Effects of Online and Face-to-Face Intuitive Eating Interventions on Body Image and Eating Behaviors among Women in China: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
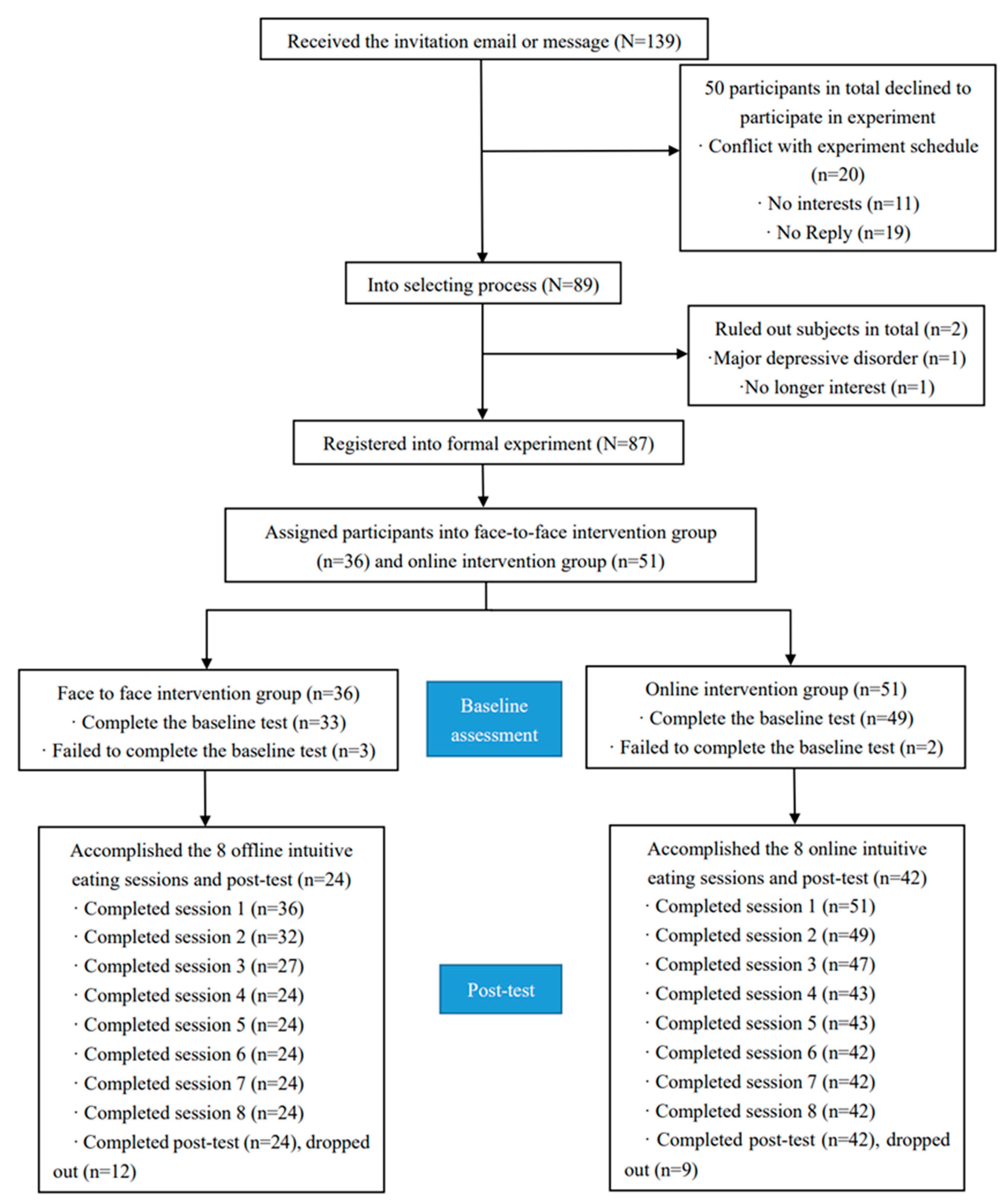
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Research Design
2.3. Intervention Characteristics
2.4. Measures
2.4.1. Short-Form Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire
2.4.2. Intuitive Eating Scale
2.4.3. Body Image Acceptance and Action Questionnaire
2.4.4. Inflexible Eating Questionnaire
2.4.5. Functionality Appreciation Scale
2.4.6. Clinical Impairment Assessment 3.0
2.4.7. Body Dissatisfaction Subscale of the Eating Disorder Inventory
2.4.8. Body Appreciation Scale-2
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Intervention Effects
3.2.1. Eating Behaviors
3.2.2. Body Image
3.2.3. Psychosocial Impairment
3.3. Interaction between Intervention Effects and Intervention Type
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucchianeri, M.M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Body dissatisfaction: An overlooked public health concern. J. Public Ment. Health 2014, 13, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, H.E.; Whiteford, H.A.; Pike, K.M. The global burden of eating disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2016, 29, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lin, R.; Guo, C.; Xiong, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, W. Prevalence of body dissatisfaction and its effects on health-related quality of life among primary school students in Guangzhou, China. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Bai, L.; Lyu, J. Secular trends in the incidence of eating disorders in China from 1990 to 2017: A joinpoint and age–period–cohort analysis. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Correlation between Socio-Cultural Influences and Body Image of Female College Students. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Normal University, Hebei, China, 5 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenaschlam, L.; López Guimerà, G. Intuitive eating: An emerging approach to eating behavior. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Aphramor, L. The impact of a weight—Centred treatment approach on women’s health and health—Seeking behaviours. J. Crit. Diet. 2012, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Austin, S.B.; Taylor, C.B.; Malspeis, S.; Rosner, B.; Rockett, H.R.; Gillman, M.W.; Colditz, G.A. Relation between dieting and weight change among preadolescents and adolescents. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, T.; Tomiyama, A.J.; Westling, E.; Lew, A.; Samuels, B.; Chatman, J. Medicare’s search for effective obesity treatments: Diets are not the answer. Am. Psychol. 2007, 62, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivy, J. Psychological Consequences of Food Restriction. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribole, E.; Resch, E. Intuitive Eating: A Recovery Book for the Chronic Dieter: Rediscover the Pleasures of Eating and Rebuild Your Body Image, 1st ed.; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 30–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tribole, E.; Resch, E. Intuitive Eating, 3rd ed.; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 14–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.A.; dos Santos Alvarenga, M.; de Andrade, L.S.; Teixeira, R.R.; Teixeira, P.C.; da Silva, W.R.; Cuppari, L. Effect of a nutritional behavioral intervention on intuitive eating in overweight women with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belon, K.E.; Serier, K.N.; VanderJagt, H.; Smith, J.E. What is healthy eating? Exploring profiles of intuitive eating and nutritionally healthy eating in college women. Am. J. Health Promot. 2022, 08901171211073870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, L.C.; Benasi, G.; St-Onge, M.-P.; Aggarwal, B. Intuitive and mindful eating to improve physiological health parameters: A short narrative review of intervention studies. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, M.J.; Wade, T.D. Does mindfulness have potential in eating disorders prevention? A preliminary controlled trial with young adult women. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2016, 10, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawks, S.; Madanat, H.; Hawks, J.; Harris, A. The relationship between intuitive eating and health indicators among college women. Am. J. Health Educ. 2005, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylka; Tracy, L. Development and psychometric evaluation of a measure of intuitive eating. J. Couns. Psychol. 2006, 53, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bush, H.E.; Rossy, L.; Mintz, L.B.; Schopp, L. Eat for life: A worksite feasibility study of a novel mindfulness-based intuitive eating intervention. Am. J. Health Promot. 2014, 28, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller-Tyszkiewicz, M.; Rodgers, R.F.; Maïano, C.; Mellor, D.; Sicilia, A.; Markey, C.H.; Aimé, A.; Dion, J.; Pietrabissa, G.; Coco, G.L.; et al. Testing of a model for risk factors for eating disorders and higher weight among emerging adults: Baseline evaluation. Body Image 2022, 40, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.S. Body image, eating attitudes, and eating behaviors among Chinese, Chinese-American and non-Hispanic white women. Diss. Abstr. Int. Sect. B Sci. Eng. 2000, 61, 544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Gu, L.; Han, H. The introduction of treatment and the cultural adaptability of western psychotherapies for eating disorders in China. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattie, E.G.; Adkins, E.C.; Winquist, N.; Stiles-Shields, C.; Wafford, Q.E.; Graham, A.K. Digital mental health interventions for depression, anxiety, and enhancement of psychological well-being among college students: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beintner, I.; Emmerich, O.L.M.; Vollert, B.; Taylor, C.B.; Jacobi, C. Promoting positive body image and intuitive eating in women with overweight and obesity via an online intervention: Results from a pilot feasibility study. Eat. Behav. 2019, 34, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnette, C.B.; Mazzeo, S.E. An uncontrolled pilot feasibility trial of an intuitive eating intervention for college women with disordered eating delivered through group and guided self-help modalities. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribole, E. Intuitive Eating: A Revolutionary Program that Works; St. Martin’s Griffin: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gideon, N.; Hawkes, N.; Mond, J.; Saunders, R.; Tchanturia, K.; Serpell, L. Development and psychometric validation of the EDE-QS, a 12-item short form of the eating disorder examination questionnaire (EDE-Q). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Sun, S.; Fan, X. Validation of the 12-item short form of the eating disorder examination questionnaire in the Chinese context: Confirmatory factor analysis and Rasch analysis. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2020, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylka, T.L. The intuitive eating scale-2: Item refinement and psychometric evaluation with college women and men. J. Couns. Psychol. 2013, 60, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, L. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of intuitive eating scale in college students. Chin. J. Behav. Med. Brain Sci. 2019, 12, 751–754. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoz, E.K.; Wilson, K.G.; Merwin, R.M.; Kellum, K.K. Assessment of body image flexibility: The body image-acceptance and action questionnaire. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 2013, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cai, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Fan, X. Validation of the Chinese version of the body image acceptance and action questionnaire and the mediating role of body image flexibility in the relationship between body dissatisfaction and psychological distress. Behav. Ther. 2020, 52, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, B.; Chen, G.; He, J. Validation of the inflexible eating questionnaire in a large sample of Chinese adolescents: Psychometric properties and gender-related differential item functioning. Eat. Weight. Disord. EWD 2021, 27, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleva, J.M.; Tylka, T.L.; Van Diest, A.M.K. The Functionality Appreciation Scale (FAS): Development and psychometric evaluation in U.S. community women and men. Body Image 2017, 23, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z. Orthorexia nervosa is associated with positive body image and life satisfaction in Chinese elderly: Evidence for a positive psychology perspective. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 54, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, K. Clinical Impairment Assessment Questionnaire (CIA); Springer: Singapore, 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Brytek-Matera, A.; Cooper, M.; Cui, S.; Chen, G. Chinese translation of the clinical impairment assessment (CIA 3.0): Psychometric properties and measurement invariance across sex and age in Chinese adolescents, young adults, and adult men. Eat. Behav. 2022, 45, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmstead, M.P.; Polivy, J. Development and validation of a multidimensional eating disorder inventory for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1983, 2, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-C.M.; Yao, G.; Hu, F.-C.; Chen, K.-Y.; Fang, D. Psychometric properties of the eating disorder inventory in clinical and nonclinical populations in Taiwan. Assessment 2014, 21, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylka, T.L.; Wood-Barcalow, N.L. The body appreciation scale-2: Item refinement and psychometric evaluation. Body Image 2015, 12, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, V.; Ng, S.-K.; Barron, D. Translation and psychometric evaluation of a standard Chinese version of the body appreciation scale-2. Body Image 2016, 18, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleiman, E. Data Management Tools for Real-Time Monitoring/Ecological Momentary Assessment Data [R Package EMAtools version 0.1.3]. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/EMAtools/index.html (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Tylka, T.L.; Wilcox, J.A. Are intuitive eating and eating disorder symptomatology opposite poles of the same construct? J. Couns. Psychol. 2006, 53, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, B.M.; Blechert, J.; Hautzinger, M.; Matthias, E.; Herbert, C. Intuitive eating is associated with interoceptive sensitivity. Effects on body mass index. Appetite 2013, 70, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatos, O.; Kurz, A.L.; Albrecht, J.; Schreder, T.; Kleemann, A.M.; SchöPf, V.; Kopietz, R.; Wiesmann, M.; Schandry, R. Reduced perception of bodily signals in anorexia nervosa. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, J.; Thomas, D. The role of family values in understanding the impact of social class on weight concerns. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1999, 25, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollings, E.K.; Paxton, S.J. Comparison of internet and face-to-face delivery of a group body image and disordered eating intervention for women: A pilot study. Eat. Disord. 2006, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Murray, S.; Compte, E.J.; Song, J.; Nagata, J.M. The muscularity-oriented eating test, drive for muscularity scale, and muscle dysmorphic disorder inventory among Chinese men: Confirmatory factor analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; He, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X. Chinese media coverage of eating disorders: Disorder representations and patient profiles. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Session | Module | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Meet intuitive eating | Basic introduction to the concept of intuitive eating, meeting course participants |
| 2 | Reject dieting | Principle 1: reject the diet mentality. Introduction to dieting’s harm and costs, explanation of the dieting mental cycle |
| 3 | Accept your hunger | Principle 2: honor your hunger. Instruction about hunger and internal body sign awareness |
| 4 | Let’s make peace with food | Principle 3: make peace with food. Overview of how to make peace with food |
| 5 | Deal with the food police | Principle 4: challenge the food police. Explanation of the food police concept and instruction about how to deal with it |
| 6 | Learn to feel fullness and satisfaction | Principles 5 and 6: feel your fullness and discover the satisfaction factor. Instruction about the internal and external appearance of fullness, exploration of self-satisfaction factors |
| 7 | Learn to respect your body with the help of making peace with food | Principles 7 and 8: cope with your feelings without using food and respect your body. Exploration of the harm of emotional eating behaviors, self-care, trust, and respect for your body |
| 8 | Practice and application | Principles 9 and 10: Exercise: feel the difference and honor your health; gentle nutrition. Exploration of pleasurable exercise activities and the advantages and disadvantages of exercise. Instruction on nutrition for food selection. Future plan development |
| Characteristics | Face-to-Face Group | Online Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (SD) | N (%) | M (SD) | N (%) | |
| Age(years) | 19.46(1.29) | 30.74(8.25) | ||
| Origin Area | ||||
| Urban | 23 (95.8%) | 39(92.9%) | ||
| Rural | 1(4.2%) | 3(7.1%) | ||
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Main | 22(91.7%) | 39(92.9%) | ||
| Minority | 2(8.3%) | 3(7.1%) | ||
| Baseline BMI | 23.05(4.66) | 23.44(3.72) | ||
| Post-test BMI | 23.03(4.63) | 23.04(3.75) | ||
| Outcomes | Face-to-Face Group | Online Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before M(SD) | After M(SD) | F Test | Cohen’s d | Before M(SD) | After M(SD) | F Test | Cohen’s d | |
| Eating disorder symptoms | 12.79(8.59) | 8.46(8.40) | F(1, 22.46) = 6.68 * | 1.09 | 12.78(5.78) | 8.48(6.73) | F(1, 41.48) = 20.80 *** | 1.42 |
| Intuitive eating | 72.71(13.30) | 87.46(16.40) | F(1, 23.69) = 30.69 *** | 2.28 | 74.29(10.53) | 84.93(9.94) | F(1, 41.33) = 29.52 *** | 1.69 |
| Body image inflexibility | 3.38(1.66) | 3.08(1.85) | F(1, 24.23) = 1.62 | 0.52 | 4.04(1.25) | 3.36(1.33) | F(1, 41.64) = 11.06 ** | 1.03 |
| Eating inflexibility | 3.08(0.81) | 2.29(0.96) | F(1, 23.92) = 23.49 *** | 1.98 | 3.18(0.70) | 2.70(0.68) | F(1, 41.41) = 18.11 *** | 1.32 |
| Functionality appreciation | 4.39(0.62) | 4.64(0.53) | F(1, 23.55) = 3.60 | 0.78 | 4.21(0.64) | 4.49(0.47) | F(1, 41.67) = 9.31 ** | 0.94 |
| Clinical impairment | 13.88(12.87) | 9.96(12.23) | F(1, 24.16) = 5.81 * | 0.98 | 13.69(9.87) | 8.48(8.99) | F(1, 41.57) = 12.88 *** | 1.11 |
| Body dissatisfaction | 38.17(10.96) | 30.83(13.34) | F(1, 23.84) = 17.92 *** | 1.73 | 41.78(8.98) | 35.90(11.14) | F(1, 42.08) = 30.37 *** | 1.70 |
| Body appreciation | 3.23(1.04) | 3.97(0.92) | F(1, 23.30) = 19.59 *** | 1.83 | 3.10(0.82) | 3.60(0.85) | F(1, 42.99) = 36.64 *** | 1.85 |
| Variables | F Test | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|
| Eating disorder symptoms | F(1, 63.05) = 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Intuitive eating | F(1, 64.07) = 1.96 | 0.35 |
| Body image inflexibility | F(1, 64.08) = 0.27 | 0.28 |
| Eating inflexibility | F(1, 64.00) = 2.88 | 0.42 |
| Functionality appreciation | F(1, 64.15) = 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Clinical impairment | F(1, 63.98) = 0.20 | 0.11 |
| Body dissatisfaction | F(1, 64.15) = 0.89 | 0.24 |
| Body appreciation | F(1, 64.28) = 2.62 | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, C.; Brytek-Matera, A.; He, J. Effects of Online and Face-to-Face Intuitive Eating Interventions on Body Image and Eating Behaviors among Women in China: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091761
Cheng Z, Gao X, Yang C, Brytek-Matera A, He J. Effects of Online and Face-to-Face Intuitive Eating Interventions on Body Image and Eating Behaviors among Women in China: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091761
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ziyue, Xueyan Gao, Chengyang Yang, Anna Brytek-Matera, and Jinbo He. 2022. "Effects of Online and Face-to-Face Intuitive Eating Interventions on Body Image and Eating Behaviors among Women in China: A Feasibility Study" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091761
APA StyleCheng, Z., Gao, X., Yang, C., Brytek-Matera, A., & He, J. (2022). Effects of Online and Face-to-Face Intuitive Eating Interventions on Body Image and Eating Behaviors among Women in China: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients, 14(9), 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091761






