Milk Exosomal miR-27b Worsen Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated Colorectal Cancer Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Validation miRNA
2.2. Milk Extract Preparation and Metabolic Profile
2.3. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Treatments
2.4. Validation of miRNA Overexpression in Transfected Cells
2.5. Viability Assay
2.6. Apoptosis Detection
2.7. ROS Evaluation
2.8. Mitochondria Damage Assessment
2.9. ER-Stress Detection
2.10. Extracellular Calcium Levels
2.11. ER-Stress Related mRNA Expression
2.12. Cell Lysis and Immunoblotting Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
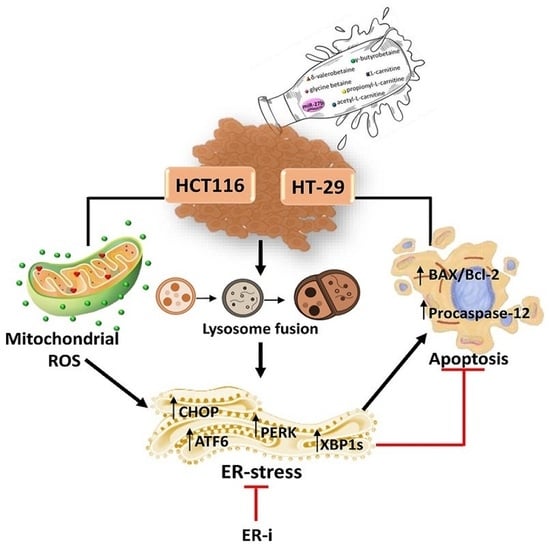
3. Results
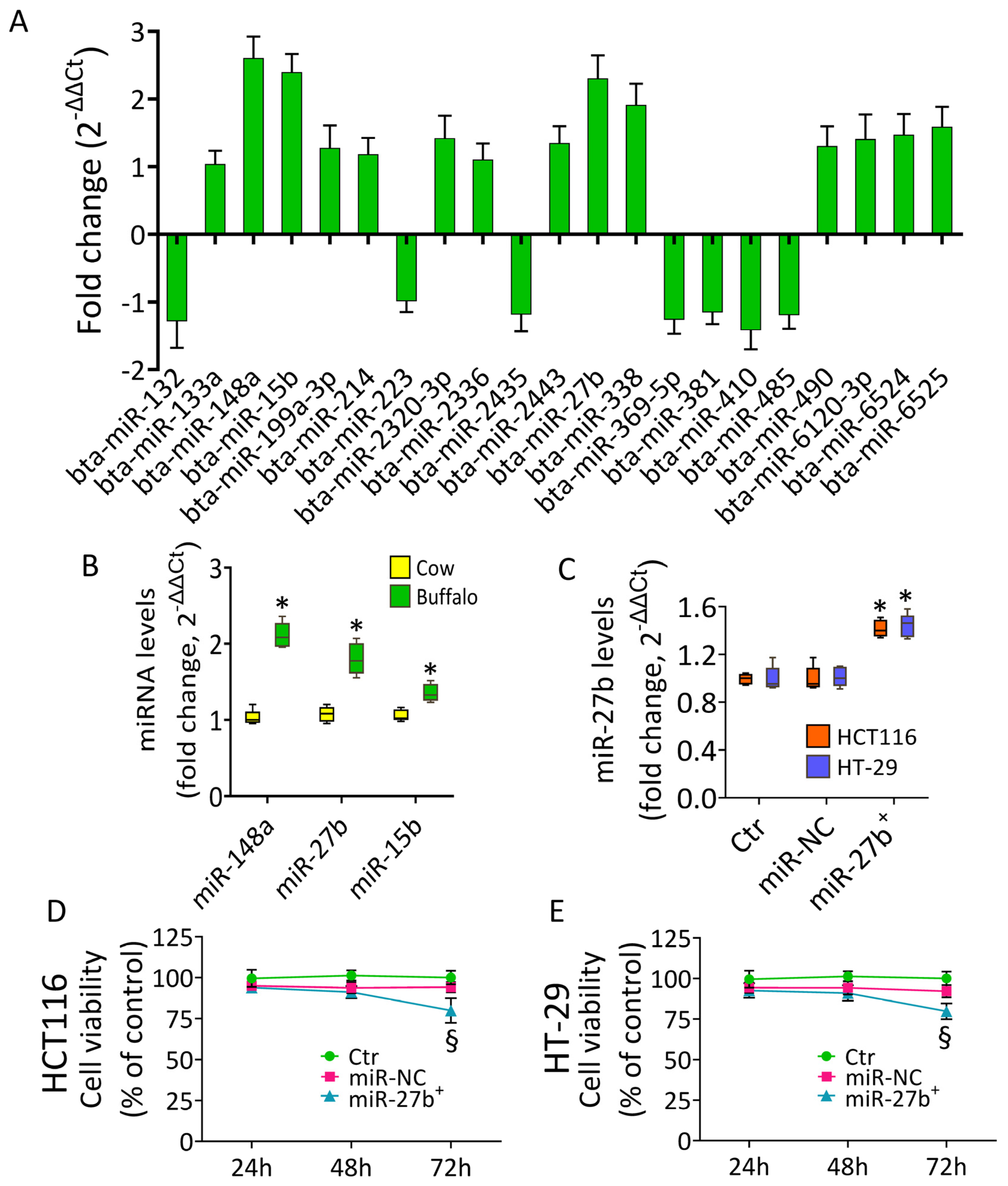
3.1. Buffalo Milk miRNA Content
3.2. Cytotoxic Effects of miR-27b
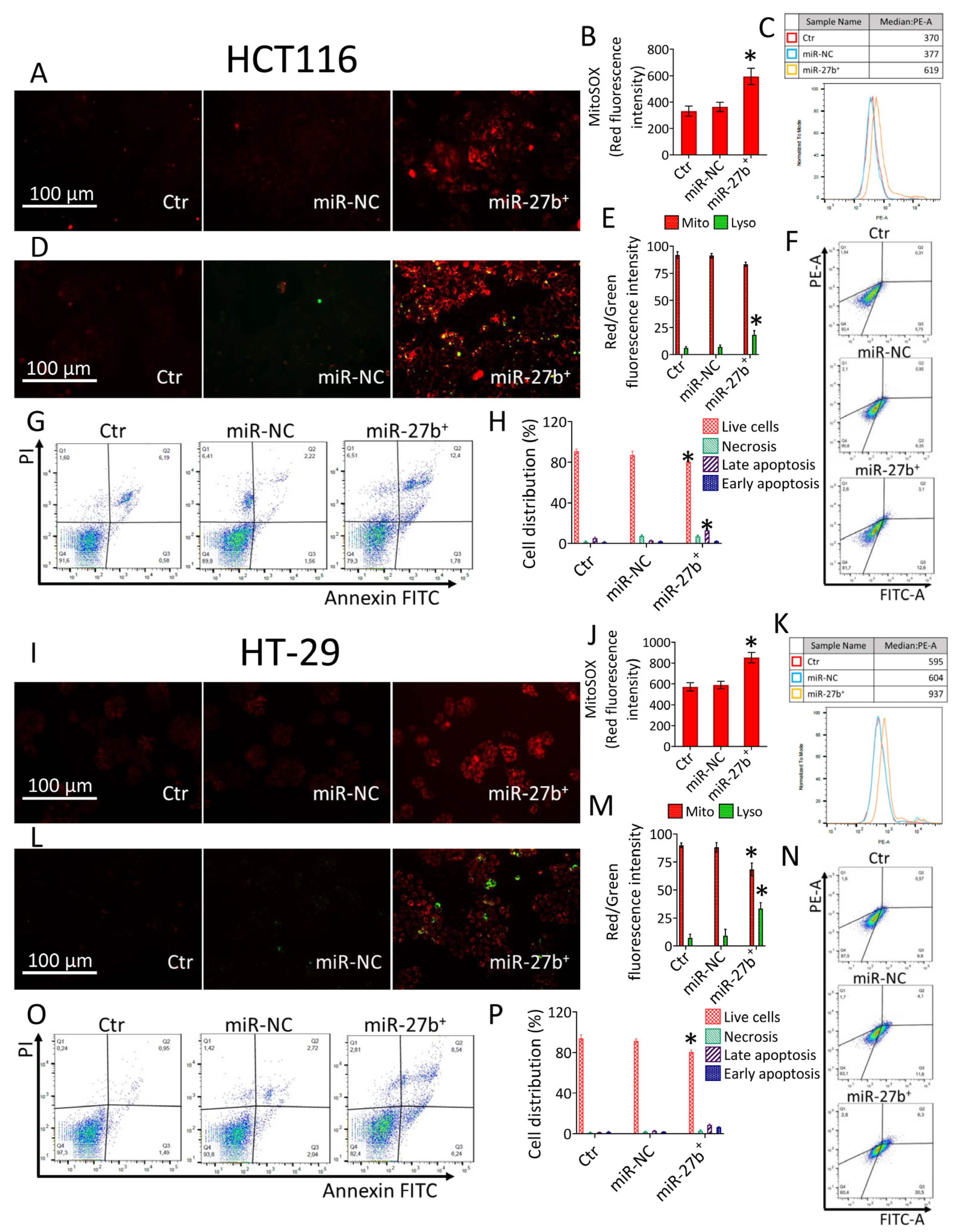
3.3. MiR-27b Promotes Mitochondrial Stress and Apoptotic Death
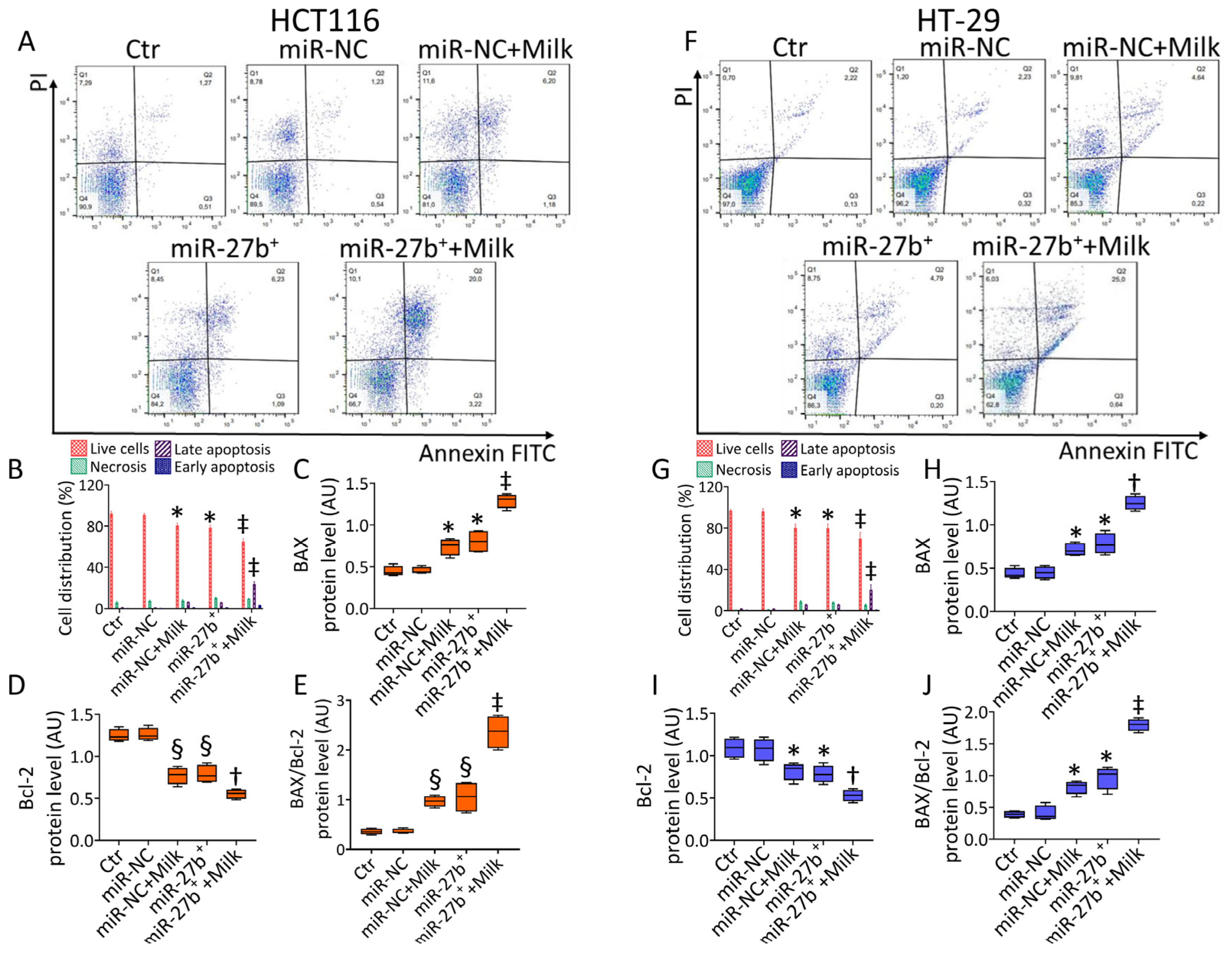
3.4. Milk Increases the Apoptotic Activity in miR-27b+ Cells
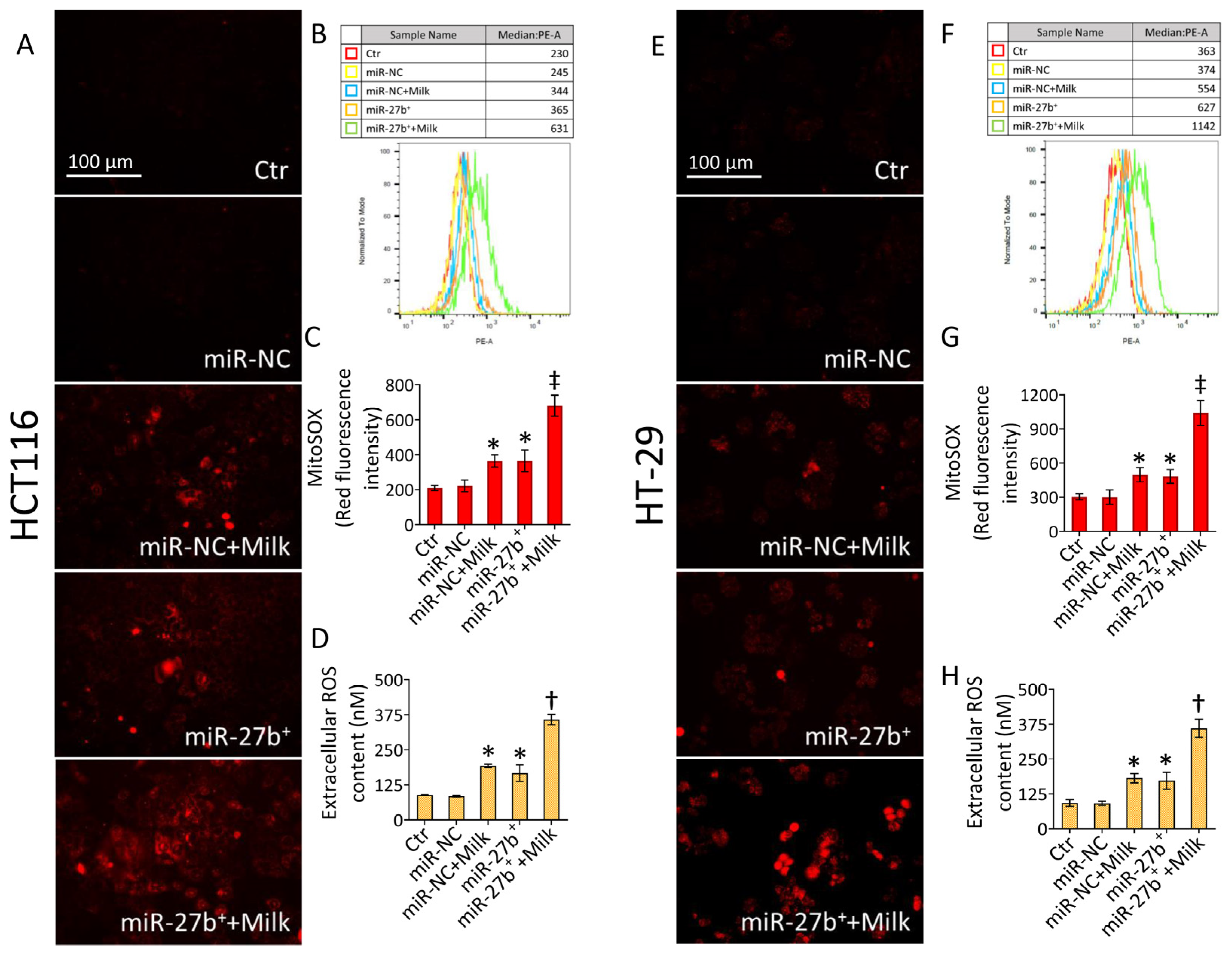
3.5. Milk Exacerbates Mitochondrial ROS Accumulation in miR-27b+ Cells
3.6. Lysosome Accumulation
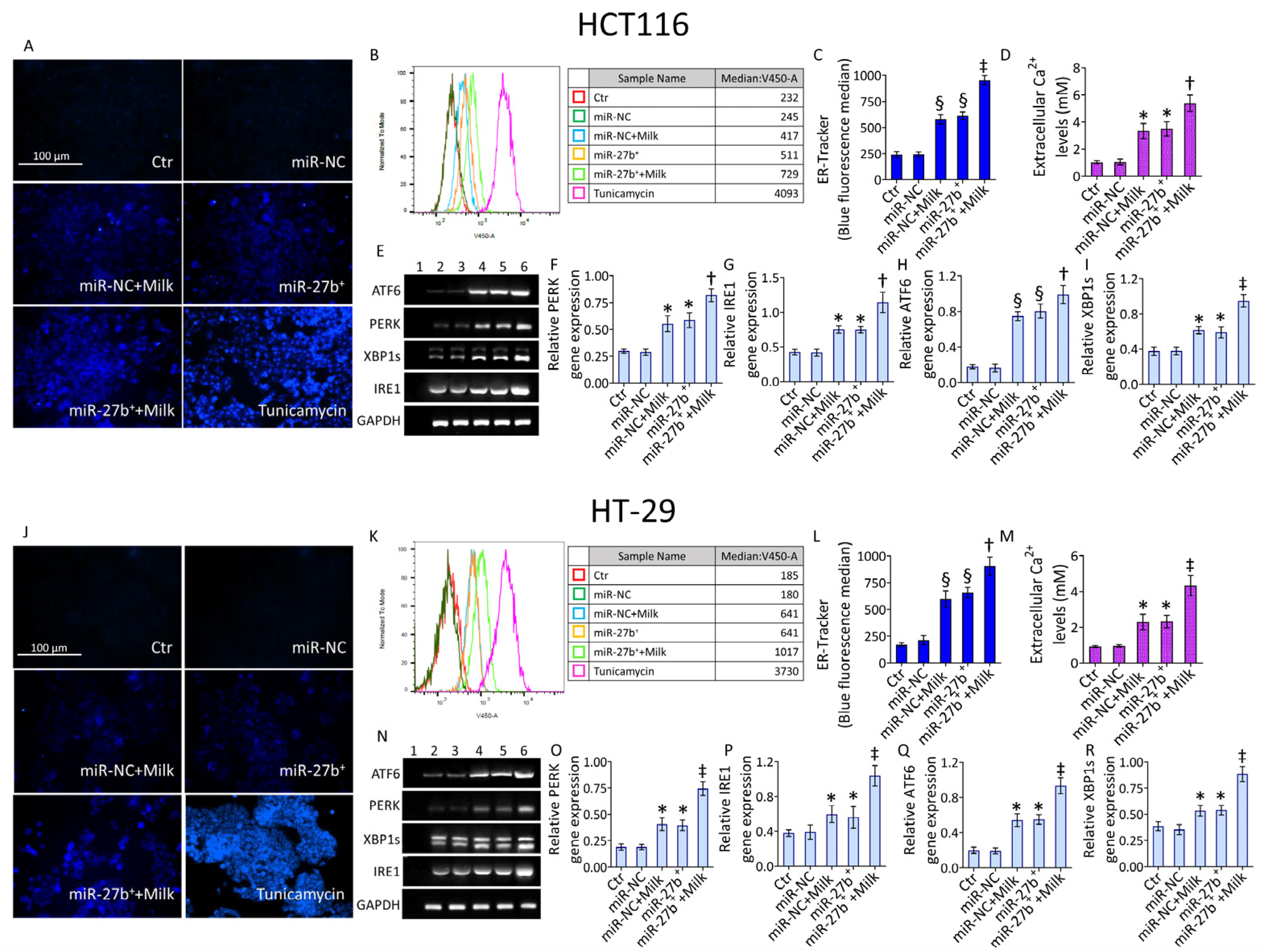
3.7. ER-Stress
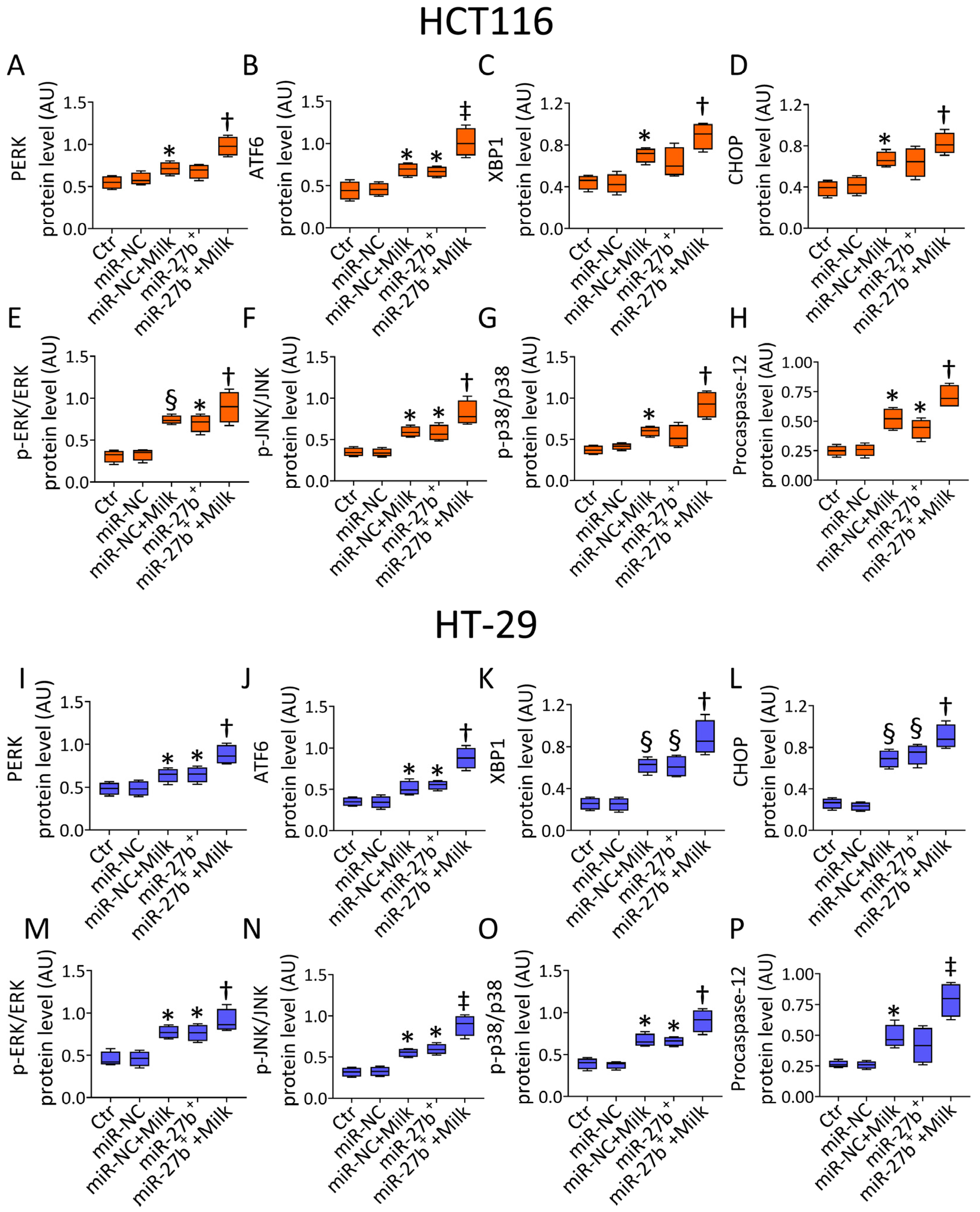
3.8. Modulation of ER-Stress Markers
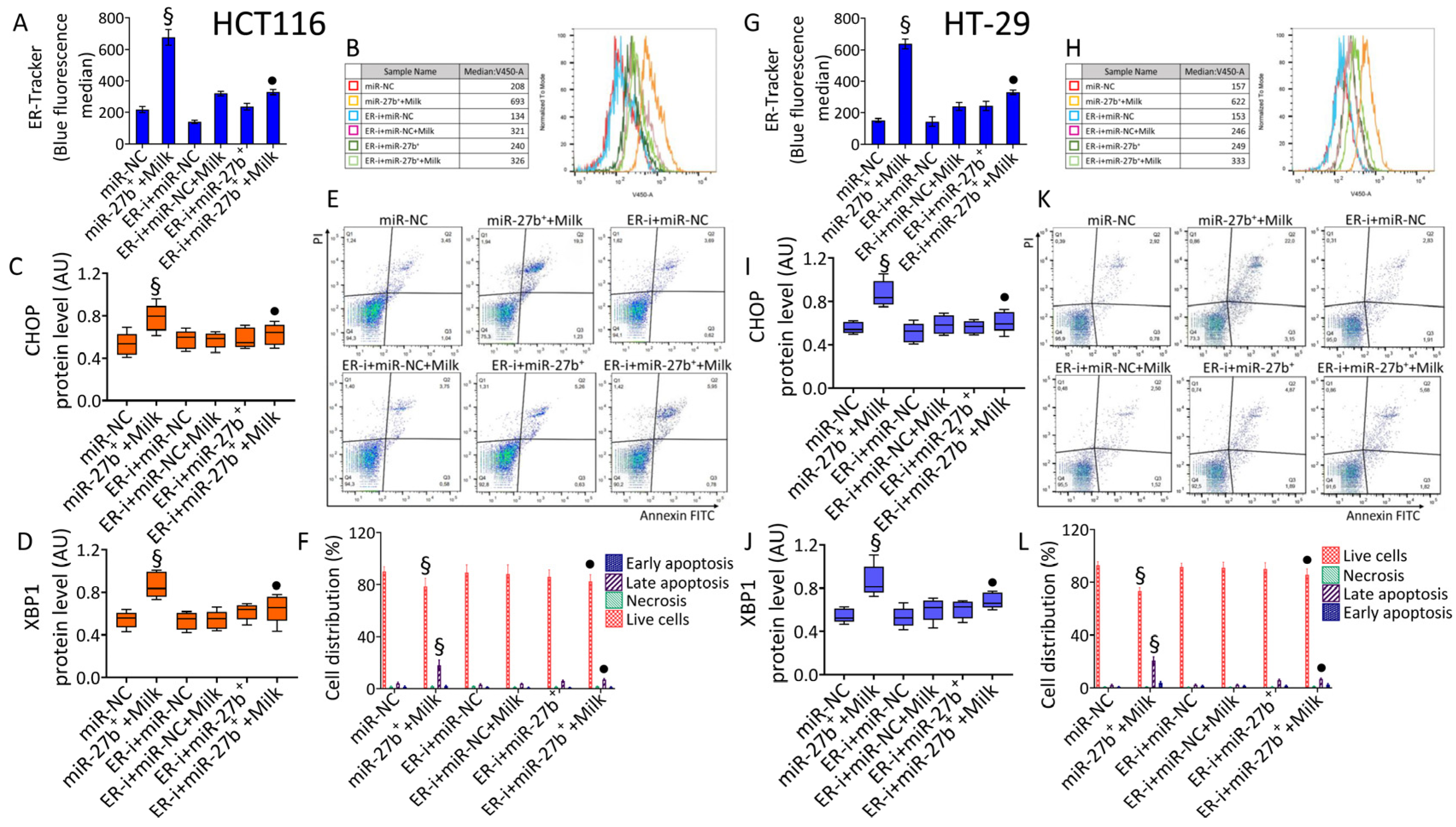
3.9. ER-i Decreases Apoptosis Induced in miR-27b+
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heck, J.M.; van Valenberg, H.J.; Dijkstra, J.; van Hooijdonk, A.C. Seasonal variation in the Dutch bovine raw milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, A.; Høstmark, A.T.; Harstad, O.M. Bovine milk in human nutrition—A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2007, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonolo, F.; Sandre, M.; Ferro, S.; Folda, A.; Scalcon, V.; Scutari, G.; Feller, E.; Marin, O.; Bindoli, A.; Rigobello, M.P. Milk-derived bioactive peptides protect against oxidative stress in a Caco-2 cell model. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.T.; Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Ullah, R.; Ajmal, M.; Jaspal, M.H. Antioxidant properties of Milk and dairy products: A comprehensive review of the current knowledge. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.L.; Simpson, J.A.; Buchholz, A.C. Dietary and total calcium intakes are associated with lower percentage total body and truncal fat in young, healthy adults. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2011, 30, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Jahandideh, F.; Wu, J. Food-derived bioactive peptides on inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 608979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liang, S.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, J.; Guo, M. Peptide profiles and antioxidant capacity of extensive hydrolysates of milk protein concentrate. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7972–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Yin, Q.; Wang, X.; Teng, X.; Jin, R.; Liu, N.; Ren, H. UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry reveals the lipidomics of bovine milk and yogurt. Food Chem. 2022, 392, 133267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Rosales, L.B.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; García-Garibay, J.M.; Gómez-Ruíz, L.C.; Contreras-López, E.; Guzmán-Rodríguez, F.; González-Olivares, L.G. Bioactive peptides of whey: Obtaining, activity, mechanism of action, and further applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servillo, L.; D’Onofrio, N.; Neglia, G.; Casale, R.; Cautela, D.; Marrelli, M.; Limone, A.; Campanile, G.; Balestrieri, M.L. Carnitine precursors and short-chain acylcarnitines in water buffalo milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8142–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servillo, L.; D’Onofrio, N.; Giovane, A.; Casale, R.; Cautela, D.; Castaldo, D.; Iannaccone, F.; Neglia, G.; Campanile, G.; Balestrieri, M.L. Ruminant meat and milk contain δ-valerobetaine, another precursor of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) like γ-butyrobetaine. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, A.; Licitra, F.; D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Limone, A.; Campanile, G.; D’Occhio, M.J.; Neglia, G. Short communication: Space allocation in intensive Mediterranean buffalo production influences the profile of functional biomolecules in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7717–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzano, A.; Neglia, G.; D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Limone, A.; Cotticelli, A.; Marrone, R.; Anastasio, A.; D’Occhio, M.J.; Campanile, G. Green feed increases antioxidant and antineoplastic activity of buffalo milk: A globally significant livestock. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, A.; Neglia, G.; Monaco, A.; Tatullo, M.; Casale, R.; Limone, A.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Campanile, G. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of buffalo milk δ-Valerobetaine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Mele, L.; Martino, E.; Salzano, A.; Restucci, B.; Cautela, D.; Tatullo, M.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Campanile, G. Synergistic effect of dietary betaines on SIRT1-mediated apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma Cal 27. Cancers 2020, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Cacciola, N.A.; Martino, E.; Borrelli, F.; Fiorino, F.; Lombardi, A.; Neglia, G.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Campanile, G. ROS-Mediated apoptotic cell death of human colon cancer LoVo cells by milk δ-valerobetaine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Martino, E.; Mele, L.; Colloca, A.; Maione, M.; Cautela, D.; Castaldo, D.; Balestrieri, M.L. Colorectal cancer apoptosis induced by dietary δ-valerobetaine involves PINK1/Parkin dependent-mitophagy and SIRT3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Martino, E.; Balestrieri, A.; Mele, L.; Neglia, G.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Campanile, G. SIRT3 and metabolic reprogramming mediate the antiproliferative effects of whey in human colon cancer cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, N.A.; Salzano, A.; D’Onofrio, N.; Venneri, T.; Cicco, P.; Vinale, F.; Petillo, O.; Martano, M.; Maiolino, P.; Neglia, G.; et al. Buffalo milk whey activates necroptosis and apoptosis in a xenograft model of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, A.L.; Enguita, F.J. A structural view of miRNA biogenesis and function. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López de Las Hazas, M.C.; Del Pozo-Acebo, L.; Hansen, M.S.; Gil-Zamorano, J.; Mantilla-Escalante, D.C.; Gómez-Coronado, D.; Marín, F.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.; Rasmussen, J.T.; Dávalos, A. Dietary bovine milk miRNAs transported in extracellular vesicles are partially stable during GI digestion, are bioavailable and reach target tissues but need a minimum dose to impact on gene expression. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, J.; Ngu, A.; Wang, H.; Ramirez, D.; Zempleni, J. Review: Milk small extracellular vesicles for use in the delivery of therapeutics. Pharm. Res. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, J.; Pérez-Castillo, Í.M.; Salto, R.; López-Pedrosa, J.M.; Rueda, R.; Girón, M.D. Beneficial effects of bovine milk exosomes in metabolic interorgan cross-talk. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Valencia, C.A.; Dong, B.; Chen, M.; Guan, P.J.; Pan, L. Transfer of microRNAs by extracellular membrane microvesicles: A nascent crosstalk model in tumor pathogenesis, especially tumor cell-microenvironment interactions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, L.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes in cancer: Small particle, big player. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávalos, A.; Pinilla, L.; López de las Hazas, M.C.; Pinto-Hernández, P.; Barbé, F.; Iglesias-Gutiérrez, E.; de Gonzalo-Calvo, D. Dietary microRNAs and cancer: A new therapeutic approach? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 73, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurazzi, M.; Cozzolino, M.; Reinelt, T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Elke Chie, S.; Natalucci, G.; Miletta, M.C. Human milk and brain development in infants. Reprod. Med. 2021, 2, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, F.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, K.; Guo, J.; Hong, Y.; Bu, G.; Lv, X.; et al. MicroRNA-181a-5p and microRNA-181a-3p cooperatively restrict vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Yuan, M.; Kang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, G.; Machens, H.G.; Rinkevich, Y.; et al. Milk exosomes-mediated miR-31-5p delivery accelerates diabetic wound healing through promoting angiogenesis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntz, O.J.; Pieters, B.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Broeren, M.G.; Bennink, M.B.; de Vries, M.; van Lent, P.L.; Koenders, M.I.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Oral administration of bovine milk derived extracellular vesicles attenuates arthritis in two mouse models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmoussa, A.; Diallo, I.; Salem, M.; Michel, S.; Gilbert, C.; Sevigny, J.; Provost, P. Concentrates of two subsets of extracellular vesicles from cow’s milk modulate symptoms and inflammation in experimental colitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stremmel, W.; Weiskirchen, R.; Melnik, B.C. Milk exosomes prevent intestinal inflammation in a genetic mouse model of ulcerative colitis: A pilot experiment. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2020, 5, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddela, V.S.; Nayan, V.; Rani, P.; Onteru, S.K.; Singh, D. Physicochemical biomolecular insights into buffalo milk-derived nanovesicles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Milk exosome-derived miRNAs from water buffalo are implicated in immune response and metabolism process. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. Exosomes of pasteurized milk: Potential pathogens of Western diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hi, X.B.; Xue, L.; Ma, A.H.; Tepper, C.G.; Kung, H.J.; White, R.W. miR-125b promotes growth of prostate cancer xenograft tumor through targeting pro-apoptotic genes. Prostate 2011, 71, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. Lifetime impact of cow’s milk on overactivation of mTORC1: From fetal to childhood overgrowth, acne, diabetes, cancers, and neurodegeneration. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Bella, F.; Torrisi, A.; Sciacca, S.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y. Milk consumption and multiple health outcomes: Umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in humans. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Nie, Y.; Wu, Q.; Fan, D.; Li, M. Let food be thy medicine: The role of diet in colorectal cancer: A narrative review. J. Gastrointest Oncol. 2022, 13, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B. LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN axis promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by acting on Wnt signaling. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Tamma, M.; Pathigadapa, U.; Reddanna, P.; Yenuganti, V.R. Drug loading and functional efficacy of cow, buffalo, and goat milk-derived exosomes: A comparative study. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, B.; Ross, S.A.; Zempleni, J. Nutrition, microRNAs, and human health. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Tsukasaki, Y.; Dasgupta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Ikebe, M.; Sauter, E.R. Exosomes in human breast milk promote EMT. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4517–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, E.; Balestrieri, A.; Anastasio, C.; Maione, M.; Mele, L.; Cautela, D.; Campanile, G.; Balestrieri, M.L.; D’Onofrio, N. SIRT3 modulates endothelial mitochondrial redox state during insulin resistance. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozpedek, W.; Pytel, D.; Mucha, B.; Leszczynska, H.; DiehlI, J.A.; Majsterek, I. the role of the PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, R.; Reed, J.C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, P.P.; Fang, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhou, H.Z.; Chen, S.T.; Chao, H. A ruthenium(II) complex containing a p-cresol group induces apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress and reactive oxygen species production. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 191, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfaillie, T.; Rubio, N.; Garg, A.D.; Bultynck, G.; Rizzuto, R.; Decuypere, J.P.; Piette, J.; Linehan, C.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A.; et al. PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, S.; Qing, T.; Xuan, J.; Couch, L.; Yu, D.; Ning, B.; Shi, L.; Guo, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK signaling pathway activation underlie leflunomide-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Toxicology 2017, 392, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.P.; Qi, Y.K.; Li, N.; Fei, H.R. Scutebarbatine A induces cytotoxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the MAPK and ER stress signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Davis, R.J. Cell signaling and stress responses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a006072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Fang, S.; Hui, J.; Rajamanickam, V.; Chen, M.; Weng, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, J. Triptonide modulates MAPK signaling pathways and exerts anticancer effects via ER stress-mediated apoptosis induction in human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5919–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Q.; Ji, Q.; Yuan, X.; Ren, D. Cleavage of caspase-12 at Asp94, mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), contributes to stretch-induced apoptosis of myoblasts. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 9473–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hua, R. Autophagy triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and C/EBP homologous protein-mediated apoptosis in OGD/R-treated neurons in a caspase-12-independent manner. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 126, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Caspase-12 is involved in stretch-induced apoptosis mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rana, T.M. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs: Current status and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Hao, N.B.; Tang, B.; Guo, H.; Yong, X.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.M. MicroRNA inhibitors: Natural and artificial sequestration of microRNA. Cancer Lett. 2017, 407, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; Chatterjee, A. Recent advances in miRNA delivery systems. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, D.Y.; Huang, L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, R.; Okuzaki, D.; Okada, M.; Oneyama, C. MicroRNA-27b suppresses tumor progression by regulating ARFGEF1 and focal adhesion signaling. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cao, L. MiR-27b targets PI3K p110α to inhibit proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer stem cell. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5988–5997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Ning, T.; Gao, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; et al. The c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Xing, B. miR-6716-5p promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer through downregulating NAT10 expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5317–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beermann, C.; Hartung, J. Physiological properties of milk ingredients released by fermentation. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howick, K.; Wallace-Fitzsimons, S.E.; Kandil, D.; Chruścicka, B.; Calis, M.; Murphy, E.; Murray, B.A.; Fernandez, A.; Barry, K.M.; Kelly, P.M.; et al. A dairy-derived ghrelinergic hydrolysate modulates food intake in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.K.; Thymann, T.; Fink, L.N.; Frokiaer, H.; Kvistgaard, A.S.; Sangild, P.T. Bovine colostrum is superior to enriched formulas in stimulating intestinal function and necrotising enterocolitis resistance in preterm pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tao, Y.; He, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, K.; Shen, J.; Gao, C. Preparation of Low-Lactose Milk Powder by Coupling Membrane Technology. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8543–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.R.; Nguyen, C.; Xie, F.; Wood, J.R.; Zempleni, J. MicroRNAs are absorbed in biologically meaningful amounts from nutritionally relevant doses of cow milk and affect gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, HEK-293 kidney cell cultures, and mouse livers. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martino, E.; Balestrieri, A.; Mele, L.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; D’Onofrio, N.; Campanile, G.; Balestrieri, M.L. Milk Exosomal miR-27b Worsen Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated Colorectal Cancer Cell Death. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5081. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235081
Martino E, Balestrieri A, Mele L, Sardu C, Marfella R, D’Onofrio N, Campanile G, Balestrieri ML. Milk Exosomal miR-27b Worsen Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated Colorectal Cancer Cell Death. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5081. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235081
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartino, Elisa, Anna Balestrieri, Luigi Mele, Celestino Sardu, Raffaele Marfella, Nunzia D’Onofrio, Giuseppe Campanile, and Maria Luisa Balestrieri. 2022. "Milk Exosomal miR-27b Worsen Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated Colorectal Cancer Cell Death" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5081. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235081
APA StyleMartino, E., Balestrieri, A., Mele, L., Sardu, C., Marfella, R., D’Onofrio, N., Campanile, G., & Balestrieri, M. L. (2022). Milk Exosomal miR-27b Worsen Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated Colorectal Cancer Cell Death. Nutrients, 14(23), 5081. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235081