In Vitro Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fatty Acids Extracted from the Halocynthia aurantium Gonad on RAW264.7 Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Fatty Acid Extraction and Fatty Acid Profile Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Macrophage Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Production Assay
2.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.7. Western Blot Assay
2.8. Phagocytic Uptake of Macrophages
2.9. Analysis of Expression of Surface Molecules
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
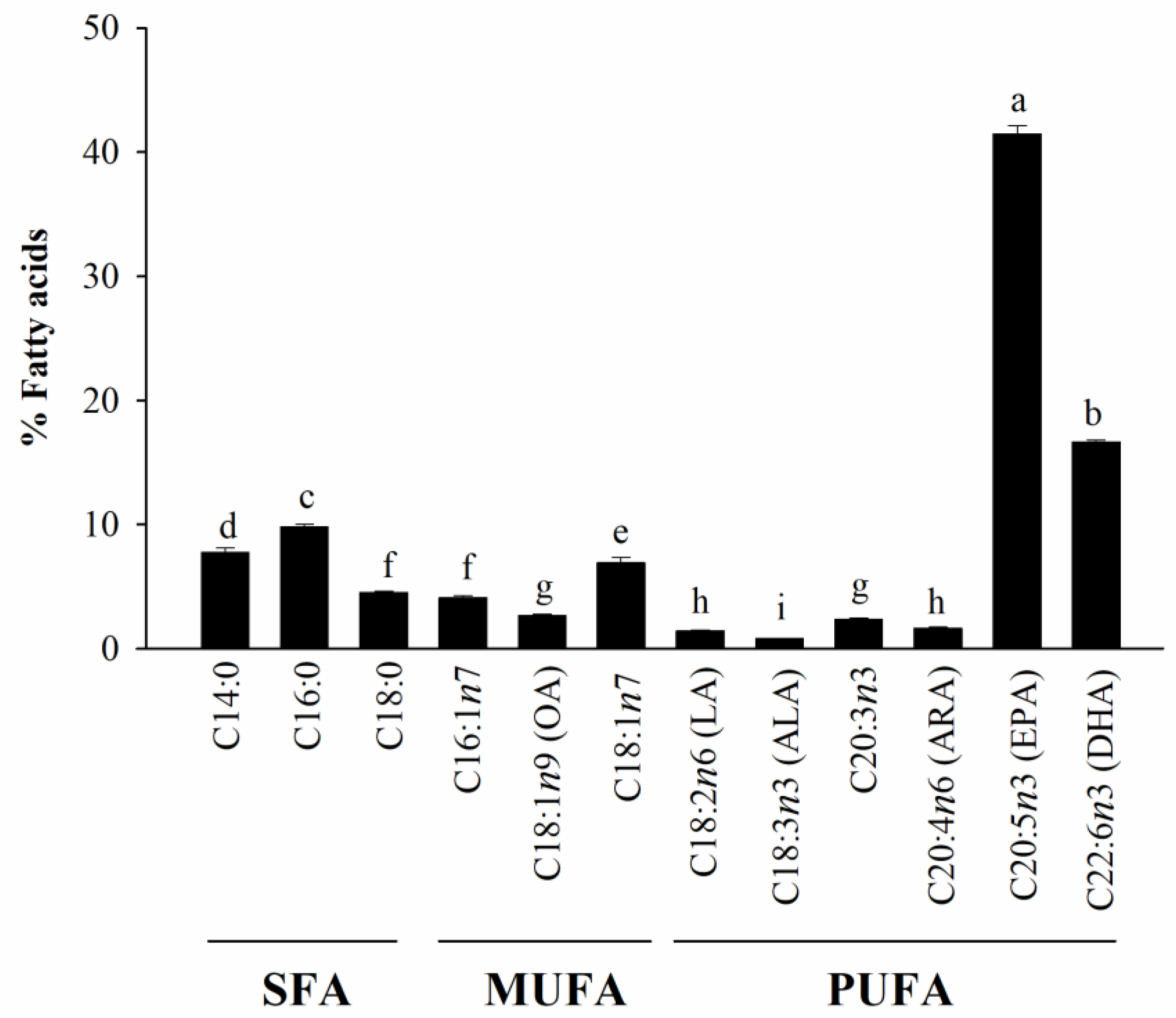
3.1. Fatty Acid Profiles of HAGF
3.2. Effects of HAGF on Cytotoxicity and NO Production in RAW264.7 Cells
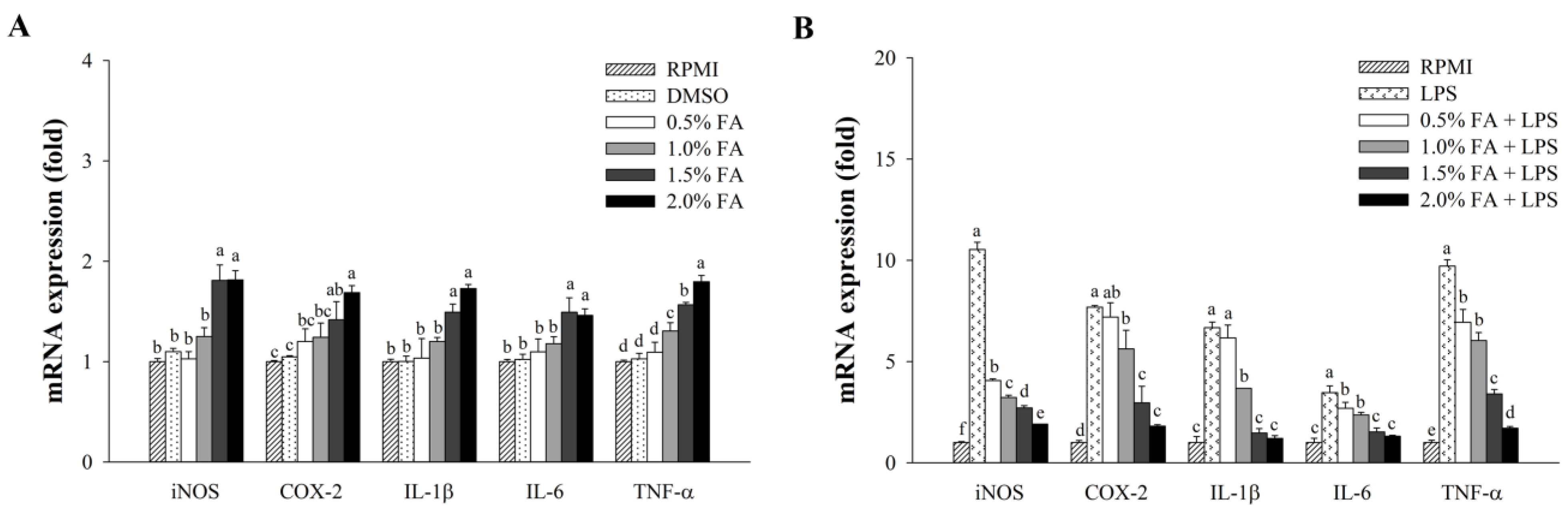
3.3. Effects of HAGF on the Expression of Immune-Related Genes
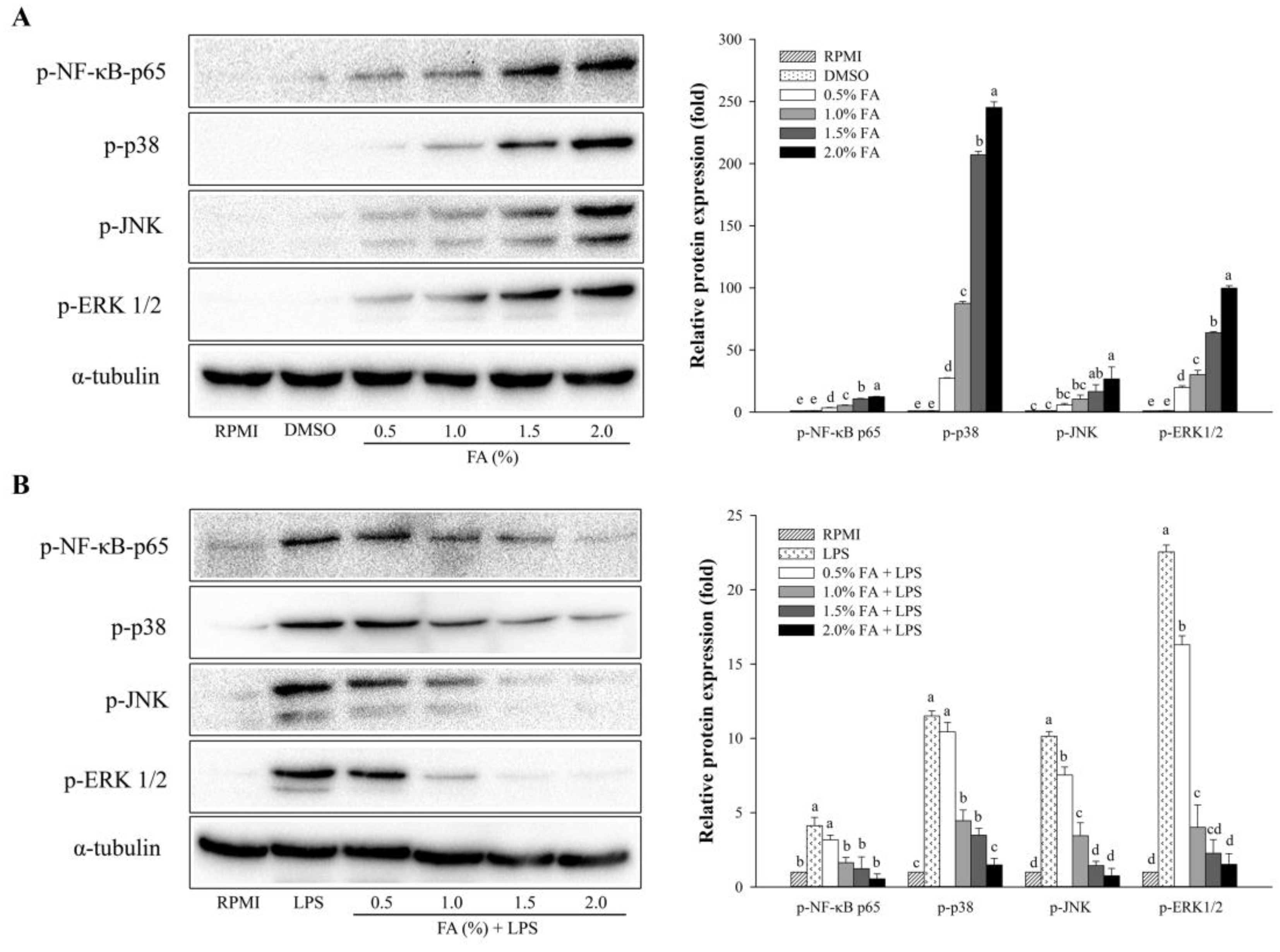
3.4. Effects of HAGF on the Activation of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways
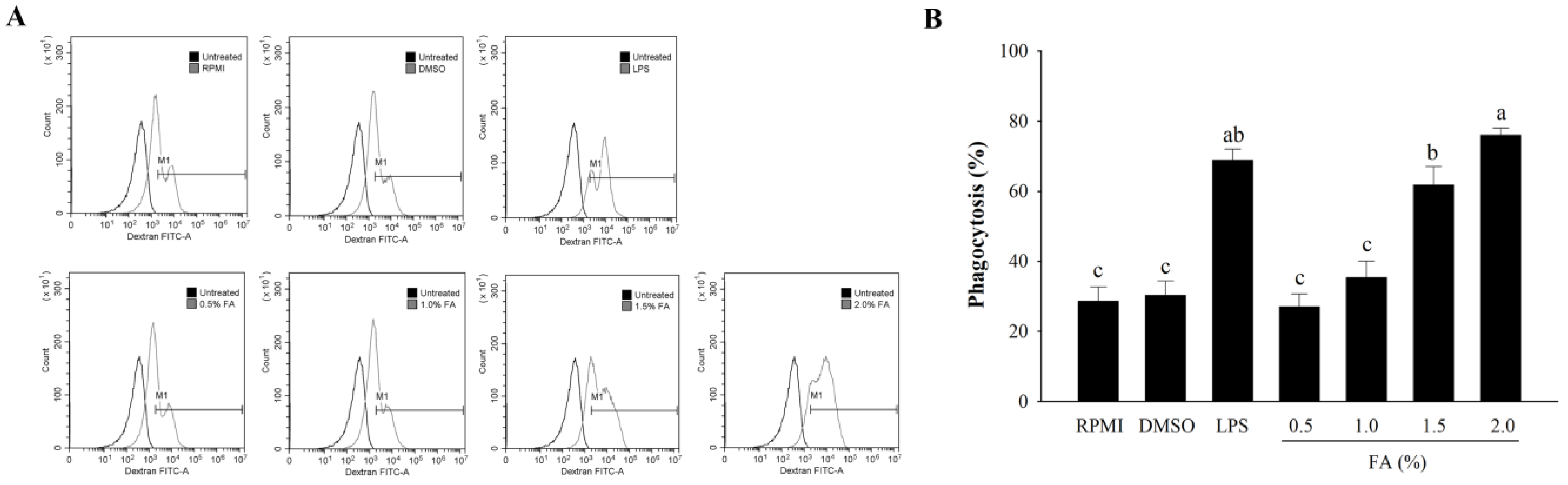
3.5. Effects of HAGF on the Phagocytosis of Macrophages
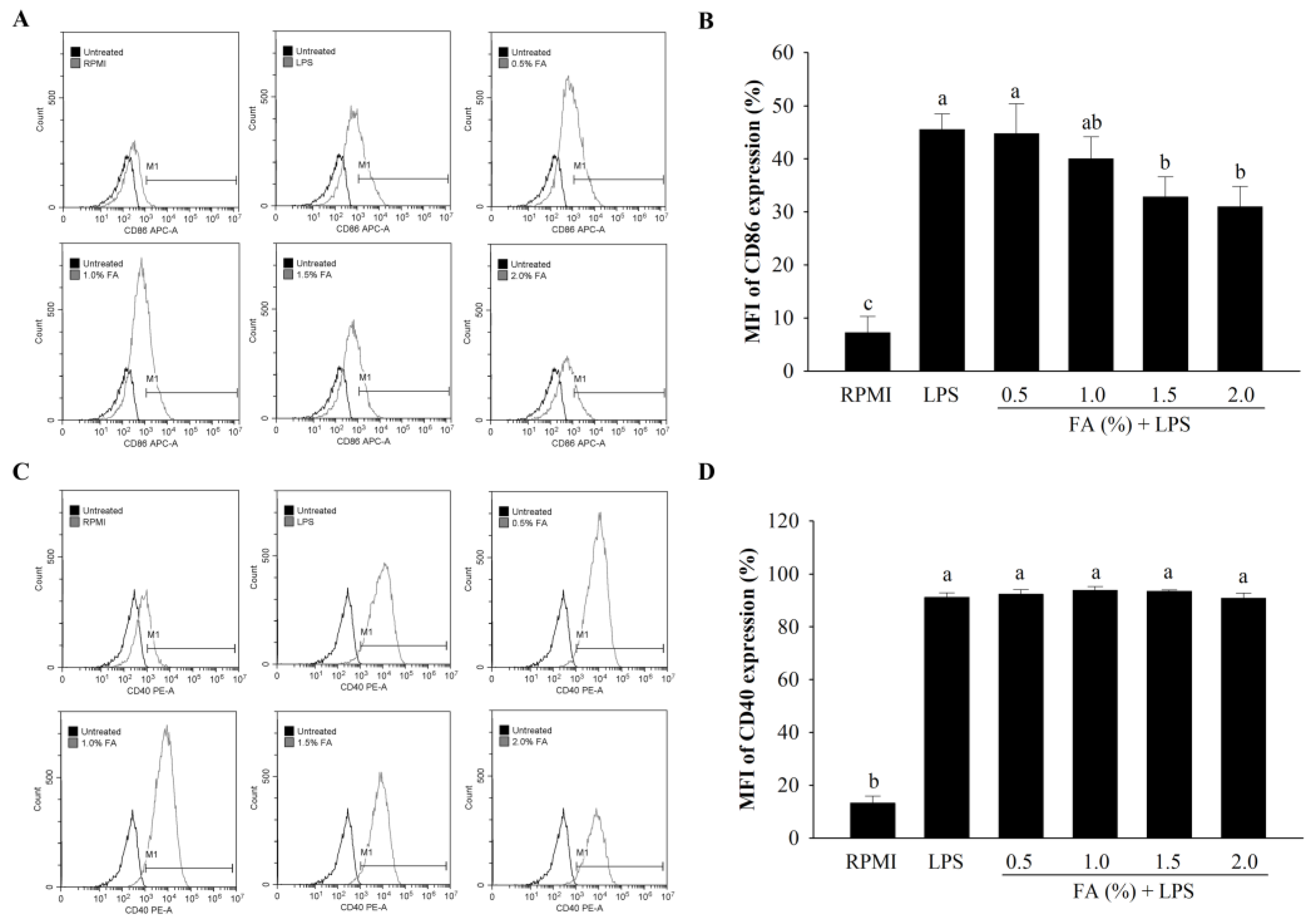
3.6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of HAGF on Cell Surface Molecule Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Kong, M.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Q.; Chen, K. Immune-enhancing activity of extracellular polysaccharides isolated from Rhizopus nigricans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Liao, K.C.; Chen, C.H. 2-phenylnaphthalene derivatives inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory mediators by downregulating of MAPK/NF-kB pathways in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168945. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in Inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.; Jarrah, A.S.; Tieri, P.; Cesareni, G.; Castiglione, F. Gene regulatory network modeling of macrophage differentiation corroborates the continuum hypothesis of polarization states. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, J.R.; Tocher, D.R.; Bell, J.G. 4-The Lipids. In Fish Nutrition, 3rd ed.; Halver, J.E., Hardy, R.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 181–257. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, R.; Eilertsen, K.-E.; Elvevoll, E.O. Health benefits of marine foods and ingredients. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Immunomodulation by omega-3 fatty acids. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2007, 77, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xue, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. Analysis of DHA-rich phospholipids from egg of squid Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2008, 21, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, N.; Higuchi, T.; Suzuki, H. Analysis of lipid classes and the fatty acid composition of the salted fish roe food products, Ikura, Tarako, Tobiko and Kazunoko. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmai, C.; Go, S.H.; Shin, I.S.; You, S.G.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.B.; Park, W.J. Immune-enhancement and anti-inflammatory activities of fatty acids extracted from Halocynthia aurantium tunic in RAW264.7 cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids improve Aβ1–40-induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, S.M.; Mullen, A.C.; Loscher, C.E.; Hurley, L.A.; Roche, H.M. Docosahexaenoic acid induces an anti-inflammatory profile in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human THP-1 macrophages more effectively than eicosapentaenoic acid. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, A.; Loscher, C.E.; Roche, H.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of EPA and DHA are dependent upon time and dose-response elements associated with LPS stimulation in THP-1-derived macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Immunomodulatory activity of docosahexenoic acid on RAW264.7 cells activation through GPR120-mediated signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, N.; Han, L.; Meng, M.; Yan, Z.; Wang, C. The immunomodulatory effect of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on the RAW264.7 cells by modification of the membrane structure and function. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monmai, C.; Jang, A.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, S.M.; You, S.; Kang, S.; Park, W.J. Immunomodulatory activities of body wall fatty acids rxtracted from Halocynthia aurantium on RAW264.7 cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Taveira, M.; Valentão, P.; Sousa, C.; Andrade, P. Fatty acids from edible sea hares: Anti-inflammatory capacity in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells involves iNOS modulation. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 8981–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Sun, L.; Niu, X.T.; Chen, X.M.; Tian, J.X.; Kong, Y.D.; Wang, G.Q. Astaxanthin protects lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in Channa argus through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.B.; Reddanna, P. Chebulagic acid (CA) attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-kB and MAPK activation in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, C.; Peng, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Z. Immune-enhancing effects of a polysaccharide PRG1-1 from Russula griseocarnosa on RAW264.7 macrophage cells via the MAPK and NF-κB signalling pathways. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, T.L.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Y.F.; Li, H.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, E.H.; Pan, S.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, K.X. Enhanced anti-inflammatory effects of DHA and quercetin in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.O.; Choi, S.S.; Seo, Y.B.; Shin, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Kim, G.D. Complete mitochondrial genome of sea peach Halocynthia aurantium (stolidobranchia: Pyuridae) from Korea. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 1007–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Effects of sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) lipids on white adipose tissue weight and blood glucose in diabetic/obese KK-Ay mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.S.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.A.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, I.H. Antifungal activity of synthetic peptide derived from halocidin, antimicrobial peptide from the tunicate, Halocynthia aurantium. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.S.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, K.N.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Son, S.M.; Lee, I.H. Biological activities of synthetic analogs of halocidin, an antimicrobial peptide from the tunicate Halocynthia aurantium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2481–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, I.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Maoka, T.; Miyashita, K. Suppressive effects of alloxanthin and diatoxanthin from Halocynthia roretzi on LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory genes in RAW264.7 cells. J. Oleo Sci. 2008, 57, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Hong, J.H. Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharides isolated from Ascidian (Halocynthia roretzi) tunic. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 44, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, R.; Mancha, M. One-step lipid extraction and fatty acid methyl esters preparation from fresh plant tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 211, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.J.; Kothapalli, K.S.D.; Lawrence, P.; Tyburczy, C.; Brenna, J.T. An alternate pathway to long-chain polyunsaturates: The FADS2 gene product Δ8-desaturates 20:2n-6 and 20:3n-3. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.A.; Lee, Y.; You, S. Water soluble sulfated-fucans with immune-enhancing properties from Ecklonia cava. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Choi, G.S.; Monmai, C.; Rod-in, W.; Jang, A.Y.; Park, W.J. Immunomodulatory activities of Ammodytes personatus egg lipid in RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, B.A.; Narayanan, N.K.; Simi, B.; Reddy, B.S. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and related proinflammatory genes by the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhule, A.; Navarro, S.; Smith, J.R.; Shepherd, D.M. Panax notoginseng attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.J.; Chiu, K.C.; Fu, M.; Chu, A.; Helton, S. Fish oil modulates macrophage P44/P42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity induced by lipopolysaccharide. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2000, 24, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-kB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalhamer, T.; McGrath, M.A.; Harnett, M.M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.S.; Kim, K.N.; Lee, Y.S.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, I.H. Halocidin: A new antimicrobial peptide from hemocytes of the solitary tunicate, Halocynthia aurantium. J. FEBS Lett. 2002, 521, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderem, A.; Underhill, D.M. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 593–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Nie, S.P.; Li, W.J.; Zheng, W.Y.; Yin, P.F.; Gong, D.M.; Xie, M.Y. Macrophage immunomodulatory activity of a purified polysaccharide isolated from Ganoderma atrum. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.; Kim, J.; Seo, C.-R.; Lee, D.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kuge, T.; Mori, T.; Kimoto, H.; Kim, J.-K. Anti-inflammatory effects of β-1,3-1,6-glucan derived from black yeast Aureobasidium pullulans in RAW264.7 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Jung, B.C.; Hong, B.I.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, W.J. Cold storage and quality stability of ascidian, Halocynthia roretzi. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 26, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Qin, T.; Qiu, F.; Song, Y.; Lin, D.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y. Immunomodulatory effects of hydroxyethylated Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide on macrophages RAW264.7. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, J.; Rod-in, W.; Monmai, C.; Jang, A.-y.; Choi, J.; Park, W.-J. In Vitro Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fatty Acids Extracted from the Halocynthia aurantium Gonad on RAW264.7 Macrophages. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214510
Lim J, Rod-in W, Monmai C, Jang A-y, Choi J, Park W-J. In Vitro Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fatty Acids Extracted from the Halocynthia aurantium Gonad on RAW264.7 Macrophages. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214510
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Junhyeok, Weerawan Rod-in, Chaiwat Monmai, A-yeong Jang, JeongUn Choi, and Woo-Jung Park. 2022. "In Vitro Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fatty Acids Extracted from the Halocynthia aurantium Gonad on RAW264.7 Macrophages" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214510
APA StyleLim, J., Rod-in, W., Monmai, C., Jang, A.-y., Choi, J., & Park, W.-J. (2022). In Vitro Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fatty Acids Extracted from the Halocynthia aurantium Gonad on RAW264.7 Macrophages. Nutrients, 14(21), 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214510





