Alcohol Dependence Modulates Amygdalar mTORC2 and PKCε Expression in a Rodent Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animal Preparation
2.3. Preliminary Study
2.4. Experimental Groups
2.5. Modified Liquid Diet (MLD)
2.6. RNA Extraction and qPCR Analysis
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
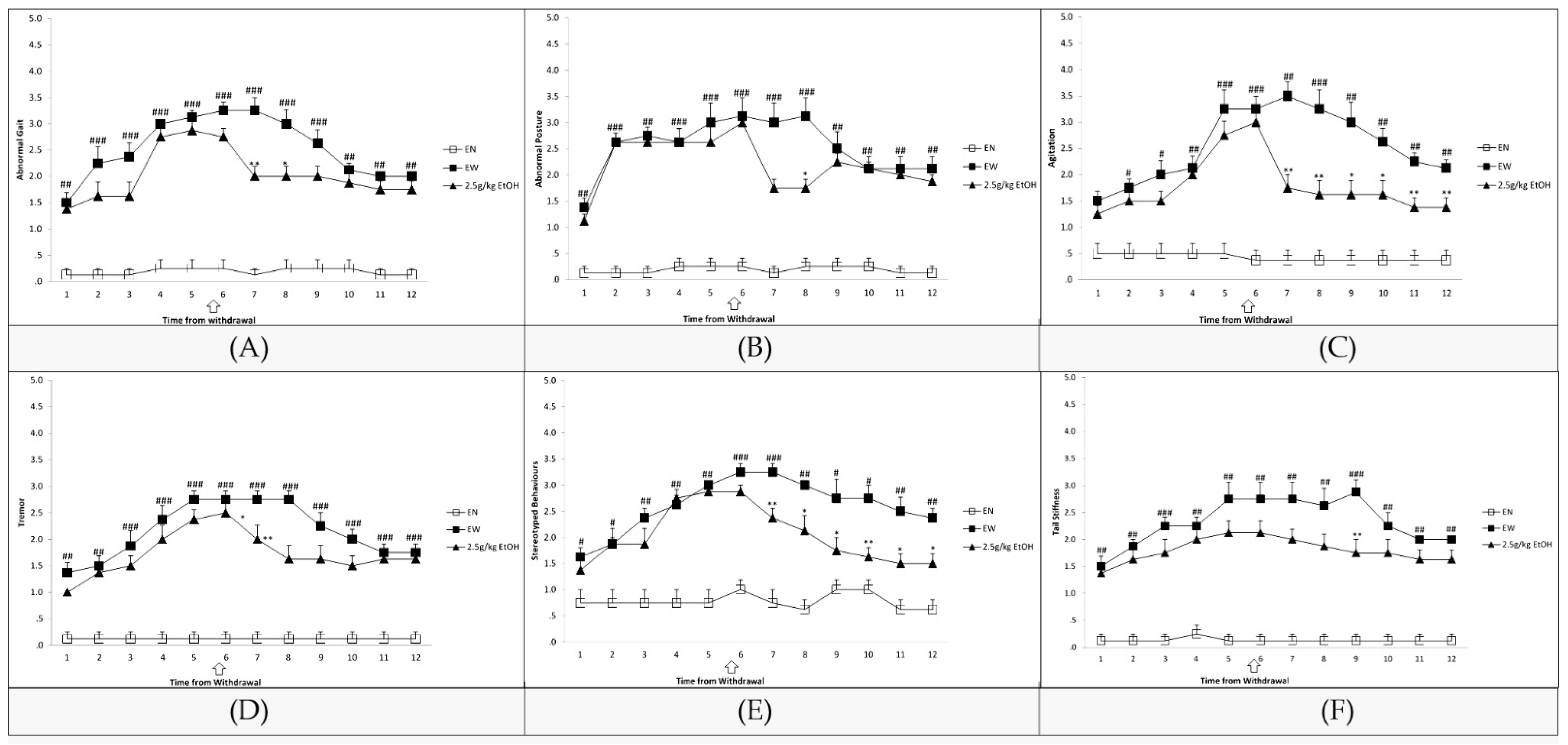
3.1. Assessment of EW Symptoms
3.2. Body Weight Changes
3.3. Daily MLD Intake
3.4. Daily Intake of Ethanol
3.5. Serum Ethanol Concentration
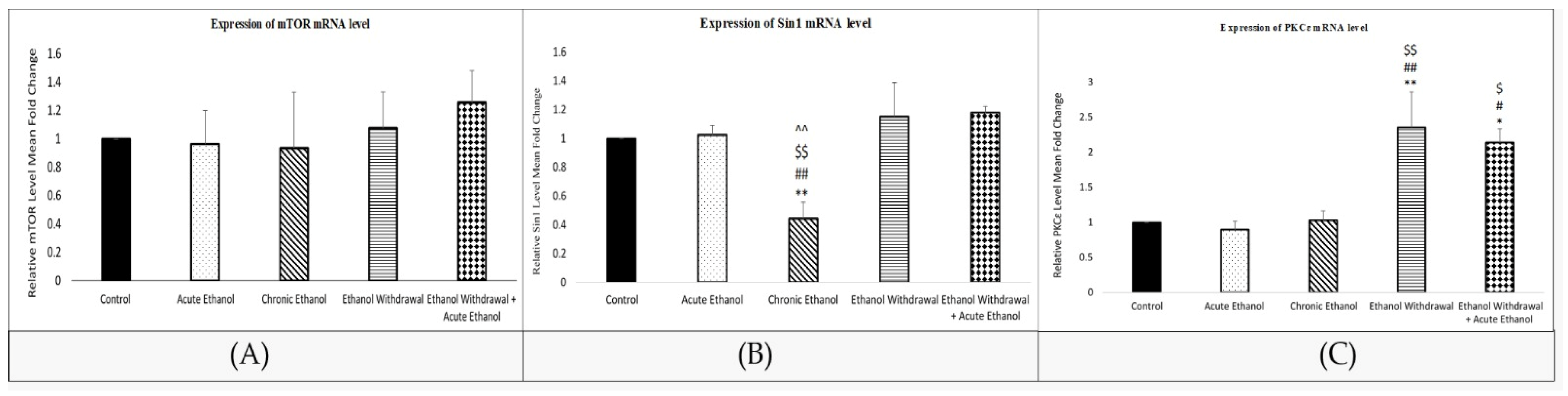
3.6. Mean Relative mRNA Level in the Rats’ Amygdalae
3.7. Mean Relative Protein Level in the Rats’ Amygdalae
3.8. Correlation Analysis between Gene and Protein Expressions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sontate, K.V.; Rahim Kamaluddin, M.; Naina Mohamed, I.; Mohamed, R.M.P.; Shaikh, M.F.; Kamal, H.; Kumar, J. Alcohol, aggression, and violence: From public health to neuroscience. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 699726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Q.; Mathurin, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, J.; Shield, K.D.; Rylett, M.; Hasan, O.S.; Probst, C.; Rehm, J. Global alcohol exposure between 1990 and 2017 and forecasts until 2030: A modelling study. Lancet 2019, 393, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiff, M.; Sidi, H.; Masiran, R.; Kumar, J.; Das, S.; Hatta, N.H.; Alfonso, C. Hypersexuality as a neuropsychiatric disorder: The neurobiology and treatment options. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Yu, J.; Shao, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Functional overlaps exist in neurological and psychiatric disorders: A proof from brain network analysis. Neuroscience 2020, 425, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.; Tan, G.C.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Shaikh, M.F.; Mohamed, I.N.; Mohamed, R.M.P.; Hamid, A.A.; Ugusman, A.; Kumar, J. Alcohol use disorder, neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: Interplay between oxidative stress, neuroimmune response and excitotoxicity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Ismail, Z.; Hatta, N.H.; Baharuddin, N.; Hapidin, H.; Get Bee, Y.-T.; Yap, E.; Pakri Mohamed, R.M. Alcohol addiction-metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 and its ligands: How they all come together? Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakri Mohamed, R.M.; Kumar, J.; Ahmad, S.U.; Mohamed, I.N. Novel pharmacotherapeutic approaches in treatment of alcohol addiction. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzoli, D.K.; Kaufman, M.N.; Nipper, M.A.; Hashimoto, J.G.; Wiren, K.M.; Finn, D.A. Functional regulation of PI3K-associated signaling in the accumbens by binge alcohol drinking in male but not female mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Hapidin, H.; Bee, Y.-T.G.; Ismail, Z. The effects of acute ethanol administration on ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like syndrome in rats: A biochemical study. Alcohol 2016, 50, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasio, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Varodayan, F.P.; Pomrenze, M.B.; Miller, J.; Lee, A.M.; McMahon, T.; Gyawali, S.; Wang, H.-Y. Novel small-molecule inhibitors of protein kinase C epsilon reduce ethanol consumption in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiya, R.; McMahon, T.; Wang, D.; Kanter, B.; Gandhi, D.; Chapman, H.L.; Miller, J.; Messing, R.O. Selective chemical genetic inhibition of protein kinase C epsilon reduces ethanol consumption in mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Smith, T.L.; Kalmijn, J. The search for genes contributing to the low level of response to alcohol: Patterns of findings across studies. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Khisti, R.T.; Morrow, A.L. Regulation of native GABA A receptors by PKC and protein phosphatase activity. Psychopharmacology 2005, 183, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, Y. Protein kinase C-ε (PKC-ε): Its unique structure and function. J. Biochem. 2002, 132, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinmura, K.; Nagai, M.; Tamaki, K.; Bolli, R. Loss of ischaemic preconditioning in ovariectomized rat hearts: Possible involvement of impaired protein kinase C ε phosphorylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Outram, S.P.; Basu, A. Upregulation of PKCη by PKCε and PDK1 involves two distinct mechanisms and promotes breast cancer cell survival. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Hu, H.; Tong, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Yuan, H.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. The mTOR–S6K pathway links growth signalling to DNA damage response by targeting RNF168. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanim, A.; Mohamed, I.N.; Mohamed, R.M.P.; Das, S.; Nor, N.S.; Harun, R.A.; Kumar, J. mTORC and PKCε in regulation of alcohol use disorder. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenoue, T.; Inoki, K.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Guan, K.L. Essential function of TORC2 in PKC and Akt turn motif phosphorylation, maturation and signalling. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.J.; Linch, M.D.; Saurin, A.T.; Escribano, C.; Parker, P.J. mTORC2 targets AGC kinases through Sin1-dependent recruitment. Biochem. J. 2011, 439, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, M.A.; Thoreen, C.C.; Jaffe, J.D.; Schroder, W.; Sculley, T.; Carr, S.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mSin1 is necessary for Akt/PKB phosphorylation, and its isoforms define three distinct mTORC2s. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong-Brown, L.Q.; Brown, C.R.; Navaratnarajah, M.; Huber, D.S.; Lang, C.H. Alcohol-induced modulation of rictor and mTORC2 activity in C2C12 myoblasts. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguesse, S.; Morisot, N.; Phamluong, K.; Sakhai, S.A.; Ron, D. mTORC2 in the dorsomedial striatum of mice contributes to alcohol-dependent F-Actin polymerization, structural modifications, and consumption. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehinger, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Phamluong, K.; Soneja, D.; Shokat, K.M.; Ron, D. Brain-specific inhibition of mTORC1 eliminates side effects resulting from mTORC1 blockade in the periphery and reduces alcohol intake in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lunde-Young, R.; Naik, V.; Ramirez, J.; Orzabal, M.; Ramadoss, J. Chronic binge alcohol exposure during pregnancy alters mTOR system in rat fetal Hippocampus. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsalan, N.; Saglam, E.; Kayir, H.; Uzbay, T. Effects of olanzapine on ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 579, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotagale, N.R.; Kedia, A.; Gite, R.; Rahmatkar, S.N.; Gawande, D.Y.; Umekar, M.J.; Taksande, B.G. Withaferin A attenuates Alcohol Abstinence Signs in Rats. Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, I.M.; Mishra, A.; Kalra, B.S.; Chawla, S. Role of Standardized Plant Extracts in Controlling Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome—An Experimental Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Hapidin, H.; Bee, Y.-T.G.; Ismail, Z. Effects of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP on ethanol withdrawal induced anxiety-like syndrome in rats. Behav. Brain Funct. 2013, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzbay, I.T.; Kayaalp, S.O. A modified liquid diet of chronic ethanol administration: Validation by ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 1995, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroor, A.R.; Shukla, S.D. Binge ethanol intake in chronically exposed rat liver decreases LDL-receptor and increases angiotensinogen gene expression. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wu, Y.; Peng, H.; Cai, X.; Hu, Z.; Lin, X.; Peng, X.-E. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in nonalcoholic fatty liver reveals predictive aberrant methylation in PRKCE and SEC14L3 promoters. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, R.; Singh, S. Ethanol-responsive genes: Identification of transcription factors and their role in metabolomics. Pharm. J. 2007, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzade Fard, A.; Samadi, M.; Shirpoor, A.; Rasmi, Y. Ethanol Consumption Promotes TNF-α Signaling Pathway in Rat Kidney: Rescue Effect of Curcumin. J. Chem. Health Risks 2022, 12, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Parikh, M.; Mishra, V.; Soni, A.; Rubi, S.; Sahota, P.; Thakkar, M. Antisense-induced downregulation of major circadian genes modulates the expression of histone deacetylase-2 (HDAC-2) and CREB-binding protein (CBP) in the medial shell region of nucleus accumbens of mice exposed to chronic excessive alcohol consumption. J. Neurochem. 2022, 161, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Huang, I.-C.; Pizzi, M.; Spano, P.; Boroni, F.; Egli, R.; Desai, P.; Fitch, O.; Malone, L.; Ahn, H.J. Regulation of nuclear factor κB in the hippocampus by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4870–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Marques, M.; Carvalho, A.; Cavadas, C.; Aveleira, C.A. PI3K/AKT/MTOR and ERK1/2-MAPK signaling pathways are involved in autophagy stimulation induced by caloric restriction or caloric restriction mimetics in cortical neurons. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijomone, O.M.; Iroegbu, J.D.; Aschner, M.; Bornhorst, J. Impact of environmental toxicants on p38-and ERK-MAPK signaling pathways in the central nervous system. Neurotoxicology 2021, 86, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroegbu, J.D.; Ijomone, O.K.; Femi-Akinlosotu, O.M.; Ijomone, O.M. ERK/MAPK signalling in the developing brain: Perturbations and consequences. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, T.; An, H. Sinapine reverses multi-drug resistance in MCF-7/dox cancer cells by downregulating FGFR4/FRS2α-ERK1/2 pathway-mediated NF-κB activation. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Ping, P.; Zhang, J.; Wead, W.B.; Cao, X.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Han, J.; Bolli, R. PKCε modulates NF-κB and AP-1 via mitogen-activated protein kinases in adult rabbit cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H1679–H1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, R.; Blando, J.; Perez, C.J.; Wang, H.; Benavides, F.J.; Kazanietz, M.G. Activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in prostate cancer is mediated by protein kinase C ϵ (PKCϵ). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37570–37582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Raval, A.P.; Hirsch, N.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Ischemic preconditioning mediates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via nuclear factor-kappa B activation in mixed cortical neuronal cultures. Transl. Stroke Res. 2010, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valjent, E.; Pagès, C.; Hervé, D.; Girault, J.A.; Caboche, J. Addictive and non-addictive drugs induce distinct and specific patterns of ERK activation in mouse brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoglia, A.E.; Sharko, A.C.; Psilos, K.E.; Holstein, S.E.; Reid, G.T.; Hodge, C.W. Alcohol alters the activation of ERK1/2, a functional regulator of binge alcohol drinking in adult C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, P.P.; Simpson, C.; Lutjens, R.; Koob, G. ERK regulation in chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal. Brain Res. 2002, 948, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwanska, K.; Wrobel, E.; Korkosz, A.; Rogowski, A.; Kostowski, W.; Bienkowski, P.; Kaczmarek, L. Alcohol relapse induced by discrete cues activates components of AP-1 transcription factor and ERK pathway in the rat basolateral and central amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, L.J.; Sutton, G. Acute Ethanol Inhibits Extracellular Signal–Regulated Kinase, Protein Kinase B, and Adenosine 3′: 5′-Cyclic Monophosphate Response Element Binding Protein Activity in an Age-and Brain Region–Specific Manner. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wei, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, E.; Lai, J. Differential phosphorylation of GluN1-MAPKs in rat brain reward circuits following long-term alcohol exposure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Fan, P.; Jiang, Z.; Gordon, A.; Mochly-Rosen, D.; Diamond, I. Dopamine and Ethanol Cause Translocation of ϵPKC Associated with ϵRACK: Cross-Talk between cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase A and Protein Kinase C Signaling Pathways. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Ter Horst, K.W.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Gaspar, R.C.; Hirabara, S.M.; Luukkonen, P.K.; Lee, S. A membrane-bound diacylglycerol species induces PKCϵ-mediated hepatic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 654–664. e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C. Acute and chronic ethanol consumption effects on the immunolabeling of Gq/11α subunit protein and phospholipase C isozymes in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, L.M.; Okazaki, T.; Karolak, L.A.; Hannun, Y. Transcriptional regulation of protein kinase C by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 2370–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiley, S.; Parker, P.; Fabbro, D.; Jaken, S. Differential regulation of protein kinase C isozymes by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH4C1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 23761–23768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontieva, O.V.; Black, J.D. Identification of two distinct pathways of protein kinase Cα down-regulation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5788–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Brognard, J.; Newton, A.C. The phosphatase PHLPP controls the cellular levels of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6300–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsura, M.; Ohkuma, S.; Chen, D.-Z.; Kuriyama, K. Ethanol-induced alteration in activities of cerebral phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-biphosphate-specific and cytosolic phospholipase C in the brain: Analysis using NG 108-15 cells and brains from ethanol-inhaled mice. Neurochem. Int. 1994, 24, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Peiffer, C. Deconstructing the role of PKC epsilon in glucose homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, L.; Semenza, E.R.; Koshkaryan, G.; Mishra, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Abramson, E.; Mishra, P.; Sei, Y.; Wank, S.A.; Donowitz, M. Loss of PI3k activity of inositol polyphosphate multikinase impairs PDK1-mediated AKT activation, cell migration, and intestinal homeostasis. Iscience 2023, 26, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzoli, D.K.; Goulding, S.P.; Zhang, P.W.; Xiao, B.; Hu, J.-H.; Ary, A.W.; Obara, I.; Rahn, A.; Abou-Ziab, H.; Tyrrel, B. Binge drinking upregulates accumbens mGluR5–Homer2–PI3K signaling: Functional implications for alcoholism. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8655–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-J.; Shin, S.; Piao, L.; Shin, E.; Li, Y.; Park, K.A.; Byun, H.S.; Won, M.; Hong, J.; Kweon, G.R. Regulation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) by Src involves tyrosine phosphorylation of PDK1 and Src homology 2 domain binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-C.; Masai, H. Claspin is required for growth recovery from serum starvation through regulating the PI3K-PDK1-mTOR pathway. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, D.B.; Ziegler, W.; Parker, P.J. Multiple pathways control protein kinase C phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB signaling: Navigating the network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, J.; Takagi, E.; Wang, F.; Saha, B.; Liu, X.; Joubert, L.-M.; Gleason, C.E.; Jin, M.; Li, C. Interactions between mTORC2 core subunits Rictor and mSin1 dictate selective and context-dependent phosphorylation of substrate kinases SGK1 and Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neasta, J.; Hamida, S.B.; Yowell, Q.V.; Carnicella, S.; Ron, D. AKT signaling pathway in the nucleus accumbens mediates excessive alcohol drinking behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Brown, L.Q.; Brown, C.R.; Kazi, A.A.; Huber, D.S.; Pruznak, A.M.; Lang, C.H. Alcohol and PRAS40 knockdown decrease mTOR activity and protein synthesis via AMPK signaling and changes in mTORC1 interaction. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 109, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckley, J.T.; Laguesse, S.; Phamluong, K.; Morisot, N.; Wegner, S.A.; Ron, D. The first alcohol drink triggers mTORC1-dependent synaptic plasticity in nucleus accumbens dopamine D1 receptor neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neasta, J.; Ben Hamida, S.; Yowell, Q.; Carnicella, S.; Ron, D. Role for mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in neuroadaptations underlying alcohol-related disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20093–20098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, P.-D.; Yang, M.-F.; Sun, J.-Y.; Mao, L.-L.; Fan, C.-D.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Li, D.-W.; Yang, X.-Y.; Sun, B.-L. The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, S.; Liu, F.; Hamida, S.B.; Yowell, Q.V.; Neasta, J.; Kharazia, V.; Janak, P.H.; Ron, D. Disruption of alcohol-related memories by mTORC1 inhibition prevents relapse. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguesse, S.; Morisot, N.; Phamluong, K.; Ron, D. Region specific activation of the AKT and mTORC1 pathway in response to excessive alcohol intake in rodents. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | D1–D7 | D8–D27 | D28 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 6 h | 7 h | |||
| Control | MLD | MLD | MLD | Saline | Euthanasia |
| Acute EtOH | MLD | MLD | MLD | Acute EtOH | Euthanasia |
| Chronic EtOH | MLD | MLD + EtOH | Acute EtOH | MLD + EtOH | Euthanasia |
| EW | MLD | MLD + EtOH | MLD | Saline | Euthanasia |
| EW + EtOH | MLD | MLD + EtOH | MLD | Acute EtOH | Euthanasia |
| Group | Day 1 (g) | Day 27 (g) | Body Weight Changes (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol naive (n = 12) | 266.43 ± 14.92 | 267.99 ± 9.57 | +0.6 |
| Ethanol fed (n = 18) | 262.53 ± 7.87 | 231.09 ± 6.16 | −11.98 ** |
| Group | Daily MLD Intake (mL/Day) |
|---|---|
| Control | 67.43 ± 3.23 |
| Acute EtOH | 71.06 ± 2.82 |
| Chronic EtOH | 59.69 ± 0.48 # |
| EW | 51.04 ± 1.07 **, ## |
| EW + EtOH | 52.04 ± 2.62 **, ## |
| Group | Daily Ethanol Intake (g/kg Day−1) |
|---|---|
| Chronic EtOH | 12.65 ± 0.44855 |
| EW | 12.02 ± 0.26170 |
| EW + EtOH | 11.38 ± 0.62499 |
| Group | Serum Ethanol Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Acute EtOH | 285.26 ± 42.10 ## |
| Chronic EtOH | 582.69 ± 70.42 |
| EW | 340.13 ± 20.55 ## |
| EW + EtOH | 384.63 ± 29.78 *, ## |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanim, A.; Mohamed, I.N.; Mohamed, R.M.P.; Mokhtar, M.H.; Makpol, S.; Naomi, R.; Bahari, H.; Kamal, H.; Kumar, J. Alcohol Dependence Modulates Amygdalar mTORC2 and PKCε Expression in a Rodent Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133036
Hanim A, Mohamed IN, Mohamed RMP, Mokhtar MH, Makpol S, Naomi R, Bahari H, Kamal H, Kumar J. Alcohol Dependence Modulates Amygdalar mTORC2 and PKCε Expression in a Rodent Model. Nutrients. 2023; 15(13):3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133036
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanim, Athirah, Isa N. Mohamed, Rashidi M. P. Mohamed, Mohd Helmy Mokhtar, Suzana Makpol, Ruth Naomi, Hasnah Bahari, Haziq Kamal, and Jaya Kumar. 2023. "Alcohol Dependence Modulates Amygdalar mTORC2 and PKCε Expression in a Rodent Model" Nutrients 15, no. 13: 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133036
APA StyleHanim, A., Mohamed, I. N., Mohamed, R. M. P., Mokhtar, M. H., Makpol, S., Naomi, R., Bahari, H., Kamal, H., & Kumar, J. (2023). Alcohol Dependence Modulates Amygdalar mTORC2 and PKCε Expression in a Rodent Model. Nutrients, 15(13), 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133036







