Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Characteristics
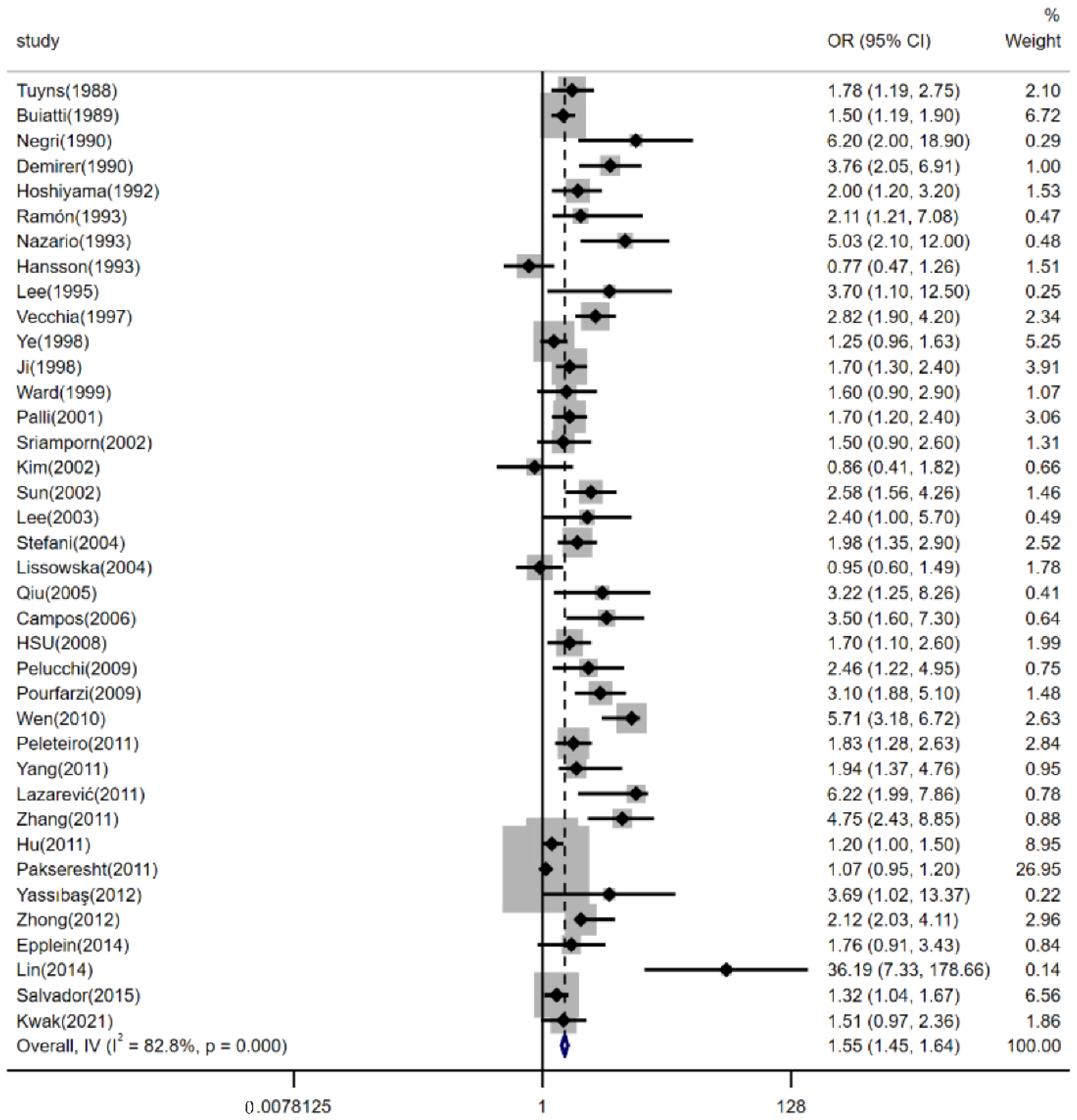
3.2. Effects of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
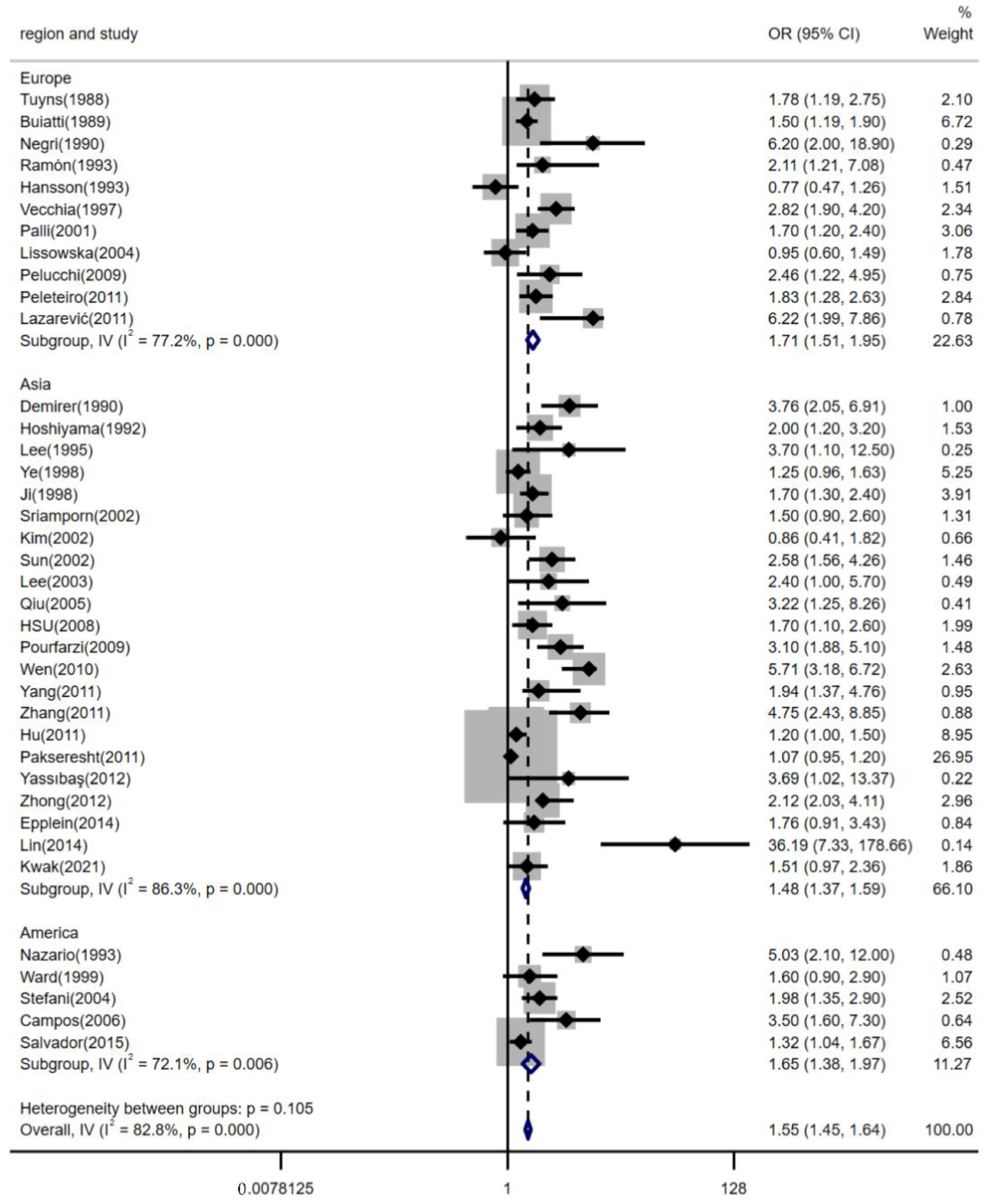
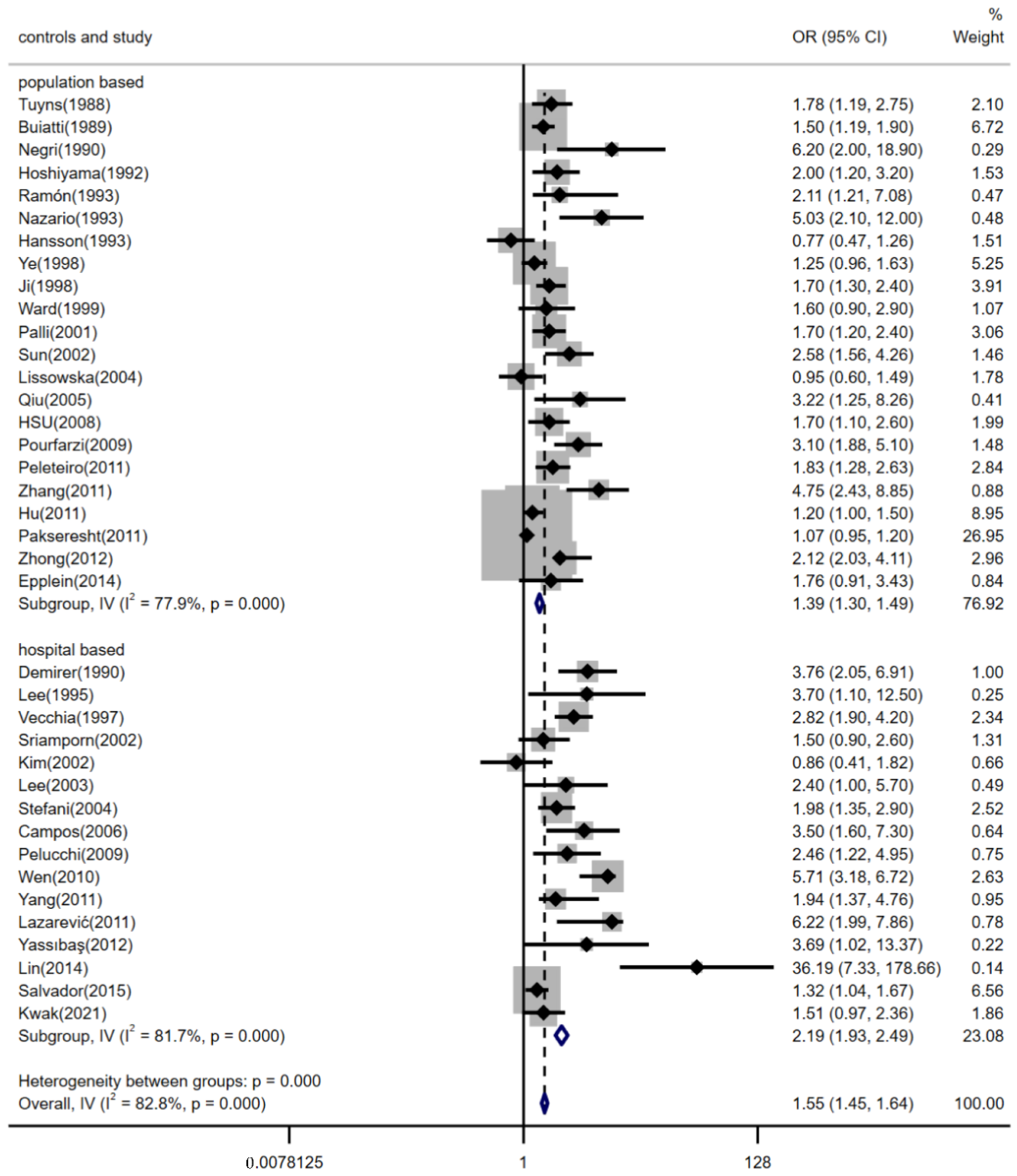
3.4. Subgroup Analyses by Region, Estimation Methods for Dietary Salt Intake and the Source of Controls
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukkamalla, S.; Recio-Boiles, A.; Babiker, H.M. Gastric Cancer; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinton, S.K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Hursting, S.D. The World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Third Expert Report on Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Cancer: Impact and Future Directions. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norat, T.; Scoccianti, C.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Anderson, A.; Berrino, F.; Cecchini, M.; Espina, C.; Key, T.; Leitzmann, M.; Powers, H.; et al. European Code against Cancer 4th Edition: Diet and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadnajafabad, S.; Ebrahimi, N.; Mohammadi, E.; Ghasemi, E.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Aminorroaya, A.; Rezaei, N.; Ghanbari, A.; Masinaei, M.; Fateh, S.M.; et al. Disparities and spatial variations of high salt intake in Iran: A subnational study of districts based on the small area estimation method. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.T.; Torres, V.J.; Cover, T.L. Regulation of Helicobacter pylori cagA expression in response to salt. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4709–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoan, L.T.; Yoshimura, T. Work, salt intake and the development of stomach cancer. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 60, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Shao, S.H. Helicobacter pylori promotes gastric cancer progression through the tumor microenvironment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 4375–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, K.N.; Bi, J.W.; Wang, B.C. Sodium intake, salt taste and gastric cancer risk according to Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking, histological type and tumor site in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2481–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peleteiro, B.; Barros, S.; Castro, C.; Ferro, A.; Morais, S.; Lunet, N. Worldwide burden of gastric cancer in 2010 attributable to high sodium intake in 1990 and predicted attributable burden for 2030 based on exposures in 2010. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.L.; Lyu, J.; Pei, J.P.; Gu, W.J.; Zhang, N.N.; Cao, S.Y.; Zeng, Y.J.; Abe, M.; Nishiyama, K.; Zhang, C.D. The burden and trend of gastric cancer and possible risk factors in five Asian countries from 1990 to 2019. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Giovannucci, E. Potential Impact of Time Trend of Lifestyle Risk Factors on Burden of Major Gastrointestinal Cancers in China. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Feng, X.; Shen, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, J. Association between Habitual Dietary Salt Intake and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 808120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.M.; Yi, Y.N.; Luo, R.X.; Zhou, T.S.; Lin, R.T.; Chen, G.D. Diet and gastric cancer: A casecontrol study in Fujian Province, China. World J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 4, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleteiro, B.; Lopes, C.; Figueiredo, C.; Lunet, N. Salt intake and gastric cancer risk according to Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking, tumour site and histological type. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, I.; Mercado, A.; Bravo, G.L.; Baldeón, M.; Fornasini, M. Risk and Protective Factors for Gastric Metaplasia and Cancer: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study in Ecuador. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.H.; Eun, C.S.; Han, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, K.S.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, H.J. Gastric Cancer and the Daily Intake of the Major Dish Groups Contributing to Sodium Intake: A Case-Control Study in Korea. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyns, A.J. Salt and gastrointestinal cancer. Nutr. Cancer 1988, 11, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiatti, E.; Palli, D.; Decarli, A.; Amadori, D.; Avellini, C.; Bianchi, S.; Biserni, R.; Cipriani, F.; Cocco, P.; Giacosa, A. A case-control study of gastric cancer and diet in Italy. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 44, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, E.; Vecchia, C.L.; D’Avanzo, B.; Gentile, A.; Boyle, P.; Franceschi, S. Salt preference and the risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Nutr. Cancer 1990, 14, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirer, T.; Icli, F.; Uzunalimoglu, O.; Kucuk, O. Diet and stomach cancer incidence. A case-control study in Turkey. Cancer 1990, 65, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiyama, Y.; Sasaba, T. A case-control study of single and multiple stomach cancers in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1992, 83, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramon, J.M.; Serra, L.; Cerdo, C.; Oromí, J. Dietary factors and gastric cancer risk. A case-control study in Spain. Cancer 1993, 71, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazario, C.M.; Szklo, M.; Diamond, E.; Román-Franco, A.; Climent, C.; Suarez, E.; Conde, J.G. Salt and gastric cancer: A case-control study in Puerto Rico. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1993, 22, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.E.; Nyren, O.; Bergstrom, R.; Wolk, A.; Lindgren, A.; Baron, J.; Adami, H.O. Diet and risk of gastric cancer. A population-based case-control study in Sweden. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 55, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, B.J.; Yoo, K.Y.; Ahn, Y.O. Dietary factors and stomach cancer: A case-control study in Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E.; Franceschi, S.; Decarli, A. Case-control study on influence of methionine, nitrite, and salt on gastric carcinogenesis in northern Italy. Nutr. Cancer 1997, 27, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.T.; Chow, W.H.; Yang, G.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.O.; Jin, F.; Gao, R.N.; Gao, Y.T.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Dietary habits and stomach cancer in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 76, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Lopez-Carrillo, L. Dietary factors and the risk of gastric cancer in Mexico City. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, D.; Russo, A.; Decarli, A. Dietary patterns, nutrient intake and gastric cancer in a high-risk area of Italy. Cancer Causes Control. 2001, 12, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriamporn, S.; Setiawan, V.; Pisani, P.; Suwanrungruang, K.; Sirijaichingkul, S.; Mairiang, P.; Parkin, D.M. Gastric Cancer: The Roles of Diet, Alcohol Drinking, Smoking and Helicobacter pylori in Northeastern Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2002, 3, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Chang, W.K.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, B.Y. Dietary factors and gastric cancer in Korea: A case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.B.; Moller, H.; Evans, H.S.; Dai, X.D.; Duan, W.J.; Lu, J.B. Residential Environment, Diet and Risk of Stomach Cancer: A Case-control Study in Linzhou, China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2002, 3, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.A.; Kang, D.; Shim, K.N.; Choe, J.W.; Hong, W.S.; Choi, H. Effect of diet and Helicobacter pylori infection to the risk of early gastric cancer. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefani, E.; Correa, P.; Boffetta, P.; Deneo-Pellegrini, H.; Ronco, A.L.; Mendilaharsu, M. Dietary patterns and risk of gastric cancer: A case-control study in Uruguay. Gastric Cancer 2004, 7, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissowska, J.; Gail, M.H.; Pee, D.; Groves, F.D.; Sobin, L.H.; Nasierowska-Guttmejer, A.; Sygnowska, E.; Zatonski, W.; Blot, W.J.; Chow, W.H. Diet and stomach cancer risk in Warsaw, Poland. Nutr. Cancer 2004, 48, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.L.; Chen, K.; Zheng, J.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Sui, L.M. Nutritional factors and gastric cancer in Zhoushan Islands, China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4311–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.; Carrasquilla, G.; Koriyama, C.; Serra, M.; Carrascal, E.; Itoh, T.; Nomoto, M.; Akiba, S. Risk factors of gastric cancer specific for tumor location and histology in Cali, Colombia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5772–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.I.; Jwo, J.J.; Yang, C.L.; Hsu, P.N.; Yang, H.B.; Lai, K.H.; Chen, I.S.; Chuah, S.K.; Wu, D.C.; Chen, A. Association of the myeloperoxidase polymorphism with the risk of gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Pelucchi, C.; Tramacere, I.; Bertuccio, P.; Tavani, A.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C. Dietary intake of selected micronutrients and gastric cancer risk: An Italian case-control study. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourfarzi, F.; Whelan, A.; Kaldor, J.; Malekzadeh, R. The role of diet and other environmental factors in the causation of gastric cancer in Iran--a population based study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.Y. Salt taste sensitivity, physical activity and gastric cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.G.; Chen, C.B.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, Y.P.; Wen, X.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Sun, T.W. A case-control study on the relationship between salt intake and salty taste and risk of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarevic, K.; Nagorni, A.; Bogdanovic, D.; Rancic, N.; Stosic, L.; Milutinovic, S. Dietary micronutrients and gastric cancer: Hospital based study. Cent. Eur. J. Med. 2011, 6, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Salt taste preference, sodium intake and gastric cancer in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; La Vecchia, C.; Morrison, H.; Negri, E.; Mery, L. Canadian Cancer Registries Epidemiology Research Group. Salt, processed meat and the risk of cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 20, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakseresht, M.; Forman, D.; Malekzadeh, R.; Yazdanbod, A.; West, R.M.; Greenwood, D.C.; Crabtree, J.E.; Cade, J.E. Dietary habits and gastric cancer risk in north-west Iran. Cancer Causes Control. 2011, 22, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassibas, E.; Arslan, P.; Yalcin, S. Evaluation of dietary and life-style habits of patients with gastric cancer: A case-control study in Turkey. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Epplein, M.; Zheng, W.; Li, H.L.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Correa, P.; Gao, J.; Michel, A.; Pawlita, M.; Cai, Q.Y.; Xiang, Y.B.; et al. Diet, Helicobacter pylori strain-specific infection, and gastric cancer risk among Chinese men. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Li, Y.H.; Leung, K.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, X.R. Salt processed food and gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 5293–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.X.; Wei, J.Y.; He, X.Y.; An, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Shao, D.D.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.D.; et al. Landscape of dietary factors associated with risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2820–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, J.M.; Chopra, A.; Loh, J.T.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Watson, M.; Leary, S.; Beckett, A.C.; Wilson, K.T.; Cover, T.L.; et al. Pan-genomic analyses identify key Helicobacter pylori pathogenic loci modified by carcinogenic host microenvironments. Gut 2018, 67, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raei, N.; Behrouz, B.; Zahri, S.; Latifi-Navid, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Dietary Factors Act Synergistically to Promote Gastric Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Sun, F.; Guo, Y.C.; Fan, H. High-Salt Diet Gets Involved in Gastrointestinal Diseases through the Reshaping of Gastroenterological Milieu. Digestion 2019, 99, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouras, E.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Triggi, M.; Siargkas, A.; Chourdakis, M.; Haidich, A.-B. Diet and Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. High salt diet can down-regulate TFF2 expression level in gastric mucosa of MGs after H. pylori infection. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.; Livingstone, V. The investigation and correction of recall bias for an ordinal response in a case-control study. Stat. Med. 2006, 25, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| First Author | Year | Country | Region | Male (n) | Age (Years) Mean/Range | Sample Size | Quality Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | |||||||
| Tuyns [20] | 1988 | France | Europe | 1597 | — | — | 4061 | 5 |
| Buiatti [21] | 1989 | Italy | Europe | 1345 | ≤75 | ≤75 | 2175 | 5 |
| Negri [22] | 1990 | England | Europe | 219 | 61 | 64 | 282 | 8 |
| Demirer [23] | 1990 | Turkey | Asia | 131 | 55 | 52 | 200 | 7 |
| Hoshiyama [24] | 1992 | Japan | Asia | 699 | — | — | 699 | 6 |
| Ramón [25] | 1993 | Spain | Europe | 297 | 62 | 61 | 351 | 8 |
| Nazario [26] | 1993 | Puerto Rico | America | — | ≥30 | ≥30 | 271 | 8 |
| Hansson [27] | 1993 | Sweden | Europe | 662 | 67.7 | 67.0 | 1017 | 8 |
| Lee [28] | 1995 | Korea | Asia | 264 | >25 | >25 | 426 | 7 |
| Vecchia [29] | 1997 | Italy | Europe | 1662 | 61 | 55 | 2799 | 5 |
| Ye [15] | 1998 | China | Asia | 699 | 30–78 | 30–78 | 816 | 8 |
| Ji [30] | 1998 | China | Asia | 1589 | 61 | 59 | 2575 | 8 |
| Ward [31] | 1999 | Mexico | America | — | ≥20 | ≥20 | 972 | 8 |
| Palli [32] | 2001 | Italy | Europe | 567 | — | — | 943 | 6 |
| Sriamporn [33] | 2002 | Thailand | Asia | 254 | — | — | 393 | 7 |
| Kim [34] | 2002 | Korea | Asia | 186 | — | — | 314 | 7 |
| Sun [35] | 2002 | China | Asia | 568 | 59.8 | 59.5 | 840 | 8 |
| Lee [36] | 2003 | Korea | Asia | 166 | — | — | 268 | 7 |
| Stefani [37] | 2004 | Uruguay | America | 840 | 30–89 | 30–89 | 1200 | 7 |
| Lissowska [38] | 2004 | Poland | Europe | 479 | — | — | 737 | 8 |
| Qiu [39] | 2005 | China | Asia | 176 | 63 | 60 | 176 | 6 |
| Campos [40] | 2006 | Colombia | America | 407 | — | — | 647 | 7 |
| Hsu [41] | 2008 | China | Asia | 131 | 66.0 | 51.8 | 349 | 8 |
| Pelucchi [42] | 2009 | Italy | Europe | 429 | 63 | 63 | 777 | 7 |
| Pourfarzi [43] | 2009 | Iran | Asia | 416 | 65.4 | 64.3 | 611 | 8 |
| Wen [44] | 2010 | China | Asia | 642 | 58.9 | 57.7 | 900 | 7 |
| Peleteiro [16] | 2011 | Portugal | Europe | 503 | 18–92 | 18–92 | 1071 | 8 |
| Yang [45] | 2011 | China | Asia | 642 | 52.1 | 52.4 | 900 | 7 |
| Lazarević [46] | 2011 | Serbia | Europe | — | 65.8 | 65.8 | 306 | 7 |
| Zhang [47] | 2011 | China | Asia | 424 | 53.3 | 52.8 | 645 | 6 |
| Hu [48] | 2011 | Canada | America | 1528 | 57.1 | 60.1 | 6221 | 6 |
| Pakseresht [49] | 2011 | Iran | Asia | 427 | 66.3 | 62.9 | 590 | 6 |
| Yassıbaş [50] | 2012 | Turkey | Asia | 132 | 57.4 | 57.9 | 212 | 7 |
| Chen [9] | 2012 | China | Asia | 390 | 53.1 | 52.8 | 617 | 6 |
| Epplein [51] | 2014 | China | Asia | 677 | 62.6 | 63.6 | 677 | 8 |
| Lin [52] | 2014 | China | Asia | 241 | 59.1 | 56.5 | 316 | 6 |
| Salvador [17] | 2015 | Ecuador | America | 95 | 62.0 | 55.5 | 257 | 7 |
| Kwak [18] | 2021 | Korea | Asia | 412 | 56.9 | 56.2 | 614 | 7 |
| First Author | Publication Year | Match | Source of Controls | Estimation Method for Dietary Salt Intake | Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuyns [20] | 1988 | Non-matched | Population-based | Addition of salt | Never |
| Buiatti [21] | 1989 | Non-matched | Population-based | Add salt | Never/seldom |
| Negri [22] | 1990 | Matched | Population-based | Levels of salt intake | Low |
| Demirer [23] | 1990 | Matched | Hospital-based | Consumption frequency of salted foods | No consumption/“rare” consumption/ Once or twice a month |
| Hoshiyama [24] | 1992 | Non-matched | Population-based | Preference for salty foods | Low |
| Ramón [25] | 1993 | Matched | Population-based | Salt intake | <1.96 (g/day) |
| Nazario [26] | 1993 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salt index | <6.979 (g/week) |
| Hansson [27] | 1993 | Matched | Population-based | Salted fish | Low |
| Lee [28] | 1995 | Non-matched | Hospital-based | Salt preference | Low |
| Vecchia [29] | 1997 | Non-matched | Hospital-based | Salt preference | Low |
| Ye [15] | 1998 | Matched | Population-based | Salt | ≤0.25 kg/month |
| Ji [30] | 1998 | Matched | Population-based | Consume salted foods | Occasionally |
| Ward [31] | 1999 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salty snacks/crackers | Never |
| Palli [32] | 2001 | Non-matched | Population-based | Sodium intake | Low tertile |
| Sriamporn [33] | 2002 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salted food | Low |
| Kim [34] | 2002 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salted food | Low |
| Sun [35] | 2002 | Matched | Population-based | Salt preference | Moderate |
| Lee [36] | 2003 | Non-matched | Hospital-based | Salt fermented fish | <1/month |
| Stefani [37] | 2004 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salted meat consumption | Low |
| Lissowska [38] | 2004 | Matched | Population-based | Weekly frequency of salt consumption | Low |
| Qiu [39] | 2005 | Non-matched | Population-based | Daily intake of sodium | Low |
| Campos [40] | 2006 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salting meals before tasting | No |
| Hsu [41] | 2008 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salty food intake | Low |
| Pelucchi [42] | 2009 | Matched | Hospital-based | Intake of sodium | Low |
| Pourfarzi [43] | 2009 | Matched | Population-based | Salt preference | Not salty |
| Wen [44] | 2010 | Matched | Hospital-based | STST ≥ 5 | STST < 5 |
| Peleteiro [16] | 2011 | Non-matched | Population-based | Use of table salt (salt consumption by visual analogical scale) | <35 (mm) |
| Yang [45] | 2011 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salt taste preference | Not salty |
| Lazarević [46] | 2011 | Matched | Hospital-based | Intake of salt | Low |
| Zhang [47] | 2011 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salt taste preference * | 0.9 (g/L) |
| Hu [48] | 2011 | Non-matched | Population-based | Added salt at table | Never |
| Pakseresht [49] | 2011 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salt | Per g |
| Yassıbaş [50] | 2012 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salt status of dishes | Salt-free |
| Chen [9] | 2012 | Non-matched | Population-based | Salt taste preference * | <1.8 |
| Epplein [51] | 2014 | Matched | Population-based | Intake of sodium | Low |
| Lin [52] | 2014 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salt taste preference | Not salty |
| Salvador [17] | 2015 | Non-matched | Hospital-based | Adding salt >50% of meals | No |
| Kwak [18] | 2021 | Matched | Hospital-based | Salt taste preference | No opinion |
| Study Omitted | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Tuyns (1988) [20] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Buiatti (1989) [21] | 1.55 | (1.45, 1.65) |
| Negri (1990) [22] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Demirer (1990) [23] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Hoshiyama (1992) [24] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Ramón (1993) [25] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Nazario (1993) [26] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.63) |
| Hansson (1993) [27] | 1.56 | (1.47, 1.66) |
| Lee (1995) [28] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Vecchia (1997) [29] | 1.52 | (1.43, 1.62) |
| Ye (1998) [15] | 1.56 | (1.47, 1.66) |
| Ji (1998) [30] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Ward (1999) [31] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Palli (2001) [32] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Sriamporn (2002) [33] | 1.55 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Kim (2002) [34] | 1.55 | (1.46, 1.65) |
| Sun (2002) [35] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Lee (2003) [36] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Stefani (2004) [37] | 1.54 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Lissowska (2004) [38] | 1.56 | (1.47, 1.66) |
| Qiu (2005) [39] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Campos (2006) [40] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.63) |
| Hsu (2008) [41] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Pelucchi (2009) [42] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Pourfarzi(2009) [43] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Wen (2010) [44] | 1.50 | (1.40, 1.59) |
| Peleteiro (2011) [16] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Yang (2011) [45] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Lazarević (2011) [46] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.62) |
| Zhang (2011) [47] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Hu (2011) [48] | 1.58 | (1.49, 1.69) |
| Pakseresht (2011) [49] | 1.77 | (1.65, 1.90) |
| Yassıbaş (2012) [50] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Chen (2012) [9] | 1.53 | (1.44, 1.63) |
| Epplein (2014) [51] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.64) |
| Lin (2014) [52] | 1.54 | (1.45, 1.63) |
| Salvador (2015) [17] | 1.56 | (1.47, 1.66) |
| Kwak (2021) [18] | 1.55 | (1.45, 1.64) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Qian, J.; Fang, Z.; Wu, J. Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204260
Wu X, Chen L, Cheng J, Qian J, Fang Z, Wu J. Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiaomin, Liling Chen, Junxia Cheng, Jing Qian, Zhongze Fang, and Jing Wu. 2022. "Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204260
APA StyleWu, X., Chen, L., Cheng, J., Qian, J., Fang, Z., & Wu, J. (2022). Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Nutrients, 14(20), 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204260







