Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Renal Osteodystrophy (ROD)
3. ROD Changes over Decades
4. Why We Need to Perform Bone Biopsy in CKD Patients
5. Indications of Bone Biopsy
6. Technique and Potential Combinations of Bone Biopsy for an Innovative Approach
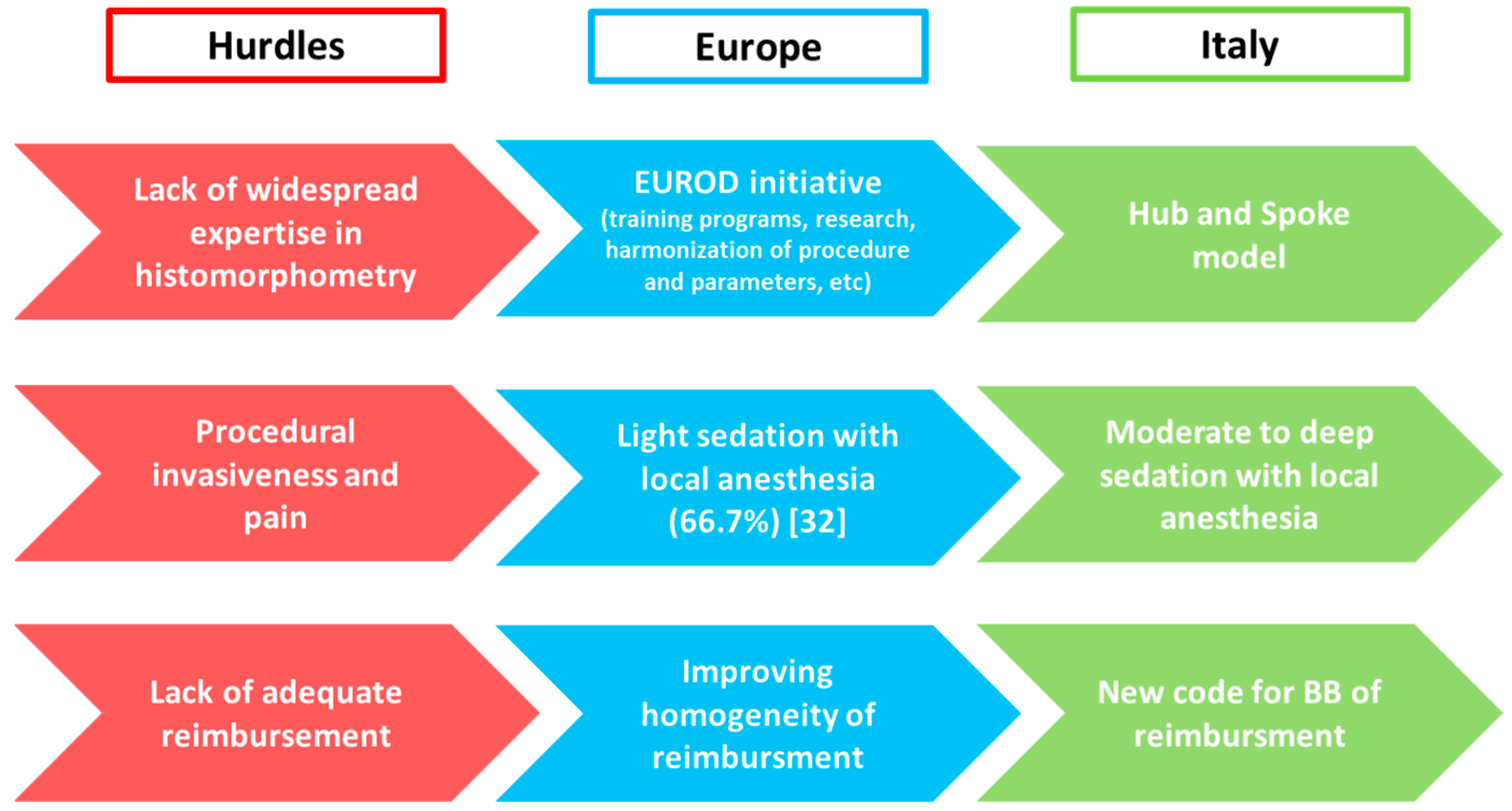
7. Bone Biopsy Practice across Europe
8. Bone Biopsy Practice across Italy
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evenepoel, P.; Behets, G.J.S.; Laurent, M.; D’Haese, P.C. Update on the role of bone biopsy in the management of patients with CKD–MBD. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Cohen-Solal, M.; D’Haese, P.C.; Ferreira, A. European Renal Osteodystrophy (EUROD), an initiative of the CKD-MBD working group of the ERA-EDTA. The Role of Bone Biopsy in the Management of CKD-MBD. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.; Drüeke, T.; Cunningham, J.; Goodman, W.; Martin, K.; Olgaard, K.; Ott, S.; Sprague, S.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bover, J.; Ureña-Torres, P.; Torregrosa, J.-V.; Rodríguez-García, M.; Castro-Alonso, C.; Górriz, J.L.; Alonso, A.M.L.; Cigarrán, S.; Benito, S.; López-Báez, V.; et al. Osteoporosis, bone mineral density and CKD–MBD complex (I): Diagnostic considerations. Nefrología (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 38, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Valenti, M.T.; Giannini, S.; Gallieni, M.; Stefani, F.; Ciresa, R.; Politi, C.; Fusaro, M. Bone Biopsy for Histomorphometry in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): State-of-the-Art and New Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Cunningham, J.; Ferrari, S.; Haarhaus, M.; Javaid, M.K.; Lafage-Proust, M.-H.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Torres, P.U.; Cannata-Andia, J.; Vervloet, M.; et al. European Consensus Statement on the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease stages G4–G5D. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Cianciolo, G.; Brandi, M.L.; Ferrari, S.; Nickolas, T.L.; Tripepi, G.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Iervasi, G.; La Manna, G.; et al. Vitamin K and Osteoporosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Claes, K.; Meijers, B.; Laurent, M.; Bammens, B.; Naesens, M.; Sprangers, B.; Pottel, H.; Cavalier, E.; Kuypers, D. Poor Vitamin K Status Is Associated with Low Bone Mineral Density and Increased Fracture Risk in End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Aghi, A.; Mereu, M.C.; Giusti, A. Fratture da fragilità nella Malattia Renale Cronica (MRC) [Fragility fracture in the Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)]. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2017, 34. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29207223/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Kazama, J.J.; Iwasaki, Y.; Fukagawa, M. Uremic osteoporosis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malluche, H.H.; Mawad, H.W.; Monier-Faugere, M.C. Renal osteodystrophy in the first decade of the new millennium: Analysis of 630 bone biopsies in black and white patients. J. Bone Miner Res. 2011, 26, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, S.M.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Jorgetti, V.; Carvalho, A.B.; Malluche, H.H.; Ferreira, A.; D’Haese, P.C.; Drueke, T.B.; Du, H.; Manley, T.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Histology in Patients with CKD Treated by Dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonara, C.E.M.; Reis, L.M.D.; Quadros, K.R.D.S.; Roza, N.A.V.; Sano, R.; Carvalho, A.B.; Jorgetti, V.; Oliveira, R.B.D. Renal osteodystrophy and clinical outcomes: Data from the Brazilian Registry of Bone Biopsies—REBRABO. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2020, 42, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasovski, G.B.; Bervoets, A.R.J.; Behets, G.; Ivanovski, N.; Sikole, A.; Dams, G.; Couttenye, M.; De Broe, M.E.; D’Haese, P.C. Spectrum of renal bone disease in end-stage renal failure patients not yet on dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P.; Behets, G.J.; Viaene, L.; D’Haese, P.C. Bone histomorphometry in de novo renal transplant recipients in-dicates a further decline in bone resorption 1 year posttransplantation. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, F.; Meng, C.; Pereira, L.; Brito, I.; Frazão, J.M. Bone biopsy: An ally in the management of fragility fractures in chronic kidney disease. Acta Reum. Port. 2018, 43, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, F.; Barreto, D.; Moysés, R.; Neves, K.; Canziani, M.; Draibe, S.; Jorgetti, V.; Carvalho, A. K/DOQI-recommended intact PTH levels do not prevent low-turnover bone disease in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Kazama, J.J.; Yokoyama, K.; Hosoya, T.; Yokoo, T.; Shigematsu, T.; Iseki, K.; Tsubakihara, Y. A higher serum alkaline phosphatase is associated with the incidence of hip fracture and mortality among patients receiving hemodialysis in Japan. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iimori, S.; Mori, Y.; Akita, W.; Kuyama, T.; Takada, S.; Asai, T.; Kuwahara, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tsukamoto, Y. Diagnostic usefulness of bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in predicting fracture in CKD stage 5D patients--a single-center cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 27, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, S.; Gallagher, O.; Gossiel, F.; Paggiosi, M.; Khwaja, A.; Eastell, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of Biomarkers and Imaging for Bone Turnover in Renal Osteodystrophy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, S.A.; Gilbert, J.; Gordon, C.; Bauer, D.C. Cortical PQCT Measures Are Associated with Fractures in Dialysis Patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickolas, T.L.; Stein, E.M.; Dworakowski, E.; Nishiyama, K.K.; Komandah-Kosseh, M.; Zhang, C.A.; McMahon, D.J.; Liu, X.S.; Boutroy, S.; Cremers, S.; et al. Rapid cortical bone loss in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, I.D.B.; Araújo, M.J.C.L.N.; Graciolli, F.G.; Dos Reis, L.M.; Pereira, R.M.; Custódio, M.R.; Jorgetti, V.; Elias, R.M.; David-Neto, E.; Moysés, R.M.A. Biopsy vs. peripheral computed tomography to assess bone disease in CKD pa-tients on dialysis: Differences and similarities. Osteoporos Int. 2017, 28, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltonen, L.; Koivuviita, N.; Seppänen, M.; Tong, X.; Kröger, H.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Metsärinne, K. Correlation between 18F-Sodium Fluoride positron emission tomography and bone histomorphometry in dialysis patients. Bone 2020, 134, 115267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltonen, L.; Koivuviita, N.; Seppänen, M.; Burton, I.S.; Kröger, H.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Metsärinne, K. Bone Histomorphometry and 18F-Sodium Fluoride Positron Emission To-mography Imaging: Comparison between Only Bone Turnover-based and Unified TMV-based Classification of Renal Os-teodystrophy. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 109, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Perez, A.; Farr, J.N. Reference Point Indentation. In Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Herrera, S.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Vilaplana, L.; Nogues, X.; Vera, M.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Mir, M.; Güerri, R.; Crespo, M.; et al. Bone density, microarchitecture, and material strength in chronic kidney disease patients at the time of kidney transplantation. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 2723–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway-Kew, K.L.; Rufus-Membere, P.; Anderson, K.B.; Betson, A.; Gaston, J.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Diez-Perez, A.; Hyde, N.; Pasco, J.A. Bone material strength index is associated with prior fracture in men with and without moderate chronic kidney disease. Bone 2020, 133, 115241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Zhao, S.; Ma, S.; Giuliani, F.; Hansen, U.; Cobb, J.P.; Abel, R.L.; Boughton, O. Microindentation-a tool for measuring cortical bone stiffness? A systematic review. Bone Joint Res. 2017, 6, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Cavalier, E.; D’Haese, P.C. Biomarkers Predicting Bone Turnover in the Setting of CKD. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; D’Haese, P.; Bacchetta, J.; Cannata-Andia, J.; Ferreira, A.; Haarhaus, M.; Mazzaferro, S.; Lafage-Proust, M.-H.; Salam, S.; Spasovski, G.; et al. Bone biopsy practice patterns across Europe: The European renal osteodystrophy initiative—A position paper. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group. KDIGO 2017 Clinical practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disor-der (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2009, 113, S1–S130. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, R.M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Alexander, R.T.; Battistella, M.; Bevilacqua, M.U.; Knoll, G.; Mac-Way, F.; Reslerova, M.; Wald, R.; Acott, P.D.; et al. Canadian Society of Nephrology Commentary on the Kidney Disease Im-proving Global Outcomes 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2020, 7, 2054358120944271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Giannini, S. Histologic diagnosis of metabolic bone diseases: Bone histomorphometry. Reumatismo 2004, 56, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cannata-Andía, J.B.; Martín-Carro, B.; Martín-Vírgala, J.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Bande-Fernández, J.J.; Alonso-Montes, C.; Carrillo-López, N. Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorders: Patho-genesis and Management. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Fusaro, M. Il Trattamento del Paziente Fratturato con Insufficienza Renale Cronica (CKD) [The Treatment of the Patient Presenting with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Fragility Fractures]. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2017. Available online: https://giornaleitalianodinefrologia.it/en/2017/11/trattamento-del-paziente-fratturato-insufficienza-renale-cronica-ckd/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Behets, G.; Viaene, L.; Bammens, B.; Claes, K.; Meijers, B.; Naesens, M.; Sprangers, B.; Kuypers, D.; d’Haese, P.C.; et al. Static histomorphometry allows for a diagnosis of bone turnover in renal osteo-dystrophy in the absence of tetracycline labels. Bone 2021, 152, 116066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerapuncharoen, K. Bone Biopsy. Medscape. May 2021. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2094043-overview (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Novel-Catin, E.; Pelletier, S.; Fouque, D.; Roux, J.-P.; Chapurlat, R.; D’Haese, P.; Behets, G.; Evenepoel, P.; Nickolas, T.L.; Lafage-Proust, M.-H. Quantitative histomorphometric analysis of halved iliac crest bone biopsies yield comparable ROD diagnosis as full 7.5mm wide samples. Bone 2020, 138, 115460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, S.; Pasquali, M. Bone biopsy in chronic kidney disease: Still neglected and in need of revitalization. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Saia, G.; Bettini, G.; Tronchet, A.; Totola, A.; Bedogni, G.; Tregnago, P.; Valenti, M.T.; Bertoldo, F.; Ferronato, G.; et al. Osteomalacia: The Missing Link in the Pathogenesis of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws? Oncologist 2012, 17, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://sinitaly.org/2020/05/04/centri-di-riferimento-per-la-biopsia-ossea (accessed on 10 October 2021).



| Type of Renal Osteodystrophy | Turnover | Mineralization | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteomalacia | Low | Abnormal | Low to Medium |
| Osteitis Fibrosa | High | Normal | Normal to High |
| Adinamic Bone Disease | Low | Normal | Low to Normal |
| Mixed Osteopathy | Normal to High | Abnormal | Low to Normal |
| Osteoporosis | Normal | Normal | Low |
| Evenpoel P et al. [32] | Brazilian Registry of Bone Biopsy (REBRABO) [14] | 2009 KDIGO CKD-MBD Guideline [34] | 2017 KDIGO CKD-MBD Guideline Update [33] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-impact fractures | Nontraumatic bone fractures | Multiple fractures | If knowledge of type of ROD will impact treatment decisions |
| Unexplained bone pain | Persistent bone pain | Persistent bone pain | |
| Prior to parathyroidectomy | Prior to parathyroidectomy | Suspected aluminium toxicity | |
| Prior to antiresorptive drugs | Prior to bisphosphonate therapy | Before osteoporosis treatment | |
| Unexplained hypercalcemia | Unexplained hypercalcemia/phosphoremia | Unexplained hypercalcemia | |
| Radiologic abnormality | Research protocol | Unexplained hypophosphatemia | |
| Suspected toxicity to heavy metals | Suspected aluminum accumulation | ||
| Discordance between PTH and ALP levels |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusaro, M.; Re Sartò, G.V.; Gallieni, M.; Cosmai, L.; Messa, P.; Rossini, M.; Chiodini, I.; Plebani, M.; Evenepoel, P.; Harvey, N.; et al. Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091742
Fusaro M, Re Sartò GV, Gallieni M, Cosmai L, Messa P, Rossini M, Chiodini I, Plebani M, Evenepoel P, Harvey N, et al. Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091742
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusaro, Maria, Giulia Vanessa Re Sartò, Maurizio Gallieni, Laura Cosmai, Piergiorgio Messa, Maurizio Rossini, Iacopo Chiodini, Mario Plebani, Pieter Evenepoel, Nicholas Harvey, and et al. 2022. "Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091742
APA StyleFusaro, M., Re Sartò, G. V., Gallieni, M., Cosmai, L., Messa, P., Rossini, M., Chiodini, I., Plebani, M., Evenepoel, P., Harvey, N., Ferrari, S., Cannata-Andía, J., Trombetti, A., Brandi, M. L., Ketteler, M., Nickolas, T. L., Cunningham, J., Salam, S., Della Rocca, C., ... on behalf of the SIN-SIOMMMS Bone Biopsy Promoting Group. (2022). Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism. Nutrients, 14(9), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091742














