Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
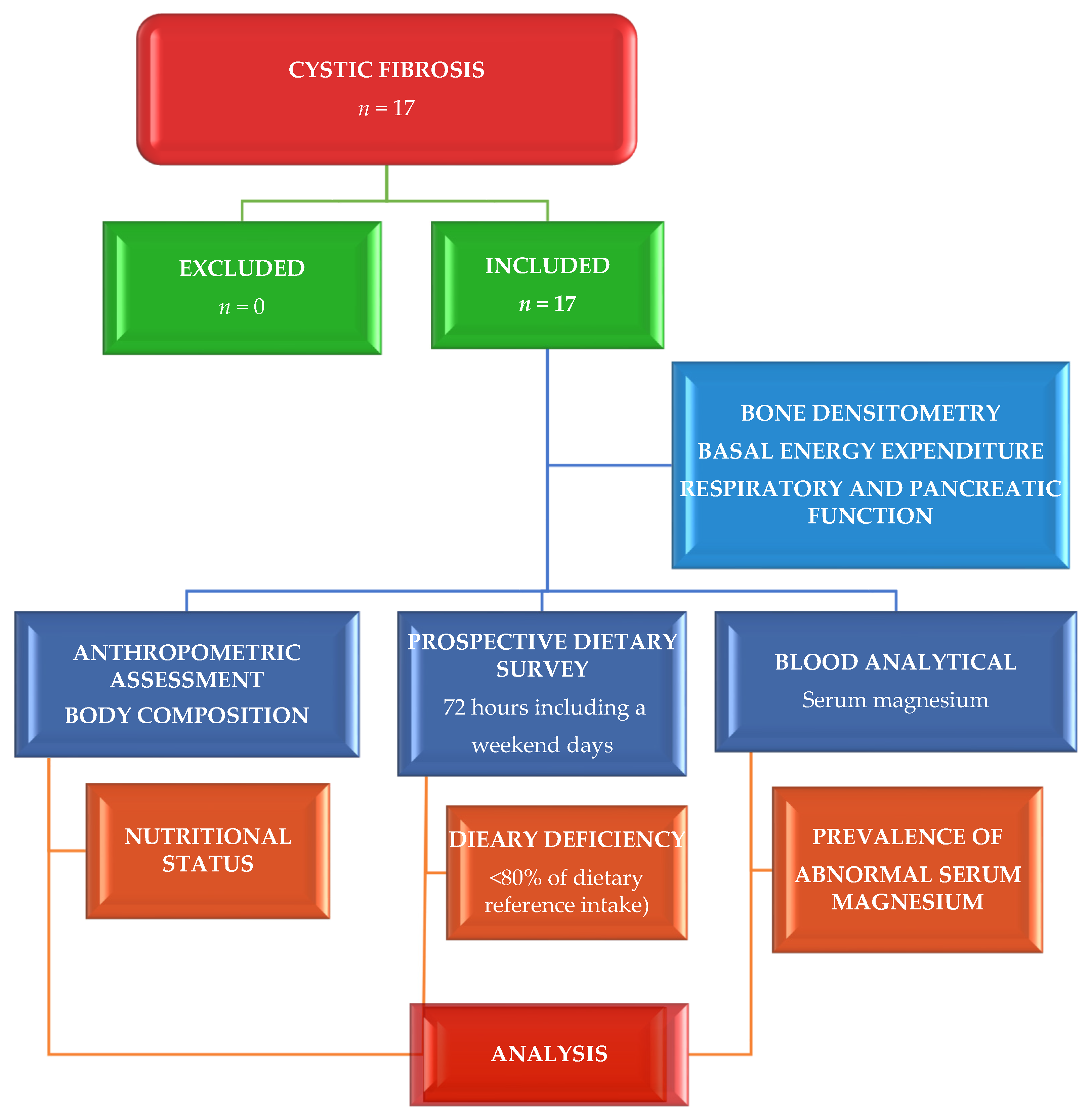
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Design, and Participants
2.2. Ethical Consideration
2.3. Assessment of Phenotypical Characteristics
2.4. Dietary Assessment
2.5. Clinical Evaluation
2.6. Laboratory Exploration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Deficient Magnesium Status
4.2. Calcium/Magnesium Ratios
4.3. Nutritional Status
4.4. Magnesium and Its Associations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaworska, J.; Marach-Mocarska, A.; Sands, D. Uncommon clinical presentation of cystic fibrosis in a patient homozygous for a rare CFTR mutation: A case report. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.C.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Bush, A. Cystic fibrosis. Br. Med. J. 2007, 335, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wrennall, J.A.; Cai, Z.; Li, H.; Sheppard, D.N. Understanding how cystic fibrosis mutations disrupt CFTR function: From single molecules to animal models. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 52, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culhane, S.; George, C.; Pearo, B.; Spoede, E. Malnutrition in cystic fibrosis: A review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrijver, I. Mutation distribution in expanded screening for cystic fibrosis: Making up the balance in a context of ethnic diversity. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matel, J.L.; Milla, C.E. Nutrition in cystic fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 30, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, J.N.; Bashaw, H.; Stallings, V.A. Growth and Nutrition in Cystic Fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Braegger, C.P.; Colombo, C.; Declercq, D.; Morton, A.; Pancheva, R.; Robberecht, E.; Stern, M.; Strandvik, B.; Wolfe, S.; et al. ESPEN-ESPGHAN-ECFS guidelines on nutrition care for infants, children, and adults with cystic fibrosis. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 3, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Eastham, K.M.; Wrightson, N.; Spencer, D.A. Hypomagnesemia in cystic fibrosis patients referred for lung transplant assessment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2007, 6, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Mg in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Soman, S.S.; Yee, J. Mg balance and measurement. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H.; Johnson, L.A.K. Data from controlled metabolic ward studies provide guidance for the determination of status indicators and dietary requirements for magnesium. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 177, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Veronese, N.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium in Aging, Health and Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xun, P.; Tang, Q.; Cai, W.; He, K. Circulating magnesium levels and incidence of coronary heart diseases, hyper-tension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebamowo, S.N.; Jimenez, M.C.; Chiuve, S.E.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; Rexrode, K.M. Plasma magnesium and risk of ischemic stroke among women. Stroke 2014, 45, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Mg in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Liu, K.; Daviglus, M.L.; Morris, S.J.; Loria, C.M.; Van Horn, L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Savage, P.J. Magnesium intake and incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation 2006, 113, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Liu, J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Mg for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre, S.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; Maalouf, N.M.; Sakhaee, K.; Toto, R.D.; Moe, O.W.; Neyra, J.A. Association of serum magnesium with all-cause mortality in patients with and without chronic kidney disease in the Dallas Heart Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 33, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes Sales, C.; Azevedo Nascimento, D.; Queiroz Medeiros, A.C.; Costa Lima, K.; Campos Pedrosa, L.F.; Colli, C. There is chronic latent Mg deficiency in apparently healthy university students. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.T.; Langford, J.R.; Liporace, F.A. Essential Nutrients for Bone Health and a Review of their Availability in the Average North American Diet. Open Orthop. J. 2012, 6, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Alonso, A.; Michos, E.D.; Loehr, L.R.; Astor, B.C.; Coresh, J.; Folsom, A.R. Serum magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium are associated with risk of incident heart failure: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Saito, A.; Kagaya, S.; Fukami, H.; Ojima, Y.; Nagasawa, T. Evaluation of the Predictive Value of the Serum Calcium-Magnesium Ratio for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients. Cardiorenal. Med. 2017, 8, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Pang, J.; Ma, J.; Ling, W.; Li, D. Associations of serum magnesium levels and calcium-magnesium ratios with mortality in patients with coronary artery disease. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Alonso Vicente, C.; Redondo del Río, M.P.; Manuel Marugán de Miguelsanz, J. Zinc Nutritional Status in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Alonso Vicente, C.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M.; Redondo del Río, M.P. Copper and Copper/Zinc Ratio in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisancho, A.R. New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.; Sobradillo, B.; Aguirre, A.; Aresti, U.; Bilbao, A.; Fernández-Ramos, C.; Lizárraga, A.; Lorenzo, H.; Madariaga, L.; Rica, I. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento (Estudios Longitudinal y Transversal); Fundación Faustino Orbegozo: Bilbao, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.J.; Redondo, D.; Conde, F.; Redondo, P.; Franch, M.A. Gráficas Longitudinales de Velocidad de Conducción Media de Ultrasonidos en Falanges. In Estudio Nutricional de Castilla y León; de CyL, J., Ed.; Junta Castilla y León: Valladolid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mataix Verdú, J.; García Diaz, J. NUTRIBER. V. 1.0.; Fundación Universitaria Iberoamericana: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo, M.; Corbalán, M.; Baladía, E.; Cabrerizo, L.; Formiguera, X.; Iglesias, C.; Lorenzo, H.; Polanco, I.; Quiles, J.; De Avila, M.D.R.; et al. Comparison of dietary reference intakes (DRI) between different countries of the European Union, the United States and the World Health Organization. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 384–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Mg basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.; Mohammed, A. Magnesium: The forgotten electrolyte—A review on hypomagnesemia. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagana, K.D.; Pagana, T.J.; Pagana, T.N. Mosby’s Diagnostic & Laboratory Test Reference, 14th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, R.B.; Elin, R.J.; Rosanoff, A.; Wallace, T.C.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Hruby, A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Nielsen, F.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Song, Y.; et al. Perspective: The Case for an Evidence-Based Reference Interval for Serum Magnesium: The Time Has Come12345. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D. Hypercalcemia. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; Updated 4 August 2019; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279037/ (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- Costello, R.B.; Rosanoff, A.; Dai, Q.; Saldanha, L.G.; Potischman, N.A. Perspective: Characterization of Dietary Supplements Containing Calcium and Magnesium and Their Respective Ratio—Is a Rising Ratio a Cause for Concern? Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Barrado, E.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Zinc Nutritional Status in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Copper and Copper/Zn Ratio in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workinger, J.L.; Doyle, R.P.; Bortz, J. Challenges in the diagnosis of Mg status. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Wilson, W. Subclinical Mg deficiency: A principal driver of cardiovascular disease and a public health crisis. Open Heart Vol. 2018, 5, e000668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, E.M.; Popkin, B.M.; Swinburn, B.; Monteiro, C.A. The share of ultra-processed foods and the overall nutritional quality of diets in the US: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study. Popul. Health Metr. 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Vaqar, S. Hypermagnesemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; Updated 5 February 2022; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549811/ (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Razzaque, M.S. Magnesium: Are We Consuming Enough? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatling, L.; Classen, H.G.; Kolpmann, W.R.; Manz, F.; Rob, P.M.; Schimatschek, H.F.; Vierling, W.; Vormann, J.; Weigert, A.; Wink, K. Diagnostik des Magnesiummangels. Aktuelle Empfehlungen der Gesellschaft für MagnesiumForschung e. V. Fortschr. Med. Orig. 2000, 2, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Micke, O.; Vormann, J.; Kraus, A.; Kisters, K. Serum magnesium: Time for a standardized and evidence-based reference range. Magnes. Res. 2021, 34, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.B. Vitamins, trace minerals, and other micronutrients. In Goldman-Cecil Medicine, 25th ed.; Goldman, L., Schafer, A.I., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; chap 218. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, M.; Milani, G.P.; Simonetti, G.D.; Fossali, E.F.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Lava, S.A.G. Mg in cystic fibrosis—Systematic review of the literature. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairi, T.; Amer, S.; Spitalewitz, S.; Alasadi, L. Severe Symptomatic Hypermagnesemia Associated with Over-the-Counter Laxatives in a Patient with Renal Failure and Sigmoid Volvulus. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 560746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, C.G. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.I.; Gunn, E.; Haworth, C.S.; Bilton, D. Characteristics of adults with and without cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; William, J.H.; Scott, D.J.; Lee, J.; Lehman, L.W.; Mark, R.G.; Howell, M.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mukamal, K.J. Proton-pump inhibitor use is associated with low serum Mg concentrations. Kidney Int. Int. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 83, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Haak, N.; King, S.J.; Crowder, T.; Kench, A.; Painter, C.; Saxby, N. Nutrition Guidelines for Cystic Fibrosis in Australia and New Zealand Authorship Group and Interdisciplinary Steering Committee. Highlights from the nutrition guidelines for cystic fibrosis in Australia and New Zealand. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, D.; Ross, D.P.; Talwar, D.; Forrest, E.; Naz Abbasi, H.; Leach, J.P.; Woods, M.; Zhu, L.Y.; Dickson, S.; Kwok, T.; et al. Low serum Mg and 1-year mortality in alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuk, J.; Gittoes, N.J. Contemporary view of the clinical relevance of Magnesium homeostasis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, R. Mg metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.A.; Bruserud, Ø. Hypomagnesemia in critically ill patients. J. Intensive Care 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarleton, E.K. Factors influencing Mg consumption among adults in the United States. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olza, J.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Gil, Á. Reported Dietary Intake, Disparity between the Reported Consumption and the Level Needed for Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Mg and Vitamin D in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zeng, C.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Xie, D.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Association between serum Mg concentration and metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension and hyperuricaemia in knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study in Hunan Province, China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.H.; Ryom, L.; Faurholt-Jepsen, D.; Pressler, T.; Katzenstein, T.L. Prevalence and characteristics of chronic kidney disease among Danish adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 17, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moheet, A.; Moran, A. CF-related diabetes: Containing the metabolic miscreant of cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, S37–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner-Cole, D.; Palmer, C.N.; Ogston, S.A.; Mehta, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Overweight and obesity in deltaF508 homozygous cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvin, M.; Yoon, J.C.; Leey Casella, J.; Blackman, S.M.; Brennan, A.L. Energy balance and obesity in individuals with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18 (Suppl. 2), S38–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cystic Fibrosis. Available online: https://www.cysticfibrosis.org.uk (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Toh, J.W.; Ong, E.; Wilson, R. Hypomagnesaemia associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitors. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laecke, S.V.; Biesen, W.V.; Vanholder, R. Hypomagnesaemia, the kidney and the vessels. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 4003–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Streja, E.; Rhee, C.M.; Mehrotra, R.; Soohoo, M.; Brunelli, S.M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Hypomagnesemia and mortality in incident hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masakane, I.; Nakai, S.; Ogata, S.; Kimata, N.; Hanafusa, N.; Hamano, T.; Wakai, K.; Wada, A.; Nitta, K. Overview of regular dialysis treatment in Japan (as of 31 December 2009). Ther. Apher. Dial. 2012, 16, 11–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.J.; Alvarez, J.A.; Smith, E.M.; Killilea, D.W.; Chmiel, J.F.; Joseph, P.M.; Grossmann, R.E.; Gaggar, A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Tangpricha, V. Vitamin D for Enhancing the Immune System in Cystic Fibrosis Investigators. Changes in Mineral Micronutrient Status During and After. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoky, Z.; Ahmadi, S.; Milman, T.; Kim, T.H.; Du, K.; Di Paola, M.; Pasyk, S.; Pekhletski, R.; Keller, J.P.; Bear, C.E.; et al. Synergy of cAMP and calcium signaling pathways in CFTR regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2086–E2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimessi, A.; Vitto, V.; Patergnani, S.; Pinton, P. Update on Calcium Signaling in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 581645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antigny, F.; Norez, C.; Becq, F.; Vandebrouck, C. CFTR and Ca signaling in cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspray, T.J. Calcium: Basic Nutritional Aspects. In Molecular, Genetic, and Nutritional Aspects of Major and Trace Minerals; Collins, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 5; pp. 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, M.J. Update on the assessment of Mg status. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl. 3), S24–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saris, N.E.L.; Mervaala, E.; Karppanen, H.; Khawaja, J.Á.; Lewenstam, A. Mg2+: An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 294, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisters, K.; Wessels, F.; Küper, H.; Tokmak, F.; Krefting, E.R.; Gremmler, B.; Kosch, M.; Barenbrock, M.; Hausberg, M. Increased calcium and decreased magnesium concentrations and an increased calcium/magnesium ratio in spontaneously hypertensive rats versus Wistar-Kyoto rats: Relation to arteriosclerosis. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Song, P.; Man, Q.; Mao, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L. Suggested Reference Ranges of Blood Mg and Ca Level in Childbearing Women of China: Analysis of China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015). Nutrients 2021, 13, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Jin, L.; Ruan, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Y. Higher levels of magnesium and lower levels of calcium in whole blood are positively correlated with the metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population: A Case-Control Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Office of Dietary Supplements: National Institutes of Health. Magnesium. 2018. Available online: http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/folate (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Moore-Schiltz, L.; Albert, J.M.; Singer, M.E.; Swain, J.; Nock, N.L. Dietary intake of calcium and Magnesium and the metabolic syndrome in the National Health and Nutrition Examination (NHANES) 2001–2010 data. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousa, A.; Havulinna, A.S.; Moltchanova, E.; Taskinen, O.; Nikkarinen, M.; Eriksson, J.; Karvonen, M. Calcium: Magnesium ratio in local groundwater and incidence of acute myocardial infarction among males in rural Finland. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.; Koklu, M.; Gusoy, E.; Gungo, M.; Yasar, S.; Gormel, S.; Yildirim, E.; Gokoglan, Y.; Yuksel, U.C.; Kaul, H.K.; et al. The serum calcium to Magnesium ratio in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q.; Sandler, R.; Barry, E.; Summers, R.; Grau, M.; Baron, J. Calcium, magnesium, and colorectal cancer. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, S.E.; Omofuma, O.O.; Su, L.J.; Maise, A.A.; Woloszynska-Read, A.; Johnson, C.S.; Zhang, H.; Bensen, J.T.; Fontham, E.T.; Mohler, J.L.; et al. Calcium, magnesium, and whole-milk intakes and high-aggressive prostate cancer in the North Carolina-Louisiana Prostate Cancer Project (PCaP). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.C.; Dai, Q.; Zhu, X.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Roumie, C.; Shrubsole, M.J. Associations between calcium and Magnesium intake and the risk of incident oesophageal cancer: An analysis of the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study prospective cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Herrera-Quintana, L.; Molina-López, J.; Gamarra-Morales, Y.; López-González, B.; Miralles-Adell, C.; Planells, E. Response of vitamin D after Magnesium intervention in a postmenopausal population from the province of Granada, Spain. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Ness, R.M.; Schlundt, D.; Cai, Q.; Smalley, W.E.; Li, M.; Shyr, Y.; Zheng, W. The relation of Magnesium and calcium intakes and a genetic polymorphism in the Magnesium transporter to colorectal neoplasia risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Cantwell, M.M.; Murray, L.J.; Zheng, W.; Anderson, L.A.; Coleman, H.G. Dietary magnesium, calcium:magnesium ratio and risk of reflux oesophagitis, Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma: A population-based case-control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Shu, X.O.; Deng, X.; Xiang, Y.B.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Ji, B.; Cai, H.; Chow, W.H.; et al. Modifying effect of calcium/magnesium intake ratio and mortality: A population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Giri, A.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ness, R.; Seidner, D.L.; Giovannucci, E.; Edwards, T.L.; et al. Calcium: Magnesium intake ratio and colorectal carcinogenesis, results from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian cancer screening trial. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibler, E.A.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Hou, L.; Dai, Q. Physical activity, dietary calcium to Magnesium intake and mortality in the National Health and Examination Survey 1999–2006 cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Borenstein, A.R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Seidner, D.L.; Ness, R.; Murff, H.J.; Li, B.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Yu, C.; et al. Ca:Mg ratio, APOE cytosine modifications, and cognitive function: Results from a randomized trial. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 75, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Xun, P.; Shikany, J.M.; He, K. Mg intake is inversely associated with risk of obesity in a 30-year prospective follow-up study among American young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, A.; Katz, T.E.; Sutherland, R.E.; Garg, M.; Liu, V.; Tong, C.W.; Brunner, R.; Quintano, J.; Collins, C.; Ooi, C.Y. Micronutrient intake in children with cystic fibrosis in Sydney, Australia. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blache, D.; Devaux, S.; Joubert, O.; Loreau, N.; Schneider, M.; Durand, P.; Prost, M.; Gaume, V.; Adrian, M.; Laurant, P.; et al. Long-term moderate magnesium-deficient diet shows relationships between blood pressure, inflammation and oxidant stress defense in aging rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 1, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micke, O.; Vormann, J.; Kisters, K. Mg and COVID-19—Some Further Comments—A Commentary on Wallace TC. Combating COVID-19 and Building Immune Resilience: A Potential Role for Mg Nutrition? J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K.; Genuis, S.J. The Importance of Mg in Clinical Healthcare. Scientifica 2017, 2017, 4179326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo-Amaral, C.; Guimarães, E.V.; Camargos, P. Oral Mg supplementation in children with cystic fibrosis improves clinical and functional variables: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Ahmed, I.; Nasrullah, A.; Haq, S.; Ghazanfar, H.; Sheikh, A.B.; Zafar, R.; Askar, G.; Hamid, Z.; Khushdil, A.; et al. Comparison of Serum Mg Levels in Overweight and Obese Children and Normal Weight Children. Cureus 2017, 9, e1607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Duff, A.J.A.; Bell, S.C.; Heijerman, H.G.; Munck, A.; Ratjen, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Southern, K.W.; Barben, J.; Flume, P.A.; et al. ECFS best practice guidelines: The 2018 revision. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, A.A.; Beser, O.F.; Ugur, E.P.; Cokugras, F.C.; Cokugras, H. The effects of nutritional status and intervention on pulmonary functions in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Int. 2021, 63, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.H. Effects of Magnesium depletion on inflammation in chronic disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Mg, Vitamin D., and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Sanchez, J.J.; Alam, A.; Haque, A.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T.; Long, K.Z. Dietary Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Animal Protein Intake and Their Association to the Linear Growth Trajectory of Children from Birth to 24 Months of Age: Results from MAL-ED Birth Cohort Study Conducted in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Nutr. Bull. 2020, 41, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lamas, C.; de Castro, M.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, Á.; Couce, M.L.; Leis, R. Effects of Dairy Product Consumption on Height and Bone Mineral Content in Children: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S88–S96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moussa, Z.; Judeh, Z.M.; Ahmed, S.A. Nonenzymatic Exogenous and Endogenous Antioxidants. In Free Radical Medicine and Biology; Das, K., Das, S., Biradar, M.S., Bobbarala, V., Tata, S.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Chae, J.S.; Shin, H.; Shin, Y.; Song, H.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, B.C.; Roh, K.; Cho, S.; Kil, E.-J. Hormetic dose response to L-ascorbic acid as an anti-cancer drug in colorectal cancer cell lines according to SVCT-2 expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Chae, J.S.; Shin, H.; Shin, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kil, E.J.; Byun, H.S.; Cho, S.H.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; et al. Enhanced Anticancer Effect of Adding Mg to Vitamin C Therapy: Inhibition of Hormetic Response by SVCT-2 Activation. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Ho, L.P.; Kalimuddin, S.; Cherng, B.P.Z.; Teh, Y.E.; Thien, S.Y.; Wong, H.M.; Tern, P.J.W.; Chandran, M.; Chay, J.W.M.; et al. Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19). Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.M.; Hu, X.S.; Yuan, B.J.; Gibson, R.; Dai, Y.; Garg, M. Association between magnesium: Iron intake ratio and diabetes in Chinese adults in Jiangsu Province. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, F.A.; Feitosa, M.M.; Sales, C.H.; Costa, D.M.; Cruz, K.J.C.; Oliveira, F.E.; Colli, C.; do Nascimento Marreiro, D. Influence of Mg on biochemical parameters of iron and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzikov, M.; Blinov, D.; Barakhoeva, Z.; Vovk, L.; Fetisova, Y.; Ovchinnikova, M.; Tischenko, M.; Zorina, I.; Yurasov, V.; Ushakova, T.; et al. Association of the Serum Folate and Total Calcium and Mg Levels Before Ovarian Stimulation with Outcomes of Fresh In Vitro Fertilization Cycles in Normogonadotropic Women. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 732731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Nazim, H.; Liang, Z.; Yang, D. Mg deficiency in plants: An urgent problem. Crop J. 2016, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, S.J.; Thomsen, A.R.; Egbuna, O.; Pang, J.; Baxi, K.; Goltzman, D.; Pollak, M.; Brown, E.M. CaSR-mediated interactions between calcium and Mg homeostasis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E724–E733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-shehawy, E.L.; Allah, S.B.; Mahmoud, A.T.; Mansour, A.E.; Elsayed, O.M. The Impact of Serum Mg Level Disorders on Parathyroid Hormone and Alkaline Phosphatase Levels in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 under Maintenance Hemodialysis. Benha J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 5, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Marginal Zinc Deficiency Increases Mg Retention and Impairs Calcium Utilization in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 128, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.P.; Kanjilal, D.; Teitelbaum, M.; Lin, S.S.; Cottrell, J.A. Zinc as a Therapeutic Agent in Bone Regeneration. Materials 2020, 13, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedifard, Z.; Farrokhian, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z.; Ghotbi, M.; Taghizadeh, M. The effects of combined Mg and zinc supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, H.; Kawashima, Y.; Yanai, H. Serum Zn/Cu Ratio Is Associated with Renal Function, Glycemic Control, and Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, A.; Chan, C.L.; Ode, K.L.; Moheet, A.; Moran, A.; Holl, R. Cystic fibrosis related diabetes: Pathophysiology, screening and diagnosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18 (Suppl. 2), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Găman, M.A.; Dobrică, E.C.; Cozma, M.A.; Antonie, N.I.; Stănescu, A.M.; Găman, A.M.; Diaconu, C.C. Crosstalk of Mg and Serum Lipids in Dyslipidemia and Associated Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, T.; Peacock, J.M.; Iso, H.; Chambless, L.E.; Rosamond, W.D.; Folsom, A.R. Serum and dietary Mg and risk of ischemic stroke: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H.; Lu, Y.F.; Cheng, F.C.; Lee, J.N.; Tsai, L.C. Correlation of Mg intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly type 2 diabetes patients: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maktabi, M.; Jamilian, M.; Amirani, E.; Chamani, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of Mg and vitamin E co-supplementation on parameters of glucose homeostasis and lipid profiles in patients with gestational diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, H.; Jafari Kashi, A.H.; Momen-Heravi, M.; Razzaghi, R.; Amirani, E.; Bahmani, F.; Gilasi, H.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of Mg and vitamin E co-supplementation on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Wound Repair. Regen. 2019, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Rastogi, S.S.; Mani, U.V.; Seth, J.; Devi, L. Does dietary Mg modulate blood lipids? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1991, 30, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogun, A.S.; Adeyinka, A. Biochemistry, Transferrin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ścibior, A.; Hus, I.; Mańko, J.; Jawniak, D. Evaluation of the level of selected iron-related proteins/receptors in the liver of rats during separate/combined vanadium and Mg administration. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbir, M.G. CAMKK2-CAMK4 signaling regulates transferrin trafficking, turnover, and iron homeostasis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mallah, C.; Ghattas, H.; Shatila, D.; Francis, S.; Merhi, K.; Hlais, S.; Toufeili, I.; Obeid, O. Urinary Mg, Calcium, and Phosphorus to Creatinine Ratios of Healthy Elementary School Lebanese Children. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 170, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Díaz, J.J.; Bousoño, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Campos, C.; Málaga, S. Riesgo de urolitiasis en pacientes con fibrosis quística [Risk of urolithiasis in patients with cystic fibrosis]. Nefrología 2009, 29, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, M.; Gómez, S.; González-Gross, M.; Marcos, A. Possible roles of Mg on immune system. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, J.; Romani, A.M.; Valentin-Torres, A.M.; Luciano, A.A.; Ramirez Kitchen, C.M.; Funderburg, N.; Mesiano, S.; Bernstein, H.B. Mg decreases inflammatory cytokine production: A novel innate immunomodulatory mechanism. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6338–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.; Skolnik, E.Y.; Prakriya, M. Ion channels and transporters in lymphocyte function and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Mg deficiency and increased inflammation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S.; Locatelli, L.; Zocchi, M.; Mazur, A. Mg and inflammation: Advances and perspectives. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 115, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Mg in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Tabata, S.; Shindo, Y.; Hotta, K.; Suzuki, K.; Soga, T.; Oka, K. Mitochondrial Mg2+ homeostasis decides cellular energy metabolism and vulnerability to stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, A.; Scarpa, A. Regulation of cell Mg2+. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 298, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, A.A.; Riordan, J.R. Regulation of CFTR ion channel gating by MgATP. FEBS Lett. 1998, 431, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebert, C.; Becq, F.; Vandebrouck, C. Focus on TRP channels in cystic fibrosis. Cell Calcium 2019, 81, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, B.J.; Tuft, B.; Elfrey, J.E.; Smith, A.; Zhao, A.; Morimoto, M.; Chmielinska, J.J.; Tejero-Taldo, M.I.; Mak, I.T.; Weglicki, W.B.; et al. Intestinal inflammation caused by magnesium deficiency alters basal and oxidative stress-induced intestinal function. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2007, 306, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, N.N.; De Smedt, S.C.; Demeester, J.; Acoxyribonucle, I. Directory of Therapeutic Enzymes; Mcgrath, B.M., Walsh, G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, A.A.; Panonnummal, R. ‘Magnesium’—The master cation—As a drug—Possibilities and evidences. Biometals 2021, 34, 955–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Characteristics | Mean ± SD or No. (%) | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 14.8 ± 8 | 15 | 2–31 |
| Body mass index Z-score | −0.95 ± 1.1 | −0.6 | −3.8–0.6 |
| Basal energy expenditure | 1078 ± 303 | 1149 | 440–1490 |
| Theoretical basal energy expenditure | 2193 ± 576 | 2200 | 1066–3251 |
| WHO basal energy expenditure | 1185 ± 233 | 1230 | 598–1559 |
| Serum magnesium (mg/dL) | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 | 1.5–2.3 |
| Serum calcium (mg/dL) | 9.8 ± 0.5 | 9.8 | 8.6–10.6 |
| Serum calcium/magnesium ratio | 4.89 ± 0.54 | 4.69 | 4.26–6.20 |
| Energy (calories) | 2595 ± 464 | 2672 | 1846–3410 |
| Magnesium intake (%DRI) | 125 ± 37 | 125 | 53–180 |
| Calcium intake (%DRI) | 127 ± 44 | 112 | 85–267 |
| Calcium/magnesium intake ratio | 1.09 ± 0.49 | 0.9 | 0.63–2.37 |
| Gender by Nutritional Status (BMI) | Age (Years) | Serum (mg/dL) | Dietary Intake (%DRI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca a | Mg b | Ca/Mg Ratio | Ca | Mg | Ca/Mg Ratio | ||
| Eutrophic | |||||||
| Male | 2 | 10.0 | 1.9 †† | 5.26 ‡ | 147 ** | 106 | 1.39 # |
| Male | 4 | 9.8 | 2.3 | 4.30 | 110 | 173 * | 0.63 # |
| Female | 6 | 9.8 | 2.0 †† | 4.95 ‡ | 122 ** | 99 | 1.24 # |
| Male | 8 | 9.9 | 2.0 †† | 4.51 ‡ | 267 ** | 179 ** | 1.49 # |
| Male | 8 | 9.6 | 2.2 | 4.36 | 154 ** | 180 ** | 0.85 # |
| Female | 9 | 10.4 | 2.1 | 4.95 ‡ | 138 ** | 92 | 1.49 # |
| Female | 9 | 10.1 | 2.2 | 4.59 | 84 | 118 | 0.72 # |
| Male | 13 | 9.7 | 2.1 | 4.62 | 109 | 134 ** | 0.82 # |
| Female | 20 | 10 | 2.2 | 4.50 | 120 | 115 | 1.04 # |
| Male | 23 | 9.5 | 2.0 †† | 4.75 ‡ | 97 | 53 * | 1.81 |
| Female | 23 | 9.3 | 1.5 † | 6.27 ‡ | 114 | 116 | 0.98 # |
| Female | 25 | 9.3 | 2.1 | 4.48 | 147 ** | 151 ** | 0.97 # |
| Undernutrition | |||||||
| Male | 15 | 9.9 | 2.2 | 4.50 | 155 ** | 65 * | 2.37 |
| Female | 15 | 10.6 | 1.9 †† | 5.58 ‡ | 103 | 152 ** | 0.68 # |
| Female | 16 | 10.2 | 2.2 | 4.64 | 87 | 111 | 0.79 # |
| Female | 18 | 8.6 | 1.9 †† | 4.68 | 95 | 132 ** | 0.72 # |
| Female | 31 | 9.7 | 1.7 † | 5.71 ‡ | 96 | 141 ** | 0.68 # |
| Colonization | Yes | No | |
| Magnesium intake (%DRI) | 107 ± 35 | 155 ± 18 | 0.009 * |
| Calcium/magnesium intake ratio | 1.31 ± 0.52 | 0.75 ± 0.13 | 0.008 * |
| Nutritional Status | Undernutrition | Eutrophic | |
| Iron intake (%DRI) | 132 ± 20 | 252 ± 118 | 0.045 * |
| Acute phase reactants | CRP high | Normal | |
| Nitrogen balance | 2.7 ± 4.3 | 13.9 | 0.034 * |
| Respiratory function | Sufficient | Insufficient | |
| Nitrogen intake | 15.1 ± 2.7 | 20.6 ± 2.0 | 0.000 * |
| Nitrogen balance | 0.7 ± 4.3 | 6.3 ± 4.9 | 0.034 * |
| Pancreatic function | Sufficient | Insufficient | |
| Nitrogen balance | 8.9 ± 6.4 | 2.3 ± 4.3 | 0.048 * |
| Serum Magnesium | Serum Calcium | Serum Ca/Mg Ratio | Magnesium Intake | Calcium Intake | Ca/Mg Intake Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | regression | analyses | |||
| r = 0.234, p = 0.049 Age in years | |||||
| r = 0.789, p = 0.003 kilogram’s fat mass by BIA | r = 0.444, p = 0.005 height-for-age Z-score | r = 0.418, p = 0.007 suprailiac skinfold Z-score | |||
| r = 0.332, p = 0.024 IGFBP3 | r = 0.465, p = 0.004 Waterloo II | r = 0.262, p = 0.043 nutritional index | |||
| r = 0.530, p = 0.001 energy intake | r = 0.341, p = 0.017 vitamin C intake | ||||
| r = 0.3454, p = 0.004 protein intake | r = 0.449, p = 0.003 niacin intake | ||||
| r = 0.532, p = 0.001 total lipids intake | r = 0.309, p = 0.025 vitamin B12 intake | ||||
| r = 0.3261, p = 0.043 folic acid intake | |||||
| r = 0.335, p = 0.019 zinc intake | |||||
| r = 0.388, p = 0.017 Ca/Mg intake ratio | |||||
| r = 0.557, p = 0.001 beta-carotene | r = 0.388, p = 0.017 serum vitamin B12 | r = 0.359, p = 0.018 serum vitamin E | |||
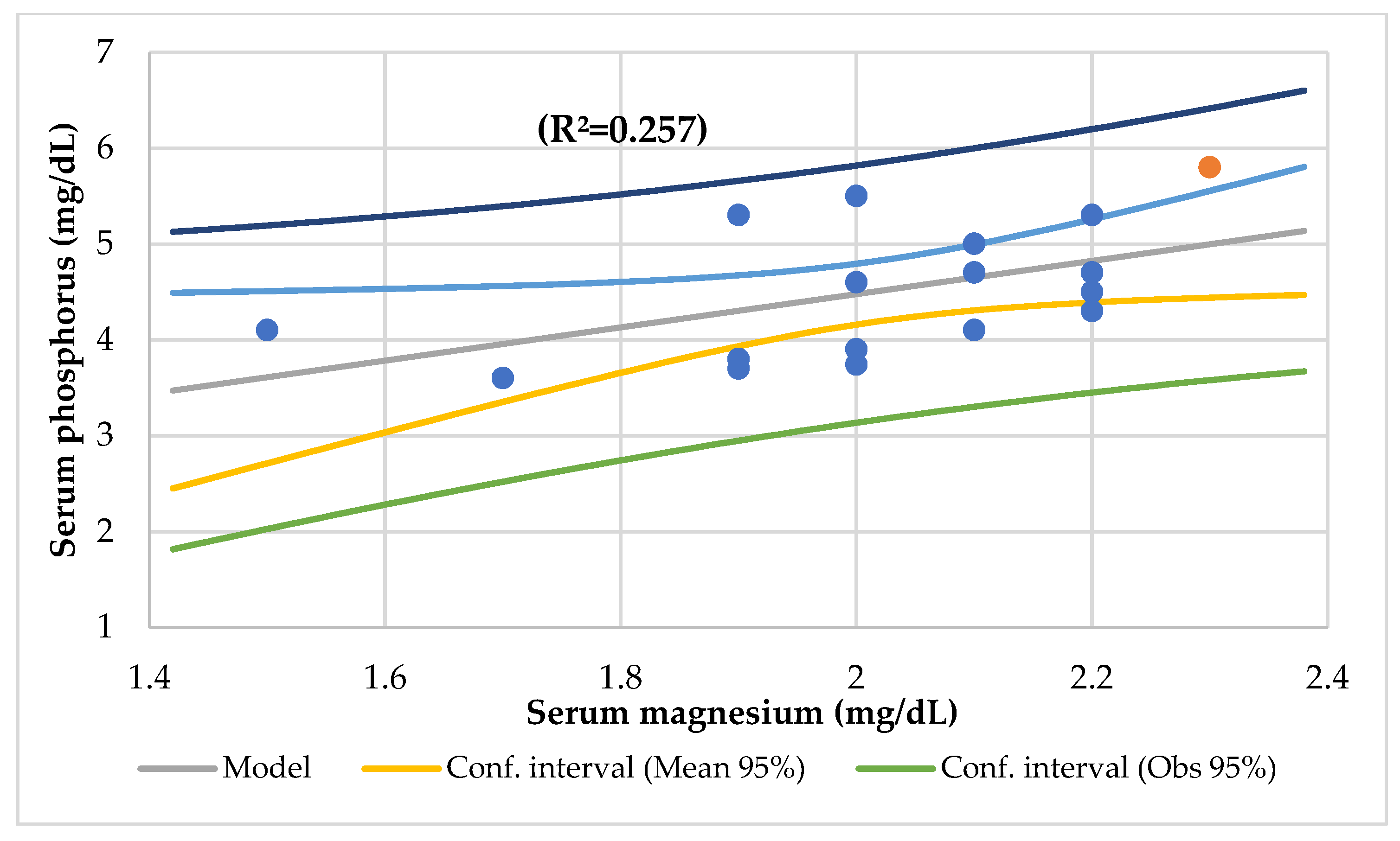
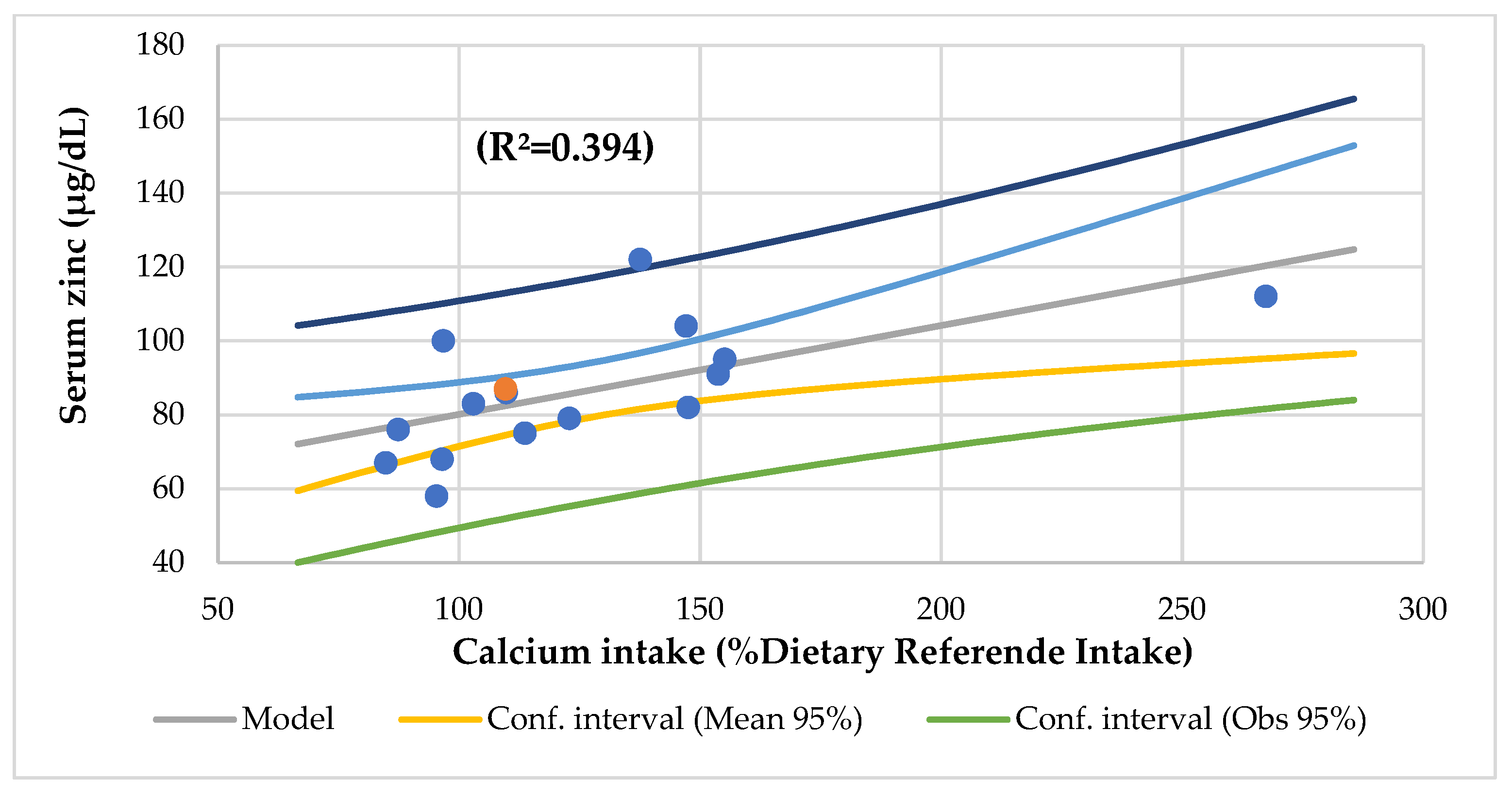
| r = 0.273, p = 0.038 serum phosphorus | r = 0.498, p = 0.002 serum total proteins | r = 0.394, p = 0.009 serum zinc | r = 0.327, p = 0.021 zinc/copper ratio | ||
| r = 0.807, p = 0.000 serum Ca/Mg ratio | r = 0.434, p = 0.006 HDL-cholesterol | ||||
| r = 0.477, p = 0.003 creatinine | r = 0.429, p = 0.006 creatinine | ||||
| r = 0.293, p = 0.030 alkaline phosphatase | |||||
| r = 0.240, p = 0.046 transferrin | r = 0.397, p = 0.009 transferrin saturation index | r = 0.345, p = 0.017 transferrin | r = 0.250, p = 0.049 transferrin saturation index | ||
| r = 0.387, p = 0.013 urine nitrogen | r = 0.270, p = 0.047 urine creatinine | ||||
| r = 0.298, p = 0.035 urine phosphorus | |||||
| r = 0.365, p = 0.017 basophiles | r = 0.281, p = 0.035 MCH | ||||
| r = 0.364, p = 0.013 lymphocytes CD8 | r = 0.268, p = 0.040 platelets | r = 0.533, p = 0.001 IgM | |||
| Multilinear | regression | analyses | |||
| r = 0.712, p = 0.000 Waterloo II, head circumference | r = 0.628, p = 0.002 niacin, folic acid intake | ||||
| r = 0.907, p = 0.000 vitamin C, protein, iron, vitamin B12, polyunsaturated fat intake | r = 0.686, p = 0.002 energy, iron, vitamin C intake | r = 0.906, p = 0.000 total lipids, vitamin B12, calcium intake | r = 0.627, p = 0.002 vitamin B12, niacin intake | ||
| r = 0.590, p = 0.003 serum iron, alkaline phosphatase | r = 0.682, p = 0.001 total lipids, zinc intake | r = 0.639, p = 0.001 serum zinc and iron | |||
| r = 0.986, p = 0.000 serum Ca/Mg ratio, calcium | r = 0.508, p = 0.010 eosinophiles, MCV | r = 0.985, p = 0.000 serum magnesium and calcium | r = 0.615, p = 0.003 platelet, eosinophiles |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marcos-Temprano, M.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091793
Escobedo-Monge MF, Barrado E, Parodi-Román J, Escobedo-Monge MA, Marcos-Temprano M, Marugán-Miguelsanz JM. Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091793
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscobedo-Monge, Marlene Fabiola, Enrique Barrado, Joaquín Parodi-Román, María Antonieta Escobedo-Monge, Marianela Marcos-Temprano, and José Manuel Marugán-Miguelsanz. 2022. "Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091793
APA StyleEscobedo-Monge, M. F., Barrado, E., Parodi-Román, J., Escobedo-Monge, M. A., Marcos-Temprano, M., & Marugán-Miguelsanz, J. M. (2022). Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients, 14(9), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091793









