Biological Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Patients with Sepsis-Induced ARDS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Plasma cfDNA
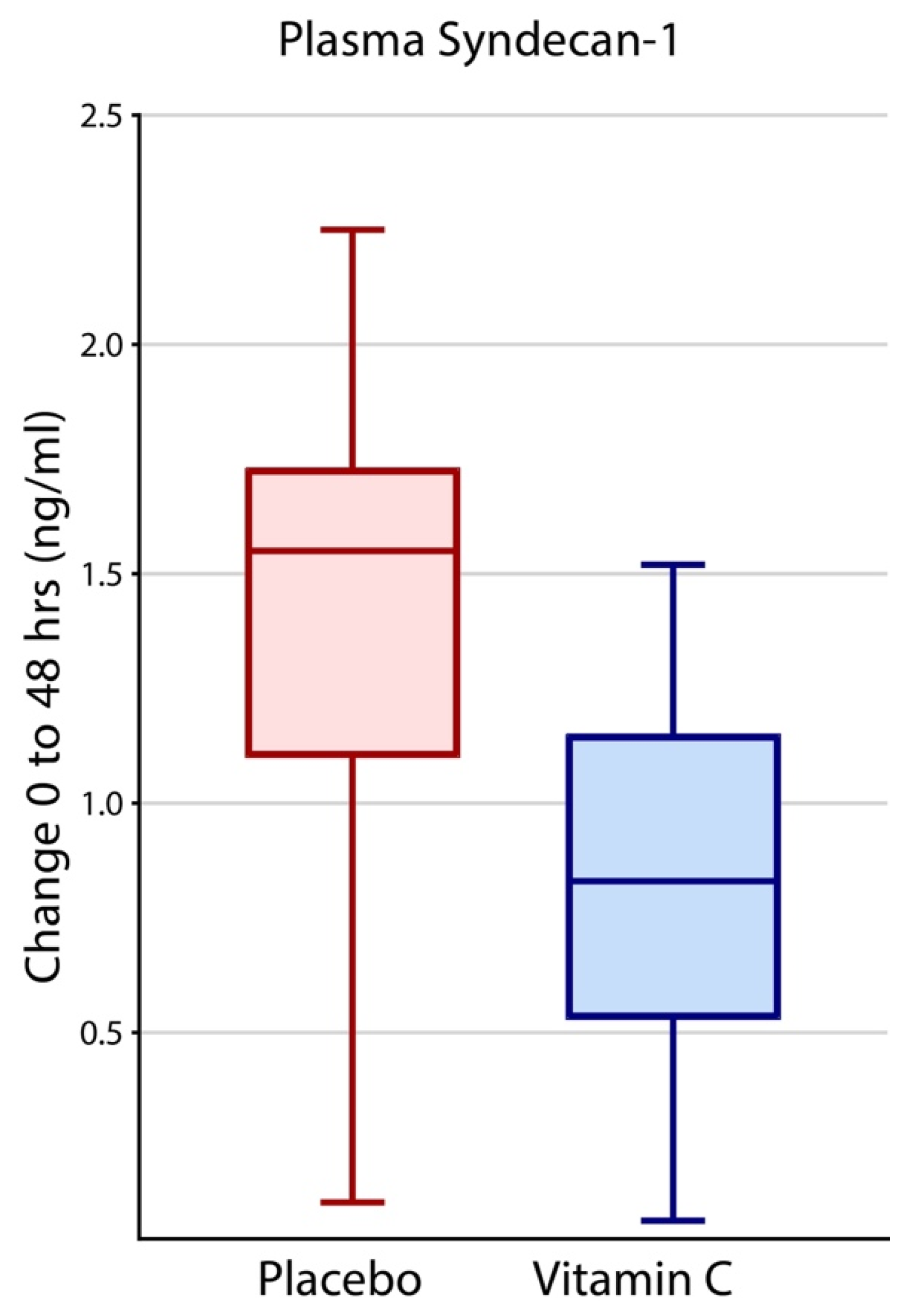
3.3. Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Plasma Syndecan-1
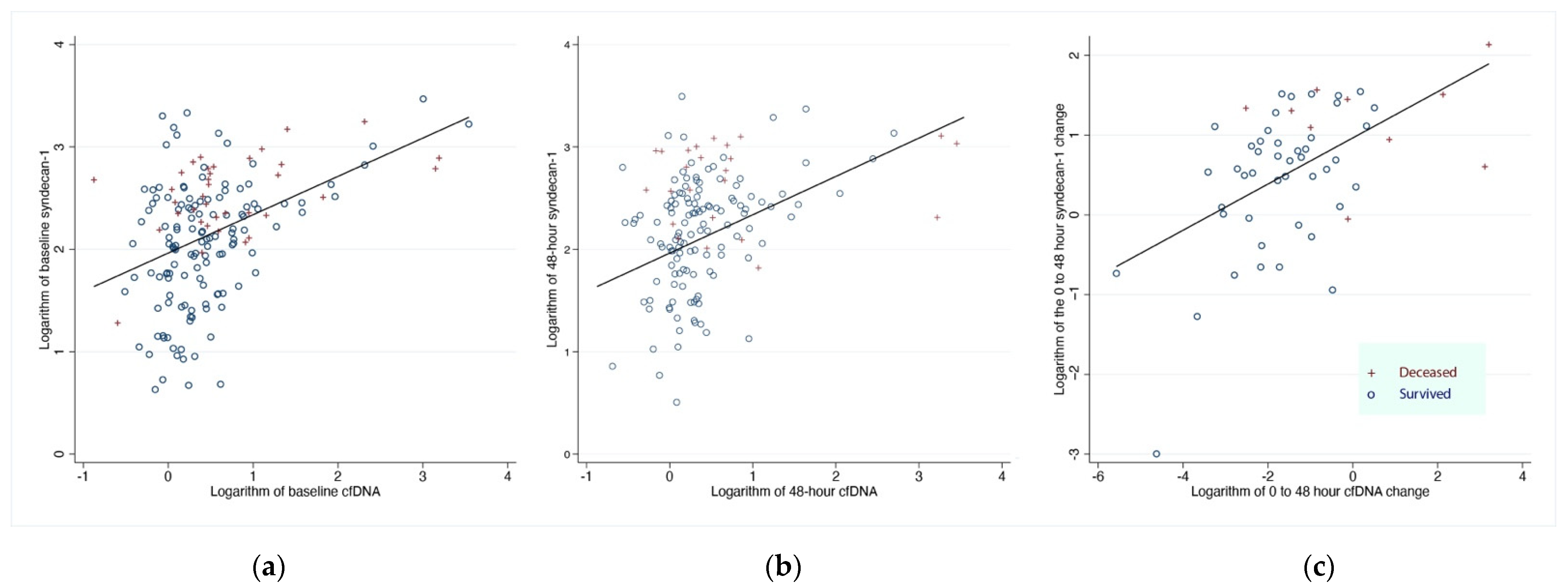
3.4. Effects of Plasma Syndecan-1 on 28-Day All-Cause Hospital Mortality
3.5. Effect of cfDNA and Syndecan-1 on Changes in Oxygenation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenfeld, G.D.; Caldwell, E.; Peabody, E.; Weaver, J.; Martin, D.P.; Neff, M.; Stern, E.J.; Hudson, L.D. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Ware, L.B.; Zimmerman, G.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, A.A., III; Syed, A.A.; Knowlson, S.; Sculthorpe, R.; Farthing, D.; Dewilde, C.; Farthing, C.A.; Larus, T.L.; Martin, E.; Brophy, D.F.; et al. Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.M.; Fisher, B.J.; Kraskauskas, D.; Farkas, D.; Brophy, D.F.; Fowler, A.A.; Natarajan, R. Vitamin C: A novel regulator of neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3131–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.J.; Kraskauskas, D.; Martin, E.J.; Farkas, D.; Wegelin, J.A.; Brophy, D.; Ward, K.R.; Voelkel, N.F.; Fowler, A.A.; Natarajan, R. Mechanisms of attenuation of abdominal sepsis induced acute lung injury by ascorbic acid. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L20–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.J.; Seropian, I.M.; Kraskauskas, D.; Thakkar, J.N.; Voelkel, N.F.; Fowler, A.A.; Natarajan, R. Ascorbic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.A.; Truwit, J.D.; Hite, R.D.; Morris, P.E.; DeWilde, C.; Priday, A.; Fisher, B.; Thacker, L.R., 2nd; Natarajan, R.; Brophy, D.F.; et al. Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients with Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.A.; Fisher, B.J.; Kashiouris, M.G. Vitamin C for Sepsis and Acute Respiratory Failure-Reply. JAMA 2020, 323, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.S.; Wickersham, N.; McNeil, J.B.; Shaver, C.M.; May, A.K.; Bastarache, J.A.; Ware, L.B. Endothelial glycocalyx degradation is more severe in patients with non-pulmonary sepsis compared to pulmonary sepsis and associates with risk of ARDS and other organ dysfunction. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Su, X.; Pan, P.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tan, H.; Wu, D.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, H.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps are indirectly triggered by lipopolysaccharide and contribute to acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, R. Impact of Intravenous Ascorbic Acid Infusion on Novel Biomarkers in Patients with Severe Sepsis. J. Pulm. Respir. Med. 2014, 4, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.S.M.J.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pflüg. Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Derangement of the endothelial glycocalyx in sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagawa, R.; Okada, H.; Takemura, G.; Suzuki, K.; Takada, C.; Yano, H.; Ando, Y.; Usui, T.; Hotta, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; et al. Ultrastructural alteration of pulmonary capillary endothelial glycocalyx during endotoxemia. Chest 2018, 154, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, L.; Bosio, E.; Macdonald, S.P.J.; Dull, R.; Fatovich, D.M.; Neil, C.; Arendts, G. Glycocalyx biomarker syndecan-1 is a stronger predictor of respiratory failure in patients with sepsis due to pneumonia, compared to endocan. J. Crit. Care 2018, 47, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimido, R.; Schmidt, E.P.; Shapiro, N.I. The glycocalyx: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic target in sepsis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, D.J.; Toltl, L.J.; Swystun, L.L.; Pogue, J.; Liaw, K.-L.; Weitz, J.I.; Cook, D.J.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Liaw, P.C.; the Canadian Critical Care Translational Biology Group. Prognostic utility and characterization of cell-free DNA in patients with severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, X.M.; Biron, B.M.; Reichner, J.S. Consequences of extracellular trap formation in sepsis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancais, E.; Mallavia, B.; Zhuo, H.; Calfee, C.S.; Looney, M.R. Maladaptive role of neutrophil extracellular traps in pathogen-induced lung injury. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.; Berkestedt, I.; Schmidtchen, A.; Ljunggren, L.; Bodelsson, M. Increased levels of glycosaminoglycans during septic shock: Relation to mortality and the antibacterial actions of plasma. Shock 2008, 30, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saukkonen, K.; Lakkisto, P.; Pettilä, V.; Varpula, M.; Karlsson, S.; Ruokonen, E.; Pulkki, K.; for the Finnsepsis Study Group. Cell-free plasma DNA as a predictor of outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, P.; Pennell, M.L.; Lemeshow, S. Standardizing the power of the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test in large data sets. Stat. Med. 2013, 32, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, O.E.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophil extracellular traps—The dark side of neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Hamaguchi, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Irisawa, T.; Seki, M.; Tasaki, O.; Hosotsubo, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Akeda, Y.; et al. Presence of neutrophil extracellular traps and citrullinated histone H3 in the bloodstream of critically ill patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojima, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Hirose, T.; Hamaguchi, S.; Tasaki, O.; Kojima, T.; Tomono, K.; Ogura, H.; Shimazu, T. Serial change of neutrophil extracellular traps in tracheal aspirate of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: Report of three cases. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Joshi, M.; Filippova, M.; Erne, P.; Hasler, P.; Hahn, S.; Resink, T.J. Activated endothelial cells induce neutrophil extracellular traps and are susceptible to NETosis-mediated cell death. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3193–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qi, H.; Kan, K.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote hypercoagulability in patients with sepsis. Shock 2017, 47, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.P.; Yang, Y.; Janssen, W.J.; Gandjeva, A.; Perez, M.J.; Barthel, L.; Zemans, R.L.; Bowman, J.C.; Koyanagi, D.E.; Yunt, Z.X.; et al. The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx regulates neutrophil adhesion and lung injury during experimental sepsis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Ogura, H.; Hirose, T.; Shimizu, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Maruyama, I.; Shimazu, T. Circulating syndecan-1 predicts the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2018, 43, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, D.; Ray, S.; Srivastava, L.M.; Bhargava, S. Evolution of serum hyaluronan and syndecan levels in prognosis of sepsis patients. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rannikko, J.; Seiskari, T.; Huttunen, R.; Tarkiainen, I.; Jylhävä, J.; Hurme, M.; Syrjänen, J.; Aittoniemi, J. Plasma cell-free DNA and qSOFA score predict 7-day mortality in 481 emergency department bacteraemia patients. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Stojkov, D.; Germic, N.; Simon, D.; Wang, X.; Benarafa, C.; Simon, H. Untangling “NETosis” from NETs. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Baseline (n = 167) | 48-Hours (n = 154) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HDIVC (n = 84) | Placebo (n = 83) | HDIVC (n = 82) | Placebo (n = 72) |
| Survived and in the ICU, n (%) | 84 (100) | 83 (100) | 82 (97.6) | 72 (86.7) |
| Age, years (mean, SD) | 52.7 (17.5) | 56.8 (15.7) | 52.3 (17.3) | 55.8 (15.7) |
| Men, n (%) | 45 (53.6) | 45 (54.2) | 44 (53.7) | 39 (54.2) |
| Subjects with ABG available, n (%) | 80 (95.2) | 82 (98.8) | 62 (75.6) | 65 (90.2) |
| Subjects with cfDNA available plasma, n (%) | 84 (100) | 83 (100) | 81 (98.8) | 70 (97.2) |
| Subjects with syndecan-1 available plasma, n (%) | 83 (98.8) | 83 (100) | 80 (96.4) | 70 (97.2) |
| Predictor | Odds Ratio | Standard Error | z | p-Value | 95% Confidence Intervals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline syndecan-1, each unit increase, ng/mL | 1.3 | 0.1 | 4.9 | <0.001 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| 48 h Δsyndecan-1, each unit increase, ng/mL | 1.3 | 0.1 | 3.2 | 0.001 | 1.1 | 1.6 |
| Baseline cfDNA, each unit increase, ng/µL | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.650 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| 48 h ΔcfDNA, each unit increase, ng/µL | 1.8 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 0.035 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| Constant | 0.0 | 0.0 | −5.7 | <0.001 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, X.; Kashiouris, M.G.; L’Heureux, M.; Fisher, B.J.; Leichtle, S.W.; Truwit, J.D.; Nanchal, R.; Hite, R.D.; Morris, P.E.; Martin, G.S.; et al. Biological Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Patients with Sepsis-Induced ARDS. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204415
Qiao X, Kashiouris MG, L’Heureux M, Fisher BJ, Leichtle SW, Truwit JD, Nanchal R, Hite RD, Morris PE, Martin GS, et al. Biological Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Patients with Sepsis-Induced ARDS. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204415
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Xian, Markos G. Kashiouris, Michael L’Heureux, Bernard J. Fisher, Stefan W. Leichtle, Jonathon D. Truwit, Rahul Nanchal, Robert Duncan Hite, Peter E. Morris, Greg S. Martin, and et al. 2022. "Biological Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Patients with Sepsis-Induced ARDS" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204415
APA StyleQiao, X., Kashiouris, M. G., L’Heureux, M., Fisher, B. J., Leichtle, S. W., Truwit, J. D., Nanchal, R., Hite, R. D., Morris, P. E., Martin, G. S., Sevransky, J., & Fowler, A. A. (2022). Biological Effects of Intravenous Vitamin C on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Patients with Sepsis-Induced ARDS. Nutrients, 14(20), 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204415





