Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation via Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in a Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material Preparation and Extraction
2.2. Animal Study
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT–qPCR)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
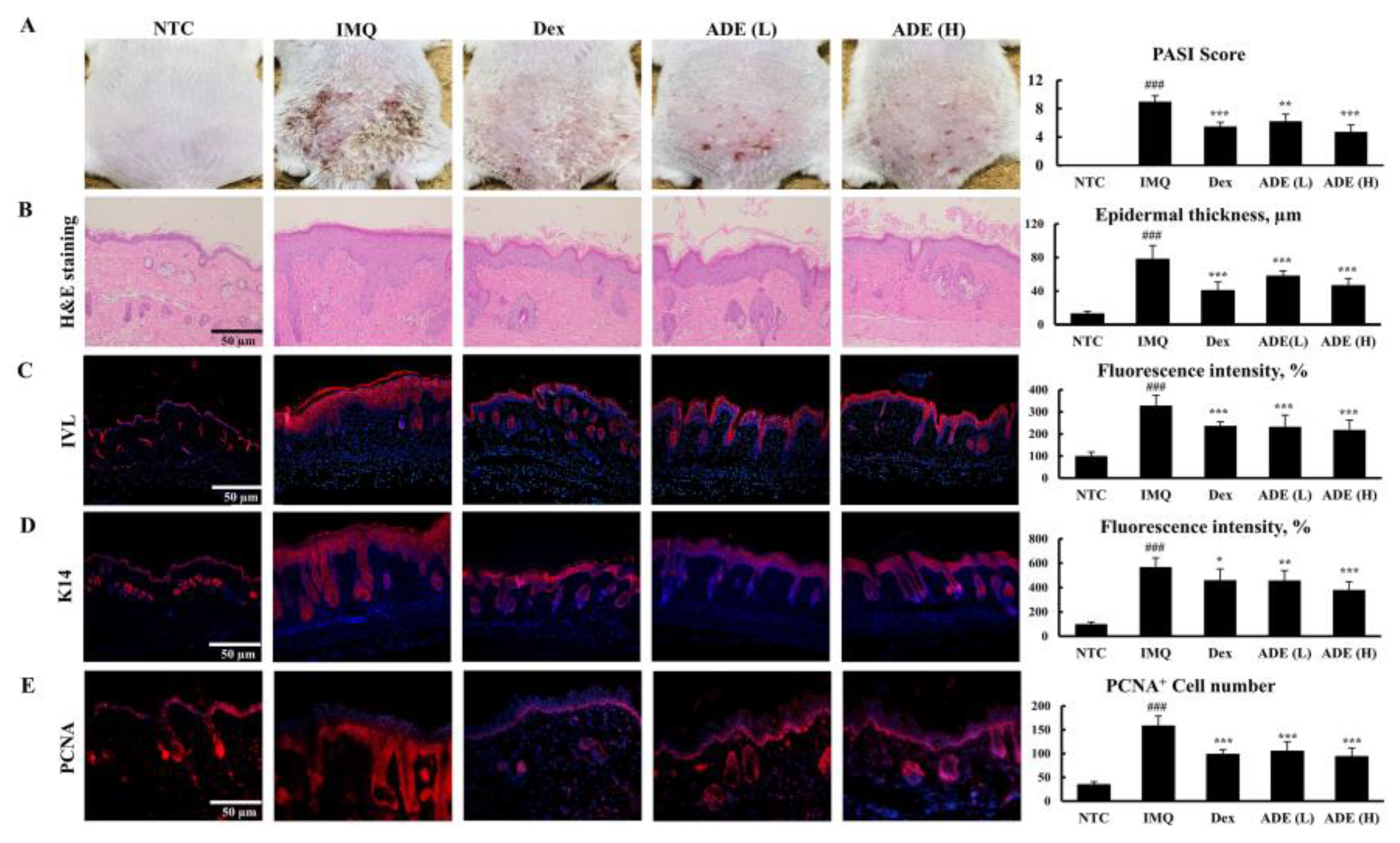
3.1. Topical Application of ADE Reduced the Development of Psoriatic Phenotypes and Improved Skin Conditions
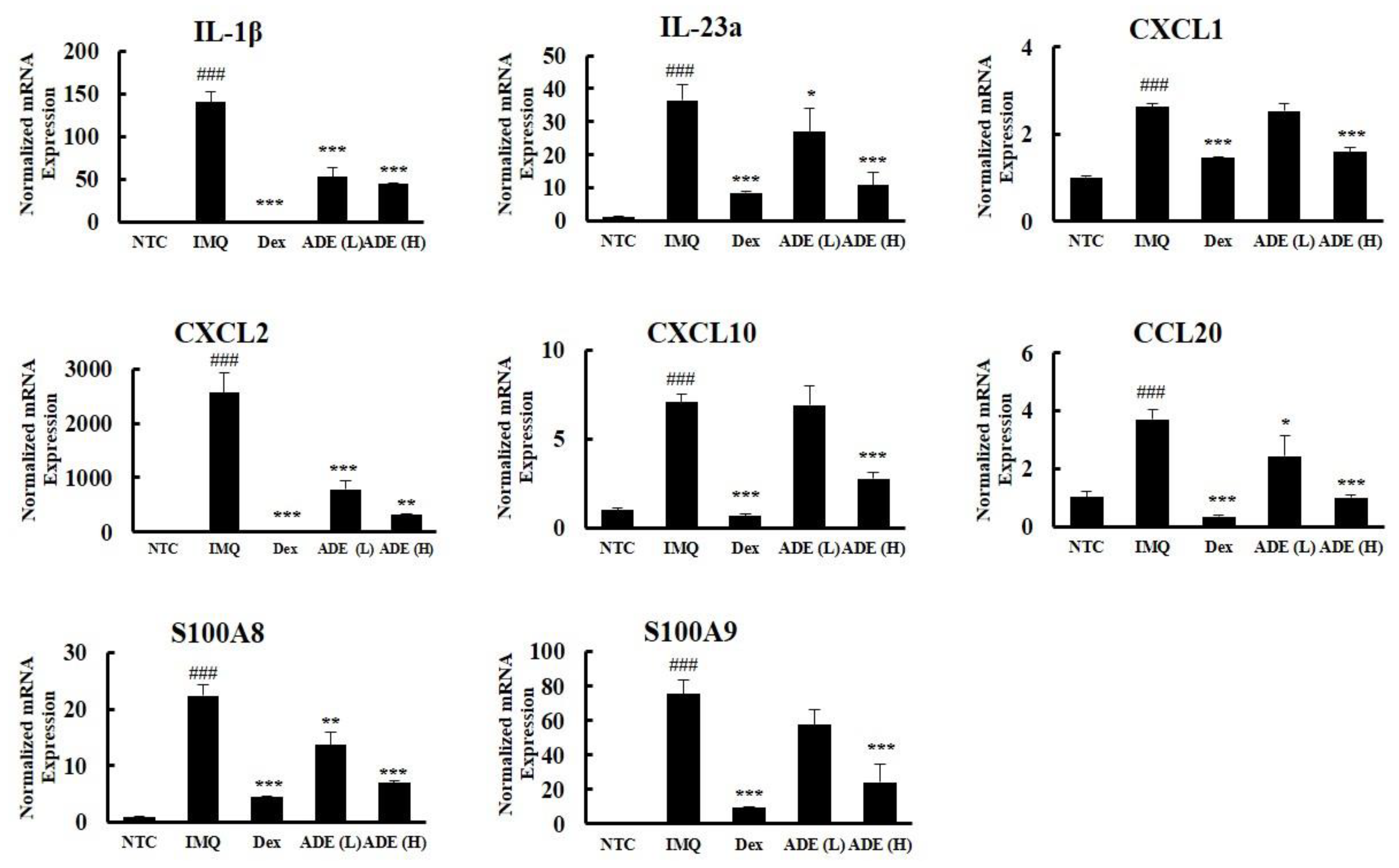
3.2. ADE Treatment Attenuates the Infiltration of Immune Cells into Psoriatic Lesions by Suppressing the Secretion of Psoriatic Markers in Mouse Skin
3.3. ADE Treatment Inhibits the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in HaCaT Cells
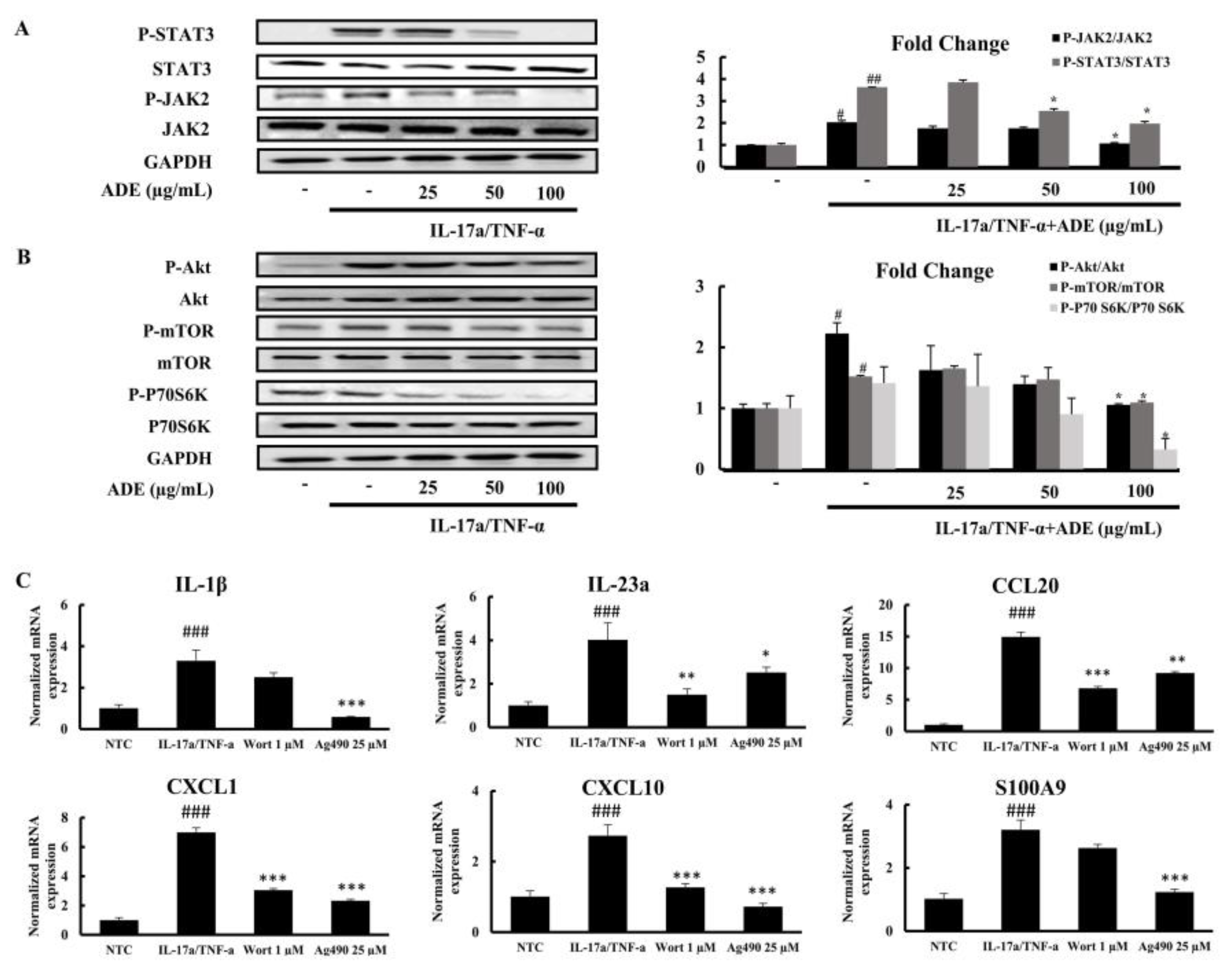
3.4. ADE Treatment Modulates JAK2/STAT3 and Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koo, J.; Marangell, L.B.; Nakamura, M.; Armstrong, A.; Jeon, C.; Bhutani, T.; Wu, J.J. Depression and suicidality in psoriasis: Review of the literature including the cytokine theory of depression. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.T.; Nijsten, T.; Elder, J.T. Recent Highlights in Psoriasis Research. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzorz-Stark, N.; Lauffer, F.; Krause, L.; Thomas, J.; Atenhan, A.; Franz, R.; Roenneberg, S.; Boehner, A.; Jargosch, M.; Batra, R.; et al. Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonists stimulate plasmacytoid dendritic cells to initiate TH17-deviated acute contact dermatitis in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nograles, K.E.; Zaba, L.C.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Cardinale, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Pierson, K.C.; White, T.R.; et al. Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliwag, J.; Barnes, D.H.; Johnston, A. Cytokines in psoriasis. Cytokine 2015, 73, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.T.; Elson, C.O.; Fouser, L.A.; Kolls, J.K. The Th17 pathway and inflammatory diseases of the intestines, lungs, and skin. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, A.; Conrad, C. Psoriasis: Classical vs. Paradoxical. The Yin-Yang of TNF and Type I Interferon. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greb, J.E.; Goldminz, A.M.; Elder, J.T.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Gladman, D.D.; Wu, J.J.; Mehta, N.N.; Finlay, A.Y.; Gottlieb, A.B. Psoriasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Nograles, K.E.; Krueger, J.G. Contrasting pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis–part I: Clinical and pathologic concepts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, K.; Holstein, J.; Laurence, A.; Ghoreschi, K. Targeting JAK/STAT signalling in inflammatory skin diseases with small molecule inhibitors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calautti, E.; Avalle, L.; Poli, V. Psoriasis: A STAT3-Centric View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, M.; Scarponi, C.; Mercurio, L.; Facchiano, F.; Pallotta, S.; Madonna, S.; Girolomoni, G.; Albanesi, C. Selective Immunomodulation of Inflammatory Pathways in Keratinocytes by the Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Implications for the Employment of JAK-Targeting Drugs in Psoriasis. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7897263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, C.; Shirsath, N.; Lang, V.; Diehl, S.; Kaufmann, R.; Weigert, A.; Han, Y.Y.; Ringel, C.; Wolf, P. Blocking mTOR Signalling with Rapamycin Ameliorates Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis in Mice. Acta. Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, A.; Perino, A.; Dapavo, P.; Soro, E.; Okkenhaug, K.; Hirsch, E.; Ji, H. Blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase PI3Kdelta or PI3Kgamma reduces IL-17 and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4612–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirnia, M.; Khodaeiani, E.; Fouladi, R.F.; Hashemi, A. Topical steroids versus PUVA therapy in moderate plaque psoriasis: A clinical trial along with cost analysis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2012, 23, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Brembilla, N.C. Pathogenesis-oriented therapy of psoriasis using biologics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Provenzano, E.; Menichini, F.; Tundis, R. Anti-Psoriasis Agents from Natural Plant Sources. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1250–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Auh, J.; Choe, E. In vitro α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities and antioxidants of Samnamul (Aruncus dioicus) during rehydration and cooking. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Yun, J.A.; Jeong, Y.K.; Baek, H.J. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of samnamul (shoot of Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Hara) in mice fed a high-fat/high-sucrose diet. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kim, H.-Y. DNA Damage Protection and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Different Solvent Fractions from Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2014, 27, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-S.; Lee, J.-W. Attenuation of Brain Injury by Water Extract of Goat’s-beard (Aruncus dioicus) and Its Ethyl Acetate Fraction in a Rat Model of Ischemia-Reperfusion. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011, 16, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Han, L. Quercetin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via the NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S.; Gisondi, P. The interplay between keratinocytes and immune cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahil, S.K.; Capon, F.; Barker, J.N. Update on psoriasis immunopathogenesis and targeted immunotherapy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Saraceno, R.; Novelli, L.; Fida, M.; Caso, F.; Scarpa, R.; Costa, L.; Perricone, R.; Romanelli, M.; Chimenti, S.; et al. Small molecules and antibodies for the treatment of psoriasis: A patent review (2010–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdowicz, L.B.; Bostwick, J.M. Psychiatric adverse effects of pediatric corticosteroid use. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 817–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Kishimoto, M.; Sugai, J.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Risk Factors for the Development of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. The role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, L.; Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S. Recent Updates on the Involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Molecular Cascade in the Pathogenesis of Hyperproliferative Skin Disorders. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 665647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, P.; Saini, N. PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation and autophagy inhibition plays a key role in increased cholesterol during IL-17A mediated inflammatory response in psoriasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.; Pan, W.; Tao, X. The PI3K/Akt Pathway: Emerging Roles in Skin Homeostasis and a Group of Non-Malignant Skin Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamcheu, J.C.; Adhami, V.M.; Esnault, S.; Sechi, M.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Satyshur, K.A.; Syed, D.N.; Dodwad, S.M.; Chaves-Rodriquez, M.I.; Longley, B.J.; et al. Dual Inhibition of PI3K/Akt and mTOR by the Dietary Antioxidant, Delphinidin, Ameliorates Psoriatic Features In Vitro and in an Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Disease in Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aittomaki, S.; Pesu, M. Therapeutic targeting of the Jak/STAT pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, M.; Lu, C.; Du, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, D. Taxifolin attenuates IMQ-induced murine psoriasis-like dermatitis by regulating T helper cell responses via Notch1 and JAK2/STAT3 signal pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, U.; Accordi, B.; Martini, V.; Oliviero, F.; Facco, M.; Cabrelle, A.; Piva, L.; Molena, B.; Caso, F.; Costa, L.; et al. JAK/STAT/PKCdelta molecular pathways in synovial fluid T lymphocytes reflect the in vivo T helper-17 expansion in psoriatic arthritis. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.; Puig, L.; Torres, T. JAK Inhibitors for Treatment of Psoriasis: Focus on Selective TYK2 Inhibitors. Drugs 2020, 80, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, J.L.; Krueger, J.G.; Bowcock, A.M. The immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, R.; Savini, I.; Avigliano, L.; Madonna, S.; Cavani, A.; Albanesi, C.; Mauriello, A.; Melino, G.; Terrinoni, A. Luteolin-7-glucoside inhibits IL-22/STAT3 pathway, reducing proliferation, acanthosis, and inflammation in keratinocytes and in mouse psoriatic model. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Di, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, D.; Li, P. Paeoniflorin inhibits imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice by regulating Th17 cell response and cytokine secretion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 772, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenders, M.I.; Marijnissen, R.J.; Devesa, I.; Lubberts, E.; Joosten, L.A.; Roth, J.; van Lent, P.L.; van de Loo, F.A.; van den Berg, W.B. Tumor necrosis factor-interleukin-17 interplay induces S100A8, interleukin-1beta, and matrix metalloproteinases, and drives irreversible cartilage destruction in murine arthritis: Rationale for combination treatment during arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flutter, B.; Nestle, F.O. TLRs to cytokines: Mechanistic insights from the imiquimod mouse model of psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 3138–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| hIL-1β | 5′-TGAGCTCGCCAGTGAAATGA-3′ | 5′-AGATTCGTAGCTGGATGCCG-3′ |
| hIL-23A | 5′ACAGAAGCTCTGCACACTGG-3′ | 5′-GTTGTCCCTGAGTCCTTGGG-3′ |
| hCXCL1 | 5′-ATTCACCCCAAGAACATCCA-3′ | 5′-TGGATTTGTCACTGTTCAGCA-3′ |
| hCXCL2 | 5′-GCAGGGAATTCACCTCAAGA-3′ | 5′-TGGATTTGCCATTTTTCAGC-3′ |
| hCXCL10 | 5′-TGCCATTCTGATTTGCTGCC-3′ | 5′-ATGCAGGTACAGCGTACAGTT-3′ |
| hCCL20 | 5′-TGTCAGTGCTGCTACTCCAC-3′ | 5′-CCGTGTGAAGCCCACAATAA-3′ |
| hS100A8 | 5′-AAGGGGAATTTCCATGCCGT-3″ | 5′-AGGACACTCGGTCTCTAGCA-3′ |
| hS100A9 | 5′-CATGCTGATGGCGAGGCTAA-3′ | 5′-GCCTCGTGCATCTTCTCGTG-3′ |
| hGAPDH | 5′-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3′ | 5′-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3′ |
| mIL-1β | 5′-CAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTCA-3′ | 5′-AGGCCACAGGTATTTTGTCG-3′ |
| mIL-23A | 5′-CCATGGAGCAACTTCACACC-3′ | 5′-CTGGAGGCTTCGAAGGATCT-3′ |
| mTNF-α | 5′-TCTTCTCGAACCCCGAGTGA-3′ | 5′-CCTCTGATGGCACCACCAG-3′ |
| mCXCL1 | 5′-GTCAGTGCCTGCAGACCAT-3′ | 5′-AACCAAGGGAGCTTCAGGG-3′ |
| mCXCL2 | 5′-ACATCCAGAGCTTGAGTGTG-3′ | 5′-GCCTTGCCTTTGTTCAGTATCT-3′ |
| mCXCL10 | 5′-TGAATCCGGAATCTAAGACCATCAA-3′ | 5′-AGGACTAGCCATCCACTGGGTAAAG-3′ |
| mCCL20 | 5′-CGACTGTTGCCTCTCGTACA-3′ | 5′-AGCCCTTTTCACCCAGTTCT-3′ |
| mS100A8 | 5′-ATGCCGTCTGAACTGGAGAA-3′ | 5′-TAGAGGGCATGGTGATTTCC-3′ |
| mS100A9 | 5′-CAGCATAACCACCATCATCG-3′ | 5′-AAGGTTGCCAACTGTGCTTC-3′ |
| mGAPDH | 5′-CATGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTA-3′ | 5′-ACTTGGCAGGTTTCTCCAGG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorjsembe, B.; Joo, H.; Nho, C.; Ham, J.; Kim, J.-C. Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation via Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in a Murine Model. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235094
Dorjsembe B, Joo H, Nho C, Ham J, Kim J-C. Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation via Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in a Murine Model. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235094
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorjsembe, Banzragch, Haneul Joo, Chuwon Nho, Jungyeob Ham, and Jin-Chul Kim. 2022. "Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation via Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in a Murine Model" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235094
APA StyleDorjsembe, B., Joo, H., Nho, C., Ham, J., & Kim, J.-C. (2022). Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation via Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in a Murine Model. Nutrients, 14(23), 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235094








