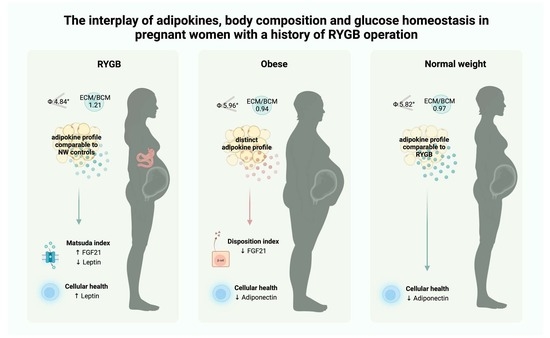
The Interplay of Adipokines, Body Composition and Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Women with a History of RYGB Operation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Tests
2.4. Bioimpedance Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Body Composition during Pregnancy
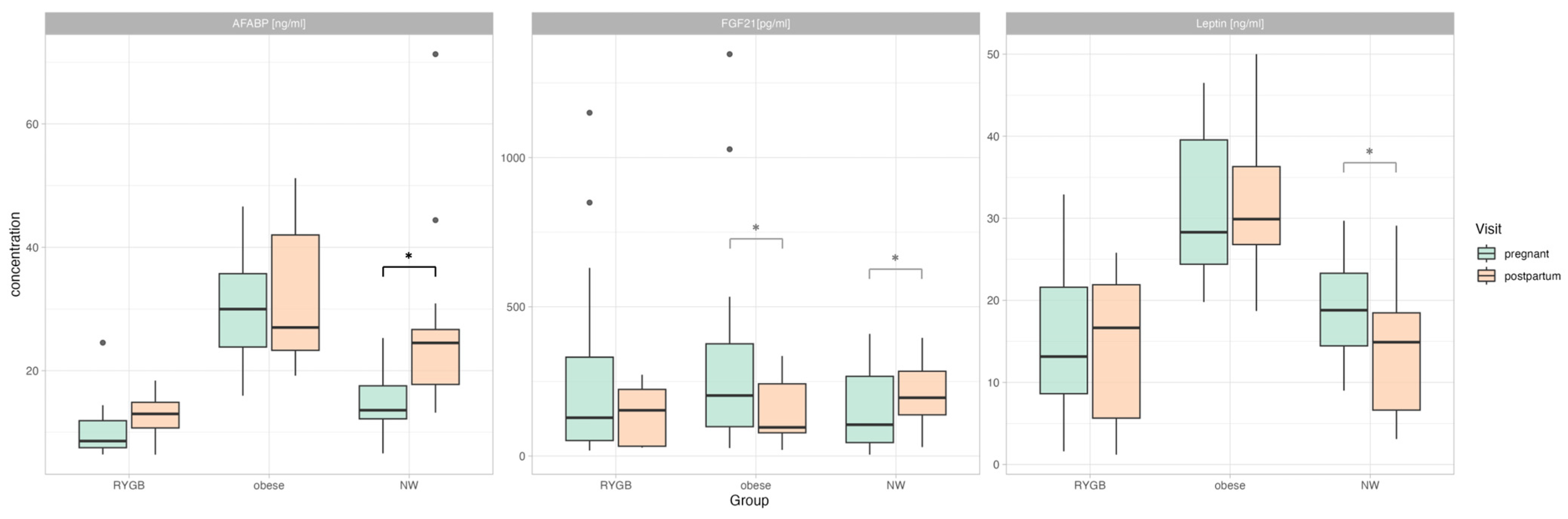
3.2. Differences in Adipokine Levels during Pregnancy
3.3. Longitudinal Changes in Adipokine Levels (Pregnancy vs. Post-Partum)
3.4. Differences in Adipokine Profiles Post-Partum
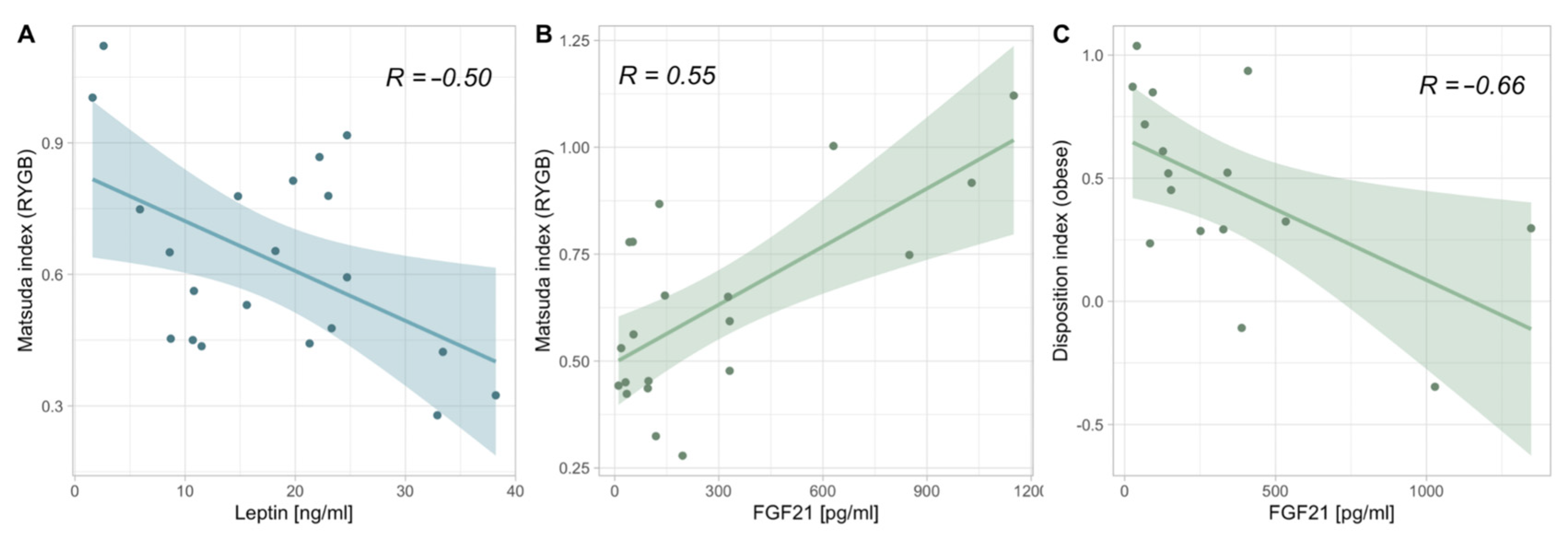
3.5. Correlations between Adipokines and Markers of Glucose Homeostasis
3.6. Correlation Matrix of Adipokines and BIA Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Nguyen, N.T.; Varela, J.E. Bariatric surgery for obesity and metabolic disorders: State of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; D’Alessio, D.A. Effects of glucagon like peptide-1 to mediate glycemic effects of weight loss surgery. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, P.R.; Burguera, B.; Ikramuddin, S.; Cottam, D.; Gourash, W.; Hamad, G.; Eid, G.M.; Mattar, S.; Ramanathan, R.; Barinas-Mitchel, E.; et al. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Surg. 2003, 238, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupoli, R.; Lembo, E.; Rainone, C.; Schiavo, L.; Iannelli, A.; Di Minno, M.N.D.; Capaldo, B. Rate of post-bariatric hypoglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring: A meta-analysis of literature studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göbl, C.S.; Bozkurt, L.; Tura, A.; Leutner, M.; Andrei, L.; Fahr, L.; Husslein, P.; Eppel, W.; Kautzky-Willer, A. Assessment of glucose regulation in pregnancy after gastric bypass surgery. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.A.; El-Ghobary, M.; Soliman, A.; El Sherbiny, M.; Abouelregal, T.E.; Albitar, A.; Abdallah, A.; Mikhail, H.M.S.; Nafea, M.A.; Sultan, A.; et al. Long-Term Changes in Leptin, Chemerin, and Ghrelin Levels Following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Llorens, S.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. An Overview of the Role of Adipokines in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Lui, D.T.W.; Lam, K.S.L. Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein, Cardiovascular Diseases and Mortality. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 589206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieplinger, H.; Dieplinger, B. Afamin—A pleiotropic glycoprotein involved in various disease states. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 446, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, M.; Wagner, L.; Tretter, V. 20 Years of Secretagogin: Exocytosis and Beyond. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deischinger, C.; Harreiter, J.; Leitner, K.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Kautzky-Willer, A. Secretagogin is Related to Insulin Secretion but Unrelated to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Status in Pregnancy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutner, M.; Klimek, P.; Göbl, C.; Bozkurt, L.; Harreiter, J.; Husslein, P.; Eppel, W.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Pacini, G.; Thurner, S.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drives postprandial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in pregnant women with a history of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass operation. Metabolism 2019, 91, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterli, R.; Steinert, R.E.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Peters, T.; Christoffel-Courtin, C.; Gass, M.; Kern, B.; von Fluee, M.; Beglinger, C. Metabolic and hormonal changes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: A randomized, prospective trial. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, L.M.; Beckman, T.R.; Earthman, C.P. Changes in gastrointestinal hormones and leptin after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure: A review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical phase angle and impedance vector analysis--clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, N.; Neovius, M.; Cnattingius, S.; Trolle Lagerros, Y.; Sääf, M.; Granath, F.; Stephansson, O. Perinatal outcomes after bariatric surgery: Nationwide population based matched cohort study. BMJ 2013, 347, f6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazart, J.; Le Guennec, D.; Accoceberry, M.; Lemery, D.; Mulliez, A.; Farigon, N.; Lahaye, C.; Miolanne-Debouit, M.; Boirie, Y. Maternal Nutritional Deficiencies and Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonates at Birth of Women Who Have Undergone Bariatric Surgery. J. Pregnancy 2017, 2017, 4168541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flippo, K.H.; Potthoff, M.J. Metabolic Messengers: FGF21. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lain, K.Y.; Catalano, P.M. Metabolic changes in pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 50, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Romero, E.; Dueñas, A.; Perez Castrillon, J.L. Relation of phase angle tertiles with blood adipocytokines levels, insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in obese women patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.-H. A meta-analysis of maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancy after bariatric surgery. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 130, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harreiter, J.; Schindler, K.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Göbl, C.; Langer, F.; Prager, G.; Gessl, A.; Leutner, M.; Ludvik, B.; Luger, A.; et al. Management of Pregnant Women after Bariatric Surgery. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 4587064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonis, C.; Lorenzini, F.; Bertrand, M.; Parant, O.; Gourdy, P.; Vaurs, C.; Cazals, L.; Ritz, P.; Hanaire, H. Glucose Profiles in Pregnant Women After a Gastric Bypass: Findings from Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, G.; Houseman, E.A.; Kelsey, K.T.; Eaton, C.B.; Buka, S.L.; Loucks, E.B. Adiposity is associated with DNA methylation profile in adipose tissue. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, P.; Sinha, I.; Thorell, A.; Rydén, M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Dahlman, I. The epigenetic signature of subcutaneous fat cells is linked to altered expression of genes implicated in lipid metabolism in obese women. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| RYGB | Obesity | NW | p-Value | Adj. p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | n = 25 | n = 19 | n = 19 | 0.79 1 | 1 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 31.44 (6.98) | 31.37 (4.89) | 30.26 (5.60) | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] * | n = 23 | n = 19 | n = 19 | <0.001 2 | <0.001 2 |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 27.2 (25–32.6) b d | 37.3 (35.9–39) b e | 22.8 (19.75–23.25) d e | ||
| BMR [cal] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 1405.63 (102.83) b | 1581.43 (75.13) b e | 1346 (78.27) e | ||
| Phase angle [°] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 4.84 (0.62) b d | 5.96 (0.5) b | 5.82 (0.57) d | ||
| Body water [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 40.17 (3.93) a d | 43.26 (3.24) a e | 33.14 (3.24) d e | ||
| Lean mass [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 54.86 (5.36) a d | 59.11 (4.43) a e | 45.27 (4.42) d e | ||
| ECM [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 3 | <0.001 3 |
| Mean (range) | 29.72 (23.99–37.76) d | 28.44 (24.38–34.67) e | 22.03 (16.71–26.49) b e | ||
| BCM [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 24.98 (3.26) b | 30.54 (2.39) b e | 23.07 (2.48) e | ||
| ECM/BCM | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 1.21 (0.2) b d | 0.94 (0.1) b | 0.97 (0.11) d | ||
| Cell fraction [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Mean (SD) | 45.52 (3.79) b d | 51.69 (2.54) b | 50.98 (2.86) d | ||
| Body fat [%] | n = 16 | n = 14 | n = 15 | <0.001 3 | <0.001 3 |
| Mean (range) | 30.48 (19.68–53.58) b c | 51.64 (39.9–70.47) b e | 23.82 (16.41–35.73) c e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellach, L.; Gard, L.-I.; Lindner, S.D.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Klimek, P.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Leutner, M. The Interplay of Adipokines, Body Composition and Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Women with a History of RYGB Operation. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112498
Bellach L, Gard L-I, Lindner SD, Baumgartner-Parzer S, Klimek P, Kautzky-Willer A, Leutner M. The Interplay of Adipokines, Body Composition and Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Women with a History of RYGB Operation. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112498
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellach, Luise, Liliana-Imi Gard, Simon David Lindner, Sabina Baumgartner-Parzer, Peter Klimek, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, and Michael Leutner. 2023. "The Interplay of Adipokines, Body Composition and Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Women with a History of RYGB Operation" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112498
APA StyleBellach, L., Gard, L.-I., Lindner, S. D., Baumgartner-Parzer, S., Klimek, P., Kautzky-Willer, A., & Leutner, M. (2023). The Interplay of Adipokines, Body Composition and Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Women with a History of RYGB Operation. Nutrients, 15(11), 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112498