Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.1.1. Study Population
2.1.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.1.3. Weight Loss Achieved by Bariatric Surgery and Dietary Treatment
2.1.4. Surgical Procedures and Tissue Collection
2.1.5. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Analytical Measurements
2.3. Analysis of Gene Expression Levels
2.4. Histological Analysis of NTN-1 and NEO-1
2.5. Adipocyte and Monocyte Cultures
2.6. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Circulating Levels of NTN-1 Are Increased in Obesity and T2D and Decreased after Conventional Weight Loss
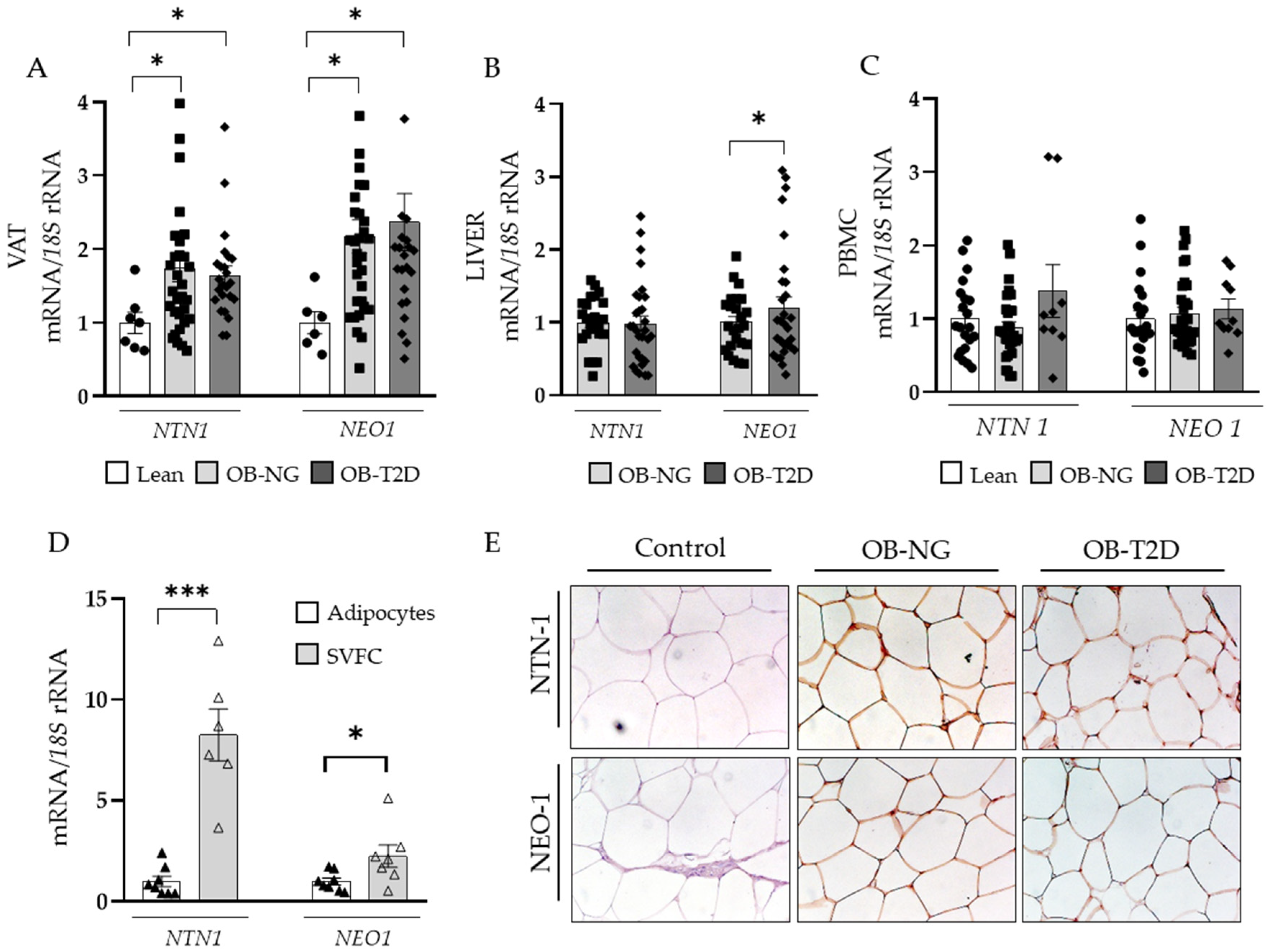
3.3. Upregulated Gene Expression Levels of NTN1 in Visceral Adipose Tissue in Obesity
3.4. NTN1 and NEO1 Are Associated with ECM Remodelling and Inflammation in VAT
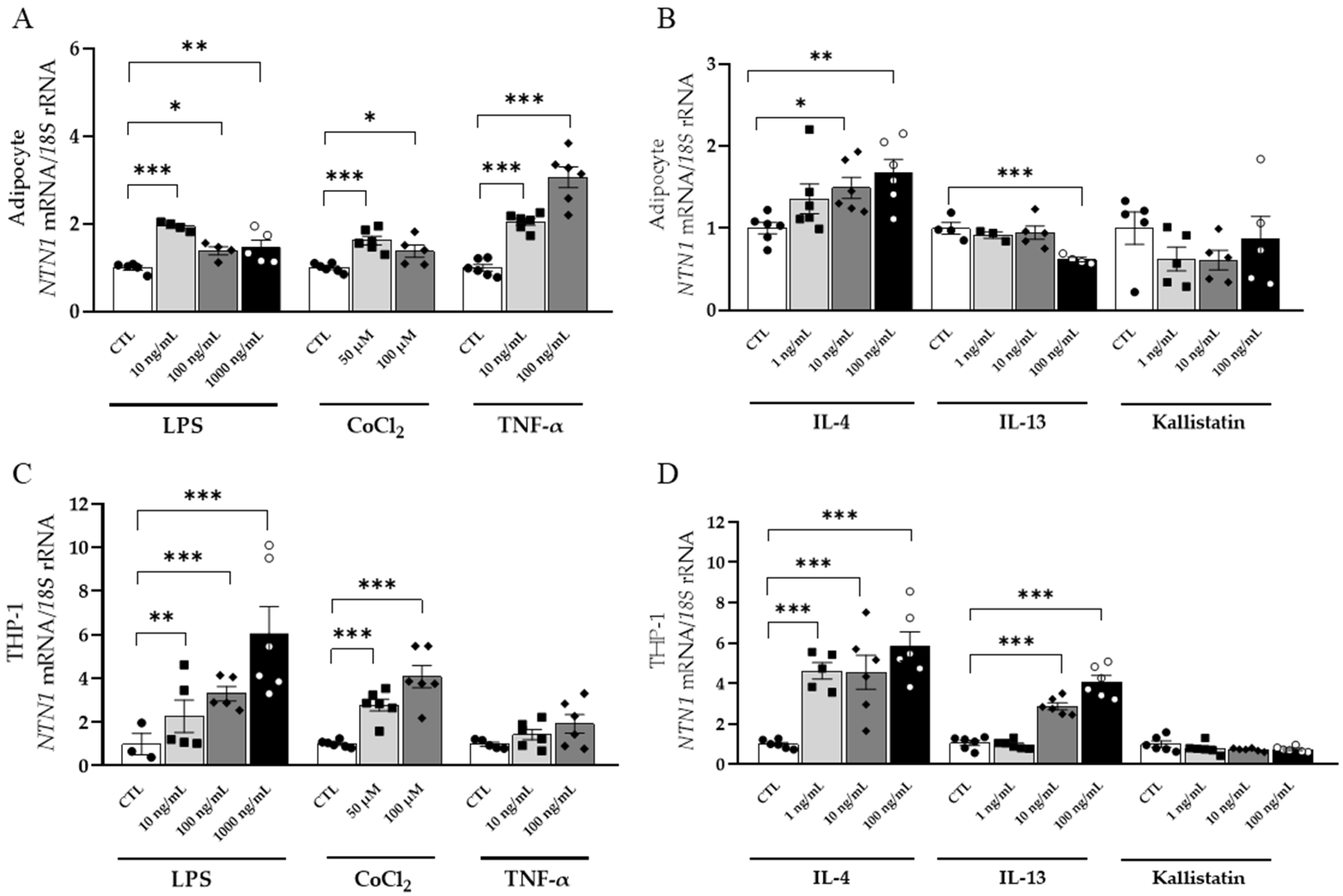
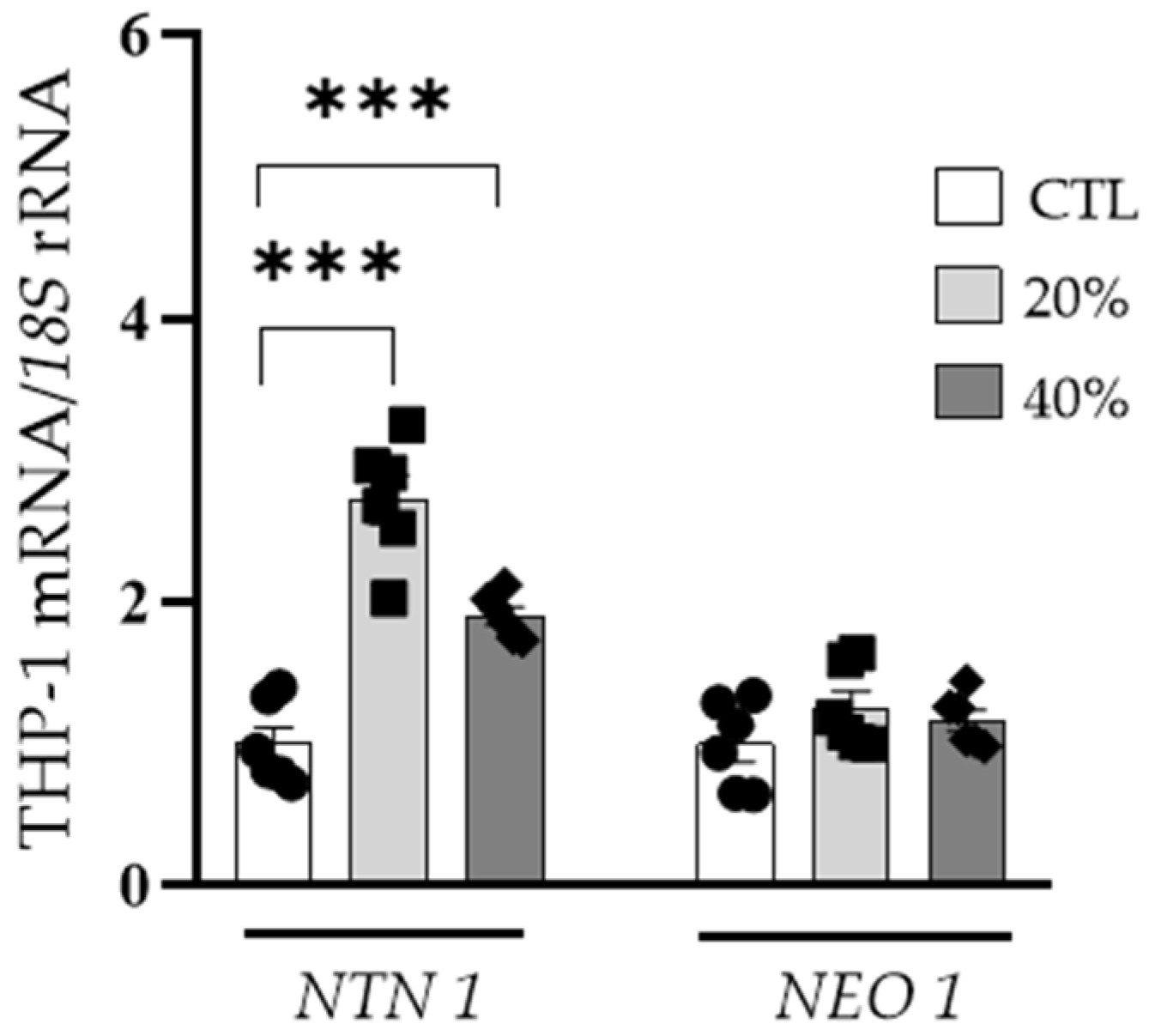
3.5. Inflammation-Related Factors Regulate NTN1 Expression Levels in Human Visceral Adipocytes and THP-1-Derived Macrophages
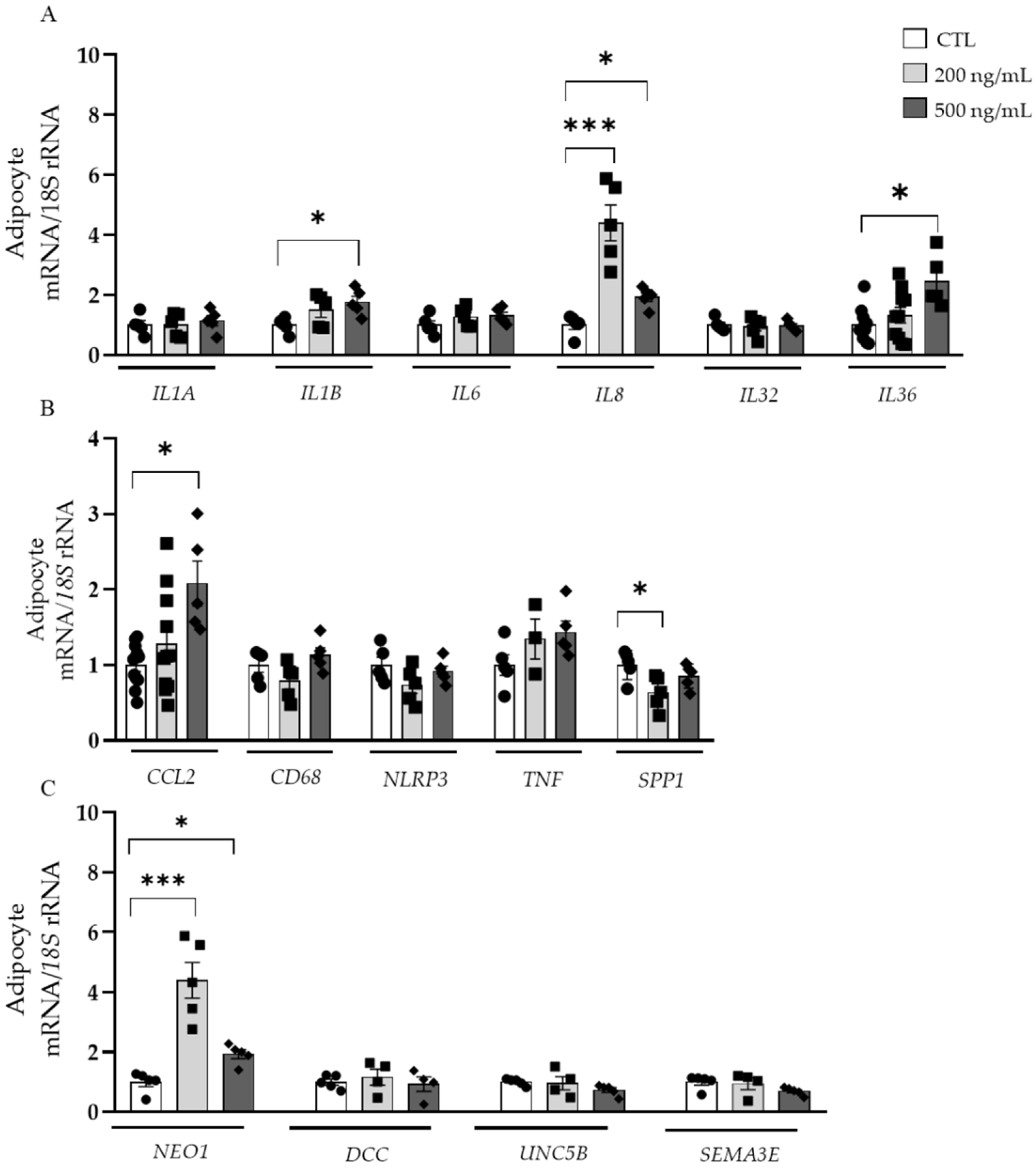
3.6. Effects of NTN-1 in the Gene Expression of Inflammation- and Chemotactic-Related Factors in Visceral Adipocytes
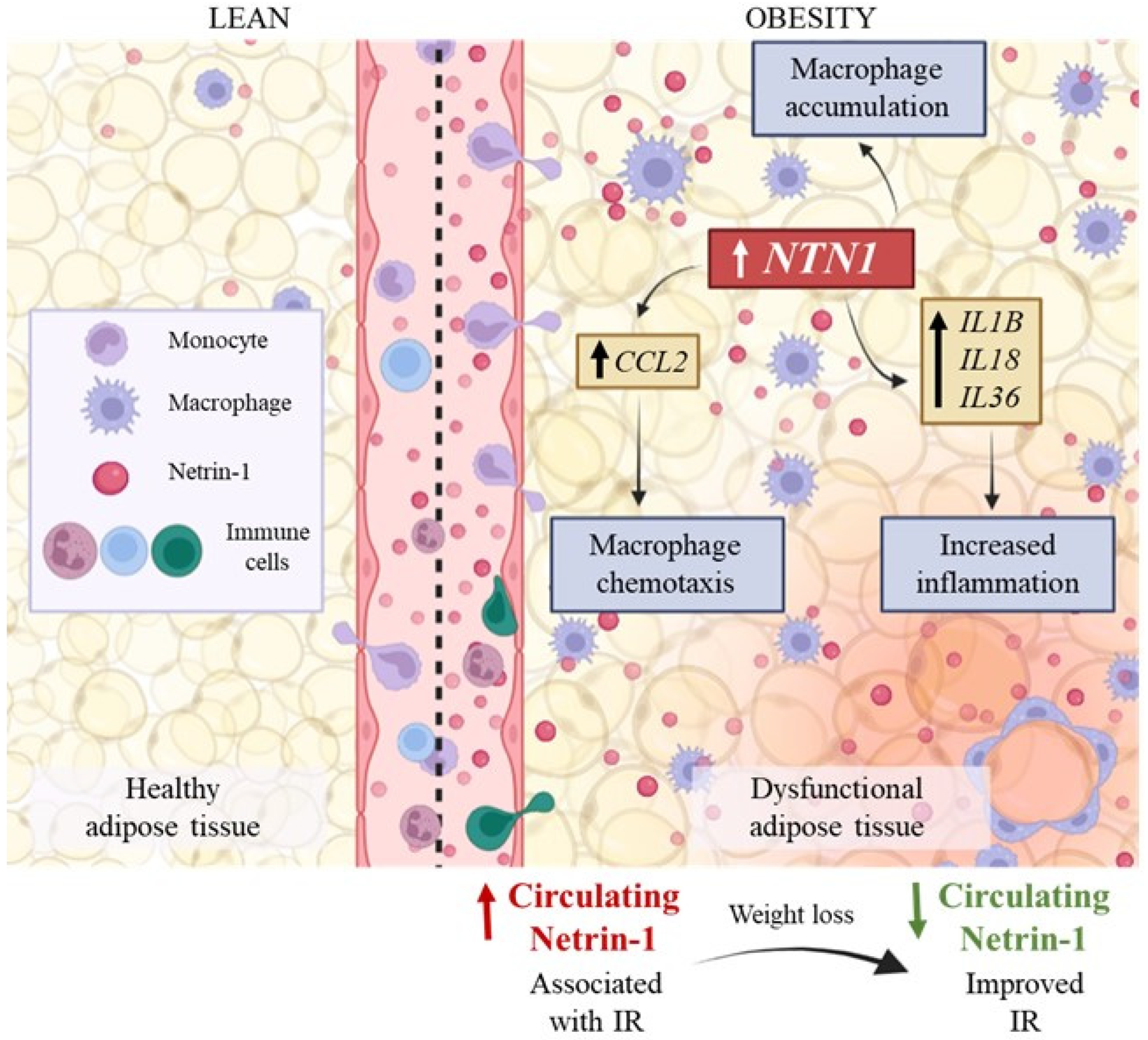
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catalán, V.; Avilés-Olmos, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Fernández-Formoso, J.A.; Kiortsis, D.; Portincasa, P.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Frühbeck, G. Time to consider the “Exposome Hypothesis” in the development of the obesity pandemic. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yárnoz-Esquiroz, P.; Olazarán, L.; Aguas-Ayesa, M.; Perdomo, C.M.; García-Goñi, M.; Silva, C.; Fernández-Formoso, J.A.; Escalada, J.; Montecucco, F.; Portincasa, P.; et al. “Obesities”: Position statement on a complex disease entity with multifaceted drivers. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypess, A.M. Reassessing human adipose tissue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Yin, K. Netrin-1: An emerging player in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022, 64, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegon, L.; Schlegel, M. Netrin-1: A modulator of macrophage driven acute and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnault, R.; Verzeroli, C.; Fournier, C.; Michelet, M.; Redavid, A.R.; Chicherova, I.; Plissonnier, M.L.; Adrait, A.; Khomich, O.; Chapus, F.; et al. Hepatic inflammation elicits production of proinflammatory netrin-1 through exclusive activation of translation. Hepatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, M.; Sharma, M.; Brown, E.J.; Newman, A.A.C.; Cyr, Y.; Afonso, M.S.; Corr, E.M.; Koelwyn, G.J.; van Solingen, C.; Guzman, J.; et al. Silencing myeloid netrin-1 induces inflammation resolution and plaque regression. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeva, I.; Gateva, A.; Assyov, Y.; Karamfilova, V.; Velikova, T.; Kamenov, Z. Relationship between circulating netrin-1 levels, obesity, prediabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Arch. Physiol. Biochem 2020, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkhelawon, B.; Hennessy, E.J.; Ménager, M.; Ray, T.D.; Sheedy, F.J.; Hutchison, S.; Wanschel, A.; Oldebeken, S.; Geoffrion, M.; Spiro, W.; et al. Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Schlegel, M.; Brown, E.J.; Sansbury, B.E.; Weinstock, A.; Afonso, M.S.; Corr, E.M.; Van Solingen, C.; Shanley, L.C.; Ramasamy, R.; et al. Netrin-1 alters adipose tissue macrophage fate and function in obesity. Immmunometabolism 2019, 1, e190010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.H.; Wu, C.H.; Chiu, C.J.; Chen, W.T.; Chang, Y.C.; Wabitsch, M.; Chang, M.S. IL-20 is involved in obesity by modulation of adipogenesis and macrophage dysregulation. Immunology 2021, 164, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkhelawon, B.; Yang, Y.; van Gils, J.M.; Hewing, B.; Rayner, K.J.; Parathath, S.; Guo, L.; Oldebeken, S.; Feig, J.L.; Fisher, E.A.; et al. Hypoxia induces netrin-1 and Unc5b in atherosclerotic plaques: Mechanism for macrophage retention and survival. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gils, J.M.; Derby, M.C.; Fernandes, L.R.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Ray, T.D.; Rayner, K.J.; Parathath, S.; Distel, E.; Feig, J.L.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I.; et al. The neuroimmune guidance cue netrin-1 promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting the emigration of macrophages from plaques. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Jin, J.; Bai, W.; Li, J.; Shan, X. Netrin-1 prevents the attachment of monocytes to endothelial cells via an anti-Inflammatory effect. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.V.; Jayakumar, C.; Ramesh, G. Netrin-1-treated macrophages protect the kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury and suppress inflammation by inducing M2 polarization. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F948–F957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, E.; Ridyard, D.; Badulak, A.; Giebler, A.; Shabeka, U.; Werner, T.; Clambey, E.; Moldovan, R.; Zimmerman, M.A.; Eltzschig, H.K.; et al. Protective role for netrin-1 during diabetic nephropathy. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Ramírez, B.; Valentí, V.; Becerril, S.; Rodríguez, A.; Moncada, R.; Baixauli, J.; Silva, C.; Escalada, J.; et al. Serum levels of IL-1 RA increase with obesity and type 2 diabetes in relation to adipose tissue dysfunction and are reduced after bariatric rurgery in parallel to adiposity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathologic patterns and biopsy evaluation in clinical research. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Domingo, P.; Moncada, R.; Valentí, V.; Salvador, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F.; et al. FGF19 and FGF21 serum concentrations in human obesity and type 2 diabetes behave differently after diet- or surgically-induced weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruzábal, F.J.; Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Archanco, M.; Burrell, M.A. Immunocytochemical detection of leptin in non-mammalian vertebrate stomach. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 128, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rotellar, F.; Silva, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Salvador, J.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Frühbeck, G. Validation of endogenous control genes in human adipose tissue: Relevance to obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; García-Navarro, S.; Rotellar, F.; Valentí, V.; Silva, C.; Gil, M.J.; Salvador, J.; Burrell, M.A.; et al. Insulin- and leptin-mediated control of aquaglyceroporins in human adipocytes and hepatocytes is eediated via the PI3K/Akt/MTOR signaling cascade. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E586–E597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Moore, K.J. The semaphorin 3E/PlexinD1 axis regulates macrophage inflammation in obesity. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, E.; Marakoğlu, K.; Kizmaz, M.; Ünlü, A. Evaluation of netrin-1 levels and albuminuria in patients with diabetes. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, Y.H. Relationship between circulating netrin-1 concentration, impaired fasting glucose, and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ke, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q. The level of netrin-1 is decreased in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2016, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, P.; Song, W.; Fu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Xi, L.; Luo, X.; et al. A randomised, open-label study of insulin glargine or neutral protamine hagedorn insulin in chinese paediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2016, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, J.B.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Noakes, M.; Belobrajdic, D.P.; Buckley, J.D.; Clifton, P.M. Effects of weight loss from a very-low-carbohydrate diet on endothelial function and markers of cardiovascular disease risk in subjects with abdominal obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Rotellar, F.; Valentí, V.; Silva, C.; Gil, M.J.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G. Increased circulating and visceral adipose tissue expression levels of YKL-40 in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes are related to inflammation: Impact of conventional weight loss and gastric bypass. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenbach, A.; Stoll, F.; Mann, O.; Busch, P.; Huber, T.B.; Kielstein, H.; Bähr, I.; Aberle, J. Long-term improvement of chronic low-grade inflammation after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Calderon, J.R.; Cuellar-Tamez, R.; Castillo, E.C.; Luna-Ceron, E.; García-Rivas, G.; Elizondo-Montemayor, L. Metabolic shift precedes the resolution of inflammation in a cohort of patients undergoing bariatric and metabolic surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, M.R.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, Y.; Garcia-Navarro, S.; Gracia-Navarro, F.; Tinahones, F.; López-Miranda, J.; Frühbeck, G.; Vázquez-Martínez, R.; Malagón, M.M. Rab18 Dynamics in adipocytes in relation to lipogenesis, lipolysis and obesity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, N.P.; Komatsuzaki, K.; Fraser, I.P.; Tseng, A.A.; Prodhan, P.; Moore, K.J.; Kinane, T.B. Netrin-1 inhibits leukocyte migration in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14729–14734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, C.; Wang, X. Netrin-1 reduces lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by increasing the proportion of regulatory T cells. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520926415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xing, H.; Mao, A.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Quan, X.; Li, L. Netrin-1 attenuates cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury and generates alternatively activated macrophages. Inflammation 2014, 37, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, N.K.; Li, J.; Kim, B.; Mills, T.; Pei, G.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, W.; Eltzschig, H.K.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent induction of myeloid-derived netrin-1 attenuates natural killer cell infiltration during endotoxin-induced lung injury. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Becerril, S.; Unamuno, X.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; et al. Novel protective role of kallistatin in obesity by limiting adipose tissue low grade inflammation and oxidative stress. Metabolism 2018, 87, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, M.; Meier, M.; Delcros, J.G.; Nikodemus, D.; Reuten, R.; Patel, T.R.; Goldschneider, D.; Orriss, G.; Krahn, N.; Boussouar, A.; et al. Structural decoding of the netrin-1/UNC5 interaction and its therapeutical implications in cancers. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, C.J.; Stienstra, R.; Joosten, L.A.; Netea, M.G. Inflammation links excess fat to insulin resistance: The role of the interleukin-1 family. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lean | Obesity with Normoglycaemia | Obesity with Type 2 Diabetes | Reference Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (male, female) | 18 (8, 10) | 32 (7, 25) | 41 (13, 28) | |
| Age (years) | 42 ± 5 | 40 ± 3 | 47 ± 2 | - |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.3 ± 0.7 | 43.4 ± 1.6 *** | 44.3 ± 1.1 *** | - |
| Body fat (%) | 22.1 ± 1.9 | 52.6 ± 1.5 *** | 49.5 ± 1.2 *** | - |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 0.87 ± 0.02 * | 1.00 ± 0.01 *** | - |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 105 ± 2 | 128 ± 3 *** | 138 ± 3 ***,† | <135 mm Hg |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 66 ± 2 | 83 ± 2 ** | 87 ± 2 *** | <85 mm Hg |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 88 ± 4 | 90 ± 2 | 130 ± 8 ***,††† | 75–100 mg/dL |
| 2h OGTT glucose (mg/dL) | ND | 119 ± 3 | 167 ± 8 ††† | <140 mg/dL |
| Fasting insulin (µU/mL) | 6.9 ± 1.3 | 16.3 ± 2.0 | 34.2 ± 7.0 **,† | 5.0–29.1 µU/mL |
| 2h OGTT insulin (µU/mL) | ND | 116 ± 17 | 154 ± 15 ††† | - |
| HOMA | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 8.6 ± 0.8 *** | - |
| QUICKI | 0.375 ± 0.016 | 0.324 ± 0.006 ** | 0.291 ± 0.005 ***,††† | - |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 65 ± 9 | 99 ± 8 | 147 ± 9 ***,†† | <150 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 168 ± 6 | 198 ± 8 | 184 ± 5 | <200 mg/dL |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 95 ± 8 | 126 ± 4 * | 111 ± 4 | <130 mg/dL |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 68 ± 5 | 53 ± 3 * | 44 ± 2 ***,† | >40/> 50 mg/dL |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 8.2 ± 1.8 | 61.6 ± 6.3 *** | 43.5 ± 6.2 ** | 2.0–10.4 mg/dL |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 6.1 ± 0.2 ** | 2.4–5.7 mg/dL |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 9.7 ± 2.3 ** | 8.8 ± 1.4 * | <5 mg/L |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 167 ± 34 | 385 ± 25 ** | 423 ± 18 *** | 150–400 mg/dL |
| von Willebrand factor (%) | 38 ± 2 | 157 ± 39 * | 154 ± 10 * | 75–125% |
| Homocysteine (µmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 9.1 ± 0.7 | 11.6 ± 1.1 * | 0–12 μmol/L |
| Leucocytes (×109) | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.4 | 4.8–10.8 × 109 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 29 ± 2 | 30 ± 1 | 29 ± 1 | 20–50% |
| Neutrophils (%) | 57 ± 2 | 61 ± 2 | 61 ± 1 | 45–75% |
| Monocytes (%) | 8.7 ± 0.9 | 6.6 ± 0.3 * | 7.1 ± 0.3 * | 2–9% |
| Eosinophils (%) | 4.5 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 0.4 ** | 2.6 ± 0.2 * | 0–6 % |
| Basophils (%) | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0–% |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 14 ± 1 | 22 ± 3 | 21 ± 2 | <32 U/L |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 10 ± 4 | 29 ± 6 * | 31 ± 3 * | <33 U/L |
| γ- glutamyltransferase (U/L) | 12 ± 2 | 28 ± 6 | 44 ± 9 | <40 U/L |
| Netrin-1 (pg/mL) | 578 ± 33 | 924 ± 64 *** | 841 ± 50 *** | - |
| Neogenin-1 (pg/mL) | 2163 ± 180 | 1967 ± 143 | 1492 ± 129 | - |
| Circulating NTN-1 Levels | ||
|---|---|---|
| r | p | |
| Age | 0.04 | 0.738 |
| Weight | 0.35 | 0.002 |
| Body mass index | 0.39 | 0.001 |
| Body fat | 0.34 | 0.004 |
| Waist circumference | 0.31 | 0.009 |
| Fasting glucose | −0.01 | 0.919 |
| Fasting insulin | 0.40 | 0.001 |
| HOMA | 0.27 | 0.032 |
| QUICKI | −0.26 | 0.037 |
| Triglycerides | 0.12 | 0.350 |
| Cholesterol | 0.03 | 0.790 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.08 | 0.490 |
| HDL-cholesterol | −0.24 | 0.059 |
| Leptin | 0.36 | 0.035 |
| Fibrinogen | 0.29 | 0.046 |
| von Willebrand factor | 0.07 | 0.719 |
| C-reactive protein | 0.20 | 0.251 |
| Conventional Diet | RYGB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before WL | After WL | Before WL | After WL | |
| n (male, female) | 14 (6, 8) | 14 (6, 8) | 23 (8, 15) | 23 (8, 15) |
| Age (years) | 47 ± 4 | 48 ± 4 | 43 ± 3 | 44 ± 3 |
| Weight (kg) | 95.1 ± 5.8 | 82.2 ± 4.7 *** | 119.7± 4.7 | 80.8 ± 3.2 ††† |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 34.2 ± 1.5 | 29.6 ± 1.2 *** | 44.5± 1.2 | 30.0 ± 0.8 ††† |
| Body fat (%) | 43.8 ± 1.2 | 37.1 ± 2.5 *** | 52.1 ± 1.2 | 35.8 ± 1.7 ††† |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 109.1 ± 3.8 | 97.6 ± 3.7 *** | 127.3 ± 2.7 | 96.13 ± 2.4 ††† |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.03 * | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.02 †† |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 94.2 ± 2.9 | 91.8 ± 1.9 | 110.4 ± 9.1 | 93.7 ± 5.6 †† |
| Fasting insulin (μU/mL) | 10.9 ± 2.1 | 9.7 ± 2.1 | 18.4 ± 3.0 | 5.39 ± 1.4 †† |
| HOMA | 2.61 ± 1.63 | 2.28 ± 1.60 | 5.64 ± 4.32 | 1.38 ± 1.58 |
| QUICKI | 0.344 ± 0.039 | 0.352 ± 0.050 | 0.315 ± 0.034 | 0.393 ± 0.052 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 120 ± 15 | 81 ± 8 ** | 131 ± 28 | 119 ± 50 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 202 ± 11 | 177 ± 7 * | 200 ± 13 | 174 ± 15 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 123 ± 10 | 108 ± 6 | 120 ± 11 | 90 ± 1 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 54 ± 3 | 52 ± 3 | 50 ± 4 | 61 ± 5 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 26.86 ± 7 | 15.9 ± 3.9 | 31.5 ± 3.2 | 9.1 ± 1.2 ††† |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | ND | ND | 371 ± 20 | 350 ± 25 |
| Homocysteine (µmol/L) | ND | ND | 7.28 ± 0.43 | 6.12 ± 0.70 |
| CRP (mg/L) | ND | ND | 0.52 ± 0.1 | 0.08 ± 0.02 † |
| Gene | Lean | Obesity with Normoglycaemia | Obesity with Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 7 | 31 | 24 |
| ADIPOQ | 1.00 ± 0.28 | 0.28 ± 0.05 ** | 0.33 ± 0.04 ** |
| ASC | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 1.44 ± 0.10 ** | 1.71 ± 0.11 *** |
| IL1A | 1.00 ± 0.34 | 0.85 ± 0.12 | 1.43 ± 0.34 |
| IL1B | 1.00 ± 0.53 | 2.13 ± 0.33 * | 6.25 ± 1.61 **,† |
| IL6 | 1.00 ± 0.40 | 5.08 ± 2.34 * | 6.18 ± 1.06 ***,† |
| MMP2 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | 1.35 ± 0.16 | 1.68 ± 0.22 |
| MMP9 | 1.00 ± 0.55 | 2.56 ± 0.74 * | 3.76 ± 0.73 *** |
| NLRP3 | 1.00 ± 0.22 | 4.41 ± 0.77 *** | 4.25 ± 0.54 *** |
| NOD2 | 1.00 ± 0.34 | 2.13 ± 0.61 * | 2.52 ± 0.36 ** |
| TGFB | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 1.41 ± 0.13 | 2.36 ± 0.25 ***,†† |
| TNC | 1.00 ± 0.20 | 7.76 ± 1.77 ** | 6.91 ± 1.27 *** |
| TNF | 1.00 ± 0.39 | 1.30 ± 0.15 * | 1.40 ± 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mentxaka, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Ramírez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Neira, G.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Silva, C.; Unamuno, X.; et al. Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204372
Mentxaka A, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Ramírez B, Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Neira G, Valentí V, Moncada R, Silva C, Unamuno X, et al. Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204372
Chicago/Turabian StyleMentxaka, Amaia, Javier Gómez-Ambrosi, Beatriz Ramírez, Amaia Rodríguez, Sara Becerril, Gabriela Neira, Víctor Valentí, Rafael Moncada, Camilo Silva, Xabier Unamuno, and et al. 2022. "Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204372
APA StyleMentxaka, A., Gómez-Ambrosi, J., Ramírez, B., Rodríguez, A., Becerril, S., Neira, G., Valentí, V., Moncada, R., Silva, C., Unamuno, X., Cienfuegos, J. A., Escalada, J., Frühbeck, G., & Catalán, V. (2022). Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance. Nutrients, 14(20), 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204372








