Mapping Research Trends and Hotspots in the Link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbes over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
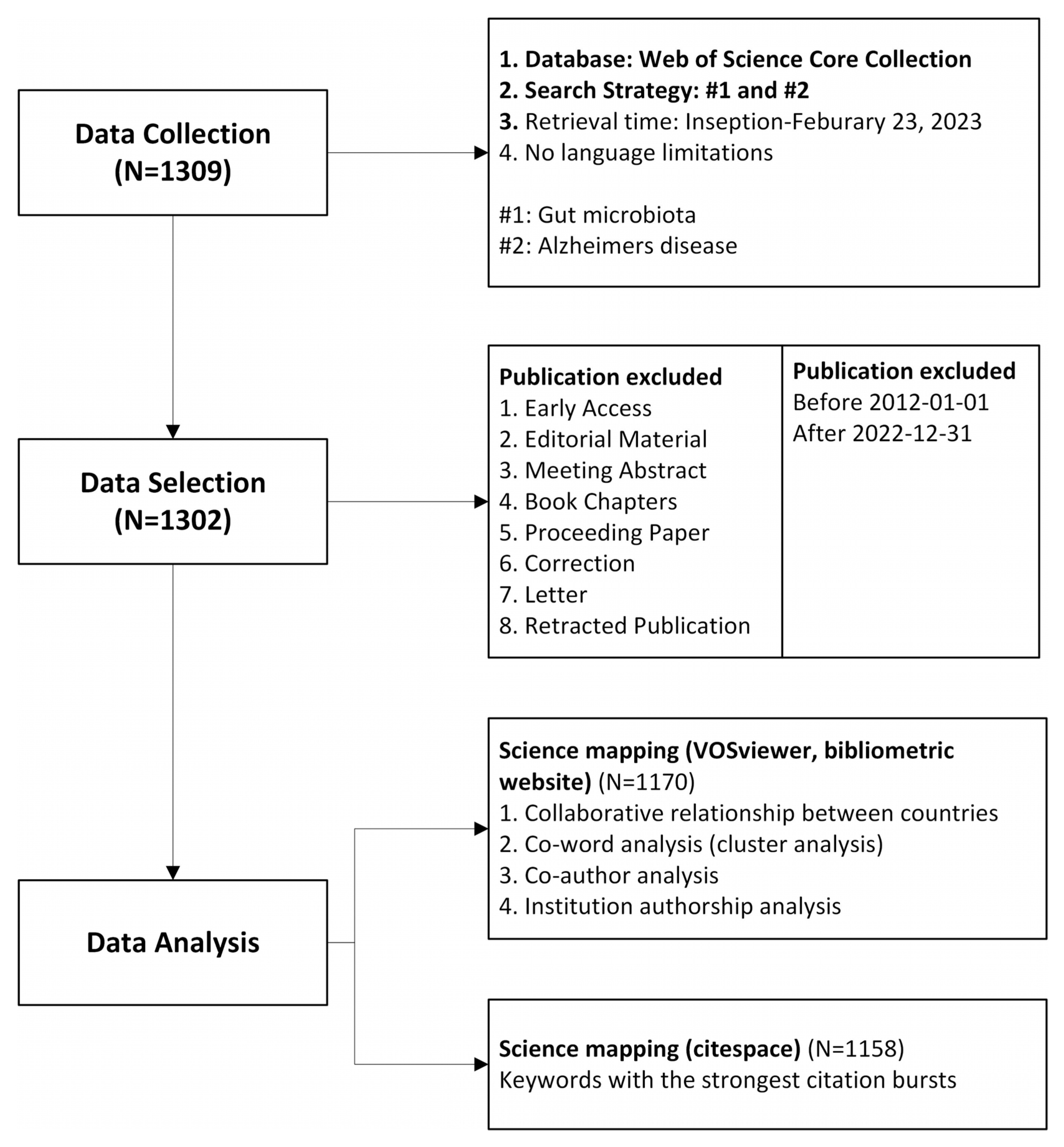
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Annual Publications and Citations
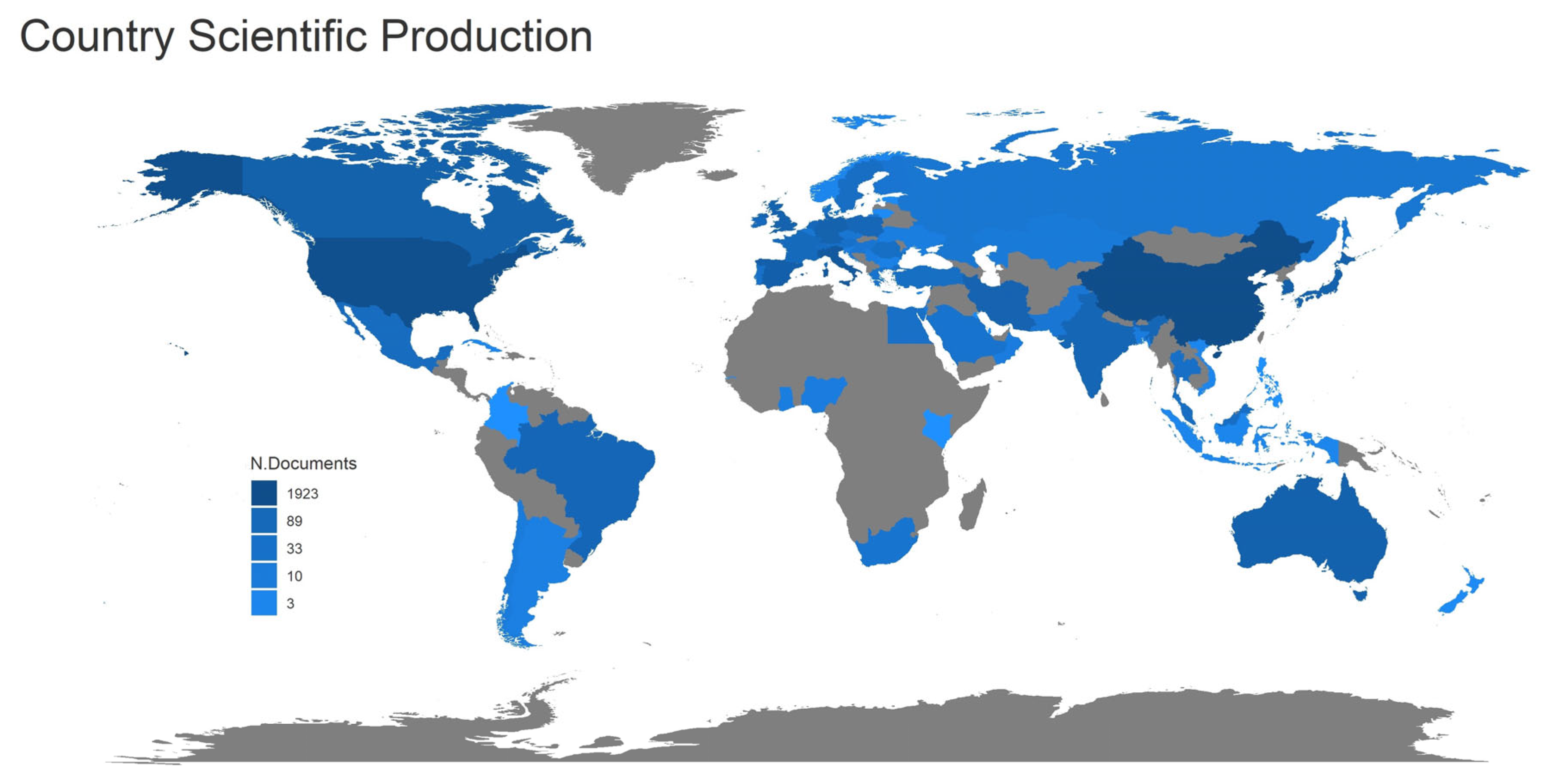
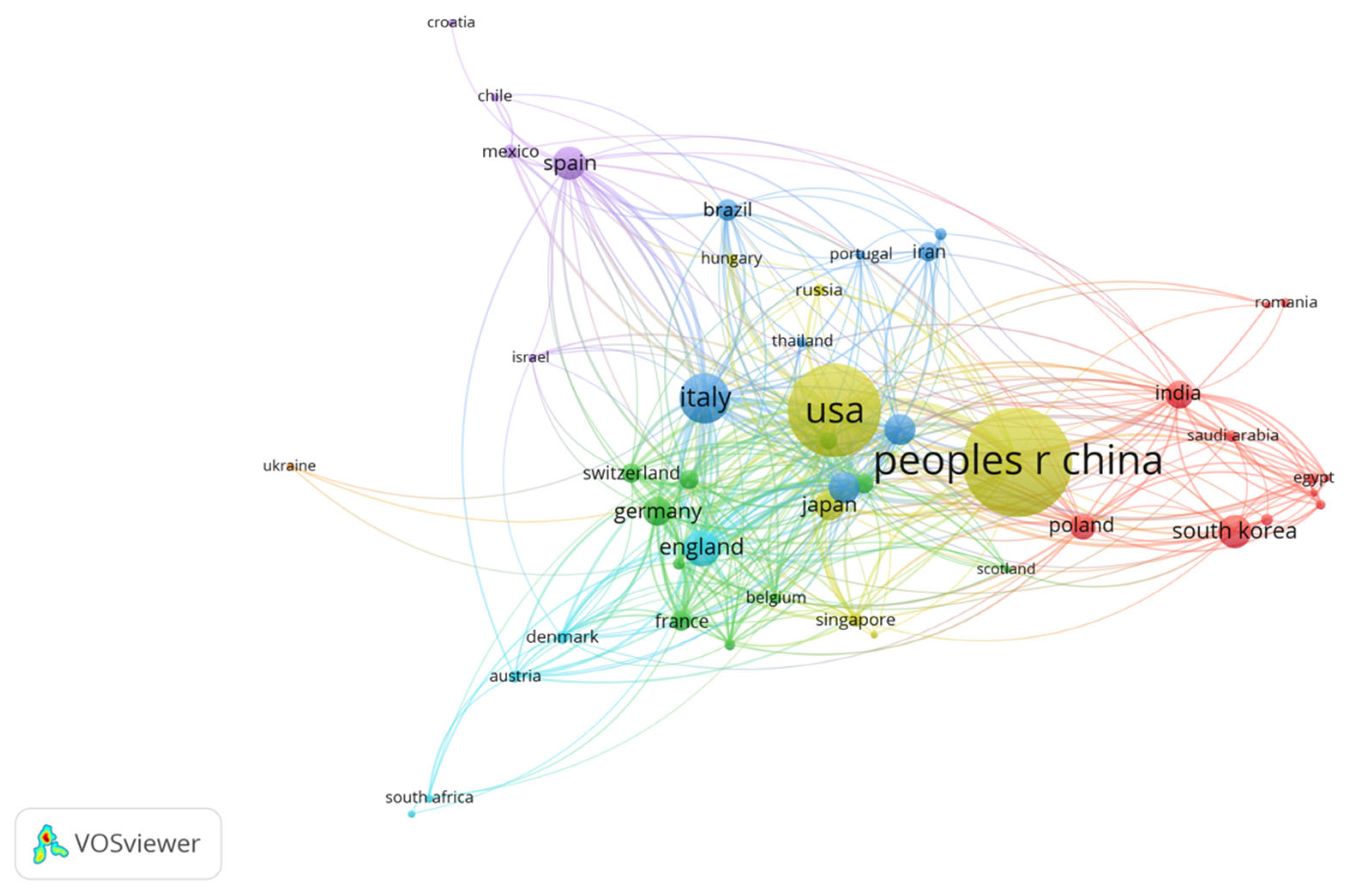
3.2. Geographical Distribution
3.3. Journals
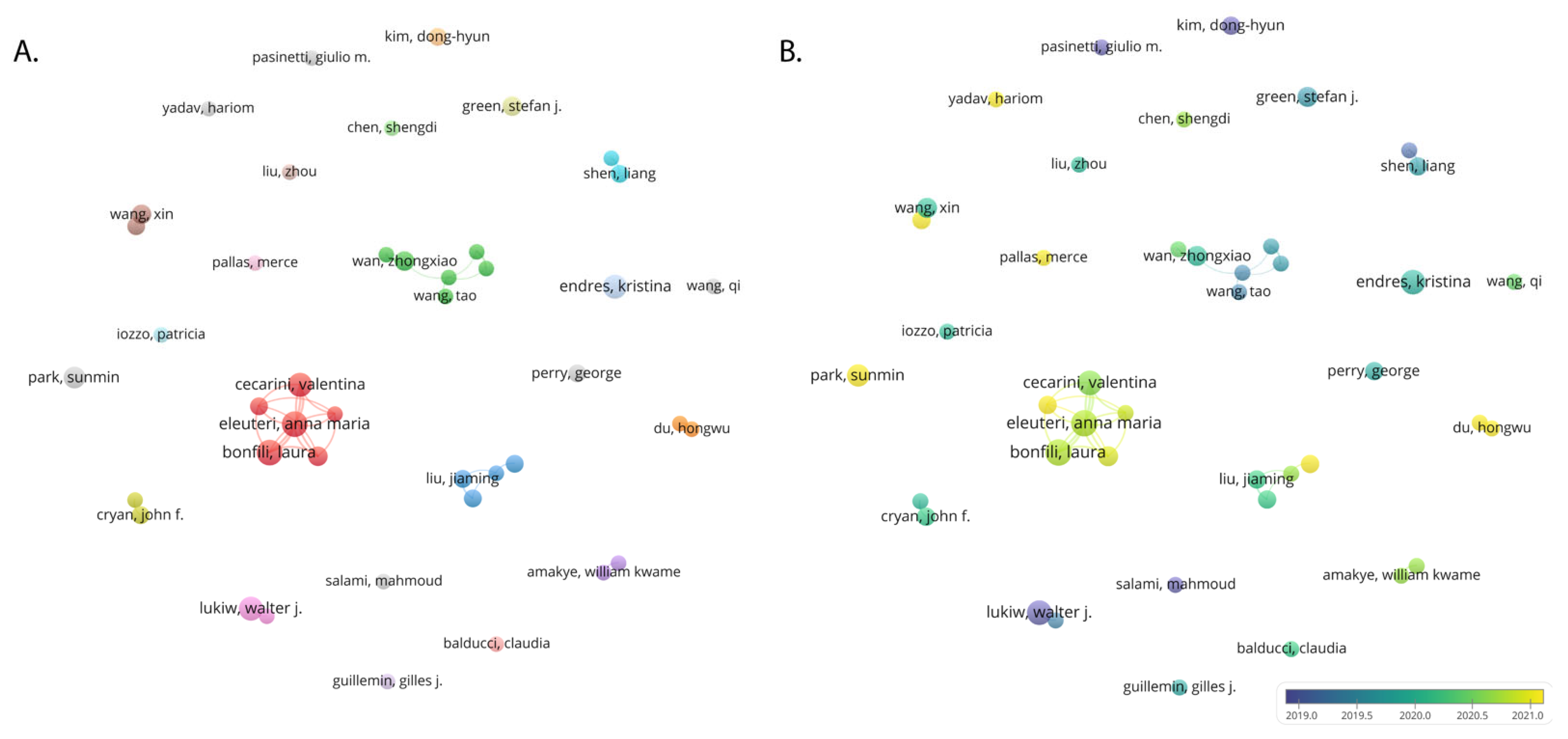
3.4. Authors and Institutions
3.5. Most Cited Articles
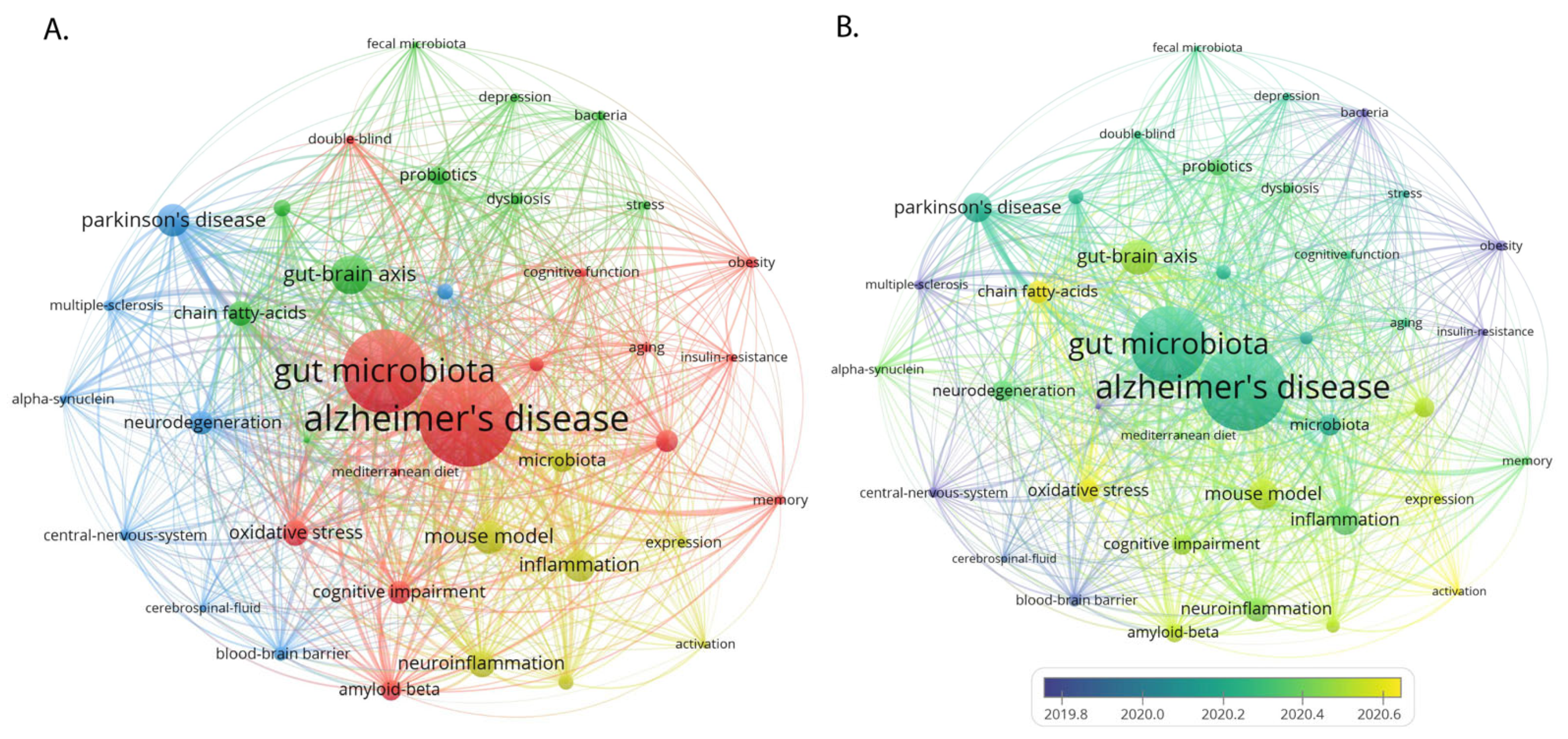
3.6. Keywords
3.6.1. Keywords Co-Occurrence Networks
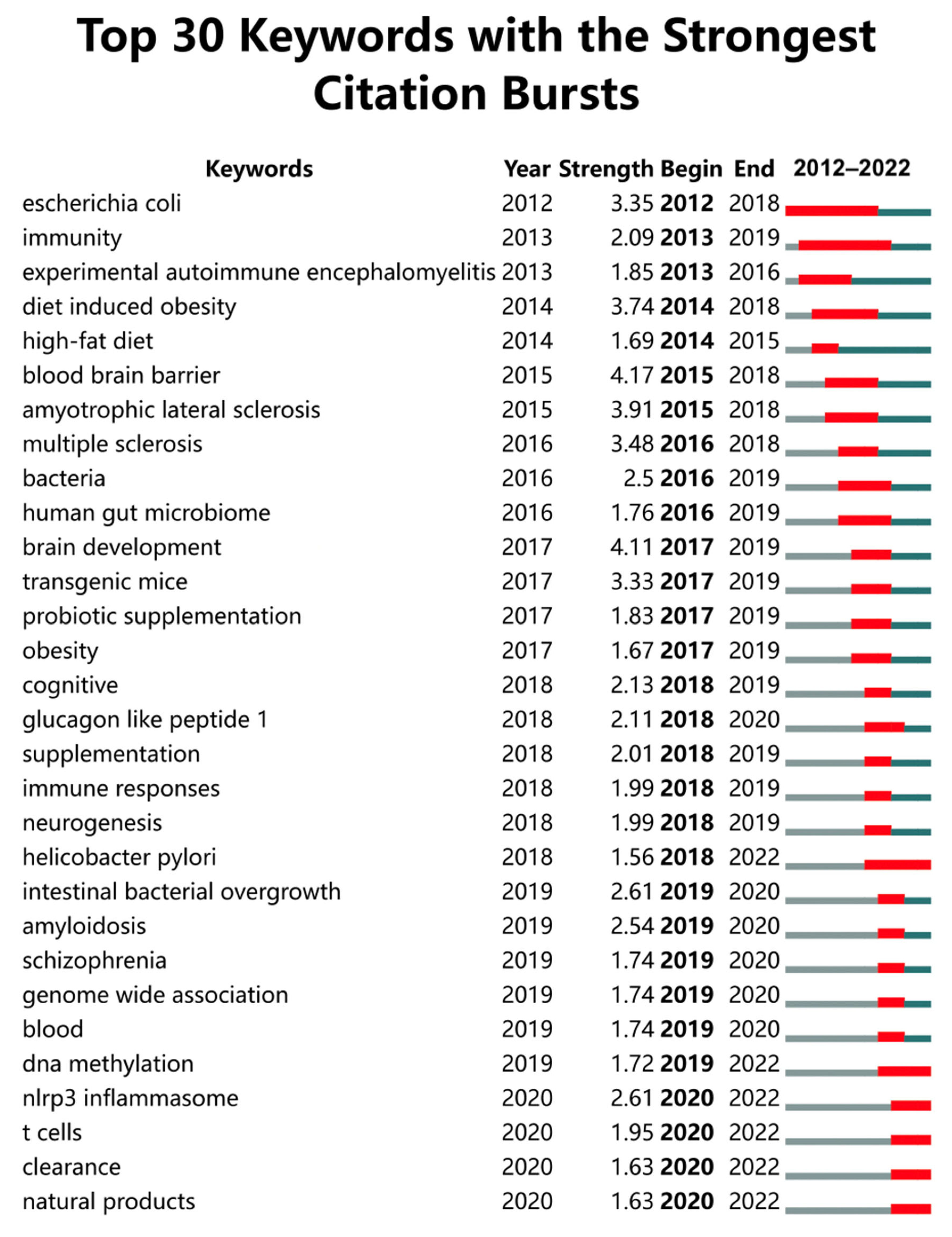
3.6.2. Keywords with the Strongest Citation Bursts
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alander, M.; Satokari, R.; Korpela, R.; Saxelin, M.; Vilpponen-Salmela, T.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; von Wright, A. Persistence of colonization of human colonic mucosa by a probiotic strain, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, after oral consumption. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schemann, M.; Neunlist, M. The human enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2004, 16, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, D.; Dennison, U.; Gaszner, G.; Cryan, J.; Dinan, T. Enhanced peripheral toll-like receptor responses in psychosis: Further evidence of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, M.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Fuentes, E.G.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Sánchez, A.; Burcelin, R.; Tinahones, F. The gut microbiota profile is associated with insulin action in humans. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, K.B.; Weuve, J.; Barnes, L.L.; McAninch, E.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A. Population estimate of people with clinical Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment in the United States (2020–2060). Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarandi, S.S.; Peterson, D.A.; Treisman, G.J.; Moran, T.H.; Pasricha, P.J. Modulatory effects of gut microbiota on the central nervous system: How gut could play a role in neuropsychiatric health and diseases. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochocka, M.; Donskow-Łysoniewska, K.; Diniz, B.S.; Kurpas, D.; Brzozowska, E.; Leszek, J. The gut microbiome alterations and inflammation-driven pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease—A critical review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chetelat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saji, N.; Niida, S.; Murotani, K.; Hisada, T.; Tsuduki, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Kimura, A.; Toba, K.; Sakurai, T. Analysis of the relationship between the gut microbiome and dementia: A cross-sectional study conducted in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osinska, V.; Klimas, R. Mapping science: Tools for bibliometric and altmetric studies. Inf. Res. Int. Electron. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, H.R. Bibliometric Analysis using Bibliometrix an R Package. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, V.; Rizk, D.E.E. Increasing importance of research metrics: Journal Impact Factor and h-index. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2018, 29, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.; Hsiao, E. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Feng, T.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Chu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, E.; Asemi, Z.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Ali Hamidi, G.; Salami, M. Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Metabolic Status in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind and Controlled Trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harach, T.; Marungruang, N.; Duthilleul, N.; Cheatham, V.; Mc Coy, K.D.; Frisoni, G.; Neher, J.J.; Fåk, F.; Jucker, M.; Lasser, T.; et al. Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. The Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Integrative HMP (iHMP) Research Network Consortium. The Integrative Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2019, 569, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Webster, C.; Servaes, S.; Morais, J.; Rosa-Neto, P. World Alzheimer Report 2022. Available online: https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2022/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Chen, P.; Li, F.; Harmer, P. Healthy China 2030: Moving from blueprint to action with a new focus on public health. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ying, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, Q. Traditional Chinese medicine for anti-Alzheimer’s disease: Berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Ma, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Li, H. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Cognitive Impairment: A Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coder, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhuge, Q.; Su, D.M. Friend or foe: The dichotomous impact of T cells on neuro-de/re-generation during aging. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7116–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebir, H.; Kreymborg, K.; Ifergan, I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Cayrol, R.; Bernard, M.; Giuliani, F.; Arbour, N.; Becher, B.; Prat, A. Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interact with the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 796288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wu, G.; Dull, R.O.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B.; Hu, G. The GTPase Rab1 Is Required for NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Inflammatory Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Wang, H.F.; Tan, C.C.; Meng, X.F.; Wang, C.; Tang, S.W.; Yu, J.T. Anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 44, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.Y.; Zhao, Q.H.; Liu, Y.; Gui, Y.Z.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhu, D.Y.; Yu, C.; Hong, Z. Phase I study on the pharmacokinetics and tolerance of ZT-1, a prodrug of huperzine A, for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marizzoni, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Mirabelli, P.; Festari, C.; Lopizzo, N.; Nicolosi, V.; Mombelli, E.; Mazzelli, M.; Luongo, D.; Naviglio, D.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Lipopolysaccharide as Mediators Between Gut Dysbiosis and Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 78, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.K.S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
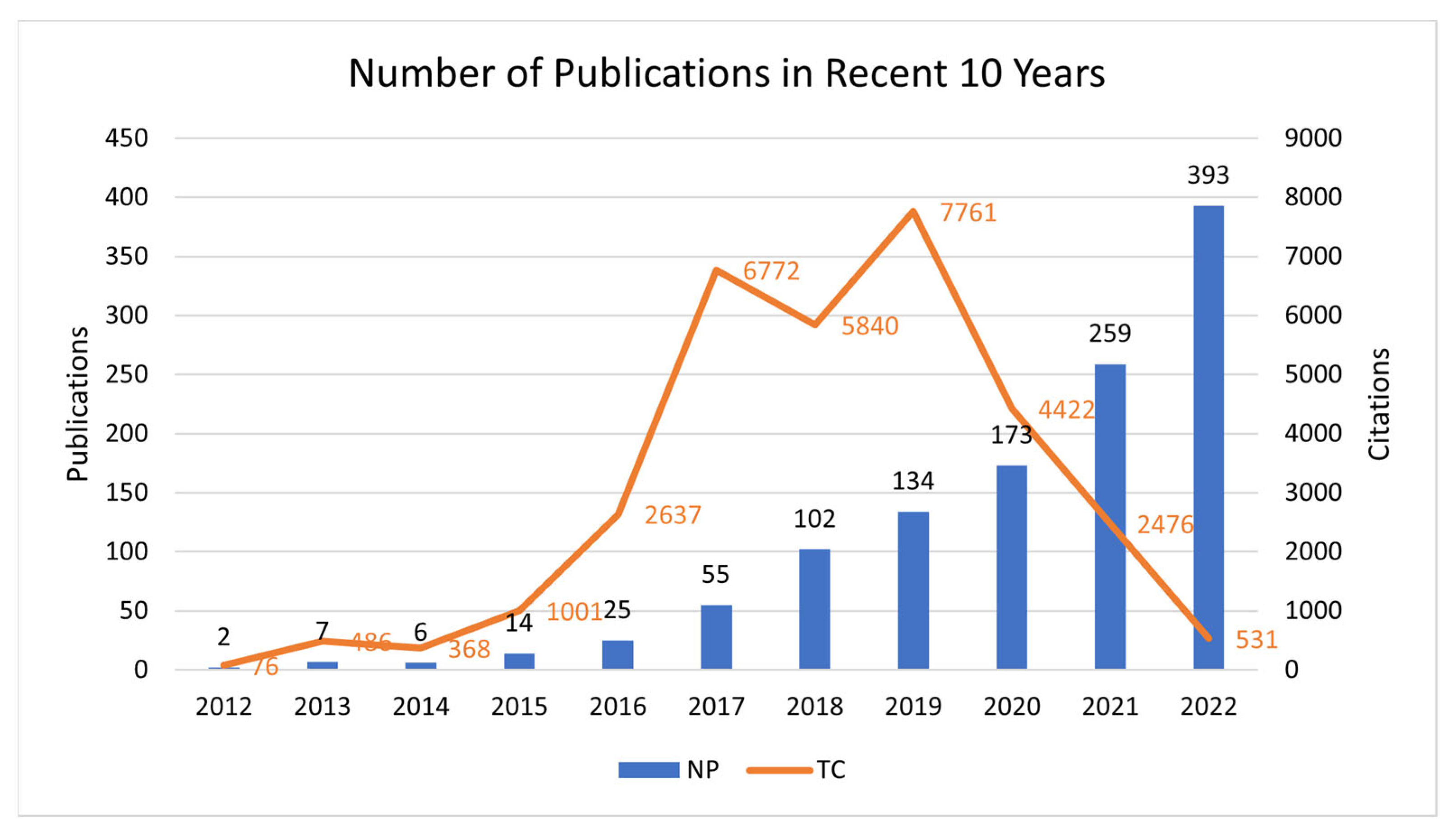
| Year | NP | Percent (%) | TC/Y | TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2 | 0.2 | 3.5 | 76 |
| 2013 | 7 | 0.6 | 6.9 | 486 |
| 2014 | 6 | 0.5 | 6.8 | 368 |
| 2015 | 14 | 1.2 | 8.9 | 1001 |
| 2016 | 25 | 2.1 | 15.1 | 2637 |
| 2017 | 55 | 4.7 | 20.5 | 6772 |
| 2018 | 102 | 8.7 | 11.5 | 5840 |
| 2019 | 134 | 11.5 | 14.5 | 7761 |
| 2020 | 173 | 14.8 | 8.5 | 4422 |
| 2021 | 259 | 22.1 | 4.8 | 2476 |
| 2022 | 393 | 33.6 | 1.4 | 531 |
| SCR | Country | NP | Percent (%) | TC | SCP | MCP | MCP_Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 374 | 40.7 | 8268 | 316 | 58 | 0.155 |
| 2 | USA | 208 | 22.6 | 9544 | 146 | 62 | 0.298 |
| 3 | Italy | 90 | 9.8 | 5159 | 65 | 25 | 0.278 |
| 4 | Korea | 50 | 5.4 | 1206 | 46 | 4 | 0.08 |
| 5 | Spain | 40 | 4.4 | 1301 | 29 | 11 | 0.275 |
| 6 | Australia | 34 | 3.7 | 1070 | 22 | 12 | 0.353 |
| 7 | Japan | 33 | 3.6 | 674 | 26 | 7 | 0.212 |
| 8 | Canada | 31 | 3.4 | 1632 | 18 | 13 | 0.419 |
| 9 | Poland | 31 | 3.4 | 1019 | 28 | 3 | 0.097 |
| 10 | India | 28 | 3.1 | 462 | 20 | 8 | 0.286 |
| Sources | NP | Percent (%) | IF (2021) | Category (JCR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Journal of Alzheimers Disease | 57 | 4.9 | 4.16 | Neurosciences (Q2) |
| Nutrients | 50 | 4.3 | 6.706 | Nutrition and Dietetics (Q1) |
| International Journal of Molecular Science | 49 | 4.2 | 6.208 | Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (Q2); Chemistry, Multidisciplinary (Q2) |
| Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 46 | 3.9 | 5.702 | Neurosciences (Q2); Geriatrics and Gerontology (Q2) |
| Frontiers in Neuroscience | 31 | 2.7 | 5.152 | Neurosciences (Q2) |
| Scientific Reports | 26 | 2.2 | 4.997 | Multidisciplinary Sciences (Q1) |
| Frontiers in Immunology | 21 | 1.8 | 8.787 | Immunology (Q1) |
| Frontiers in Pharmacology | 16 | 1.4 | 5.988 | Phamacology and Phamacy (Q1) |
| Cells | 13 | 1.1 | 7.666 | Cell Biology (Q2) |
| Brain Behavior and Immunity | 12 | 1.0 | 19.227 | Neurosciences (Q1); Immunology (Q1); Psychiatry (Q1) |
| SCR | Author (N = 4683) | H-Index | TC | NP | Institution (N = 1940) | NP | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wang Y | 13 | 770 | 31 | Shanghai Jiaotong University | 66 | 5.6 |
| 2 | Zhang X | 13 | 1504 | 28 | University of Kentucky | 60 | 5.1 |
| 3 | ZhangY | 7 | 189 | 26 | Zhejiang University | 59 | 5.0 |
| 4 | Li Y | 11 | 354 | 25 | Louisiana University | 49 | 4.2 |
| 5 | Wang X | 10 | 790 | 25 | Fudan University | 41 | 3.5 |
| 6 | Liu Y | 8 | 184 | 22 | Soochow University | 41 | 3.5 |
| 7 | Chen Y | 10 | 487 | 17 | Capital Medical University | 39 | 3.3 |
| 8 | Liu J | 8 | 788 | 17 | Peking University | 38 | 3.3 |
| 9 | Zhang L | 7 | 566 | 17 | University College Cork | 37 | 3.2 |
| 10 | Zhao Y | 7 | 419 | 17 | Central South University | 36 | 3.1 |
| SCR | Author and Year | Title | Journal (IF-2022) | TC | TC/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cryan JF, 2019 [19] | The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis | Physiological Reviews (46.513; Q1) | 1212 | 242.4 |
| 2 | Rinninella E, 2019 [20] | What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases | Microorganisms (4.926; Q3) | 980 | 196.0 |
| 3 | Fung TC, 2017 [21] | Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease | Nature Neuroscience (28.771; Q1) | 887 | 126.7 |
| 4 | Vogt NM, 2017 [10] | Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease | Scientific Reports (4.997; Q3) | 809 | 115.6 |
| 5 | Hickman S, 2018 [22] | Microglia in neurodegeneration | Nature Neuroscience (28.771; Q1) | 635 | 105.8 |
| 6 | Cattaneo A, 2017 [23] | Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly | Neurobiology of Aging (5.133; Q2/3) | 578 | 82.6 |
| 7 | Wang X, 2019 [24] | Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression | Cell Research (46.351, Q1) | 445 | 89.0 |
| 8 | Akbari E, 2016 [25] | Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Metabolic Status in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind and Controlled Trial | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience (5.702; Q2/3) | 423 | 52.9 |
| 9 | Harach T, 2017 [26] | Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota | Scientific Reports (4.997; Q3) | 418 | 59.7 |
| 10 | Jiang C, 2017 [27] | The Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease | Journal of Alzheimers Disease (4.160, Q3) | 394 | 56.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiu, R.; Sun, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Mapping Research Trends and Hotspots in the Link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbes over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143203
Xiu R, Sun Q, Li B, Wang Y. Mapping Research Trends and Hotspots in the Link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbes over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143203
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiu, Ruipu, Qingyuan Sun, Boya Li, and Yanqing Wang. 2023. "Mapping Research Trends and Hotspots in the Link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbes over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143203
APA StyleXiu, R., Sun, Q., Li, B., & Wang, Y. (2023). Mapping Research Trends and Hotspots in the Link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbes over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis. Nutrients, 15(14), 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143203




