DIetary ASSessment (DIASS) Study: Design of an Evaluation Study to Assess Validity, Usability and Perceived Burden of an Innovative Dietary Assessment Methodology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
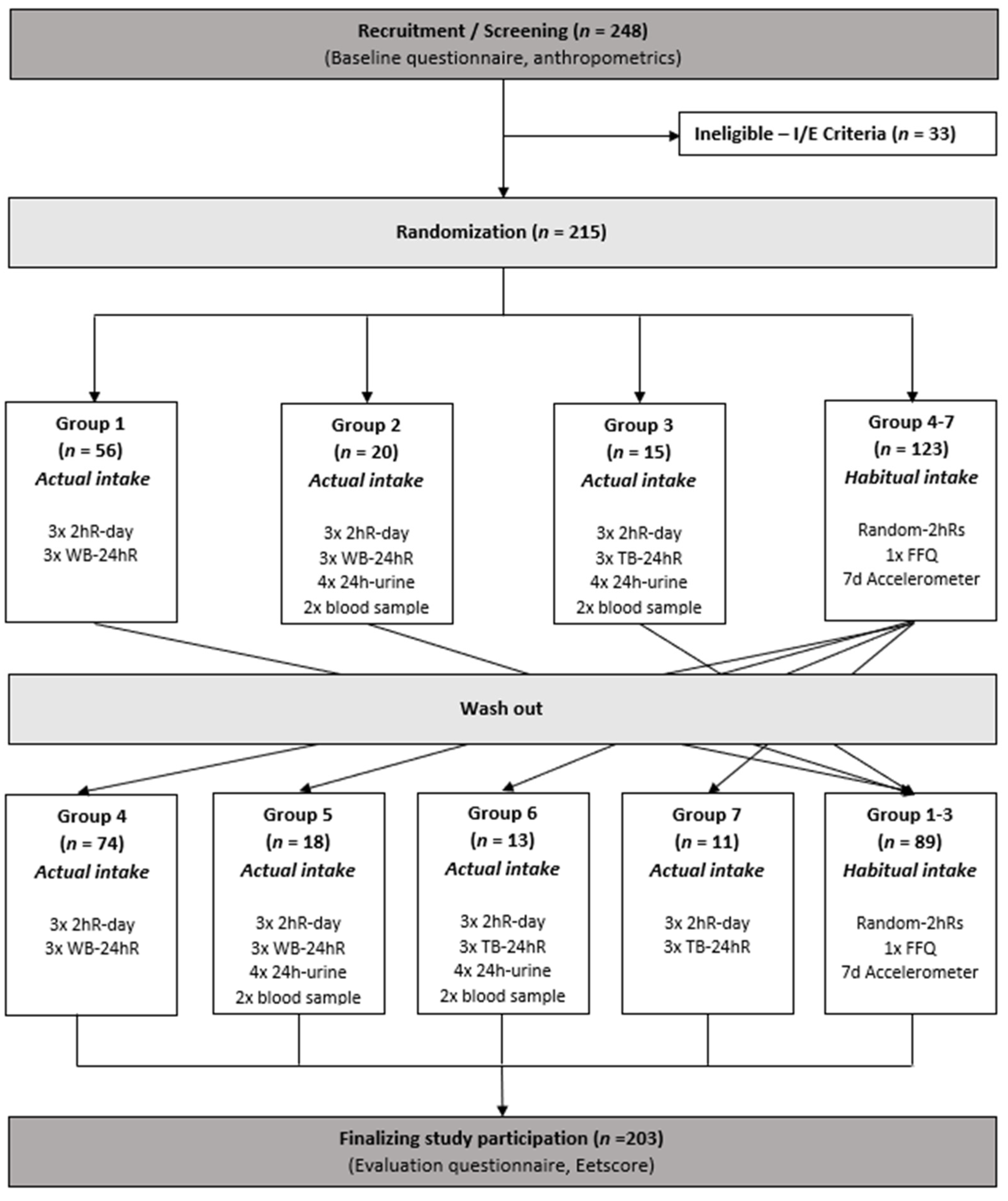
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Dietary Intake Assessment
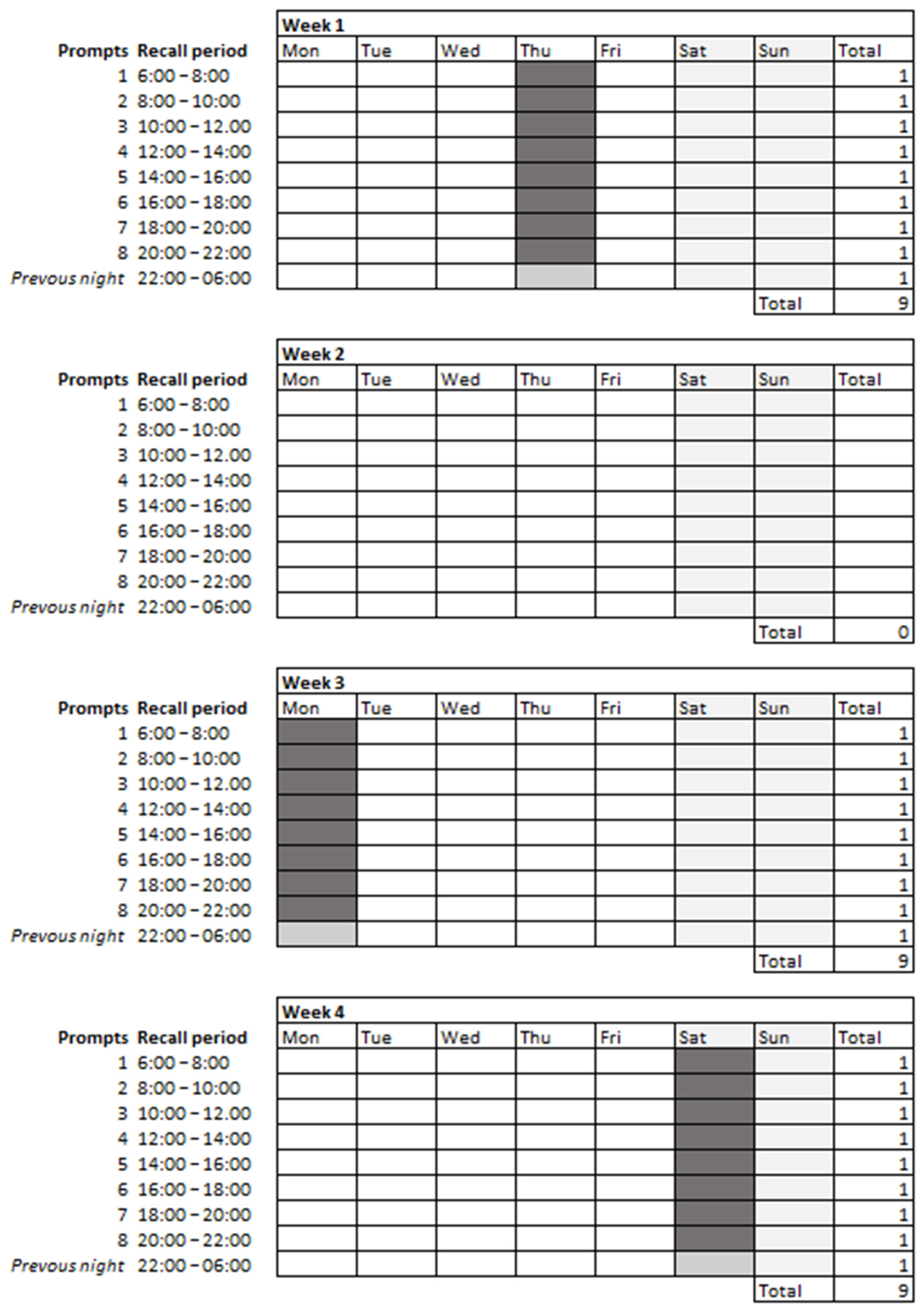
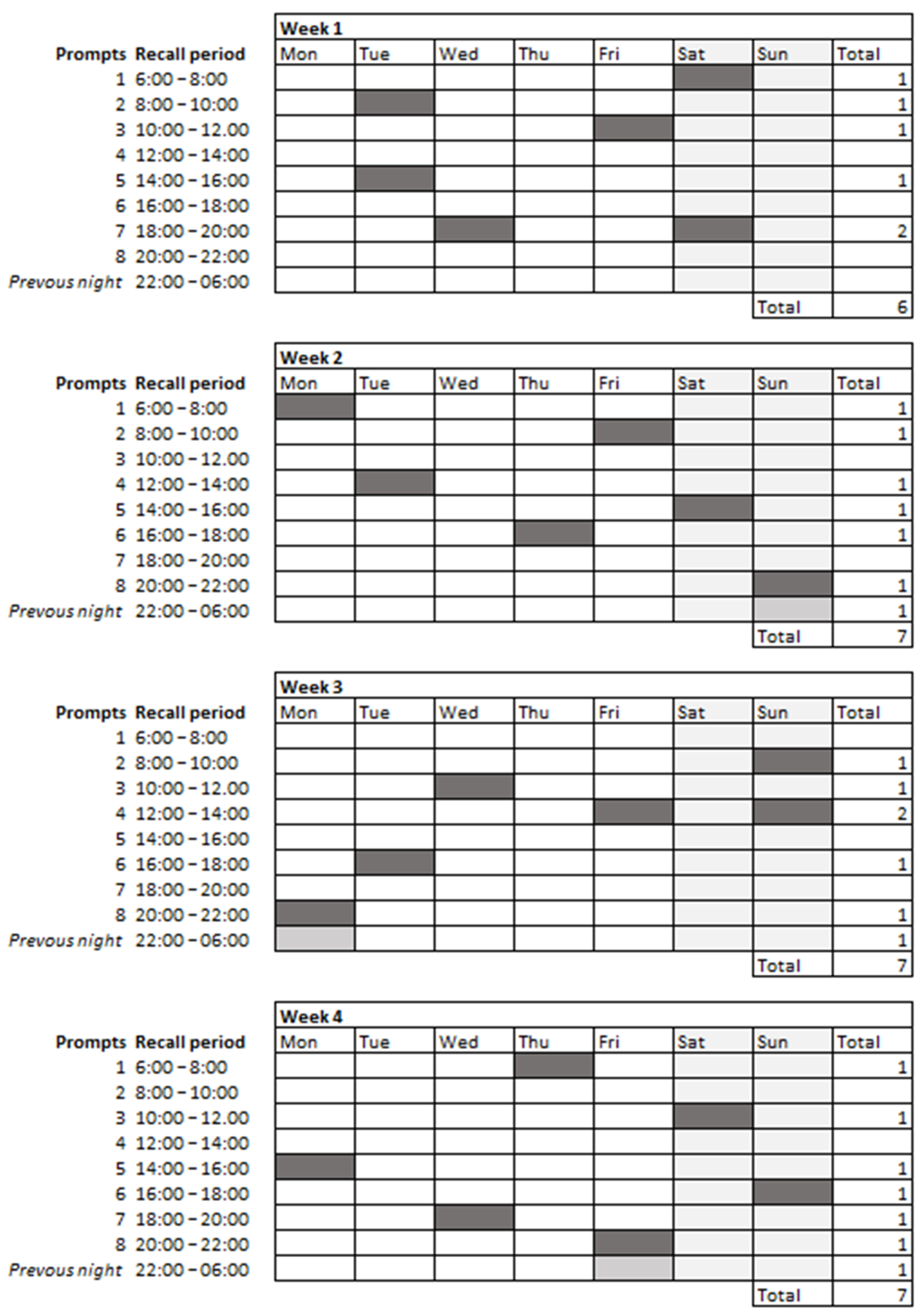
2.3.1. 2hRs
2.3.2. Web-Based 24 h
2.3.3. Telephone-Based 24 h
2.3.4. Computation of Dietary Recall Data
2.3.5. FFQ
2.3.6. Diet Quality
2.4. Urine Collection
2.5. Blood Collection
2.6. Anthropometrics
2.7. Total Energy Expenditure
2.8. Demographics
2.9. Evaluation Questionnaire
3. Statistical Analyses
4. Baseline Characteristics
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, F.E.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Subar, A.F.; Reedy, J.; Schap, T.E.; Wilson, M.M.; Krebs-Smith, S.M. The National Cancer Institute’s Dietary Assessment Primer: A Resource for Diet Research. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subar, A.F.; Freedman, L.S.; Tooze, J.A.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Boushey, C.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Thompson, F.E.; Potischman, N.; Guenther, P.M.; Tarasuk, V.; et al. Addressing Current Criticism Regarding the Value of Self-Report Dietary Data. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Lucassen, D.; de Rijk, M.G.; Slotegraaf, A.; Perenboom, C.; Borgonjen, K.; Siebelink, E.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Vries, J.H.M. Dietary Intake Assessment: From Traditional Paper-Pencil Questionnaires to Technology-Based Tools. In Environmental Software Systems. Data Science in Action; Athanasiadis, I., Frysinger, S., Schimak, G., Knibbe, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, H.; Walsh, M.C.; Gibney, M.J.; Brennan, L.; Gibney, E.R. Personalised nutrition: The role of new dietary assessment methods. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothman, K.J.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T.L. Modern Epidemiology; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, F.E.; Subar, A.F. Dietary Assessment Methodology. In Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 5–48. [Google Scholar]
- Young, L.R.; Nestle, M.S. Portion sizes in dietary assessment: Issues and policy implications. Nutr. Rev. 1995, 53, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, N.; Ritenbaugh, C.; Taren, D.L.; Tobar, M. A qualitative study of participants’ experiences with dietary assessment. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timon, C.M.; van den Barg, R.; Blain, R.J.; Kehoe, L.; Evans, K.; Walton, J.; Flynn, A.; Gibney, E.R. A review of the design and validation of web- and computer-based 24-h dietary recall tools. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timon, C.M.; Blain, R.J.; McNulty, B.; Kehoe, L.; Evans, K.; Walton, J.; Flynn, A.; Gibney, E.R. The Development, Validation, and User Evaluation of Foodbook24: A Web-Based Dietary Assessment Tool Developed for the Irish Adult Population. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eldridge, A.L.; Piernas, C.; Illner, A.K.; Gibney, M.J.; Gurinovic, M.A.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Cade, J.E. Evaluation of New Technology-Based Tools for Dietary Intake Assessment-An ILSI Europe Dietary Intake and Exposure Task Force Evaluation. Nutrients 2018, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo, J.; Engelen, A.; Molag, M.; Roesle, J.; Garcia-Segovia, P.; Serra-Majem, L. A review of the use of information and communication technologies for dietary assessment. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101 (Suppl. 2), S102–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, A.; Shiffman, S.; Atienza, A.; Nebeling, L. The Science of Real-Time Data Capture: Self-Reports in Health Research; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shiffman, S.; Stone, A.A.; Hufford, M.R. Ecological momentary assessment. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2008, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucassen, D.A.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; van de Wiel, A.M.; Siebelink, E.; Feskens, E.J.M. Iterative Development of an Innovative Smartphone-Based Dietary Assessment Tool: Traqq. JoVE 2021, 169, e62032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; van Lee, L.; Streppel, M.T.; Sluik, D.; van de Wiel, A.M.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Geelen, A.; Feskens, E.J.M. Nutrition Questionnaires plus (NQplus) study, a prospective study on dietary determinants and cardiometabolic health in Dutch adults. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM); NEVO. Dutch Food Composition Table version 2016/5.0; Dutch Nutrition Centre: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Donders-Engelen, M.R.; Van der Heijden, L.J.M.; Hulshof, K.F.A.M. Maten, Gewichten en Codenummers 2003. Food Portion Sizes and Coding Instructions; Wageningen University: Division of Human Nutrition and TNO Nutrition: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Freyne, J.; Yin, J.; Brindal, E.; Hendrie, G.A.; Berkovsky, S.; Noakes, M. Push Notifications in Diet Apps: Influencing Engagement Times and Tasks. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Int. 2017, 33, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijboom, S.; van Houts-Streppel, M.T.; Perenboom, C.; Siebelink, E.; van de Wiel, A.M.; Geelen, A.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Vries, J.H.M. Evaluation of dietary intake assessed by the Dutch self-administered web-based dietary 24-h recall tool (Compl-eat™) against interviewer-administered telephone-based 24-h recalls. J. Nutr. Sci. 2017, 6, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, J.M.; Ingwersen, L.A.; Vinyard, B.T.; Moshfegh, A.J. Effectiveness of the US Department of Agriculture 5-step multiple-pass method in assessing food intake in obese and nonobese women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siebelink, E.; Geelen, A.; de Vries, J.H. Self-reported energy intake by FFQ compared with actual energy intake to maintain body weight in 516 adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molag, M. Towards Transparent Development of Food Frequency Questionnaires: Scientific Basis of the Dutch FFQ-TOOL tm: A Computer System to Generate, Apply and Process FFQs; Wageningen University Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- The Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM); NEVO. Dutch Food Composition Table version 2010/2.0; Dutch Nutrition Centre: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- de Rijk, M.G.; Slotegraaf, A.I.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Perenboom, C.W.M.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Vries, J.H.M. Development and evaluation of a diet quality screener to assess adherence to the Dutch food-based dietary guidelines. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looman, M.; Feskens, E.J.; de Rijk, M.; Meijboom, S.; Biesbroek, S.; Temme, E.H.; de Vries, J.; Geelen, A. Development and evaluation of the Dutch Healthy Diet index 2015. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassale, C.; Castetbon, K.; Laporte, F.; Camilleri, G.M.; Deschamps, V.; Vernay, M.; Faure, P.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Kesse-Guyot, E. Validation of a Web-based, self-administered, non-consecutive-day dietary record tool against urinary biomarkers. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subar, A.F.; Midthune, D.; Tasevska, N.; Kipnis, V.; Freedman, L.S. Checking for completeness of 24-h urine collection using para-amino benzoic acid not necessary in the Observing Protein and Energy Nutrition study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, S.A. Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenab, M.; Slimani, N.; Bictash, M.; Ferrari, P.; Bingham, S.A. Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology: Applications, needs and new horizons. Hum. Genet. 2009, 125, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, S.A. Urine nitrogen as a biomarker for the validation of dietary protein intake. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 921S–924S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Delaimy, W.; Ferrari, P.; Slimani, N.; Pala, V.; Johansson, I.; Nilsson, S.; Mattisson, I.; Wirfalt, E.; Galasso, R.; Palli, D. Plasma carotenoids as biomarkers of intake of fruits and vegetables: Individual-level correlations in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatian-Elahi, M.; Slimani, N.; Chajès, V.; Jenab, M.; Goudable, J.; Biessy, C.; Ferrari, P.; Byrnes, G.; Autier, P.; Peeters, P.H. Plasma phospholipid fatty acid profiles and their association with food intakes: Results from a cross-sectional study within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, C.J.K. Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: Measurement and development of new equations. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Mokhtar, N.; Byrne, N.M. Assessment of physical activity and energy expenditure: An overview of objective measures. Front. Nutr. 2014, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.S.; Evenson, K.R.; Vaughn, A.; Rodgers, A.B.; Troiano, R.P. Accelerometer Use in Physical Activity: Best Practices and Research Recommendations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, S582–S588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Masse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; McDowell, M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Energy and Protein Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation [Held in Rome from 5 to 17 October 1981]; 9241207248; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Spook, J.E.; Paulussen, T.; Kok, G.; Van Empelen, P. Monitoring dietary intake and physical activity electronically: Feasibility, usability, and ecological validity of a mobile-based Ecological Momentary Assessment tool. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, G.L.; Hurworth, M.; Giglia, R.; Trapp, G.; Strauss, P. Feasibility of a commercial smartphone application for dietary assessment in epidemiological research and comparison with 24-h dietary recalls. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J. SUS—A quick and dirty usability scale. Usability Eval. Ind. 1996, 189, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Plourde, H.; Bouzo, V.; Kilgour, R.D.; Cohen, T.R. Validity and Usability of a Smartphone Image-Based Dietary Assessment App Compared to 3-Day Food Diaries in Assessing Dietary Intake Among Canadian Adults: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e16953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.A.; Pollard, C.M.; Howat, P.; Delp, E.J.; Pickering, M.; Kerr, K.R.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Pratt, I.S.; Wright, J.; Boushey, C.J. Connecting Health and Technology (CHAT): Protocol of a randomized controlled trial to improve nutrition behaviours using mobile devices and tailored text messaging in young adults. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bucher Della Torre, S.; Carrard, I.; Farina, E.; Danuser, B.; Kruseman, M. Development and Evaluation of e-CA, an Electronic Mobile-Based Food Record. Nutrients 2017, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangan, A.M.; O’Connor, S.; Giannelli, V.; Yap, M.L.; Tang, L.M.; Roy, R.; Louie, J.C.; Hebden, L.; Kay, J.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Electronic Dietary Intake Assessment (e-DIA): Comparison of a Mobile Phone Digital Entry App for Dietary Data Collection With 24-Hour Dietary Recalls. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2015, 3, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellard-Cole, L.; Chen, J.; Davies, A.; Wong, A.; Huynh, S.; Rangan, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Relative Validity of the Eat and Track (EaT) Smartphone App for Collection of Dietary Intake Data in 18-to-30-Year Olds. Nutrients 2019, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.M.; Chin, M.K.; Gilhooly, C.H.; Barger, K.; Matuszek, G.; Miki, A.J.; Cote, R.G.; Eldridge, A.L.; Green, H.; Mainardi, F.; et al. Evaluation of PIQNIQ, a Novel Mobile Application for Capturing Dietary Intake. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, M.E.; Ash, S.; Lyons-Wall, P.; Russell, A.W. Evaluation of a Mobile Phone Image-Based Dietary Assessment Method in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4897–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pendergast, F.J.; Ridgers, N.D.; Worsley, A.; McNaughton, S.A. Evaluation of a smartphone food diary application using objectively measured energy expenditure. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Z.; Kerr, D.A.; Bosch, M.; Boushey, C.J.; Delp, E.J.; Khanna, N.; Zhu, F. A Mobile Food Record for Integrated Dietary Assessment. MADiMa16 2016, 2016, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boushey, C.J.; Spoden, M.; Delp, E.J.; Zhu, F.; Bosch, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; DeLany, J.P.; Kerr, D.A. Reported energy intake accuracy compared to doubly labeled water and usability of the mobile food record among community dwelling adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, V.; Subar, A.F.; Midthune, D.; Freedman, L.S.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Troiano, R.P.; Bingham, S.; Schoeller, D.A.; Schatzkin, A.; Carroll, R.J. Structure of Dietary Measurement Error: Results of the OPEN Biomarker Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 158, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Brennan, L.; Drevon, C.A.; van Kranen, H.; Manach, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Roche, H.M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bouwman, J.; et al. Combining traditional dietary assessment methods with novel metabolomics techniques: Present efforts by the Food Biomarker Alliance. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illner, A.K.; Freisling, H.; Boeing, H.; Huybrechts, I.; Crispim, S.P.; Slimani, N. Review and evaluation of innovative technologies for measuring diet in nutritional epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Kanthawala, S.; Yuan, S.; Hussain, S.A. A qualitative study of user perceptions of mobile health apps. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| N | Total | Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men (n, %) | 215 | 60 (28) | 60 (100) | 155 (0) |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 215 | 39 (19) | 45 (19) | 37 (18) |
| Age category (n, %) | 215 | |||
| <25 years | 90 (42) | 19 (32) | 71 (46) | |
| 25–50 years | 43 (20) | 10 (16) | 33 (21) | |
| ≥50 years | 82 (38) | 31 (52) | 51 (33) | |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (SD) | 215 | 23.8 (4.0) | 25.0 (4.3) | 23.4 (3.8) |
| BMI category (n, %) | 215 | |||
| <18.5 kg/m2 | 7 (3) | 1 (1) | 6 (4) | |
| 18.5–25 kg/m2 | 148 (69) | 34 (57) | 114 (73) | |
| ≥25 kg/m2 | 60 (28) | 25 (42) | 35 (23) | |
| Mean BMR, kcal/day (SD) | 215 | 1545 (211) | 1799 (174) | 1446 (122) |
| Mean PAL | 203 | 1.46 (0.02) | 1.46 (0.02) | 1.46 (0.01) |
| Educational level (n, %) | 215 | |||
| Low | 5 (2) | 0 (0) | 5 (3) | |
| Intermediate | 85 (40) | 26 (43) | 59 (38) | |
| High | 125 (58) | 34 (57) | 91 (59) | |
| Marital status (n, %) | 215 | |||
| Married/registered partnership | 69 (32) | 25 (42) | 44 (28) | |
| Cohabiting | 25 (12) | 8 (13) | 17 (11) | |
| Serious relationship, not cohabiting | 20 (9) | 6 (10) | 14 (9) | |
| Single | 90 (42) | 17 (28) | 73 (47) | |
| Divorced | 7 (3) | 3 (5) | 4 (3) | |
| Widowed | 3 (1) | 0 (0) | 3 (2) | |
| Other | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | |
| Paid job currently (n, %) | 215 | |||
| Yes | 112 (52) | 33 (55) | 79 (51) | |
| No | 103 (48) | 27 (45) | 76 (49) | |
| Diet regimen (n, %) | 204 | |||
| Yes, always | 35 (17) | 4 (7) | 31 (21) | |
| Yes, sometimes | 24 (12) | 6 (11) | 18 (12) | |
| Never | 145 (71) | 45 (82) | 100 (67) | |
| Number of complete dietary data collections (n, %) | ||||
| 2hR-day 1 | 214 | 591 (92) | 158 (88) | 433 (94) |
| WB-24hR | 167 | 474 (90) | 126 (88) | 348 (91) |
| TB-24hR | 39 | 117 (98) | 33 (92) | 84 (100) |
| Linked 24-h urine collections | 66 | 238 (86) | 73 (83) | 165 (88) |
| Blood sample | 66 | 138 (100) | 44 (100) | 94 (100) |
| Random 2hRs | 212 | 4669 (96) | 1322 (95) | 3347 (96) |
| FFQ | 212 | 204 (96) | 55 (92) | 149 (98) |
| Eetscore | 203 | 192 (95) | 54 (98) | 138 (93) |
| Mean System Usability Score (SD) | 190 | 72 (14) | 73 (15) | 72 (13) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucassen, D.A.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Slotegraaf, A.I.; Kok, E.; Feskens, E.J.M. DIetary ASSessment (DIASS) Study: Design of an Evaluation Study to Assess Validity, Usability and Perceived Burden of an Innovative Dietary Assessment Methodology. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061156
Lucassen DA, Brouwer-Brolsma EM, Slotegraaf AI, Kok E, Feskens EJM. DIetary ASSessment (DIASS) Study: Design of an Evaluation Study to Assess Validity, Usability and Perceived Burden of an Innovative Dietary Assessment Methodology. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061156
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucassen, Desiree A., Elske M. Brouwer-Brolsma, Anne I. Slotegraaf, Esther Kok, and Edith J. M. Feskens. 2022. "DIetary ASSessment (DIASS) Study: Design of an Evaluation Study to Assess Validity, Usability and Perceived Burden of an Innovative Dietary Assessment Methodology" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061156
APA StyleLucassen, D. A., Brouwer-Brolsma, E. M., Slotegraaf, A. I., Kok, E., & Feskens, E. J. M. (2022). DIetary ASSessment (DIASS) Study: Design of an Evaluation Study to Assess Validity, Usability and Perceived Burden of an Innovative Dietary Assessment Methodology. Nutrients, 14(6), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061156





