Emotional Eating and Dietary Patterns: Reflecting Food Choices in People with and without Abdominal Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
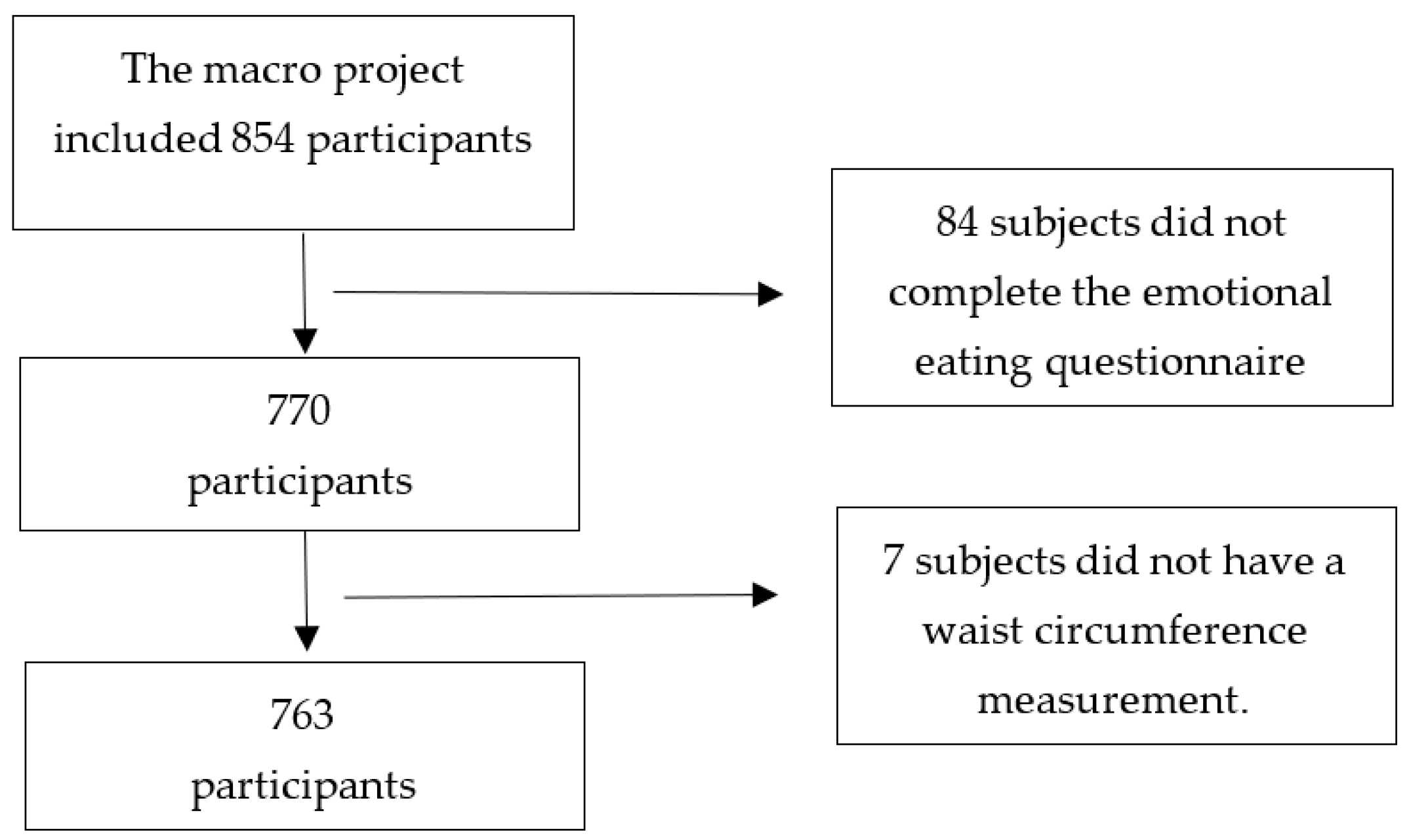
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Participants
2.2. Sociodemographic Characteristics
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Emotional Eating
2.5. Dietary Intake
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Description of the Dietary Patterns in Participants with and without Abdominal Obesity
3.3. Adherence to Dietary Patterns According to the Emotional Eating Classification in Participants with and without Abdominal Obesity
3.4. Association between Dietary Patterns and Emotional Eating Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raine, K.D. Determinants of healthy eating in Canada: An overview and synthesis. Can. J. Public Heal. 2005, 96, S8–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Adan, R.A.H.; Belot, M.; Brunstrom, J.M.; De Graaf, K.; Dickson, S.L.; Hare, T.; Maier, S.; Menzies, J.; Preissl, H.; et al. The determinants of food choice. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macht, M. How emotions affect eating: A five-way model. Appetite 2008, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canetti, L.; Bachar, E.; Berry, E.M. Food and emotion. Behav. Process. 2002, 60, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, C.; Marijn Stok, F.; de Ridder, D.T.D. Feeding your feelings: Emotion regulation strategies and emotional eating. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 36, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Strien, T. Causes of Emotional Eating and Matched Treatment of Obesity. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camilleri, G.M.; Méjean, C.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Andreeva, V.A.; Bellisle, F.; Hercberg, S.; Péneau, S. The associations between emotional eating and consumption of energy-dense snack foods are modified by sex and depressive symptomatology. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lauzon, B.; Romon, M.; Deschamps, V.; Lafay, L.; Borys, J.M.; Karlsson, J.; Ducimetière, P.; Charles, M.A. The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R18 is able to distinguish among different eating patterns in a general population. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Michel, S.T.; Unger, J.B.; Spruijt-Metz, D. Dietary correlates of emotional eating in adolescence. Appetite 2007, 49, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paans, N.P.G.; Gibson-Smith, D.; Bot, M.; van Strien, T.; Brouwer, I.A.; Visser, M.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Depression and eating styles are independently associated with dietary intake. Appetite 2019, 134, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Zahry, N.R. Relationships among perceived stress, emotional eating, and dietary intake in college students: Eating self-regulation as a mediator. Appetite 2021, 163, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elran Barak, R.; Shuval, K.; Li, Q.; Oetjen, R.; Drope, J.; Yaroch, A.L.; Fennis, B.M.; Harding, M. Emotional eating in adults: The role of sociodemographics, lifestyle behaviors, and self-regulation—findings from a U.S. National Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anschutz, D.J.; Van Strien, T.; Van De Ven, M.O.M.; Engels, R.C.M.E. Eating styles and energy intake in young women. Appetite 2009, 53, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, P.; Jansen, A. Emotional Eating Is Not What You Think It Is and Emotional Eating Scales Do Not Measure What You Think They Measure. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konttinen, H.; Männistö, S.; Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S.; Silventoinen, K.; Haukkala, A. Emotional eating, depressive symptoms and self-reported food consumption. A population-based study. Appetite 2010, 54, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, H.; Van Strien, T.; Männistö, S.; Jousilahti, P.; Haukkala, A. Depression, emotional eating and long-term weight changes: A population-based prospective study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Cepero, A.; Frisard, C.F.; Lemon, S.C.; Rosal, M.C. Association of Dysfunctional Eating Patterns and Metabolic Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease among Latinos. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L.; Blanco, E.; Burrows, R.; Correa-Burrows, P.; Santos, J.; Gahagan, S. Eating behavior and body composition in Chilean young adults. Appetite 2021, 156, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunot-Alexander, C.; Arellano-Gómez, L.P.; Smith, A.D.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Vásquez-Garibay, E.M.; Romero-Velarde, E.; Fildes, A.; Croker, H.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Beeken, R.J. Examining the validity and consistency of the Adult Eating Behaviour Questionnaire-Español (AEBQ-Esp) and its relationship to BMI in a Mexican population. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevich, I.; Irigoyen Camacho, M.E.; Velázquez-Alva, M.d.C.; Zepeda Zepeda, M. Relationship among obesity, depression, and emotional eating in young adults. Appetite 2016, 107, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayn, M.; Knäuper, B. Emotional Eating and Weight in Adults: A Review. Curr. Psychol. 2018, 37, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Guimerà, G.; Dashti, H.S.; Smith, C.E.; Sánchez-Carracedo, D.; Ordovas, J.M.; Garaulet, M. CLOCK 3111 T/C SNP interacts with emotional eating behavior for weight-loss in a Mediterranean population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnet, G.; Gómez-Abellán, P.; Vera, B.; Sánchez-Romera, J.F.; Hernández-Martínez, A.M.; Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J.; Garaulet, M. Serotonin-transporter promoter polymorphism modulates the ability to control food intake: Effect on total weight loss. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalo, E.; Konttinen, H.; Vepsäläinen, H.; Chaput, J.P.; Hu, G.; Maher, C.; Maia, J.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Standage, M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; et al. Emotional eating, health behaviours, and obesity in children: A 12-country cross-sectional study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pentikäinen, S.; Arvola, A.; Karhunen, L.; Pennanen, K. Easy-going, rational, susceptible and struggling eaters: A segmentation study based on eating behaviour tendencies. Appetite 2018, 120, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Tao, F.; Hou, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, L.-L. Emotion regulation, emotional eating and the energy-rich dietary pattern. A population-based study in Chinese adolescents. Appetite 2016, 99, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B. Dietary pattern analysis: A new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2002, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body Mass Index Obesity, BMI, and Health: A Critical Review. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Després, J.; Lemieux, I.; Bergeron, J.; Pibarot, P.; Mathieu, P.; Larose, E.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Bertrand, O.; Poirier, P. Abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Contribution to global cardiometabolic risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Choi, S.; Son, J.S.; Oh, S.W.; Park, S.M. Impact of discrepancies in general and abdominal obesity on major adverse cardiac events. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist–Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garaulet, M.; Canteras, M.; Morales, E.; López-Guimera, G.; Sánchez-Carracedo, D.; Corbalán-Tutau, M.D. Validation of a questionnaire on emotional eating for use in cases of obesity: The Emotional Eater Questionnaire (EEQ). Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabéu, E.; Marchena, C.; Iglesias, M.T. Factor structure and psychometric properties of emotional eater questionnaire (EEQ) in spanish colleges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics notes: Cronbach’s alpha. BMJ 1997, 314, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macedo-Ojeda, G.; Vizmanos-Lamotte, B.; Márquez-Sandoval, Y.F.; Rodríguez-Rocha, N.P.; López-Uriarte, P.J.; Fernández-Ballart, J.D. Validation of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire to assess food groups and nutrient intake. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Orozco, M.; Vizmanos-Lamotte, B.; Rodríguez-Rocha, N.; Macedo-Ojeda, G.; Orozco-Valerio, M.; Rovillé-Sausse, F.; León-Estrada, S.; Márquez-Sandoval, F.; Fernández-Ballart, J. Validation of a Mexican food photograph album as a tool to visually estimate food amounts in adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledesma Solano, J.; Chávez Villasana, A.; Pérez-Gil, F.; Mendoza Martínez, E.; Calvo Carrillo, C. Composición de Alimentos Miriam Muñoz de Chávez. Valor Nutritivo de Los Alimentos de Mayor Consumo; McGraw-Hill, Ed.: Ciudad de México, México, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference. Release 25. Available online: http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search/list (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Taherdoost, H.; Sahibuddin, S.; Jalaliyoon, N. Exploratory factor analysis; concepts and theory. Adv. Appl. Pure Math. 2014, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Onsman, A.; Brown, T. Exploratory factor analysis: A five-step guide for novices. J. Emerg. Prim. Heal. Care 2010, 8, 990399. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.475.8594&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 22 January 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costello, A.; Osborne, J. Best Practices in Exploratory Factor Analysis: Four Recommendations for Getting the Most From Your Analysis. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2005, 10, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, M.; Elena, B.; Teresa, I.M. Are adherence to the mediterranean diet, emotional eating, alcohol intake, and anxiety related in university students in Spain? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastelum Strozzi, V.; Márquez-Sandoval, Y.F. Disponibilidad y costo de alimentos ofertados dentro y fuera de los Centros Universitarios de la Universidad de Guadalajara de la Zona Metropolitana. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12104/83822 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- van der Valk, E.; Savas, M.; van Rossum, E. Stress and Obesity: Are There More Susceptible Individuals? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, T.; Epel, E. Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicennati, V.; Pasqui, F.; Cavazza, C.; Garelli, S.; Casadio, E.; di Dalmazi, G.; Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R. Cortisol, energy intake, and food frequency in overweight/obese women. Nutrition 2011, 27, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiker, N.; Astrup, A.; Hjorth, M.; Sjödin, A.; Pijls, L.; Markus, C. Does stress influence sleep patterns, food intake, weight gain, abdominal obesity and weight loss interventions and vice versa? Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incollingo Rodriguez, A.; Epel, E.; White, M.; Standen, E.; Seckl, J.; Tomiyama, A. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation and cortisol activity in obesity: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 62, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laugero, K.; Falcon, L.; Tucker, K. Relationship between perceived stress and dietary and activity patterns in older adults participating in the Boston Puerto Rican Health Study. Appetite 2011, 56, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hewagalamulage, S.; Lee, T.; Clarke, I.; Henry, B. Stress, cortisol, and obesity: A role for cortisol responsiveness in identifying individuals prone to obesity. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, S112–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, A.E.; Wildes, J.E.; Coccaro, E.F. Identification and regulation of emotions in adults of varying weight statuses. J. Health Psychol. 2019, 24, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, M.; Boncompagni, I.; Forte, G.; Guarino, A.; Favieri, F. Emotion and overeating behavior: Effects of alexithymia and emotional regulation on overweight and obesity. Eat. Weight Disord. 2020, 25, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpina, F.; Varallo, G.; Castelnuovo, G.; Capodaglio, P.; Molinari, E.; Mauro, A. Implicit facial emotion recognition of fear and anger in obesity. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zysberg, L.; Rubanov, A. Emotional intelligence and emotional eating patterns: A new insight into the antecedents of eating disorders? J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2010, 42, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.; Smith, N.; Ashwell, M. A structured literature review on the role of mindfulness, mindful eating and intuitive eating in changing eating behaviours: Effectiveness and associated potential mechanisms. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siervo, M.; Lara, J.; Chowdhury, S.; Ashor, A.; Oggioni, C.; Mathers, J.C. Effects of the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J.; Salvador, G.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Food frequency questionnaires. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usubini, A.G.; Cattivelli, R.; Varallo, G.; Castelnuovo, G.; Molinari, E.; Giusti, E.M.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manari, T.; Filosa, M.; Franceschini, C.; et al. The Relationship between Psychological Distress during the Second Wave Lockdown of COVID-19 and Emotional Eating in Italian Young Adults: The Mediating Role of Emotional Dysregulation. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Food Group | Foods Considered in the Group |
|---|---|
| 1. Fish and Seafood | Oysters, squid, crustaceans, white fish, bluefish, salted fish, canned tuna (in oil or water), canned prepared tuna. |
| 2. Meat | Beef, pork, pork rinds, lamb, offal, and liver. |
| 3. Chicken | Chicken with and without skin. |
| 4. Egg | Egg. |
| 5. Semimature cheeses | Manchego, Gouda, Oaxaca and mozzarella cheeses. |
| 6. Fresh cheeses | Requesón (curd), cottage cheese, panela cheese, adobera cheese. |
| 7. Whole milk and yogurt | Whole milk, evaporated milk, Petit, whole yogurt, and smoothies. |
| 8. Skimmed milk | Skimmed milk. |
| 9. Processed meats | Ham and processed meats. |
| 10. Fast food | Hamburger, industrialized French fries, popcorn, sachet soups. |
| 11. Industrialized sauces and dressings | Mustard, hot sauce, ketchup, mayonnaise. |
| 12. Breakfast cereals | Breakfast cereals. |
| 13. Industrialized bakery | María type cookies, chocolate cookies, industrialized bread, vegetable shortening, and margarine. |
| 14. Sweets, sugar, and honey | Honey, jam, candies, fruit in syrup, ate (quince paste), cajeta (caramel sauce), condensed milk, sugar, and piloncillo (brown sugar). |
| 15. Desserts | Custard, chocolate, cocoa, ice cream. |
| 16. Industrialized sweetened beverages | Light soda, regular soda, canned juices, fermented-milk beverages (e.g., Yakult). |
| 17. Alcoholic beverages | Distilled spirits, liquor, beer, white wine, rosé wine, young red wine, and aged red wine. |
| 18. Oils (various) | Corn oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, mixed oils, canola oil, safflower oil. |
| 19. Olive oil | Extra-virgin olive oil, olive oil, olives. |
| 20. Animal fats | Bacon, lard, cream, cream cheese, and butter. |
| 21. Corn products | Corn dough, corn tortilla, and toast. |
| 22. Pasta | Pasta: noodle, spaghetti, macaroni. |
| 23. Rice | Rice. |
| 24. White bread | Bolillo, white bread, and buns. |
| 25. Whole grain cereals | Whole grain cereals (oatmeal, granola), whole grain crackers, whole wheat bread. |
| 26. Non-industrialized sweet bread | Sweetbread, cake, homemade bread, mantecada (shortbread), doughnut, churro. |
| 27. Flour tortilla | Flour tortilla. |
| 28. Vegetables frequently consumed in Mexico | Onion, garlic, tomato, chili, bell pepper, poblano chili, lemon |
| 29. Vegetables | Green bean, cabbage, chard, asparagus, herbs, other vegetables, eggplant, chayote (squash) and jicama (yam bean), carrot and pumpkin flower, lettuce, peas, mushrooms, and nopales (prickly pear leaf). |
| 30. Fruits | Orange, kiwi, guava, lime, mango, pineapple, strawberry, plum, prune, tuna (prickly pear fruit), grape, peach, watermelon, melon, papaya, apple, raisins, tamarind, banana, dates, prune, natural fruit juices. |
| 31. Avocado | Avocado. |
| 32. Elote | Fresh corn. |
| 33. Potatoes | Potatoes prepared homemade. |
| 34. Nuts | Almonds, walnuts, and peanuts. |
| 35. Beans | Frijoles and alubias (beans and white beans). |
| 36. Leguminous plants | Lentils and chickpeas. |
| 37. Tea | Tea. |
| 38. Coffee | Coffee. |
| 39. Natural water | Natural water. |
| 40. Salt | Salt added. |
| Total | Abdominal Obesity | Non-Abdominal Obesity | Abdominal Obesity | Non-Abdominal Obesity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-EE | Low EE | EE or Very EE | Non-EE | Low-EE | EE or Very EE | ||||
| N (%) | 763 | 494 (64.7) | 269 (35.3) | 153 (31.0) | 159 (32.2) | 182 (36.8) *** | 114 (42.4) | 95 (35.3) | 60 (22.3) |
| Age (years) | 38 ± 11 | 40 ± 11 *** | 34 ± 9 | 42 ± 11 | 41 ± 11 | 38 ± 11 ●** | 36 ± 10 | 33 ± 9 | 32 ± 6 ●** |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 5.2 | 29.8 ± 4.6 *** | 22.8 ± 2.4 | 28.7 ± 3.6 | 29.7 ± 4.4 | 30.8 ± 5.2 ●*** | 22.4 ± 2.5 | 23.1 ± 2.4 | 23.1 ± 2.2 |
| WC (cm) | 88.2 ± 13.4 | 95.1 ± 11 *** | 75.5 ± 6.1 | 94.4 ± 9.7 | 95.5 ± 11.5 | 95.4 ± 11.5 | 76 ± 6.5 | 75.6 ± 6.2 | 74.4 ± 4.7 |
| Sex | |||||||||
| Female | 530 (69.5) | 330 (66.8) * | 200 (74.3) | 85 (55.6) | 102 (64.2) | 143 (78.6) *** | 78 (68.4) | 68 (71.6) | 54 (90.0) ** |
| Occupation | |||||||||
| Academic | 74 (9.8) | 45 (9.3) | 29 (10.9) | 14 (9.3) | 14 (8.9) | 17 (9.6) | 10 (8.9) | 14 (14.9) | 5 (8.3) + |
| Managerial | 54 (7.2) | 35 (7.2) | 19 (7.1) | 15 (9.9) | 10 (6.4) | 10 (5.6) | 7 (6.3) | 8 (8.5) | 4 (6.7) |
| Administrative | 546 (72.6) | 348 (71.6) | 198 (74.4) | 97 (64.2) | 118 (75.2) | 133 (74.7) | 85 (75.9) | 65 (69.1) | 48 (80.0) |
| Operative | 37 (4.9) | 31 (6.4) | 6 (2.3) | 12 (7.9) | 8 (5.1) | 11 (6.2) | 3 (2.7) | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0) |
| Academic and other | 41 (5.5) | 27 (5.6) | 14 (5.3) | 13 (8.6) | 7 (4.5) | 7 (3.9) | 7 (6.3) | 4 (4.3) | 3 (5.0) |
| Physical activity | |||||||||
| Sedentary | 519 (68) | 353 (71.5) *** | 166 (61.7) | 104 (68.0) | 108 (67.9) | 141 (77.5) * | 67 (58.8) | 59 (62.1) | 40 (66.7) |
| Active | 151 (19.8) | 96 (19.4) | 55 (20.4) | 31 (20.3) | 33 (20.8) | 32 (17.6) | 26 (22.8) | 19 (20.0) | 10 (16.7) |
| Very active | 93 (12.2) | 45 (9.1) | 48 (17.8) | 18 (11.8) | 18 (11.3) | 9 (4.9) | 21 (18.4) | 17 (17.9) | 10 (16.7) |
| Abdominal Obesity (n = 494) | ||||||||
| Snacks and Fast Food | Traditional Westernized | Healthy | Animal Products and Cereals | |||||
| No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | |
| Age (years) | 42 ± 11 | 38 ± 10 *** | 40 ± 11 | 40 ± 11 | 37 ± 10 | 43 ± 12 *** | 42 ± 11 | 39 ± 11 ** |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.7 ± 4.3 | 29.9 ± 4.9 | 29.3 ± 4.3 | 30.3 ± 4.8 * | 29.9 ± 4.8 | 29.8 ± 4.3 | 29.5 ± 4.4 | 30.1 ± 4.7 |
| WC (cm) | 94.9 ± 10.6 | 95.4 ± 11.3 | 92.9 ± 10.2 | 97.4 ± 11.2 *** | 94.7 ± 11.3 | 95.6 ± 10.7 | 95.0 ± 11.3 | 95.3 ± 10.7 |
| Energy intake | 2058 ± 758 | 2616 ± 1097 *** | 1920 ± 801 | 2754 ± 971 *** | 2104 ± 770 | 2571 ± 1110 *** | 2185 ± 954 | 2490 ± 989 *** |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 163 (49.4) | 167 (50.6) | 192 (58.2) | 138 (41.8) *** | 165 (50.0) | 165 (50.0) | 163 (49.4) | 167 (50.6) |
| Male | 84 (51.2) | 80 (48.8) | 55 (33.5) | 109 (66.5) | 82 (50.0) | 82 (50.0) | 84 (51.2) | 80 (48.8) |
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Academic | 26 (57.8) | 19 (42.2) * | 22 (48.9) | 23 (51.1) | 22 (48.9) | 23 (51.1) | 23 (51.1) | 22 (48.9) |
| Managerial | 24 (68.6) | 11 (31.4) | 18 (51.4) | 17 (48.6) | 15 (42.9) | 20 (57.1) | 18 (51.4) | 17 (48.6) |
| Administrative | 163 (46.8) | 185 (53.2) | 183 (52.6) | 165 (47.4) | 177 (50.9) | 171 (49.1) | 177 (50.9) | 171 (49.1) |
| Operative | 13 (41.9) | 18 (58.1) | 8 (25.8) | 23 (74.2) | 15 (48.4) | 16 (51.6) | 17 (54.8) | 14 (45.2) |
| Academic and other | 17 (63.0) | 10 (37.0) | 12 (44.4) | 15 (55.6) | 16 (59.3) | 11 (40.7) | 10 (37.0) | 17 (63.0) |
| Physical activity | ||||||||
| Sedentary | 174 (49.3) | 179 (50.7) | 160 (45.3) | 193 (54.7) *** | 192 (54.4) | 161 (45.6) ** | 168 (47.6) | 185 (52.4) * |
| Active | 51 (53.1) | 45 (46.9) | 65 (67.7) | 31 (32.3) | 38 (39.6) | 58 (60.4) | 59 (61.5) | 37 (38.5) |
| Very active | 22 (48.9) | 23 (51.1) | 22 (48.9) | 23 (51.1) | 17 (37.8) | 28 (62.2) | 20 (44.4) | 25 (55.6) |
| Non-Abdominal Obesity (n = 269) | ||||||||
| Traditional Westernized | Animal Products, Cereals, and Vegetables | Healthy | Snacks | |||||
| No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | No Adherence | Adherence | |
| Age (years) | 36 ± 9 | 32 ± 8 *** | 34 ± 8 | 34 ± 10 | 34 ± 9 | 34 ± 9 | 34 ± 9 | 34 ± 9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 ± 2.4 | 22.5 ± 2.4 | 22.7 ± 2.4 | 22.9 ± 2.4 | 23.0 ± 2.5 | 22.7 ± 2.3 | 22.9 ± 2.4 | 22.7 ± 2.4 |
| WC (cm) | 75.1 ± 5.9 | 75.9 ± 6.2 | 75.6 ± 6.2 | 75.4 ± 5.9 | 76.0 ± 6.0 | 75.0 ± 6.1 | 75.9 ± 6.1 | 75.1 ± 6.0 |
| Energy intake | 1951 ± 647 | 2744 ± 848 *** | 2050 ± 786 | 2650 ± 811 *** | 2192 ± 801 | 2507 ± 875 *** | 2126 ± 819 | 2574 ± 827 *** |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 112 (56.0) | 88 (44.0) *** | 105 (52.5) | 95 (47.5) | 99 (49.5) | 101 (50.5) | 97 (48.5) | 103 (51.5) |
| Male | 22 (31.9) | 47 (68.1) | 30 (43.5) | 39 (56.5) | 36 (52.2) | 33 (47.8) | 38 (55.1) | 31 (44.9) |
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Academic | 16 (55.2) | 13 (44.8) * | 15 (51.7) | 14 (48.3) | 14 (48.3) | 15 (51.7) | 17 (58.6) | 12 (41.4) ** |
| Managerial | 9 (47.4) | 10 (52.6) | 9 (47.4) | 10 (52.6) | 9 (47.4) | 10 (52.6) | 3 (15.8) | 16 (84.2) |
| Administrative | 95 (48.0) | 103 (52.0) | 100 (50.5) | 98 (49.5) | 101 (51.0) | 97 (49.0) | 99 (50.0) | 99 (50.0) |
| Operative | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | 3 (50.0) | 3 (50.0) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 3 (50.0) | 3 (50.0) |
| Academic and other | 12 (85.7) | 2 (14.3) | 5 (35.7) | 9 (64.3) | 8 (57.1) | 6 (42.9) | 11 (78.6) | 3 (21.4) |
| Physical activity | ||||||||
| Sedentary | 80 (48.2) | 86 (51.8) | 92 (55.4) | 74 (44.6) * | 88 (53.0) | 78 (47.0) | 80 (48.2) | 86 (51.8) |
| Active | 32 (58.2) | 23 (41.8) | 26 (47.3) | 29 (52.7) | 28 (50.9) | 27 (49.1) | 27 (49.1) | 28 (50.9) |
| Very active | 22 (45.8) | 26 (54.2) | 17 (35.4) | 31 (64.6) | 19 (39.6) | 29 (60.4) | 28 (58.3) | 20 (41.7) |
| Dietary Patterns | Abdominal Obesity (n = 494) | Non-Abdominal Obesity (n = 269) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-EE (n = 153) | Low EE (n = 159) | Emotional or Very EE (n = 182) | Dietary Patterns | Non-EE (n = 114) | Low EE (n = 95) | Emotional or Very EE (n = 60) | |
| Snacks and fast food DP | Traditional Westernized DP | ||||||
| Crude | 1 | 1.27 (0.81, 1.99) | 1.98 (1.28, 3.07) * | Crude | 1 | 1.02 (0.59, 1.76) | 1.00 (0.53, 1.87) |
| Model I | 1 | 1.25 (0.79, 1.97) | 1.83 (1.17, 2.88) * | Model I | 1 | 0.87 (0.49, 1.58) | 1.02 (0.52, 1.98) |
| Model II | 1 | 1.37 (0.85, 2.22) | 1.88 (1.17, 3.03) * | Model II | 1 | 0.71 (0.36, 1.38) | 0.76 (0.35, 1.65) |
| Model III | 1 | 1.40 (0.86, 2.26) | 1.95 (1.19, 3.18) * | Model III | 1 | 0.77 (0.39, 1.51) | 0.86 (0.39, 1.9) |
| Traditional Westernized DP | Animal products, cereals and vegetables DP | ||||||
| Crude | 1 | 0.81 (0.52, 1.27) | 0.87 (0.56, 1.34) | Crude | 1 | 1.73 (1.00, 3.01) * | 1.68 (0.89, 3.15) |
| Model I | 1 | 0.88 (0.55, 1.39) | 1.08 (0.69, 1.71) | Model I | 1 | 1.79 (1.02, 3.15) * | 1.89 (0.98, 3.65) |
| Model II | 1 | 0.95 (0.56, 1.61) | 1.00 (0.59, 1.68) | Model II | 1 | 1.79 (0.98, 3.28) | 1.77 (0.88, 3.58) |
| Model III | 0.92 (0.54, 1.56) | 0.92 (0.54, 1.57) | Model III | 1 | 1.74 (0.94, 3.21) | 1.70 (0.83, 3.46) | |
| Healthy DP | Healthy DP | ||||||
| Crude | 1 | 0.73 (0.46, 1.14) | 0.50 (0.32, 0.78) * | Crude | 1 | 0.94 (0.55, 1.63) | 0.90 (0.48, 1.69) |
| Model I | 1 | 0.74 (0.47, 1.17) | 0.56 (0.35, 0.89) * | Model I | 1 | 0.97 (0.56, 1.68) | 0.91 (0.47, 1.73) |
| Model II | 1 | 0.75 (0.46, 1.23) | 0.53 (0.33, 0.88) * | Model II | 1 | 0.92 (0.52, 1.63) | 0.83 (0.42, 1.60) |
| Model III | 1 | 0.76 (0.46, 1.24) | 0.54 (0.33, 0.90) * | Model III | 1 | 0.95 (0.53, 1.69) | 0.86 (0.44, 1.69) |
| Animal products and cereals DP | Snacks DP | ||||||
| Crude | 1 | 0.95 (0.61, 1.48) | 1.08 (0.70, 1.66) | Crude | 1 | 1.32 (0.76, 2.27) | 1.61 (0.86, 3.03) |
| Model I | 1 | 0.92 (0.59, 1.44) | 0.96 (0.62, 1.51) | Model I | 1 | 1.34 (0.77, 2.33) | 1.59 (0.83, 3.05) |
| Model II | 1 | 0.95 (0.60, 1.51) | 0.96 (0.61, 1.52) | Model II | 1 | 1.28 (0.71, 2.31) | 1.47 (0.74, 2.92) |
| Model III | 1 | 0.92 (0.58, 1.46) | 0.89 (0.56, 1.420) | Model III | 1 | 1.33 (0.73, 2.41) | 1.54 (0.77, 3.10) |
| Abdominal Obesity (n = 494) | Non-Abdominal Obesity (n = 269) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-EE | Low EE | EE or Very EE | Non-EE | Low EE | EE or Very EE | |
| Energy (Kcal) | 2400.5 ± 1096.7 | 2287.4 ± 1018.0 | 2328.0 ± 841.9 | 2290.6 ± 819.5 | 2397.8 ± 901.9 | 2382.7 ± 837.6 |
| CH (g) | 287.3 ± 132.4 | 268.5 ± 128.7 | 273.6 ± 108.2 | 268.0 ± 101.3 | 273.3 ± 105.8 | 280.0 ± 122.6 |
| Fiber (g) | 22.5 ± 9.9 | 20.3 ± 10.1 | 18.9 ± 8.8 ●*** | 20.8 ± 8.0 | 20.9 ± 8.4 | 21.2 ± 9.6 |
| Proteins (g) | 89.6 ± 42.3 | 84.6 ± 31.0 | 85.2 ± 33.0 | 85.2 ± 32.0 | 93.8 ± 39.5 | 92.2 ± 36.6 |
| Lipids (g) | 96.4 ± 50.8 | 95.5 ± 43.9 | 99.6 ± 39.5 ●*** | 95.3 ± 34.6 | 103.5 ± 48.8 | 99.8 ± 34.4 |
| SFA (g) | 26.3 ± 16.0 | 26.3 ± 11.6 | 28.4 ± 12.8 ●*** | 26.4 ± 11.7 | 29.7 ± 15.9 | 29.1 ± 10.8 |
| MFA (g) | 32.9 ± 16.9 | 33.4 ± 16.9 | 33.5 ± 13.7 ●* | 33.5 ± 13.5 | 36.4 ± 20.5 | 35.7 ± 13.7 |
| PUFA (g) | 20.8 ± 13.4 | 20.8 ± 13.3 | 22.5 ± 12.7 ●* | 20.4 ± 9.9 | 22.1 ± 13.5 | 19.7 ± 9.8 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 364.2 ± 296.8 | 354.6 ± 220.0 | 376.4 ± 239.3 | 363.3 ± 234.7 | 441.1 ± 330.5 | 432.7 ± 255.1 |
| Ethanol (g) | 11.1 ± 28.5 | 8.3 ± 21.3 | 5.9 ± 11.4 | 9.0 ± 25.8 | 6.3 ± 9.6 | 6.5 ± 7.6 |
| Calcium (mg) | 881.8 ± 536.1 | 790.7 ± 307.4 | 818.5 ± 348.0 | 803.2 ± 348.7 | 902.0 ± 462.7 | 876.2 ± 340.7 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1433.6 ± 644.2 | 1345.4 ± 496.2 | 1346.7 ± 505.4 | 1368.7 ± 505.6 | 1517.3 ± 650.4 | 1452.3 ± 572.7 |
| Iron (mg) | 20.8 ± 9.4 | 19.3 ± 8.4 | 19.4 ± 8.8 | 20.2 ± 8.2 | 21.6 ± 10.1 | 20.9 ± 9.2 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 466.8 ± 189.3 | 423.5 ± 170.1 | 411.4 ± 155.6 ●** | 434.6 ± 150.7 | 450.0 ± 170.2 | 430.3 ± 172.1 |
| Sodium (mg) | 1841.3 ± 1227.3 | 1815.0 ± 982.9 | 1994.3 ± 1006.3 ●* | 1840.1 ± 956.4 | 1988.7 ± 1093.6 | 2009.3 ± 1047.2 |
| Potassium (mg) | 4084.6 ± 1728.0 | 3750.0 ± 1597.8 | 3591.6 ± 1426.3 ●** | 3840.6 ± 1285.5 | 3956.9 ± 1477.9 | 4000.2 ± 1545.3 |
| Zinc (mg) | 10.5 ± 4.9 | 10.0 ± 4.3 | 9.9 ± 4.1 | 10.0 ± 3.6 | 10.6 ± 4.6 | 10.4 ± 4.1 |
| Selenium (mcg) | 38.6 ± 16.2 | 36.3 ± 22.6 | 37.9 ± 25.7 | 38.6 ± 19.3 | 39.5 ± 21.0 | 43.9 ± 25.1 |
| Vitamin A (mcg) | 961.7 ± 647.2 | 849.6 ± 499.4 | 872.9 ± 447.0 | 871.6 ± 354.3 | 989.7 ± 544.6 | 1015.2 ± 607.9 |
| Vitamin B1 (mg) | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.6 ●* | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.7 |
| Vitamin B2 (mg) | 2.9 ± 2.1 | 2.8 ± 1.5 | 2.6 ± 1.4 | 2.9 ± 2.1 | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 3.4 ± 2.3 |
| Vitamin B3 (mg) | 22.5 ± 9.7 | 21.3 ± 9.8 | 20.7 ± 8.3 | 22.1 ± 8.4 | 22.6 ± 8.9 | 23.2 ± 9.8 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 1.0 |
| Folate (mcg) | 266.8 ± 141.4 | 243.4 ± 141.6 | 227.6 ± 113.6 ●* | 252.4 ± 99.6 | 273.6 ± 131.8 | 264.6 ± 140.6 |
| Vitamin B12 (mcg) | 7.5 ± 5.4 | 7.0 ± 4.4 | 6.7 ± 3.8 | 6.6 ± 3.8 | 8.5 ± 8.0 | 8.1 ± 5.5 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 346.7 ± 225.2 | 296.3 ± 205.2 | 268.8 ± 174.2 ●*** | 303.9 ± 160.9 | 279.5 ± 137.0 | 309.1 ± 164.2 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.4 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Betancourt-Núñez, A.; Torres-Castillo, N.; Martínez-López, E.; De Loera-Rodríguez, C.O.; Durán-Barajas, E.; Márquez-Sandoval, F.; Bernal-Orozco, M.F.; Garaulet, M.; Vizmanos, B. Emotional Eating and Dietary Patterns: Reflecting Food Choices in People with and without Abdominal Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071371
Betancourt-Núñez A, Torres-Castillo N, Martínez-López E, De Loera-Rodríguez CO, Durán-Barajas E, Márquez-Sandoval F, Bernal-Orozco MF, Garaulet M, Vizmanos B. Emotional Eating and Dietary Patterns: Reflecting Food Choices in People with and without Abdominal Obesity. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071371
Chicago/Turabian StyleBetancourt-Núñez, Alejandra, Nathaly Torres-Castillo, Erika Martínez-López, César O. De Loera-Rodríguez, Elvira Durán-Barajas, Fabiola Márquez-Sandoval, María Fernanda Bernal-Orozco, Marta Garaulet, and Barbara Vizmanos. 2022. "Emotional Eating and Dietary Patterns: Reflecting Food Choices in People with and without Abdominal Obesity" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071371
APA StyleBetancourt-Núñez, A., Torres-Castillo, N., Martínez-López, E., De Loera-Rodríguez, C. O., Durán-Barajas, E., Márquez-Sandoval, F., Bernal-Orozco, M. F., Garaulet, M., & Vizmanos, B. (2022). Emotional Eating and Dietary Patterns: Reflecting Food Choices in People with and without Abdominal Obesity. Nutrients, 14(7), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071371








