The Mediation and Moderation Effect Association among Physical Activity, Body-Fat Percentage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipids among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
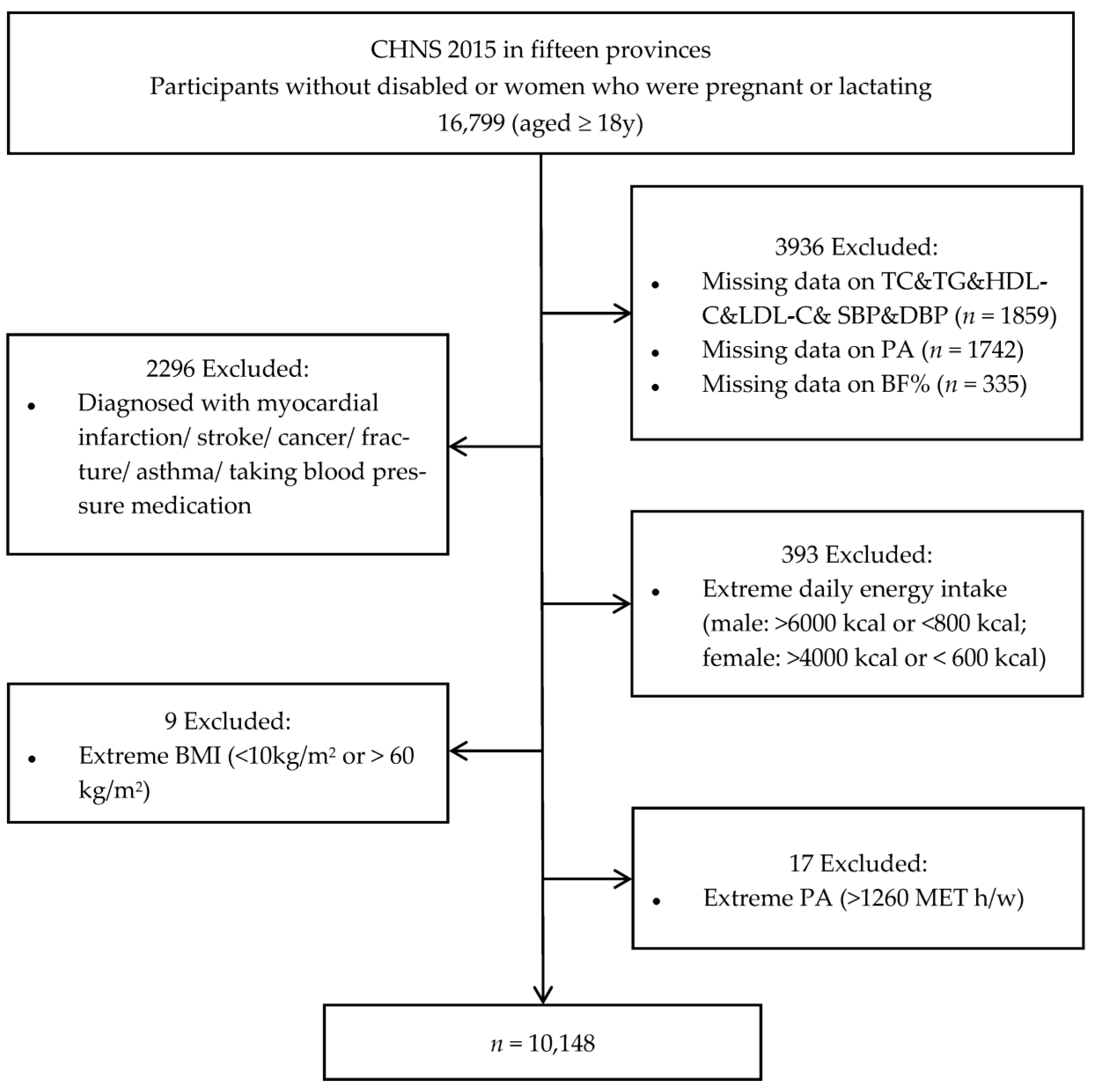
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Physical Activity and Sedentary Assessment
2.3. Anthropometrics and Blood Biomarker Measurements
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. The Simple Mediation Effect Models
2.5.2. The Serial Multiple-Mediator Models
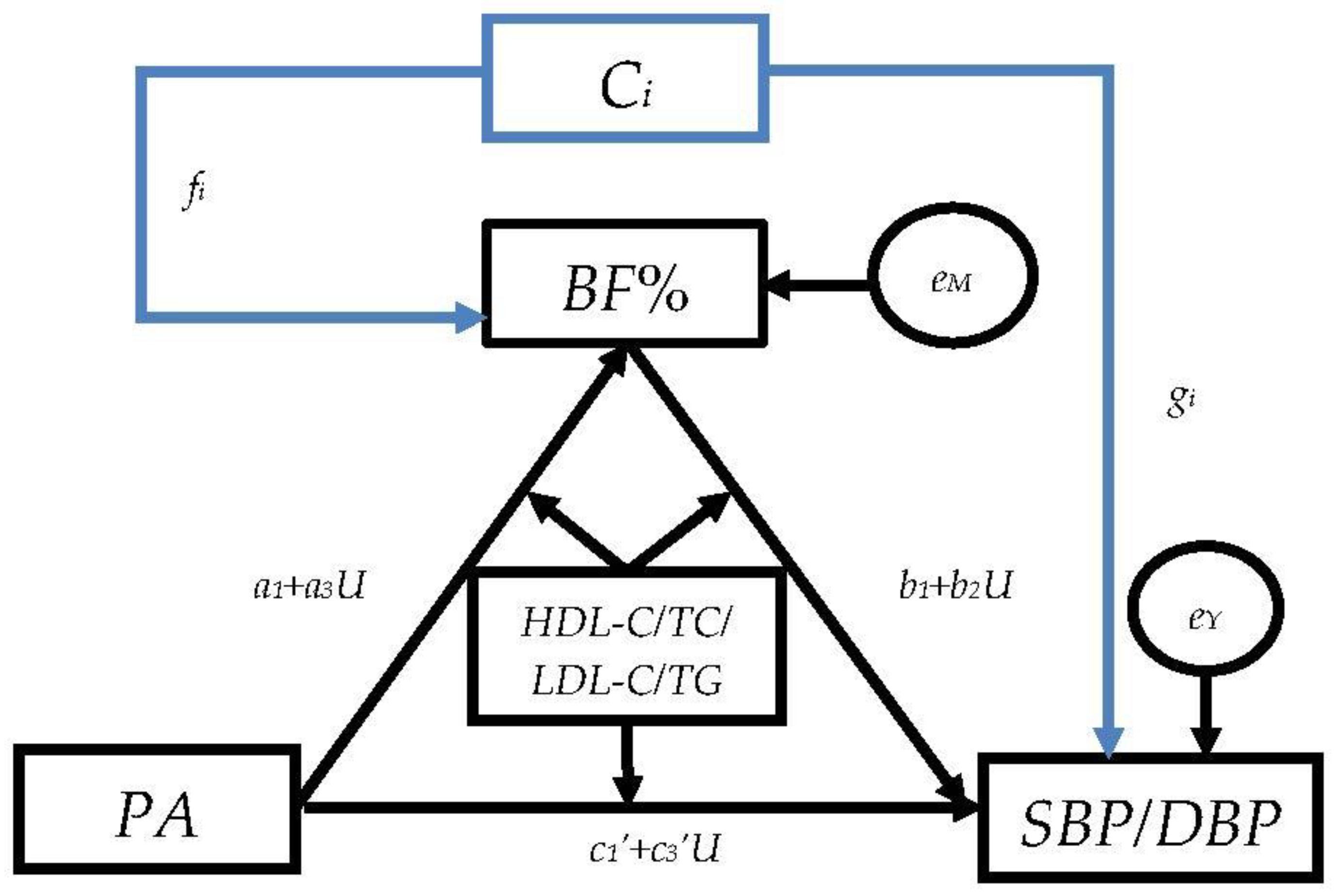
2.5.3. The Moderated Mediation Models
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Participants in 2015
3.2. The Simple Mediation Models
3.3. The Serial Two Mediator Models
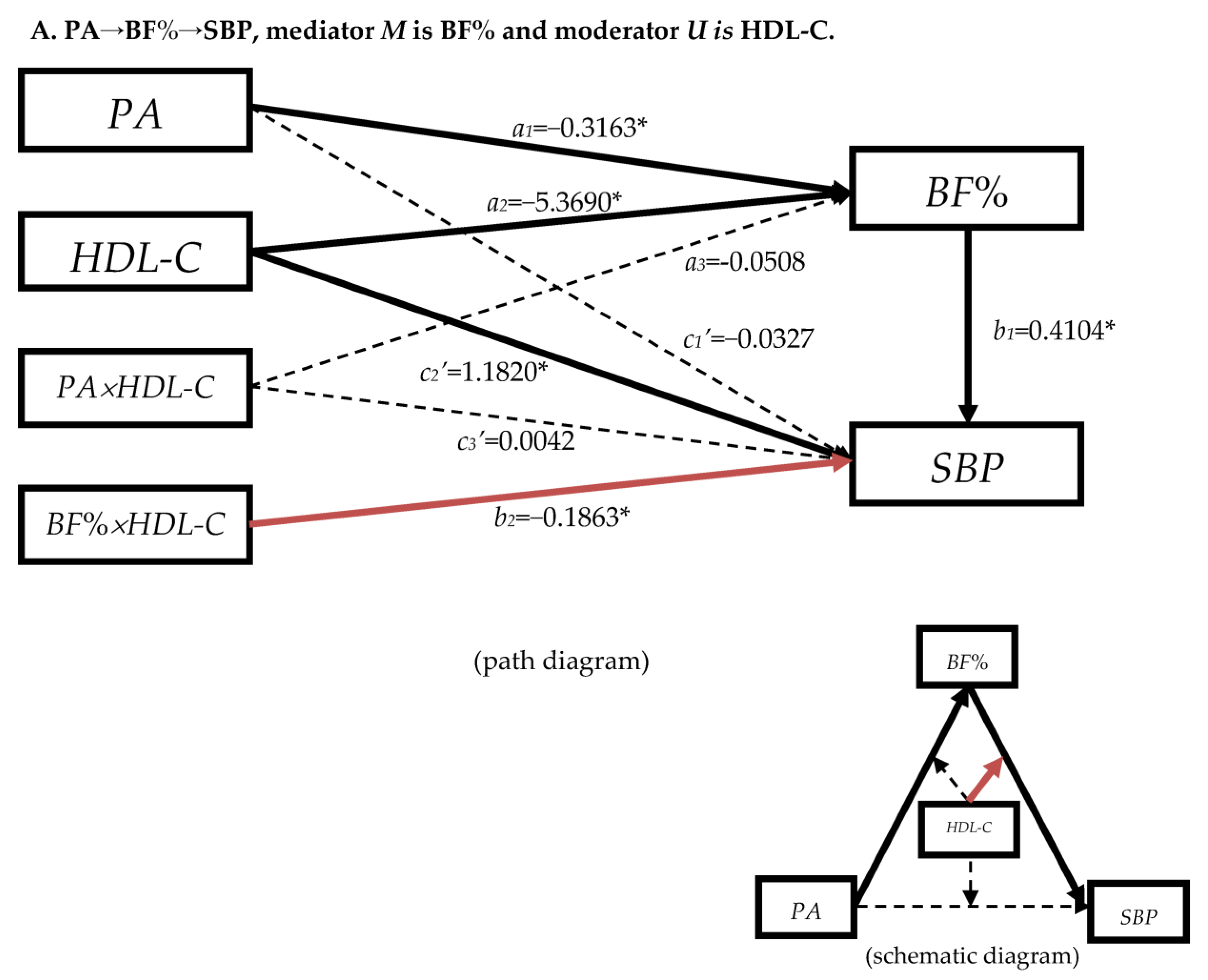
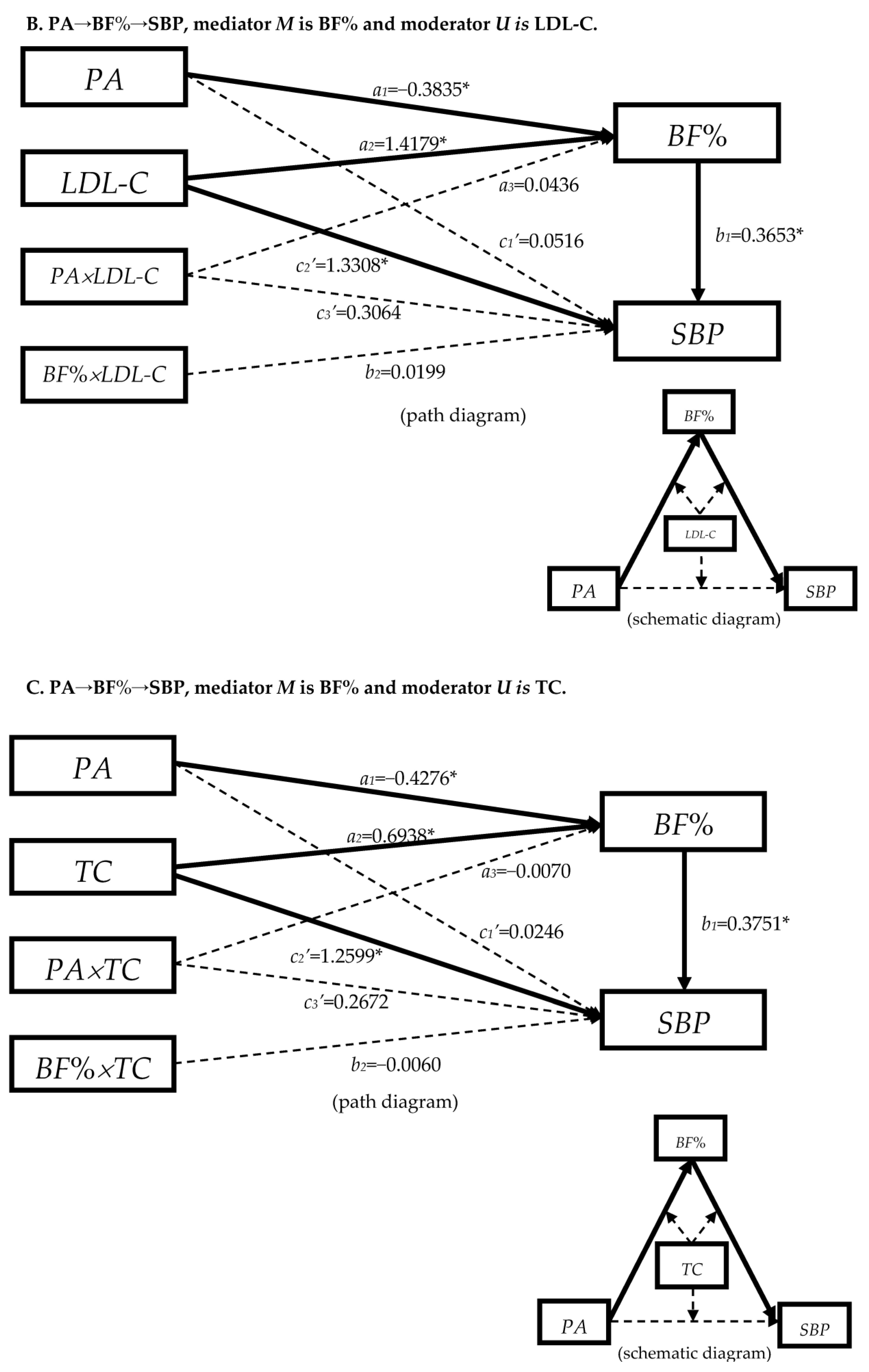
3.4. The Moderated Mediation Models
3.4.1. The Moderation Effect of Blood Lipids in Mediation Model “PA→BF%→SBP”
3.4.2. The Moderation Effect of Blood Lipids in Mediation Model “PA→BF%→DBP”
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


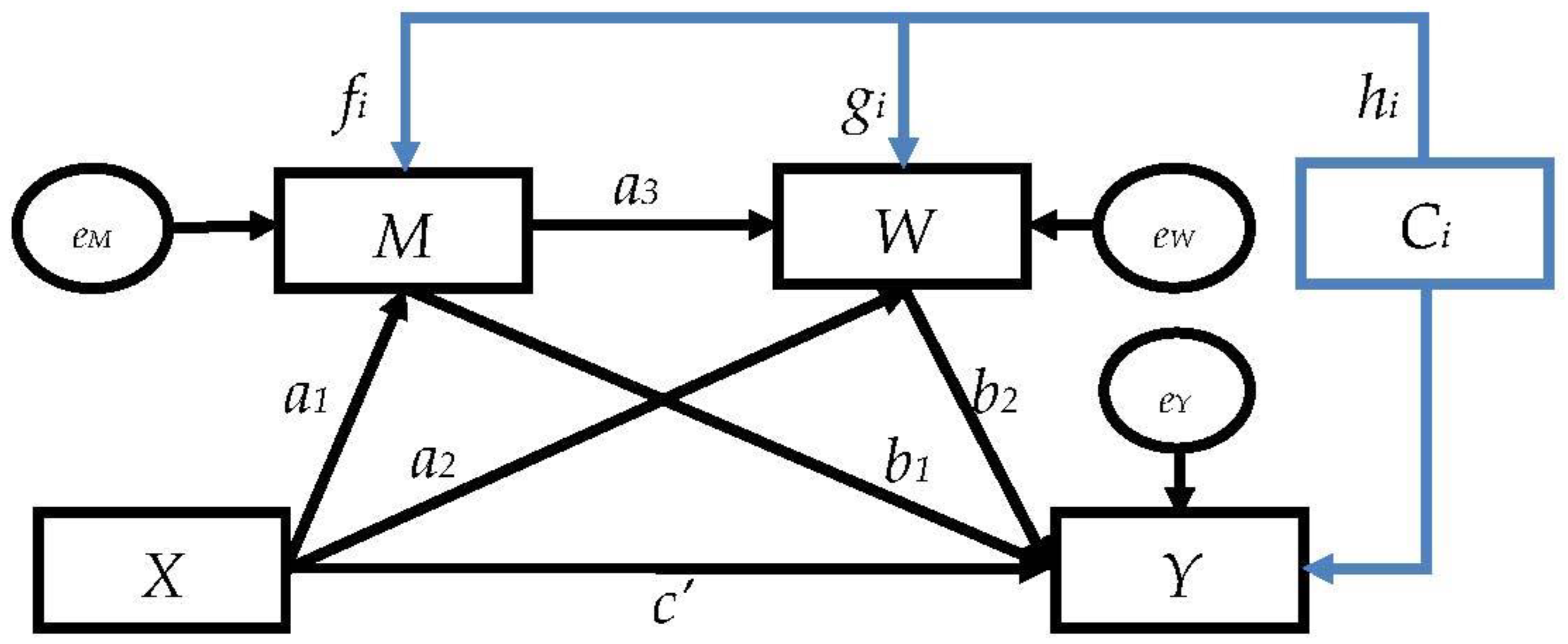
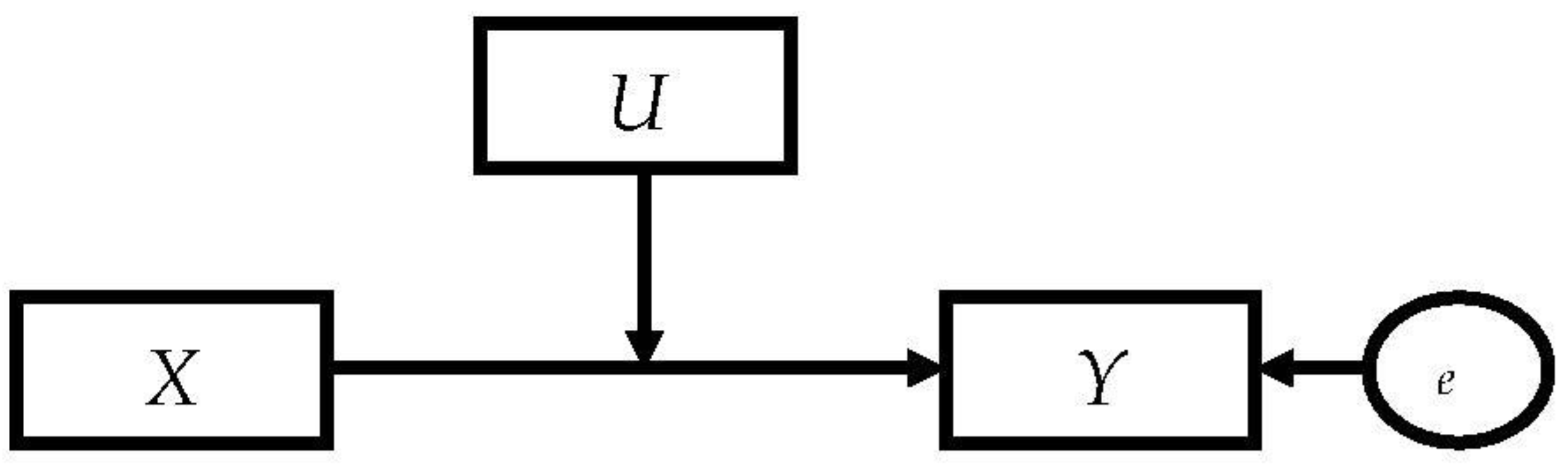
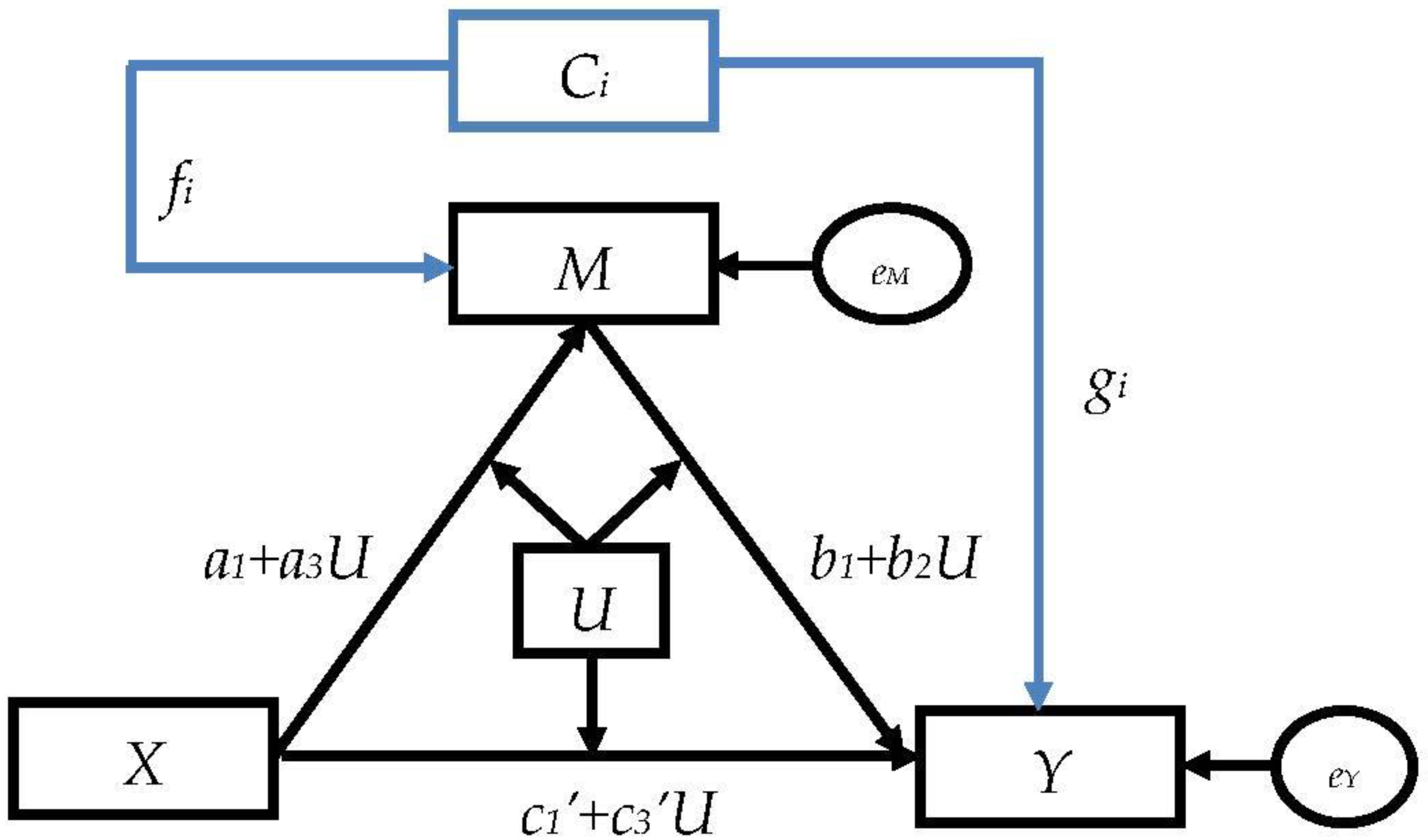

Appendix B
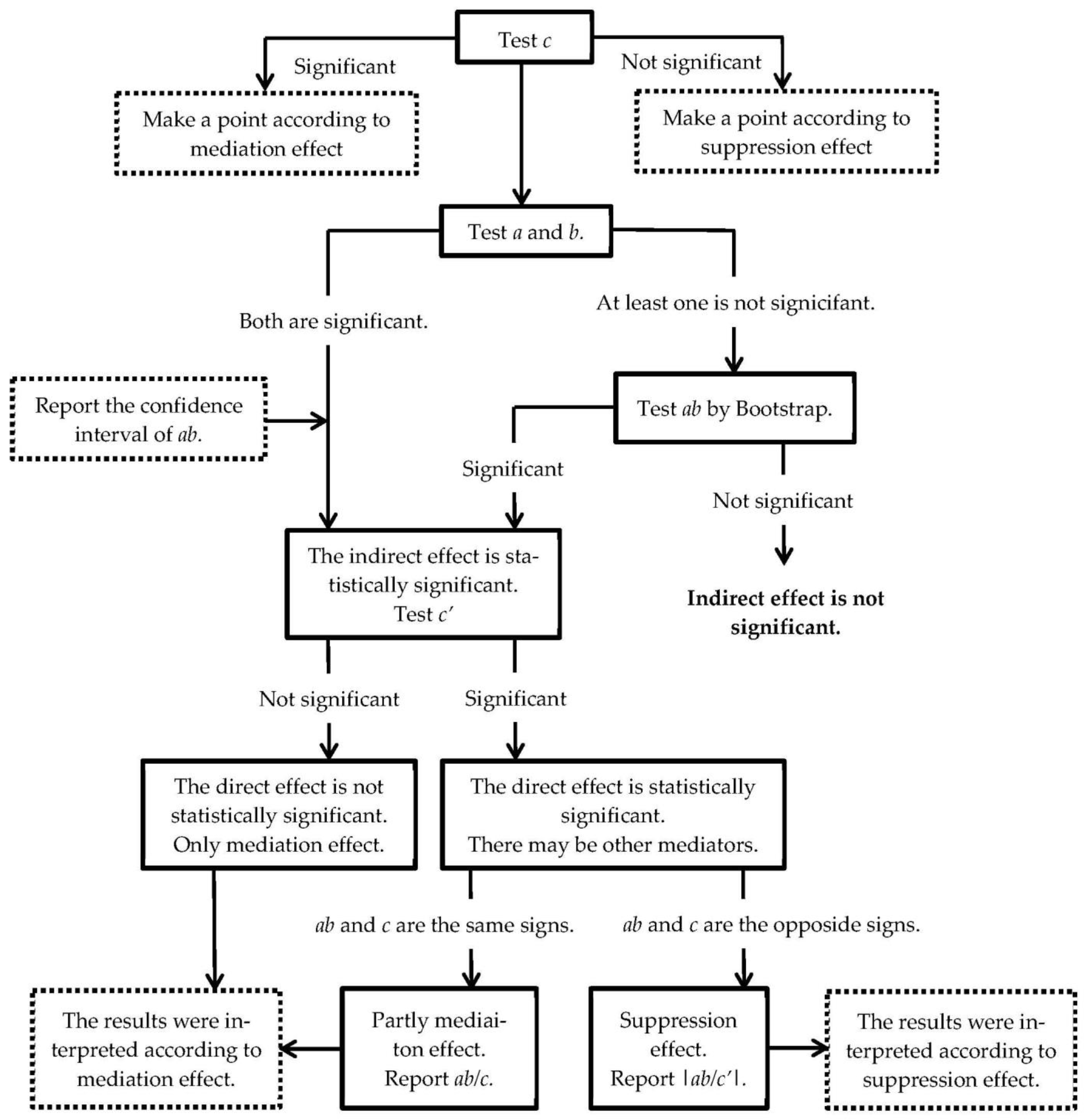
Appendix C
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Tang, W.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Xu, R.H.; Wang, T.D.; Huang, X.B. The prevalence of obesity-related hypertension among middle-aged and older adults in China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 865870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension in Adults. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240050969 (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, L.; Tian, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. Status of Hypertension in China: Results from the China Hypertension Survey, 2012–2015. Circulation 2018, 137, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on Chinese Nutrition and Chronic Diseases (2020); National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.K.; Man, Q.Q.; Li, H.; Pang, S.J.; Jia, S.S.; Li, Y.Q.; He, L.; Zhao, W.H.; Zhang, J. Trends in Lipids Level and Dyslipidemia among Chinese Adults, 2002–2015. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhang, B. The association between physical activity and body fat percentage with adjustment for body mass index among middle-aged adults: China health and nutrition survey in 2015. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariri, A.A.; Oliver, N.S.; Johnston, D.G.; Stevenson, J.C.; Godsland, I.F. Adiposity measurements by BMI, skinfolds and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in relation to risk markers for cardiovascular disease and diabetes in adult males. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, U.; Blaschke, K.; Turan, S.; Distler, A.; Sharma, A.M. Relationship between angiotensinogen, leptin and blood pressure levels in young normotensive men. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Ma, R.; Ma, D.; Ma, J. Mediating effect of blood lipids on correlation between body fat and blood pressure among overweight adults. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2015, 36, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Sato, S.; Koyamatsu, J.; Yamanashi, H.; Nagayoshi, M.; Kadota, K.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Maeda, T. Association between high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and hypertension in relation to circulating CD34-positive cell levels. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2017, 36, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgyi, E.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Lyytikainen, A.; Suominen, H.; Alen, M.; Cheng, S. Assessing body composition with DXA and bioimpedance: Effects of obesity, physical activity, and age. Obesity 2008, 16, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Society of Nutrition. Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 32–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.S. Body fatness charts based on BMI and waist circumference. Obesity 2016, 24, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calling, S.; Hedblad, B.; Engstrom, G.; Berglund, G.; Janzon, L. Effects of body fatness and physical activity on cardiovascular risk: Risk prediction using the bioelectrical impedance method. Scand. J. Public Health 2006, 34, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques-Vidal, P.; Bochud, M.; Mooser, V.; Paccaud, F.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P. Obesity markers and estimated 10-year fatal cardiovascular risk in Switzerland. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmann, P.H.; Lissner, L.; Gullberg, B.; Berglund, G.r. A Prospective Study of Adiposity and All-Cause Mortality—The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Obes. Rev. 2002, 5, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Silva, C.; Galofré, J.C.; Escalada, J.; Santos, S.; Millán, D.; Vila, N.; Ibañez, P.; Gil, M.J.; Valentí, V.; et al. Body mass index classification misses subjects with increased cardiometabolic risk factors related to elevated adiposity. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 36, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Graubard, B.I. Estimates of excess deaths associated with body mass index and other anthropometric variables. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.; Leslie, W.D.; Lix, L.M.; Majumdar, S.R. Relationship among Body Fat Percentage, Body Mass Index, and All-Cause Mortality: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Loerbroks, A.; Angerer, P. Physical activity and risk of cardiovascular disease: What does the new epidemiological evidence show? Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2013, 28, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Bennett, D.; Li, L.; Whitlock, G.; Guo, Y.; Collins, R.; Chen, J.; Bian, Z.; Hong, L.-S.; Feng, S.; et al. Physical activity and sedentary leisure time and their associations with BMI, waist circumference, and percentage body fat in 0.5 million adults: The China Kadoorie Biobank study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, K.E.; Guo, W.; Cairns, B.J.; Armstrong, M.E.; Key, T.J. Association between physical activity and body fat percentage, with adjustment for BMI: A large cross-sectional analysis of UK Biobank. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e011843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Li, J.X.; Cao, J.; Hu, D.S.; Shen, C.; Lu, X.F.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.D.; Yang, X.L.; et al. The relationship between physical activity and incident hypertension in rural Chinese. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 52, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprinzi, P.D. Accelerometer-determined physical activity and all-cause mortality in a national prospective cohort study of hypertensive adults. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Wildman, R.P.; Wu, X.; Reynolds, K.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.-S.; He, J. Incidence and predictors of hypertension over 8 years among Chinese men and women. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.T. A cohort study of incident hypertension in relation to changes in vigorous physical activity in men and women. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.A.; Du, H.; Clarke, R.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Millwood, I.; Yu, C.; He, P.; et al. Association of Physical Activity with Risk of Major Cardiovascular Diseases in Chinese Men and Women. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, K.M.; Booth, J.N., 3rd; Seals, S.R.; Abdalla, M.; Dubbert, P.M.; Sims, M.; Ladapo, J.A.; Redmond, N.; Muntner, P.; Shimbo, D. Physical Activity and Incident Hypertension in African Americans: The Jackson Heart Study. Hypertension 2017, 69, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, Y.; Jellinger, P.S.; Guerin, C.K.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Brinton, E.A.; Budoff, M.J.; Davidson, M.H.; Einhorn, D.; Fazio, S.; Fonseca, V.A.; et al. Consensus Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the Management of Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Algorithm—2020 Executive Summary. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 1196–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/physical-activity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Zou, Q.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhang, B. Longitudinal association between physical activity and blood pressure, risk of hypertension among Chinese adults: China Health and Nutrition Survey 1991–2015. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.P.B.; Veenbrink, A.I.; de Mutsert, R.; Visser, A.W.; van Dijk, K.W.; le Cessie, S.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Kloppenburg, M. The role of leptin and adiponectin as mediators in the relationship between adiposity and hand and knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, E.-Y.; Park, Y. Mediating effect of waist:height ratio on the association between BMI and frailty: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 124, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, E.M.; Mroczek, D.K.; Christ, S.L. Multimorbidity, inflammation, and disability: A longitudinal mediational analysis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Fan, S.Y.; Guan, J.Q.; Song, W.J.; Obore, N.; Chen, W.Q.; Zhi, H.; Wang, L.N. Mediation analysis for the relationship between dyslipidemia and coronary artery disease via hypersensitive C-reactive protein in a case-control study. Coron. Artery Dis. 2020, 31, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989–2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S1), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.W.; Howard, A.G.; Wang, H.J.; Su, C.; Zhang, B. The physical activity transition among adults in China: 1991–2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S1), 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of Physical Activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Off. J. Am. Coll. Sport. Med. 2000, 32, S498–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Herrmann, S.D.; Meckes, N.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Greer, J.L.; Vezina, J.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Leon, A.S. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.J. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A Second Update of Codes and MET Values. Yearb. Sport. Med. 2012, 2012, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motadi, S.A.; Veldsman, T.; Mohlala, M.; Mabapa, N.S. Overweight and Obesity among Adults Aged 18–45 Years Residing in and around Giyani Town in Mopani District of Limpopo Province, South Africa. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2018, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.; Reddy, R.P.L. Effect of Lifestyle on Body Fat Percentage and Visceral Fat in Indian Women with Above Normal Body Mass Index. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2017, 9, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis—A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Analyses of Mediating Effects: The Development of Methods and Models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 22, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Xiaofang, J.; Zhihong, W.; Huijun, W.; Bing, Z. Study on the relationships between dietary cholesterol and serum cholesterol among Chinese adults. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuicui, S.; Xin, Z. Research progress of adipokines and cardiovascular diseases. Chin. Circ. J. 2014, 29, 858–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, C.; Dai, Z.; He, T. The visceral adipose index in relation to incidence of hypertension in Chinese adults: China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Nutrients 2020, 12, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, F. The effects of body mass index and its dynamic shift on hypertension in Chinese adults. Chin. J. Hypertens. 2010, 18, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Barengo, N.C.; Tuomilehto, J.; Lakka, T.A.; Nissinen, A.; Jousilahti, P. Relationship of physical activity and body mass index to the risk of hypertension: A prospective study in Finland. Hypertension 2004, 43, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenehjem, J.S.; Hjerkind, K.V.; Nilsen, T.I.L. Adiposity, physical activity, and risk of hypertension: Prospective data from the population-based HUNT Study, Norway. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.; Herber-Gast, G.C.; Brown, W. Joint effects of physical activity and BMI on risk of hypertension in women: A longitudinal study. J. Obes. 2014, 2014, 271532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, D.; Chen, J. Association between obesity indices and blood pressure or hypertension: Which index is the best? Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, U.; Schram, M.T.; Houben, A.J.; Muris, D.M.; Stehouwer, C.D. Microvascular dysfunction as a link between obesity, insulin resistance and hypertension. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Bedi, U.S.; Singh, P.P.; Arora, R.; Khosla, S. Leptin and the clinical cardiovascular risk. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 140, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneckova, I.; Maletinska, L.; Behuliak, M.; Nagelova, V.; Zicha, J.; Kunes, J. Obesity-related hypertension: Possible pathophysiological mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, R63–R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J. Relationship between hypertension and dyslipidemia in physical examination population. China Foreign Med. Treat. 2019, 27, 187–189. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Tsujiguchi, H.; Kambayashi, Y.; Hara, A.; Miyagi, S.; Yamada, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hori, D.; Nakamura, H. Relationship between saturated fatty acid intake and hypertension and oxidative stress. Nutrition 2019, 61, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yide, Y.; Yiting, Y.; Lianguo, F.; Shuo, W.; Renhuai, C.; Xiaoling, W.; Zhenghe, W.; Dongmei, M.; Rui, M.; Zhiyong, Z.; et al. Mediating effect of insulin related indices on the association between body fat with blood pressure among overweight adults. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 50, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Wen, Z. A Discussion on Testing Methods for Mediated Moderation Models:Discrimination and Integration. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2013, 45, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
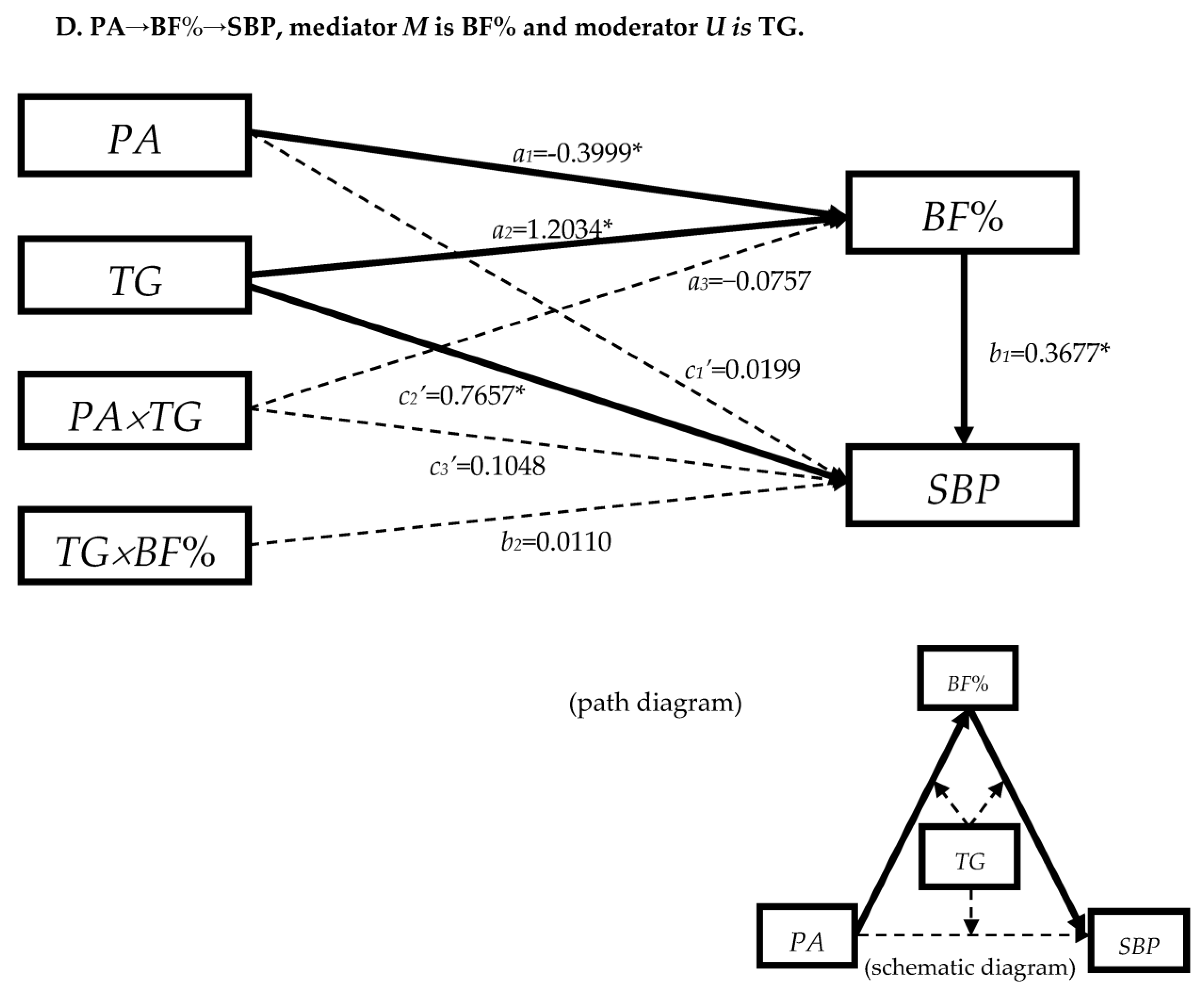
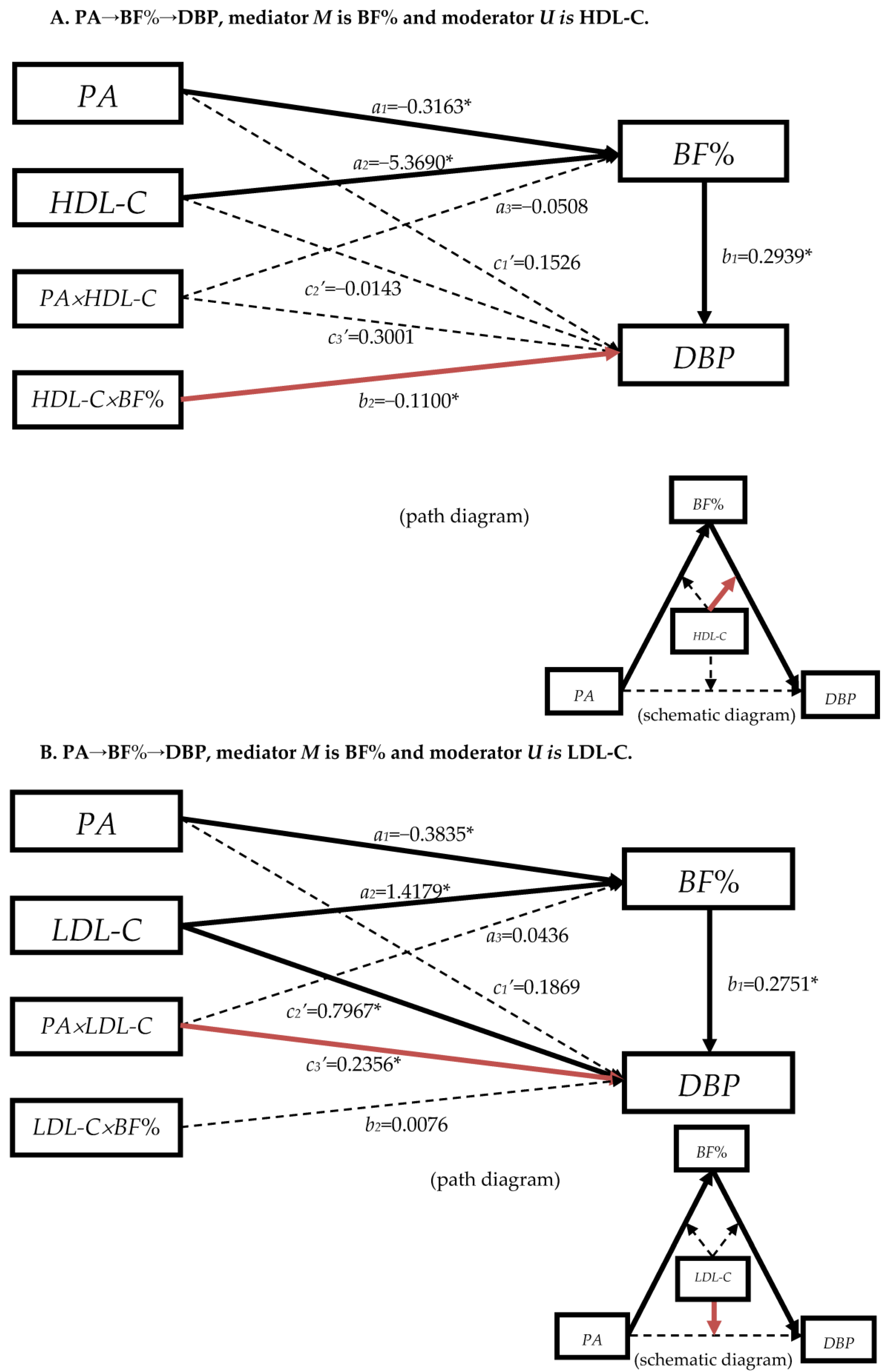
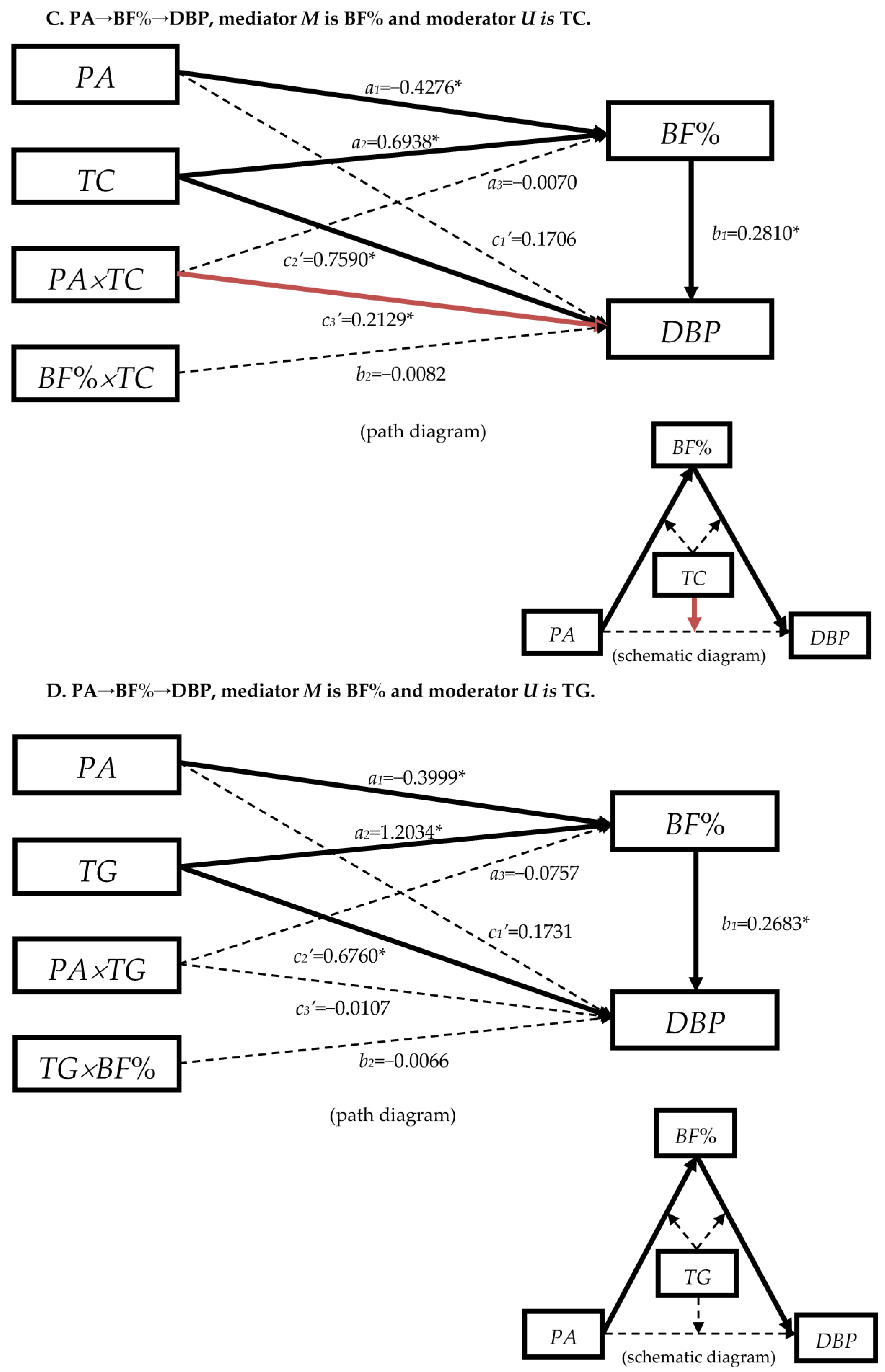
| Characteristics | Male (n = 4647) | Female (n = 5501) | Total (n = 10,148) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old) | 50.95 (40.70, 61.16) | 50.08 (39.82, 60.38) | 50.57 (40.19, 60.73) |
| Education (%) | |||
| High school and above (%) | 1841 (39.62) | 1826 (33.19) | 3667 (36.14) |
| Junior school (%) | 1628 (35.03) | 1697 (30.85) | 3325 (32.77) |
| Primary school and illiteracy (%) | 1178 (25.35) | 1978 (35.96) | 3156 (31.10) |
| Married (%) | 4177 (89.89) | 4825 (87.71) | 9002 (88.71) |
| Annual per capita household income (/1000 yuan) | 16.5 (7.5, 28.9) | 15.7 (6.9, 28.2) | 16.1 (7.2, 28.6) |
| Current smoker (%) | 2355 (50.68) | 87 (1.58) | 2442 (24.06) |
| Alcohol drinker (%) | 2544 (54.74) | 363 (6.60) | 2907 (28.65) |
| PA (MET·h/week) | 110.00 (33.40, 217.58) | 107.45 (48.30, 202.20) | 108.27 (42.48, 209.92) |
| Sedentary activity time (h/week) | 17.50 (11.50, 30.00) | 15.50 (9.33, 28.00) | 16.00 (10.50, 28.00) |
| Energy intake (1000 kcal/day) | 2.14 (1.71, 2.66) | 1.77 (1.42, 2.21) | 1.93 (1.53, 2.43) |
| Energy from dietary fat (%) | 35.24 (27.25, 43.54) | 35.43 (27.61, 43.54) | 35.34 (27.43, 43.54) |
| Dietary cholesterol (mg/d) | 226.44 (112.75, 374.03) | 194.61 (92.76, 324.46) | 207.21 (101.48, 346.50) |
| Dietary sodium-to-potassium ratio | 2.71 (1.78, 3.98) | 2.65 (1.73, 3.96) | 2.67 (1.75, 3.97) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.88 (21.57, 26.35) | 23.49 (21.32, 25.90) | 23.67 (21.41, 26.12) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 86.00 (79.00, 93.00) | 81.00 (74.00, 88.00) | 83.20 (76.00, 90.40) |
| BF% (%) | 22.60 (18.10, 26.50) | 33.40 (28.70, 37.80) | 28.00 (22.10, 34.60) |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 125.33 (116.67, 137.33) | 120.00 (110.00, 132.00) | 122.00 (112.33, 134.67) |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 80.67 (76.00, 88.66) | 78.67 (71.00, 83.33) | 80.00 (72.67, 86.00) |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.18 (0.99, 1.41) | 1.30 (1.10, 1.52) | 1.25 (1.05, 1.48) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.06 (2.51, 3.63) | 2.99 (2.43, 3.60) | 3.02 (2.47, 3.62) |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.26 (0.85, 1.98) | 1.11 (0.77, 1.64) | 1.18 (0.80, 1.78) |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.80 (4.19, 5.44) | 4.85 (4.20, 5.50) | 4.83 (4.20, 5.48) |
| Dependent Variable | Direct Effect c′ | Indirect Effect ab | Total Effect c = ab + c′ | ab/c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | 0.0556 (−0.2208, 0.3321) | −0.1491 (−0.2030, −0.0991) * | −0.0935 (−0.3736, 0.1865) | - |
| DBP | 0.2328 (0.0546, 0.4109) * | −0.1120 (−0.1508, −0.0754) * | 0.1208 (−0.0606, 0.3022) | 0.48 # |
| HDL-C | 0.0177 (0.0117, 0.0238) * | 0.0052 (0.0036, 0.0069) * | 0.0229 (0.0167, 0.0292) * | 0.23 |
| LDL-C | −0.0287 (−0.0451, −0.0124) * | −0.0097 (−0.0130, −0.0067) * | −0.0384 (−0.0550, −0.0219) * | 0.25 |
| TC | −0.0117 (−0.0312, 0.0077) | −0.0067 (−0.0092, −0.0043) * | −0.0184 (−0.0380, 0.0011) | - |
| TG | −0.0167 (−0.0387, 0.0053) | −0.0151 (−0.0201, −0.0103) * | −0.0317 (−0.0542, −0.0093) * | - |
| Y | W | Total Effect | Direct Effect c′ | Mediation Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1b1 + a2b2 + a1a3b2 | Path 1 (a1b1) | Path 2 (a2b2) | Path 3 (a1a3b2) | ||||
| SBP | HDL-C | −0.1700 (−0.4698, 0.1298) | −0.0225 (−0.3188, 0.2738) | −0.1475 (−0.2068, −0.0887) * | −0.1798 (−0.2398, −0.1206) * | 0.0250 (0.0065, 0.0480) * | 0.0073 (0.0019, 0.0140) * |
| SBP | LDL-C | −0.1684 (−0.4681, 0.1313) | 0.0422 (−0.2530, 0.3373) | −0.2105 (−0.2729, −0.1519) * | −0.1598 (−0.2142, −0.1085) * | −0.0380 (−0.0638, −0.0155) * | −0.0127 (−0.0189, −0.0078) * |
| SBP | TC | −0.1665 (−0.4662, 0.1332) | 0.0211 (−0.2738, 0.3160) | −0.1876 (−0.2516, −0.1262) * | −0.1652 (−0.2203, −0.1124) * | −0.0143 (−0.0393, 0.0102) | −0.0081 (−0.0122, −0.0049) * |
| SBP | TG | −0.1652 (−0.4649, 0.1346) | 0.0191 (−0.2763, 0.3145) | −0.1843 (−0.2456, −0.1270) * | −0.1603 (−0.2149, −0.1085) * | −0.0125 (−0.0315, 0.0046) | −0.0114 (−0.0174, −0.0066) * |
| DBP | HDL-C | 0.0328 (−0.1617, 0.2272) | 0.1586 (−0.0327, 0.3499) | −0.1258 (−0.1699, −0.0837) * | −0.1288 (−0.1717, −0.0881) * | 0.0023 (−0.0096, 0.0146) | 0.0007 (−0.0029, 0.0043) |
| DBP | LDL-C | 0.0301 (−0.1643, 0.2244) | 0.1808 (−0.0098, 0.3714) | −0.1507 (−0.1960, −0.1083) * | −0.1206 (−0.1599, −0.0835) * | −0.0226 (−0.0381, −0.0090) * | −0.0076 (−0.0114, −0.0046) * |
| DBP | TC | 0.0313 (−0.1631, 0.2257) | 0.1686 (−0.0218, 0.3589) | −0.1373 (−0.1817, −0.0945) * | −0.1239 (−0.1650, −0.0855) * | −0.0085 (−0.0236, 0.0063) | −0.0048 (−0.0073, −0.0028) * |
| DBP | TG | 0.0348 (−0.1596, 0.2291) | 0.1737 (−0.0166, 0.3640) | −0.1389 (−0.1856, −0.0962) * | −0.1177 (−0.1585, −0.0800) * | −0.0111 (−0.0275, 0.0040) | −0.0101 (−0.0150, −0.0063) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Q.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Luo, S.; Tan, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; et al. The Mediation and Moderation Effect Association among Physical Activity, Body-Fat Percentage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipids among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143113
Zou Q, Su C, Du W, Ouyang Y, Wang H, Zhang B, Luo S, Tan T, Chen Y, Zhong X, et al. The Mediation and Moderation Effect Association among Physical Activity, Body-Fat Percentage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipids among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143113
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Qinpei, Chang Su, Wenwen Du, Yifei Ouyang, Huijun Wang, Bing Zhang, Shuquan Luo, Tao Tan, Yaokai Chen, Xiaoni Zhong, and et al. 2023. "The Mediation and Moderation Effect Association among Physical Activity, Body-Fat Percentage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipids among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143113
APA StyleZou, Q., Su, C., Du, W., Ouyang, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, B., Luo, S., Tan, T., Chen, Y., Zhong, X., & Zhang, H. (2023). The Mediation and Moderation Effect Association among Physical Activity, Body-Fat Percentage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Lipids among Chinese Adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015. Nutrients, 15(14), 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143113






