Prebiotic Supplementation during Lactation Affects Microbial Colonization in Postnatal-Growth-Restricted Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
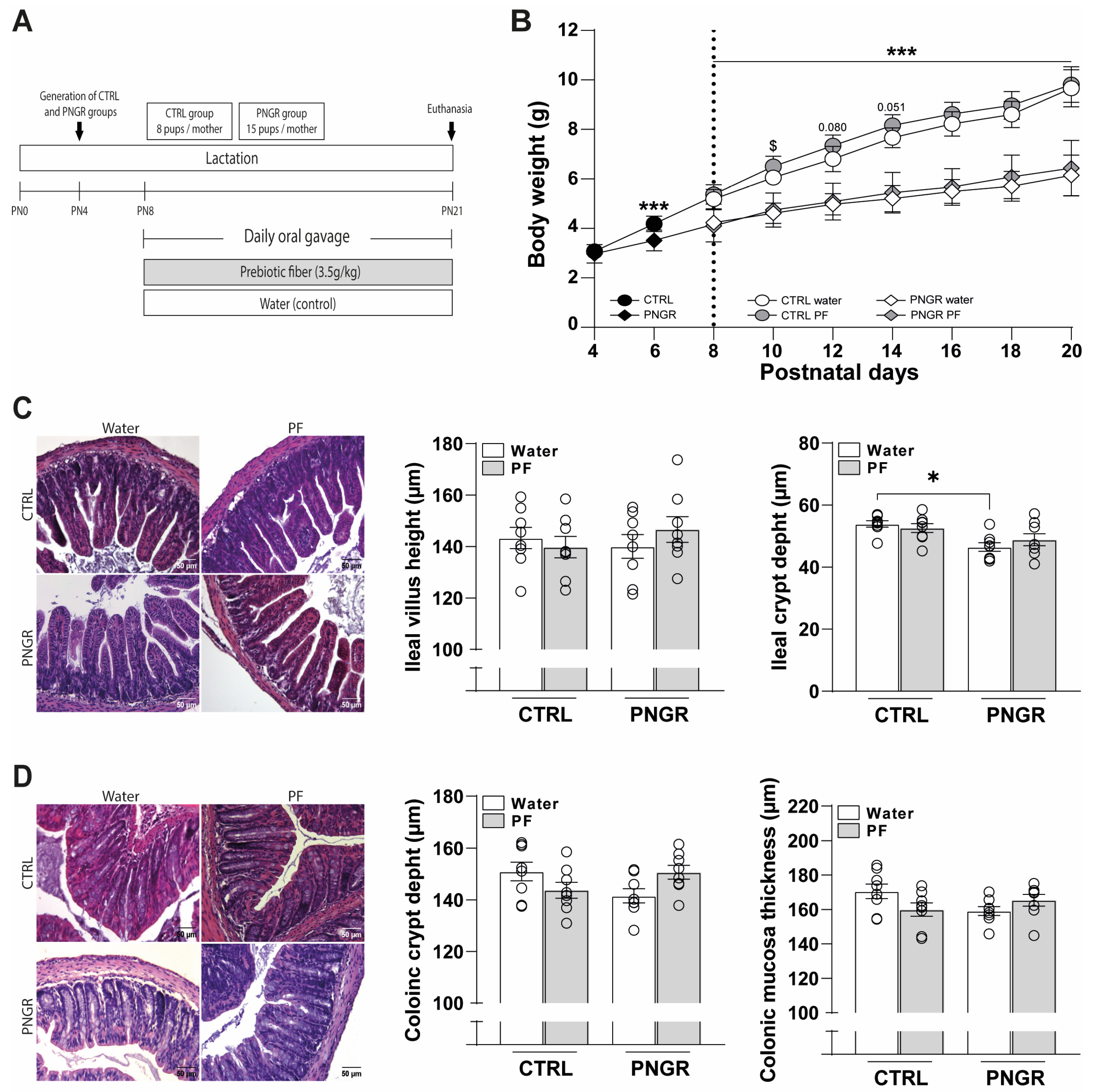
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Intestinal Morphology
2.3. Intestinal Microbiota
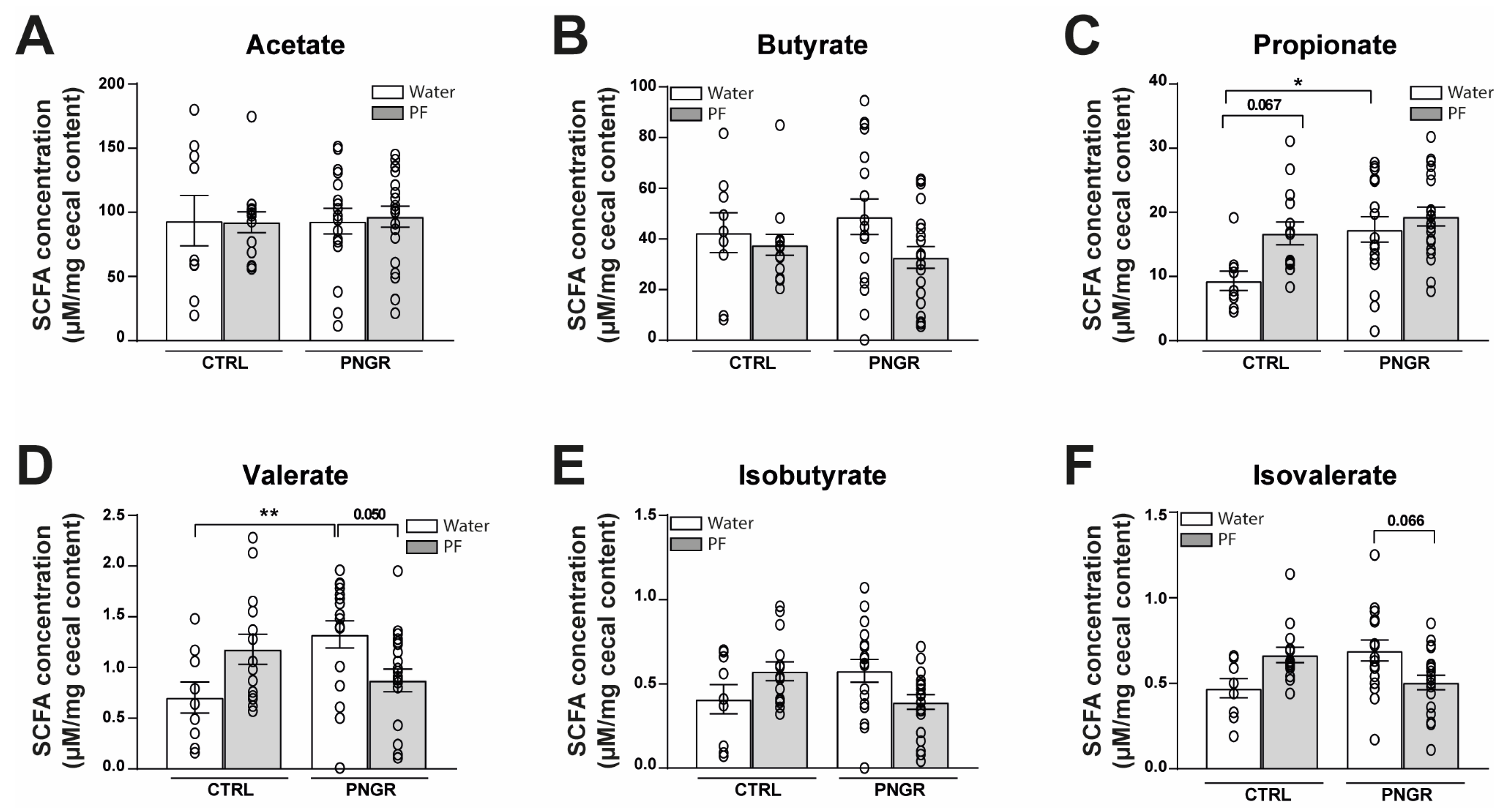
2.4. Dosage of Cecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PNGR and PF Supplementation on Pups’ Growth and Intestinal Morphology
3.2. Effects of PNGR and PF Supplementation on Intestinal Microbial Colonization and SCFA Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpinello, O.J.; DeCherney, A.H.; Hill, M.J. Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: The History of the Barker Hypothesis and Assisted Reproductive Technology. In Seminars in Reproductive Medicine; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 36, pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.P. The origins of the developmental origins theory. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.J.; Reynolds, R.M.; Hardy, D.B. Developmental origins of health and disease: Current knowledge and potential mechanisms. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, M.A.; Gluckman, P.D. Early developmental conditioning of later health and disease: Physiology or pathophysiology? Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1027–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, D.; Desseyn, J.-L.; Mischke, M.; Knol, J.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Early-life origin of intestinal inflammatory disorders. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratsika, A.; Codagnone, M.C.; O’Mahony, S.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Priming for Life: Early Life Nutrition and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.Y.; Stevens, B.W.; Wilson, R.G.; Russell, C.N.; Cohen, M.A.; Sturgeon, H.C.; Thornton, A.; Giallourakis, C.; Khalili, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Early life environment and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.M.; van Roest, M.; Vermeulen, J.L.M.; Meisner, S.; Smit, W.L.; Silva, J.; Koelink, P.J.; Koster, J.; Faller, W.J.; Wildenberg, M.E.; et al. Early Life Antibiotics Influence In Vivo and In Vitro Mouse Intestinal Epithelium Maturation and Functioning. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 943–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, K.; Van Daele, E.; Vlieger, A.M.; Daams, J.G.; Knol, J.; van Elburg, R.M. Early life antibiotics and childhood gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2021, 5, e001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdowski, L.A.; Clandinin, T.; Thomson, A.B. Ontogeny, growth and development of the small intestine: Understanding pediatric gastroenterology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.M.; Hill, D.R.; Aurora, M.; Spence, J.R. Morphogenesis and maturation of the embryonic and postnatal intestine. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 66, pp. 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, U.; Aich, P. Postnatal intestinal mucosa and gut microbial composition develop hand in hand: A mouse study. Biomed. J. 2022, 46, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, D.; Desseyn, J.-L.; Gouyer, V.; Plet, S.; Tims, S.; Renes, I.; Mischke, M.; Gottrand, F. Early life nutrition influences susceptibility to chronic inflammatory colitis in later life. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabhani, Z.A.; Dulauroy, S.; Marques, R.; Cousu, C.; Bounny, S.A.; Déjardin, F.; Sparwasser, T.; Bérard, M.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Eberl, G. A Weaning Reaction to Microbiota Is Required for Resistance to Immunopathologies in the Adult. Immunity 2019, 50, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Eberl, G. Imprinting of the immune system by the microbiota early in life. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J. Fiber and Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, D.M.; Ross, P.; Stanton, C. Beneficial Microbes: The pharmacy in the gut. Bioengineered 2015, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, F.B.; Oozeer, R.; Piloquet, H.; Moyon, T.; Pagniez, A.; Knol, J.; Darmaun, D.; Michel, C. Preweaning modulation of intestinal microbiota by oligosaccharides or amoxicillin can contribute to programming of adult microbiota in rats. Nutrition 2015, 31, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knol, J.; Boehm, G.; Lidestri, M.; Negretti, F.; Jelinek, J.; Agosti, M.; Stahl, B.; Marini, A.; Mosca, F. Increase of faecal bifidobacteria due to dietary oligosaccharides induces a reduction of clinically relevant pathogen germs in the faeces of formula-fed preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2005, 94, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, N.; Jacobs, J.P.; Larauche, M.; Biraud, M.; Million, M.; Mayer, E.; Taché, Y. Chronic Early-life Stress in Rat Pups Alters Basal Corticosterone, Intestinal Permeability, and Fecal Microbiota at Weaning: Influence of Sex. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloteau, E.; Coll, P.; Lu, Z.; Djouina, M.; Cazaunau, M.; Waxin, C.; Bergé, A.; Caboche, S.; Gratien, A.; Marj, E.A.; et al. Murine in utero exposure to simulated complex urban air pollution disturbs offspring gut maturation and microbiota during intestinal suckling-to-weaning transition in a sex-dependent manner. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch, J.; Servant, F.; Païssé, S.; Valle, C.; Valière, S.; Kuchly, C.; Vilchez, G.; Donnadieu, C.; Courtney, M.; Burcelin, R.; et al. The Characterization of Novel Tissue Microbiota Using an Optimized 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Pipeline. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudié, F.; Auer, L.; Bernard, M.; Mariadassou, M.; Cauquil, L.; Vidal, K.; Maman, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G.; Combes, S.; Pascal, G. FROGS: Find, Rapidly, OTUs with Galaxy Solution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.K.; Boberg, J.R.; Walsh, M.T.; Wolf, V.; Trujillo, A.; Duke, M.S.; Palme, R.; Felton, L.A. A less stressful alternative to oral gavage for pharmacological and toxicological studies in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 260, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.-Y.; Dong, D.; Du, J.; Gu, L.; Ge, Y.-B. α-fetoprotein involvement during glucocorticoid-induced precocious maturation in rat colon. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shin, Y.-C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, M.-N.; Eunju, O.; Kim, K.S.; Kweon, M.-N. Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1892441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Anti-inflammatory actions of acetate, propionate, and butyrate in fetal mouse jejunum cultures ex vivo and immature small intestinal cells in vitro. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, K.G.; Dike, P.N.; Suh, J.H.; Halder, T.; Edwards, P.T.; Foong, J.P.P.; Conner, M.E.; Preidis, G.A. Early-life malnutrition causes gastrointestinal dysmotility that is sexually dimorphic. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.-H.; Sommer, F.; Falk-Paulsen, M.; Ulas, T.; Best, P.; Fazio, A.; Kachroo, P.; Luzius, A.; Jentzsch, M.; Rehman, A.; et al. Exposure to the gut microbiota drives distinct methylome and transcriptome changes in intestinal epithelial cells during postnatal development. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Xiong, X.; Yin, Y. Energy metabolism in intestinal epithelial cells during maturation along the crypt-villus axis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Elsen, L.W.J.; Rekima, A.; Verhasselt, V. Early-Life Nutrition and Gut Immune Development. Hum. Milk Compos. Clin. Benefits Future Oppor. 2019, 90, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Do Nascimento Arifa, R.D.; Acúrcio, L.; Brito, C.B.; Gouvea, J.O.; Lima, R.L.; Bastos, R.W.; Dias, A.C.F.; Dourado, L.P.A.; Bastos, L.F.S.; et al. Colonization by Enterobacteriaceae is crucial for acute inflammatory responses in murine small intestine via regulation of corticosterone production. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Dréan, G.; Pocheron, A.-L.; Billard, H.; Grit, I.; Pagniez, A.; Parnet, P.; Chappuis, E.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Michel, C. Neonatal Consumption of Oligosaccharides Greatly Increases L-Cell Density without Significant Consequence for Adult Eating Behavior. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, S.O.; Tkacz, A.; Savignac, H.M.; Cooper, M.; Giallourou, N.; Mann, E.O.; Bannerman, D.M.; Swann, J.R.; Anthony, D.C.; Poole, P.S.; et al. Postnatal prebiotic supplementation in rats affects adult anxious behaviour, hippocampus, electrophysiology, metabolomics, and gut microbiota. iScience 2021, 24, 103113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Roles of intestinal Parabacteroides in human health and diseases. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wexler, A.G.; Goodman, A.L. An insider’s perspective: Bacteroides as a window into the microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaakoush, N.O. Insights into the Role of Erysipelotrichaceae in the Human Host. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirpuri, J.; Raetz, M.; Sturge, C.R.; Wilhelm, C.L.; Benson, A.; Savani, R.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Proteobacteria-specific IgA regulates maturation of the intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhu, H.; Feng, L.; Zhang, D.; Xue, Y.; He, F.; Wang, S. Oral administration of Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 on neonatal mice prevents the intestinal inflammation in adulthood. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marousez, L.; Tran, L.C.; Micours, E.; Antoine, M.; Gottrand, F.; Lesage, J.; Ley, D. Prebiotic Supplementation during Lactation Affects Microbial Colonization in Postnatal-Growth-Restricted Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122771
Marousez L, Tran LC, Micours E, Antoine M, Gottrand F, Lesage J, Ley D. Prebiotic Supplementation during Lactation Affects Microbial Colonization in Postnatal-Growth-Restricted Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(12):2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122771
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarousez, Lucie, Léa Chantal Tran, Edwina Micours, Matthieu Antoine, Frédéric Gottrand, Jean Lesage, and Delphine Ley. 2023. "Prebiotic Supplementation during Lactation Affects Microbial Colonization in Postnatal-Growth-Restricted Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 12: 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122771
APA StyleMarousez, L., Tran, L. C., Micours, E., Antoine, M., Gottrand, F., Lesage, J., & Ley, D. (2023). Prebiotic Supplementation during Lactation Affects Microbial Colonization in Postnatal-Growth-Restricted Mice. Nutrients, 15(12), 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122771





