Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.2. Statistical Analyses
2.3. Evidence Classification and Quality Assessment
3. Results
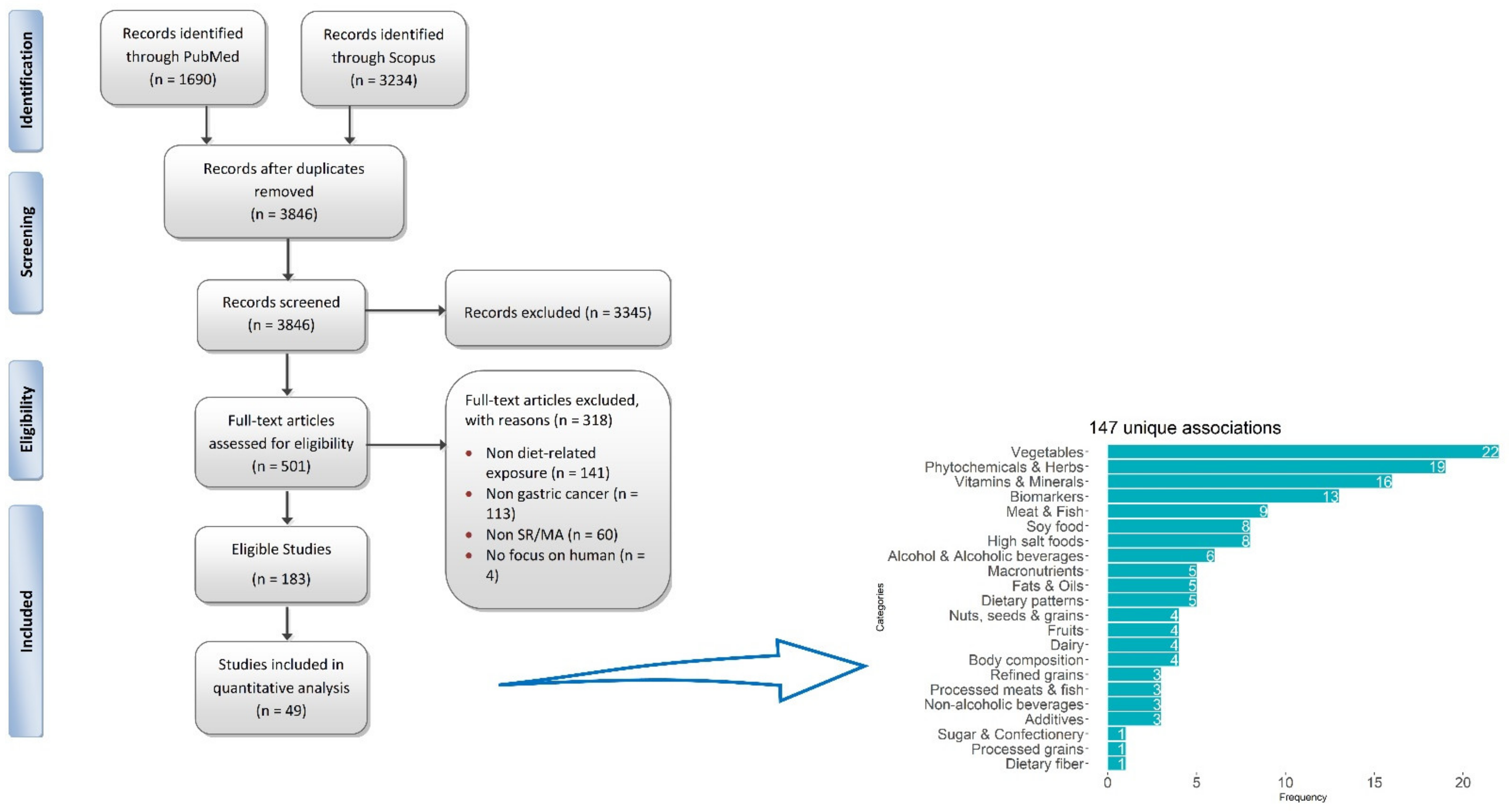
3.1. Overview of the Included Studies
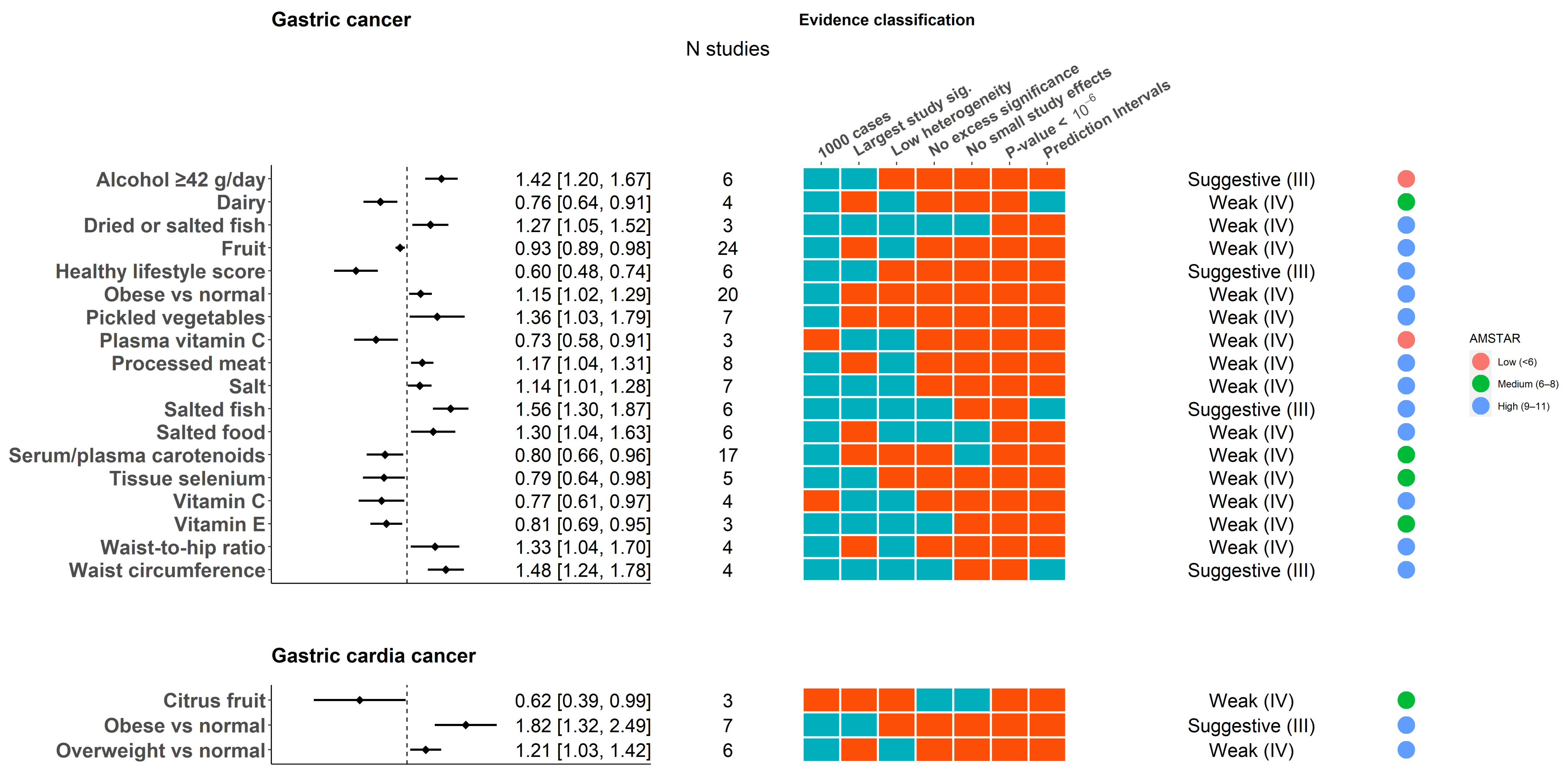
3.2. Gastric Cancer
3.3. Gastric Cardia and Non-Cardia Cancer
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.5. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; El Hajj, N.; Sittler, S.; Lammert, N.; Barnes, R.; Meloni-Ehrig, A. Gastric cancer: Classification, histology and application of molecular pathology. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquhoun, A.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Goodman, K.J.; Forman, D.; Soerjomataram, I. Global patterns of cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer incidence in 2012. Gut 2015, 64, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, T.L.; Fock, K.M. Clinical epidemiology of gastric cancer. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Pearson-Stuttard, J.; Islami, F.; Fedewa, S.A.; Sauer, A.G.; Shuval, K.; Gapstur, S.M.; Jacobs, E.J.; et al. Global patterns in excess body weight and the associated cancer burden. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 69, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibañez, M.; Alguacil, J.; de la Hera, M.G.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.M.; Llorca, J.; Aragonés, N.; Kauppinen, T.; Vioque, J. Occupational exposures and risk of stomach cancer by histological type. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research. Continuous Update Project Expert Report Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Stomach Cancer. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/stomach-cancer/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Papadimitriou, N.; Markozannes, G.; Kanellopoulou, A.; Critselis, E.; Alhardan, S.; Karafousia, V.; Kasimis, J.C.; Katsaraki, C.; Papadopoulou, A.; Zografou, M.; et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Liakos, A.; Tsapas, A.; Ntzani, E.; Haidich, A.-B. Preferred reporting items for overviews of systematic reviews including harms checklist: A pilot tool to be used for balanced reporting of benefits and harms. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 93, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Bouras, E.; Apostolidou-Kiouti, F.; Kokkali, S.; Arvanitidou, M.; Haidich, A.-B. Reporting guidelines on how to write a complete and transparent abstract for overviews of systematic reviews of health care interventions. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 106, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der Simonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Higgins, J.; Deeks, J. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ 2011, 342, d549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; A Trikalinos, T. An exploratory test for an excess of significant findings. Clin. Trials 2007, 4, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Évid. Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P. Integration of evidence from multiple meta-analyses: A primer on umbrella reviews, treatment networks and multiple treatments meta-analyses. Can. Med Assoc. J. 2009, 181, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; A Wells, G.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.; Haenszel, W.; Cuello, C.; Tannenbaum, S.; Archer, M. A model for gastric cancer epidemiology. Lancet 1975, 306, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.; Lam, S.-K. Epidemiology of gastric cancer in relation to diet and Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 13, S166–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosawa, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Xu, J.; Inaba, Y. Highly salted food and mountain herbs elevate the risk for stomach cancer death in a rural area of Japan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, R.M. Measuring Population Sodium Intake: A Review of Methods. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4651–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerstad, M.; Skog, K. Genotoxicity of heat-processed foods. Mutat. Res. 2005, 574, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.G.; A Dangler, C.; Taylor, N.S.; King, A.; Koh, T.J.; Wang, T.C. High-salt diet induces gastric epithelial hyperplasia and parietal cell loss, and enhances Helicobacter pylori colonization in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4823–4828. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Kalliala, I.; Markozannes, G.; Gunter, M.J.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Gabra, H.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Tsilidis, K.K. Adiposity and cancer at major anatomical sites: Umbrella review of the literature. BMJ 2017, 356, j477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Gucalp, A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Hudis, C.A. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Abraham, N.S.; El-Serag, H.B. Meta-Analysis: Obesity and the Risk for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Its Complications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffetta, P.; Hashibe, M. Alcohol and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Personal Habits and Indoor Combustions. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100E. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Li, G.; Li, C. Consumption of fruit, but not vegetables, may reduce risk of gastric cancer: Results from a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.A.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.A.; Jenab, M.; Duell, E.J.; Agudo, A.; Riboli, E. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of gastric adenocarcinoma: A reanalysis of the European Pro-spective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST) study after a longer follow-up. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2910–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, K.A.; Potter, J.D. Vegetables, fruit, and cancer: II. Mechanisms. Cancer Causes Control. 1991, 2, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, E.J.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Llivina, C.; Muñoz, X.; Jenab, M.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Racine, A.; Boeing, H.; Buijsse, B.; et al. Vitamin C transporter gene (SLC23A1 and SLC23A2) polymorphisms, plasma vitamin C levels, and gastric cancer risk in the EPIC cohort. Genes Nutr. 2013, 8, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Koh, W.-P.; Jin, A.; Wang, R.; Yuan, J.-M. Composite protective lifestyle factors and risk of developing gastric adenocarcinoma: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buckland, G.; Travier, N.; Huerta, J.M.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.; Siersema, P.; Skeie, G.; Weiderpass, E.; Engeset, D.; Ericson, U.; Ohlsson, B.; et al. Healthy lifestyle index and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma in the EPIC cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 137, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fung, T.T.; Wang, M.; A Smith-Warner, S.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Tabung, F.K. Association of the Insulinemic Potential of Diet and Lifestyle with Risk of Digestive System Cancers in Men and Women. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Pan, X.F.; Chen, J.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xia, L.; Pan, A. Combined lifestyle factors, incident cancer, and cancer mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, A.; Morais, S.; Rota, M.; Pelucchi, C.; Bertuccio, P.; Bonzi, R.; Galeone, C.; Zhang, Z.F.; Matsuo, K.; Ito, H.; et al. Alcohol intake and gastric cancer: Meta-analyses of published data versus individual participant data pooled analyses (StoP Project). Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 54, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Systematic review: Primary and secondary prevention of gastrointestinal cancers with antioxidant supplements. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Selenium Exposure and Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-analysis and Meta-regression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, J.; Gong, G.; Li, G. Body Mass Index and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-analysis of a Population with More Than Ten Million from 24 Prospective Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2013, 22, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Dai, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Deng, Y.J.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, Q.; Yang, S.; et al. Meta-analysis of the association between nut consumption and the risks of cancer incidence and cancer-specific mortality. Aging 2020, 12, 10772–10794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Bai, Z.-G.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z. Coffee consumption and the risk of incident gastric cancer—A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Hidayat, K.; Shi, B.-M. Abdominal obesity and gastroesophageal cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zha, W.; Hong, X.; Luo, Q. Chili Consumption and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 73, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wei, J.; He, X.; An, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Shao, D.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Landscape of dietary factors associated with risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2820–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Nunes, A.; Jakszyn, P.; Agudo, A. Iron and Cancer Risk—A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Godos, J.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.; Ray, S.; Micek, A.; Pajak, A.; Sciacca, S.; D'Orazio, N.; Del Rio, D.; Galvano, F. A comprehensive meta-analysis on dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and cancer risk: Level of evidence and limitations. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shan, Z.; Ren, H.; Chen, W. Dairy Consumption and Gastric Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Studies. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Xi, Q.; Zhuang, Q.; Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wu, G. Dietary Fat Intake and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Yi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Song, Q.; et al. Association between green tea intake and risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayatzadeh, S.; Feizi, A.; Saneei, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Vitamin D intake, serum Vitamin D levels, and risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.R.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.A.; Kwon, S.O.; Lee, J.-K.; Keum, N.; Park, S.M. Effect of red, processed, and white meat consumption on the risk of gastric cancer: An overall and dose-response meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Cai, Q.; Geng, Q.; Wang, J.; Lan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, D. Vitamin Intake Reduce the Risk of Gastric Cancer: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized and Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e116060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yan, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. The correlation between chili pepper consumption and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 30, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, T.K.; Freedman, N.D.; Fan, J.-H.; Qiao, Y.-L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Taylor, P.R.; Abnet, C. Prediagnostic plasma vitamin C and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, J.; Shi, Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, K.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Association between zinc intake and risk of digestive tract cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Association between dietary antioxidant vitamins intake/blood level and risk of gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ying, X.; Shan, F.; Ji, J. The association of garlic with Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Pan, C.; Ye, C.; Duan, H.; Xu, F.; Yin, L.; Tian, W.; Zhang, S. Meta-analysis of Soy Consumption and Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzen, S.; Van Der Sloot, K.W.J.; Vonk, R.J.; De Bock, G.H.; Alizadeh, B.Z. Diet Quality and Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers Risk: A Meta-Analysis and Critical Assessment of Evidence Quality. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, S.; Briarava, M.; Pilati, P. Vitamin B6 and Cancer Risk: A Field Synopsis and Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 109, djw230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Guan, L. Association of Dietary Cholesterol Intake With Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 722450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabalan, N.; Jarjanazi, H.; Ozcelik, H. The Impact of Capsaicin Intake on Risk of Developing Gastric Cancers: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2014, 45, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, C.; Bosetti, C.; Negri, E.; Lipworth, L.; La Vecchia, C. Olive Oil and Cancer Risk: An Update of Epidemiological Findings through 2010. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Schwedhelm, C.; Galbete, C.; Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wu, L.; Guan, W. Dietary Nitrates, Nitrites, and Nitrosamines Intake and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9872–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhan, R.; Lu, J.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, M.; Tang, S. Grain consumption and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tio, M.; Andrici, J.; Cox, M.R.; Eslick, G.D. Folate intake and the risk of upper gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, G.; Eslick, G.D. Egg consumption and risk of GI neoplasms: Dose–response meta-analysis and systematic review. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turati, F.; Pelucchi, C.; Guercio, V.; La Vecchia, C.; Galeone, C. Allium vegetable intake and gastric cancer: A case-control study and meta-analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 59, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingeliene, S.; Chan, D.S.M.; Aune, D.; Vieira, A.R.; Polemiti, E.; Stevens, C.; Abar, L.; Rosenblatt, D.N.; Greenwood, D.C.; Norat, T. An update of the WCRF/AICR systematic literature review on esophageal and gastric cancers and citrus fruits intake. Cancer Causes Control 2016, 27, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Zhuo, H.; Vasiliou, V.; Zhang, Y. Alcohol consumption and risk of stomach cancer: A meta-analysis. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2021, 336, 109365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, L.-H.; Xiang, Y.-B. Cruciferous vegetable consumption and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Miao, D. Fish consumption and the risk of gastric cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, E.; Yang, J. Association between vitamin A, retinol intake and blood retinol level and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, Y.J.; Guan, X.X.; Guo, Y.; Fan, J.M.; Cui, L.L. Association of whole grains intake and the risk of digestive tract cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Jiao, H.; Qu, L.; Liu, H. Positive association between dietary inflammatory index and gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 72, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, F.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cui, L.; Liu, L.E. The association between soy-based food and soy isoflavone intake and the risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5314–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z. The role of tomato products and lycopene in the prevention of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 80, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ding, K.; Shan, X.; Xia, D. Association between dietary carbohydrate intake, glycemic index and glycemic load, and risk of gastric cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, G.; Ma, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Dietary Fiber Intake Reduces Risk for Gastric Cancer: A Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 113–120.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, Q. Red and processed meat consumption and gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30563–30575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Meng, Q.; Zhai, S. Association of carotenoids with risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouras, E.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Triggi, M.; Siargkas, A.; Chourdakis, M.; Haidich, A.-B. Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091764
Bouras E, Tsilidis KK, Triggi M, Siargkas A, Chourdakis M, Haidich A-B. Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091764
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouras, Emmanouil, Konstantinos K. Tsilidis, Marianthi Triggi, Antonios Siargkas, Michail Chourdakis, and Anna-Bettina Haidich. 2022. "Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091764
APA StyleBouras, E., Tsilidis, K. K., Triggi, M., Siargkas, A., Chourdakis, M., & Haidich, A.-B. (2022). Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients, 14(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091764





