Flavor Wheel Construction and Sensory Profile Description of Human Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Donors
2.2. Samples
2.3. Sensory Evaluation Panel Training
2.4. Sensory Lexicon Generation and Screening
2.5. Construction of the Sensory Wheel
2.6. Establishment and Application of Quantitative Descriptors for Breast Milk
2.7. Sensory Panelists Performance Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
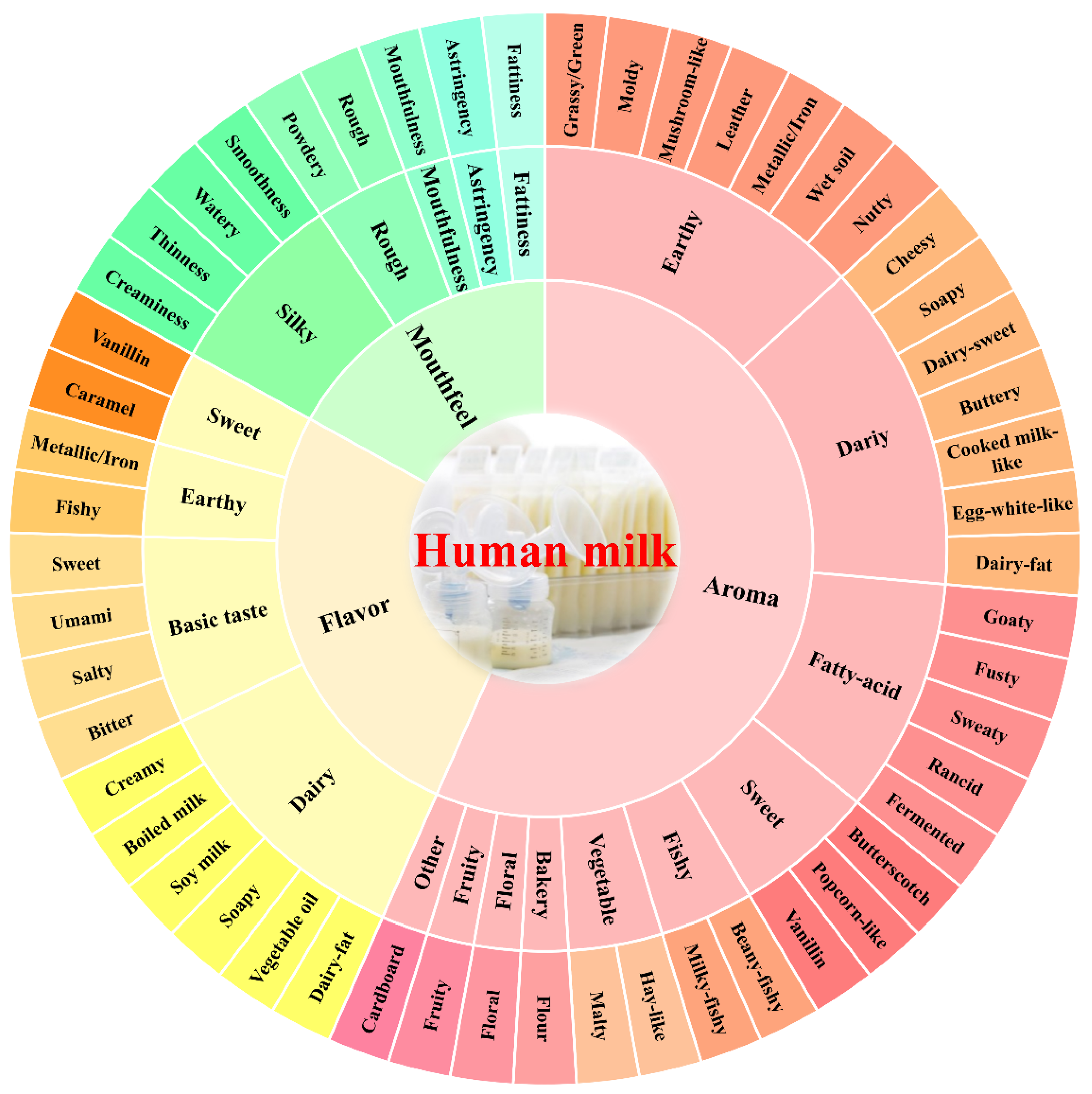
3.1. Construction of Breast Milk Flavor Wheel
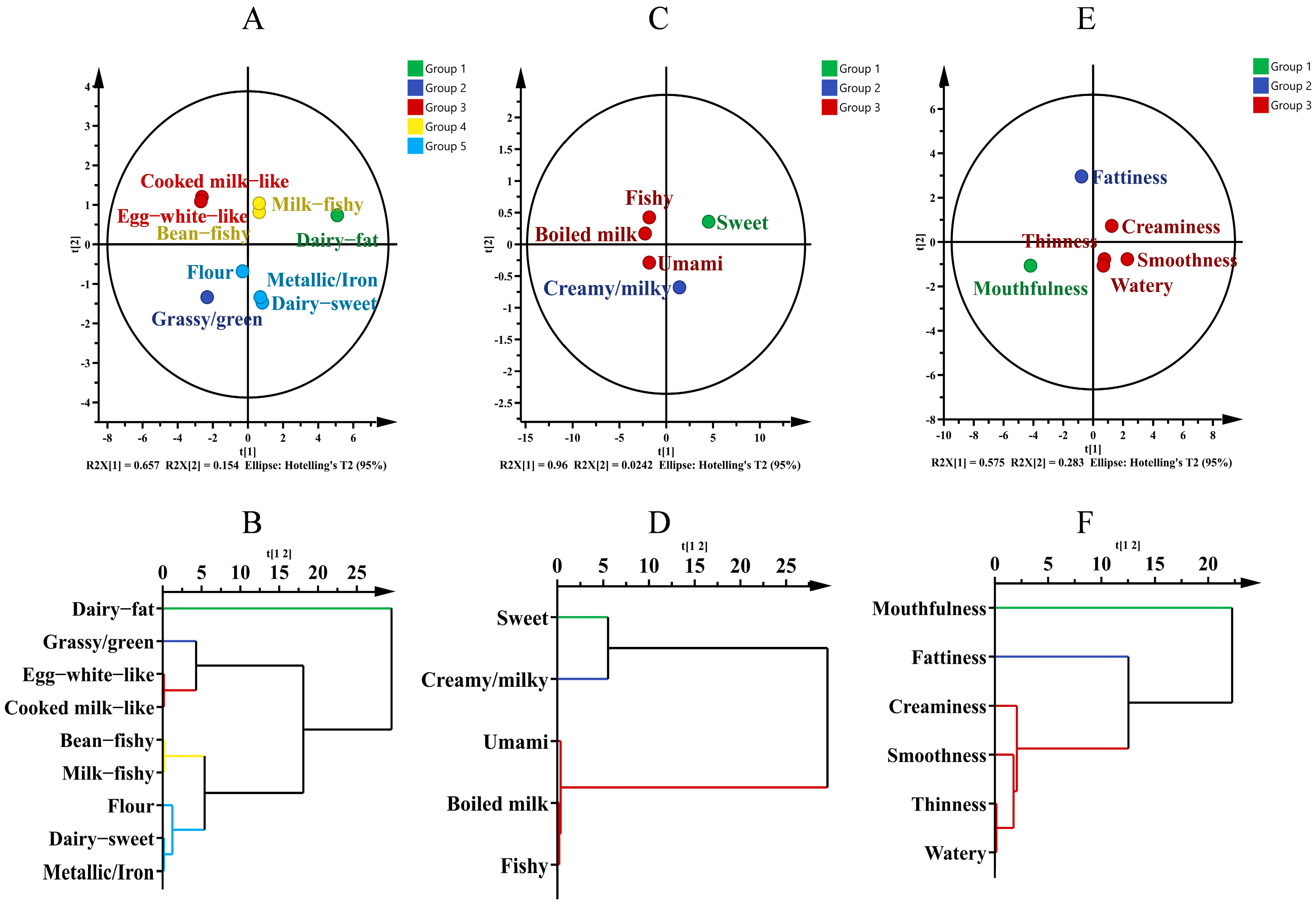
3.2. Screening of Breast Milk Sensory Profile Descriptors
3.3. Evaluation of the Sensory Panel Performance
3.3.1. Consistency
3.3.2. Discrimination Ability and Repeatability
3.4. Application of Sensory Profile Descriptors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arabi, M.; Frongillo, E.A.; Avula, R.; Mangasaryan, N. Infant and young child feeding in developing countries. Child Dev. 2012, 83, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.R.; Ling, P.R.; Blackburn, G.L. Review of infant feeding: Key features of human milk and infant formula. Nutrients 2016, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.L.; Marconi, E.; Protano, C.; Vitali, M.; Schiavi, E.; Mastromarino, P.; Canepari, S. Optimization and validation of a fast digestion method for the determination of major and trace elements in human milk by ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1040, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbok, M.H. Effects of breastfeeding on the mother. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 48, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.D.E.; Marlier, L.; Schaal, B. Learning at the breast: Preference formation for an artificial scent and its attraction against the odor of maternal milk. Infant Behav. Dev. 2006, 29, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimbault, C.; Saliba, E.; Porter, R.H. The effect of the odour of mother’s milk on breastfeeding behaviour of premature neonates. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chanville, A.B.; Brevaut-Malaty, V.; Garbi, A.; Tosello, B.; Baumstarck, K.; Gire, C. Analgesic effect of maternal human milk odor on premature neonates: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, L.; Fildes, A. The impact of flavor exposure in utero and during milk feeding on food acceptance at weaning and beyond. Appetite 2011, 57, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darici, M.; Ozcan, K.; Beypinar, D.; Cabaroglu, T. Sensory lexicon and major volatiles of Raki using descriptive analysis and GC-FID/MS. Foods 2021, 10, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigwedere, C.M.; Wanasundara, J.P.D.; Shand, P.J. Sensory descriptors for pulses and pulse-derived ingredients: Toward a standardized lexicon and sensory wheel. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lee, J. Application of sensory descriptive analysis and consumer studies to investigate traditional and authentic foods: A review. Foods 2019, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgaard, L.; Mielby, L.A.; Heymann, H.; Byrne, D.V. Effect of product involvement on panels’ vocabulary generation, attribute identification, and sample configurations in beer. Foods 2019, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, L.J.R.; Civille, G.V. Developing lexicons: A review. J. Sens. Stud. 2013, 28, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwonsichon, S. The importance of sensory lexicons for research and development of food products. Foods 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, L.J.R.; Hottenstein, A.; Ellingsworth, J. The McCormick spice wheel: A systematic and visual approach to sensory lexicon development. J. Sens. Stud. 2012, 27, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larssen, W.E.; Monteleone, E.; Hersleth, M. Sensory description of marine oils through development of a sensory wheel and vocabulary. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, I.S.; Muller, M.; Joubert, E.; van der Rijst, M.; Naes, T. Sensory characterization of rooibos tea and the development of a rooibos sensory wheel and lexicon. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.; Sage, E.; Velez, M.; Guinard, J.X. Using single free sorting and multivariate exploratory methods to design a new coffee taster’s flavor wheel. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, S2997–S3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, R.; Oberholster, A.; Francis, I.L. A “mouth-feel wheel”: Terminology for communicating the mouth-feel characteristics of red wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2000, 6, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; De Clercq, G.; Gellynck, X.; Schouteten, J.J. Development of a sensory wheel and lexicon for chocolate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, J.; Buettner, A. Characterization of aroma changes in human milk during storage at −19 °C. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Li, Z. Detection of odor difference between human milk and infant formula by sensory-directed analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, P.; Wang, H.L.; Song, H.L. Identification of odor compounds and odor-active compounds of yogurt using DHS, SPME, SAFE, and SBSE/GC-O-MS. LWT 2022, 154, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, C.; Song, H.L.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Hua, J.C. Sensory-directed flavor analysis of off-flavor compounds in infant formula with deeply hydrolyzed milk protein and their possible sources. LWT 2020, 119, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T. Flavor description of white wine by ‘expert’ and nonexpert wine consumers. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11035:1994; Sensory Analysis-Identification and Selection of Descriptors for Establishing a Sensory Profile by a Multidimensional Approach. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- Tomic, O.; Nilsen, A.; Martens, M.; Naes, T. Visualization of sensory profiling data for performance monitoring. LWT 2007, 40, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.A.; Karagul-Yuceer, Y.; Cadwallader, K.R.; Civille, G.V.; Tong, P.S. Determination of the sensory attributes of dried milk powders and dairy ingredients. J. Sens. Stud. 2003, 18, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Kouka, K.D.; Klein, B.P.; Lee, S.Y. Developing a lexicon for descriptive analysis of soymilks. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, S259–S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.B.; Dijksterhuis, G.; Martens, M. Sensory perception of fat in milk. Food Qual. Prefer. 2001, 12, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisserer, D.M.; Chambers, E.I. Determination of the sensory flavor attributes of aged natural cheese. J. Sens. Stud. 1993, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastorakou, D.; Ruark, A.; Weenen, H.; Stahl, B.; Stieger, M. Sensory characteristics of human milk: Association between mothers’ diet and milk for bitter taste. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.; Bassereau, J.F.; Pense-Lheritier, A.M.; Rivere, C.; Harris, N.; Duchamp, R. Recruitment and training of a sensory expert panel to measure the touch of beverage packages: Issue and methods employed. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, O.; Luciano, G.; Nilsen, A.; Hyldig, G.; Lorensen, K.; Naes, T. Analysing sensory panel performance in a proficiency test using the PanelCheck software. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losó, V.; Gere, A.; Györey, A.; Kókai, Z.; Sipos, L. Comparison of the performance of a trained and an untrained sensory panel on sweetcorn varieties with the panelcheck software. Appl. Stud. Agribus. Commer. 2012, 6, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussignan, R.; Schaal, B.; Marlier, L.; Jiang, T. Facial and autonomic responses to biological and artificial olfactory stimuli in human neonates: Re-examining early hedonic discrimination of odors. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 62, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, A. A selective and sensitive approach to characterize oclour-active and volatile constituents in small-scale human milk samples. Flavor Frag. J. 2007, 22, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, A.; Quintaes, K.D.; Barbera, R.; Alegria, A. Phospholipids in human milk and infant formulas: Benefits and needs for correct infant nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, H.M.; Reger, D.; Schaal, B. The odour of human milk: Its chemical variability and detection by newborns. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples a | Regions | Lactation Periods (Month) | Content (g/100 mL) | Energy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | Protein | Carbohydrate | TS b | (kcal/100 mL) | |||
| M1 | Beijing | 3 | 2.13 ± 0.09 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 5.62 ± 0.19 | 8.83 ± 0.26 | 46.00 ± 1.63 |
| M2 | Beijing | 4 | 3.07 ± 0.09 | 0.97 ± 0.05 | 6.20 ± 0.14 | 10.50 ± 0.22 | 58.00 ± 1.41 |
| M3 | Beijing | 6 | 4.53 ± 0.05 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 6.43 ± 0.05 | 11.90 ± 0.00 | 71.00 ± 0.00 |
| M4 | Beijing | 2 | 1.80 ± 0.14 | 0.67 ± 0.05 | 4.27 ± 0.54 | 8.17 ± 0.50 | 40.67 ± 2.05 |
| M5 | Beijing | 6 | 4.50 ± 0.08 | 1.17 ± 0.12 | 7.27 ± 0.05 | 13.13 ± 0.12 | 75.67 ± 0.47 |
| M6 | Beijing | 3 | 2.33 ± 0.05 | 1.23 ± 0.05 | 4.57 ± 0.09 | 9.13 ± 0.12 | 50.45 ± 0.36 |
| M7 | Jiangsu | 4 | 2.40 ± 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 6.30 ± 0.08 | 9.73 ± 0.05 | 51.67 ± 0.94 |
| M8 | Jiangsu | 2 | 2.37 ± 0.05 | 0.80 ± 0.08 | 5.63 ± 0.45 | 8.50 ± 0.75 | 50.00 ± 4.55 |
| M9 | Jiangsu | 5 | 3.43 ± 0.12 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 8.00 ± 0.08 | 12.43 ± 0.12 | 67.33 ± 1.25 |
| M10 | Jiangsu | 4 | 4.57 ± 0.05 | 1.10 ± 0.03 | 4.40 ± 0.05 | 11.77 ± 0.05 | 68.33 ± 0.47 |
| M11 | Jiangsu | 3 | 3.33 ± 0.05 | 0.53 ± 0.05 | 4.87 ± 0.05 | 10.13 ± 0.05 | 56.33 ± 0.47 |
| M12 | Jiangsu | 4 | 3.40 ± 0.08 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 4.70 ± 0.10 | 10.53 ± 0.09 | 57.67 ± 0.47 |
| M13 | Anhui | 2 | 1.83 ± 0.12 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 6.47 ± 0.05 | 9.10 ± 0.08 | 45.33 ± 1.25 |
| M14 | Anhui | 5 | 5.30 ± 0.37 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 5.60 ± 0.14 | 11.87 ± 0.42 | 75.00 ± 3.74 |
| M15 | Anhui | 1 | 2.90 ± 0.28 | 0.97 ± 0.05 | 6.30 ± 0.08 | 10.40 ± 0.29 | 56.33 ± 2.62 |
| M16 | Anhui | 5 | 4.33 ± 0.12 | 0.83 ± 0.12 | 4.63 ± 0.05 | 11.53 ± 0.05 | 66.33 ± 0.47 |
| M17 | Anhui | 6 | 3.20 ± 0.24 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 5.77 ± 0.05 | 10.17 ± 0.26 | 57.33 ± 2.49 |
| M18 | Anhui | 4 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 1.10 ± 0.05 | 4.65 ± 0.04 | 10.43 ± 0.08 | 58.00 ± 0.36 |
| No. | Descriptors a | Fb | Ic | Md | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aroma | |||||
| 1 | dairy fat | 0.9167 | 0.4741 | 0.6592 | 0.1931 |
| 2 | metallic/iron | 0.8796 | 0.4519 | 0.6304 | 0.1550 |
| 3 | flour | 0.8056 | 0.3426 | 0.5253 | 0.1391 |
| 4 | dairy-sweet | 0.7593 | 0.3278 | 0.4989 | 0.1250 |
| 5 | grassy/green | 0.7222 | 0.2926 | 0.4597 | 0.5048 |
| 6 | egg-white-like | 0.7315 | 0.2648 | 0.4401 | 0.1658 |
| 7 | cooked-milk-like | 0.6852 | 0.2667 | 0.4275 | 0.1219 |
| 8 | milky-fishy | 0.6204 | 0.2815 | 0.4179 | 0.2214 |
| 9 | beany-fishy | 0.5463 | 0.2537 | 0.3723 | 0.1969 |
| 10 | sweaty | 0.5741 | 0.2204 | 0.3557 | 0.0692 |
| 11 | rancid | 0.3704 | 0.1981 | 0.2709 | 0.0480 |
| 12 | vanillin | 0.3426 | 0.1370 | 0.2167 | 0.0552 |
| 13 | soapy | 0.3704 | 0.1222 | 0.2128 | 0.1127 |
| 14 | goaty | 0.3241 | 0.1370 | 0.2107 | 0.0691 |
| 15 | wet soil | 0.3056 | 0.1444 | 0.2101 | 0.0525 |
| 16 | cheesy | 0.2963 | 0.1167 | 0.1859 | 0.0664 |
| 17 | buttery | 0.2870 | 0.1204 | 0.1859 | 0.1185 |
| 18 | butterscotch | 0.2778 | 0.0944 | 0.1620 | 0.0247 |
| 19 | hay-like | 0.2870 | 0.0778 | 0.1494 | 0.0463 |
| 20 | floral | 0.2407 | 0.0778 | 0.1368 | 0.0509 |
| 21 | cardboard | 0.2407 | 0.0759 | 0.1352 | 0.0434 |
| 22 | moldy | 0.2500 | 0.0704 | 0.1326 | 0.0336 |
| 23 | fusty | 0.2222 | 0.0722 | 0.1267 | 0.0432 |
| 24 | popcorn-like | 0.1759 | 0.0870 | 0.1237 | 0.0552 |
| 25 | fermented | 0.1944 | 0.0778 | 0.1230 | 0.0478 |
| 26 | mushroom-like | 0.2130 | 0.0648 | 0.1175 | 0.0192 |
| 27 | leather | 0.1389 | 0.0852 | 0.1088 | 0.0130 |
| 28 | nutty | 0.2037 | 0.0519 | 0.1028 | 0.0377 |
| 29 | fruity | 0.1481 | 0.0519 | 0.0876 | 0.0501 |
| 30 | malty | 0.1667 | 0.0426 | 0.0843 | 0.0233 |
| Flavor | |||||
| 31 | sweet | 1.0000 | 0.7528 | 0.8676 | 0.1161 |
| 32 | creamy | 0.9028 | 0.4833 | 0.6606 | 0.0417 |
| 33 | umami | 0.6667 | 0.2056 | 0.3702 | 0.0583 |
| 34 | fishy | 0.5694 | 0.2056 | 0.3421 | 0.1173 |
| 35 | boiled milk | 0.4167 | 0.1944 | 0.2846 | 0.0590 |
| 36 | vanillin | 0.2500 | 0.1361 | 0.1845 | 0.0177 |
| 37 | salty | 0.3056 | 0.0972 | 0.1724 | 0.0397 |
| 38 | vegetable oil | 0.2361 | 0.1222 | 0.1699 | 0.1474 |
| 39 | bitter | 0.2361 | 0.1167 | 0.1660 | 0.0174 |
| 40 | metallic/iron | 0.1944 | 0.1083 | 0.1451 | 0.0347 |
| 41 | caramel | 0.2500 | 0.0778 | 0.1394 | 0.1752 |
| 42 | soy milk | 0.1667 | 0.0722 | 0.1097 | 0.1404 |
| 43 | dairy fat | 0.1806 | 0.0639 | 0.1074 | 0.1462 |
| 44 | soapy | 0.0833 | 0.0556 | 0.0680 | 0.1590 |
| Mouthfeel | |||||
| 45 | smoothness | 0.9722 | 0.4778 | 0.6815 | 0.3488 |
| 46 | fattiness | 0.9444 | 0.4194 | 0.6294 | 0.1277 |
| 47 | creaminess | 0.8472 | 0.4528 | 0.6194 | 0.0814 |
| 48 | watery | 0.8750 | 0.4167 | 0.6038 | 0.3472 |
| 49 | thinness | 0.7500 | 0.4319 | 0.5692 | 0.1728 |
| 50 | mouthfulness | 0.5972 | 0.2778 | 0.4522 | 0.0386 |
| 51 | powdery | 0.3750 | 0.1639 | 0.2479 | 0.0386 |
| 52 | astringency | 0.3056 | 0.1278 | 0.1976 | 0.3858 |
| 53 | rough | 0.1111 | 0.0333 | 0.0609 | 0.0104 |
| Sensory Modalities | Descriptors | Definition | References | Intensity f |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aroma | fishy (aroma) | the aromatics associated with fresh fish | dried fillet a | 3 |
| dairy fat | the oily aromatics reminiscent of milk or dairy fat | whipping cream b | 3 | |
| flour | the aromatics associated with wheat flour | wheat flour (pure) | 3 | |
| metallic/iron | the aromatics associated with iron rust | iron rust (IR) a | 0.1 g IR/1 g water = 1.5 | |
| 0.2 g IR/1 g water = 3 | ||||
| 0.4 g IR/1 g water = 4 | ||||
| cooked | the combination of brown flavor notes and aromatics associated with heated milk | milk heated to 85 °C for 45 min c | 50% heated milk = 1.5 | |
| 100% heated milk = 3 | ||||
| dairy-sweet | the sweet aromatics associated with fresh dairy products | vitamin D milk b | 50% vitamin D milk = 1.5 | |
| pure vitamin D milk = 3 | ||||
| grassy/green | the aromatics associated with lawns after it’s been mowed | hexanal | 10 μL/100 mL = 1 | |
| 30 μL/100 mL = 3 | ||||
| 40 μL/100 mL = 4 | ||||
| flavor | sweet | fundamental taste sensation of which sucrose is typical | sucrose d | 1.06% sucrose = 1.5 |
| 2.12% sucrose = 3 | ||||
| umami | fundamental taste sensation of which monosodium glutamate (MSG) is typical | MSG d | 0.05% MSG = 1 | |
| 0.15% MSG = 3 | ||||
| 0.20% MSG = 4 | ||||
| creamy | the flavor reminiscent of milk or dairy fat | milk fat (MF) d | 50% MF = 1.5 | |
| pure MF = 3 | ||||
| fishy (flavor) | the flavor associated with juice of canned fish | canned tuna juice (CTJ) c | 20% CTJ = 2 | |
| 30% CTJ = 3 | ||||
| 40% CTJ = 4 | ||||
| boiled milk | the flavor reminiscent of heated milk | milk heated to 85 °C for 45 min c | 50% heated milk = 1.5 | |
| 100% heated milk = 3 | ||||
| mouthfeel | silky | degree of smoothness felt in the mouth | pure milk e | 3 |
| fattiness | the perceived of creaminess-like in the mouth | pure milk e | 3 | |
| mouthfulness | the feel of coating, long-lasting, thickness | pure milk e | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; Zheng, C.; Xie, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Song, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, R. Flavor Wheel Construction and Sensory Profile Description of Human Milk. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245387
Yu M, Zheng C, Xie Q, Tang Y, Wang Y, Wang B, Song H, Zhou Y, Xu Y, Yang R. Flavor Wheel Construction and Sensory Profile Description of Human Milk. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245387
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Mingguang, Chengdong Zheng, Qinggang Xie, Yuan Tang, Ying Wang, Baosong Wang, Huanlu Song, Yalin Zhou, Yajun Xu, and Rongqiang Yang. 2022. "Flavor Wheel Construction and Sensory Profile Description of Human Milk" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245387
APA StyleYu, M., Zheng, C., Xie, Q., Tang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Song, H., Zhou, Y., Xu, Y., & Yang, R. (2022). Flavor Wheel Construction and Sensory Profile Description of Human Milk. Nutrients, 14(24), 5387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245387







