Liver-Specific Bmal1 Depletion Reverses the Beneficial Effects of Nobiletin on Liver Cholesterol Homeostasis in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animal
2.3. Rhythm Detection Program
2.4. NOB Treatment Experiment
2.5. Serum and Liver Collection
2.6. Assay of Biochemical Parameters
2.7. Liver Histology
2.8. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
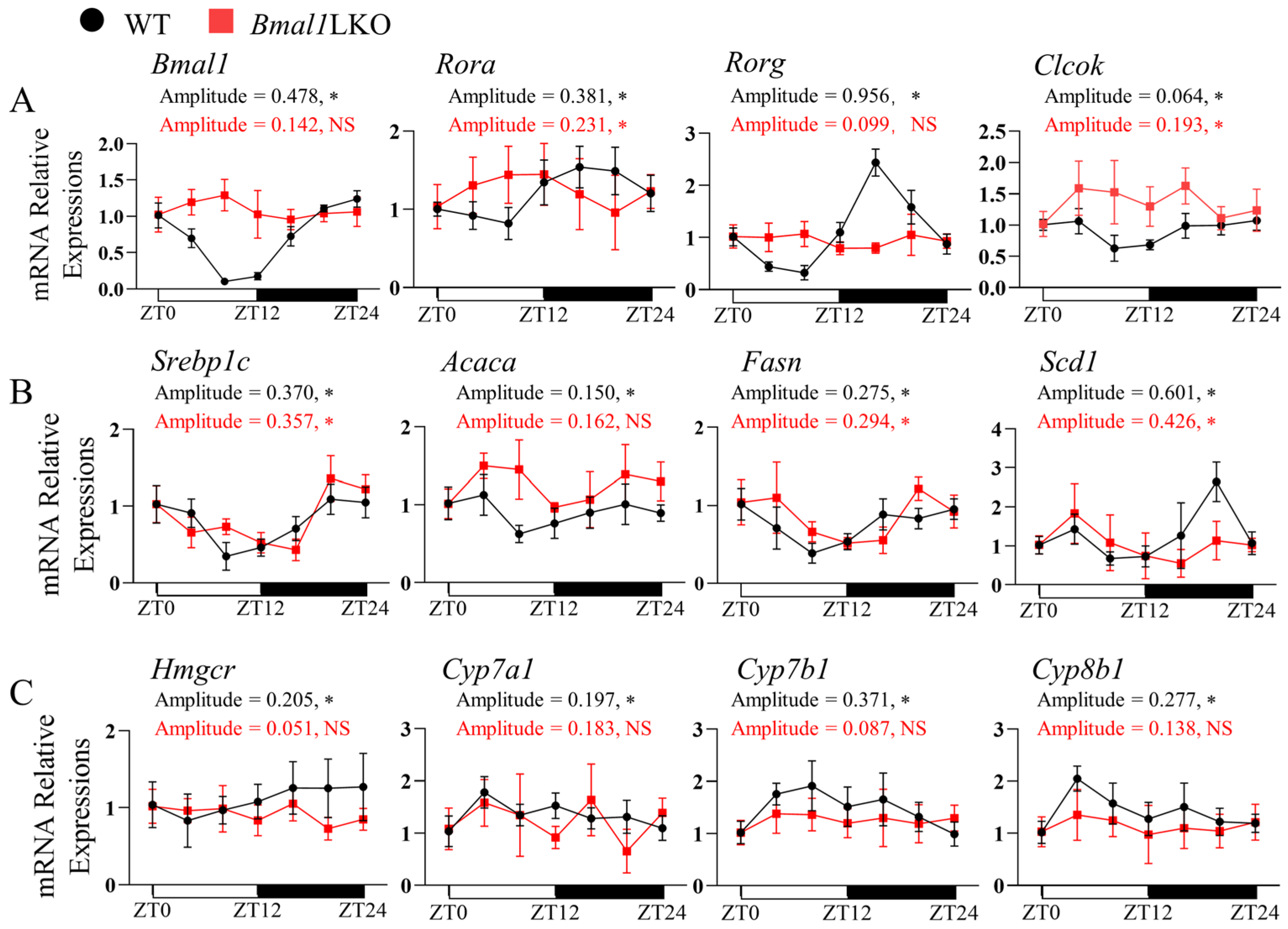
3.1. Liver-Specific Bmal1 Knockout Remodels 24-h Rhythmicity of Liver and Serum Metabolic Parameters in NC-Fed Mice
3.2. Liver-Specific Bmal1 Knockout Altered the Expression of Clock Genes and Clock-Controlled Genes in the Liver
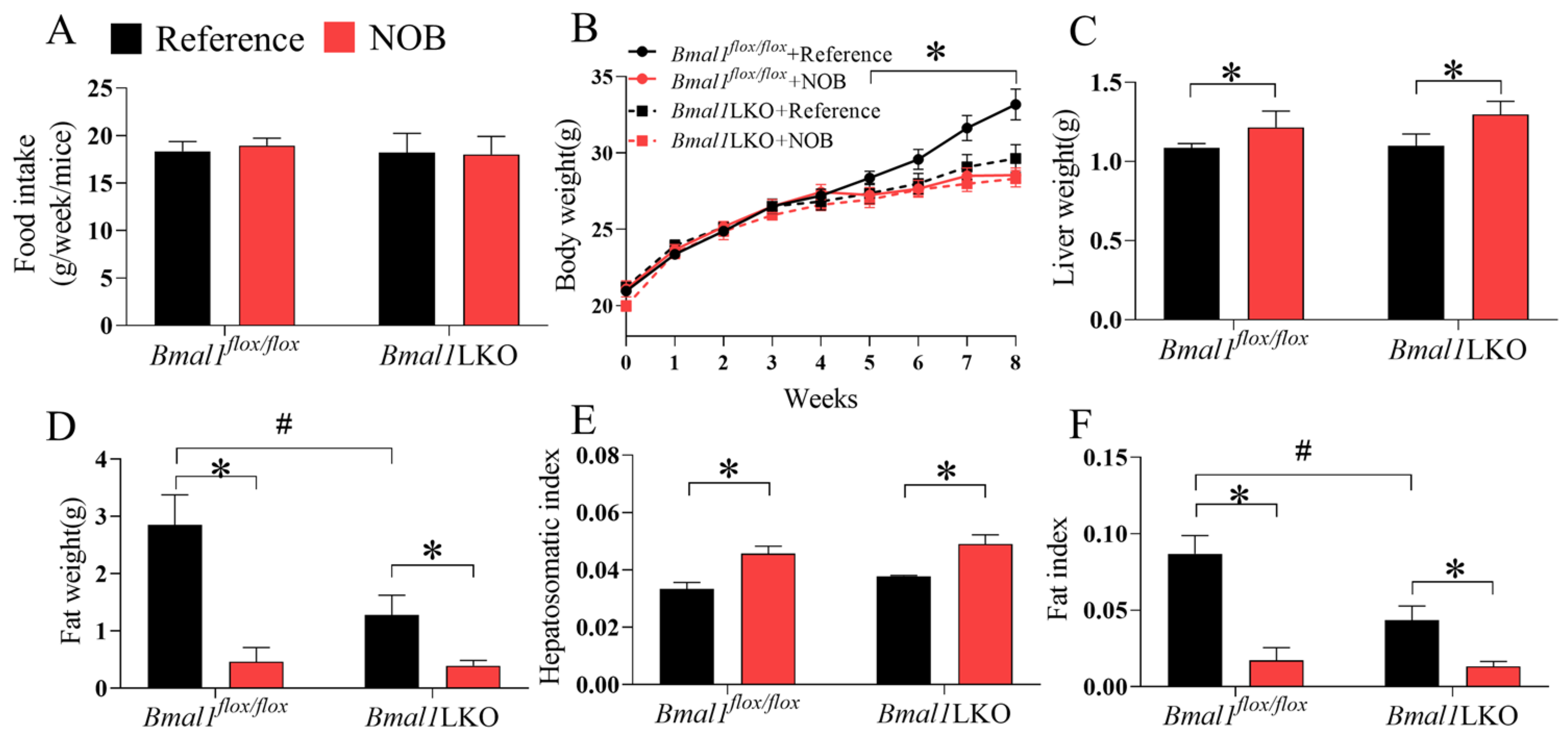
3.3. NOB Prevents HFD-Fed Bmal1flox/flox and Bmal1LKO Mice from Gaining Body Weight and White Adipose Tissue Content
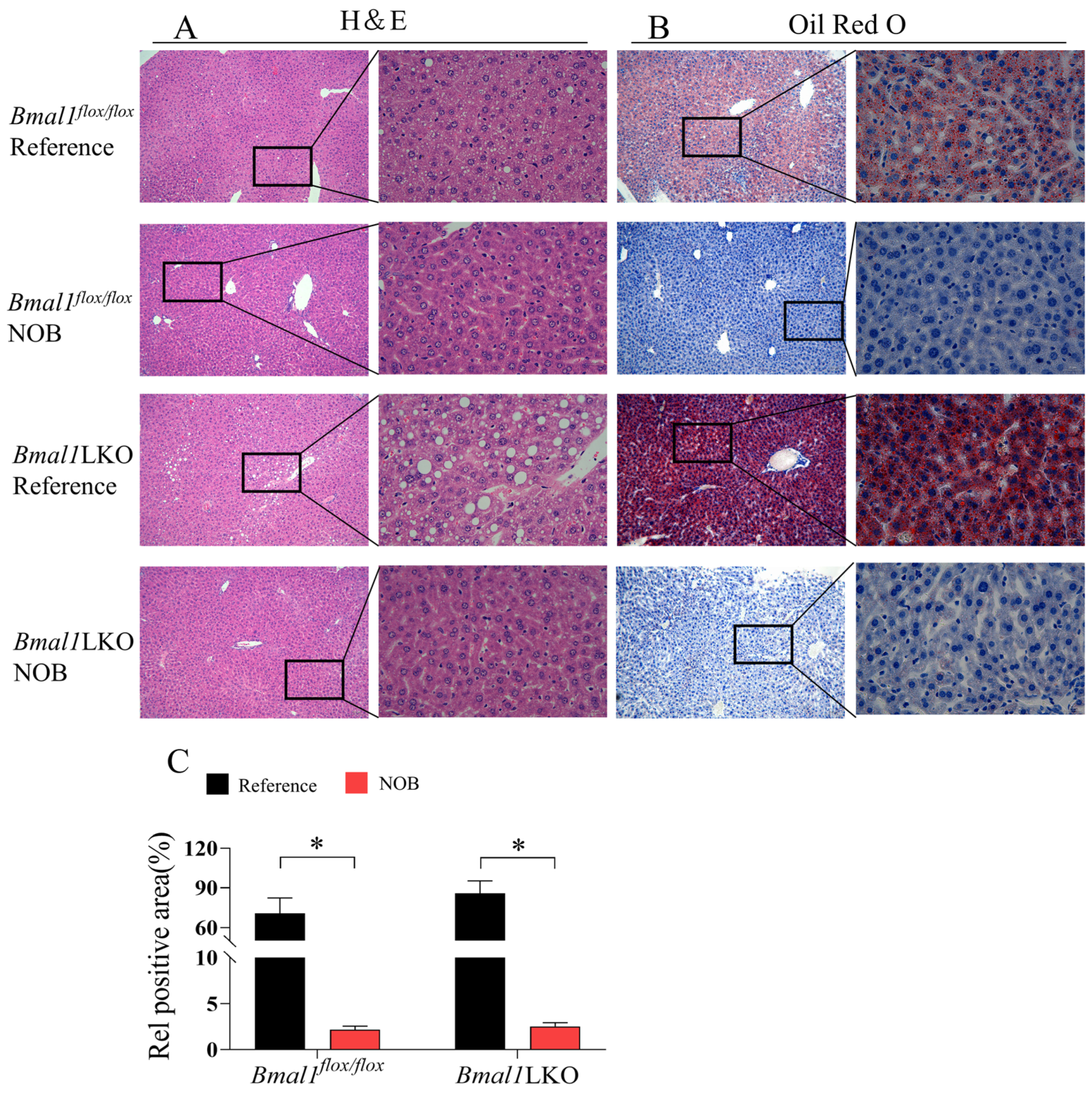
3.4. Effects of NOB on Liver Pathological Features in HFD-Fed Mice
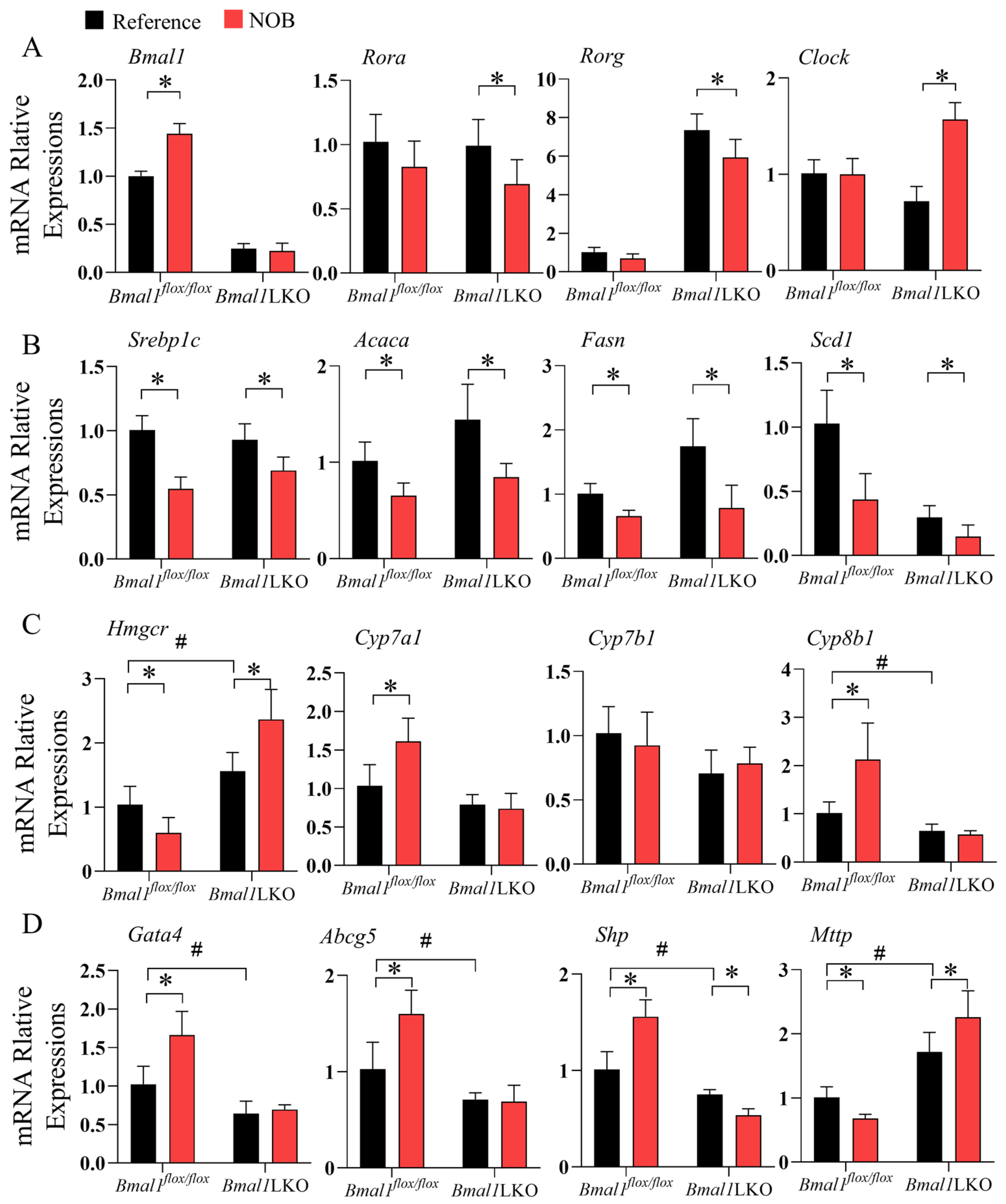
3.5. NOB Improves Liver and Serum Lipid Homeostasis in HFD-Fed Mice in a Hepatic Bmal1-Dependent or Bmal1-Independent Manner
3.6. NOB Altered Liver Expression of Clock Genes and Clock-Controlled Genes in HFD-Fed Bmal1flox/flox and Bmal1LKO Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, M.C.; Vatner, D.F.; Shulman, G.I. Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.H.; Koo, S.H. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.P.; Hannivoort, R.A.; Gerken, G.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Trauner, M.; Canbay, A. The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, C.E.; Hepler, C.; Higgins, M.R.; Renquist, B.J. Hepatic adaptations to maintain metabolic homeostasis in response to fasting and refeeding in mice. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, H.; Asher, G. Crosstalk between metabolism and circadian clocks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S. Circadian physiology of metabolism. Science 2016, 354, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaple, L.; Rambaud, J.; Dkhissi-Benyahya, O.; Rayet, B.; Tan, N.S.; Michalik, L.; Delaunay, F.; Wahli, W.; Laudet, V. Reciprocal regulation of brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha defines a novel positive feedback loop in the rodent liver circadian clock. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Martelot, G.; Claudel, T.; Gatfield, D.; Schaad, O.; Kornmann, B.; Lo Sasso, G.; Moschetta, A.; Schibler, U. REV-ERBalpha participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile acid homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamia, K.A.; Sachdeva, U.M.; DiTacchio, L.; Williams, E.C.; Alvarez, J.G.; Egan, D.F.; Vasquez, D.S.; Juguilon, H.; Panda, S.; Shaw, R.J.; et al. AMPK regulates the circadian clock by cryptochrome phosphorylation and degradation. Science 2009, 326, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.D.; Lamia, K.A. AMPK at the crossroads of circadian clocks and metabolism. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 366, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Bradfield, C.A.; Hussain, M.M. Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Hussain, M.M. Bmal1 regulates production of larger lipoproteins by modulating cAMP-responsive element-binding protein H and apolipoprotein AIV. Hepatology 2022, 76, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaix, A.; Lin, T.; Le, H.D.; Chang, M.W.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 303–319.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yu, J.; Frazier, K.; Weng, X.; Li, Y.; Cham, C.M.; Dolan, K.; Zhu, X.; Hubert, N.; Tao, Y.; et al. Circadian Clock Regulation of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism by Modulation of m(6)A mRNA Methylation. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1816–1828.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manella, G.; Sabath, E.; Aviram, R.; Dandavate, V.; Ezagouri, S.; Golik, M.; Adamovich, Y.; Asher, G. The liver-clock coordinates rhythmicity of peripheral tissues in response to feeding. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, D.; Liu, S.; Burkewitz, K.; Kory, N.; Knudsen, N.H.; Alexander, R.K.; Unluturk, U.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Hyde, A.L.; et al. Hepatic Bmal1 Regulates Rhythmic Mitochondrial Dynamics and Promotes Metabolic Fitness. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamia, K.A.; Storch, K.F.; Weitz, C.J. Physiological significance of a peripheral tissue circadian clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15172–15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, F.W.; Joshu, C.; Kohsaka, A.; Lin, E.; Ivanova, G.; McDearmon, E.; Laposky, A.; Losee-Olson, S.; Easton, A.; Jensen, D.R.; et al. Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science 2005, 308, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Queiroz, J.; Hussain, M.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in CLOCK mutant mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4282–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Yuan, X.; Eltzschig, H.K. Circadian rhythm as a therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagiani, F.; Di Marino, D.; Romagnoli, A.; Travelli, C.; Voltan, D.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Racchi, M.; Govoni, S.; Lanni, C. Molecular regulations of circadian rhythm and implications for physiology and diseases. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Burke, A.C.; Huff, M.W. Citrus Flavonoids as Regulators of Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Vasconcelos, A.B.S.; Wu, D.T.; Li, H.B.; Antony, P.J.; Li, H.; Geng, F.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Narain, N.; Gan, R.Y. Citrus Flavonoids as Promising Phytochemicals Targeting Diabetes and Related Complications: A Systematic Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Guo, H.; Geng, F.; Zhuang, Q.G.; Li, H.B.; Wu, D.T. Natural sources, refined extraction, biosynthesis, metabolism, and bioactivities of dietary polymethoxyflavones(PMFs). Food Sci. Human Wellness 2022, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Nohara, K.; Park, N.; Park, Y.S.; Guillory, B.; Zhao, Z.; Garcia, J.M.; Koike, N.; Lee, C.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; et al. The Small Molecule Nobiletin Targets the Molecular Oscillator to Enhance Circadian Rhythms and Protect against Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solt, L.A.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Hughes, T.; Kojetin, D.J.; Lundasen, T.; Shin, Y.; Liu, J.; Cameron, M.D.; Noel, R.; et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature 2012, 485, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Assini, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Allister, E.M.; Sutherland, B.G.; Koppes, J.B.; Sawyez, C.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Telford, D.E.; Charbonneau, A.; et al. Nobiletin attenuates VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in mice with diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tong, X.; Nelson, B.B.; Jin, E.; Sit, J.; Charney, N.; Yang, M.; Omary, M.B.; Yin, L. The hepatic BMAL1/AKT/lipogenesis axis protects against alcoholic liver disease in mice via promoting PPARα pathway. Hepatology 2018, 68, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratov, R.V.; Kondratova, A.A.; Gorbacheva, V.Y.; Vykhovanets, O.V.; Antoch, M.P. Early aging and age-related pathologies in mice deficient in BMAL1, the core componentof the circadian clock. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcheva, B.; Ramsey, K.M.; Buhr, E.D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Su, H.; Ko, C.H.; Ivanova, G.; Omura, C.; Mo, S.; Vitaterna, M.H.; et al. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature 2010, 466, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, G.K.; Ibrahim, S.; Song, W.L.; Kunieda, T.; Grant, G.; Reyes, T.M.; Bradfield, C.A.; Vaughan, C.H.; Eiden, M.; Masoodi, M.; et al. Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Arntl. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, S.; Kim, H.K.; Hirooka, R.; Tanaka, M.; Shimoda, T.; Chijiki, H.; Kojima, S.; Sasaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Makino, S.; et al. Distribution of dietary protein intake in daily meals influences skeletal muscle hypertrophy via the muscle clock. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harfmann, B.D.; Schroder, E.A.; Kachman, M.T.; Hodge, B.A.; Zhang, X.; Esser, K.A. Muscle-specific loss of Bmal1 leads to disrupted tissue glucose metabolism and systemic glucose homeostasis. Skelet. Muscle 2016, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, L.; Chen, M.; Liu, K.; Wu, B. Deficiency of intestinal Bmal1 prevents obesity induced by high-fat feeding. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, N.M.; Burke, A.C.; Samsoondar, J.P.; Seigel, K.E.; Wang, A.; Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; O’Dwyer, C.; Steinberg, G.R.; Fullerton, M.D.; et al. The citrus flavonoid nobiletin confers protection from metabolic dysregulation in high-fat-fed mice independent of AMPK. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.; Lazar, M.A. Interconnections between circadian clocks and metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e148278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Tong, X.; Arthurs, B.; Guha, A.; Rui, L.Y.; Kamath, A.; Inoki, K.; Yin, L. Liver Clock Protein BMAL1 Promotes de Novo Lipogenesis through Insulin-mTORC2-AKT Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25925–25935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronowski, K.B.; Kinouchi, K.; Welz, P.S.; Smith, J.G.; Zinna, V.M.; Shi, J.; Samad, M.; Chen, S.; Magnan, C.N.; Kinchen, J.M.; et al. Defining the Independence of the Liver Circadian Clock. Cell 2019, 177, 1448–1462.e1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, A.; Laposky, A.D.; Ramsey, K.M.; Estrada, C.; Joshu, C.; Kobayashi, Y.; Turek, F.W.; Bass, J. High-fat diet disrupts behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in mice. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Xiong, Y.; Borck, P.C.; Jang, C.; Doulias, P.T.; Papazyan, R.; Fang, B.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Briggs, E.R.; et al. Diet-Induced Circadian Enhancer Remodeling Synchronizes Opposing Hepatic Lipid Metabolic Processes. Cell 2018, 174, 831–842.e812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognini, P.; Murakami, M.; Liu, Y.; Eckel-Mahan, K.L.; Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E.; Baldi, P.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Distinct Circadian Signatures in Liver and Gut Clocks Revealed by Ketogenic Diet. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 523–538.e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, W.C.; Levitt, D.G.; Mueller, S.M.; Behrens, J.C. Regulation of bile acid synthesis in man. Presence of a diurnal rhythm. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 72, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Jiang, X.C.; Hussain, M.M. Impaired cholesterol metabolism and enhanced atherosclerosis in clock mutant mice. Circulation 2013, 128, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, A.; Depoortere, I. Circadian clocks in the digestive system. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDearmon, E.L.; Patel, K.N.; Ko, C.H.; Walisser, J.A.; Schook, A.C.; Chong, J.L.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; Song, E.J.; Hong, H.K.; Bradfield, C.A.; et al. Dissecting the functions of the mammalian clock protein BMAL1 by tissue-specific rescue in mice. Science 2006, 314, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Zou, R.; Qin, D.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA lncRHL Regulates Hepatic VLDL Secretion by Modulating hnRNPU/BMAL1/MTTP Axis. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, R.; Wu, F.; Li, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, B. Liver-Specific Bmal1 Depletion Reverses the Beneficial Effects of Nobiletin on Liver Cholesterol Homeostasis in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112547
Lu Z, Li X, Wang M, Zhang X, Zhuang R, Wu F, Li W, Zhu W, Zhang B. Liver-Specific Bmal1 Depletion Reverses the Beneficial Effects of Nobiletin on Liver Cholesterol Homeostasis in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112547
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Zhitian, Xudong Li, Min Wang, Xiaojun Zhang, Runxuan Zhuang, Fan Wu, Wenxue Li, Wei Zhu, and Bo Zhang. 2023. "Liver-Specific Bmal1 Depletion Reverses the Beneficial Effects of Nobiletin on Liver Cholesterol Homeostasis in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112547
APA StyleLu, Z., Li, X., Wang, M., Zhang, X., Zhuang, R., Wu, F., Li, W., Zhu, W., & Zhang, B. (2023). Liver-Specific Bmal1 Depletion Reverses the Beneficial Effects of Nobiletin on Liver Cholesterol Homeostasis in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Nutrients, 15(11), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112547






