BRD9 Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols Targets DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Treatments
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. BROMOscan® Screening
2.4. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Immunoblotting
2.7. Apoptosis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. BRD9 Overexpression Is Associated with Reduced Survival in CRC Patients
3.2. BRD9 Regulates DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells
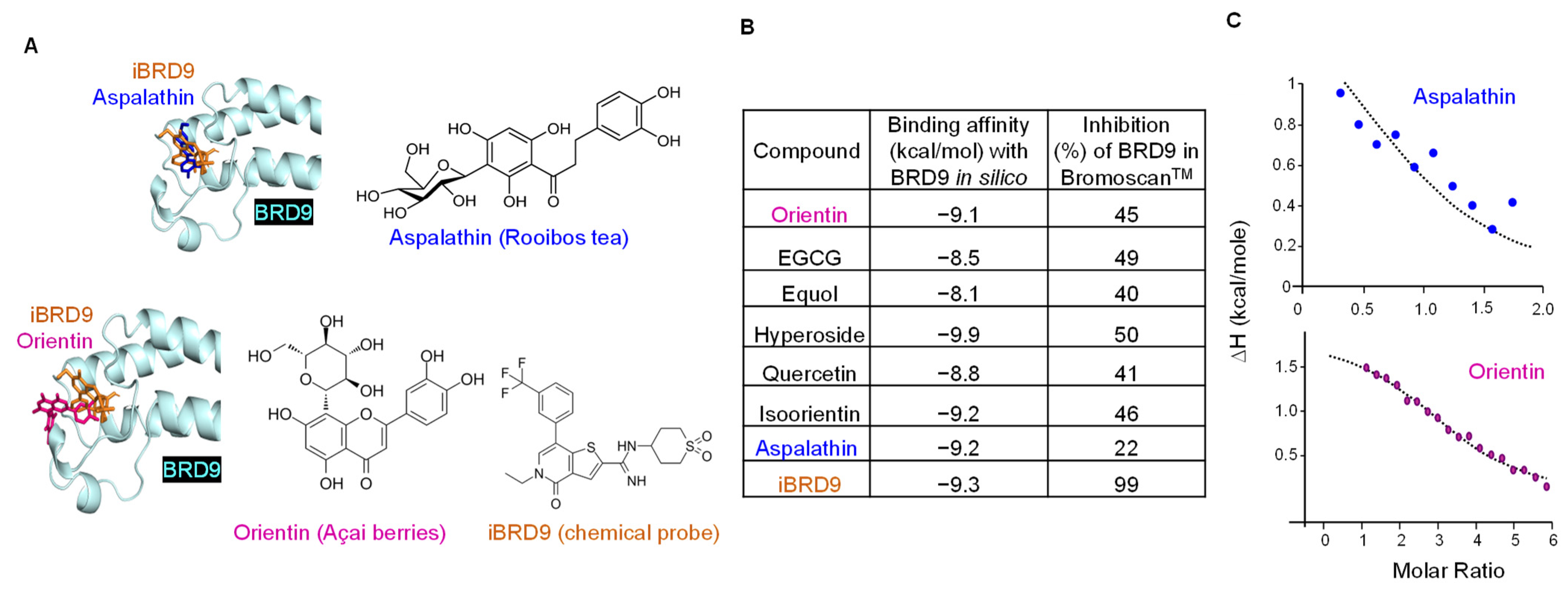
3.3. BRD9 Interacts with Natural Polyphenols
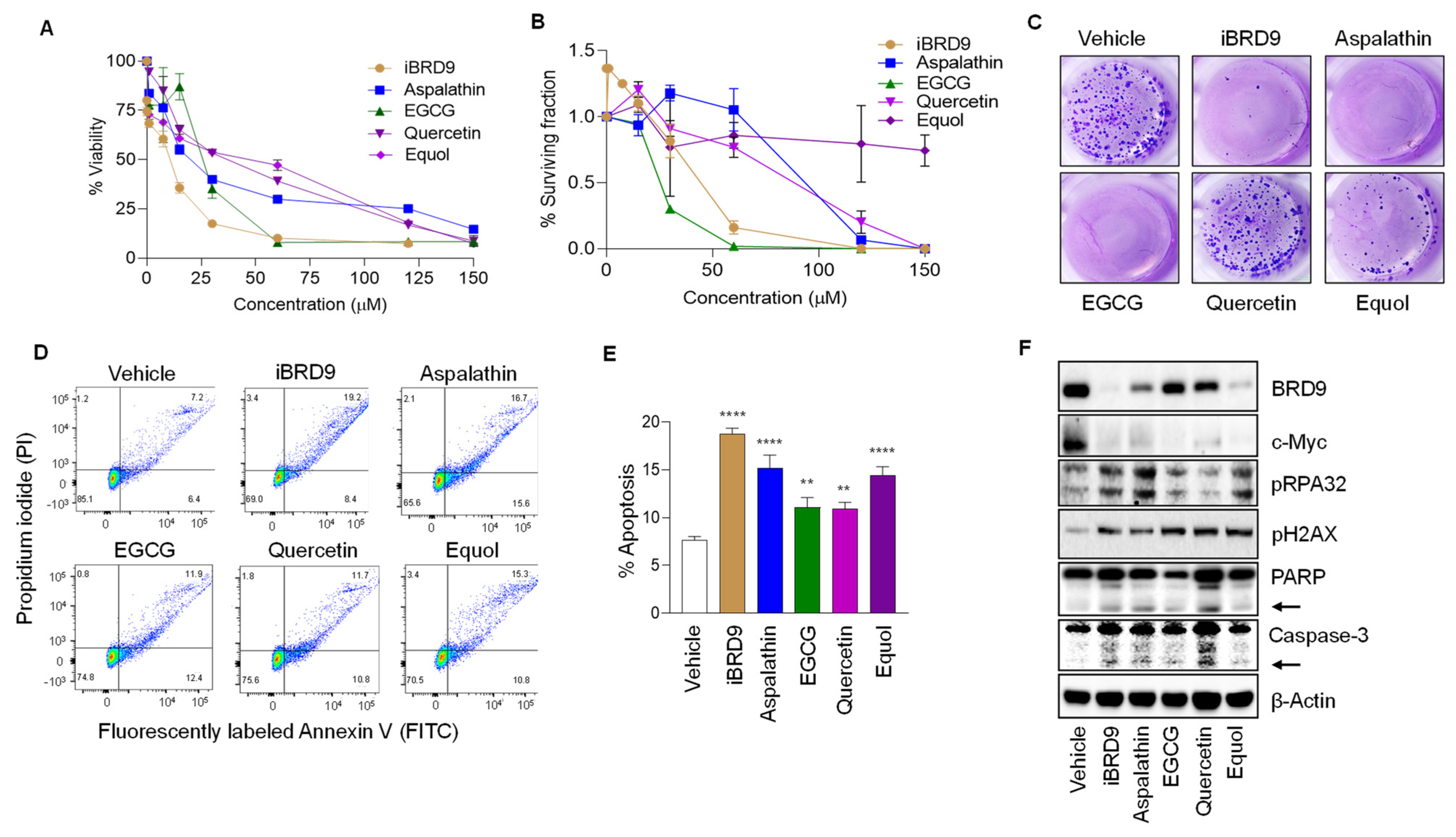
3.4. BRD9 Inhibition Reduces Colon Cancer Cell Viability and Increases DNA Damage and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, G.; Hernández-Illán, E.; Moreira, L.; Balaguer, F.; Goel, A. Epigenetics of colorectal cancer: Biomarker and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Filippakopoulos, P. Functions of bromodomain-containing proteins and their roles in homeostasis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, E.; Duran, M.N.; Mohan, N.; Rajendran, P.; Dashwood, R.H. Targeting epigenetic ‘Readers’ with natural compounds for cancer interception. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 25, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Picaud, S.; Mangos, M.; Keates, T.; Lambert, J.P.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Felletar, I.; Volkmer, R.; Müller, S.; Pawson, T.; et al. Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell 2012, 149, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qi, J.; Bradner, J.; Nair, S.; Chen, L.F. Brd4 maintains constitutively active NF-κB in cancer cells by binding to acetylated RelA. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; Zhou, M.M. The role of human bromodomains in chromatin biology and gene transcription. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2009, 12, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.G.; Roberts, C.W. SWI/SNF nucleosome remodellers and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. Targeting BRD9 for Cancer Treatment: A New Strategy. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 13191–13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Fragoso, S.; Luís, R.; Pinto, F.; Brito, C.; Esteves, S.; Pataco, M.; Santos, S.; Machado, P.; Vicente, J.B.; et al. High-throughput sequencing identifies 3 novel susceptibility genes for hereditary melanoma. Genes 2020, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Vakoc, C.R. Targeting Cancer Cells with BET Bromodomain Inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a026674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Ho, E.; Williams, D.E.; Dashwood, R.H. Dietary phytochemicals, HDAC inhibition, and DNA damage/repair defects in cancer cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2011, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.Y.; Kim, H.; Li, W.; Kong, A.-N.T. Natural compound-derived epigenetic regulators targeting epigenetic readers, writers and erasers. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Li, J.; Neja, S.; Kapoor, S.; Tovar Perez, J.E.; Tripathi, C.; Menon, R.; Jayaraman, A.; Lee, K.; Dashwood, W.M.; et al. Metabolomics of Acute vs. Chronic Spinach Intake in an Apc–Mutant Genetic Background: Linoleate and Butanoate Metabolites Targeting HDAC Activity and IFN–γ Signaling. Cells 2022, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Johnson, G.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.S.; Dashwood, M.; Nguyen, N.; Ulusan, A.; Ertem, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; et al. Acetylation of CCAR2 Establishes a BET/BRD9 Acetyl Switch in Response to Combined Deacetylase and Bromodomain Inhibition. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Delage, B.; Dashwood, W.M.; Yu, T.W.; Wuth, B.; Williams, D.E.; Ho, E.; Dashwood, R.H. Histone deacetylase turnover and recovery in sulforaphane treated colon cancer cells: Competing actions of 14-3-3 and Pin1 in HDAC3/SMRT corepressor complex dissociation/reassembly. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Kidane, A.I.; Yu, T.W.; Dashwood, W.M.; Bisson, W.H.; Löhr, C.V.; Ho, E.; Williams, D.E.; Dashwood, R.H. HDAC turnover, CtIP acetylation and dysregulated DNA damage signaling in colon cancer cells treated with sulforaphane and related dietary isothiocyanates. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gille, C.; Fähling, M.; Weyand, B.; Wieland, T.; Gille, A. Alignment-Annotator web server: Rendering and annotating sequence alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W3–W6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxman, J.J.; Heras, B. Bioinformatics tools and resources for analyzing protein structures. In Proteome Bioinformatics; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.; Sorokine, A.; Prilusky, J.; Abola, E.E.; Edelman, M. Automated analysis of interatomic contacts in proteins. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, E.; Tresadern, G.; Bembenek, S.; Wroblowski, B.; Buyck, C.; Neefs, J.M.; Rassokhin, D.; Poncelet, A.; Hunt, J.; van Vlijmen, H. Extending kinome coverage by analysis of kinase inhibitor broad profiling data. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, T.; Williston, S.; Brandts, J.F.; Lin, L.N. Rapid measurement of binding constants and heats of binding using a new titration calorimeter. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 179, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Gustafson, T.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.S.; Li, J.; Nguyen, N.; Perez, J.E.T.; Dashwood, W.M.; Rajendran, P.; Dashwood, R.H. Deacetylase Plus Bromodomain Inhibition Downregulates ERCC2 and Suppresses the Growth of Metastatic Colon Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, D.; Ito, E.; Lau, K.S.; Mocanu, J.D.; Bastianutto, C.; Schimmer, A.D.; Liu, F.F. Increased efficiency for performing colony formation assays in 96-well plates: Novel applications to combination therapies and high-throughput screening. Biotechniques 2008, 44, ix–xiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, H.; Bisson, W.H.; Dashwood, W.M.; Pinto, J.T.; Dashwood, R.H. Alpha-keto acid metabolites of organoselenium compounds inhibit histone deacetylase activity in human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, A.; Mitra, J.; Johnson, G.S.; Li, L.; Dashwood, W.M.; Hegde, M.L.; Yue, C.; Dashwood, R.H.; Rajendran, P. Heterocyclic Analogs of Sulforaphane Trigger DNA Damage and Impede DNA Repair in Colon Cancer Cells: Interplay of HATs and HDACs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoulou, N.H.; Bamborough, P.; Bannister, A.J.; Becher, I.; Bit, R.A.; Che, K.H.; Chung, C.W.; Dittmann, A.; Drewes, G.; Drewry, D.H.; et al. Discovery of I-BRD9, a Selective Cell Active Chemical Probe for Bromodomain Containing Protein 9 Inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.; Dean, A.W.; Woolven, J.M.; Bamborough, P. Fragment-based discovery of bromodomain inhibitors part 1: Inhibitor binding modes and implications for lead discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Martínez, F.D.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Flavonoids as putative epi-modulators: Insight into their binding mode with BRD4 bromodomains using molecular docking and dynamics. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, L.A.; Heidenreich, D.; Silva, G.D.; Chin, C.M.; Knapp, S.; Santos, J.L. Dietary compound resveratrol is a pan-BET bromodomain inhibitor. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, P. BRD9 inhibition promotes PUMA-dependent apoptosis and augments the effect of imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Insight into selective mechanism of class of I-BRD9 inhibitors toward BRD9 based on molecular dynamics simulations. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.D.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Crozier, A. Anthocyanins and flavanones are more bioavailable than previously perceived: A review of recent evidence. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, S.V.; Macovei, I.; Bujor, A.; Miron, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Trifan, A. Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: The role of metabolites. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 626–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, A.F.; Martin, L.J.; Minder, J.L.; Roe, J.S.; Shi, J.; Steurer, S.; Bader, G.; McConnell, D.; Pearson, M.; Gerstberger, T.; et al. Sensitivity and engineered resistance of myeloid leukemia cells to BRD9 inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, M.; Wei, Y.; Niu, W.; Yang, J.; Fan, S.; Xie, Y.; Li, H.; et al. BRD7 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth Through Stabilization of c-Myc in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.M.; Raffeiner, P.; Hart, J.R.; Vogt, P.K. PIK3CA cooperates with KRAS to promote MYC activity and tumorigenesis via the bromodomain protein BRD9. Cancers 2019, 11, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, C.; Alvino, S.; Buglioni, S.; Assisi, D.; Lapenta, R.; Grassi, A.; Stigliano, V.; Mottolese, M.; Casale, V. Activation of c-MYC and c-MYB proto-oncogenes is associated with decreased apoptosis in tumor colon progression. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Moreno, J.J. Polyphenols, food and pharma. Current knowledge and directions for future research. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Bisson, W.H.; Löhr, C.V.; Williams, D.E.; Ho, E.; Dashwood, R.H.; Rajendran, P. Histone and Non-Histone Targets of Dietary Deacetylase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Williams, D.E.; Ho, E.; Dashwood, R.H. Metabolism as a key to histone deacetylase inhibition. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 46, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Natural Polyphenols for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samodien, S.; Kock, M.; Joubert, E.; Swanevelder, S.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. Differential Cytotoxicity of Rooibos and Green Tea Extracts against Primary Rat Hepatocytes and Human Liver and Colon Cancer Cells—Causal Role of Major Flavonoids. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Huang, S.H.; Kao, C.L.; Muller, C.J.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Chang, K.H.; Wen, H.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Shih, L.J.; Kao, Y.H.; et al. Aspalathus linearis suppresses cell survival and proliferation of enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer cells via inhibition of c-Myc and stability of androgen receptor. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmeeta, A.; Adhikary, S.; Dharshnaa, V.; Swarnamughi, P.; Ummul Maqsummiya, Z.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Plant-derived bioactive compounds in colon cancer treatment: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.N.D.; Stempel, S.; Shields, M.A.; Spaulding, C.; Kumar, K.; Bentrem, D.J.; Matsangou, M.; Munshi, H.G. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, B.; Vázquez, L.; Flórez, A.B. Equol: A Bacterial Metabolite from The Daidzein Isoflavone and Its Presumed Beneficial Health Effects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapoor, S.; Damiani, E.; Wang, S.; Dharmanand, R.; Tripathi, C.; Tovar Perez, J.E.; Dashwood, W.M.; Rajendran, P.; Dashwood, R.H. BRD9 Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols Targets DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204317
Kapoor S, Damiani E, Wang S, Dharmanand R, Tripathi C, Tovar Perez JE, Dashwood WM, Rajendran P, Dashwood RH. BRD9 Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols Targets DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204317
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapoor, Sabeeta, Elisabetta Damiani, Shan Wang, Ravirajan Dharmanand, Chakrapani Tripathi, Jorge Enrique Tovar Perez, Wan Mohaiza Dashwood, Praveen Rajendran, and Roderick Hugh Dashwood. 2022. "BRD9 Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols Targets DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204317
APA StyleKapoor, S., Damiani, E., Wang, S., Dharmanand, R., Tripathi, C., Tovar Perez, J. E., Dashwood, W. M., Rajendran, P., & Dashwood, R. H. (2022). BRD9 Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols Targets DNA Damage/Repair and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Nutrients, 14(20), 4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204317








