Association between Fathers’ and Mothers’ Parenting Styles and the Risk of Overweight/Obesity among Adolescents in San José Province, Costa Rica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Parenting Styles Questionnaire
2.4. Anthropometric Assessment
2.5. Sociodemographic Variables
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weihrauch-Blüher, S.; Schwarz, P.; Klusmann, J.-H. Childhood Obesity: Increased Risk for Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer in Adulthood. Metabolism 2019, 92, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.Á.; de Cossío, T.G.; Pedraza, L.S.; Aburto, T.C.; Sánchez, T.G.; Martorell, R. Childhood and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity in Latin America: A Systematic Review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud, Costa Rica. Encuesta Colegial de Vigilancia Nutricional y de Actividad Física [High School Survey of Nutritional Surveillance and Physical Activity]; Ministerio de Salud: San José, Costa Rica, 2020. Available online: https://www.ministeriodesalud.go.cr/index.php/biblioteca-de-archivos-left/documentos-ministerio-de-salud/vigilancia-de-la-salud/normas-protocolos-guias-y-lineamientos/vigilancia-nutricional/censos-y-encuestas/encuesta-colegial-de-vigilancia-nutricional-y-actividad-fisica-2018-vigilancia-de-la-salud/5296-informe-de-resultados-encuesta-colegial-2018/file (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Wong-McClure, R.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Barceló, A.; Lee, K.; Abarca-Gómez, L.; Sanabria-López, L.; Tortós-Guzmán, J. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Central America: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2015, 38, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; French, S. Individual and Environmental Influences on Adolescent Eating Behaviors. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, S40–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, M.H.; Modi, A.C. Psychosocial Factors Related to Obesity in Children and Adolescents. In Handbook of Childhood and Adolescent Obesity; Jelalian, E., Steele, R.G., Eds.; Issues in Clinical Child Psychology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 25–42. ISBN 978-0-387-76922-6. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, S.; Thomas, J. Social Influences on Eating. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuemmeler, B.F.; Yang, C.; Costanzo, P.; Hoyle, R.H.; Siegler, I.C.; Williams, R.B.; Østbye, T. Parenting Styles and Body Mass Index Trajectories from Adolescence to Adulthood. Health Psychol. 2012, 31, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okol, R.L.; Qin, B.; Poti, J.M. Parenting Styles and Body Mass Index: A Systematic Review of Prospective Studies among Children: Parenting Styles and Body Mass Index. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, R.L.; Mobley, A.R. Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, and Their Influence on Child Obesogenic Behaviors and Body Weight. A Review. Appetite 2013, 71, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.M.; Wall, M.; Loth, K.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Parenting Style as a Predictor of Adolescent Weight and Weight-Related Behaviors. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 46, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.M.; Wall, M.; Bauer, K.W.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Parenting Characteristics in the Home Environment and Adolescent Overweight: A Latent Class Analysis. Obesity 2010, 18, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, N.; Steinberg, L. Parenting Style as Context: An Integrative Model. Psychol. Bull. 1993, 113, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Thijs, C.; de Vries, N.K.; Kremers, S.P.J. General Parenting, Childhood Overweight and Obesity-Inducing Behaviors: A Review. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, e12–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera, N.; Power, T.G. Brief Report: Parenting Styles and Obesity in Mexican American Children: A Longitudinal Study. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2010, 35, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shloim, N.; Edelson, L.R.; Martin, N.; Hetherington, M.M. Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, Feeding Practices, and Weight Status in 4–12 Year-Old Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinami, L.; Barnett, T.A.; Séguin, L.; Paradis, G. Parenting Style and Obesity Risk in Children. Prev. Med. 2015, 75, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, K.E.; Lumeng, J.C.; Appugliese, D.P.; Kaciroti, N.; Bradley, R.H. Parenting Styles and Overweight Status in First Grade. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefner-Burmeister, A.; Hinman, N. The Role of General Parenting Style in Child Diet and Obesity Risk. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.K.; Gicevic, S.; Aftosmes-Tobio, A.; Ganter, C.; Simon, C.L.; Newlan, S.; Manganello, J.A. Fathers’ Representation in Observational Studies on Parenting and Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Content Analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, e14–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwairy, M.; Achoui, M.; Abouserie, R.; Farah, A.; Sakhleh, A.A.; Fayad, M.; Khan, H.K. Parenting Styles in Arab Societies: A First Cross-Regional Research Study. J. Cross. Cult. Psychol. 2006, 37, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwairy, M.; Menshar, K.E. Parenting Style, Individuation, and Mental Health of Egyptian Adolescents. J. Adolesc. 2006, 29, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayuri, K.; Divya, V.; Kiran, K. Parenting Styles as Perceived by Parents and Children. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 6, 2319–7064. [Google Scholar]
- Sondhi, R. Parenting Adolescents in India: A Cultural Perspective. In Child and Adolescent Mental Health; Maurer, M.H., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3189-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sorkhabi, N. Applicability of Baumrind’s Parent Typology to Collective Cultures: Analysis of Cultural Explanations of Parent Socialization Effects. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 2005, 29, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febiyanti, A.; Rachmawati, Y. Is Authoritative Parenting the Best Parenting Style? Atlantis Press: Bandung, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Davids, E.L.; Roman, N.V.; Leach, L. Decision Making Styles: A Systematic Review of Their Associations with Parenting. Adolescent. Res. Rev. 2016, 1, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos, Costa Rica. Personas Menores de Edad a la Luz del Censo 2011 [Minors in Light of the Census 2011]; INEC: San José, Costa Rica, 2011. Available online: https://accionsocial.ucr.ac.cr/sites/default/files/documentos/personas_menores_de_edad_a_la_luz_del_censo_2011.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Programa Estado de la Nación. Séptimo Informe Estado de La Educación/Seventh State of Education Report; Programa Estado de la Nación: San José, Costa Rica, 2019; Available online: https://estadonacion.or.cr/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Estado-Educacio%CC%81n-RESUMEN-2019-WEB.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Ryan, T.P. Sample Size Determination and Power, 1st ed.; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-43760-5. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M. Selection of the Samples with Probability Proportional to Size. Sci. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2015, 3, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.C.; Mandleco, B.; Olsen, S.F.; Hart, C.H. The Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire. In Handbook of Family Measurement Techniques; SAGE Publishing: London, UK, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 319–321. [Google Scholar]
- Baumrind, D. Parenting Styles and Adolescent Development. In The Encyclopedia of Adolescence; Garland Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 746–758. [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Castro, V.; Molina, M. La Entrevista Cognitiva: Guía Para Su Aplicación En La Evaluación y Mejoramiento de Instrumentos de Papel y Lápiz [Cognitive Interviewing: A Guide for Its Application for Evaluating and Improving Paper and Pencil Instruments]. Cuadernos Metodológicos No 5 2011. Available online: https://iip.ucr.ac.cr/sites/default/files/contenido/Entrevista%20Cognitiva%20%282011%29.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Reyes-Fernández, B.; Smith-Castro, V. Análisis Psicométrico de las Escalas Utilizadas Para la Recolección de datos del Proyecto: “Influencia del Fumado, la Familia, el Grupo de Pares y los Estereotipos de Género en la Adopción de Hábitos Alimentarios Saludables Durante la Adolescencia” [Psychometric Analysis of the Scales Used to Collect Data from the Study: “Influence of Smoking, Family, Peer Group and Gender Stereotypes in the Adoption of Healthy Eating Habits during Adolescence”] 2018. Available online: https://www.inciensa.sa.cr/investigacion/investigadores/VALIDACION%20ESCALAS%20PSICOMETRICAS.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Series in Psychology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-07-047849-7. [Google Scholar]
- Olivari, M.G.; Tagliabue, S.; Confalonieri, E. Parenting Style and Dimensions Questionnaire: A Review of Reliability and Validity. Marriage Fam. Rev. 2013, 49, 465–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuar, L.R.; Chien, K.; Lentine, J.; Cooley, V.; Gerber, L.M.; Ward, M.J.; Keefer, L. Does Parenting Style Affect Adolescent IBD Transition Readiness and Self-Efficacy Scores? Children 2021, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccì, G.; O’Leary, K.D.; Olivari, M.G.; Bonanomi, A.; Confalonieri, E. Adolescent Dating Violence Perpetration, Emotion Dysregulation, and Parenting Styles. J. Fam. Psychol. 2019, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, C.; Gonsalves, K.; Ramesh, N. Parenting Styles and Mental Health of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in South India. J. Mental Health Hum. Behav. 2022, 27, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, N.V.; Davids, E.L.; Moyo, A.; Schilder, L.; Lacante, M.; Lens, W. Parenting Styles and Psychological Needs Influences on Adolescent Life Goals and Aspirations in a South African Setting. J. Psychol. Afr. 2015, 25, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedy, V.R. (Ed.) . Handbook of Anthropometry: Physical Measures of Human Form in Health and Disease; Springer: New York, NY. USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4419-1787-4. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age; Methods and Development; de Onis, M., Ed.; WHO Child Growth Standards; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; ISBN 978-92-4-154693-5.
- Madrigal-Pana, J.; Gómez-Barrantes, M. Propuesta de Un Índice de Nivel Socioeconómico Para Los Estudiantes y Colegios de Secundaria de Costa Rica; Cuadernos de Trabajo de PROCESOS 2021; Centro Centroamericano de Población, Universidad de Costa Rica: San José, Costa Rica, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew, D.J.; Steele, F.; Steele, F.; Moustaki, I. Analysis of Multivariate Social Science Data, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-429-14567-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Hill, J. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchical Models, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-86706-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J.F.; Richter, A.W. Probing Three-Way Interactions in Moderated Multiple Regression: Development and Application of a Slope Difference Test. J. Appl. Psychol. 2006, 91, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, R.; Brame, R.; Mazerolle, P.; Piquero, A. Using the Correct Statistical Test for the Equality of Regression Coefficients. Criminology 1998, 36, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, M.; Nicholson, J.M.; Hardy, P.; Smith, K. Preschooler Obesity and Parenting Styles of Mothers and Fathers: Australian National Population Study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e1520–e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, P.; Gallardo-Cooper, M.; Delgado-Romero, E.A.; Zapata, A.L. Culturally Responsive Counseling with Latinas/Os, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-55620-241-4. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, H.; Kärtner, J. The Cultural Solution of Universal Developmental Tasks. In Advances in Culture and Psychology; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2013; Volume 3, pp. 63–117. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, G.L.; Cupito, A.M.; Mendez, J.L.; Prandoni, J.; Huq, N.; Westerberg, D. Familism through a Developmental Lens. J. Lat. Psychol. 2014, 2, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, K.M.; Caughy, M.O.; Schuster, M.A.; Bogart, L.M.; Dittus, P.J.; Franzini, L. Cultural Orientations, Parental Beliefs and Practices, and Latino Adolescents’ Autonomy and Independence. J. Youth Adolesc. 2014, 43, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Michel, S.T.; Unger, J.B.; Spruijt-Metz, D. Dietary Correlates of Emotional Eating in Adolescence. Appetite 2007, 49, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosabal-Coto, M. Creencias y prácticas de crianza: El estudio del parentaje en el contexto costarricense. Rev. Costarric. Psicol. 2012, 31, 65–100. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, A.K.; Russell, S.T.; Crockett, L.J. Parenting Styles and Youth Well-Being Across Immigrant Generations. J. Fam. Issues 2008, 29, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.; Renk, K. Differential Parenting Between Mothers and Fathers: Implications for Late Adolescents. J. Fam. Issues 2008, 29, 806–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosley, C.A.; Montemayor, R. Fathers and Adolescents. In The Role of the Father in Child Development; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 162–178. [Google Scholar]
- Halgunseth, L.C.; Ispa, J.M.; Rudy, D. Parental Control in Latino Families: An Integrated Review of the Literature. Child. Dev. 2006, 77, 1282–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-B.; Delvecchio, E.; Miconi, D.; Salcuni, S.; Di Riso, D. Parental Attachment among Chinese, Italian, and Costa Rican Adolescents: A Cross-Cultural Study. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2014, 71, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Welk, G.; Saint-Maurice, P.F.; Ihmels, M. Parenting Styles and Home Obesogenic Environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccia, C.; Darling, C.A.; Rehm, M.; Cui, M.; Sathe, S.K. Adolescent Health, Stress and Life Satisfaction: The Paradox of Indulgent Parenting: Indulgent Parenting and Life Satisfaction. Stress Health 2012, 28, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.J.; See, H.M.; Tarkow, A.K.H.; Cabrera, N.; McFadden, K.E.; Shannon, J.D. Conducting Studies with Fathers: Challenges and Opportunities. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2007, 11, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.K.; Charles, J.N.; Khandpur, N.; Nelson, T.J. Fathers’ Perceived Reasons for Their Underrepresentation in Child Health Research and Strategies to Increase Their Involvement. Matern. Child Health J. 2017, 21, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, R.M.; Jonyniene, J. Psychometric Properties of the Lithuanian Version of the Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire (PSDQ): Pilot Study. Fam. J. 2012, 20, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

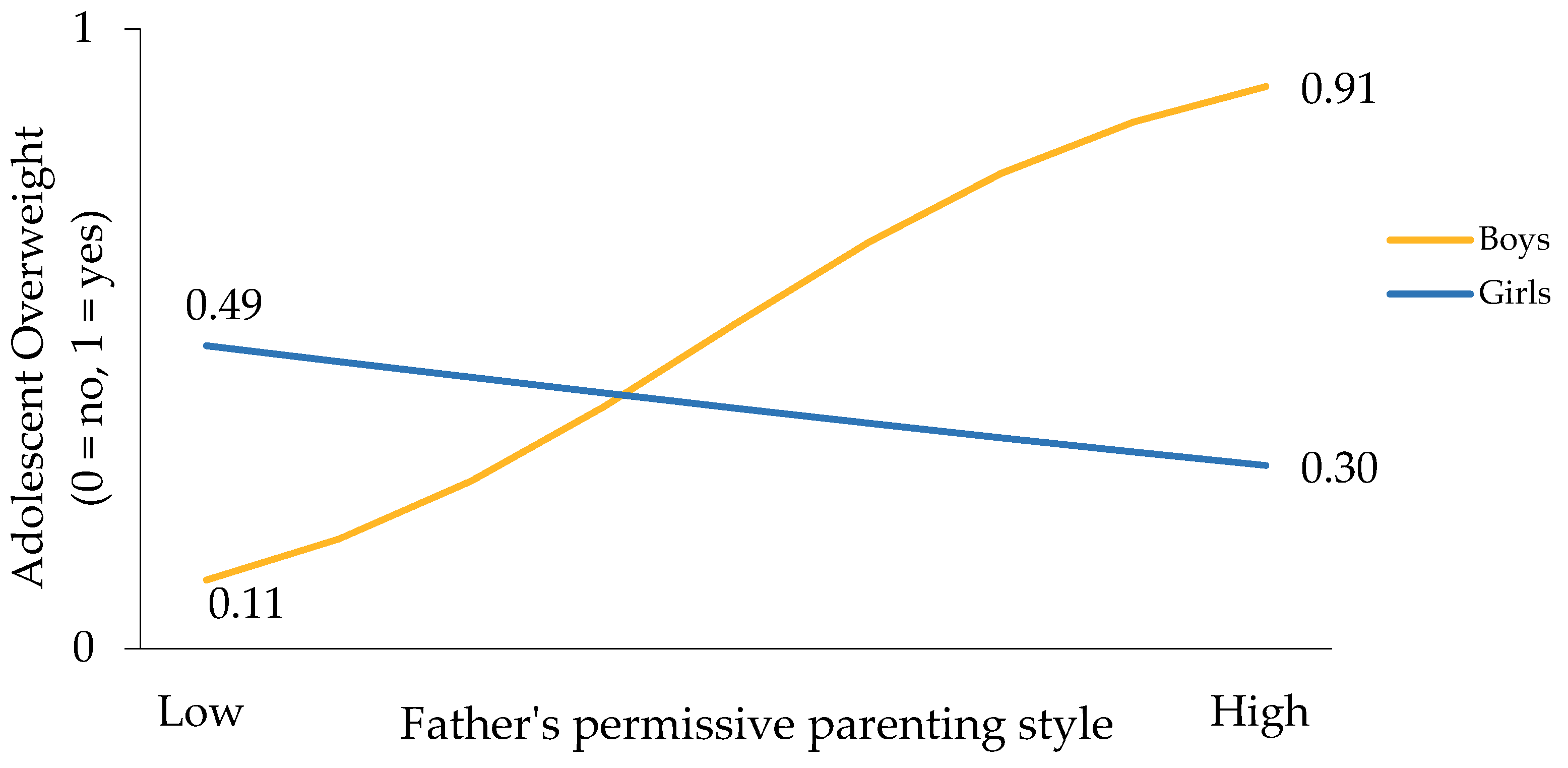
| Study Population Characteristics | Overall (n = 695) | Sex | p-Value | Area of Residence | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girls n = 451 (65%) | Boys n = 244 (35%) | Urban n = 349 (50.2%) | Rural n = 346 (49.8%) | |||||||||
| Age (years) | 14.9 | (1.7) | 14.9 | (1.7) | 14.9 | (1.6) | 0.874 | 14.9 | (1.6) | 15.0 | (1.7) | 0.314 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.3 | (4.3) | 22.4 | (4.7) | 21.9 | (4.0) | 0.167 | 22.2 | (4.3) | 22.3 | (4.6) | 0.929 |
| Healthy weight (%) | 67.5 | - | 68.1 | - | 66.4 | - | 0.436 | 69.1 | - | 65.9 | - | 0.659 |
| Overweight/obese (%) 3 | 32.5 | - | 31.9 | - | 33.6 | - | 0.532 | 30.9 | - | 32.5 | - | 0.079 |
| Parenting Style | Fathers (n = 695) | SD | Mothers (n = 695) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy weight | ||||
| Authoritative | 3.07 | (1.06) | 3.42 | (0.97) |
| Permissive | 2.18 | (0.76) | 2.36 | (0.76) |
| Authoritarian | 1.88 | (0.61) | 2.09 | (0.64) |
| Overweight | ||||
| Authoritative | 3.08 | (1.06) | 3.47 | (0.94) |
| Permissive | 2.20 | (0.78) | 2.39 | (0.79) |
| Authoritarian | 1.87 | (0.56) | 2.09 | (0.66) |
| Total sample | ||||
| Authoritative | 3.07 a | (1.06) | 3.43 a | (0.96) |
| Permissive | 2.19 b | (0.77) | 2.36 b | (0.77) |
| Authoritarian | 1.88 c | (0.59) | 2.08 c | (0.65) |
| Variable | B2 | Standard Error | Wald Chi-Square Test | p-Value 3 | Exp(B)4 | 95% CI for Exp(B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.088 | 0.052 | 2.799 | 0.094 | 0.916 | 0.827 | 1.015 |
| Sex (0 = Boys) | −0.104 | 0.186 | 0.312 | 0.576 | 0.901 | 0.626 | 1.298 |
| Area (0 = Urban) | 0.242 | 0.177 | 1.869 | 0.172 | 1.274 | 0.900 | 1.802 |
| SES (0 = Low) | 0.079 | 0.242 | 0.108 | 0.742 | 1.083 | 0.674 | 1.739 |
| Authoritative Fathers | −0.254 | 0.336 | 0.571 | 0.445 | 0.776 | 0.401 | 1.499 |
| Authoritarian Fathers | −0.159 | 0.374 | 0.181 | 0.671 | 0.853 | 0.410 | 1.775 |
| Permissive Fathers | 0.968 | 0.438 | 4.870 | 0.027 | 2.632 | 1.114 | 6.215 |
| Authoritative Mothers | −0.239 | 0.385 | 0.384 | 0.536 | 0.788 | 0.37 | 1.676 |
| Authoritarian Mothers | −0.039 | 0.376 | 0.011 | 0.917 | 0.962 | 0.461 | 2.008 |
| Permissive Mothers | −0.398 | 0.417 | 0.914 | 0.339 | 0.672 | 0.297 | 1.519 |
| Authoritative Fathers x Sex 5 | 0.762 | 0.419 | 3.306 | 0.069 | 2.143 | 0.942 | 4.875 |
| Authoritarian Fathers x Sex | 0.007 | 0.483 | 0.001 | 0.988 | 1.007 | 0.390 | 2.597 |
| Permissive Fathers x Sex | −1.367 | 0.544 | 6.313 | 0.012 | 0.255 | 0.088 | 0.740 |
| Authoritative Mothers x Sex | −0.013 | 0.466 | 0.001 | 0.978 | 0.988 | 0.396 | 2.463 |
| Authoritarian Mothers x Sex | 0.542 | 0.486 | 1.244 | 0.265 | 1.719 | 0.663 | 4.456 |
| Permissive Mothers x Sex | 0.343 | 0.523 | 0.431 | 0.512 | 1.410 | 0.506 | 3.930 |
| Authoritative Fathers x Area | 0.203 | 0.555 | 0.134 | 0.715 | 1.225 | 0.413 | 3.634 |
| Authoritarian Fathers x Area | 1.403 | 0.660 | 4.528 | 0.033 | 4.069 | 1.117 | 14.821 |
| Permissive Fathers x Area | −1.677 | 0.685 | 5.988 | 0.014 | 0.187 | 0.049 | 0.716 |
| Authoritative Mothers x Area | 0.544 | 0.597 | 0.829 | 0.362 | 1.722 | 0.535 | 5.547 |
| Authoritarian Mothers x Area | −0.839 | 0.619 | 1.837 | 0.175 | 0.432 | 0.128 | 1.454 |
| Permissive Mothers x Area | 1.131 | 0.618 | 3.342 | 0.068 | 3.098 | 0.922 | 10.41 |
| Authoritative Fathers x Sex x Area | −0.601 | 0.657 | 0.835 | 0.361 | 0.548 | 0.151 | 1.989 |
| Authoritarian Fathers x Sex x Area | −1.007 | 0.830 | 1.472 | 0.225 | 0.365 | 0.072 | 1.859 |
| Permissive Fathers x Sex x Area | 1.845 | 0.816 | 5.113 | 0.024 | 6.328 | 1.278 | 31.332 |
| Authoritative Mothers x Sex x Area | −0.525 | 0.706 | 0.553 | 0.457 | 0.592 | 0.148 | 2.361 |
| Authoritarian Mothers x Sex x Area | −0.213 | 0.793 | 0.072 | 0.788 | 0.808 | 0.171 | 3.822 |
| Permissive Mothers x Sex x Area | −0.778 | 0.756 | 1.057 | 0.304 | 0.460 | 0.104 | 2.023 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monge-Rojas, R.; Smith-Castro, V.; O’Connor, T.M.; Vargas-Quesada, R.; Reyes-Fernández, B. Association between Fathers’ and Mothers’ Parenting Styles and the Risk of Overweight/Obesity among Adolescents in San José Province, Costa Rica. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245328
Monge-Rojas R, Smith-Castro V, O’Connor TM, Vargas-Quesada R, Reyes-Fernández B. Association between Fathers’ and Mothers’ Parenting Styles and the Risk of Overweight/Obesity among Adolescents in San José Province, Costa Rica. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245328
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonge-Rojas, Rafael, Vanessa Smith-Castro, Teresia M. O’Connor, Rulamán Vargas-Quesada, and Benjamín Reyes-Fernández. 2022. "Association between Fathers’ and Mothers’ Parenting Styles and the Risk of Overweight/Obesity among Adolescents in San José Province, Costa Rica" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245328
APA StyleMonge-Rojas, R., Smith-Castro, V., O’Connor, T. M., Vargas-Quesada, R., & Reyes-Fernández, B. (2022). Association between Fathers’ and Mothers’ Parenting Styles and the Risk of Overweight/Obesity among Adolescents in San José Province, Costa Rica. Nutrients, 14(24), 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245328






