Abstract
The association between mother’s education and the World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) eight Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) core indicators has yet to be explored in South Asia (SA). This study aimed to explore the association between mother’s education and the WHO’s eight IYCF core indicators in SA. We analyzed data from the most recent nationally representative Demographic and Health Surveys of six South Asian Countries (SACs)—Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, and Pakistan. We found significantly higher odds (adjusted odds ratio, AOR, 1.13 to 1.47) among mothers who completed secondary or higher education than among mothers with education levels below secondary for the following seven IYCF indicators: early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF), exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months (EBF), the introduction of solid, semisolid or soft foods (ISSSF), minimum dietary diversity (MDD), minimum meal frequency (MMF), minimum acceptable diet (MAD), and consumption of iron-rich or iron-fortified foods (CIRF); the exception was for the indicator of continued breastfeeding at one year. Country-specific analyses revealed significantly higher odds in EIBF (AOR 1.14; 95% CI: 1.11, 1.18) and EBF (AOR 1.27; 95% CI: 1.19, 1.34) among mothers with secondary or higher education levels in India. In contrast, the odds were lower for EIBF in Bangladesh and for EBF in Pakistan among mothers with secondary or higher education levels. For country-specific analyses for complementary feeding indicators such as ISSSF, MDD, MMF, MAD, and CIRF, significantly higher odds (AOR, 1.15 to 2.34) were also observed among mothers with secondary or higher education levels. These findings demonstrate a strong positive association between mother’s education and IYCF indicators. Strengthening national policies to educate women at least to the secondary level in SACs might be a cost-effective intervention for improving IYCF practices.
1. Introduction
Globally, inappropriate and suboptimal feeding practices during the first year of life are responsible for two-thirds of child deaths [1]. In low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), only one-half of infants are put to the breast within one hour of birth [2]. Below the optimal level, only 37% of children 0–5 months of age in LMICs are exclusively breastfed [3]. According to the 2010 Global Burden of Disease study, suboptimal breastfeeding was one of the three main causes of disease across much of the Sub-Saharan African region [4]. In South Asia (SA), poor nutritional status and suboptimal and inappropriate IYCF practices prevail [5]. Globally, about 50% of undernourished children reside in SA [6]. The early initiation of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding rates are also low in this region, at 39% and 46%, respectively [7]. Although half of the children start timely complementary feeding, the rates of dietary diversity and meal frequency remain low in SA [8].
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended initiating breastfeeding within one hour of birth, exclusive breastfeeding for up to six months with continued breastfeeding at one year, and the timely introduction of complementary feeding with feedings including the recommended number of diversified foods [9]. Early initiation of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding practices can reduce neonatal mortality by 22% and mortality in children under two years of age by 13.8%, especially in LMICs [10,11]. To ensure optimum growth and development of a child, the timely introduction of complementary feeding with sufficient quantities and qualities of complementary foods is compulsory [12,13,14]. Appropriate feeding during the first two years of life reduces vulnerability to illnesses such as acute respiratory infections, diarrheal diseases, undernutrition and also reduces childhood mortality to approximately 6% [15,16,17].
Various studies have been conducted in SA to explore the associated factors of IYCF practices [18,19,20,21,22] and have identified a range of detrimental factors, including but not limited to the place of residence, household wealth status, household income, cultural beliefs, parental education, mother’s age, mother’s occupation, antenatal and postnatal care, child’s age, child’s sex, modes of delivery, place of delivery, and women’s and mother’s exposure to mass media [18,19,20,21,22]. Among all these factors, the role of mother’s education is beneficial to health and nutritional well-being [23,24,25,26,27,28]. Some single-country-specific studies also found a positive association between mother’s education and IYCF practices [5,29,30]. However, the data that were used in these studies were neither up-to-date nor did they cover all South Asian Countries (SACs). The assessment of all the WHO’s IYCF core indicators is also scarce in SA. Furthermore, there is a lack of pooled evidence regarding the association between mother’s education and IYCF practices. The pooled estimates at the regional level are particularly important for cross-regional comparison and for designing and implementing interventions at the regional level. Therefore, there is a need for strong evidence both for pooled and country-specific data regarding the association between mother’s education and the WHO’s IYCF core indicators.
In our study, we hypothesized that there is a positive association between mother’s education and the WHO’s IYCF core indicators. Mother’s education is positively associated with the nutritional status of children [23]. Also, mother’s education is strongly associated with access to healthcare facilities or skilled birth attendants for childbirth [24], childhood immunization through vaccination [25], and hygiene practices [26]. By its profound impact on healthcare-seeking behavior, mother’s education has helped to reduce childhood undernutrition and mortality [27,28]. Given the importance of mother-child interactions and the role of mothers in childcare and health-related practices, we considered mother’s education as the main exposure variable. However, evidence-based inference on this hypothesis remains unseen in SA. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to explore the association between mother’s education and all of the WHO’s IYCF core indicators in SACs. The findings generated from this study might be directives for policymakers in SACs to design interventions for improving IYCF practices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Design
This study analyzed the most recent nationally representative data of six SACs—Afghanistan (2015), Bangladesh (2017–2018), India (2016), Maldives (2017), Nepal (2016), and Pakistan (2018). Though Bhutan and Sri Lanka are on the list of SACs, we excluded these two countries because in Bhutan the DHS program is not functioning, and the latest Sri Lankan DHS data are restricted. The DHS follows a similar methodology to collect cross-sectional data by applying a multistage cluster sampling technique. The use of the unique methodology of the DHS allows the cross-country comparison of estimates. The DHS compiles information on a variety of health-related indicators and their sociodemographic factors, including the socioeconomic status of the household, women’s empowerment, and healthcare-seeking behaviors. The interviews are conducted only where the respondent gives voluntary informed consent. The DHS data are publicly available from the DHS program website (https://dhsprogram.com/, accessed on 3 April 2020) [31].
2.2. Participants
The participants in this study were the youngest children, aged 0–23 months, and their mothers, aged 15–49 years. The DHS usually collects data on IYCF practices for the most recent birth child of the mother. Therefore, we included mothers and their most recent birth child of 0–23 months of age as our study participants.
2.3. Outcome Variables
The outcome variables of this study were the eight WHO IYCF core indicators: early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF), exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months (EBF), continuing breastfeeding at 1 year (CBF), the introduction of solid, semi-solid or soft foods (ISSSF), minimum dietary diversity (MDD), minimum meal frequency (MMF), minimum acceptable diet (MAD), and consumption of iron-rich or iron-fortified foods (CIRF). The outcome variables were dichotomous (yes, no). We used the standard definitions of the WHO for constructing the IYCF core indicators [9].
2.4. Exposure Variables
The main exposure variable of this study was the level of mother’s education. Based on the percentage distribution among the different levels of mother’s education status (no education, primary, secondary, and higher education), we categorized mother’s education into two levels: below secondary (no education or primary-level education) and secondary or above (secondary education or higher). We also considered the years of mother’s schooling as a continuous variable for sensitivity analysis. In most cases, the mother becomes the primary caregiver of a child and mother’s knowledge of feeding practices directly reflects the nutrition intake of the child. Mother’s education also has multiple benefits for improving the nutritional status of children as well. Given the importance of mother’s education, we selected it as our main exposure variable for establishing the linkage between mother’s education and IYCF practices.
2.5. Independent Variables
The independent variables of this study were mother’s age (categorized as 15–24 years, 25–34 years, and ≥35 years), age of the children (continuous), sex of the children (male and female), type of place of residence (urban and rural), and wealth index (poorest, poorer, middle, richer, and richest). We included some selective independent variables in our study. The selection of independent variables was made in terms of their commonness, significance, and existence in the existing literature or dataset [32,33,34,35,36]. Therefore, the association between mother’s education and IYCF practices was explored by controlling the effect of these selected independent variables. We also included the study years (2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018) in which the studies were conducted to control for variations due to different survey periods in the pooled estimates.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
All the data analyses were performed by the statistical software package Stata, version 15.0 SE (College Station, TX, USA). The weighted estimates of sociodemographic and IYCF indicators were performed for both pooled and country-specific analyses. We adjusted the effect of complex survey design, including for country-specific sampling weights and clusters, while estimating the percentages. For pooled datasets, we denormalized the sampling weight and created a new population-level weight by dividing the sampling weight by the denormalized weight. We also constructed a unique cluster variable by combining country and cluster numbers. The population-level weight and unique cluster were used to calculate the pooled estimates. The population-level weight was calculated to avoid the effect of countries with a large population (such as India) balancing countries with a smaller population (such as the Maldives).
We performed generalized estimating equation (GEE) models for pooled and country-specific data to explore the association between mother’s education and IYCF indicators at both the regional and country levels, respectively. In the multiple GEE models, we adjusted the models by mother’s age, child’s age, child’s sex, place of residence, and wealth index. We used the log-binomial model with logit link in the GEE models. When the log-binomial model was unable to achieve convergence, we used Poisson models with log links. The strength of association was measured in adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We also performed a sensitivity analysis that considered mother’s education as a continuous variable (years of schooling) to explore the pattern of association. A p-value of <0.05 was considered to determine the statistical significance of all the two-sided tests performed. We checked the collinearity among the independent variables and found the variance inflation factor <1.50, indicating negligible collinearity among the independent variables. We performed a pooled analysis since a pooled estimate is crucial to obtaining a firm conclusion from the results or data of different studies when the same methodology and analysis techniques are applied. The complete observations of the outcomes, exposure, and independent variables were included in the regression models. The extraction of the total sample size used in the regression models is presented in Figure 1.
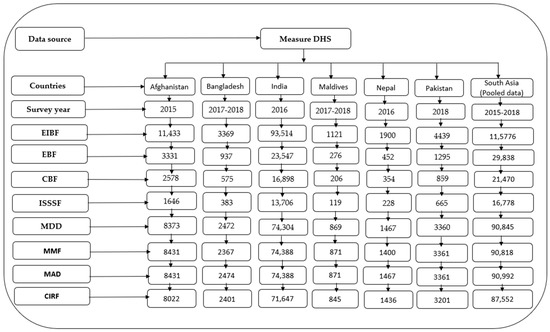
Figure 1.
Sample flowchart for multiple regression models. DHS = Demographic and Health Surveys, EIBF = early initiation of breastfeeding, EBF = exclusive breastfeeding, CBF = continued breastfeeding at 1 year, ISSSF = introduction of solid, semi-solid and soft foods, MDD = minimum dietary diversity, MMF = minimum meal frequency, MAD = minimum acceptable diet, and CIRF = consumption of iron-rich or iron-fortified foods.
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics of the Study Participants
The analysis included 120,830 mother–child (youngest) dyads. Overall, the mean age of the children was 11 months, with half of the children being female. Nearly half (47.3%) of the mothers of the index children were aged between 25 and 34 years, while a little more than half of the mothers (54%) had obtained secondary or higher education levels. The majority of the children were from rural areas (72%) and a little less than a quarter (24%) belonged to the poorest households. These estimates varied across SACs, with the child’s rural residence highest in the Maldives (90%), with the secondary or higher education of the mother lowest in Afghanistan (11%), and with belonging to the poorest household highest in the Maldives (27%). See Table S1 for details.
3.2. Prevalence of IYCF Practices
In SACs, overall, about 45% of mothers practiced EIBF, whereas the prevalence of EBF and CBF were 54% and 83%, respectively. In the case of complementary feeding, overall, the ISSSF, MDD, MMF, MAD, and CIRF practices were 50%, 22%, 40%, 13%, and 21%, respectively. The lowest prevalence of EIBF was noticed in Pakistan (21%), of EBF in Afghanistan (42%), and of MAD in India (13%) (Table S2).
3.3. Association between Mother’s Education and IYCF Practices
In the bivariate analysis of the pooled data, we found significantly higher IYCF (except for CBF) practices among higher educated mothers compared with mothers with no formal or below secondary-level education. In the country-specific estimates, similar higher IYCF practices were observed among mothers with secondary or higher levels of education. In contrast, in Bangladesh, significantly higher EIBF practices, and in Pakistan significantly higher EBF and CBF, were observed among women with no formal or below secondary-level education (Table S3).
In the multiple GEE models of the pooled data, we found significantly higher odds (AOR range, 1.13 to 1.47) of IYCF practices among mothers with secondary or higher education levels than mothers with below secondary-level education. These findings across SACs show that the odds were highest among mothers with secondary or higher education levels compared with mothers with below secondary education levels for EIBF (AOR 1.14; 95% CI: 1.11, 1.18) in India and for EBF (AOR 1.27; 95% CI: 1.19, 1.34) in India also. In contrast, mothers with secondary or higher education had the lowest odds compared with mothers with below secondary-level education for EIBF in Bangladesh (AOR 0.84; 95% CI: 0.72, 0.99) and for EBF in Pakistan (AOR 0.64; 95% CI: 0.48, 0.85). In the case of complementary feeding (ISSSF, MMD, MMF, MAD, and CIRF) in the pooled data, significantly higher odds (AOR range: 1.17 to 1.47) were found among mothers with secondary or higher education levels. These findings for country-specific analyses show the odds were highest among mothers with secondary or higher education compared with mothers with below secondary-level education for ISSSF (AOR 1.55; 95% CI: 1.03, 2.32) in Pakistan, and for MDD (AOR 2.25; 95% CI: 1.72, 2.94), MMF (AOR 1.61; 95% CI: 1.24, 2.08), MAD (AOR 2.34; 95% CI: 1.76, 3.11), and CIRF (AOR 1.47; 95% CI: 1.14, 1.91) in Nepal (Figure 2).
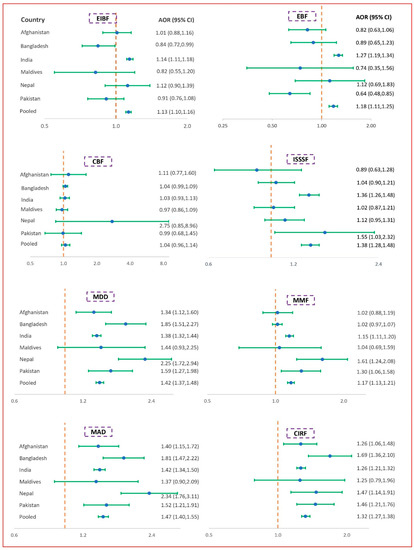
Figure 2.
Association between mother’s education and IYCF indicators. The x-axis of the graph represents AOR (adjusted odds ratio) and the y-axis represents different pooled and SACs data; CI = confidence interval; adjusted odds ratios, 95% confidence intervals, and p-values were obtained from the log-binomial regression model using the generalized estimating equation. Models adjusted for child’s age, child’s sex, maternal age, place of residence, and wealth index. For pooled data, in addition to these factors, we adjusted the model by survey year. EIBF = early initiation of breastfeeding, EBF = exclusive breastfeeding, CBF = continued breastfeeding at 1 year, ISSSF = introduction of solid, semi-solid and soft foods, MDD = minimum dietary diversity, MMF = minimum meal frequency, MAD = minimum acceptable diet, and CIRF = consumption of iron-rich or iron-fortified foods.
3.4. Sensitivity Analyses
We performed sensitivity analyses and considered our exposure variable as continuous (mother’s completed years of schooling). Sensitivity analyses included the multiple GEE modeling of mother’s completed years of schooling and all IYCF indicators, adjusting the similar independent variables as performed in the main regression analysis. The objective of the sensitivity analyses was to see how IYCF practices change (either increase or decrease) with each additional year of mother’s schooling. We found that all IYCF practices increased with a one-year increase in mother’s years of completed schooling. Similar results were observed in the country-specific analyses. In contrast, we found significantly lower odds for mother’s education with EIBF in Bangladesh and for mother’s education with EBF in Pakistan. The regression findings for sensitivity analyses (Table S4) were similar to our main regression analyses findings.
4. Discussion
Ensuring the recommended IYCF practices are present to start a healthy life is the right of every child. To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the association between mother’s education and the WHO’s eight IYCF core indicators in SACs by using both pooled and country-specific data from the latest DHS. The findings of our pooled results indicated that mothers with secondary or higher education levels had significantly higher odds of practicing all of the WHO’s IYCF core indicators except for continued breastfeeding at one year. In the country-specific analyses, we also found a similar, significant positive association between mother’s education and IYCF indicators, but we found a significant negative association between EIBF and mother’s education in Bangladesh and between EBF and mother’s education in Pakistan.
Our findings on the higher rate and likelihood of IYCF practices among mothers with secondary or higher levels of education coincide with previous studies. In particular, children of mothers with secondary or higher levels of education reported a higher likelihood of EIBF in Ghana [32], Ethiopia [33,34], Tanzania [35], and China [36]; of EBF in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia [37], Indonesia [38], and Sub-Saharan Africa [39]; of introducing complementary feeding in Northwest [40] and Southwest Ethiopia [41]; and of MDD, MMF, MAD, and CIRF in Ethiopia, Zambia, and the Sub-Saharan African region [42,43,44,45,46]. The positive association between higher maternal education and improved IYCF practices was well-expected. Educated mothers are likely to be more exposed to mass media, to have adequate knowledge about health, nutrition, and feeding practices, and to understand the importance of feeding diversified foods to their offspring [42]. Educated mothers are also likely to have more opportunities to earn income and make decisions regarding the spending money of their health and their children’s health care services [47]. There is evidence that earning income and having autonomy in making decisions are associated with optimal IYCF practices [48]. Educated mothers might have the ability to adopt social and behavioral changes and to practice them in real life [49]. Interventions in social and behavioral change communication among mothers have proven impact on increased IYCF practices, particularly on MMD, MMF, and MAD [50]. These strong positive associations between mother’s education and IYCF practices suggest that policymakers of SACs should increase and sustain maternal education at least through the secondary level by implementing appropriate interventions.
In contrary to the positive association between mother’s education and IYCF practices, we found negative associations between high maternal education and low IYCF practices, particularly practices related to breastfeeding (such as EIBF in Bangladesh and EBF in Pakistan). A systematic review conducted in developed countries found that women with the highest level of education had a 2.28 times higher probability of not initiating breastfeeding within one hour of birth [51], which supports our finding. Another study conducted on 81 LMICs found a negative association between mothers’ education and EIBF [52]. A significant negative association between mother’s education and EBF practices was also observed in China, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Lebanon [36,53,54,55,56]. A previous study in Bangladesh found that educated mothers were more prone to undergo caesarean section (C-section) delivery [57]. The C-section delivery rate is the highest (59%) in Bangladesh among SACs and South-East Asian countries [58]. Evidence has suggested that C-section delivery is one of the major risk factors for not initiating breastfeeding early after birth [22,59,60]. This might be the reason why mother’s education is negatively associated with EIBF in Bangladesh. To improve EIBF in Bangladesh, lowering the rate of C-section delivery in private facilities, and the counselling of mothers by doctors during antenatal visits highlighting the negative effects of C-section delivery might be effective. Also, skin-to-skin contact immediately after C-section delivery was found to be a significant predictor for improving EIBF practices in LMICs [61]. The reason for the negative association between mother’s education and EBF in Pakistan is that highly educated women have more opportunities to engage in formal employment, and there was evidence that most of the highly educated mothers were employed [62]. To improve EBF in SACs, multiple visits at the beginning of and during pregnancy, interpersonal education and counseling, community mobilization, and mass media exposure were found to be effective [63]. Also, to improve EBF, emphasis should be given to educating women in SACs through the strengthening of policies to prevent early marriage, through interventions for building awareness of female education, and through policies for ensuring education for females. Strengthening nutritional education for mothers, caregivers, family members, and relatives, and building community awareness might be helpful for the timely introduction of complementary feeding [64]. In addition to that, we suggest the policymakers in SACs ensure education for women through proper policies which ultimately help women to improve appropriate knowledge of the timely initiation of complementary feeding.
Our study has several strengths. The pooled estimate of SACs provided firm evidence of the association between mothers’ education and IYCF practices. The country-specific analyses will help policymakers to set appropriate interventions for women’s education which help to achieve optimal IYCF practices. The positive association between mother’s education and the WHO’s core indicators has generated new evidence for the South Asian context. Our study has some limitations, too. First of all, we cannot make causal inferences due to the cross-sectional nature of the data. However, to explore the association between outcome and exposure, cross-sectional studies are well accepted. Second, the measurements of breastfeeding and the child’s diet-related responses were based on mother’s 24-hour recall reports, which may include mother’s subjective response and recall bias. However, in the case of calculating breastfeeding and the child’s diet-related IYCF indicators, without mother’s 24-hour recall response, there is a lack of an alternative method. Third, for calculating the IYCF indicators, we included only children under two years of age and their mothers; also, for calculating some indicators, such as EBF, CIBF, and ISSSF, we used sub-samples of the child’s specific age, which reduced the estimated sample size.
5. Conclusions
In summary, IYCF practices in SA are still low. Overall, our findings indicated that mother’s education has a significantly and consistently positive association with IYCF practices in SA. The strong positive association between IYCF practices and mother’s education indicates mother’s education has a significant role in improving IYCF practices. To improve IYCF practices in SACs, one of the major cost-effective interventions might be educating females at least through the secondary level. The national-level policies in each SAC must be prioritized to ensure at least secondary-level education for women and mothers to ensure optimal IYCF practices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu14071514/s1, Table S1: Description of the WHO’s eight IYCF core indicators; Table S2: Sociodemographic characteristics of the study participants; Table S3: Prevalence of IYCF practices among South Asian countries; Table S4: Sensitivity analyses of the association between IYCF and mother’s education (years of schooling).
Author Contributions
M.T., M.M.H. and M.H. conceptualized the paper. M.T. and M.M.H. managed and analyzed the data. M.T. prepared the first draft. T.A., M.M., M.M.H. and M.H. critically reviewed, edited, and commented on the subsequent and the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by icddr,b under the Rainy Day Funding for Young Scientists category.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of icddr,b. The ethical clearance for the DHS data collection was reviewed and approved by the ICF Institutional Review board. The ICF International also provided technical assistance to the survey as part of its DHS programs (MEASURE DHS). The DHS program obtained informed consent from the respondents before the onset of the interviews.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data of this study are publicly available. Data can be downloaded at https://dhsprogram.com/data/available-datasets.cfm, accessed on 3 April 2020.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to MEASURE DHS, Calverton, MD, USA for granting permission to use the DHS datasets. icddr,b is grateful to the Governments of Bangladesh, Canada, Sweden, and the UK for providing core and unrestricted support. The authors would also like to acknowledge icddr,b for funding this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO. Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, L.; Benova, L.; Macleod, D.; Lynch, C.A.; Campbell, O.M.R. Early breastfeeding practices: Descriptive analysis of recent Demographic and Health Surveys. Matern. Child Nutr. 2018, 14, e12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.D.; França, G.V.A.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senarath, U.; Agho, K.E.; Akram, D.E.S.; Godakandage, S.S.P.; Hazir, T.; Jayawickrama, H.; Joshi, N.; Kabir, I.; Khanam, M.; Patel, A.; et al. Comparisons of complementary feeding indicators and associated factors in children aged 6-23 months across five South Asian countries. Matern. Child Nutr. 2012, 8, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, S. Child malnutrition and gender discrimination in South Asia. Econ. Polit. Wkly. 2006, 41, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. The State Of The World’s Children 2016—A Fair Chance for Every Child; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/7531/-The_state_of_the_worlds_children_2016_A_fair_chance_for_every_child-2016The_State_of_the_Worlds_Children_2016.pdf.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (accessed on 17 July 2021).
- Aguayo, V.M. Complementary feeding practices for infants and young children in South Asia. A review of evidence for action post-2015. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Indicators for Assessing Infant And Young Child Feeding Practices; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 1–19. ISBN 9789241599757. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.; Salam Khan, A.N.; Tasnim, F.; Kabir Chowdhury, M.A.; Billah, S.M.; Karim, T.; El Arifeen, S.; Garnett, S.P. Prevalence and determinants of initiation of breastfeeding within one hour of birth: An analysis of the Bangladesh demographic and health survey, 2014. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufunlayo, T.F.; Roberts, A.A.; MacArthur, C.; Thomas, N.; Odeyemi, K.A.; Price, M.; Jolly, K. Improving exclusive breastfeeding in low and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2019, 15, e12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabir, I.; Khanam, M.; Agho, K.E.; Mihrshahi, S.; Dibley, M.J.; Roy, S.K. Determinants of inappropriate complementary feeding practices in infant and young children in Bangladesh: Secondary data analysis of Demographic Health Survey 2007. Matern. Child Nutr. 2012, 8, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.F.; Mahmud, S.; Baig-Ansari, N.; Zaidi, A.K.M. Impact of Maternal Education about Complementary Feeding on Their Infants’ Nutritional Outcomes in Low- and Middle-income Households: A Community-based Randomized Interventional Study in Karachi, Pakistan. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2014, 32, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senarath, U.; Dibley, M.J. Complementary feeding practices in South Asia: Analyses of recent national survey data by the South Asia Infant Feeding Research Network. Matern. Child Nutr. 2012, 8, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Ahmed, T.; Black, R.E.; Cousens, S.; Dewey, K.; Giugliani, E.; Haider, B.A.; Kirkwood, B.; Morris, S.S.; Sachdev, H.; et al. What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival. Lancet 2008, 371, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Morris, S.S.; Bryce, J. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet 2003, 361, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.K.; Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, C. Factors associated with minimum dietary diversity failure among Indian children. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikam, L.; Robinson, A.; Lever, I.; Kuah, J.Y.; Vaidya, H.J.; Alexander, E.C.; Miller, G.W.; Singh, K.K.; Dawe, V.; Ahmed, S.; et al. G309 A systematic review of infant and young children complementary feeding practices in south asian families. Int. Child Health 2017, 102, A121–A122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.K.; Byrne, A. Early initiation of breastfeeding: A systematic literature review of factors and barriers in South Asia. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2016, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senarath, U.; Dibley, J.M.; Agho, E.K. Factors Associated With Nonexclusive Breastfeeding in 5 East and Southeast Asian Countries: A Multilevel Analysis. J. Hum. Lact. 2010, 26, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, R.K.; Craig, H.C.; Torlesse, H.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Trends and predictors of optimal breastfeeding among children 0–23 months, South Asia: Analysis of national survey data. Matern. Child Nutr. 2018, 14, e12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.; Amare, M.; Mavrotas, G.; Akerele, D.; Ogunniyi, A. Mother’s nutrition-related knowledge and child nutrition outcomes: Empirical evidence from Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, J.; Biswas, R.K.; Ananna, N. Women’s education and coverage of skilled birth attendance: An assessment of Sustainable Development Goal 3.1 in the South and Southeast Asian Region. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forshaw, J.; Gerver, S.M.; Gill, M.; Cooper, E.; Manikam, L.; Ward, H. The global effect of maternal education on complete childhood vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armar-Klemesu, M.; Ruel, M.T.; Maxwell, D.G.; Levin, C.E.; Morris, S.S. Poor maternal schooling is the main constraint to good child care practices in Accra. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuya, B.A.; Ciera, J.; Kimani-Murage, E. Effect of mother’s education on child’s nutritional status in the slums of Nairobi. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiross, G.T.; Chojenta, C.; Barker, D.; Tiruye, T.Y.; Loxton, D. The effect of maternal education on infant mortality in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e020076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, G.N.; Ariff, S.; Khan, U.; Habib, A.; Umer, M.; Suhag, Z.; Hussain, I.; Bhatti, Z.; Ullah, A.; Turab, A.; et al. Determinants of infant and young child feeding practices by mothers in two rural districts of Sindh, Pakistan: A cross-sectional survey. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2017, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, K.P.; Adhikari, M.; Khatri, R.B.; Devkota, M.D. Determinants of infant and young child feeding practices in Rupandehi, Nepal. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DHS Program. 2021. Available online: https://dhsprogram.com/data/available-datasets.cfm (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Duodu, P.A.; Duah, H.O.; Dzomeku, V.M.; Boamah Mensah, A.B.; Aboagye Mensah, J.; Darkwah, E.; Agbadi, P. Consistency of the determinants of early initiation of breastfeeding in Ghana: Insights from four Demographic and Health Survey datasets. Int. Health 2021, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebremeskel, S.G.; Gebru, T.T.; Gebrehiwot, B.G.; Meles, H.N.; Tafere, B.B.; Gebreslassie, G.W.; Welay, F.T.; Mengesha, M.B.; Weldegeorges, D.A. Early initiation of breastfeeding and associated factors among mothers of aged less than 12 months children in rural eastern zone, Tigray, Ethiopia: Cross-sectional study. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemichael, B. Timely Initiation of Breastfeeding and Its Associated Factors among Mothers in Tiyo Woreda, Arsi Zone, Ethiopia: A Community- Based Cross Sectional Study. Clin. Mother Child Health 2016, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavery, A.; Kanté, A.M.; Hingora, A.; Phillips, J.F. Determinants of early initiation of breastfeeding in rural Tanzania. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2015, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, K.; Wang, H.; Tan, S.H.; Xin, T.; Qu, X.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gaoshan, J. Association between maternal education and breast feeding practices in China: A population-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgham, L.S.; Hafez, S.K.; Kamhawy, H.E.; Hassan, W.B. Assessment of initiation of breastfeeding, prevalence of exclusive breast feeding and their predictors in taif, KSA. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Laksono, A.D.; Wulandari, R.D.; Ibad, M.; Kusrini, I. The effects of mother’s education on achieving exclusive breastfeeding in Indonesia. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçin, S.S.; Berde, A.S.; Yalçin, S. Determinants of Exclusive Breast Feeding in sub-Saharan Africa: A Multilevel Approach. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, A.; Edmealem, A.; Tegegne, B.; Tilahun, L.; Damtie, Y. Timely initiation of complementary feeding and associated factors among mothers of children aged 6–24 months in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia, 2019. J. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 2020, 6756202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, B.; Ejamo, E.; Thangavel, T.; Yohannis, M. Timely initiation of complementary feeding to children aged 6-23 months in rural Soro district of Southwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyene, M.; Worku, A.G.; Wassie, M.M. Dietary diversity, meal frequency and associated factors among infant and young children in Northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molla, A.; Egata, G.; Getacher, L.; Kebede, B.; Sayih, A.; Arega, M.; Bante, A. Minimum acceptable diet and associated factors among infants and young children aged 6-23 months in Amhara region, Central Ethiopia: Community-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiruneh, S.A.; Ayele, B.A.; Yitbarek, G.Y.; Asnakew, D.T.; Engidaw, M.T.; Gebremariam, A.D. Spatial distribution of iron rich foods consumption and its associated factors among children aged 6-23 months in Ethiopia: Spatial and multilevel analysis of 2016 Ethiopian demographic and health survey. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, S.R.; Houghton, L.A.; Filteau, S.; Mullen, A.; Nieuwelink, J.; Chisenga, M.; Siame, J.; Gibson, R.S. Dietary diversity at 6 months of age is associated with subsequent growth and mediates the effect of maternal education on infant growth in Urban Zambia. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalu, Y.; Yeshaw, Y.; Tesema, G.A.; Demissie, G.D.; Molla, M.D.; Muche, A.; Diress, M.; Tiruneh, S.A. Iron-rich food consumption and associated factors among children aged 6–23 months in sub-Saharan Africa: A multilevel analysis of Demographic and Health Surveys. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kate, P.C.; Jennifer, A.M. Maternal Education and Investments in Children’s Health. J. Marriage Fam. 2016, 78, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Na, M.; Jennings, L.; Talegawkar, S.A.; Ahmed, S. Association between women’s empowerment and infant and child feeding practices in sub-Saharan Africa: An analysis of Demographic and Health Surveys. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 3155–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangrio, E.; Hansen, K.; Lindström, M.; Köhler, M.; Rosvall, M. Maternal educational level, parental preventive behavior, risk behavior, social support and medical care consumption in 8-month-old children in Malmö, Sweden. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workicho, A.; Biadgilgn, S.; Kershaw, M.; Gizaw, R.; Stickland, J.; Assefa, W.; Abuye, C.; Woldegiorgis, B.; Berhanu, L.; Kennedy, E. Social and behaviour change communication to improve child feeding practices in Ethiopia. Matern. Child Nutr. 2021, 17, e13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.S.; Alexander, D.D.; Krebs, N.F.; Young, B.E.; Cabana, M.D.; Erdmann, P.; Hays, N.P.; Bezold, C.P.; Levin-Sparenberg, E.; Turini, M.; et al. Factors Associated with Breastfeeding Initiation and Continuation: A Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. 2018, 203, 190–196.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, P.A.R.; Barros, A.J.D.; Gatica-Domínguez, G.; Vaz, J.S.; Baker, P.; Lutter, C.K. Maternal education and equity in breastfeeding: Trends and patterns in 81 low- and middle-income countries between 2000 and 2019. Int. J. Equity Health 2021, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, T.; Hablas, H.; Al Qader, A.A. Determinants of initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding in al Hassa, Saudi Arabia. Breastfeed. Med. 2011, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, H. Patterns and determinants of breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices of Emirati Mothers in the United Arab Emirates. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batal, M.; Boulghourjian, C.; Abdallah, A.; Afifi, R. Breast-feeding and feeding practices of infants in a developing country: A national survey in Lebanon. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, M.B.; Haridi, H.K. Prevalence and determinants of exclusive breastfeeding practice among mothers of children aged 6–24 months in hail, Saudi Arabia. Scientifica 2021, 2021, 2761213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, F.; Alam, M.M.; Hossain, M.G. Associated factors and their individual contributions to caesarean delivery among married women in Bangladesh: Analysis of Bangladesh demographic and health survey data. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Vishwakarma, R.K.; Nath, D.C.; Khan, H.T.A.; Prakash, R.; Abid, O. Prevalence and determinants of caesarean section in South and South-East Asian women. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, A.J.; Mannion, C.A.; McDonald, S.W.; Brockway, M.; Tough, S.C. The impact of caesarean section on breastfeeding initiation, duration and difficulties in the first four months postpartum. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prior, E.; Santhakumaran, S.; Gale, C.; Philipps, L.H.; Modi, N.; Hyde, M.J. Breastfeeding after cesarean delivery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of world literature. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Analysis, C.A.T.; Mallick, L.; Wang, W.; Farid, S. Initiation of Breastfeeding in Low- and Middle-Income. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2020, 9, 308–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.; Ali, S.M.; Aziz, A.; Bashir, R.; Buriro, A.A.; Khan, Z.U.; Eskar, M.; Hashmi, D.M.H. Pakistan demographic and health survey 2012-13; National Institute of Population Studies: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, R.K.; Craig, H.C.; Torlesse, H.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Effectiveness of programmes and interventions to support optimal breastfeeding among children 0–23 months, South Asia: A scoping review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2018, 14, e12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.K.; Roy, S.; Islam, Q.R.; Islam, M.Z.; Akteruzzaman, M.; Rouf, M.A.; Kabir, A.L.; Afroza, S. Barriers of Appropriate Complementary Feeding Practices in Under—2 Children. J. Bangladesh Coll. Physicians Surg. 2016, 33, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).