Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients—A Merged Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assessment of Nutritional Status and Food Intake
2.2. Geriatric Assessment
2.3. Assessment of C-Reactive Protein
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
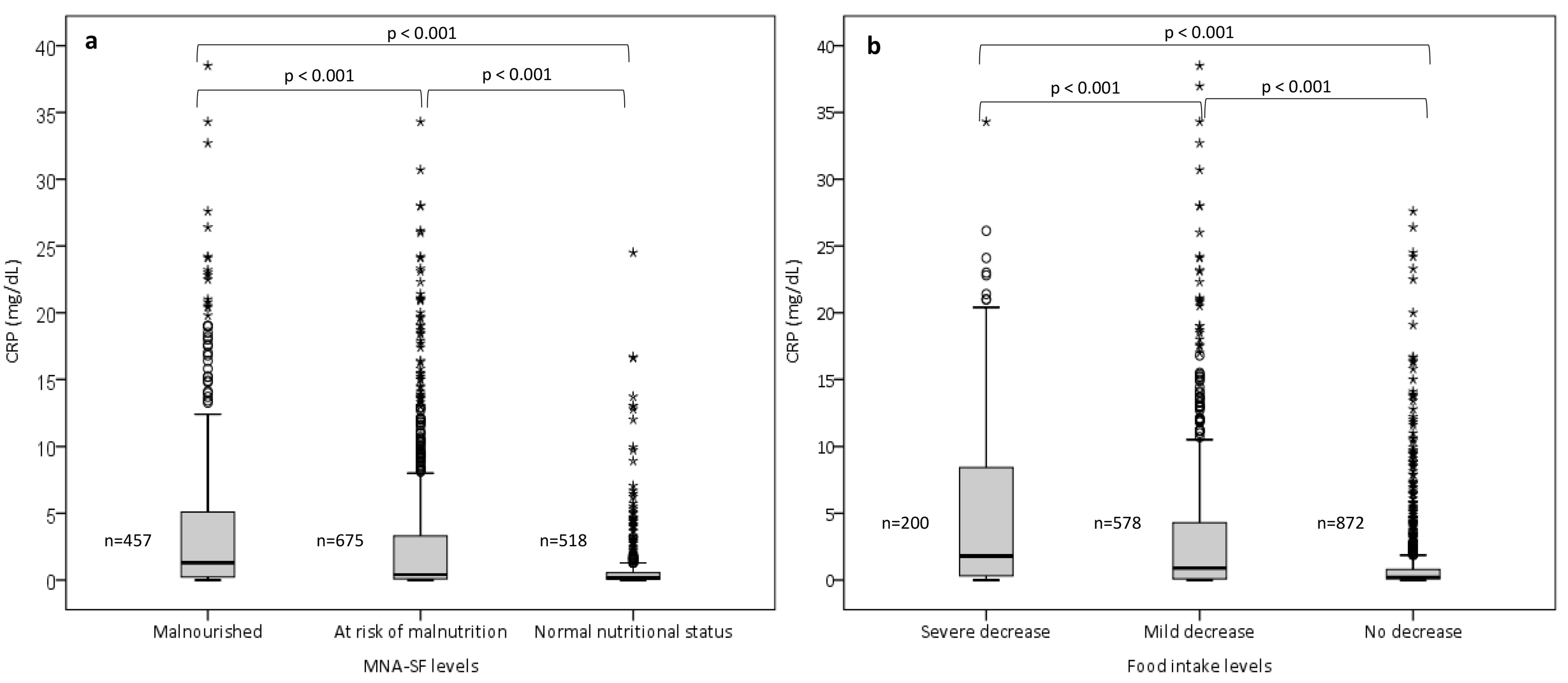
3.2. Comparison of CRP Concentrations across the MNA-SF and Food Intake Levels
3.3. Relationship between Inflammation and Food Intake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, T.; Haboubi, N. Assessment and management of nutrition in older people and its importance to health. Clin. Interv. Aging 2010, 5, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cereda, E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; de Groot, L.; Grosshauser, F.; Kiesswetter, E.; Norman, K.; et al. Management of Malnutrition in Older Patients-Current Approaches, Evidence and Open Questions. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer-Borst, S.; Hercberg, S.; Morabia, A.; Bernstein, M.S.; Galan, P.; Galasso, R.; Giampaoli, S.; McCrum, E.; Panico, S.; Preziosi, P.; et al. Dietary patterns in six european populations: Results from EURALIM, a collaborative European data harmonization and information campaign. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leij-Halfwerk, S.; Verwijs, M.H.; van Houdt, S.; Borkent, J.W.; Guaitoli, P.R.; Pelgrim, T.; Heymans, M.W.; Power, L.; Visser, M.; Corish, C.A.; et al. Prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition risk in European older adults in community, residential and hospital settings, according to 22 malnutrition screening tools validated for use in adults ≥65 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2019, 126, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, D.; Kiesswetter, E.; Cederholm, T.; Donini, L.M.; Eglseer, D.; Norman, K.; Schneider, S.M.; Strobele-Benschop, N.; Torbahn, G.; Wirth, R.; et al. Development of a Model on Determinants of Malnutrition in Aged Persons: A MaNuEL Project. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 5, 2333721419858438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.M.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; Sisto, A.; Marzetti, E. Anorexia of Aging: Risk Factors, Consequences, and Potential Treatments. Nutrients 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E. Anorexia of Aging: Assessment and Management. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 33, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Daubert, D.; Wirth, R. Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieske, L.; Janssen, G.; Babel, N.; Westhoff, T.H.; Wirth, R.; Pourhassan, M. Inflammation, Appetite and Food Intake in Older Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Muscaritoli, M.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Kubrak, C.; Laird, B.; Gagnon, B.; Chasen, M.; Gioulbasanis, I.; Wallengren, O.; Voss, A.C.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for cancer cachexia: Reduced food intake and inflammation predict weight loss and survival in an international, multi-cohort analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Bottger, S.; Janssen, G.; Sieske, L.; Wirth, R. The Association of Inflammation with Food Intake in Older Hospitalized Patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.X.; Xue, Q.L.; Tian, J.; Walston, J.D.; Fried, L.P. Inflammation and frailty in older women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Babel, N.; Sieske, L.; Westhoff, T.H.; Wirth, R. Longitudinal Changes of Cytokines and Appetite in Older Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Babel, N.; Sieske, L.; Westhoff, T.H.; Wirth, R. Inflammatory cytokines and appetite in older hospitalized patients. Appetite 2021, 166, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Davis, L.; Hurley, T.G.; Ortaglia, A.; Drayton, R.; Blair, S.N.; Hébert, J.R. Construct Validation of the Dietary Inflammatory Index among African Americans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, I.; Rzewnicki, D.; Samols, D. What does minor elevation of C-reactive protein signify? Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 166.e17–166.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyne, B.; Olshaker, J.S. The C-reactive protein11Clinical Laboratory in Emergency Medicine is coordinated by Jonathan S. Olshaker, MD, of the University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wener, M.H.; Daum, P.R.; McQuillan, G.M. The influence of age, sex, and race on the upper reference limit of serum C-reactive protein concentration. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar]
- Pourhassan, M.; Cederholm, T.; Trampisch, U.; Volkert, D.; Wirth, R. Inflammation as a diagnostic criterion in the GLIM definition of malnutrition-what CRP-threshold relates to reduced food intake in older patients with acute disease? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goisser, S.; Schrader, E.; Singler, K.; Bertsch, T.; Gefeller, O.; Biber, R.; Bail, H.J.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Malnutrition According to Mini Nutritional Assessment Is Associated With Severe Functional Impairment in Geriatric Patients Before and up to 6 Months After Hip Fracture. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goisser, S.; Schrader, E.; Singler, K.; Bertsch, T.; Gefeller, O.; Biber, R.; Bail, H.-J.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Low postoperative dietary intake is associated with worse functional course in geriatric patients up to 6 months after hip fracture. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Savina, C.; Piredda, M.; Cucinotta, D.; Fiorito, A.; Inelmen, E.M.; Sergi, G.; Domiguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Cannella, C. Senile anorexia in acute-ward and rehabilitations settings. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, L.M.; Scardella, P.; Piombo, L.; Neri, B.; Asprino, R.; Proietti, A.R.; Carcaterra, S.; Cava, E.; Cataldi, S.; Cucinotta, D.; et al. Malnutrition in elderly: Social and economic determinants. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.L.; Houlind, M.B.; Nielsen, R.L.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Treldal, C.; Damgaard, M.; Bengaard, A.K.; Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Laursen, L.B.; Iversen, E.; et al. Optimization of Nutrition And Medication (OptiNAM) for acutely admitted older patients: Protocol for a randomized single-blinded controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Ramsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Validation of the Mini Nutritional Assessment short-form (MNA®-SF): A practical tool for identification of nutritional status. JNHA-J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, J.E.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K. A simple frailty questionnaire (FRAIL) predicts outcomes in middle aged African Americans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bedirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenblut, S.; Zank, S. Entwicklung eines neuen Depressionsscreenings für den Einsatz in der Geriatrie. Z. Für Gerontol. Und Geriatr. 2010, 43, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourhassan, M.; Sieske, L.; Janssen, G.; Babel, N.; Westhoff, T.H.; Wirth, R. The impact of acute changes of inflammation on appetite and food intake among older hospitalised patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Block, G.; McAllister, C.J.; Humphreys, M.H.; Kopple, J.D. Appetite and inflammation, nutrition, anemia, and clinical outcome in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, R.; Ash, S.; King, N.; Bauer, J. The relationship between subjective appetite sensations, markers of inflammation and appetite in dialysis patients. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2009, 22, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareh, N.; Kiesswetter, E.; Kob, R.; Hannink, A.; Brandl, B.; Skurk, T.; Hauner, H.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Association Between Inflammation and Appetite in Healthy Community-Dwelling Older Adults—An enable Study. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 826816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Axelsson, J.; Avesani, C.M.; Suliman, M.E.; Kato, S.; Barany, P.; Snaedal-Jonsdottir, S.; Alvestrand, A.; Heimburger, O.; et al. Comparison of nutritional and inflammatory markers in dialysis patients with reduced appetite. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariballa, S.; Forster, S. Effects of acute-phase response on nutritional status and clinical outcome of hospitalized patients. Nutrition 2006, 22, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Sugama, S.; Brennan, M.; Fernandez, R.; Bartfai, T.; Conti, B. Interleukin-18 controls energy homeostasis by suppressing appetite and feed efficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11097–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengelé, L.; Bruyère, O.; Beaudart, C.; Reginster, J.Y.; Locquet, M. Impact of Malnutrition Status on Muscle Parameter Changes over a 5-Year Follow-Up of Community-Dwelling Older Adults from the SarcoPhAge Cohort. Nutrients 2021, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaensen, W.; Matheï, C.; Vaes, B.; van Pottelbergh, G.; Wallemacq, P.; Degryse, J.-M. Interleukin-6 predicts short-term global functional decline in the oldest old: Results from the BELFRAIL study. Age 2014, 36, 9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, S.S.Y.; Chan, R.S.M.; Kwok, T.; Lee, J.S.W.; Woo, J. Malnutrition According to GLIM Criteria and Adverse Outcomes in Community-Dwelling Chinese Older Adults: A Prospective Analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total Population (n = 1650) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female (n; %) | 1047 (63) |
| Male (n; %) | 603 (37) |
| Age (y) | 79.6 ± 7.4 |
| Height (m) | 1.60 ± 0.10 |
| Actual body weight (kg) | 70.8 ± 17.6 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 6.1 |
| MNA-SF, Median (IQR) | 10 (7–12) |
| Malnourished (n; %) | 457 (28) |
| At risk of malnutrition (n; %) | 675 (41) |
| Normal nutritional status (n; %) | 518 (31) |
| MNA-SF, reduction in food intake | |
| Severe decrease in food intake (n; %) | 200 (12) |
| Moderate decrease in food intake (n; %) | 578 (35) |
| No decrease in food intake (n; %) | 872 (53) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 2.6 ± 5.3 |
| No inflammation (0.0–0.49 (mg/dL), n; %) | 881 (53) |
| Mild inflammation (0.5–3.0 (mg/dL), n; %) | 393 (24) |
| Moderate to severe inflammation (≥3.0 (mg/dL), n; %) | 376 (23) |
| Severe Decrease in Food Intake | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | t | p Value | |
| CRP levels (<3 and ≥3 mg/dL) | −0.172 | 0.021 | −0.229 | −8.217 | <0.000 |
| Age | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.031 | −1.123 | 0.262 |
| Gender | −0.045 | 0.017 | −0.073 | −2.693 | 0.007 |
| CCI | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.041 | 1.506 | 0.511 |
| Moderate and severe decrease in food intake | |||||
| CRP levels (<3 and ≥3 mg/dL) | −0.359 | 0.034 | −0.287 | −10.674 | <0.000 |
| Age | −0.005 | 0.002 | −0.072 | −2.709 | 0.007 |
| Gender | −0.198 | 0.027 | −0.194 | −7.452 | <0.000 |
| CCI | 0.013 | 0.007 | −0.051 | −1.954 | 0.053 |
| Malnutrition | |||||
| CRP levels (<3 and ≥3 mg/dL) | −0.222 | 0.029 | −0.212 | −7.730 | <0.000 |
| Age | −0.009 | 0.002 | −0.164 | −4.993 | <0.000 |
| Gender | −0.055 | 0.023 | −0.065 | −2.442 | 0.015 |
| CCI | −0.015 | 0.006 | −0.067 | −2.507 | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pourhassan, M.; Cederholm, T.; Donini, L.M.; Poggiogalle, E.; Schwab, U.; Nielsen, R.L.; Andersen, A.L.; Małgorzewicz, S.; Volkert, D.; Wirth, R. Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients—A Merged Data Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143079
Pourhassan M, Cederholm T, Donini LM, Poggiogalle E, Schwab U, Nielsen RL, Andersen AL, Małgorzewicz S, Volkert D, Wirth R. Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients—A Merged Data Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143079
Chicago/Turabian StylePourhassan, Maryam, Tommy Cederholm, Lorenzo M. Donini, Eleonora Poggiogalle, Ursula Schwab, Rikke Lundsgaard Nielsen, Aino Leegaard Andersen, Sylwia Małgorzewicz, Dorothee Volkert, and Rainer Wirth. 2023. "Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients—A Merged Data Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143079
APA StylePourhassan, M., Cederholm, T., Donini, L. M., Poggiogalle, E., Schwab, U., Nielsen, R. L., Andersen, A. L., Małgorzewicz, S., Volkert, D., & Wirth, R. (2023). Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients—A Merged Data Analysis. Nutrients, 15(14), 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143079










