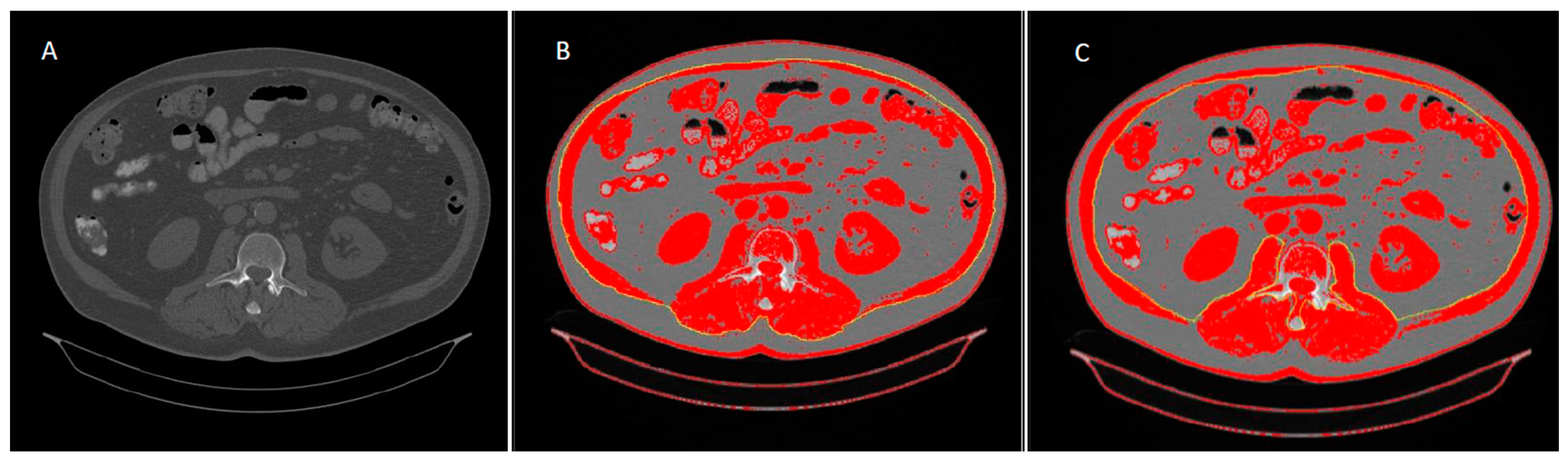
| Parameter | Value | p |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | ||
| Gender, n (%) | ||
| Female/Male | 16/84 (15/85) | |
| Age (AM ± SD [95% CI]) | ||
| Total | 59 ± 9.5 (57–61) y | |
| Female | 59.3 ± 8.9 y | 0.731 * |
| Male | 58.4 ± 12.6 y | |
| Body mass (AM ± SD) | ||
| Female | 65.8 ± 14 kg | |
| Male | 91 ± 17 kg | |
| Body height (AM ± SD) | ||
| Female | 166 ± 4.2 cm | |
| Male | 179.8 ± 7.3 cm | |
| BMI (AM ± SD [95% CI]) | ||
| Total | 27.5 ± 5.3 (26.4–28.5) kg/m2 | |
| Female | 23.8 ± 4.8 (21–26) kg/m2 | 0.002 * |
| Male | 28 ± 5.1 (27–29) kg/m2 | |
| Clinical characteristics | ||
| Etiology, n (%) † | ||
| Ethylic | 87 (83) | |
| Chronic HBV infection | 3 (3) | |
| Chronic HCV infection | 11 (10.5) | |
| NAFLD | 4 (3.8) | |
| Other | 8 (7.6) | |
| Prev.decomp, n (%) † | ||
| None | 31 (30) | |
| Ascites | 55 (53) | |
| Portal encephalopathy | 18 (17) | |
| Variceal bleeding | 18 (17) | |
| CTP score, n (%) | ||
| A | 22 (21.2) | |
| B | 36 (34.6) | |
| C | 46 (44.2) | |
| Ascites grade, n (%) | ||
| 0 | 32 (30.8) | |
| 1 | 25 (24) | |
| 2 | 18 (17.3) | |
| 3 | 29 (27.9) | |
| Peripheral edema grade, n (%) | ||
| 0 | 60 (57.1) | |
| 1 | 21 (20) | |
| 2 | 21 (20) | |
| 3 | 3 (2.9) | |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 61 (58) | |
| Laboratory values (Mdn (Q1–Q3; min–max)) | ||
| Platelets (×109/L) | 110.5 (74.5–151; 26–299) | |
| INR | 1.47 (1.28–1.83; 0.61–4.5) | |
| Albumins (g/L) | 30.3 (26–35; 18–48) | |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 45 (26.5–92; 6–457) | |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 69 (59–85; 27–305) | |
| Natrium (mmol/L) | 136.5 (134–139; 117–144) | |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4 (3.7–4.4; 2–6) | |
| MELD score | 15 (11–19; 7–42) | |
| MELD-sarcopenia score | 22 (15–27; 7–43) | |
| MSCT and BIA parameters (AM ± SD [95% CI]) | ||
| MSCT | ||
| L3 surface (cm2) | 152 ± 32 (146–159) | |
| Body height (cm) | 178 ± 8.7 (176–179) | |
| L3 SMI (cm2/m2) | 47.9 ± 8.9 (46.3–49.7) | |
| BIA | ||
| SMM (kg) | 35.8 ± 9 (34–37) | |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 11.3 ± 2.4 (10.8–11.7) | |
| ECW (kg) | 19.9 ± 3.6 (19–21) | |
| ICW (kg) | 26.9 ± 6.7 (25.6–28) | |
| TBW (kg) | 47.2 ± 10.1 (45.3–49) | |
| FFM (kg) | 66 ± 12.8 (63.6–68.4) | |
| PA (°) | 4.8 ± 0.89 (4.6–5) |
| R (p) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Ascites/Peripheral Edema | ||
| Grade 0 and 1 | Grade 2 and 3 | ||
| SMM | 0.443 (<0.001) | 0.498 (<0.001) | 0.390 (0.007) |
| SMI | 0.525 (<0.001) | 0.614 (<0.001) | 0.470 (0.001) |
| FFM | 0.404 (<0.001) | 0.434 (0.003) | 0.418 (0.004) |
| PA | 0.571 (<0.001) | 0.524 (<0.001) | 0.676 (<0.001) |
| Sarcopenia (L3-SMI) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 49) | Yes (n = 56) | ||
| Gender; n (%) | 0.599 * | ||
| Male | 43 (88) | 46 (82) | |
| Female | 6 (12) | 10 (18) | |
| Age (years) | |||
| (AM ± SD (min–max)) | 57.6 ± 9.3 (36–77) | 60.4 ± 9.6 (43–85) | 0.100 ** |
| BIA variables (AM ± SD (min–max)) | |||
| SMM (kg) | 38.8 ± 8.8 (23–56) | 33.2 ± 8.4 (17.4–57.4) | 0.001 ** |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 12.3 ± 2.3 (8.4–17.3) | 10.4 ± 2.1 (6.7–18) | <0.001 ** |
| FFM (kg) | 69.6 ± 12 (43.6–90.5) | 62.7 ± 12.6 (34–87) | 0.005 ** |
| PA (°) | 5.3 ± 0.62 (3.6–6.6) | 4.45 ±0.94 (2.6–6.5) | <0.001 ** |
| Area (SE) | 95% CI | p | Sp (%) | Se (%) | Cut-Off | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMM (kg) | 0.679 (0.052) | 0.577–0.781 | 0.002 | 62 | 66 | 36.5 |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 0.737 (0.048) | 0.643–0.831 | <0.001 | 66 | 73 | 11.1 |
| FFM (kg) | 0.646 (0.053) | 0.542–0.750 | 0.010 | 58 | 59 | 66.8 |
| TBW (kg) | 0.690 (0.051) | 0.590–0.790 | 0.001 | 60 | 64 | 48.2 |
| PA (°) | 0.762 (0.048) | 0.669–0.855 | <0.001 | 60 | 79 | 5.05 |
| Sarcopenia (L3-SMI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Total | X2; p * | OR (95% CI) | p ** | |
| SMM (kg) | 7.3; 0.007 | 3.2 (1.4–7) | 0.004 | |||
| ≤36.5 | 37 (66) | 19 (38) | 56 (53) | |||
| >36.5 † | 19 (34) | 31 (62) | 50 (47) | |||
| SMI (kg/m2) | 14.9; <0.001 | 5.3 (2.3–12) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤11.1 | 41 (73) | 17 (34) | 58 | |||
| >11.1 † | 15 (27) | 33 (66) | 48 | |||
| PA (°) | 14.9; <0.001 | 5.5 (2.3–13) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤5.05 | 44 (79) | 20 (40) | 64 | |||
| >5.05 † | 12 (21) | 30 (60) | 42 | |||
| TBW (kg) | 5.3; 0.021 | 2.7 (1.2–6) | 0.012 | |||
| ≤48.2 | 36 (64) | 20 (40) | 56 | |||
| >48.2 † | 20 (36) | 30 (60) | 50 | |||
| FFM (kg) | 2.4; 0.12 | |||||
| ≤66.8 | 33 (59) | 21 (42) | 54 | |||
| >66.8 † | 23 (41) | 29 (58) | 52 | |||
| 56 | 50 | |||||
| Sarcopenia (L3-SMI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | p | OR (95% CI) | |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 0.001 | 4.5 (1.9–11) | ||
| ≤11.1 | 41 (73) | 17 (34) | ||
| >11.1 | 15 (27) | 33 (66) | ||
| PA (°) | 0.001 | 4.7 (1.9–11.6) | ||
| ≤5.05 | 44 (79) | 20 (40) | ||
| >5.05 | 12 (21) | 30 (60) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bozic, D.; Grgurevic, I.; Mamic, B.; Capkun, V.; Bilandzic-Ivisic, J.; Ivanovic, T.; Bozic, I.; Zaja, I.; Podrug, K.; Puljiz, Z.; et al. Detection of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153335
Bozic D, Grgurevic I, Mamic B, Capkun V, Bilandzic-Ivisic J, Ivanovic T, Bozic I, Zaja I, Podrug K, Puljiz Z, et al. Detection of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153335
Chicago/Turabian StyleBozic, Dorotea, Ivica Grgurevic, Bisera Mamic, Vesna Capkun, Josipa Bilandzic-Ivisic, Tomislav Ivanovic, Ivona Bozic, Ivan Zaja, Kristian Podrug, Zeljko Puljiz, and et al. 2023. "Detection of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153335
APA StyleBozic, D., Grgurevic, I., Mamic, B., Capkun, V., Bilandzic-Ivisic, J., Ivanovic, T., Bozic, I., Zaja, I., Podrug, K., Puljiz, Z., Perko, Z., & Mikolasevic, I. (2023). Detection of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Nutrients, 15(15), 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153335








