Show Me What You Have Inside—The Complex Interplay between SIBO and Multiple Medical Conditions—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
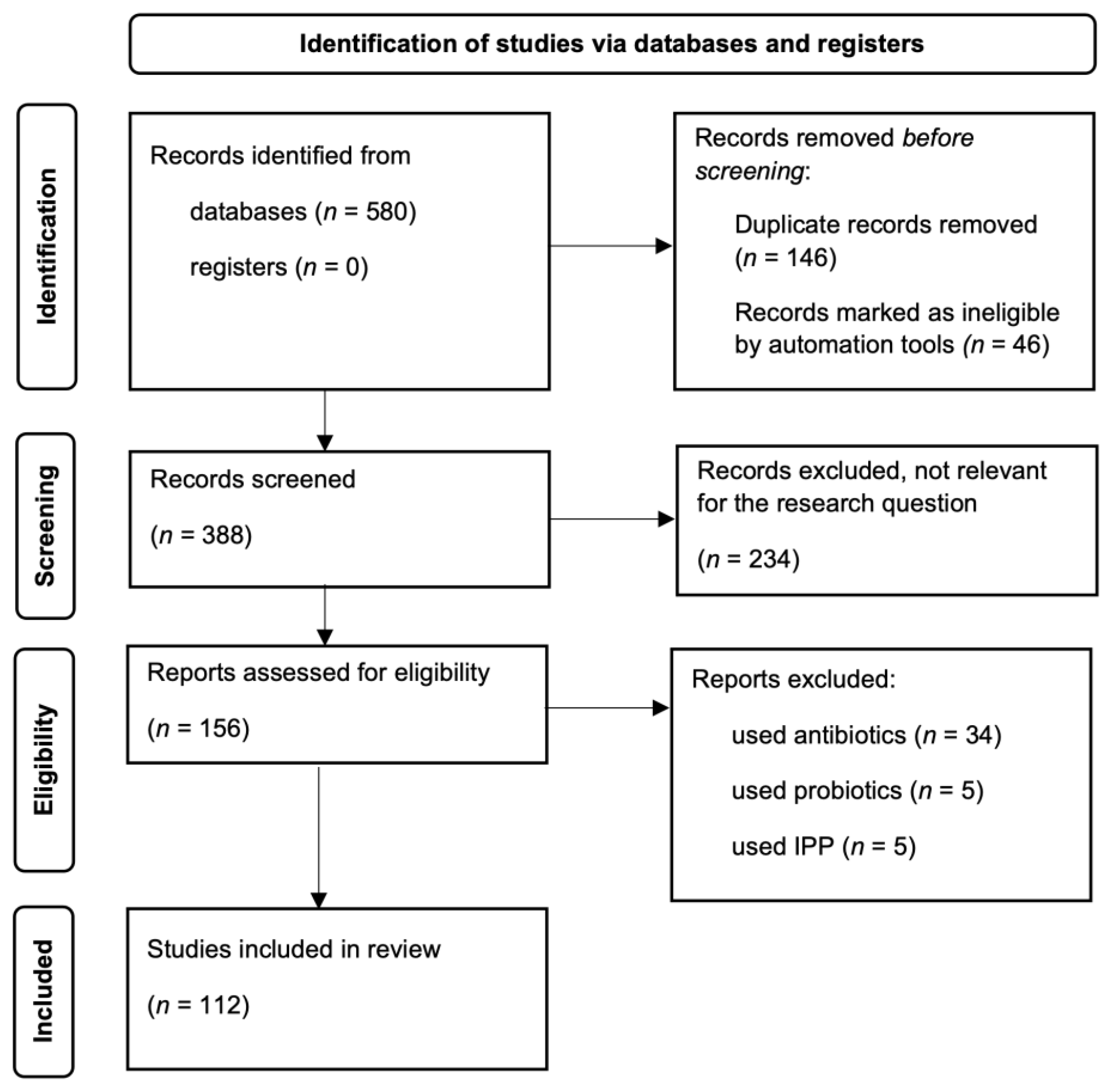
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Definition and Pathophysiology
4.2. Diagnosis
4.3. Prevalence in Other Conditions
4.3.1. Gastroenterology
4.3.2. Cardiology
4.3.3. Endocrinology
4.3.4. Neurology
4.3.5. Rheumatology and Cutaneous Diseases
4.3.6. Nephrology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robles-Alonso, V.; Guarner, F. Progress in the knowledge of the instestinal human mucrobiota. Nutricion Hospitalaria 2013, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwani, P.; Grover, K. Gut Microbiota in Health and Diseases—A Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2019, 8, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human Gut Microbiota/Microbiome in Health and Diseases: A Review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazza, G.R.; Menozzi, M.G.; Strocchi, A.; Rasciti, L.; Vaira, D.; Lecchini, R.; Avanzini, P.; Chezzi, C.; Gasbarrini, G. The Diagnosis of Small Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adike, A.; DiBaise, J.K. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enko, D.; Kriegshäuser, G. Functional 13C-Urea and Glucose Hydrogen/Methane Breath Tests Reveal Significant Association of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Individuals with Active Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Chow, E.J.; Lin, H.C. Normalization of Lactulose Breath Testing Correlates with Symptom Improvement in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M. A Link between Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Fibromyalgia May Be Related to Findings on Lactulose Breath Testing. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, B.; Vanner, S.J. Detection of Bacterial Overgrowth in IBS Using the Lactulose H2 Breath Test: Comparison with 14C-d-Xylose and Healthy Controls. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupascu, A.; Gabrielli, M.; Lauritano, E.C.; Scarpellini, E.; Santoliquido, A.; Cammarota, G.; Flore, R.; Tondi, P.; Pola, P.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Hydrogen Glucose Breath Test to Detect Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Prevalence Case-Control Study in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Aliment. Pharm. 2005, 22, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posserud, I.; Stotzer, P.-O.; Björnsson, E.S.; Abrahamsson, H.; Simrén, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gut 2007, 56, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratten, J.R.; Spanier, J.; Jones, M.P. Lactulose Breath Testing Does Not Discriminate Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome from Healthy Controls. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Park, D.I.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, B.I.; Won, K.H.; Park, S.M. The Relationship between Small-Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Intestinal Permeability in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gut Liver 2009, 3, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Dulbecco, P.; Savarino, E.; Giannini, E.G.; Bodini, G.; Corbo, M.; Isola, L.; De Conca, S.; Marabotto, E.; Savarino, V. Positive Glucose Breath Testing Is More Prevalent in Patients with IBS-like Symptoms Compared with Controls of Similar Age and Gender Distribution. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Kumar, S.; Mehrotra, M.; Lakshmi, C.; Misra, A. Frequency of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Chronic Non-Specific Diarrhea. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 16, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Comparison of Lactulose and Glucose Breath Test for Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Digestion 2012, 85, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, S.; Rawat, A.K.; Reddy, R.S.; Puri, A.S. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Frequency and Predictors: SIBO in IBS: Frequency and Predictors. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Srivastava, D.; Ghoshal, U.; Misra, A. Breath Tests in the Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Comparison with Quantitative Upper Gut Aspirate Culture. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.H.; Zahedi, M.; Darvish Moghadam, S.; Shafieipour, S.; HayatBakhsh Abbasi, M. Small Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The First Study in Iran. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 7, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Chu, H.; Zhao, J.; Cong, Y.; Fried, M.; Fox, M.; Dai, N. A Study of the Methodological and Clinical Validity of the Combined Lactulose Hydrogen Breath Test with Scintigraphic Oro-Cecal Transit Test for Diagnosing Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in IBS Patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgeerts, P.; Ghoos, Y.; Vantrappen, G.; Eyssen, H. IIeal Dysfunction and Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 11, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Rispo, A.; Petrelli, G.; Amalfi, G.; Cozzolino, A.; Cuccaro, I.; Mazzacca, G. Orocecal Transit Time and Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2000, 31, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, J.; Spaniol, U.; Adler, G.; Mason, R.A.; Reinshagen, M.; von Tirpitz, C.C. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Mimicking Acute Flare as a Pitfall in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Brignolo, P.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Reggiani, S.; Sguazzini, C.; Smedile, A.; Pellicano, R.; Resegotti, A.; Astegiano, M.; et al. Glucose Breath Test and Crohn’s Disease: Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Evaluation of Therapeutic Response. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, J.E.R.; Chebli, L.A.; Ribeiro, T.C.d.R.; Castro, A.C.S.; Gaburri, P.D.; Pace, F.H.d.L.; Barbosa, K.V.B.D.; Ferreira, L.E.V.V.d.C.; Passos, M.d.C.F.; Malaguti, C.; et al. Small-Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Associated with Concurrent Intestinal Inflammation but Not with Systemic Inflammation in Crohn’s Disease Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Kochhar, R.; Malik, A.; Morya, R.K. Relationship of Cytokines, Oxidative Stress and GI Motility with Bacterial Overgrowth in Ulcerative Colitis Patients. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2014, 8, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Huo, X.; Wang, J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Evaluation of Intestinal Barrier Function in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6605–6610. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Malik, A.; Kaur, J.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Orocecal Transit Time in Patients of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2594–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.-M.; Chung, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, D.B.; Sung, H.J.; Chung, W.C.; Paik, C.-N. Clinical Significance of the Glucose Breath Test in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, M.; Gologan, Ş. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome Prevalence in Romanian Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2016, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Yadav, A.; Fatima, B.; Agrahari, A.P.; Misra, A. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case-Control Study. Indian, J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prizont, R.; Hersh, T.; Floch, M.H. Jejunal Bacterial Flora in Chronic Small Bowel Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1970, 23, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursi, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Giorgetti, G. High Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Celiac Patients with Persistence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms after Gluten Withdrawal. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Ghoshal, U.; Misra, A.; Choudhuri, G. Partially Responsive Celiac Disease Resulting from Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Lactose Intolerance. BMC Gastroenterol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Sinha, S.K.; Lal, S.; Sikander, A.; Singh, K. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in North Indian Patients with Celiac Disease. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2007, 28, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Barton, S.H.; Rosenblatt, J.E.; Murray, J.A. Prevalence of Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth Diagnosed by Quantitative Culture of Intestinal Aspirate in Celiac Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.S.; Minaya, M.T.; Cheng, J.; Connor, B.A.; Lewis, S.K.; Green, P.H.R. Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial of Rifaximin for Persistent Symptoms in Patients with Celiac Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, J.S.; Zubiaurre, I.; Fanjul, I.; Olivera, P.; Soifer, L. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Prevalence in Celiac Disease Patients Is Similar in Healthy Subjects and Lower in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients. Rev. Gastroenterol. México (Engl. Ed.) 2015, 80, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paik, C.N.; Choi, M.-G.; Lim, C.H.; Park, J.M.; Chung, W.C.; Lee, K.-M.; Jun, K.-H.; Song, K.Y.; Jeon, H.M.; Chin, H.-M.; et al. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Postgastrectomy Patients: Bacterial Overgrowth and Gastrectomy. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, e191–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, H.M.; Zaborowski, A.; Fanning, M.; McHugh, A.; Doyle, S.; Moore, J.; Ravi, N.; Reynolds, J.V. Prospective Study of Malabsorption and Malnutrition After Esophageal and Gastric Cancer Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabate, J.-M.; Coupaye, M.; Ledoux, S.; Castel, B.; Msika, S.; Coffin, B.; Jouet, P. Consequences of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Obese Patients Before and After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.B.; Paik, C.-N.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Jun, K.-H.; Chung, W.C.; Lee, K.-M.; Yang, J.-M.; Choi, M.-G. Positive Glucose Breath Tests in Patients with Hysterectomy, Gastrectomy, and Cholecystectomy. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Tan, G.; Abdulla, H.; Yu, S.; Larion, S.; Leelasinjaroen, P. Does Colectomy Predispose to Small Intestinal Bacterial (SIBO) and Fungal Overgrowth (SIFO)? Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouillot, T.; Rhyman, N.; Gauthier, C.; Paris, J.; Lang, A.-S.; Lepers-Tassy, S.; Manfredi, S.; Lepage, C.; Leloup, C.; Jacquin-Piques, A.; et al. Study of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in a Cohort of Patients with Abdominal Symptoms Who Underwent Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté, J.-M.; Jouët, P.; Harnois, F.; Mechler, C.; Msika, S.; Grossin, M.; Coffin, B. High Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Morbid Obesity: A Contributor to Severe Hepatic Steatosis. Obes. Surg. 2008, 18, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, A.M.; Poniachik, J.; Quera, R.; Defilippi, C. Small Intestinal Clustered Contractions and Bacterial Overgrowth: A Frequent Finding in Obese Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.; Shen, B. Higher Visceral to Subcutaneous Fat Ratio Is Associated with Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, B.C.; Lee, D.; Miller, L.S.; Vegesna, A.; Yolken, R.; Severance, E.; Prandovszky, E.; Zheng, X.E.; Mullin, G.E. Obesity Increases the Risk of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO). Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigg, A.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Dymock, R.B.; McCarthy, P.J.; Grose, R.H.; Cummins, A.G. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth, Intestinal Permeability, Endotoxaemia, and Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gut 2001, 48, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Mottershead, M.; Syn, W.K.; Jones, R.; Smith, S.; Nwokolo, C.U. Ciprofloxacin Suppresses Bacterial Overgrowth, Increases Fasting Insulin but Does Not Correct Low Acylated Ghrelin Concentration in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharm. 2005, 22, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased Intestinal Permeability and Tight Junction Alterations in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanab, A.A.; Scully, P.; Crosbie, O.; Buckley, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Shanahan, F.; Gazareen, S.; Murphy, E.; Quigley, E.M.M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Association with Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression and Plasma Levels of Interleukin 8. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.J.; Shen, B. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Associated with Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JGLD 2016, 25, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Baba, C.S.; Ghoshal, U.; Alexander, G.; Misra, A.; Saraswat, V.A.; Choudhuri, G. Low-Grade Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Common in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis on Quantitative Jejunal Aspirate Culture. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 36, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolasevic, I.; Delija, B.; Mijic, A.; Stevanovic, T.; Skenderevic, N.; Sosa, I.; Krznaric-Zrnic, I.; Abram, M.; Krznaric, Z.; Domislovic, V.; et al. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosed by Transient Elastography and Liver Biopsy. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Mao, L.; Wang, L.; Quan, X.; Xu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Dai, F. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Orocecal Transit Time in Patients of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, e535–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesta, J.; Silva, M.; Thompson, L.; del Canto, E.; Defilippi, C. Bacterial overgrowth in small intestine in patients with liver cirrhosis. Rev. Med. Chil. 1991, 119, 626–632. [Google Scholar]
- Casafont Morencos, F.; de las Heras Castano, G.; Martín Ramos, L.; López Arias, M.J.; Ledesma, F.; Pons Romero, F. Small Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Alcoholic Cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1995, 40, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, A.M.; Cumsille, F.; Defilippi, C. Altered Small Bowel Motility in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Depends on Severity of Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-S.; Chen, G.-H. Small- Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis, Diagnosed with Glu- Cose H2 or CH4 Breath Tests. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.M.; Schwacha, H.; Steinbrückner, B.; Brinkmann, F.E.; Ditzen, A.K.; Kist, M.; Blum, H.E. Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Cirrhosis of the Liver: Poor Performance of the Glucose Breath Hydrogen Test. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsdottir, S.A.; Sadik, R.; Shev, S.; Simren, M.; Sjovall, H.; Stotzer, P.-O.; Abrahamsson, H.; Olsson, R.; Bjornsson, E.S. Small Intestinal Motility Disturbances and Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancey, S.; Moussata, D.; Roman, S.; Benmansour, H.; Claudel, S.; Flourié, B. A Positive Breath Hydrogen Test Does Not Predict the Occurrence of a Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhotic Patients with Ascites. Digestion 2009, 79, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, C.; Kumar, A.; Sarin, S.K. Small-Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Cirrhosis Is Related to the Severity of Liver Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, D.W.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, O.Y.; Chae, J.D.; Son, B.K.; Kim, S.H.; Jo, Y.J.; Park, Y.S. Association Between Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Peripheral Bacterial DNA in Cirrhotic Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dhiman, R.K.; Kumari, S.; Rana, S.; Agarwal, R.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y. Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Delayed Gastrointestinal Transit Time in Cirrhotic Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cao, B.; Tian, Q. The Effect of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth on Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Rana, S.V.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, V.; Sharma, S.K.; Dhawan, D.K. Prolonged Orocecal Transit Time Enhances Serum Bile Acids Through Bacterial Overgrowth, Contributing Factor to Gallstone Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Paik, C.-N.; Song, D.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.M. The Characteristics of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Gallstone Diseases: Gallstone Diseases and SIBO. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellas, F.; Guarner, L.; Vaquero, E.; Antolín, M.; de Gracia, X.; Malagelada, J.R. Hydrogen Breath Test with Glucose in Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency. Pancreas 1998, 16, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trespi, E.; Ferrieri, A. Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth During Chronic Pancreatitis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1999, 15, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signoretti, M.; Stigliano, S.; Valente, R.; Piciucchi, M.; Fave, G.D.; Capurso, G. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients With Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, S52–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Srivastava, D.; Misra, A.; Mohindra, S. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Common Both among Patients with Alcoholic and Idiopathic Chronic Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.B.; Paik, C.-N.; Sung, H.J.; Chung, W.C.; Lee, K.-M.; Yang, J.-M.; Choi, M.-G. Breath Hydrogen and Methane Are Associated with Intestinal Symptoms in Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ní Chonchubhair, H.M.; Bashir, Y.; Dobson, M.; Ryan, B.M.; Duggan, S.N.; Conlon, K.C. The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Non-Surgical Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency (PEI). Pancreatology 2018, 18, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.A.; Baker, J.R.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Saad, R.; DiMagno, M.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Common in Chronic Pancreatitis and Associates with Diabetes, Chronic Pancreatitis Severity, Low Zinc Levels, and Opiate Use. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.-M.; He, F.; Li, B.-Y.; Li, X.-C. Association between Acute Pancreatitis and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Assessed by Hydrogen Breath Test. WJG 2017, 23, 8591–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Paik, C.-N.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.-J. Association between Increased Breath Hydrogen Methane Concentration and Prevalence of Glucose Intolerance in Acute Pancreatitis. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 026006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowska, A.; Wójtowicz, J.; Walkowiak, J. Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth Is Frequent in Cystic Fibrosis: Combined Hydrogen and Methane Measurements Are Required for Its Detection. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, J.; Gonska, T. Bacterial Overgrowth, Dysbiosis, Inflammation, and Dysmotility in the Cystic Fibrosis Intestine. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnari, M.; De Alessandri, A.; Cresta, F.; Haupt, M.; Bassi, M.; Calvi, A.; Haupt, R.; Bodini, G.; Ahmed, I.; Bagnasco, F.; et al. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomized Case-Controlled Clinical Trial with Rifaximin. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasini, E.; Aquilani, R.; Testa, C.; Baiardi, P.; Angioletti, S.; Boschi, F.; Verri, M.; Dioguardi, F. Pathogenic Gut Flora in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, B.; Cui, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Li, F.; Shen, D.; Zhang, X.; et al. Association of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth with Heart Failure and Its Prediction for Short-Term Outcomes. JAHA 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Pompili, M.; Di Stasio, E.; Zocco, M.A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Flore, R. Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Linked to Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth via Vitamin K2-Dependent Mechanisms. WJG 2017, 23, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Kochhar, G.; Schenone, A.L.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.J.; Shen, B. Association Between Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth by Glucose Breath Test and Coronary Artery Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Schenone, A.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.; Shen, B. Association between Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 4, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, N.-C.; Xu, H.-L.; Lian, Y.-J. Association between Small-intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojetti, V.; Pitocco, D.; Scarpellini, E.; Zaccardi, F.; Scaldaferri, F.; Gigante, G.; Gasbarrini, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Small Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth and Type 1 Diabetes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 13, 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, M.; Pavin, E.J.; Parisi, M.C.R.; Lorena, S.L.S.; Brunetto, S.Q.; Ramos, C.D.; Pavan, C.R.; Mesquita, M.A. Delayed Small Intestinal Transit in Patients with Long-Standing Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Investigation of the Relationships with Clinical Features, Gastric Emptying, Psychological Distress, and Nutritional Parameters. Diabetes. Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Morya, R.K.; Bhadada, S.K.; Rana, S. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Complex Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Cytokines, Gastrointestinal Motility and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e13021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Bhansali, A.; Bhadada, S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Singh, K. Orocecal Transit Time and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Type 2 Diabetes Patients from North India. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Malik, A.; Bhadada, S.K.; Sachdeva, N.; Morya, R.K.; Sharma, G. Malabsorption, Orocecal Transit Time and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Connection. Ind. J. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 32, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietz, B.; Lock, G.; Straub, R.H.; Braun, B.; Scholmerich, J.; Palitzsch, K.D. Small-Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth in Diabetic Subjects Is Associated with Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1200–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, E.C.; Bilotta, A.L.; Gabrielli, M.; Scarpellini, E.; Lupascu, A.; Laginestra, A.; Novi, M.; Sottili, S.; Serricchio, M.; Cammarota, G.; et al. Association between Hypothyroidism and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4180–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechmann, T.; Sperlbaum, A.; Schmiegel, W. Levothyroxine Therapy and Impaired Clearance Are the Strongest Contributors to Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Results of a Retrospective Cohort Study. WJG 2017, 23, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, P.; Chojnacki, J.; Kaczka, A.; Pawłowicz, M.; Rudnicki, C.; Chojnacki, C. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Pol. Merkur. Lek. 2018, 44, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli, M.; Bonazzi, P.; Scarpellini, E.; Bendia, E.; Lauritano, E.C.; Fasano, A.; Ceravolo, M.G.; Capecci, M.; Rita Bentivoglio, A.; Provinciali, L.; et al. Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.; Charlett, A.; Dobbs, S.M.; Weller, C.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Iguodala, O.; Smee, C.; Plant, J.; Lawson, A.J.; Taylor, D.; et al. Leukocyte-Subset Counts in Idiopathic Parkinsonism Provide Clues to a Pathogenic Pathway Involving Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. A Surveillance Study. Gut Pathog. 2012, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Liu, L.W.C.; Lang, A.E.; Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.H.; Mahadeva, S.; Thalha, A.M.; Gibson, P.R.; Kiew, C.K.; Yeat, C.M.; Ng, S.W.; Ang, S.P.; Chow, S.K.; Tan, C.T.; et al. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.-L.; Liu, L.; Song, Z.-X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Li, H.-H. Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Chinese Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2016, 123, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.; Gandhy, R.; Barlow, C.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Utility of the Wireless Motility Capsule and Lactulose Breath Testing in the Evaluation of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Who Present with Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasuike, Y.; Endo, T.; Koroyasu, M.; Matsui, M.; Mori, C.; Yamadera, M.; Fujimura, H.; Sakoda, S. Bile Acid Abnormality Induced by Intestinal Dysbiosis Might Explain Lipid Metabolism in Parkinson’s Disease. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 134, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, N.; Liu, N. Hydrogen Breath Test to Detect Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Prevalence Case–Control Study in Autism. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 27, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Rehman, A.; Yu, S.; Andino, N.M. de Brain Fogginess, Gas and Bloating: A Link between SIBO, Probiotics and Metabolic Acidosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Sessarego, M.; Greco, A.; Bazzica, M.; Filaci, G.; Setti, M.; Savarino, E.; Indiveri, F.; Savarino, V.; Ghio, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients Suffering from Scleroderma: Clinical Effectiveness of Its Eradication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Ducrotte, P.; Denis, P.; Menard, J.-F.; Levesque, H. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynne, L.; Worsøe, J.; Gregersen, T.; Schlageter, V.; Laurberg, S.; Krogh, K. Gastrointestinal Transit in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, E.; Mei, F.; Parodi, A.; Ghio, M.; Furnari, M.; Gentile, A.; Berdini, M.; Di Sario, A.; Bendia, E.; Bonazzi, P.; et al. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorder Assessment in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemignani, L.; Savarino, V.; Ghio, M.; Parodi, A.; Zentilin, P.; de Bortoli, N.; Negrini, S.; Furnari, M.; Dulbecco, P.; Giambruno, E.; et al. Lactulose Breath Test to Assess Oro-Cecal Transit Delay and Estimate Esophageal Dysmotility in Scleroderma Patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 42, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Leroi, A.-M.; Menard, J.-F.; Levesque, H.; Quillard, M.; Ducrotte, P. Fecal Calprotectin in Systemic Sclerosis and Review of the Literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adarsh, M.B.; Sharma, S.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rana, S.; Dhir, V.; Singh, S. Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Infections in Systemic Sclerosis- An Indian Scenario. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2018, 14, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadpanich, K.; Soison, P.; Chunlertrith, K.; Mairiang, P.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Sangchan, A.; Suttichaimongkol, T.; Foocharoen, C. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth among Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Collinot, G.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.O.; Martínez-Bencomo, M.A.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Jara, L.J.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Montes-Cortes, D.H.; Medina, G.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces Boulardii and Metronidazole for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 65, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Paolino, S.; Greco, A.; Drago, F.; Mansi, C.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A.; Savarino, V. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Rosacea: Clinical Effectiveness of Its Eradication. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; De Col, E.; Agnoletti, A.F.; Schiavetti, I.; Savarino, V.; Rebora, A.; Paolino, S.; Cozzani, E.; Parodi, A. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Rosacea: A 3-Year Follow-Up. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, e113–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strid, H.; Simrén, M.; Stotzer, P.-O.; Ringström, G.; Abrahamsson, H.; Björnsson, E.S. Patients with Chronic Renal Failure Have Abnormal Small Intestinal Motility and a High Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Digestion 2003, 67, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, H.; Knoke, M. Recent Studies on the Microbial Ecology of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Infection 1989, 17, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukowicz, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Levine, G.M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Comprehensive Review. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 3, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhnik, Y.; Alain, S.; Attar, A.; Flourié, B.; Raskine, L.; Sanson-Le Pors, M.J.; Rambaud, J.-C. Bacterial Populations Contaminating The Upper Gut in Patients With Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.; Buresi, M.; Lembo, A.; Lin, H.; McCallum, R.; Rao, S.; Schmulson, M.; Valdovinos, M.; Zakko, S.; Pimentel, M. Hydrogen and Methane-Based Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Disorders: The North American Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, B.C.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Clarke, J.O.; Semler, J.R.; Tomakin, E.; Mullin, G.E.; Pasricha, P.J. Low Ileocecal Valve Pressure Is Significantly Associated with Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshini, R.; Dai, S.-C.; Lezcano, S.; Pimentel, M. A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Tests for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, C.; Coss Adame, E.; Attaluri, A.; Valestin, J.; Rao, S.S.C. Dysmotility and Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Are Independent Risk Factors for Small Intestinal Bacterial and/or Fungal Overgrowth. Aliment. Pharm. 2013, 37, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, L.; Foti, M.; Ruggia, O.; Chiecchio, A. Increased Incidence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth During Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, J.R.; Kowdley, K.V.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Sepe, T.; Golner, B.; Perrone, G.; Russell, R.M. Bacterial Overgrowth without Clinical Malabsorption in Elderly Hypochlorhydric Subjects. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.D.; Shiner, M. Influence of Gastric PH on Gastric and Jejunal Flora. Gut 1967, 8, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, A.P.; Biddle, W.L.; Bhatia, P.S.; Miner, P.B. Terminal Ileal Mucosal Mast Cells in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzmann, J.L.; Peltier-Koch, F.; Bloch, F.; Petite, J.P.; Camilleri, J.P. Morphometric Study of Colonic Biopsies: A New Method of Estimating Inflammatory Diseases. Lab. Investig. 1989, 60, 847–851. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.C. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Framework for Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome. JAMA 2004, 292, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth as a Cause for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Guilty or Not Guilty? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Mathur, R.; Chang, C. Gas and the Microbiome. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Mekelburg, S.; Tafesh, Z.; Coburn, E.; Weg, R.; Malik, N.; Webb, C.; Hammad, H.; Scherl, E.; Bosworth, B.P. Testing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Reduces Symptoms in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraquelli, M.; Bardella, M.T.; Peracchi, M.; Cesana, B.M.; Bianchi, P.A.; Conte, D. Gallbladder Emptying and Somatostatin and Cholecystokinin Plasma Levels in Celiac Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardella, M.T.; Fraquelli, M.; Peracchi, M.; Cesana, B.M.; Bianchi, P.A. Gastric Emptying and Plasma Neurotensin Levels in Untreated Celiac Patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; Adames, K.; Castillo-Rodal, A.I.; Ramírez, T.; Barreto-Zuñiga, R.; López-Vidal, Y.; Uscanga, L.F. Intraepithelial Γδ+ Lymphocytes: A Comparative Study between Celiac Disease, Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The Diagnosis and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.R.; Rosso, N.; Bedogni, G.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Global Epidemiology of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: What We Need in the Future. Liver Int. 2018, 38 (Suppl. 1), 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; DuGar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.-M.; et al. Gut Flora Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine Promotes Cardiovascular Disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of Gut Microbiomes in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Patients: A Connection between Endogenous Alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Timmons, L.; Benson, J.T.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Chari, S.T. Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival of Chronic Pancreatitis: A Population-Based Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C. How to Interpret Hydrogen Breath Tests. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Ling, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cai, T.; Yuan, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, K. Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Inflammation Involved in the Progression of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2015, 44, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lisle, R.C. Altered Transit and Bacterial Overgrowth in the Cystic Fibrosis Mouse Small Intestine. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G104–G111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Somerset, S. Digestive System Dysfunction in Cystic Fibrosis: Challenges for Nutrition Therapy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandek, A.; Bjarnason, I.; Volk, H.-D.; Crane, R.; Meddings, J.B.; Niebauer, J.; Kalra, P.R.; Buhner, S.; Herrmann, R.; Springer, J.; et al. Studies on Bacterial Endotoxin and Intestinal Absorption Function in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 157, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimichas, T.; Ohtani, T.; Motooka, D.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kioka, H.; Nakamoto, K.; Konishi, S.; Chimura, M.; Sengoku, K.; Miyawaki, H.; et al. Non-Ischemic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction Is Associated with Altered Intestinal Microbiota. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandek, A.; Swidsinski, A.; Schroedl, W.; Watson, A.; Valentova, M.; Herrmann, R.; Scherbakov, N.; Cramer, L.; Rauchhaus, M.; Grosse-Herrenthey, A.; et al. Intestinal Blood Flow in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollar, A.; Villanueva, M.P.; NÚÑez, E.; CarratalÁ, A.; Mora, F.; BayÉs-GenÍs, A.; MÍnguez, M.; Marrachelli, V.G.; Monleon, D.; Navarro, D.; et al. Hydrogen- and Methane-Based Breath Testing and Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebauer, J.; Volk, H.-D.; Kemp, M.; Dominguez, M.; Schumann, R.R.; Rauchhaus, M.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Coats, A.J.; Anker, S.D. Endotoxin and Immune Activation in Chronic Heart Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 1999, 353, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandek, A.; Rauchhaus, M.; Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. The Emerging Role of the Gut in Chronic Heart Failure. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. Inflammatory Mediators in Chronic Heart Failure: An Overview. Heart 2004, 90, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerhofer, C.C.K.; Awoyemi, A.O.; Moscavitch, S.D.; Lappegård, K.T.; Hov, J.R.; Aukrust, P.; Hovland, A.; Lorenzo, A.; Halvorsen, S.; Seljeflot, I.; et al. Design of the GutHeart-Targeting Gut Microbiota to Treat Heart Failure-Trial: A Phase II, Randomized Clinical Trial: GutHeart Design. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Koeth, R.A.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal Microbial Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine and Cardiovascular Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ran, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Mi, M. Resveratrol Attenuates Trimethylamine- N -Oxide (TMAO)-Induced Atherosclerosis by Regulating TMAO Synthesis and Bile Acid Metabolism via Remodeling of the Gut Microbiota. mBio 2016, 7, e02210-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virally-Monod, M.; Tielmans, D.; Kevorkian, J.P.; Bouhnik, Y.; Flourie, B.; Porokhov, B.; Ajzenberg, C.; Warnet, A.; Guillausseau, P.J. Chronic Diarrhoea and Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Diabetes Metab. 1998, 24, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 Links Innate Immunity and Fatty Acid–Induced Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Everard, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B. Gut Microorganisms as Promising Targets for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated With Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Survey of 15,000 Adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddymasu, S.C.; McCallum, R.W. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Gastroparesis: Are There Any Predictors? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, e8–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Tsagarakis, S. Microbiome and Diabetes: Where Are We Now? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 146, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborska, K.E.; Cummings, B.P. Rethinking Bile Acid Metabolism and Signaling for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders in Endocrine Diseases. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 121, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almandoz, J.P.; Gharib, H. Hypothyroidism: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 96, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.; Yazbeck, T.; Jaoude, J.B.; Abboud, B. Consequences of Dysthyroidism on the Digestive Tract and Viscera. WJG 2009, 15, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Ahmed, A.; Wu, D.; Liu, L.; Qiu, J.; Yan, Y.; Jin, M.; Xin, Y. Gut Microbe Analysis Between Hyperthyroid and Healthy Individuals. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penhale, W.J.; Young, P.R. The Influence of the Normal Microbial Flora on the Susceptibility of Rats to Experimental Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1988, 72, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Ihnatowicz, P.; Drywień, M.; Wątor, P.; Wojsiat, J. The Importance of Nutritional Factors and Dietary Management of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, J.L.; Okun, M.S.; Moshiree, B. The Treatment of Gastroparesis, Constipation and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 2449–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, J.K.; Crowell, M.D.; Driver-Dunckley, E.; Mehta, S.H.; Hoffman-Snyder, C.; Lin, T.; Adler, C.H. Weight Loss in Parkinson’s Disease: No Evidence for Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. J. Park. Dis. 2018, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Bove, F.; Gabrielli, M.; Petracca, M.; Zocco, M.A.; Ragazzoni, E.; Barbaro, F.; Piano, C.; Fortuna, S.; Tortora, A.; et al. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Parkinson’s Disease: Sibo in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, S.P.; El Aidy, S. Contributions of Gut Bacteria and Diet to Drug Pharmacokinetics in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, D.A.; Kern, J.K.; Geier, M.R. A Comparison of the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC) and the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) for the Quantitative Evaluation of Autism. J. Ment. Health Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2013, 6, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-Altering Microorganisms: The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Brain and Behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegold, S.M.; Summanen, P.H.; Downes, J.; Corbett, K.; Komoriya, T. Detection of Clostridium Perfringens Toxin Genes in the Gut Microbiota of Autistic Children. Anaerobe 2017, 45, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegold, S.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Gontcharova, V.; Liu, C.; Henley, K.E.; Wolcott, R.D.; Youn, E.; Summanen, P.H.; Granpeesheh, D.; Dixon, D.; et al. Pyrosequencing Study of Fecal Microflora of Autistic and Control Children. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfabe, D.; Cain, D.; Rodriguezcapote, K.; Franklin, A.; Hoffman, J.; Boon, F.; Taylor, A.; Kavaliers, M.; Ossenkopp, K. Neurobiological Effects of Intraventricular Propionic Acid in Rats: Possible Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids on the Pathogenesis and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 176, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hodgson, N.W.; Trivedi, M.S.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Fournier, M.; Cuenod, M.; Do, K.Q.; Deth, R.C. Decreased Brain Levels of Vitamin B12 in Aging, Autism and Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalighi, A.R.; Khalighi, M.R.; Behdani, R.; Jamali, J.; Khosravi, A.; Kouhestani, S.; Radmanesh, H.; Esmaeelzadeh, S.; Khalighi, N. Evaluating the Efficacy of Probiotic on Treatment in Patients with Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)—A Pilot Study. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 140, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Romdalvik, J.; Levine, K.E.; Hu, L.-W. Mercury in First-Cut Baby Hair of Children with Autism versus Typically-Developing Children. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2008, 90, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C. D-Lactic Acidosis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2005, 20, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A. Severe Organ Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis with Diffuse Scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyger, G.; Baron, M. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Scleroderma: Recent Progress in Evaluation, Pathogenesis, and Management. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, R.W. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders in Scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Tandon, P.; Gohel, T.; Corrigan, M.L.; Coughlin, K.L.; Shatnawei, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Kirby, D.F. Gastrointestinal Manifestations, Malnutrition, and Role of Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition in Patients with Scleroderma. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-P. Gastrointestinal Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. WJG 2013, 19, 7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellaard, F.; Sauerbruch, T.; Luderschmidt, C.H.; Leisner, B.; Paumgartner, G. Intestinal Involvement in Progressive Systemic Sclerosis Detected by Increased Unconjugated Serum Bile Acids. Gut 1987, 28, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi, G. Diagnosis of Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease and the Role of Rifaximin in Management. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, N.; Rawn, S.M.; Wang, M.; Masetto, A.; Beattie, K.A.; Larché, M. Treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebora, A. The Management of Rosacea. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, R.; Clark, M.L.; Beard, R.J.; Kwok, M.; Robertson, W.B. Gastrointestinal Observations in Rosacea. Lancet 1967, 289, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina Mikusic, N.L.; Kouyoumdzian, N.M.; Choi, M.R. Gut Microbiota and Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidences and Mechanisms That Mediate a New Communication in the Gastrointestinal-Renal Axis. Pflugers Arch-Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Dure-Smith, B.; Miller, R.; Mirahmadi, M.K. Pathology of Gastrointestinal Tract in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: An Autopsy Study of 78 Cases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1985, 80, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Barrios, C.; Beaumont, M.; Pallister, T.; Villar, J.; Goodrich, J.K.; Clark, A.; Pascual, J.; Ley, R.E.; Spector, T.D.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Gut-Microbiota-Metabolite Axis in Early Renal Function Decline. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallu, A.; Sharma, S.; Ramezani, A.; Muralidharan, J.; Raj, D. Gut Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease: Challenges and Opportunities. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Hayashi, H.; Watanabe, M.; Ueda, K.; Yamato, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Motojima, M. Uremic Toxins Overload Accelerates Renal Damage in a Rat Model of Chronic Renal Failure. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 2003, 95, e111–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.R.; Gandolfo, M.T.; Ko, G.J.; Satpute, S.; Racusen, L.; Rabb, H. Early Exposure to Germs Modifies Kidney Damage and Inflammation after Experimental Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F1457–F1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadhani, R.; Pascual, M.; Bonventre, J.V. Acute Renal Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, C.J.; Go, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.-G.; Oh, S.W.; Cho, W.Y.; Im, S.-H.; Jo, S.K. Intestinal Microbiota Control Acute Kidney Injury Severity by Immune Modulation. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Amano, M.T.; Correa-Costa, M.; Castoldi, A.; Felizardo, R.J.F.; de Almeida, D.C.; Bassi, E.J.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Hiyane, M.I.; Rodas, A.C.D.; et al. Gut Bacteria Products Prevent AKI Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion. JASN 2015, 26, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodpoor, F.; Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Barzegari, A.; Ardalan, M.; Zununi Vahed, S. The Impact of Gut Microbiota on Kidney Function and Pathogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Scolari, F.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Choi, M.; Verbitsky, M.; Fasel, D.; Lata, S.; Prakash, S.; Shapiro, S.; et al. Discovery of New Risk Loci for IgA Nephropathy Implicates Genes Involved in Immunity against Intestinal Pathogens. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Santisteban, M.M.; Rodriguez, V.; Li, E.; Ahmari, N.; Carvajal, J.M.; Zadeh, M.; Gong, M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Is Linked to Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgan, D.J.; Ganesh, B.P.; Cope, J.L.; Ajami, N.J.; Phillips, S.C.; Petrosino, J.F.; Hollister, E.B.; Bryan, R.M. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Obstructive Sleep Apnea–Induced Hypertension. Hypertension 2016, 67, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.M.; Moazami, S.; Qiu, Y.; Kurland, I.; Chen, Z.; Agalliu, I.; Burk, R.; Davies, K.P. Evidence for a Distinct Gut Microbiome in Kidney Stone Formers Compared to Non-Stone Formers. Urolithiasis 2016, 44, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disorder | Years of Publications | Number of Studies | Authors, References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastroenterology | ||||
| Helicobacter pylori infection | 2017 | 1 | Enko et al. [6] | |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 1991–2016 | 14 | Pimental et al. [7], Pimental et al. [8], Walters et al. [9], Lupascu et al. [10], Posserud et al. [11], Bratten et al. [12], Park et al. [13], Parodi et al. [14], Ghoshal et al. [15], Rana et al. [16], Sachdeva et al. [17], Ghoshal et al. [18], Abbasi et al. [19], Zhao et al. [20] | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Crohn’s disease | 1981–2018 | 5 | Rutgeerts et al. [21], Castiglione et al. [22], Klaus et al. [23], Greco et al. [24], Ricci et al. [25] |
| Ulcerative colitis | 2014, 2021 | 2 | Rana et al. [26], Yang et al. [27] | |
| Both | 2013–2016, 2022 | 4 | Rana et al. [28], Lee et al. [29], Andrei et al. [30], Ghoshal et al. [31] | |
| Celiac disease | 1970; 2002–2015 | 7 | Prizont et al. [32], Tursi et al. [33], Ghoshal et al. [34], Rana et al. [35], Rubio-Tapia et al. [36], Chang et al. [37], Lasa et al. [38] | |
| Abdominal surgery | 2011–2020 | 6 | Paik et al. [39], Heneghan et al. [40], Sabate et al. [41], Kim et al. [42], Rao et al. [43], Mouillot et al. [44] | |
| Obesity | 2008–2018 | 4 | Sabate et al. [45], Madrid et al. [46], Fialho et al. [47], Roland et al. [48] | |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 2001–2017 | 8 | Wigg et al. [49], Sajjad et al. [50], Miele et al. [51], Shanab et al. [52], Fialho et al. [53], Ghoshal et al. [54], Mikolasevic et al. [55], Shi et al. [56] | |
| Cirrhosis | 1991–2016 | 11 | Chesta et al. [57], Casafont Morencos et al. [58], Madrid et al. [59], Yang et al. [60], Bauer et al. [61], Gunnarsdottir et al. [62], Nancey et al. [63], Pande et al. [64], Jun et al. [65], Gupta et al. [66], Zhang et al. [67] | |
| Gall stone disease | 2014, 2018 | 2 | Kaur et al. [68], Kim et al. [69] | |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 1985–2019 | 8 | Casellas et al. [70], Trespi et al. [71], Signoretti et al. [72], Kumar et al. [73], Kim et al. [74], Ni Chonchubhair et al. [75], Lee et al. [76] | |
| Acute pancreatitis | 2017, 2020 | 2 | Zhang et al. [77], Kim et al. [78] | |
| Cystic fibrosis | 2009–2019 | 3 | Lisowska et al. [79], Dorsey et al. [80]., Furnari et al. [81] | |
| Cardiology | ||||
| Heart failure | 2016, 2021 | 2 | Pasini et al. [82], Song et al. [83] | |
| Atherosclerosis | 2017, 2018 | 2 | Ponziani et al. [84], Fialho et al. [85] | |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 2016, 2017 | 2 | Fialho et al. [86], Cheng et al. [87] | |
| Endocrinology | ||||
| Diabetes | Type 1 | 2009, 2013, 2018 | 3 | Ojetti et al. [88], Faria et al. [89], Malik et al. [90] |
| Type 2 | 2011, 2017 | 2 | Rana et al. [91], Rana et al. [92] | |
| Both | 2000, 2002 | 1 | Zietz et al. [93] | |
| Thyroid disorders | 2007, 2017, 2018 | 3 | Lauritano et al. [94], Brechmann et al. [95], Konrad et al. [96] | |
| Neurology | ||||
| Parkinson disease | 1996–2020 | 7 | Gabrielli et al. [97], Dobbs et al. [98], Fasano et al. [99], Tan et al. [100], Niu et al. [101], Su et al. [102], Hasuike et al. [103] | |
| Autism | 2018 | 1 | Wang et al. [104] | |
| Brain fogginess | 2018 | 1 | Rao et al. [105] | |
| Rheumatology and cutaneous disaeses | ||||
| Systemic sclerosis | 1980–2020 | 9 | Parodi et al. [106], Marie et al. [107], Fynne et al. [108], Savarino et al. [109], Gemignani et al. [110], Marie et al. [111], Adarsh et al. [112], Sawadpanich et al. [113], Garcia-Collinot et al. [114] | |
| Rosacea | 2008, 2016 | 2 | Parodi et al. [115], Drago et al. [116] | |
| Nephrology | ||||
| Chronic kidney disease | 2003 | 1 | Strid et al. [117] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sroka, N.; Rydzewska-Rosołowska, A.; Kakareko, K.; Rosołowski, M.; Głowińska, I.; Hryszko, T. Show Me What You Have Inside—The Complex Interplay between SIBO and Multiple Medical Conditions—A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010090
Sroka N, Rydzewska-Rosołowska A, Kakareko K, Rosołowski M, Głowińska I, Hryszko T. Show Me What You Have Inside—The Complex Interplay between SIBO and Multiple Medical Conditions—A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleSroka, Natalia, Alicja Rydzewska-Rosołowska, Katarzyna Kakareko, Mariusz Rosołowski, Irena Głowińska, and Tomasz Hryszko. 2023. "Show Me What You Have Inside—The Complex Interplay between SIBO and Multiple Medical Conditions—A Systematic Review" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010090
APA StyleSroka, N., Rydzewska-Rosołowska, A., Kakareko, K., Rosołowski, M., Głowińska, I., & Hryszko, T. (2023). Show Me What You Have Inside—The Complex Interplay between SIBO and Multiple Medical Conditions—A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 15(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010090







