The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
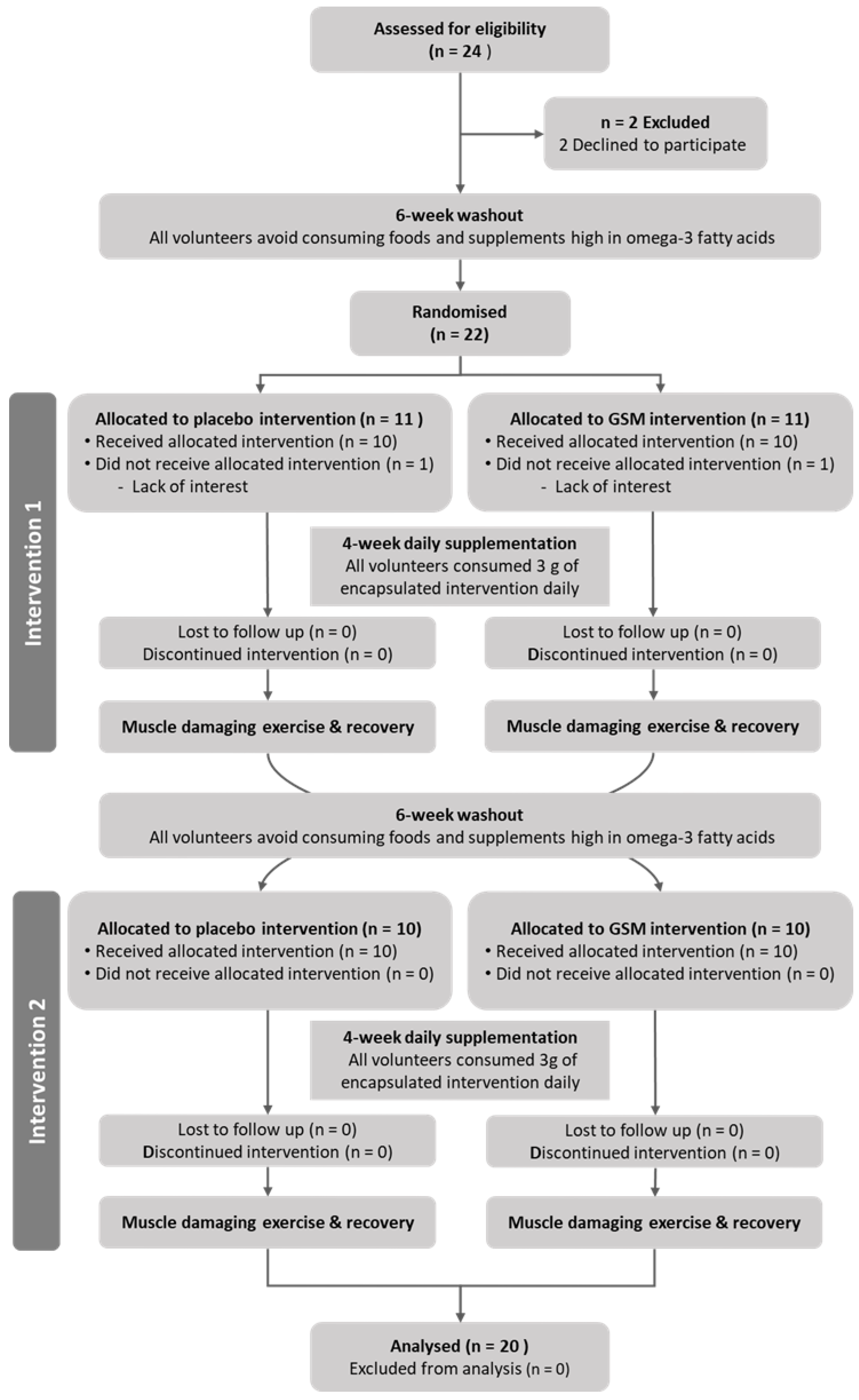
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Dietary Intervention
2.4. Exercise Protocol
2.5. Muscle Function Assessment
2.6. Subjective Pain Assessments
2.7. Blood Sampling
2.8. Creatine Kinase
2.9. Immune Measures
2.9.1. Plasma Cytokine
2.9.2. Immune Cell Phenotyping
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics of Participants
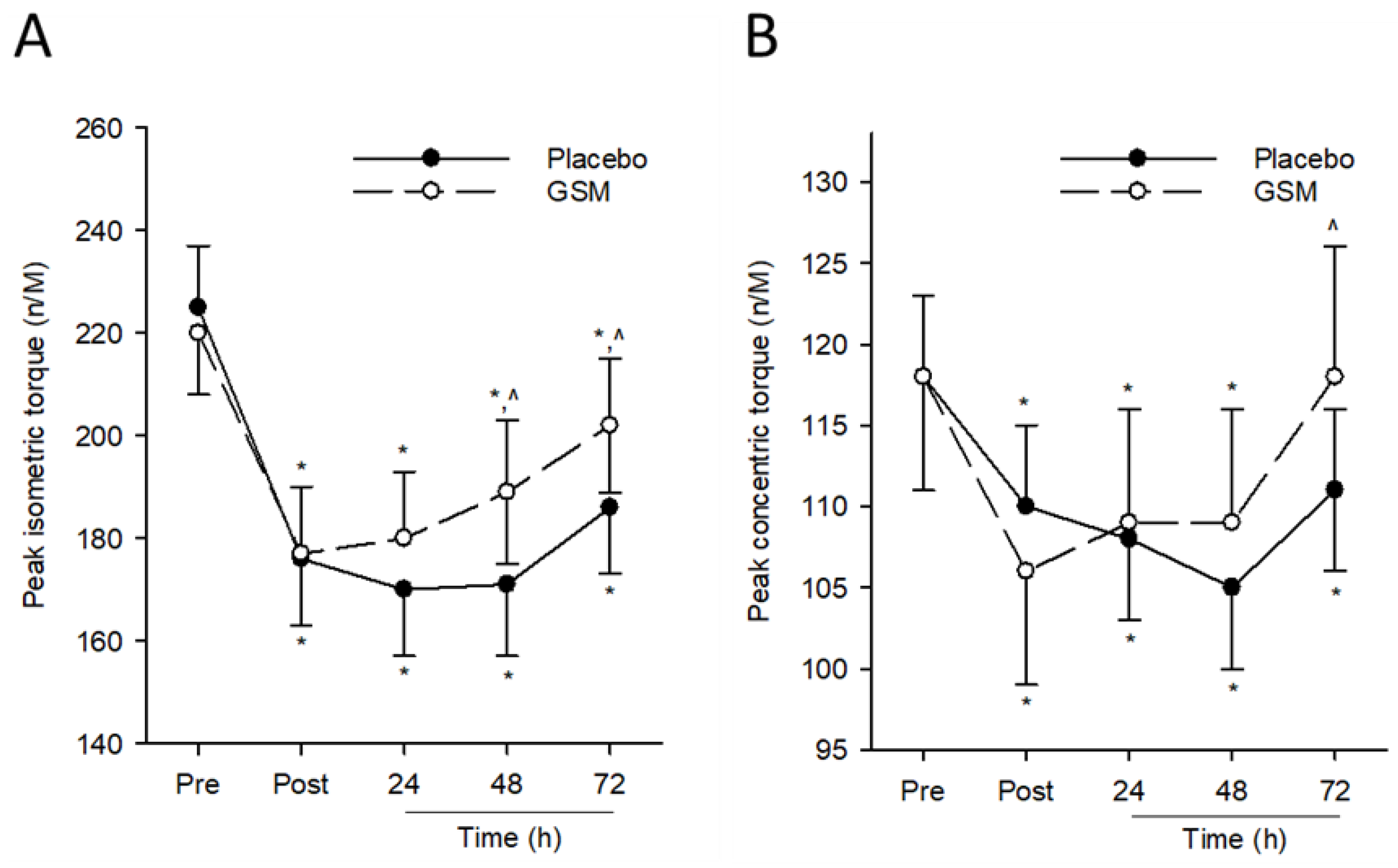
3.2. Muscle Function
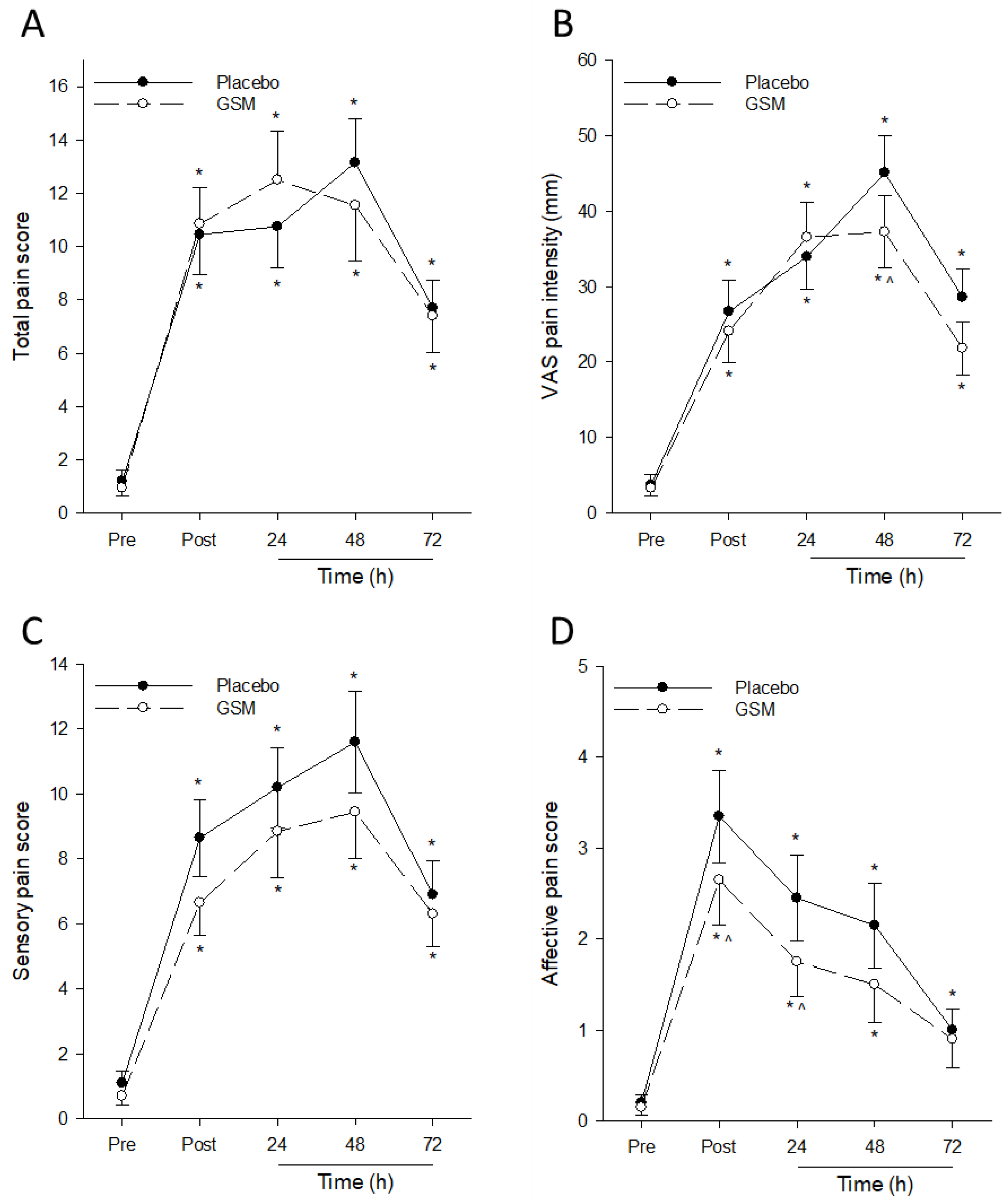
3.3. Subjective Pain Assessments
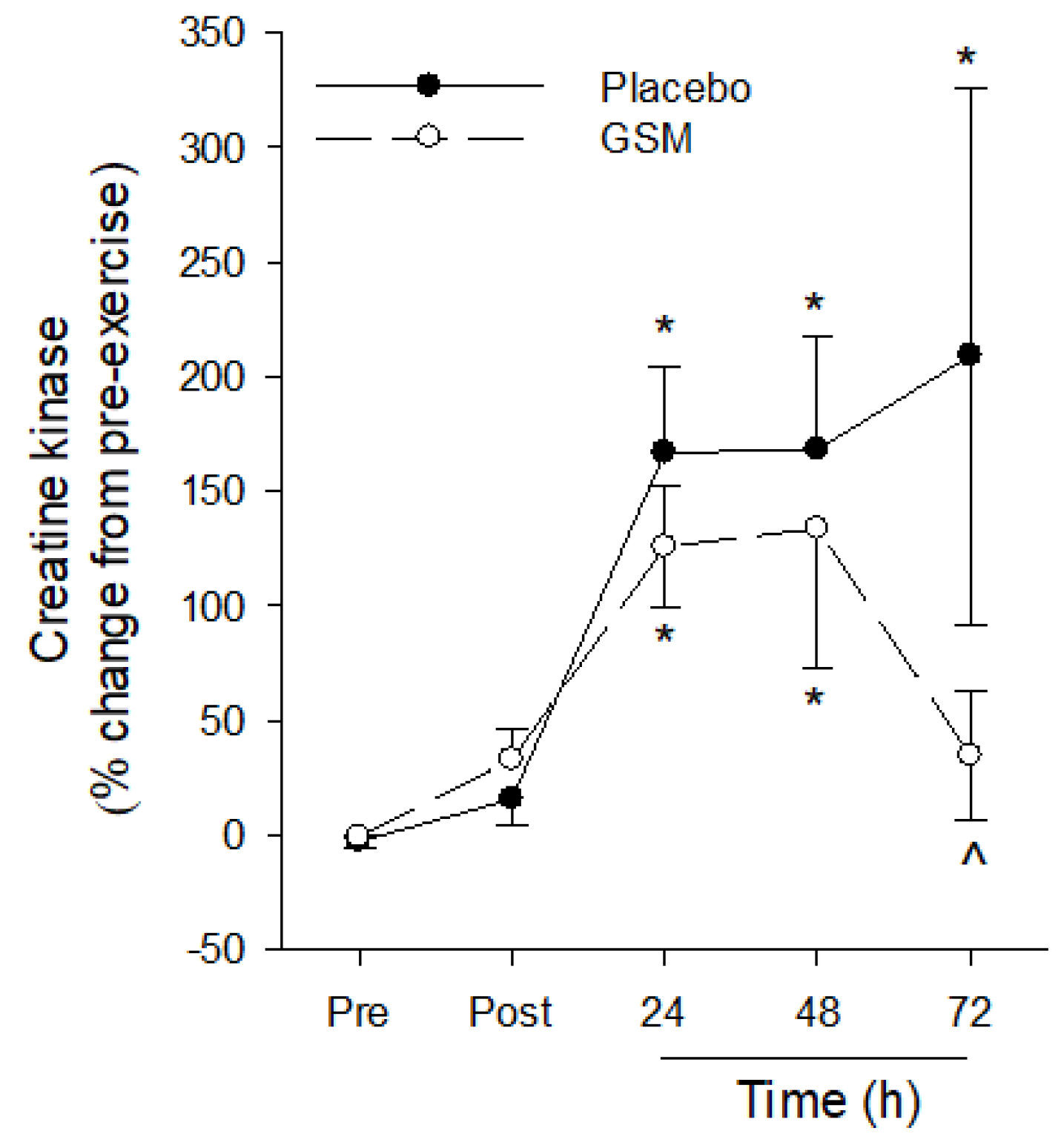
3.4. Creatine Kinase
3.5. Immune Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newham, D.J.; Jones, D.A.; Edwards, R.H.T. Large Delayed Plasma Creatine-Kinase Changes after Stepping Exercise. Muscle Nerve 1983, 6, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamurtas, A.Z.; Theocharis, V.; Tofas, T.; Tsiokanos, A.; Yfanti, C.; Paschalis, V.; Koutedakis, Y.; Nosaka, K. Comparison between leg and arm eccentric exercises of the same relative intensity on indices of muscle damage. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 95, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A.J. Time course of muscle soreness following different types of exercise. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2001, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheung, K.; Hume, P.A.; Maxwell, L. Delayed onset muscle soreness—Treatment strategies and performance factors. Sport. Med. 2003, 33, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friden, J.; Sjöström, M.; Ekblom, B. A morphological study of delayed muscle soreness. Experientia 1981, 37, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.L.; Ingalls, C.P.; Lowe, D.A.; Armstrong, R. Excitation-contraction uncoupling: Major role in contraction-induced muscle injury. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Tidball, J.G.; Villalta, S.A. Regulatory interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1173–R1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rickards, L.; Lynn, A.; Harrop, D.; Barker, M.E.; Russell, M.; Ranchordas, M.K. Effect of Polyphenol-Rich Foods, Juices, and Concentrates on Recovery from Exercise Induced Muscle Damage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Escobar, K.A.; Johnson, K.E.; Stratton, M.T.; Moriarty, T.; Kerksick, C.M.; Mangine, G.T.; Holmes, A.J.; Lee, M.T.; Endito, M.R.; et al. Impact of Varying Dosages of Fish Oil on Recovery and Soreness Following Eccentric Exercise. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartibian, B.; Maleki, B.H.; Abbasi, A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation Attenuates Inflammatory Markers After Eccentric Exercise in Untrained Men. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2011, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubuchi, A.; Katsumoto, S.; Tsuboi, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Nomura, Y.; Higashi, K.; Miyata, S. Isolation and structural characterization of bioactive glycosaminoglycans from the green-lipped mussel Perna canaliculus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 612, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Tian, H. Changes in proximate composition, lipid class and fatty acid profile in Greenshell mussels (Perna canaliculus) over an annual cycle. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Abshirini, M.; Wolber, F.M.; Tuterangiwhiu, T.R.; Kruger, M.C. Greenshell Mussel Products: A Comprehensive Review of Sustainability, Traditional Use, and Efficacy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickleborough, T.D.; Vaughn, C.L.; Shei, R.J.; Davis, E.M.; Wilhite, D.P. Marine lipid fraction PCSO-524 (lyprinol/omega XL) of the New Zealand green lipped mussel attenuates hyperpnea-induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gibson, S.L.M.; Gibson, R.G. The treatment of arthritis with a lipid extract of Perna canaliculus: A randomized trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 1998, 6, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, J.D.; Sarris, J.; Scholey, A.; Silberstein, R.; Downey, L.A.; Stough, C. Reduced inattention and hyperactivity and improved cognition after marine oil extract (PCSO-524®) supplementation in children and adolescents with clinical and subclinical symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mickleborough, T.D.; A Sinex, J.; Platt, D.; Chapman, R.F.; Hirt, M. The effects PCSO-524®, a patented marine oil lipid and omega-3 PUFA blend derived from the New Zealand green lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus), on indirect markers of muscle damage and inflammation after muscle damaging exercise in untrained men: A randomized, placebo controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2015, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barenie, M.J.; Freemas, J.A.; Baranauskas, M.N.; Goss, C.S.; Freeman, K.L.; Chen, X.; Dickinson, S.L.; Fly, A.D.; Kawata, K.; Chapman, R.F. Effectiveness of a combined New Zealand green-lipped mussel and Antarctic krill oil supplement on markers of exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation in untrained men. J. Diet. Suppl. 2022, 19, 184–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, K.; Telford, R.D.; Cunningham, R.B. Marine oil dietary supplementation reduces delayed onset muscle soreness after a 30 km run. Open Access J. Sport. Med. 2013, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Doggrell, S.A. Lyprinol-Is It a Useful Anti-Inflammatory Agent? Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. 2011, 2011, 307121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whitehouse, M.W.; Macrides, T.A.; Kalafatis, N.; Betts, W.H.; Haynes, D.R.; Broadbent, J. Anti-inflammatory activity of a lipid fraction (lyprinol) from the NZ green-lipped mussel. Inflammopharmacology 1997, 5, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford Bioactives. PernaUltra—Greenshell Mussel Powder. Available online: https://sanfordbioactives.co.nz/our-products/pernaultra/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Baecke, J.A.; Burema, J.; Frijters, J.E. A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzack, R. The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain 1987, 30, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abshirini, M.; Coad, J.; Wolber, F.M.; von Hurst, P.; Miller, M.R.; Tian, H.S.; Kruger, M.C. Effect of Greenshell(TM) mussel on osteoarthritis biomarkers and inflammation in healthy postmenopausal women: A study protocol for a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abshirini, M.; Coad, J.; Wolber, F.M.; von Hurst, P.; Miller, M.R.; Tian, H.S.; Kruger, M.C. Effects of Greenshell™ mussel intervention on biomarkers of cartilage metabolism, inflammatory markers and joint symptoms in overweight/obese postmenopausal women: A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1063336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamlin, M.J.; Quigley, B.M. Quadriceps concentric and eccentric exercise 1: Changes in contractile and electrical activity following eccentric and concentric exercise. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2001, 4, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumpa, K.L.; Fallon, K.E.; Bensoussan, A.; Papalia, S. The effects of Lyprinol® on delayed onset muscle soreness and muscle damage in well trained athletes: A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2011, 19, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, G.; Benestad, H.B.; Strøm-Gundersen, I.; Mørkrid, L.; Lappegård, K.T.; Raastad, T. Delayed Leukocytosis and Cytokine Response to High-Force Eccentric Exercise. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2005, 37, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissing, K.; Overgaard, K.; Nedergaard, A.; Fredsted, A.; Schjerling, P. Effects of concentric and repeated eccentric exercise on muscle damage and calpain–calpastatin gene expression in human skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 103, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Chapman, P.; Brown, S.; Johnson, N.; Stannard, S. Indirect measures of substrate utilisation following exercise-induced muscle damage. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, K.; Madden, V.; Jones, S.; Moseley, G. The sensory and affective components of pain: Are they differentially modifiable dimensions or inseparable aspects of a unitary experience? A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e263–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazaud, B.; Brigitte, M.; Yacoub-Youssef, H.; Arnold, L.; Gherardi, R.; Sonnet, C.; Lafuste, P.; Chretien, F. Dual and Beneficial Roles of Macrophages During Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2009, 37, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, C.; Lenkei, R.; Sjödin, B. Effects of eccentric exercise on the immune system in men. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 86, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, G.; Ramer Mikkelsen, U.; Raastad, T.; Peake, J.M. Leucocytes, cytokines and satellite cells: What role do they play in muscle damage and regeneration following eccentric exercise? Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 18, 42–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubal, M.J.; Chen, T.; Thompson, P.D.; Clarkson, P.M. Inflammatory gene changes associated with the repeated-bout effect. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1628–R1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyhle, M.R.; Gier, A.M.; Evans, K.C.; Eggett, D.L.; Nelson, W.B.; Parcell, A.C.; Hyldahl, R.D. Skeletal Muscle Inflammation Following Repeated Bouts of Lengthening Contractions in Humans. Front. Physiol. 2016, 6, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wells, A.J.; Hoffman, J.R.; Jajtner, A.R.; Varanoske, A.N.; Church, D.D.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Townsend, J.R.; Boone, C.H.; Baker, K.M.; Beyer, K.S.; et al. The Effect of Post-Resistance Exercise Amino Acids on Plasma MCP-1 and CCR2 Expression. Nutrients 2016, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Hoffman-Goetz, L. Exercise and the Immune System: Regulation, Integration, and Adaptation. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1055–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nieman, D.C.; Nehlsen-Cannarella, S.L.; Markoff, P.A.; Balk-Lamberton, A.J.; Yang, H.; Chritton, D.B.W.; Lee, J.W.; Arabatzis, K. The Effects of Moderate Exercise Training on Natural Killer Cells and Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. Int. J. Sport. Med. 1990, 11, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, C.; Nyberg, P.; Engstrom, M.; Sjodin, B.; Lenkei, R.; Ekblom, B.; Lundberg, I. Immunological changes in human skeletal muscle and blood after eccentric exercise and multiple biopsies. J. Physiol. 2000, 529 Pt 1, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakka, K.; Hachmer, S.; Mokhtari, Z.; Kovac, R.; Bandukwala, H.; Bernard, C.; Li, Y.; Xie, G.; Liu, C.; Fallahi, M.; et al. JMJD3 activated hyaluronan synthesis drives muscle regeneration in an inflammatory environment. Science 2022, 377, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, R.; Purpura, M.; Kingsley, M. Phospholipids and sports performance. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2007, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Joshi, I. EGLLGDVF: A Novel Peptide from Green Mussel Perna viridis Foot Exerts Stability and Anti-inflammatory Effects on LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.8 ± 7.8 |
| Height (cm) | 177 ± 7 |
| Weight (kg) | 80.7 ± 11.7 |
| Habitual activity | |
| Work Index | 2.4 ± 0.6 |
| Sport Index | 3.2 ± 1.1 |
| Vest weight (kg) | 12.0 ± 1.8 |
| Bench height (cm) | 53.4 ± 3.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lomiwes, D.; Barnes, M.; Shaw, O.; Ngametua, N.; Sawyer, G.; Burr, N.; Hedderley, D.; Kanon, A.; Bear, T.; Carroll, A.; et al. The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102316
Lomiwes D, Barnes M, Shaw O, Ngametua N, Sawyer G, Burr N, Hedderley D, Kanon A, Bear T, Carroll A, et al. The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLomiwes, Dominic, Matthew Barnes, Odette Shaw, Nayer Ngametua, Greg Sawyer, Natalie Burr, Duncan Hedderley, Alexander Kanon, Tracey Bear, Andrew Carroll, and et al. 2023. "The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102316
APA StyleLomiwes, D., Barnes, M., Shaw, O., Ngametua, N., Sawyer, G., Burr, N., Hedderley, D., Kanon, A., Bear, T., Carroll, A., Bentley-Hewitt, K., Tian, H. S., & Miller, M. R. (2023). The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males. Nutrients, 15(10), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102316









