Effectiveness of an Intervention Programme on Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Preschool Child: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
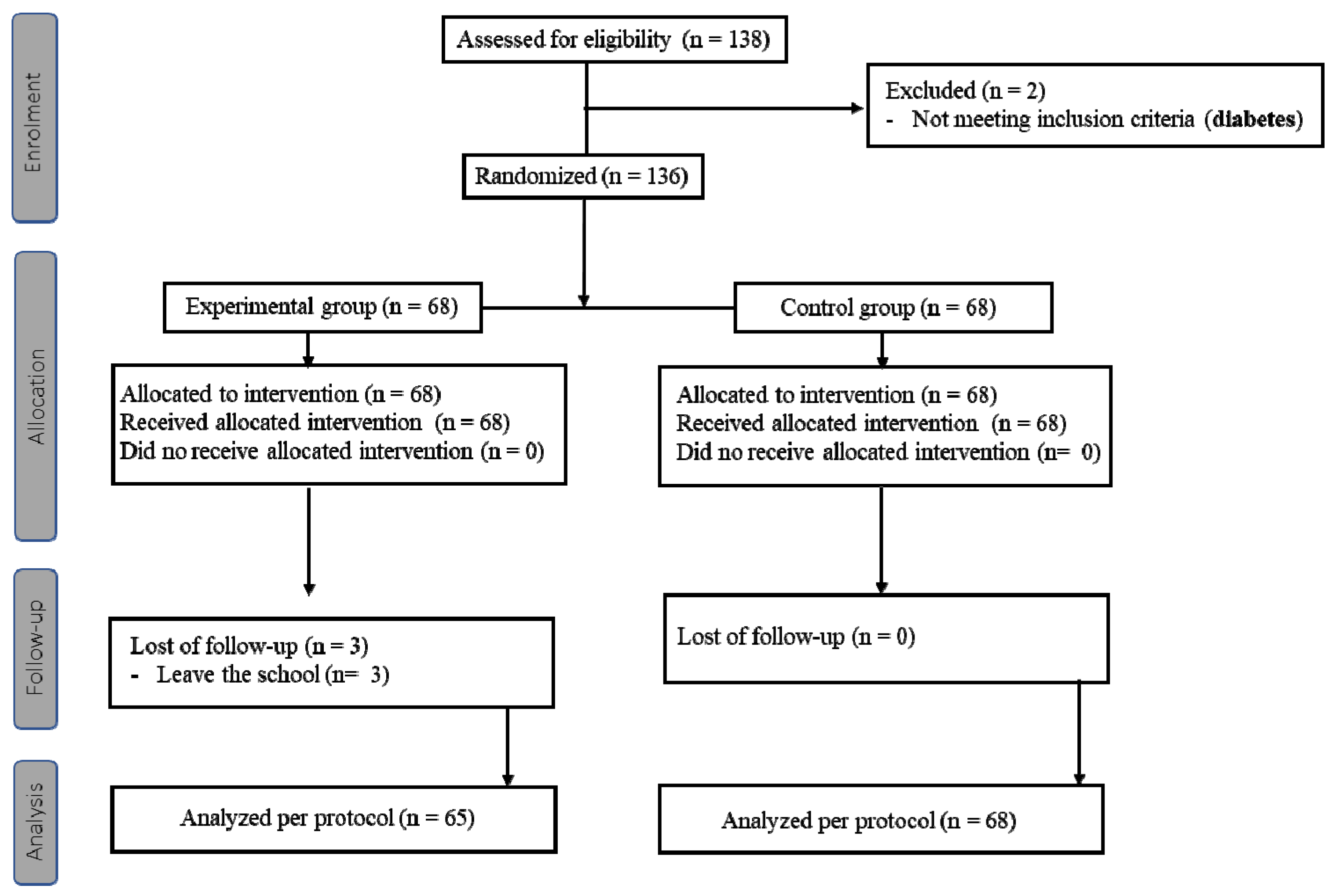
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Main Outcome Measures
2.4. Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Sample Size and Power Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Somatometric Characteristics
3.2. KIDMED Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keys, A. Coronary Heart Disease in Seven Countries. 1970. Nutrition 1997, 13, 250–252, discussion 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, A. Mediterranean Diet and Public Health: Personal Reflections. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1321s–1323s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussaillant, C.; Echeverría, G.; Urquiaga, I.; Velasco, N.; Rigotti, A. Current Evidence on Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet. Rev. Med. Child. 2016, 144, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccio, M.; Iacoviello, L.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G. The Tenth Anniversary as a UNESCO World Cultural Heritage: An Unmissable Opportunity to Get Back to the Cultural Roots of the Mediterranean Diet. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Andersen, L.B.; Byrne, N.M. Physical Activity and Obesity in Children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R. Diet Quality and Physical Activity in Relation to Childhood Obesity. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villanueva, J.; González-Leal, R.; Argente, J.; Martos-Moreno, G. Parental Obesity is Associated with the Severity of Childhood Obesity and its Comorbidities. An. Pediatr. Engl. Ed. 2019, 90, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeste, D.; Carrascosa, A. Management of Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence: From Diet to Surgery. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2012, 59, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zuo, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J.; Chen, C.; Xiang, E.; Li, H.; Cheng, X.; Chen, P. Childhood Obesity Leads to Adult Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Artery Diseases: A 2-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Med. Baltim. 2019, 98, e16825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón García, A.; Marrodán Serrano, M.D.; Villarino Marín, A.; Martínez Álvarez, J.R. Valoración del Estado Nutricional y de Hábitos y Preferencias Alimentarias en Una Población Infanto-Juvenil (7 a 16 Años) de la Comunidad de Madrid. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 394–404. [Google Scholar]
- Weihrauch-Blüher, S.; Wiegand, S. Risk Factors and Implications of Childhood Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompella, P.; Vasquez, K.M. Obesity and Cancer: A Mechanistic Overview of Metabolic Changes in Obesity That Impact Genetic Instability. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1531–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O‘Neil, A.; Quirk, S.E.; Housden, S.; Brennan, S.L.; Williams, L.J.; Pasco, J.A.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F.N. Relationship between Diet and Mental Health in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Public Health 2014, 104, e31–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsberger, M.; Lehtinen-Jacks, S.; Mehlig, K.; Gwozdz, W.; Russo, P.; Michels, N.; Bammann, K.; Pigeot, I.; Fernández-Alvira, J.M.; Thumann, B.F.; et al. Bidirectional Associations between Psychosocial Well-Being and Body Mass Index in European Children: Longitudinal Findings from the IDEFICS Study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; Brands, B.; Poston, L.; Godfrey, K.; Demmelmair, H. Early Nutrition Programming of Long-Term Health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, D.A.; Georgoulis, M.; Psarra, G.; Tambalis, K.D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sidossis, L.S. Prevalence and Lifestyle Determinants of Central Obesity in Children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos-Nanclares, A.; Zazpe, I.; Santiago, S.; Marín, L.; Rico-Campà, A.; Martín-Calvo, N. Influence of Parental Healthy-Eating Attitudes and Nutritional Knowledge on Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality among Preschoolers: The SENDO Project. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Dollman, J.; Petkov, J.; Parletta, N. Associations between Parenting Styles and Nutrition Knowledge and 2–5-Year-Old Children‘s Fruit, Vegetable and Non-Core Food Consumption. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, E.; Rico-Cabanas, L.; Rosgaard, N.; Estruch, R.; Bach-Faig, A. Mediterranean Diet and Cardiodiabesity: A Review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3474–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-da-Silva, L.; Rêgo, C.; Pietrobelli, A. The Diet of Preschool Children in the Mediterranean Countries of the European Union: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaccarino Idelson, P.; Scalfi, L.; Valerio, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquitt, J.L.; Loveman, E.; O‘Malley, C.; Azevedo, L.B.; Mead, E.; Al-Khudairy, L.; Ells, L.J.; Metzendorf, M.I.; Rees, K. Diet, Physical Activity, and Behavioural Interventions for the Treatment of Overweight or Obesity in Preschool Children up to the Age of 6 Years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 3, CD012105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, Youth and the Mediterranean Diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in Children and Adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Kouris-Blazos, A.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Gnardellis, C.; Lagiou, P.; Polychronopoulos, E.; Vassilakou, T.; Lipworth, L.; Trichopoulos, D. Diet and Overall Survival in Elderly People. BMJ Res. Ed. 1995, 311, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognon, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lanfer, A.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Siani, A.; Tornaritis, M.; De Henauw, S.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnár, D.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Overweight and Body Composition in Children from Eight European Countries: Cross-Sectional and Prospective Results from the IDEFICS Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Moore, T.H.; Hooper, L.; Gao, Y.; Zayegh, A.; Ijaz, S.; Elwenspoek, M.; Foxen, S.C.; Magee, L.; O‘Malley, C.; et al. Interventions for Preventing Obesity in Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hamzah, S.H.; Gu, E.; Wang, H.; Xi, Y.; Sun, M.; Rong, S.; Lin, Q. Is School Gardening Combined with Physical Activity Intervention Effective for Improving Childhood Obesity? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochira, A.; Tedesco, D.; Ubiali, A.; Fantini, M.P.; Gori, D. School Gardening Activities Aimed at Obesity Prevention Improve Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference Parameters in School-Aged Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Child. Obes. 2020, 16, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, J.; Carof, M.; Baccar, R.; Bareille, N.; Bastian, S.; Brogna, D.; Burgio, G.; Couvreur, S.; Cupiał, M.; Dufrêne, M.; et al. A Dataset for Sustainability Assessment of Agroecological Practices in a Crop-Livestock Farming System. Data Brief. 2021, 36, 107078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaibi, W.; Mezrhab, A.; Sy, O.; Morton, J.F. Perception and Adaptation of Pastoralists to Climate Variability and Change in Morocco‘s Arid Rangelands. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjdian, D.S.; Cunningham, K.; Bras, H.; Koelen, M.; Vaandrager, L.; Adhikari, R.P.; Talsma, E.F. Unravelling Adolescent Girls‘ Aspirations in Nepal: Status and Associations with Individual-, Household-, and Community-Level Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.; Kelly, B.; McMahon, A.T.; Boyland, E.; Chapman, K.; King, L. Remember Me? Exposure to Unfamiliar Food Brands in Television Advertising and Online Advergames Drives Children‘s Brand Recognition, Attitudes, and Desire to Eat Foods: A Secondary Analysis from a Crossover Experimental-Control Study with Randomization at the Group Level. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Cabrera, S.; Herrera Fernández, N.; Rodríguez Hernández, C.; Nissensohn, M.; Román-Viñas, B.; Serra-Majem, L. Kidmed Test; Prevalence of Low Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Children And Young; A Systematic Review. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazpe, I.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Schröder, H.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Corella, D.; Fiol, M.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Aros, F.; et al. A Large Randomized Individual and Group Intervention Conducted by Registered Dietitians Increased Adherence to Mediterranean-Type Diets: The PREDIMED Study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1134–1144, discussion 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nittari, G.; Scuri, S.; Petrelli, F.; Pirillo, I.; di Luca, N.M.; Grappasonni, I. Fighting Obesity in Children from European World Health Organization Member States. Epidemiological Data, Medical-Social Aspects, and Prevention Programs. Clin. Ter. 2019, 170, e223–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Intemann, T.; Labayen, I.; Artero, E.G.; Alvarez-Bueno, C.; Sanchis-Moysi, J.; Benito, P.J.; Beltran-Valls, M.R.; Pérez-Bey, A.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; et al. Prevalence of Severe/Morbid Obesity and Other Weight Status and Anthropometric Reference Standards in Spanish Preschool Children: The PREFIT Project. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, S.; Goli, S.; Vedantam, S.; Rammohan, A. Progress in Child Stunting across the World from 1990 to 2015: Testing the Global Convergence Hypothesis. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 5598–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brug, J.; van Stralen, M.M.; Te Velde, S.J.; Chinapaw, M.J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Lien, N.; Bere, E.; Maskini, V.; Singh, A.S.; Maes, L.; et al. Differences in Weight Status and Energy-Balance Related Behaviors among Schoolchildren across Europe: The ENERGY-Project. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, F.; Torres Capcha, P.; Serral Cano, G.; Valmayor Safont, S.; Castell Abat, C.; Ariza Cardenal, C. Factors Associated with Overweight and Obesity in Schoolchildren from 8 to 9 Years Old. Barcelona, Spain. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2016, 90, e1–e11. [Google Scholar]
- Eliason, J.; Acciai, F.; DeWeese, R.S.; Vega-López, S.; Ohri-Vachaspati, P. Children‘s Consumption Patterns and Their Parent‘s Perception of a Healthy Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, J.; Cañada, F.; Costillo, E.; Franco, L.; Calderón, A.; Santos, A.L.; Padez, C.; Ruiz, C. La Alimentación Preescolar: Educación para la Salud de Los 2 a Los 6 Años. Enferm. Glob. 2012, 11, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- López del Val, T.; Estivariz, C.F.; Martínez de Icaya, P.; Jaunsolo, M.A.; del Olmo, D.; Vázquez Martínez, C. Consumption of Sweets and Snacks by a Population of School Children in the Autonomous Community of Madrid. The CAENPE Group. Med. Clin. Barc. 1997, 109, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leis Trabazo, R.; Moreno Villares, J.M.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Gil Hernández, Á. Nutritional Study in Spanish Pediatric Population (EsNuPI). Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 37, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpin, L.; Jebb, S.A.; Johnson, L.; Llewellyn, C.; Ambrosini, G.L. Sources and Pattern of Protein Intake and Risk of Overweight or Obesity in Young UK Twins. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B. Diet Quality, Saturated Fat and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sobaler, A.M.; Aparicio, A.; Rubio, J.; Marcos, V.; Sanchidrián, R.; Santos, S.; Pérez-Farinós, N.; Dal-Re, M.; Villar-Villalba, C.; Yusta-Boyo, M.J.; et al. Adequacy of Usual Macronutrient Intake and Macronutrient Distribution in Children and Adolescents in Spain: A National Dietary Survey on the Child and Adolescent Population, ENALIA 2013–2014. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Maggi, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet is Associated with Better Quality of Life: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, B.; Ortega, R.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Aparicio, A.; Perea, J.M. Mother‘s Age as a Conditioning Factor of Food Consumption and Energy and Nutrients Intake of Their Offspring at Pre-School Age. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Díez López, I.; Sarasua Miranda, A. Immigrant Children Have More Risk for Childhood Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. An. Pediatr. Barc. Spain 2014, 80, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serral Cano, G.; Bru Ciges, R.; Sánchez-Martínez, F.; Ariza Cardenal, C. Overweight and Childhood Obesity According to Socioeconomic Variables in Third Grade School-Age Children in the City of Barcelona. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambalia, A.Z.; Dickinson, S.; Hardy, L.L.; Gill, T.; Baur, L.A. A Synthesis of Existing Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of School-Based Behavioural Interventions for Controlling and Preventing Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Robbins, L.B.; Wen, F.; Zhang, N. Lifestyle Interventions in Preschool Children: A Meta-analysis of Effectiveness. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 53, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ek, A.; Delisle Nyström, C.; Chirita-Emandi, A.; Tur, J.A.; Nordin, K.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Martínez, J.A.; Frost, G.; Garcia-Perez, I.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Overweight and Obesity in Preschoolers: The More and Less Europe Study: An Intervention within the STOP project. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguacel, I.; Fernández-Alvira, J.M.; Ahrens, W.; Bammann, K.; Gwozdz, W.; Lissner, L.; Michels, N.; Reisch, L.; Russo, P.; Szommer, A.; et al. Prospective Associations between Social Vulnerabilities and Children‘s Weight Status. Results from the IDEFICS Study. Int. J. Obes. Lond. 2018, 42, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, A.; Backholer, K. Reducing Socioeconomic Inequalities in Obesity: The role of Population Prevention. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioret, S.; Betoko, A.; Forhan, A.; Charles, M.A.; Heude, B.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B. Dietary Patterns Track from Infancy to Preschool Age: Cross-sectional and Longitudinal Perspectives. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Adolph, A.L.; Sacher, P.M.; Barlow, S.E.; Pont, S.; Sharma, S.; Byrd-Williams, C.; Hoelscher, D.M.; Butte, N.F. Behavior Modification of Diet and Parent Feeding Practices in a Community- vs. Primary Care-Centered Intervention for Childhood Obesity. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2019, 51, 150–161.e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, S.M.; Ziegler, M.L.; McCullough, M.B.; Stough, C.O.; Zion, C.; Simon, S.L.; Ittenbach, R.F.; Stark, L.J. Changes in Diet Quality and Home Food Environment in Preschool Children following Weight Management. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, D.L. Childhood Obesity: Influential Factors and Interventions. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2018, 42, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experimental Group (n = 65) | Control Group (n = 68) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (SD) | 48.47 (2.837) | 47.86 (2.888) | 0.24 | |
| Sex, n (%) | Boys | 33 (55.0) | 34 (50.7) | 0.632 |
| Girls | 27 (45.0) | 33 (49.3) | ||
| Weight, Kg (SD) | 18.023 (2.226) | 18.075 (1.874) | 0.887 | |
| BMI, n (%) | Normal | 35 (58.3) | 45 (69.2) | 0.370 |
| Overweight | 18 (30.0) | 16 (24.6) | ||
| Obesity | 7 (11.7) | 4 (6.2) | ||
| Height, cm (SD) | 104.16 (5.359) | 105.16 (4.106) | 0.246 | |
| BMI, Kg/m2 (SD) | 16.55 (1.199) | 16.31 (1.131) | 0.247 | |
| Groups | n | Mean (SD) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI at the start of the study | Experimental | 60 | 16.5570 (1.19939) | 0.247 |
| Control | 65 | 16.3143 (1.13131) | ||
| BMI after 12 months of monitoring | Experimental | 59 | 16.12004 (1.12004) | 0.026 |
| Control | 63 | 16.07826 (1.07926) | ||
| BMI after 36 months | Experimental | 61 | 15.7430 (1.29284) | <0.001 |
| Control | 64 | 16.5111 (1.06097) |
| Beginning | 12 Months | End of Follow-Up | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total KIDMED score | Experimental Group: 5.90 | Experimental Group: 6.09 | Experimental Group: 6.48 |
| Control Group: 6.08 | Control Group: 5.88 | Control Group: 6.08 | |
| p = 0.459 | p = 0.367 | p = 0.076 | |
| Eats fresh or cooked vegetables at least once a day | Experimental Group: 43.3% | Experimental Group: 40.7%, | Experimental Group: 44.3% |
| Control Group: 50.8% | Control Group: 64.1% | Control Group: 60.9% | |
| p = 0.405 | p = 0.009 | p = 0.063 | |
| Consumes legumes more than once a week | Experimental Group: 68.3% | Experimental Group:88.9% | Experimental Group:88.5% |
| Control Group: 67.7% | Control Group:64.1% | Control Group:64.1% | |
| p = 0.939 | p = 0.002 | p = 0.001 | |
| Consumes dried fruit and nuts at least 2–3 times a week | Experimental Group: 73.3% | Experimental Group: 86.4% | Experimental Group: 83.6% |
| Control Group: 70.8% | Control Group: 70.3% | Control Group: 70.3% | |
| p = 0.750 | p = 0.031 | p = 0.078 | |
| Has milk and/or dairy for breakfast | Experimental Group: 86.7% | Experimental Group: 86.4% | Experimental Group: 72.1% |
| Control Group: 86.2% | Control Group: 85.9% | Control Group: 84.4% | |
| p = 0.930 | p = 0.933 | p = 0.096 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martíncrespo-Blanco, M.C.; Varillas-Delgado, D.; Blanco-Abril, S.; Cid-Exposito, M.G.; Robledo-Martín, J. Effectiveness of an Intervention Programme on Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Preschool Child: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081536
Martíncrespo-Blanco MC, Varillas-Delgado D, Blanco-Abril S, Cid-Exposito MG, Robledo-Martín J. Effectiveness of an Intervention Programme on Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Preschool Child: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2022; 14(8):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartíncrespo-Blanco, María Cristina, David Varillas-Delgado, Saray Blanco-Abril, María Gema Cid-Exposito, and Juana Robledo-Martín. 2022. "Effectiveness of an Intervention Programme on Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Preschool Child: A Randomised Controlled Trial" Nutrients 14, no. 8: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081536
APA StyleMartíncrespo-Blanco, M. C., Varillas-Delgado, D., Blanco-Abril, S., Cid-Exposito, M. G., & Robledo-Martín, J. (2022). Effectiveness of an Intervention Programme on Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Preschool Child: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 14(8), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081536









