Sodium and Potassium Concentrations and Somatic Cell Count of Human Milk Produced in the First Six Weeks Postpartum and Their Suitability as Biomarkers of Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Milk Composition Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
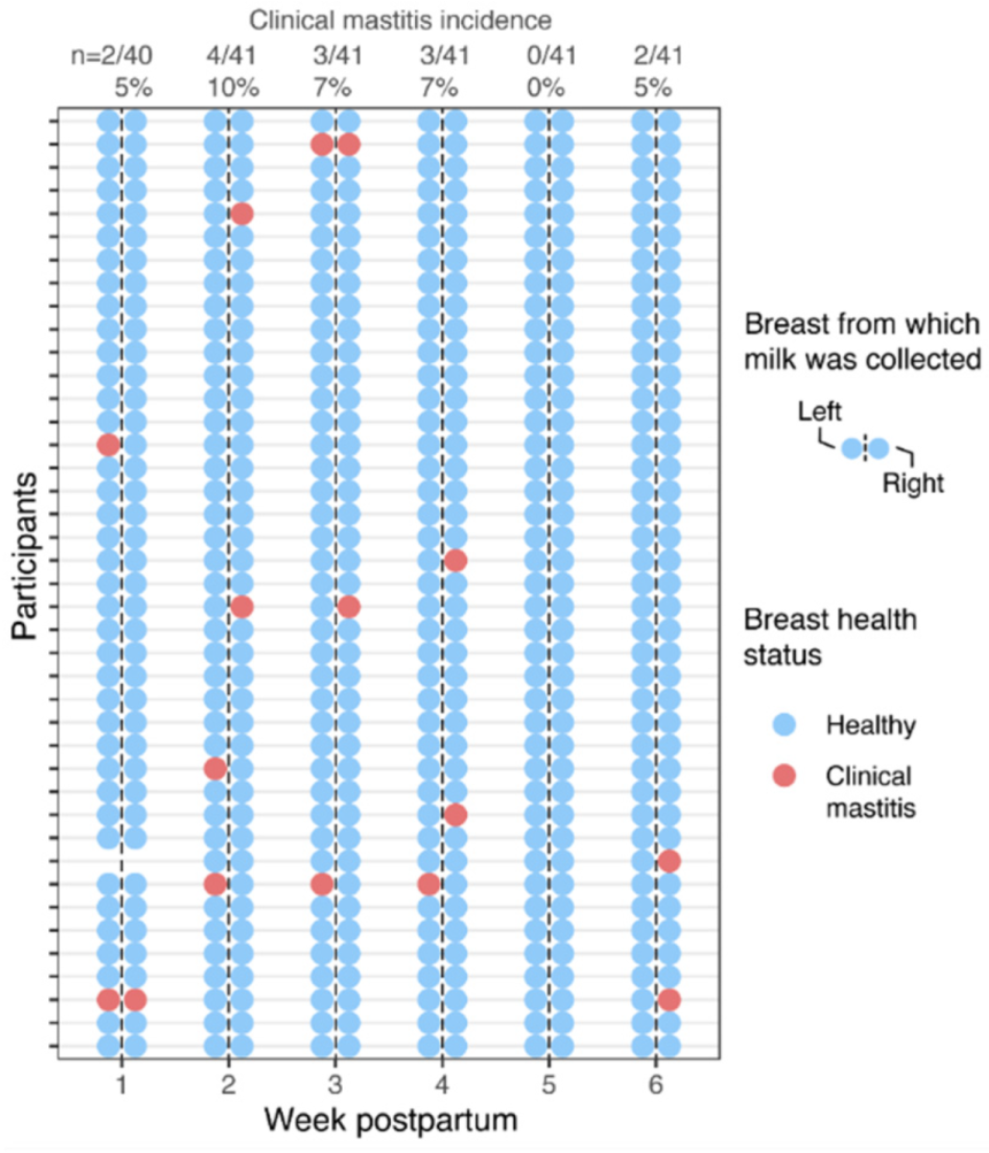
3.1. Cohort Characteristics and Incidence of Clinical Mastitis
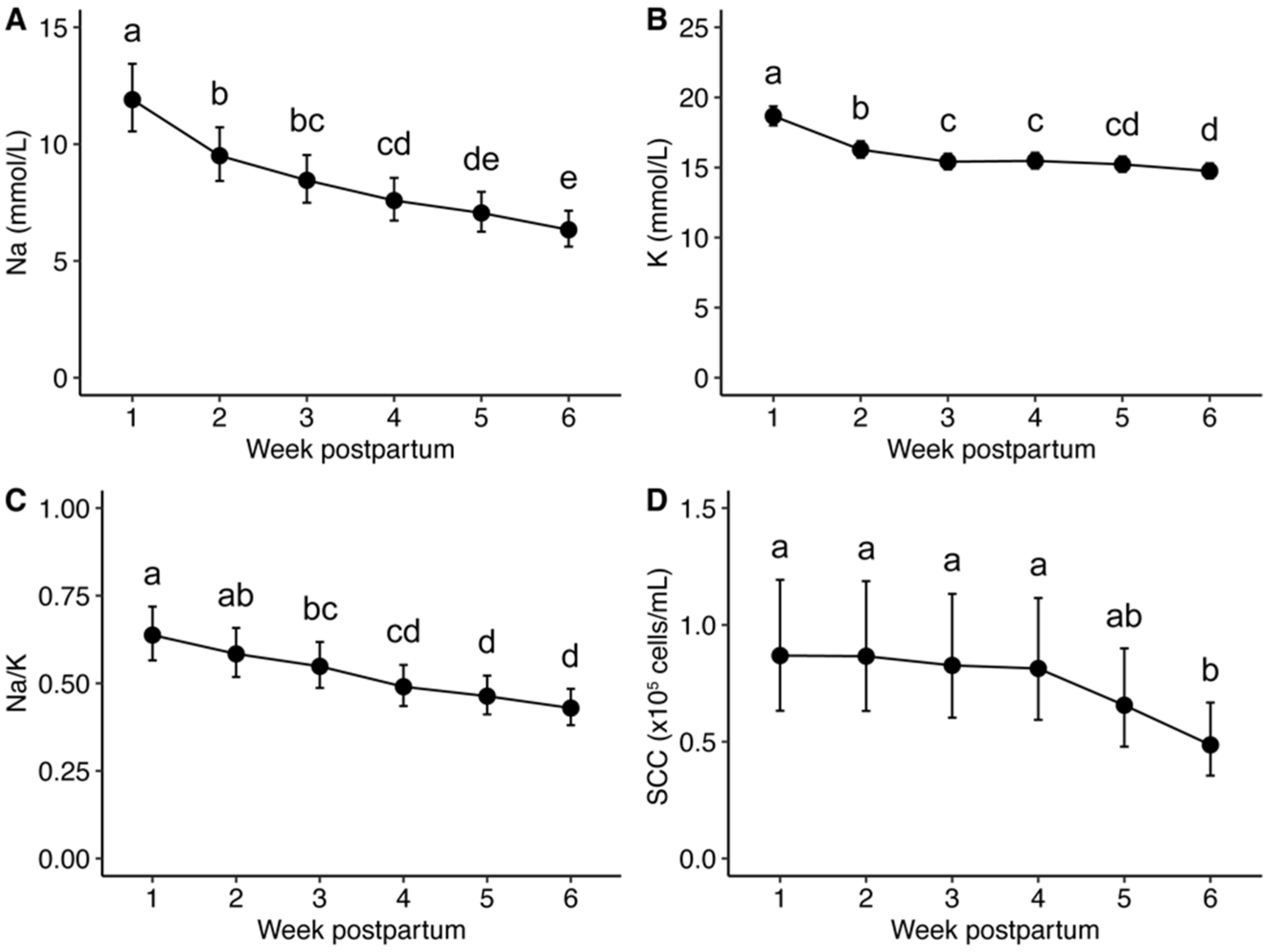
3.2. Na and K Concentrations and SCC of Milk Produced by Healthy Participants
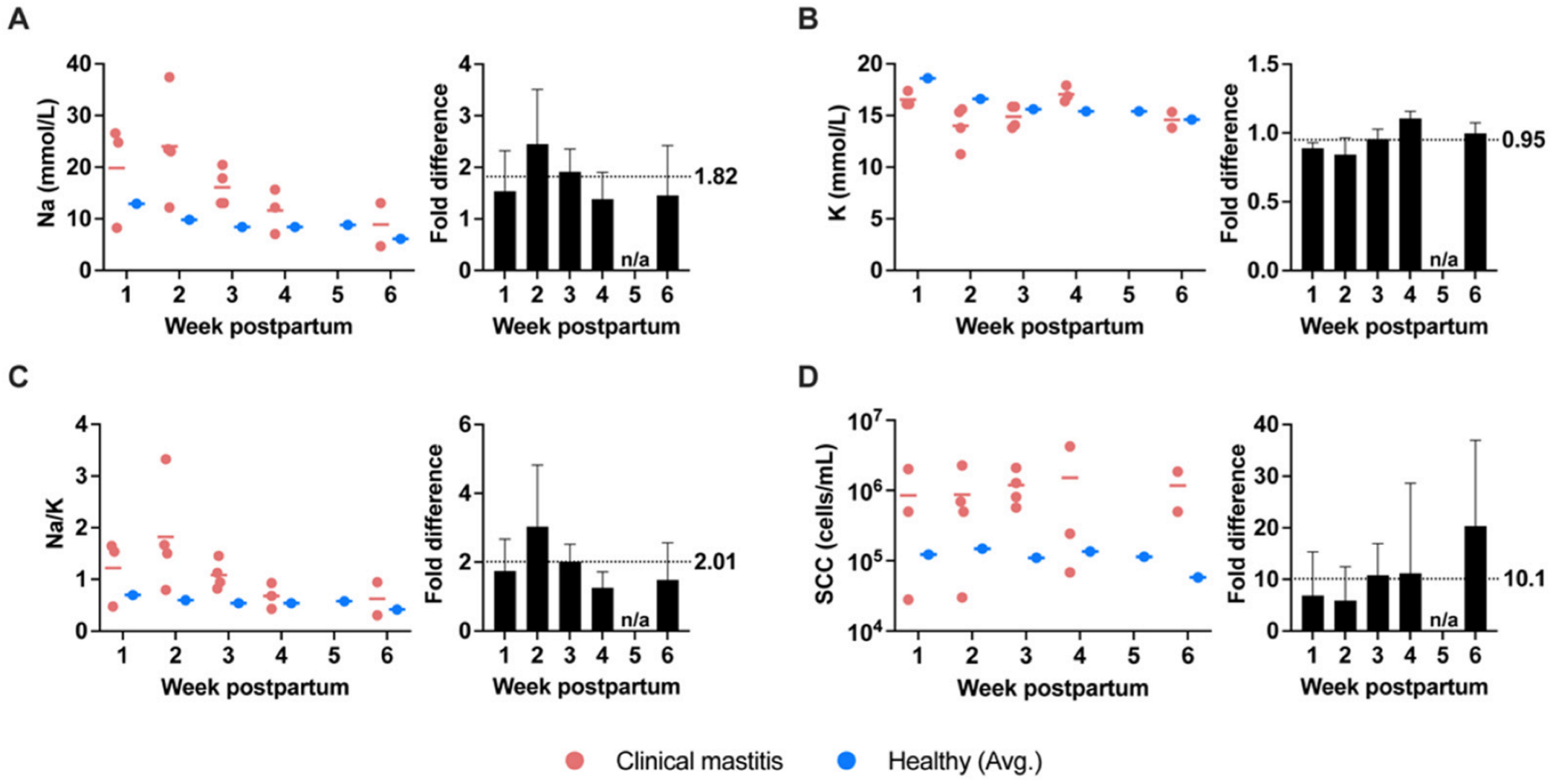
3.3. Na and K Concentrations and SCC of Milk Produced during Clinical Mastitis
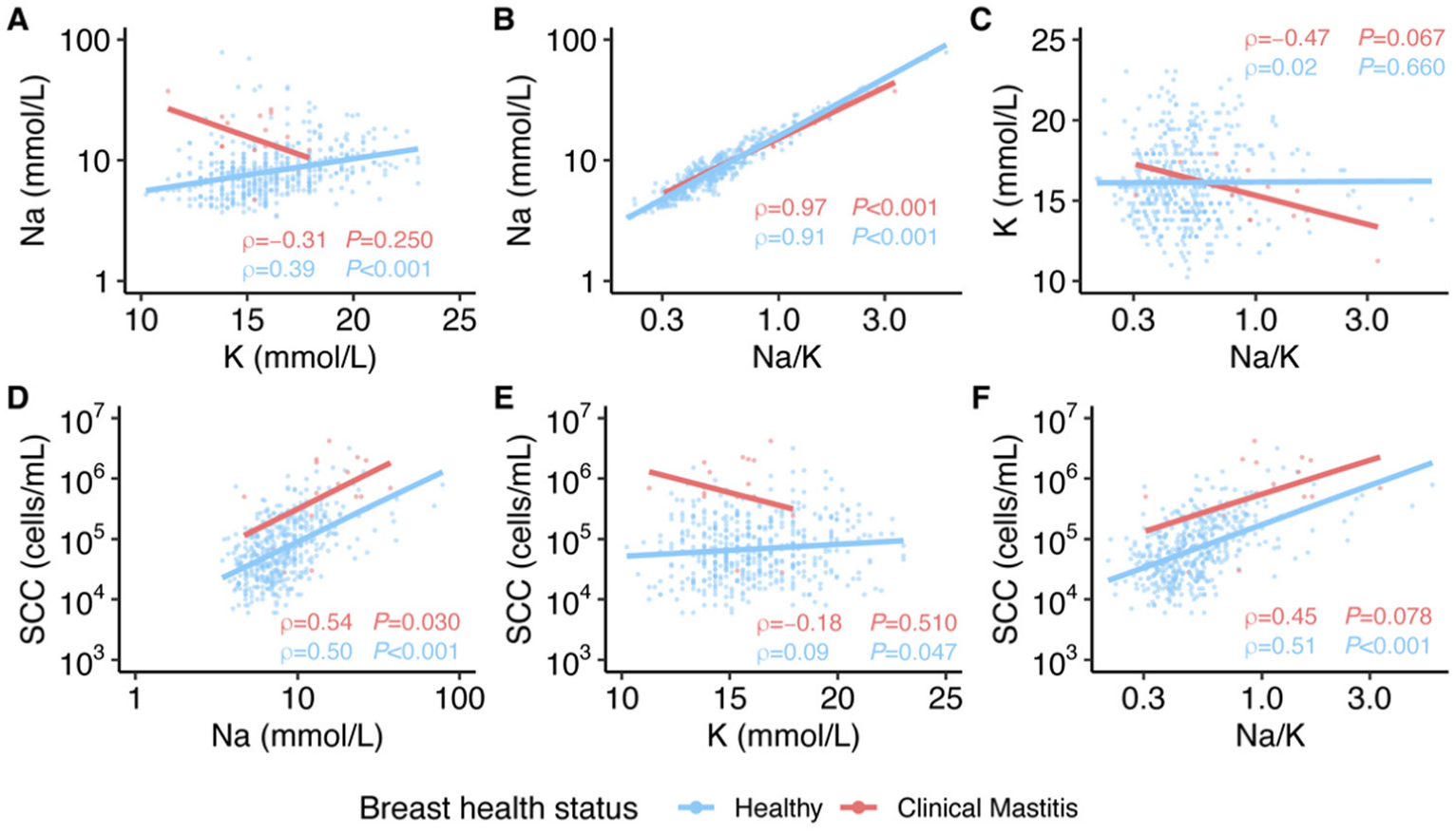
3.4. Relationships among Na Concentration, K Concentration, and SCC of Milk
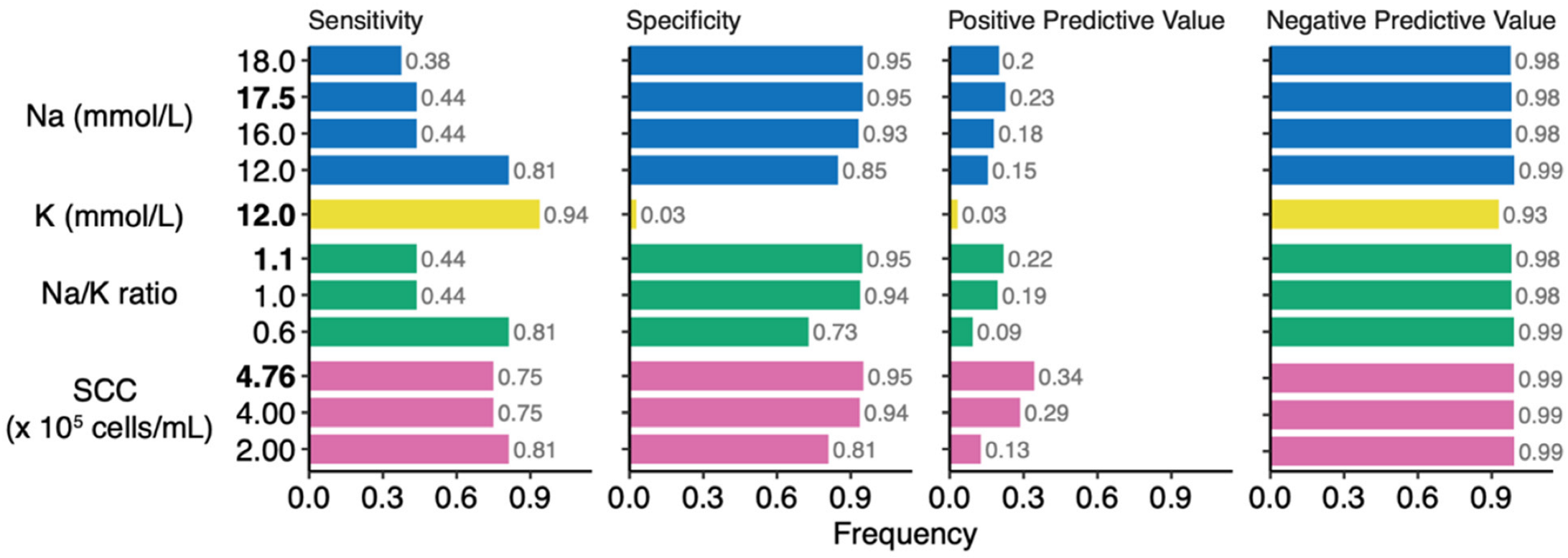
3.5. Performance and Thresholds for Classification of Clinical Mastitis Using Na and K Concentrations and SCC of Milk
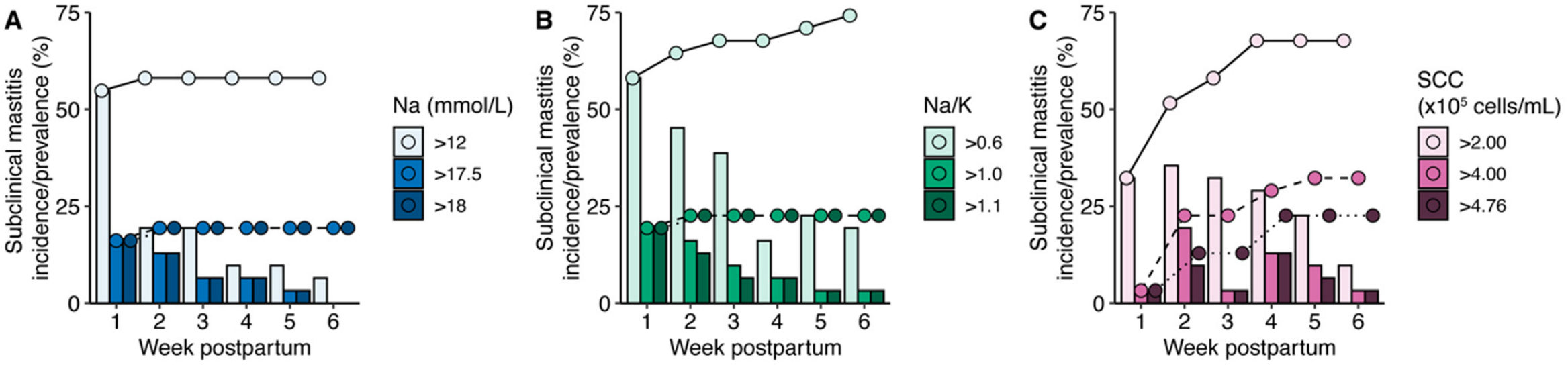
3.6. Incidence and Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis over the First 6 Weeks Postpartum
4. Discussion
4.1. Na and K Concentrations, Na/K, and SCC in Milk Produced during the Early Postpartum Period
4.2. Milk Na, K, Na/K, and SCC as Biomarkers for Clinical Mastitis
4.3. Estimation of the Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis
4.4. Relevance for Adequate Intake (AI) Values for Na and K in Early Life
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amir, L.H.; Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. ABM Clinical Protocol #4: Mastitis, Revised March 2014. Breastfeed. Med. 2014, 9, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.B.; Johnson, H.M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Eglash, A.; Scherzinger, C.; Zakarija-Grkovic, I.; Cash, K.W.; Berens, P.; Miller, B.; Stehel, E.; et al. Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Clinical Protocol #36: The Mastitis Spectrum, Revised 2022. Breastfeed. Med. 2022, 17, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvist, L.J. Toward a Clarification of the Concept of Mastitis as Used in Empirical Studies of Breast Inflammation during Lactation. J. Hum. Lact. 2010, 26, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P. Management of Mastitis in Breastfeeding Women. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 78, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kvist, L.J.; Larsson, B.W.; Hall-Lord, M.L.; Steen, A.; Schalén, C. The Role of Bacteria in Lactational Mastitis and Some Considerations of the Use of Antibiotic Treatment. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2008, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Mastitis: Causes and Management; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Filteau, S.M.; Rice, A.L.; Ball, J.J.; Chakraborty, J.; Stoltzfus, R.; de Francisco, A.; Willumsen, J.F. Breast Milk Immune Factors in Bangladeshi Women Supplemented Postpartum with Retinol or β-Carotene. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filteau, S.M.; Lietz, G.; Mulokozi, G.; Bilotta, S.; Henry, C.J.K.; Tomkins, A.M. Milk Cytokines and Subclinical Breast Inflammation in Tanzanian Women: Effects of Dietary Red Palm Oil or Sunflower Oil Supplementation. Immunology 1999, 97, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, R.D.; Kumwenda, N.; Hoover, D.R.; Taha, T.E.; Quinn, T.C.; Mtimavalye, L.; Biggar, R.J.; Broadhead, R.; Miotti, P.G.; Sokoll, L.J.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Load in Breast Milk, Mastitis, and Mother-to-Child Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, R.D.; Kumwenda, N.; Taha, T.E.; Hoover, D.R.; Lan, Y.; Eisinger, W.; Mtimavalye, L.; Broadhead, R.; Miotti, P.G.; van der Hoeven, L.; et al. Mastitis and Immunological Factors in Breast Milk of Lactating Women in Malawi. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomo, E.; Filteau, S.M.; Tomkins, A.M.; Ndhlovu, P.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Friis, H. Subclinical Mastitis among HIV-Infected and Uninfected Zimbabwean Women Participating in a Multimicronutrient Supplementation Trial. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 97, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willumsen, J.F.; Filteau, S.M.; Coutsoudis, A.; Uebel, K.E.; Newell, M.-L.; Tomkins, A.M. Short and Long Term Effects of Breast Feeding on Child Health. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, M.C.; Allen, J.C.; Archer, P.C.; Casey, C.E.; Seacat, J.; Keller, R.P.; Lutes, V.; Rasbach, J.; Neifert, M. Studies in Human Lactation: Milk Volume and Nutrient Composition during Weaning and Lactogenesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.A. The Clinical Usefulness of Breast Milk Sodium in the Assessment of Lactogenesis. Pediatrics 1994, 93, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, M.; Wagner, E.A.; Chantry, C.J.; Dewey, K.G.; Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. The Relation between Breast Milk Sodium to Potassium Ratio and Maternal Report of a Milk Supply Concern. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 294–297.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willumsen, J.F.; Filteau, S.M.; Coutsoudis, A.; Newell, M.-L.; Rollins, N.C.; Coovadia, H.M.; Tomkins, A.M. Breastmilk RNA Viral Load in HIV-Infected South African Women: Effects of Subclinical Mastitis and Infant Feeding. AIDS 2003, 17, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquart, P.; Courgnaud, V.; Willumsen, J.; de Perre, P.V. Diversity of HIV-1 RNA and DNA in Breast Milk from HIV-1-Infected Mothers. Virology 2007, 363, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aryeetey, R.N.O.; Marquis, G.S.; Timms, L.; Lartey, A.; Brakohiapa, L. Subclinical Mastitis Is Common among Ghanaian Women Lactating 3 to 4 Months Postpartum. J. Hum. Lact. 2008, 24, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.-B.W.; Hansen, D.H.; Kaestel, P.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Friis, H.; Larsen, T. Milk Enzyme Activities and Subclinical Mastitis among Women in Guinea-Bissau. Breastfeed. Med. 2008, 3, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuaillon, E.; Viljoen, J.; Dujols, P.; Cambonie, G.; Rubbo, P.-A.; Nagot, N.; Bland, R.M.; Badiou, S.; Newell, M.-L.; de Perre, P.V. Subclinical Mastitis Occurs Frequently in Association with Dramatic Changes in Inflammatory/Anti-Inflammatory Breast Milk Components. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, T.M.; Castro, C.A.D.; Dubascoux, S.; Affolter, M.; Giuffrida, F.; Billeaud, C.; Picaud, J.-C.; Agosti, M.; Al-Jashi, I.; Pereira, A.B.; et al. Subclinical Mastitis in a European Multicenter Cohort: Prevalence, Impact on Human Milk (HM) Composition, and Association with Infant HM Intake and Growth. Nutrients 2020, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Järvinen, K.M.; Belfort, M.B.; Pace, C.D.W.; Lackey, K.A.; Gogel, A.C.; Nguyen-Contant, P.; Kanagaiah, P.; Fitzgerald, T.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, Antibodies, and Neutralizing Capacity in Milk Produced by Women with COVID-19. Mbio 2021, 12, e03192-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, R.J. Physiology of Mastitis and Factors Affecting Somatic Cell Counts. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohoo, I.R.; Meek, A.H. Somatic Cell Counts in Bovine Milk. Can. Vet. J. 1982, 23, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zank, W.; Schlatterer, B. Assessment of Subacute Mammary Inflammation by Soluble Biomarkers in Comparison to Somatic Cell Counts in Quarter Milk Samples from Dairy Cows. J. Vet. Medicine Ser. 1998, 45, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellnitz, O.; Baumert, A.; Saudenowa, M.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Immune Response of Bovine Milk Somatic Cells to Endotoxin in Healthy Quarters with Normal and Very Low Cell Counts. J. Dairy Res. 2010, 77, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A.C.; Espersen, T.; Maigaard, S. Course and Treatment of Milk Stasis, Noninfectious Inflammation of the Breast, and Infectious Mastitis in Nursing Women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1984, 149, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussenblatt, V.; Lema, V.; Kumwenda, N.; Broadhead, R.; Neville, M.C.; Taha, T.E.; Semba, R.D. Epidemiology and Microbiology of Subclinical Mastitis among HIV-Infected Women in Malawi. Int. J. Std. Aids 2005, 16, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantt, S.; Shetty, A.K.; Seidel, K.D.; Matasa, K.; Musingwini, G.; Woelk, G.; Zijenah, L.S.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Frenkel, L.M. Laboratory Indicators of Mastitis Are Not Associated with Elevated HIV-1 DNA Loads or Predictive of HIV-1 RNA Loads in Breast Milk. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeel, S.A.; Megahed, A.A.; Constable, P.D. Evaluation of Hand-held Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, and Electrical Conductivity Meters for Diagnosing Subclinical Mastitis and Intramammary Infection in Dairy Cattle. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerra-Zwiers, A.; Vroom, A.; Geddes, D.; Lai, C.T. Use of a Portable Point-of-Care Instrumentation to Measure Human Milk Sodium and Potassium Concentrations. Breastfeed. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Scott, M. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-98140-6. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, W.W.; Gupta, J.M. Breast Milk Sodium. Arch. Dis. Child. 1982, 57, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semrau, K.; Ghosh, M.; Kankasa, C.; Sinkala, M.; Kasonde, P.; Mwiya, M.; Thea, D.M.; Kuhn, L.; Aldrovandi, G.M. Temporal and Lateral Dynamics of HIV Shedding and Elevated Sodium in Breast Milk among HIV-Positive Mothers during the First 4 Months of Breast-Feeding. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2008, 47, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Hillerton, J.E.; Harmon, R.J. NMC Guidelines on Normal and Abnormal Raw Milk Based on SCC and Signs of Clinical Mastitis; National Mastitis Council: Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schukken, Y.H.; Wilson, D.J.; Welcome, F.; Garrison-Tikofsky, L.; Gonzalez, R.N. Monitoring Udder Health and Milk Quality Using Somatic Cell Counts. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, R.; Rošić, N.; Kuleš, J.; Horvatić, A.; Gelemanovic, A.; Galen, A.; Ljubić, B.B.; Benić, M.; Stevanović, V.; Mrljak, V.; et al. Milk and Serum Proteomes in Subclinical and Clinical Mastitis in Simmental Cows. J. Proteomics 2021, 244, 104277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K.; Mizuno, K.; Azuma, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Den, H.; Iyoda, M.; Nagao, S.; Tsujimori, Y. Reliability of an Ion-Selective Electrode as a Simple Diagnostic Tool for Mastitis. J. Hum. Lact. 2021, 38, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingess, K.A.; Valentine, C.J.; Ollberding, N.J.; Davidson, B.S.; Woo, J.G.; Summer, S.; Peng, Y.M.; Guerrero, M.L.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Ran-Ressler, R.R.; et al. Branched-Chain Fatty Acid Composition of Human Milk and the Impact of Maternal Diet: The Global Exploration of Human Milk (GEHM) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 105, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; du Toit, E.; Kulkarni, A.; Aakko, J.; Linderborg, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Nicol, M.P.; Isolauri, E.; Yang, B.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Distinct Patterns in Human Milk Microbiota and Fatty Acid Profiles Across Specific Geographic Locations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, M.K.; Meehan, C.L.; McGuire, M.A.; Williams, J.E.; Foster, J.; Sellen, D.W.; Kamau-Mbuthia, E.W.; Kamundia, E.W.; Mbugua, S.; Moore, S.E.; et al. What’s Normal? Oligosaccharide Concentrations and Profiles in Milk Produced by Healthy Women Vary Geographically. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; García-Carral, C.; Manzano, S.; McGuire, M.K.; Meehan, C.L.; McGuire, M.A.; Williams, J.E.; Foster, J.; Sellen, D.W.; et al. What’s Normal? Immune Profiling of Human Milk from Healthy Women Living in Different Geographical and Socioeconomic Settings. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, M.C.L.; Koleva, P.T.; Slupsky, C.M.; du Toit, E.; Eggesbø, M.; Johnson, C.C.; Wegienka, G.; Shimojo, N.; Campbell, D.E.; Prescott, S.L.; et al. Worldwide Variation in Human Milk Metabolome: Indicators of Breast Physiology and Maternal Lifestyle? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Robertson, B.; Lackey, K.A.; Meehan, C.L.; Price, W.J.; Foster, J.A.; Sellen, D.W.; Kamau-Mbuthia, E.W.; Kamundia, E.W.; et al. Variation in Human Milk Composition Is Related to Differences in Milk and Infant Fecal Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.T.; Kim, J.; Seo, N.; Lee, A.H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jung, J.A.; Li, D.; To, X.H.M.; Huynh, K.T.N.; Le, T.V.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Fatty Acids in Human Milk of Four Asian Countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 6496–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinjamuri, A.; Davis, J.C.C.; Totten, S.M.; Wu, L.D.; Klein, L.D.; Martin, M.; Quinn, E.A.; Scelza, B.; Breakey, A.; Gurven, M.; et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Compositions Illustrate Global Variations in Early Nutrition. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780309488341. [Google Scholar]
- Hassiotou, F.; Geddes, D.T. Immune Cell–Mediated Protection of the Mammary Gland and the Infant during Breastfeeding. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twigger, A.-J.; Engelbrecht, L.K.; Bach, K.; Schultz-Pernice, I.; Pensa, S.; Stenning, J.; Petricca, S.; Scheel, C.H.; Khaled, W.T. Transcriptional Changes in the Mammary Gland during Lactation Revealed by Single Cell Sequencing of Cells from Human Milk. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutinaud, M.; Jammes, H. Potential Uses of Milk Epithelial Cells: A Review. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2002, 42, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koess, C.; Hamann, J. Detection of Mastitis in the Bovine Mammary Gland by Flow Cytometry at Early Stages. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainard, P.; Foucras, G.; Boichard, D.; Rupp, R. Invited Review: Low Milk Somatic Cell Count and Susceptibility to Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6703–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.; Diesterbeck, U.S.; König, S.; Brügemann, K.; Schlez, K.; Zschöck, M.; Wolter, W.; Czerny, C.-P. Flow Cytometric Differential Cell Counts in Milk for the Evaluation of Inflammatory Reactions in Clinically Healthy and Subclinically Infected Bovine Mammary Glands. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5033–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.; Williams, J.E.; Shafii, B.; Hunt, M.K.; Behre, R.; Ting, R.; McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Mastitis Is Associated with Increased Free Fatty Acids, Somatic Cell Count, and Interleukin-8 Concentrations in Human Milk. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarci, S.; Koulinska, I.N.; Aboud, S.; Fawzi, W.W.; Villamor, E. Subclinical Mastitis, Cell-Associated HIV-1 Shedding in Breast Milk, and Breast-Feeding Transmission of HIV-1. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 46, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutagwera, D.G.; Molès, J.-P.; Kankasa, C.; Mwiya, M.; Tuaillon, E.; Peries, M.; Nagot, N.; de Perre, P.V.; Tylleskär, T. Recurrent Severe Subclinical Mastitis and the Risk of HIV Transmission Through Breastfeeding. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 822076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-309-09158-6. [Google Scholar]
- Aryeetey, R.N.O.; Marquis, G.S.; Brakohiapa, L.; Timms, L.; Lartey, A. Subclinical Mastitis May Not Reduce Breastmilk Intake During Established Lactation. Breastfeed. Med. 2009, 4, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Total | Healthy | Mastitis | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants, No. | 41 (100) | 31 (76) | 10 (24) | |
| Age, median (IQR), y | 30 (28–32) | 30 (28–33) | 28 (26–30) | 0.082 |
| Race, Ethnicity | 0.314 | |||
| American Indian/Alaskan | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | |
| Asian | 1 (2) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| Black, Hispanic | 1 (2) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| White, Hispanic | 5 (12) | 5 (16) | 0 (0) | |
| White, Non-Hispanic | 32 (78) | 23 (74) | 9 (90) | |
| Not reported | 1 (2) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI, median (IQR), kg/m2 | 23 (21–25) | 23 (21–25) | 23 (22–24) | 0.819 |
| Education level | 0.447 | |||
| High school or less | 3 (7) | 3 (10) | 0 (0) | |
| Some college | 9 (22) | 7 (23) | 2 (20) | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 13 (32) | 8 (26) | 5 (50) | |
| Graduate/professional degree | 16 (39) | 13 (42) | 3 (30) | |
| Pets in home | 25 (61) | 19 (61) | 5 (50) | 0.714 |
| History of mastitis | 6 (15) | 5 (16) | 1 (10) | >0.999 |
| Gravidity, median (IQR), No. | 3 (1–4) | 3 (2–4) | 2 (1–4) | 0.456 |
| Parity, median (IQR), No. | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 0.962 |
| Mode of delivery | >0.999 | |||
| Vaginal | 30 (73) | 23 (68) | 7 (70) | |
| Cesarean | 11 (27) | 8 (32) | 3 (30) | |
| Gestational age at delivery, median (IQR), wk | 40 (39–41) | 40 (39–41) | 40 (40–41) | 0.463 |
| Infant sex, female | 22 (54) | 19 (61) | 3 (30) | 0.145 |
| Model 1 (First Week Postpartum) | Model 2 (Previous Week) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarker | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p |
| Na (mmol/L) | ||||
| >12.0 | 1.20 (0.28–4.92) | 0.798 | 5.28 (1.57–17.80) | 0.007 |
| >16.0 | 2.19 (0.42–9.54) | 0.309 | 2.21 (0.46–10.60) | 0.322 |
| >17.5 | 1.94 (0.26–9.66) | 0.451 | 0.00 (0.00–) | >0.999 |
| >18.0 | 1.94 (0.26–9.66) | 0.451 | 0.00 (0.00–) | >0.999 |
| Na/K | ||||
| >0.6 | 1.01 (0.23–4.11) | 0.993 | 2.71 (0.81–9.04) | 0.106 |
| >1.0 | 0.85 (0.04–5.48) | 0.882 | 1.09 (0.14–8.81) | 0.933 |
| >1.1 | 0.97 (0.05–6.39) | 0.977 | 1.31 (0.16–10.60) | 0.802 |
| SCC (×105 cells/mL) | ||||
| >2.00 | 1.59 (0.31–6.73) | 0.543 | 1.97 (0.56–6.89) | 0.288 |
| >4.00 | 9.86 (1.05–93.60) | 0.033 | 6.08 (1.70–21.80) | 0.006 |
| >4.76 | 9.86 (1.05–93.60) | 0.033 | 7.81 (2.15–28.30) | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pace, R.M.; Pace, C.D.W.; Fehrenkamp, B.D.; Price, W.J.; Lewis, M.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.A.; McGuire, M.K. Sodium and Potassium Concentrations and Somatic Cell Count of Human Milk Produced in the First Six Weeks Postpartum and Their Suitability as Biomarkers of Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224708
Pace RM, Pace CDW, Fehrenkamp BD, Price WJ, Lewis M, Williams JE, McGuire MA, McGuire MK. Sodium and Potassium Concentrations and Somatic Cell Count of Human Milk Produced in the First Six Weeks Postpartum and Their Suitability as Biomarkers of Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(22):4708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224708
Chicago/Turabian StylePace, Ryan M., Christina D. W. Pace, Bethaney D. Fehrenkamp, William J. Price, Meghan Lewis, Janet E. Williams, Mark A. McGuire, and Michelle K. McGuire. 2022. "Sodium and Potassium Concentrations and Somatic Cell Count of Human Milk Produced in the First Six Weeks Postpartum and Their Suitability as Biomarkers of Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis" Nutrients 14, no. 22: 4708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224708
APA StylePace, R. M., Pace, C. D. W., Fehrenkamp, B. D., Price, W. J., Lewis, M., Williams, J. E., McGuire, M. A., & McGuire, M. K. (2022). Sodium and Potassium Concentrations and Somatic Cell Count of Human Milk Produced in the First Six Weeks Postpartum and Their Suitability as Biomarkers of Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis. Nutrients, 14(22), 4708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224708





