Association among Olfactory Function, Lifestyle and BMI in Female and Male Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Assessment of Physical, Social and Cognitive Activity
2.3. Olfactory Sensitivity Sssessment
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
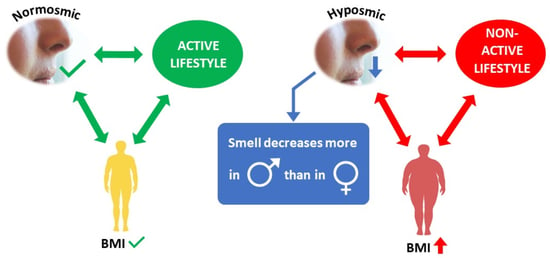
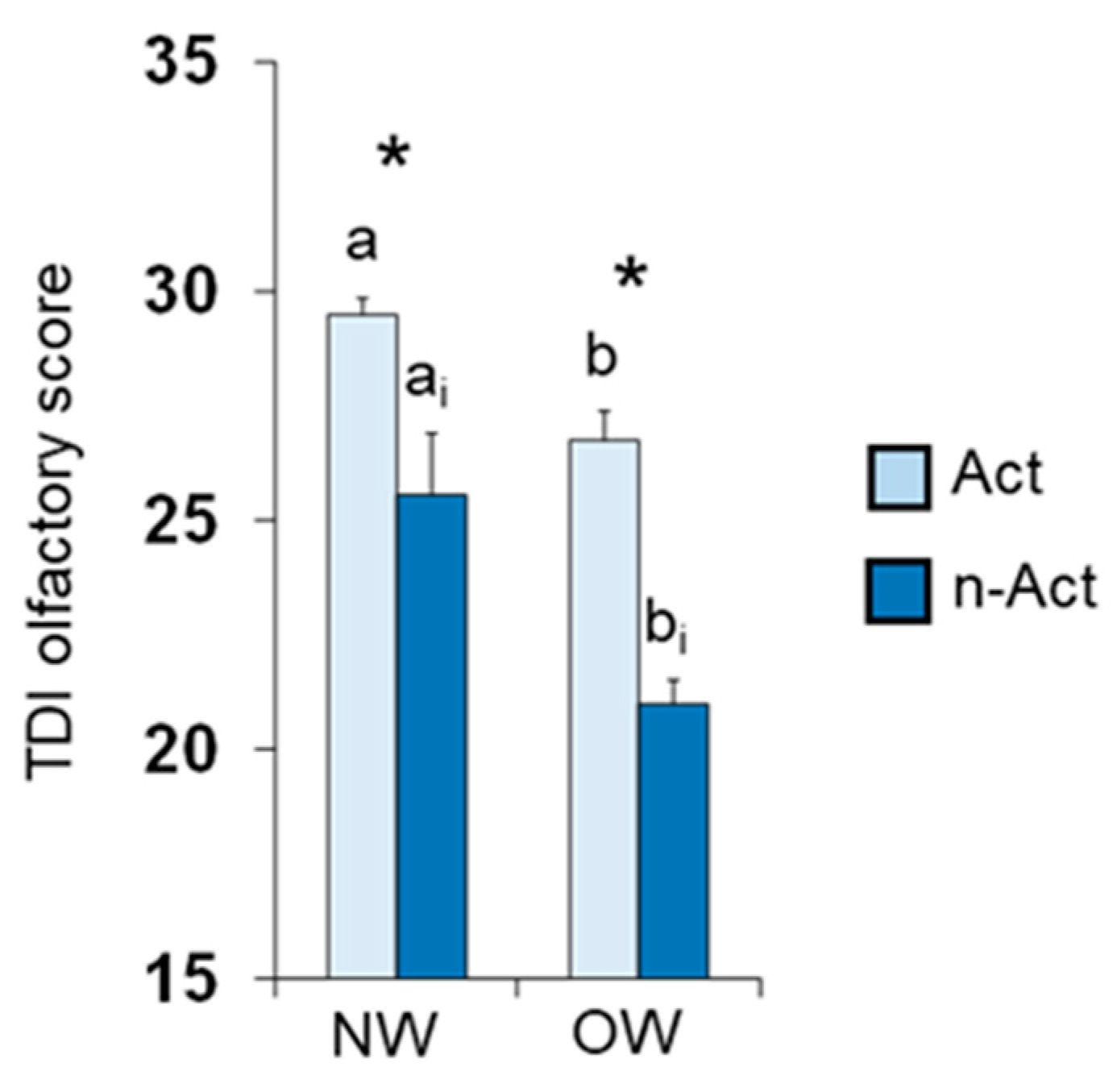
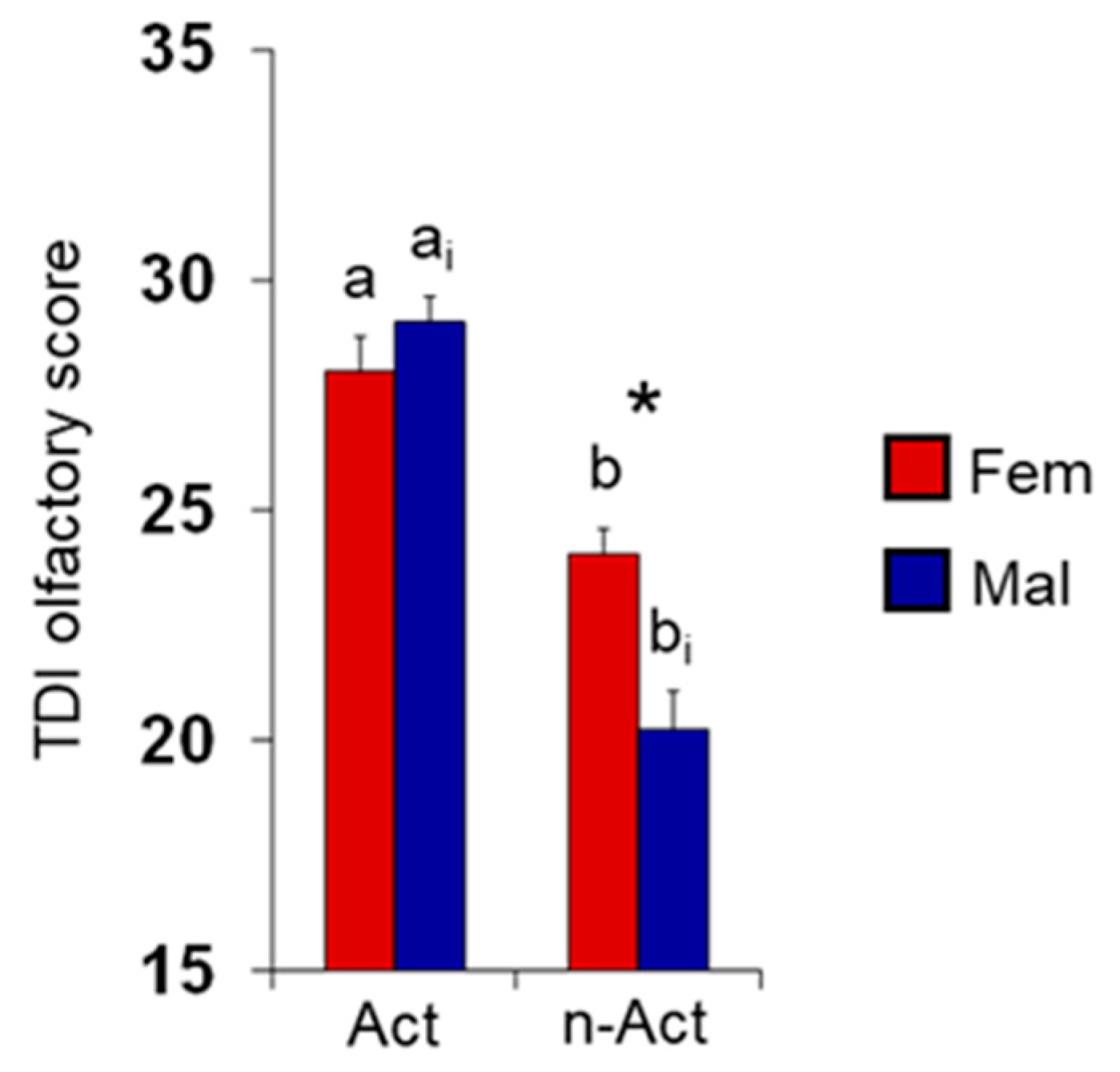
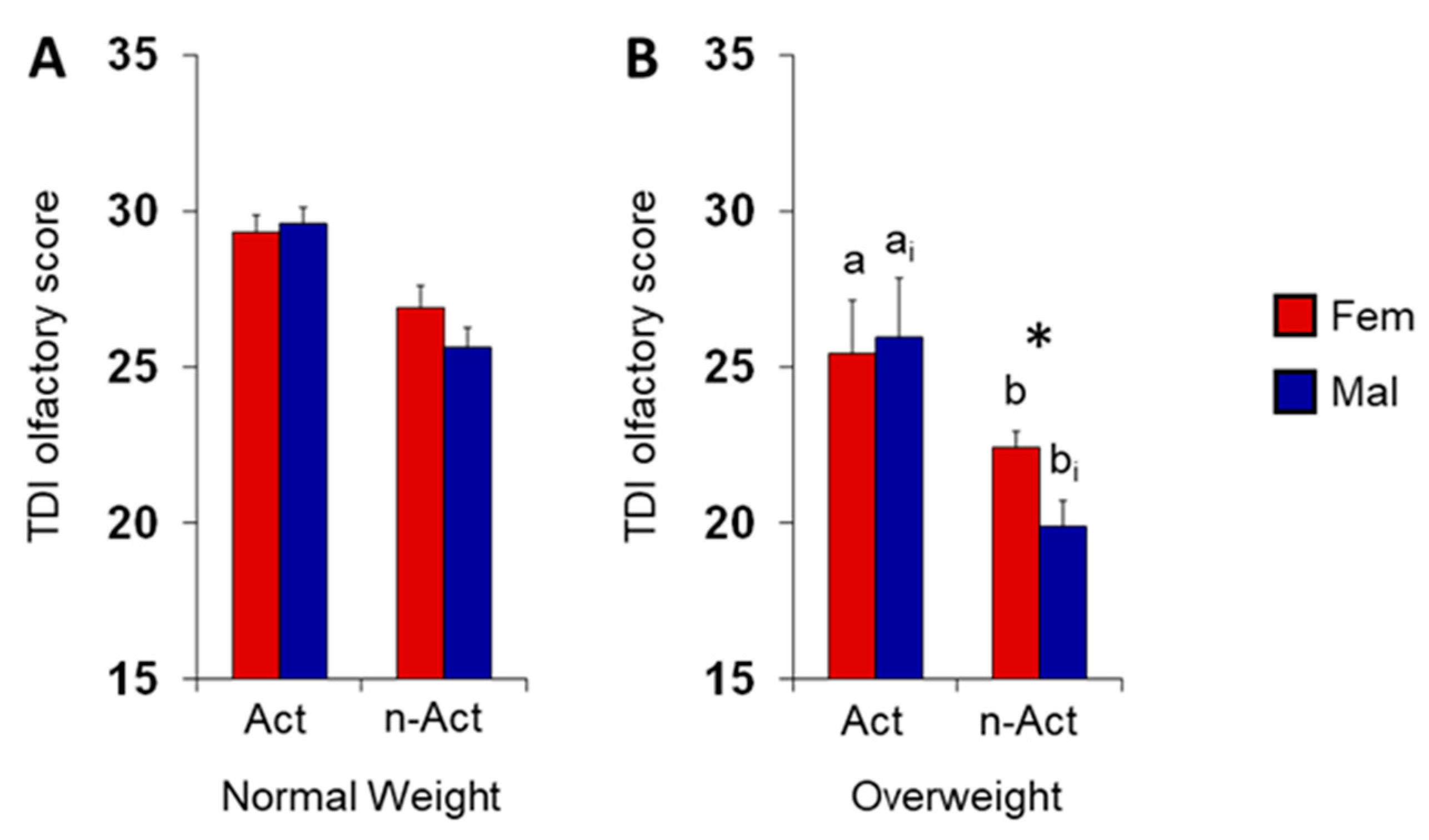
3.1. Olfactory Scores and BMI in Female and Male Actine or Non-Active Elderly Subjects
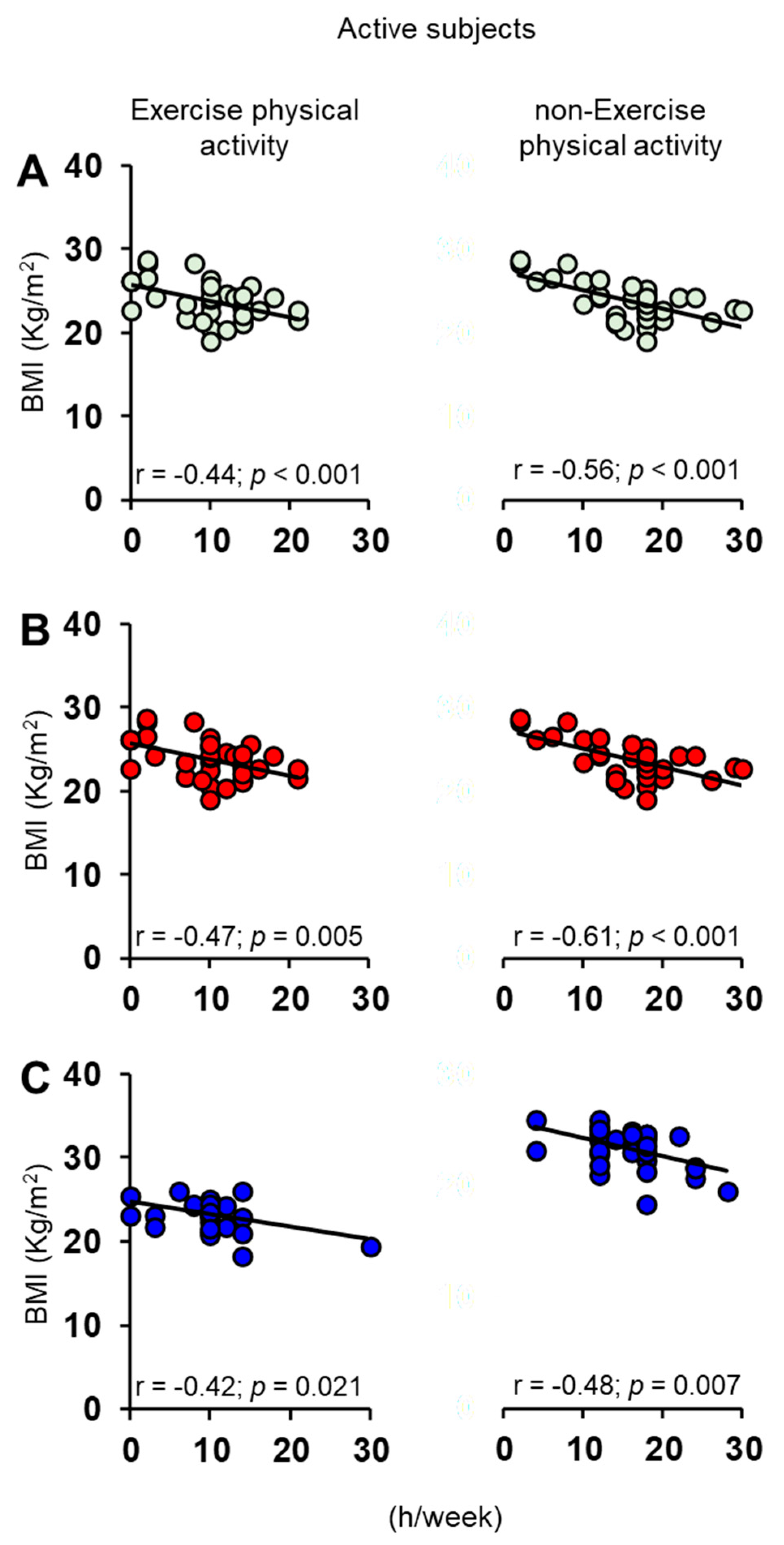
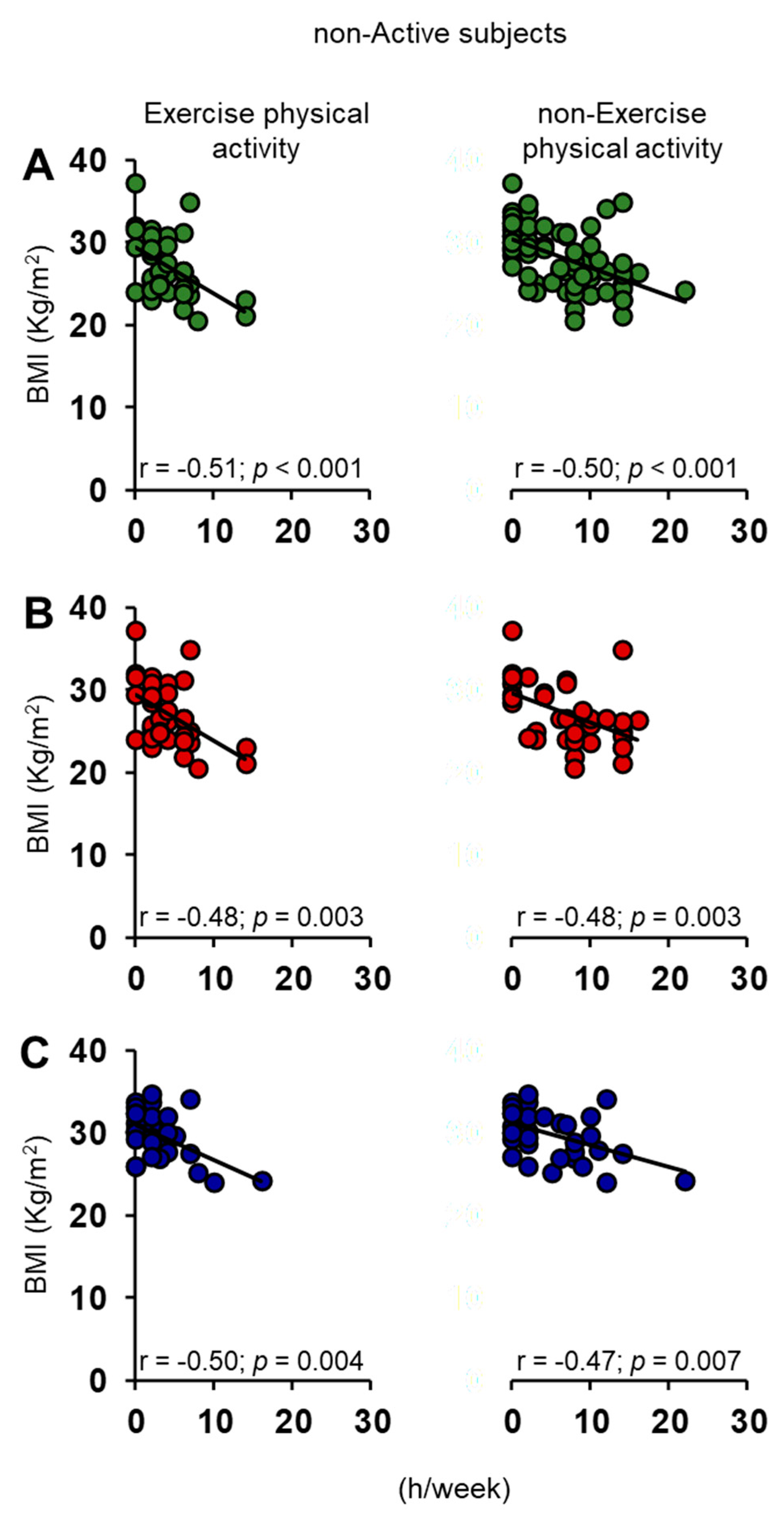
3.2. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Franco-Lira, M.; Henríquez-Roldán, C.; Osnaya, N.; González-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; Herritt, L.; Brooks, D.; Keefe, S.; et al. Urban air pollution: Influences on olfactory function and pathology in exposed children and young adults. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 62, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crnjar, R.; Solari, P.; Sollai, G. The Human Nose as a Chemical Sensor in the Perception of Coffee Aroma: Individual Variability. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Zhuang, H.; Chi, Q.; Vosshall, L.B.; Matsunami, H. Genetic variation in a human odorant receptor alters odour perception. Nature 2007, 449, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Crnjar, R.; Sollai, G. Olfactory Sensitivity Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Polymorphism in the Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels Kv1.3. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Hummel, T.; Crnjar, R.; Sollai, G. Effect of the rs2890498 polymorphism of the OBPIIa gene on the human ability to smell single molecules. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 402, 113127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menashe, I.; Abaffy, T.; Hasin, Y.; Goshen, S.; Yahalom, V.; Luetje, C.W.; Lancet, D. Genetic elucidation of human hyperosmia to isovaleric acid. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollai, G.; Melis, M.; Magri, S.; Usai, P.; Hummel, T.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Crnjar, R. Association between the rs2590498 polymorphism of Odorant Binding Protein (OBPIIa) gene and olfactory performance in healthy subjects. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 372, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollai, G.; Melis, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Crnjar, R. A polymorphism in the human gene encoding OBPIIa affects the perceived intensity of smelled odors. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 427, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollai, G.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Usai, P.; Hummel, T.; Crnjar, R. Association between human olfactory performance and ability to detect single compounds in complex chemical mixtures. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 217, 112820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokowska, A.; Sorokowski, P.; Frackowiak, T. Determinants of human olfactory performance: A cross-cultural study. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokowska, A.; Sorokowski, P.; Hummel, T.; Huanca, T. Olfaction and environment: Tsimane’ of Bolivian rainforest have lower threshold of odor detection than industrialized German people. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, W.S.; Stevens, J.C. Uniformity of olfactory loss in aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 561, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L.; Shaman, P.; Applebaum, S.L.; Giberson, R.; Siksorski, L.; Rosenberg, L. Smell identification ability: Changes with age. Science 1984, 226, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Han, D.H.; Kim, K.S. The sniffing bead system, an olfactory dysfunction screening tool for geriatric subjects: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attems, J.; Walker, L.; Jellinger, K.A. Olfaction and Aging: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2015, 61, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L.; Kamath, V. The influences of age on olfaction: A review. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiberling, K.A.; Conley, D.B. Aging and olfactory and taste function. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 37, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesveldt, S.; Verbaan, D.; Knol, D.L.; Visser, M.; van Rooden, S.M.; van Hilten, J.J.; Berendse, H.W. A comparative study of odor identification and odor discrimination deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disord. 2008, 23, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.; Semb, H.; Winblad, B.; Amberla, K.; Wahlund, L.O.; Bäckman, L. Odor identification in normal aging and early Alzheimer’s disease: Effects of retrieval support. Neuropsychology 1999, 13, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizako, M.; Makizako, H.; Doi, T.; Uemura, K.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Miyaguchi, H.; Shimada, H. Olfactory identification and cognitive performance in community-dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, C.; Shoenfeld, N.; Agmon-Levin, N.; de Carolis, C.; Perricone, R.; Shoenfeld, Y. Smell and autoimmunity: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, S.; Reindl, W.; Dempfle, A.; Schuster, A.; Wolf, P.; Hundt, W.; Huber, W. Smell and taste in inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velluzzi, F.; Deledda, A.; Lombardo, M.; Fosci, M.; Crnjar, R.; Grossi, E.; Sollai, G. Application of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) to Elucidate the Connections among Smell, Obesity with Related Metabolic Alterations, and Eating Habit in Patients with Weight Excess. Metabolites 2023, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croy, I.; Nordin, S.; Hummel, T. Olfactory Disorders and Quality of Life—An Updated Review. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Nordin, S. Olfactory disorders and their consequences for quality of life. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2005, 125, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.M.; Wroblewski, K.E.; Kern, D.W.; Schumm, L.P.; McClintock, M.K. Olfactory dysfunction predicts 5-year mortality in older adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesveldt, S.; Parma, V. The importance of the olfactory system in human well-being, through nutrition and social behavior. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, V.B.; Backstrand, J.R.; Ferris, A.M. Olfactory dysfunction and related nutritional risk in free-living, elderly women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1995, 95, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Boyle, P.A.; Yu, L.; Shah, R.C.; Wilson, R.S.; Bennett, D.A. Total daily physical activity and the risk of AD and cognitive decline in older adults. Neurology 2012, 78, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotman, C.W.; Berchtold, N.C.; Christie, L.A. Exercise builds brain health: Key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croy, I.; Symmank, A.; Schellong, J.; Hummel, C.; Gerber, J.; Joraschky, P.; Hummel, T. Olfaction as a marker for depression in humans. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 160, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, O.; De Laet, C.; Peeters, A.; Jonker, J.; Mackenbach, J.; Nusselder, W. Effects of Physical Activity on Life Expectancy With Cardiovascular Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Windon, M.J.; Lin, S.Y. The association between diabetes and olfactory impairment in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, G.W.; Petrovitch, H.; Abbott, R.D.; Tanner, C.M.; Popper, J.; Masaki, K.; Launer, L.; White, L.R. Association of olfactory dysfunction with risk for future Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A.; Arnold, S.E.; Tang, Y.; Boyle, P.A.; Bennett, D.A. Olfactory Identification and Incidence of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Age. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollai, G.; Crnjar, R. Age-Related Olfactory Decline Is Associated With Levels of Exercise and Non-exercise Physical Activities. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 695115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, D.W.; Wroblewski, K.E.; Schumm, L.P.; Pinto, J.M.; Chen, R.C.; McClintock, M.K. Olfactory Function in Wave 2 of the National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project. J. Gerontol. Ser. B 2014, 69, S134–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokowska, A.; Schriever, V.A.; Gudziol, V.; Hummel, C.; Hähner, A.; Iannilli, E.; Sinding, C.; Aziz, M.; Seo, H.S.; Negoias, S.; et al. Changes of olfactory abilities in relation to age: Odor identification in more than 1400 people aged 4 to 80 years. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokowski, P.; Karwowski, M.; Misiak, M.; Marczak, M.K.; Dziekan, M.; Hummel, T.; Sorokowska, A. Sex Differences in Human Olfaction: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Sekinger, B.; Wolf, S.R.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. ‘Sniffin’ sticks’: Olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Kobal, G.; Gudziol, H.; Mackay-Sim, A. Normative data for the “Sniffin’ Sticks” including tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds: An upgrade based on a group of more than 3000 subjects. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, G.; Erlacher, B.; Aydinkoc-Tuzcu, K.; Liu, D.T.; Pablik, E.; Niebauer, V.; Koenighofer, M.; Renner, B.; Mueller, C.A. Body-Mass-Index Associated Differences in Ortho- and Retronasal Olfactory Function and the Individual Significance of Olfaction in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palouzier-Paulignan, B.; Lacroix, M.C.; Aimé, P.; Baly, C.; Caillol, M.; Congar, P.; Julliard, A.K.; Tucker, K.; Fadool, D.A. Olfaction under metabolic influences. Chem. Senses 2012, 37, 769–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford, L.D.; Whittle, A. Obese individuals have higher preference and sensitivity to odor of chocolate. Chem. Senses 2015, 40, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J. An initial evaluation of the functions of human olfaction. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velluzzi, F.; Deledda, A.; Onida, M.; Loviselli, A.; Crnjar, R.; Sollai, G. Relationship between Olfactory Function and BMI in Normal Weight Healthy Subjects and Patients with Overweight or Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manesse, C.; Ferdenzi, C.; Sabri, M.; Bessy, M.; Rouby, C.; Faure, F.; Bellil, D.; Jomain, S.; Landis, B.N.; Hugentobler, M.; et al. Dysosmia-Associated Changes in Eating Behavior. Chemosens. Percept. 2017, 10, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Coutts, D.; Wang, T.; Cakmak, Y.O. Systematic review of olfactory shifts related to obesity. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwend, O.; Beroud, J.; Vincis, R.; Rodriguez, I.; Carleton, A. Dense encoding of natural odorants by ensembles of sparsely activated neurons in the olfactory bulb. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliard, A.K.; Al Koborssy, D.; Fadool, D.A.; Palouzier-Paulignan, B. Nutrient Sensing: Another Chemosensitivity of the Olfactory System. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirotin, Y.B.; Shusterman, R.; Rinberg, D. Neural Coding of Perceived Odor Intensity. eNeuro 2015, 2, e0083-15.2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Tang, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, A. Leptin modulates olfactory discrimination and neural activity in the olfactory bulb. Acta Physiol. 2019, 227, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Weyer, C.; Tataranni, P.A.; Devanarayan, V.; Ravussin, E.; Heiman, M.L. Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 2001, 50, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, E.E.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, G.E. The essence of appetite: Does olfactory receptor variation play a role? J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Aranda, F.; Agüera, Z.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Alcaide-Torres, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Giner-Bartolomé, C.; Baños, R.M.; Botella, C.; Cebolla, A.; et al. Smell-taste dysfunctions in extreme weight/eating conditions: Analysis of hormonal and psychological interactions. Endocrine 2016, 51, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, J.C.; Alcaide, J.; Santiago-Fernandez, C.; Roca-Rodriguez, M.M.; Aguera, Z.; Baños, R.; Botella, C.; de la Torre, R.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Fruhbeck, G.; et al. An increase in visceral fat is associated with a decrease in the taste and olfactory capacity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollai, G.; Melis, M.; Mastinu, M.; Paduano, D.; Chicco, F.; Magri, S.; Usai, P.; Hummel, T.; Barbarossa, I.T.; Crnjar, R. Olfactory Function in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Is Associated with Their Body Mass Index and Polymorphism in the Odor Binding-Protein (OBPIIa) Gene. Nutrients 2021, 13, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M.L.; Schulkin, J. Anticipatory physiological regulation in feeding biology: Cephalic phase responses. Appetite 2008, 50, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egecioglu, E.; Skibicka, K.P.; Hansson, C.; Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Friberg, P.A.; Jerlhag, E.; Engel, J.A.; Dickson, S.L. Hedonic and incentive signals for body weight control. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2011, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, E.; Graaf, C.; Boesveldt, S. Food preferences and intake in a population of Dutch individuals with self-reported smell loss: An online survey. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 79, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Schreder, T.; Kleemann, A.M.; Schöpf, V.; Kopietz, R.; Anzinger, A.; Demmel, M.; Linn, J.; Kettenmann, B.; Wiesmann, M. Olfactory detection thresholds and pleasantness of a food-related and a non-food odour in hunger and satiety. Rhinology 2009, 47, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stafford, L.D. Olfactory Specific Satiety depends on degree of association between odour and food. Appetite 2016, 98, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesveldt, S.; Postma, E.M.; Boak, D.; Welge-Luessen, A.; Schöpf, V.; Mainland, J.D.; Martens, J.; Ngai, J.; Duffy, V.B. Anosmia-A Clinical Review. Chem. Senses 2017, 42, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmel, A.F.; Quint, C.; Schickinger-Fischer, B.; Klimek, L.; Stoller, E.; Hummel, T. Characteristics of olfactory disorders in relation to major causes of olfactory loss. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 128, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, A.B.; Bowen, J.D.; Rajaram, L.; McCormick, W.C.; McCurry, S.M.; Schellenberg, G.D.; Larson, E.B. Impaired olfaction as a marker for cognitive decline: Interaction with apolipoprotein E epsilon4 status. Neurology 1999, 53, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, M.; Sabia, S.; Batty, G.D.; Shipley, M.J.; Tabák, A.G.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Kivimaki, M. Physical activity and inflammatory markers over 10 years: Follow-up in men and women from the Whitehall II cohort study. Circulation 2012, 126, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Arnold, S.E.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Olfactory impairment in presymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
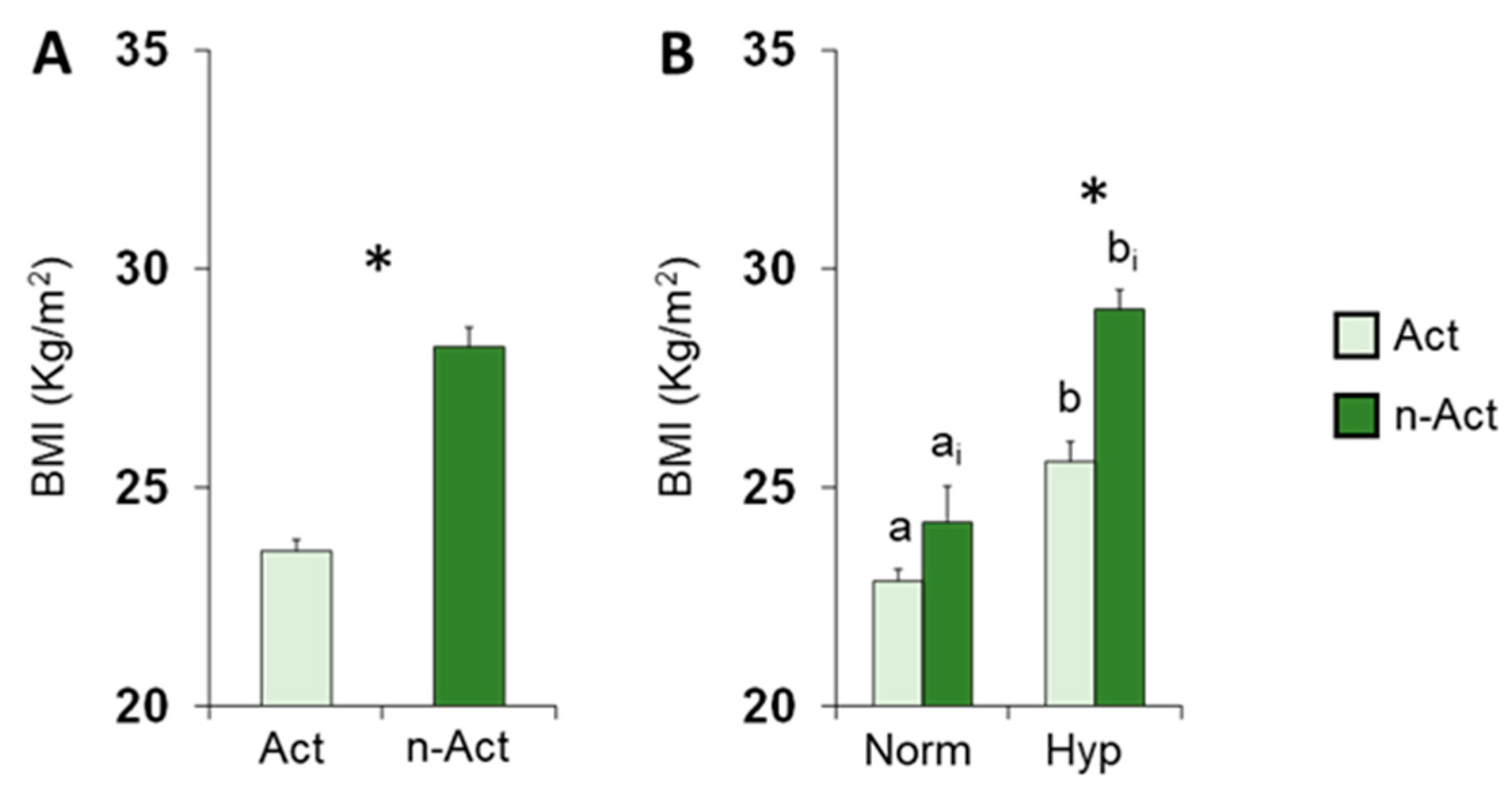
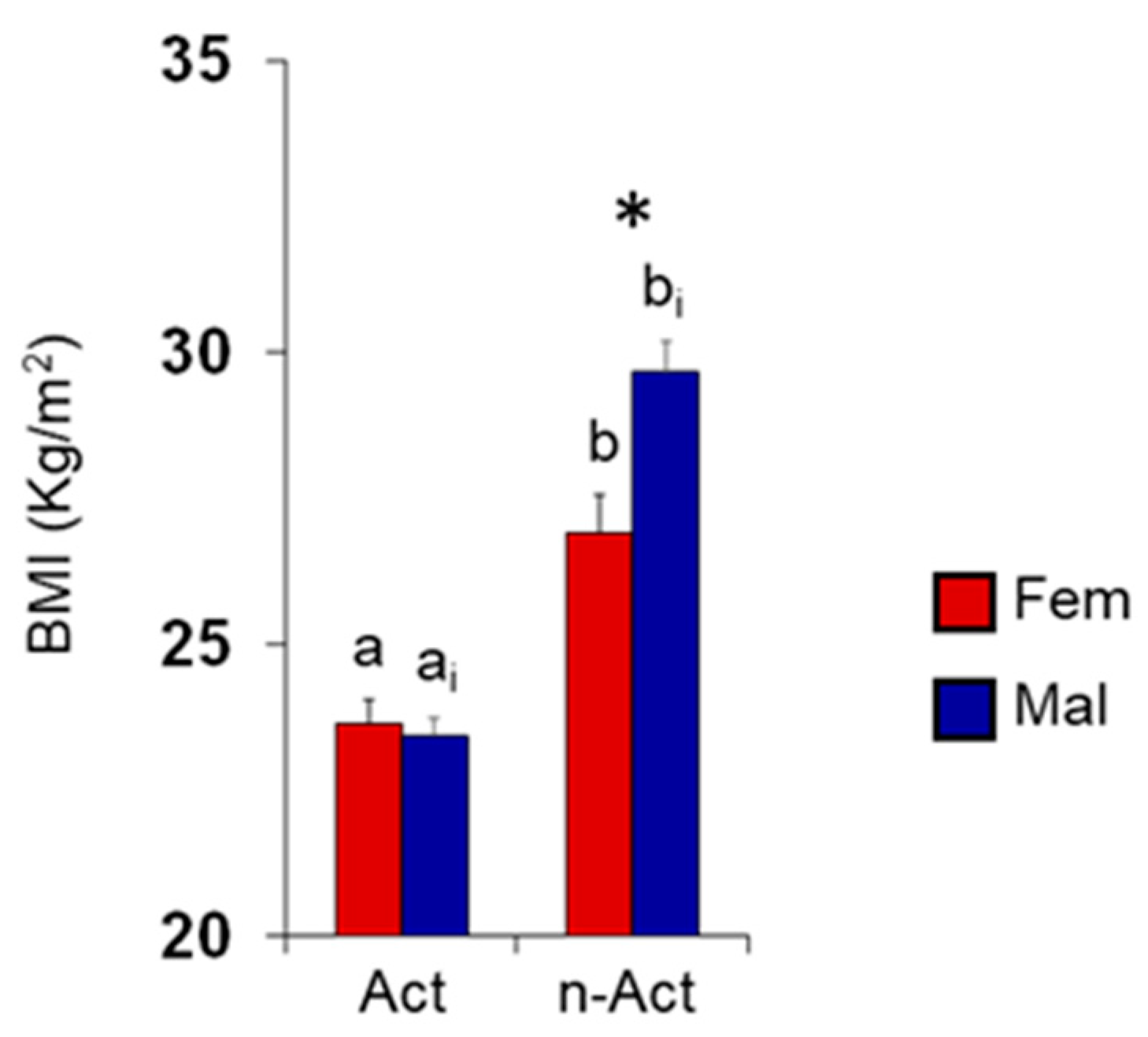
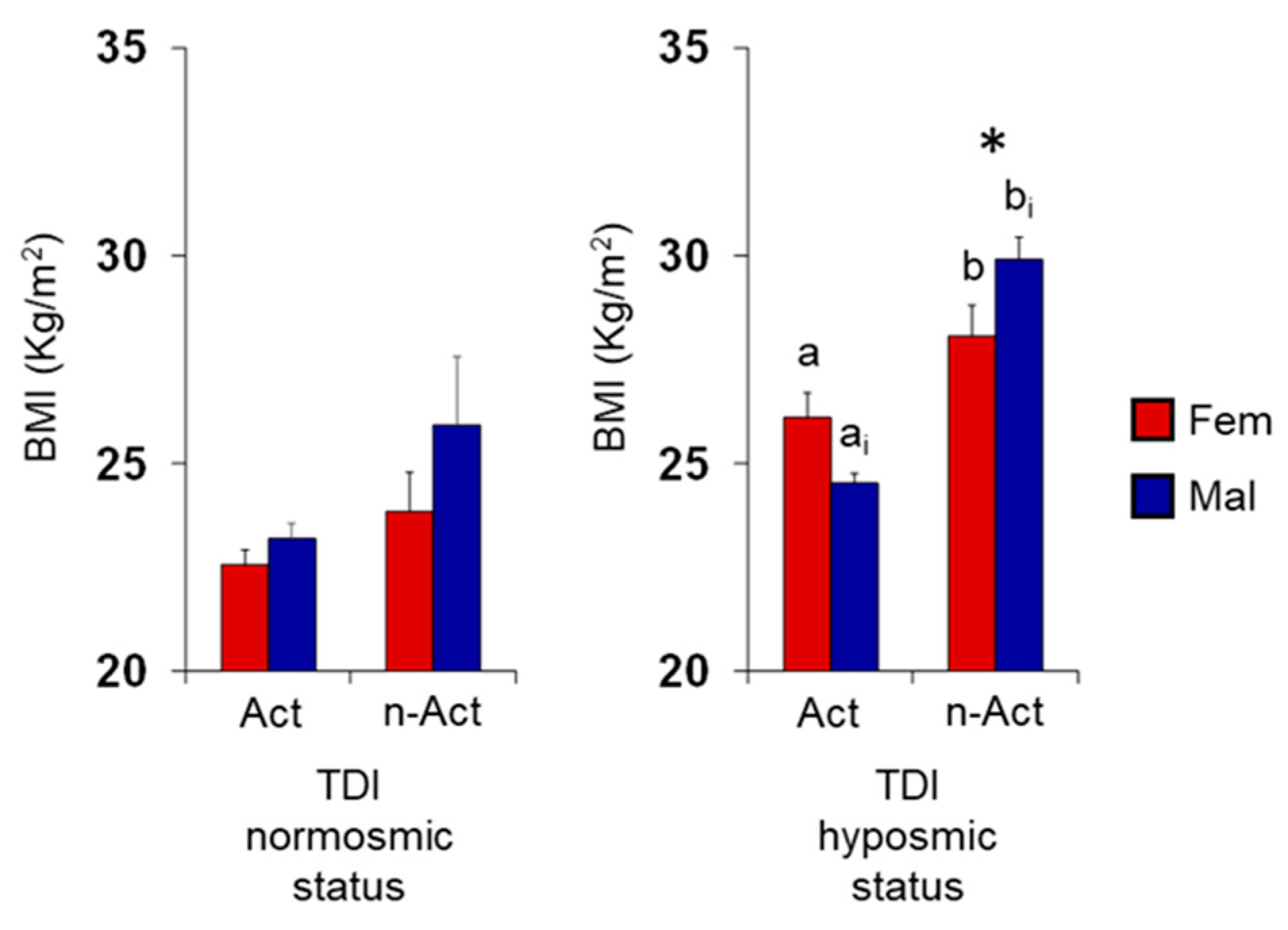
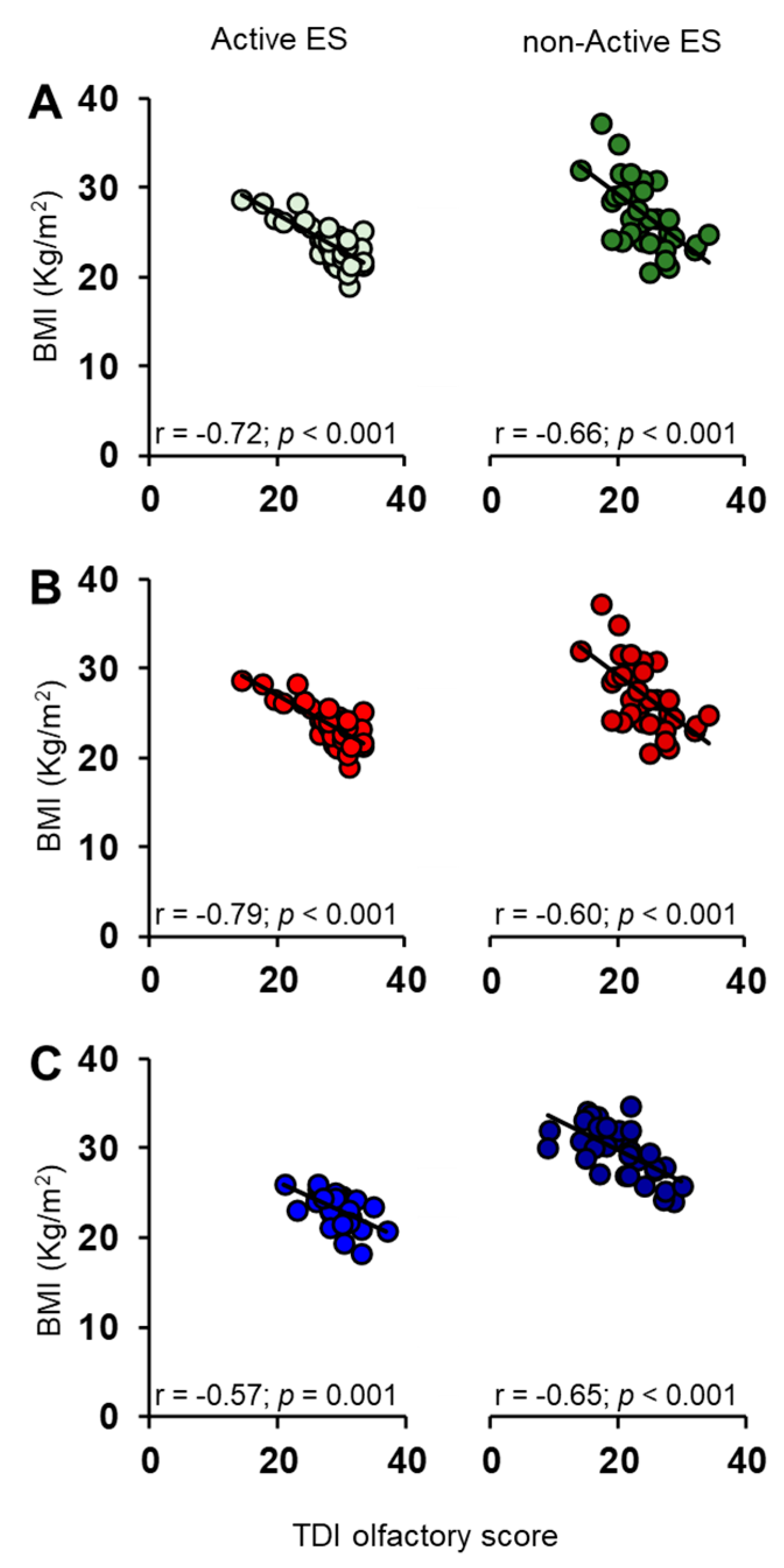
| Panel | Active ES | n-Active ES |
|---|---|---|
| n | 65 | 68 |
| Age (years) | 67.7 ± 1.06 | 70.5 ± 1.08 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 23.6 ± 0.27 | 28.2 ± 0.46 |
| TDI olfactory score | 28.5 ± 0.48 | 22.3 ± 0.53 |
| Exercise activities | 10.1 ± 0.67 | 3.56 ± 0.42 |
| non-Exercise activities | 15.9 ± 0.75 | 6.46 ± 0.65 |
| ES with co-morbidities | ||
| Hypertension | 6 | 5 |
| Hyperglycemia | 4 | 3 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 2 | 2 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sollai, G.; Crnjar, R. Association among Olfactory Function, Lifestyle and BMI in Female and Male Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112492
Sollai G, Crnjar R. Association among Olfactory Function, Lifestyle and BMI in Female and Male Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSollai, Giorgia, and Roberto Crnjar. 2023. "Association among Olfactory Function, Lifestyle and BMI in Female and Male Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112492
APA StyleSollai, G., & Crnjar, R. (2023). Association among Olfactory Function, Lifestyle and BMI in Female and Male Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 15(11), 2492. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112492